Wide-Angle-Tail (WAT) Radio Sources
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Radio Properties
2.1. Narrow Range of Radio Luminosity
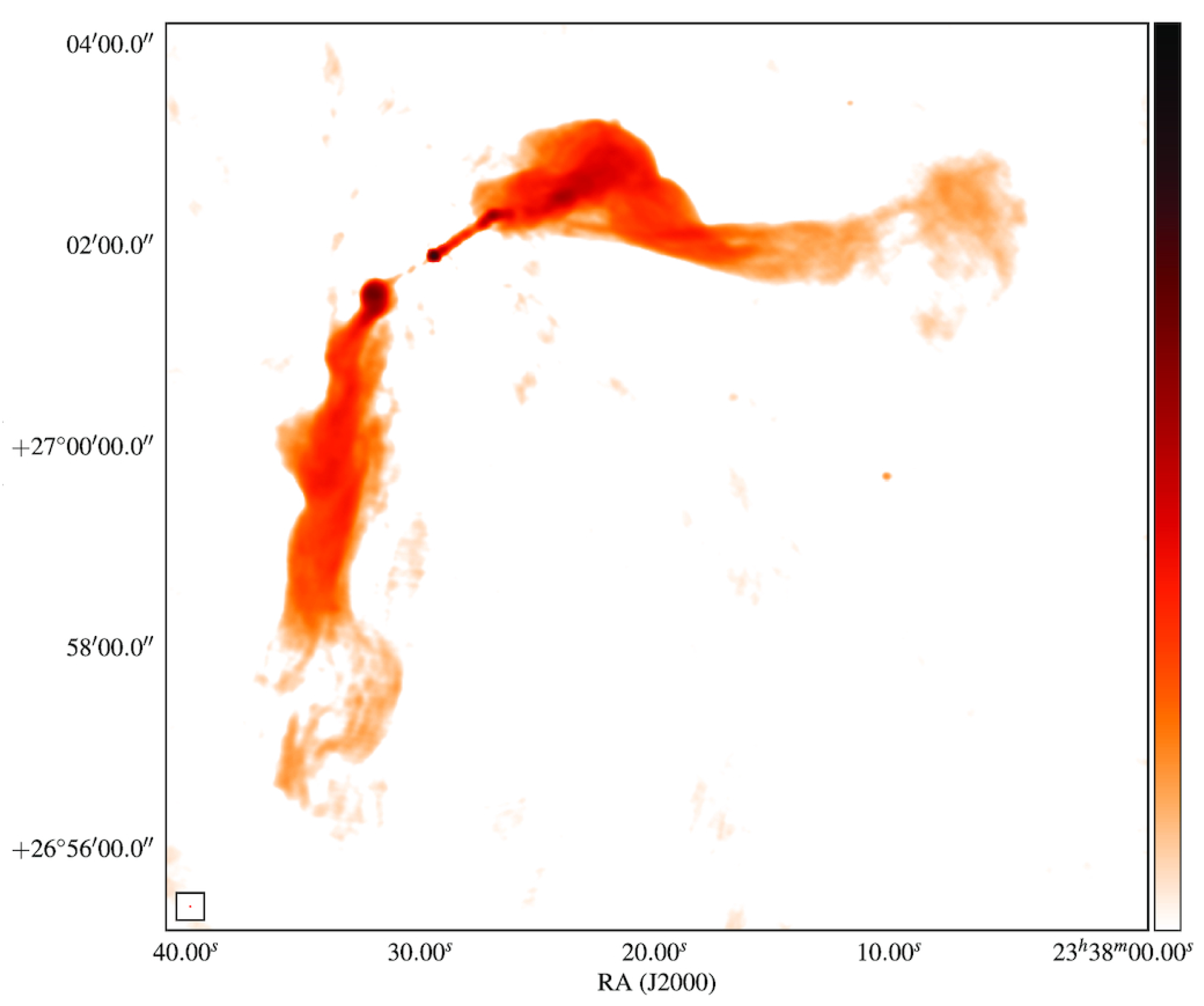
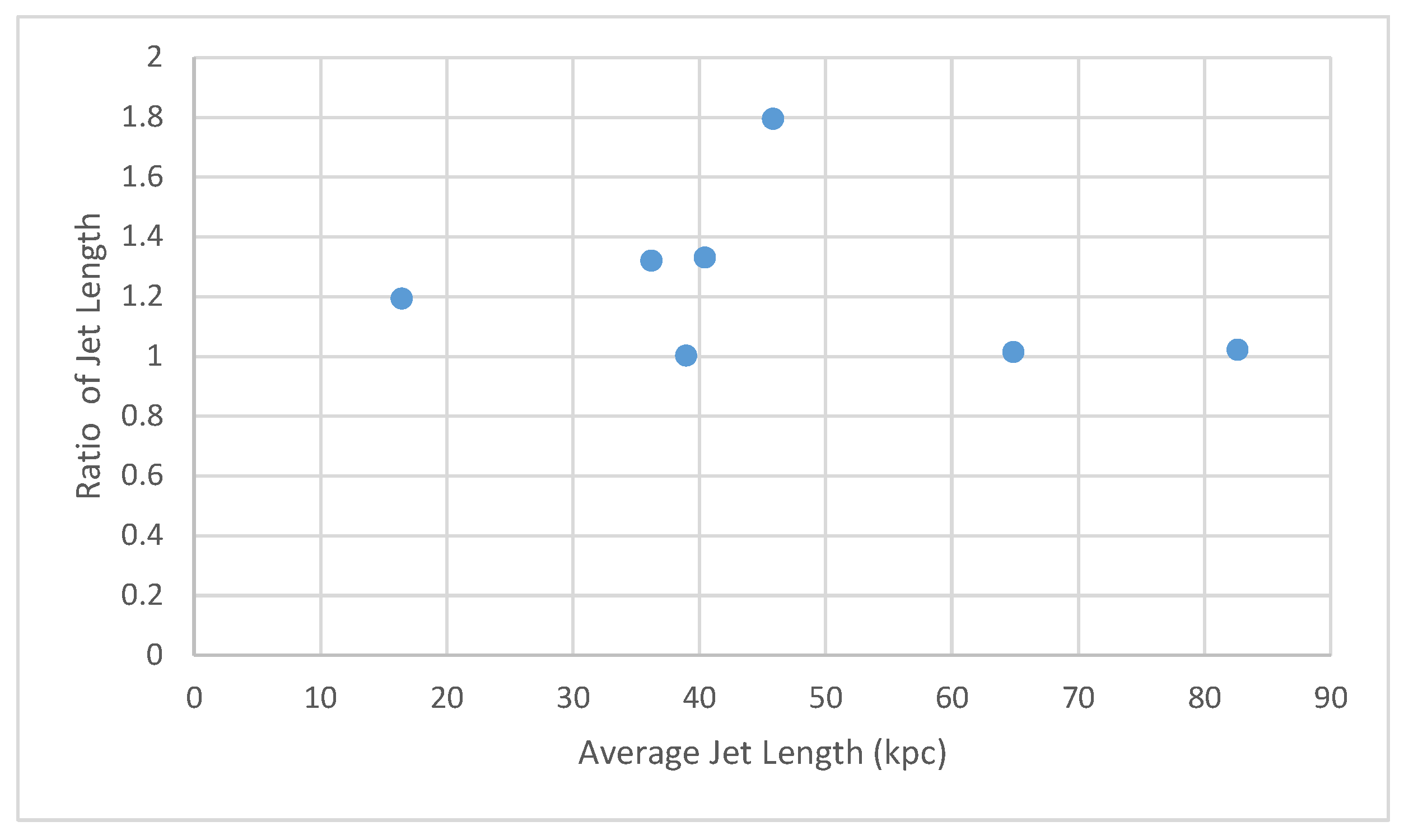
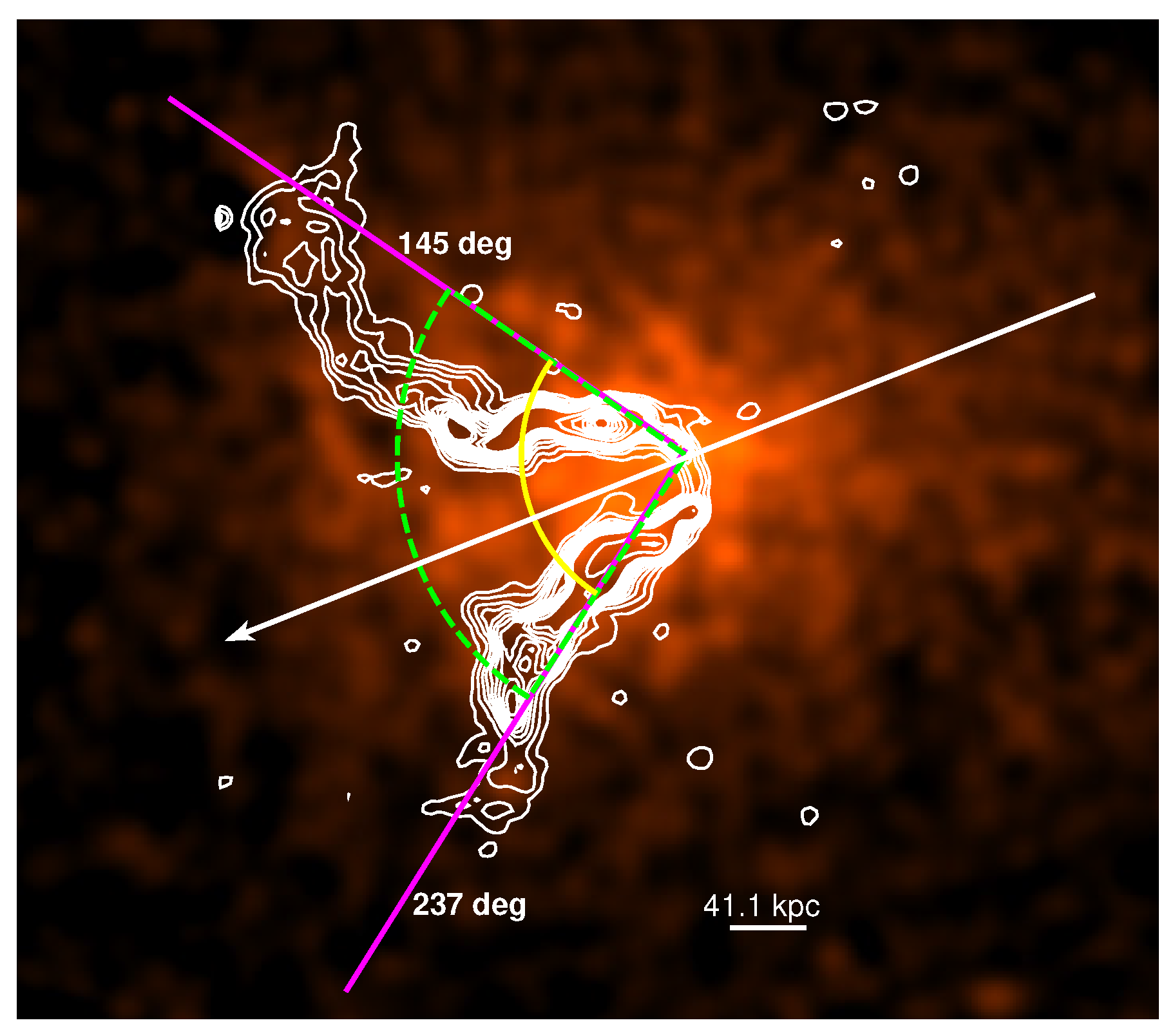
2.2. Radio Morphology
Caveat Regarding Bending Angle
2.3. Jet Velocities
2.4. Spectral Index Properties
2.4.1. Evidence for Jet Flow Down the Tails
2.5. Polarization Properties
3. Host Galaxies and Environments
3.1. Host Galaxies
3.2. Environments
3.3. Relative Velocities of WAT Hosts
3.4. Are WATs Preferentially Found in Merging Clusters?
3.4.1. Sloshing Gas in Merging Clusters
3.5. Why Do WATs Avoid Clusters with Cool Cores?
- 1.
- X-ray studies show that cool cores are apparently disrupted by cluster mergers, e.g., [127,128,129]. There is support for this from recent numerical simulations, e.g., [130,131,132]. Since WATs are in clusters undergoing mergers (Section 3.4), WATs should not be in clusters with cool cores if cool cores are disrupted by the type of cluster mergers that create WATs;
- 2.
- Radio jets may be disrupted in cool cores. Soker and Sarazin [133] suggested that cool cores could disrupt radio jets on sub-kpc scales. This is consistent with the amorphous radio morphology often seen in cool cores, e.g., [125,134,135,136]. In addition, VLBI shows two-sided jets on the pc scale in some cool core radio sources, e.g., [137,138], suggesting that the initially relativistic jets have already decelerated to sub-relativistic speeds on pc scales. However, WATs have narrow, relatively straight, powerful jets out to tens of kpc from the nucleus with estimated jet velocities of 0.2–0.7c (Section 2), consistent with the jets in WATs not being disrupted on sub-kpc scales by a cool core.
3.6. Using WATs to Find Clusters of Galaxies
3.7. What about WATs Outside of Clusters?
4. Models for WATs
4.1. What Causes the Jet-Tail Transition?
4.1.1. Current-Driven Instabilities
4.1.2. Kelvin–Helmholtz Instabilities
4.1.3. A Transition from High-Density, Cool ISM to Lower-Density, Hotter ICM
4.1.4. Shocks at the ISM/ICM Interface
4.1.5. Summary of Section 4.1
4.2. What Bends WATs?
4.2.1. Collisions with Dense Clouds
4.2.2. Buoyancy
4.2.3. Electrodynamic Effects ()
4.2.4. Ram Pressure Due to Cluster Mergers
4.2.5. What about WATs That Are Not in Clusters of Galaxies?
5. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGN | Active Galactic Nuclei |
| BCG | Brightest Cluster Galaxy |
| CDI | Current-driven instability |
| HT | Head-Tail |
| ICM | Intracluster Medium |
| IGM | Intergalactic Medium |
| ISM | Interstellar Medium |
| LERG | Low-Excitation Radio Galaxy |
| MHD | Magnetohydrodynamical |
| NAT | Narrow Angle Tail |
| VLA | Very Large Array |
| VLBI | Very Long Baseline Interferometry |
| WAT | Wide-Angle-Tail |
| 1 | |
| 2 | Young et al. [56] note that the simple electron aging models are not a good fit to the spectral index data of two WATs, 1231+674 and 1433+553. This could be due to complexity in the magnetic field structure and electron populations. |
| 3 | |
| 4 | The SI unit for current seemed more appropriate here. |
| 5 | This was suggested to us by one of our referees. |
| 6 | An additional assumption that is occasionally adopted is that ram pressure will balance buoyancy forces at some point in the tails [102,103]. However, this assumes constant jet velocity down the tails which may not be valid (See Section 2.4.1). |
References
- Feretti, L.; Giovannini, G. Clusters of Galaxies in the Radio: Relativistic Plasma and ICM/Radio Galaxy Interaction Processes. In A Pan-Chromatic View of Clusters of Galaxies and the Large-Scale Structure; Plionis, M., López-Cruz, O., Hughes, D., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; Volume 740, pp. 143–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, D.J. Jets in radio galaxies and quasars: An observational perspective. J. Astrophys. Astron. 2022, 43, 97–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, F.N.; Rudnick, L. Radio sources with wide-angle tails in Abell clusters of galaxies. Astrophys. J. 1976, 205, L1–L4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, J.O. Wide-angle tailed radio galaxies. Can. J. Phys. 1986, 64, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donoghue, A.A.; Eilek, J.A.; Owen, F.N. Flow Dynamics and Bending of Wide-Angle Tailed Radio Sources. Astrophys. J. 1993, 408, 428–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hintzen, P.; Scott, J.S. The use of radio source morphology in detecting clusters of galaxies associated with QSOs. Astrophys. J. 1978, 224, L47–L50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hintzen, P. Wide-angle radio tail QSOs as members of clusters of galaxies. II. Direct optical observations and spectroscopy of QSO fields. Astrophys. J.Suppl. Ser. 1984, 55, 533–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanton, E.L.; Gregg, M.D.; Helfand, D.J.; Becker, R.H.; White, R.L. FIRST Bent-Double Radio Sources: Tracers of High-Redshift Clusters. Astrophys. J. 2000, 531, 118–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolčić, V.; Schinnerer, E.; Finoguenov, A.; Sakelliou, I.; Carilli, C.L.; Botzler, C.S.; Brusa, M.; Scoville, N.; Ajiki, M.; Capak, P.; et al. A Wide-Angle Tail Radio Galaxy in the COSMOS Field: Evidence for Cluster Formation. Astrophys. J.Suppl. Ser. 2007, 172, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglass, E.M.; Blanton, E.L.; Clarke, T.E.; Randall, S.W.; Wing, J.D. The Merger Environment of the Wide Angle Tail Hosting Cluster A562. Astrophys. J. 2011, 743, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.W.; Nolting, C.; O’Neill, B.J.; Mendygral, P.J. Using collisions of AGN outflows with ICM shocks as dynamical probes. Phys. Plasmas 2017, 24, 041402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.W.; Owen, F.N. Hot gas in elliptical galaxies and the formation of head-tail radio sources. Astrophys. J. 1979, 234, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begelman, M.C.; Rees, M.J.; Blandford, R.D. A twin-jet model for radio trails. Nature 1979, 279, 770–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eilek, J.A.; Burns, J.O.; O’Dea, C.P.; Owen, F.N. What bends 3C 465? Astrophys. J. 1984, 278, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dea, C.P. Constraints on bent beams in narrow angle tail radio sources. Astrophys. J. 1985, 295, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsony, B.J.; Miller, J.J.; Heinz, S.; Freeland, E.; Wilcots, E.; Brüggen, M.; Ruszkowski, M. Simulations of bent-double radio sources in galaxy groups. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 431, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, L.; Owen, F.N. Head-tail radio sources in clusters of galaxies. Astrophys. J. 1976, 203, L107–L111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dea, C.P.; Owen, F.N. The global properties of a representative sample of 51 narrow-angle-tail radio sources in the directions of Abell clusters. Astron. J. 1985, 90, 954–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentijn, E.A.; Perola, G.C. A Westerbork survey of rich clusters of galaxies. V. Multi-frequency observations of the radio tail galaxy NGC 6034 in the Hercules cluster. Astron. Astrophys. 1978, 63, 29–35. [Google Scholar]
- van Breugel, W.J.M. Multifrequency observations of extended radio galaxies III: 3C 465. Astron. Astrophys. 1980, 88, 248–258. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, J.G. Multifrequency observations of the complex radio galaxy 1919+479 (4C 47.51). Astron. Astrophys. 1984, 138, 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Leahy, J.P. 3C 465: Dynamics of a wide-tail radio source. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1984, 208, 323–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feretti, L.; Giovannini, G.; Gregorini, L.; Padrielli, L.; Roland, J.; Valentijn, E.A. The wide angle tailed radio source NGC 2329 in the cluster A 569. Astron. Astrophys. 1985, 147, 321–327. [Google Scholar]
- Patnaik, A.R.; Malkan, M.A.; Salter, C.J. Multifrequency observations of the wide-angle tail radio source 1313+073. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1986, 220, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donoghue, A.A.; Owen, F.N.; Eilek, J.A. VLA Observations of Wide-Angle Tailed Radio Sources. Astrophys. J.Suppl. Ser. 1990, 72, 75–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.B.; Barton, E.J.; Ge, J. Searching for Cluster Magnetic Fields in the Cooling Flows of 0745-191, A2029, and A4059. Astron. J. 1994, 107, 1942–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz-Stone, D.M.; Rudnick, L.; Butenhoff, C.; O’Donoghue, A.A. Coaxial Jets and Sheaths in Wide-Angle-tailed Radio Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 1999, 516, 716–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardcastle, M.J.; Sakelliou, I. Jet termination in wide-angle tail radio sources. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2004, 349, 560–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Kharb, P.; Morganti, R.; Nandi, S. The peculiar WAT NGC 2329 with Seyfert/FR I-like radio lobes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 504, 4416–4427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, J.E. Projection Effects and Radio Source Morphology. Publ. Astron. Soc. Aust. 1980, 4, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missaglia, V.; Massaro, F.; Capetti, A.; Paolillo, M.; Kraft, R.P.; Baldi, R.D.; Paggi, A. WATCAT: A tale of wide-angle tailed radio galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 626, A8–A27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasmal, T.K.; Bera, S.; Pal, S.; Mondal, S. A New Catalog of Head-Tail Radio Galaxies from the VLA FIRST Survey. Astrophys. J.Suppl. Ser. 2022, 259, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanaroff, B.L.; Riley, J.M. The morphology of extragalactic radio sources of high and low luminosity. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1974, 167, 31P–36P. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridle, A.H.; Perley, R.A. Extragalactic Radio Jets. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1984, 22, 319–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, S.A.; Zirbel, E.L.; O’Dea, C.P. Toward Understanding the Fanaroff-Riley Dichotomy in Radio Source Morphology and Power. Astrophys. J. 1995, 451, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicknell, G.V. Relativistic Jets and the Fanaroff-Riley Classification of Radio Galaxies. Astrophys. J.Suppl. Ser. 1995, 101, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, C.R.; Best, P.N. Luminosity function, sizes and FR dichotomy of radio-loud AGN. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2007, 381, 1548–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laing, R.A.; Bridle, A.H. Systematic properties of decelerating relativistic jets in low-luminosity radio galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 437, 3405–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchekhovskoy, A.; Bromberg, O. Three-dimensional relativistic MHD simulations of active galactic nuclei jets: Magnetic kink instability and Fanaroff-Riley dichotomy. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 461, L46–L50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaglia, S.; Bodo, G.; Rossi, P.; Capetti, S.; Mignone, A. Making Faranoff-Riley I radio sources. I. Numerical hydrodynamic 3D simulations of low-power jets. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 596, A12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlert, K.; Weinberger, R.; Pfrommer, C.; Pakmor, R.; Springel, V. Simulations of the dynamics of magnetized jets and cosmic rays in galaxy clusters. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 481, 2878–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingo, B.; Croston, J.H.; Hardcastle, M.J.; Best, P.N.; Duncan, K.J.; Morganti, R.; Rottgering, H.J.A.; Sabater, J.; Shimwell, T.W.; Williams, W.L.; et al. Revisiting the Fanaroff-Riley dichotomy and radio-galaxy morphology with the LOFAR Two-Metre Sky Survey (LoTSS). Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 488, 2701–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bempong-Manful, E.; Hardcastle, M.J.; Birkinshaw, M.; Laing, R.A.; Leahy, J.P.; Worrall, D.M. A high-resolution view of the jets in 3C 465. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 496, 676–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaegers, W.J. The cluster around 3C130. Astron. Astrophys. 1983, 125, 172–174. [Google Scholar]
- Hardcastle, M.J. Jets, plumes and hotspots in the wide-angle tail source 3C 130. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1998, 298, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardcastle, M.J. The complex radio spectrum of 3C 130. Astron. Astrophys. 1999, 349, 381–388. [Google Scholar]
- Jetha, N.N.; Sakelliou, I.; Hardcastle, M.J.; Ponman, T.J.; Stevens, I.R. Interactions of radio galaxies and the intracluster medium in Abell 160 and Abell 2462. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2005, 358, 1394–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.B.; Perley, R.A.; Inoue, M.; Kato, T.; Tabara, H.; Aizu, K. VLA Observations of the Radio Galaxy Hydra A (3C 218). Astrophys. J. 1990, 360, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garon, A.F.; Rudnick, L.; Wong, O.I.; Jones, T.W.; Kim, J.A.; Andernach, H.; Shabala, S.S.; Kapińska, A.D.; Norris, R.P.; de Gasperin, F.; et al. Radio Galaxy Zoo: The Distortion of Radio Galaxies by Galaxy Clusters. Astron. J. 2019, 157, 126–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jetha, N.N.; Hardcastle, M.J.; Sakelliou, I. Jet speeds in wide-angle tailed radio galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2006, 368, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandford, R.D.; Königl, A. Relativistic jets as compact radio sources. Astrophys. J. 1979, 232, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturi, T.; Castaldini, C.; Cotton, W.D.; Feretti, L.; Giovannini, G.; Lara, L.; Marcaide, J.M.; Wehrle, A.E. VLBI Observations of a Complete Sample of Radio Galaxies. VI. The Two FR I Radio Galaxies B2 0836+29 and 3C 465. Astrophys. J. 1995, 454, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, J.O.; O’Dea, C.P.; Gregory, S.A.; Balonek, T.J. Observational Constraints on Bending the Wide-Angle Tailed Radio Galaxy 1919+479. Astrophys. J. 1986, 307, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, J.M.; Branson, N.J.B.A. New observations of 3C 382, 3C 452 and 3C 465 at 2.7 and 5 GHz. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1973, 164, 271–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feretti, L.; Giovannini, G.; Klein, U.; Mack, K.H.; Sijbring, L.G.; Zech, G. Electron ageing and polarization in tailed radio galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. 1998, 331, 475–484. [Google Scholar]
- Young, A.; Rudnick, L.; Katz-Stone, D.M.; O’Donoghue, A.A. Electron population aging models for wide-angle tails. New A Rev. 2002, 46, 105–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eilek, J.A.; Owen, F.N. Magnetic Fields in Cluster Cores: Faraday Rotation in A400 and A2634. Astrophys. J. 2002, 567, 202–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burn, B.J. On the depolarization of discrete radio sources by Faraday dispersion. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1966, 133, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioffi, D.F.; Jones, T.W. Internal Faraday rotation effects in transparent synchrotron sources. Astron. J. 1980, 85, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lari, C.; Perola, G.C. Radio Properties of Abell Clusters. In The Large Scale Structures in the Universe; Longair, M.S., Einasto, J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1978; Volume 79, pp. 137–147. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, A.J.B. Radio sources with complex morphologies in clusters of galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1978, 184, 537–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentijn, E.A. The distribution of some intrinsic parameters of head-tail radio sources. Astron. Astrophys. 1979, 78, 367–372. [Google Scholar]
- Wing, J.D.; Blanton, E.L. Galaxy Cluster Environments of Radio Sources. Astron. J. 2011, 141, 88–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, M.Y.; Sharp, R.; Saikia, D.J.; Norris, R.P.; Johnston-Hollitt, M.; Middelberg, E.; Lovell, J.E.J. ATLAS, and Wide-Angle Tail Galaxies in ATLAS. J. Astrophys. Astron. 2011, 32, 585–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miraghaei, H.; Best, P.N. The nuclear properties and extended morphologies of powerful radio galaxies: The roles of host galaxy and environment. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 466, 4346–4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverstein, E.M.; Anderson, M.E.; Bregman, J.N. Increased Prevalence of Bent Lobes for Double-lobed Radio Galaxies in Dense Environments. Astron. J. 2018, 155, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.X.; Xu, H.G.; Zheng, D.C.; Li, W.T.; Zhu, Z.H.; Ma, Z.X.; Lian, X.L. The environment of C- and S-shaped radio galaxies. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 19, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Kumari, S. A new catalog of head-tail radio galaxies from LoTSS DR1. J. Astrophys. Astron. 2023, 44, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden-Marx, E.; Blanton, E.L.; Paterno-Mahler, R.; Brodwin, M.; Ashby, M.L.N.; Moravec, E.; Shen, L.; Lemaux, B.C.; Lubin, L.M.; Gal, R.R.; et al. The High-redshift Clusters Occupied by Bent Radio AGN (COBRA) Survey: Radio Source Properties. Astrophys. J. 2021, 907, 65–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, M.E.; Wilcots, E.; Hooper, E.; Heinz, S. How Does Environment Affect the Morphology of Radio AGN? Astron. J. 2022, 163, 280–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, T.A.; Morgan, W.W.; Schmidt, M. A Discussion of Galaxies Indentified with Radio Sources. Astrophys. J. 1964, 140, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Robertis, M.M.; Yee, H.K.C. Optical Nuclear Activity in the Radio Galaxy 3C 465. Astron. J. 1990, 100, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttiglione, S.; Capetti, A.; Celotti, A.; Axon, D.J.; Chiaberge, M.; Macchetto, F.D.; Sparks, W.B. An optical spectroscopic survey of the 3CR sample of radio galaxies with z < 0.3. II. Spectroscopic classes and accretion modes in radio-loud AGN. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 509, A6–A21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanton, E.L.; Gregg, M.D.; Helfand, D.J.; Becker, R.H.; Leighly, K.M. The Environments of a Complete Moderate-Redshift Sample of FIRST Bent-Double Radio Sources. Astron. J. 2001, 121, 2915–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wing, J.D.; Blanton, E.L. An Examination of the Optical Substructure of Galaxy Clusters Hosting Radio Sources. Astrophys. J. 2013, 767, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkney, J.; Rhee, G.; Burns, J.O.; Hill, J.M.; Oegerle, W.; Batuski, D.; Hintzen, P. The Dynamics of the Galaxy Cluster Abell 2634. Astrophys. J. 1993, 416, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, L.O.V.; Fadda, D.; Frayer, D.T. The First Bent Double Lobe Radio Source in a Known Cluster Filament: Constraints on the Intrafilament Medium. Astrophys. J. 2010, 724, L143–L147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardoulaki, E.; Vazza, F.; Jiménez-Andrade, E.F.; Gozaliasl, G.; Finoguenov, A.; Wittor, D. Bent It Like FRs: Extended Radio AGN in the COSMOS Field and Their Large-Scale Environment. Galaxies 2021, 9, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, A.N.; Norris, R.P.; Tothill, N.F.H.; Filipović, M.D. The spatial correlation of bent-tail galaxies and galaxy clusters. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 481, 5247–5262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, J.O. The structure and environment of the wide-angle tailed radio galaxy 1919+479. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1981, 195, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, H.; Lawrie, D.G. On the determination of velocity dispersions for cD clusters of galaxies. Astron. J. 1982, 87, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.D.M. The dynamics of rich clusters of galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1976, 177, 717–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.D.M.; Rees, M.J. Core condensation in heavy halos: A two-stage theory for galaxy formation and clustering. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1978, 183, 341–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beers, T.C.; Gebhardt, K.; Forman, W.; Huchra, J.P.; Jones, C. A Dynamical Analysis of Twelve Clusters of Galaxies. Astron. J. 1991, 102, 1581–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebhardt, K.; Beers, T.C. Bound Populations around cD Galaxies and cD Velocity Offsets in Clusters of Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 1991, 383, 72–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malumuth, E.M.; Kriss, G.A.; Dixon, W.V.D.; Ferguson, H.C.; Ritchie, C. Dynamics of Clusters of Galaxies with Central Dominant Galaxies. I. Galaxy Redshifts. Astron. J. 1992, 104, 495–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, C.M. Substructure in Clusters and Central Galaxy Peculiar Velocities. Astron. J. 1994, 107, 1637–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oegerle, W.R.; Hill, J.M. Dynamics of cD Clusters of Galaxies. IV. Conclusion of a Survey of 25 Abell Clusters. Astron. J. 2001, 122, 2858–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coziol, R.; Andernach, H.; Caretta, C.A.; Alamo-Martínez, K.A.; Tago, E. The Dynamical State of Brightest Cluster Galaxies and The Formation of Clusters. Astron. J. 2009, 137, 4795–4809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beers, T.C.; Geller, M.J. The environment of D and cD galaxies. Astrophys. J. 1983, 274, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabludoff, A.I.; Mulchaey, J.S. The Properties of Poor Groups of Galaxies. I. Spectroscopic Survey and Results. Astrophys. J. 1998, 496, 39–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skibba, R.A.; van den Bosch, F.C.; Yang, X.; More, S.; Mo, H.; Fontanot, F. Are brightest halo galaxies central galaxies? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 410, 417–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martel, H.; Robichaud, F.; Barai, P. Major Cluster Mergers and the Location of the Brightest Cluster Galaxy. Astrophys. J. 2014, 786, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, M.J.; Jones, C.; Forman, W. Substructure: Clues to the Formation of Clusters of Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 1995, 451, L5–L8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, J.O. Stormy Weather in Galaxy Clusters. Science 1998, 280, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, J.O.; Balonek, T.J. The curvature of radio jets and tails in the intracluster media of Abell 1446 and 2220. Astrophys. J. 1982, 263, 546–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, J.O.; Rhee, G.; Owen, F.N.; Pinkney, J. Clumped X-ray Emission around Radio Galaxies in Abell Clusters. Astrophys. J. 1994, 423, 94–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkney, J.; Burns, J.O.; Hill, J.M. 1919+479: Big WAT in a Poor Cluster. Astron. J. 1994, 108, 2031–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, P.L.; Pinkney, J.; Burns, J.O.; Wang, Q.; Owen, F.N.; Voges, W. ROSAT X-ray Observations of Abell Clusters with Wide-Angle Tailed Radio Sources. Astrophys. J. 1997, 474, 580–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, P.L.; Ledlow, M.J.; Burns, J.O.; Pinkey, J.; Hill, J.M. The Cluster Dynamics, X-ray Emission, and Radio Galaxies in Abell 578 = Abell 1569. Astron. J. 1997, 114, 1711–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, S.; Prieto, M.A. X-ray analysis of Abell 2634 and its central galaxy 3C 465. Astron. Astrophys. 1997, 327, 37–46. [Google Scholar]
- Sakelliou, I.; Merrifield, M.R.; McHardy, I.M. What bent the jets in 4C 34.16? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1996, 283, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakelliou, I.; Merrifield, M.R. The distorted jets and gaseous environment of 3C 465. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1999, 305, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakelliou, I.; Merrifield, M.R. The origin of wide-angle tailed radio galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2000, 311, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakelliou, I.; Acreman, D.M.; Hardcastle, M.J.; Merrifield, M.R.; Ponman, T.J.; Stevens, I.R. The cool wake around 4C 34.16 as seen by XMM-Newton. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2005, 360, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikov, D.I.; Melott, A.L.; Wilhite, B.C.; Kaufman, M.; Burns, J.O.; Miller, C.J.; Batuski, D.J. Cluster winds blow along supercluster axes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1999, 304, L5–L9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglass, E.M.; Blanton, E.L.; Clarke, T.E.; Sarazin, C.L.; Wise, M. Chandra Observation of the Cluster Environment of a WAT Radio Source in Abell 1446. Astrophys. J. 2008, 673, 763–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglass, E. The Galaxy Cluster Environments of Wide Angle Tail Radio Sources. Ph.D. Thesis, Boston University, Boston, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez, P.L.; Calderón, D. The Dynamics of the Wide-angle Tailed (WAT) Galaxy Cluster A562. Astron. J. 2020, 160, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterno-Mahler, R.; Blanton, E.L.; Randall, S.W.; Clarke, T.E. Deep Chandra Observations of the Extended Gas Sloshing Spiral in A2029. Astrophys. J. 2013, 773, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterno-Mahler, R.; Randall, S.W.; Bulbul, E.; Andrade-Santos, F.; Blanton, E.L.; Jones, C.; Murray, S.; Johnson, R.E. Merger Signatures in the Galaxy Cluster A98. Astrophys. J. 2014, 791, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasadia, S.; Sun, M.; Morandi, A.; Sarazin, C.; Clarke, T.; Nulsen, P.; Massaro, F.; Roediger, E.; Harris, D.; Forman, B. Shocking features in the merging galaxy cluster RXJ0334.2-0111. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 458, 681–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglass, E.M.; Blanton, E.L.; Randall, S.W.; Clarke, T.E.; Edwards, L.O.V.; Sabry, Z.; ZuHone, J.A. The Megaparsec-scale Gas-sloshing Spiral in the Remnant Cool Core Cluster Abell 1763. Astrophys. J. 2018, 868, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Randall, S.; Su, Y.; Alvarez, G.E.; Sarazin, C.L.; Jones, C.; Blanton, E.; Nulsen, P.; Chakraborty, P.; Bulbul, E.; et al. Gas Sloshing and Cold Fronts in Pre-merging Galaxy Cluster A98. Astrophys. J. 2023, 944, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, J.; Singh, K.P. The complex intracluster medium of Abell 1569 and its interaction with central radio galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 509, 3321–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, T.E.; Blanton, E.L.; Sarazin, C.L. The Complex Cooling Core of A2029: Radio and X-ray Interactions. Astrophys. J. 2004, 616, 178–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkney, J. The Dynamics of Galaxy Clusters Containing Wide-Angle Tailed Radio Sources. Ph.D. Thesis, New Mexico State University, Las Cruces, NM, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Pinkney, J.; Burns, J.O.; Ledlow, M.J.; Gómez, P.L.; Hill, J.M. Substructure in Clusters Containing Wide-Angle-Tailed Radio Galaxies. I. New Redshifts. Astron. J. 2000, 120, 2269–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krempec-Krygier, J.; Krygier, B. Dynamics of the Abell 98 cluster and the radio structure of 4C+20.04. Astron. Astrophys. 1995, 296, 359–369. [Google Scholar]
- Markevitch, M.; Vikhlinin, A. Shocks and cold fronts in galaxy clusters. Phys. Rep. 2007, 443, 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roettiger, K.; Burns, J.; Loken, C. When Clusters Collide: A Numerical Hydro/N-Body Simulation of Merging Galaxy Clusters. Astrophys. J. 1993, 407, L53–L56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roettiger, K.; Burns, J.O.; Loken, C. The Observational Consequences of Merging Clusters of Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 1996, 473, 651–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roettiger, K.; Stone, J.M.; Mushotzky, R.F. Anatomy of a Merger: A Numerical Model of A754. Astrophys. J. 1998, 493, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricker, P.M.; Sarazin, C.L. Off-Axis Cluster Mergers: Effects of a Strongly Peaked Dark Matter Profile. Astrophys. J. 2001, 561, 621–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, J.O. The Radio Properties of cD Galaxies in Abell Clusters. I. an X-ray Selected Sample. Astron. J. 1990, 99, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A.D.; Stocke, J.T.; Buote, D.A. Chandra Observations of Abell 2029: No Cooling Flow and a Steep Abundance Gradient. Astrophys. J. 2002, 573, L13–L17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, L.P.; Kempner, J. Chandra and XMM-Newton Observations of the Double Cluster A1758. Astrophys. J. 2004, 613, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, H.R.; Sanders, J.S.; Fabian, A.C.; Baum, S.A.; Donahue, M.; Edge, A.C.; McNamara, B.R.; O’Dea, C.P. Chandra observation of two shock fronts in the merging galaxy cluster Abell 2146. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 406, 1721–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finoguenov, A.; Henriksen, M.J.; Briel, U.G.; de Plaa, J.; Kaastra, J.S. XMM-Newton Study of A3562 and Its Immediate Shapley Environs. Astrophys. J. 2004, 611, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZuHone, J.A.; Markevitch, M.; Johnson, R.E. Stirring Up the Pot: Can Cooling Flows in Galaxy Clusters be Quenched by Gas Sloshing? Astrophys. J. 2010, 717, 908–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZuHone, J.A. A Parameter Space Exploration of Galaxy Cluster Mergers. I. Gas Mixing and the Generation of Cluster Entropy. Astrophys. J. 2011, 728, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, O.; Martizzi, D.; Wu, H.Y.; Evrard, A.E.; Teyssier, R.; Wechsler, R.H. rhapsody-g simulations—I. The cool cores, hot gas and stellar content of massive galaxy clusters. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 470, 166–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soker, N.; Sarazin, C.L. Cooling Flows and the Stability of Radio Jets. Astrophys. J. 1988, 327, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dea, C.P.; Baum, S.A. Radio properties of central dominant galaxies in cluster cooling flows. Natl. Radio Astron. Obs. Workshop 1986, 16, 141–146. [Google Scholar]
- Baum, S.A.; O’Dea, C.P. Multifrequency VLA observations of PKS 0745-191: The archetypal “cooling flow” radio source? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1991, 250, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanton, E.L.; Randall, S.W.; Clarke, T.E.; Sarazin, C.L.; McNamara, B.R.; Douglass, E.M.; McDonald, M. A Very Deep Chandra Observation of A2052: Bubbles, Shocks, and Sloshing. Astrophys. J. 2011, 737, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.B.; O’Dea, C.P.; Peck, A.B.; Koekemoer, A.M. H I Absorption toward the Nucleus of the Radio Galaxy PKS 2322-123 in A2597. Astrophys. J. 1999, 512, L27–L30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liuzzo, E.; Giovannini, G.; Giroletti, M.; Taylor, G.B. Parsec-scale properties of brightest cluster galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 516, A1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hintzen, P.; Ulvestad, J.; Owen, F. Are wide-angle radio-tail QSOs members of clusters of galaxies? I. VLA maps at 20 CM of 117 radio quasars. Astron. J. 1983, 88, 709–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanton, E.L.; Gregg, M.D.; Helfand, D.J.; Becker, R.H.; White, R.L. Discovery of a High-Redshift (z = 0.96) Cluster of Galaxies Using a FIRST Survey Wide-Angle-Tailed Radio Source. Astron. J. 2003, 125, 1635–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanton, E.L.; Paterno-Mahler, R.; Wing, J.D.; Ashby, M.L.N.; Golden-Marx, E.; Brodwin, M.; Douglass, E.M.; Randall, S.W.; Clarke, T.E. Extragalactic jets as probes of distant clusters of galaxies and the clusters occupied by bent radio AGN (COBRA) survey. In Proceedings of the Extragalactic Jets from Every Angle, Virtual, 29 November–3 December 2021; Massaro, F., Cheung, C.C., Lopez, E., Siemiginowska, A., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2015; Volume 313, pp. 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, W.H.; Becker, R.H.; White, R.L. Double-Lobed Radio Quasars from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. Astron. J. 2006, 131, 666–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeland, E.; Cardoso, R.F.; Wilcots, E. Bent-Double Radio Sources as Probes of Intergalactic Gas. Astrophys. J. 2008, 685, 858–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacintucci, S.; Venturi, T. Tailed radio galaxies as tracers of galaxy clusters. Serendipitous discoveries with the GMRT. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 505, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oklopčić, A.; Smolčić, V.; Giodini, S.; Zamorani, G.; Bîrzan, L.; Schinnerer, E.; Carilli, C.L.; Finoguenov, A.; Lilly, S.; Koekemoer, A.; et al. Identifying Dynamically Young Galaxy Groups Via Wide-angle Tail Galaxies: A Case Study in the COSMOS Field at z = 0.53. Astrophys. J. 2010, 713, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oklopčić, A.; Smolčić, V.; Giodini, S.; Zamorani, G.; Bhatirzan, L.; Schinnerer, E.; Carilli, C.L.; Finoguenov, A.; Lilly, S.; Koekemoer, A.; et al. A wide-angle tail galaxy at z = 0.53 in the COSMOS field. Mem. Della Soc. Astron. Ital. 2011, 82, 161. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, M.Y.; Sharp, R.; Saikia, D.J.; Norris, R.P.; Johnston-Hollitt, M.; Middelberg, E.; Lovell, J.E.J. Wide-angle tail galaxies in ATLAS. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 406, 2578–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banfield, J.K.; Andernach, H.; Kapińska, A.D.; Rudnick, L.; Hardcastle, M.J.; Cotter, G.; Vaughan, S.; Jones, T.W.; Heywood, I.; Wing, J.D.; et al. Radio Galaxy Zoo: Discovery of a poor cluster through a giant wide-angle tail radio galaxy. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 460, 2376–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterno-Mahler, R.; Blanton, E.L.; Brodwin, M.; Ashby, M.L.N.; Golden-Marx, E.; Decker, B.; Wing, J.D.; Anand, G. The High-redshift Clusters Occupied by Bent Radio AGN (COBRA) Survey: The Spitzer Catalog. Astrophys. J. 2017, 844, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden-Marx, E.; Blanton, E.L.; Paterno-Mahler, R.; Brodwin, M.; Ashby, M.L.N.; Lemaux, B.C.; Lubin, L.M.; Gal, R.R.; Tomczak, A.R. The High-redshift Clusters Occupied by Bent Radio AGN (COBRA) Survey: Follow-up Optical Imaging. Astrophys. J. 2019, 887, 50–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeland, E.; Wilcots, E. Intergalactic Gas in Groups of Galaxies: Implications for Dwarf Spheroidal Formation and the Missing Baryons Problem. Astrophys. J. 2011, 738, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhukta, N.; Mondal, S.K.; Pal, S. Tailed radio galaxies from the TIFR GMRT sky survey. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 516, 372–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan, S.; Johnston-Hollitt, M.; Franzen, T.M.O.; Norris, R.P.; Miller, N.A. Bent-tailed Radio Sources in the Australia Telescope Large Area Survey of the Chandra Deep Field South. Astron. J. 2014, 148, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, R.P.; Hopkins, A.M.; Afonso, J.; Brown, S.; Condon, J.J.; Dunne, L.; Feain, I.; Hollow, R.; Jarvis, M.; Johnston-Hollitt, M.; et al. EMU: Evolutionary Map of the Universe. Publ. Astron. Soc. Aust. 2011, 28, 215–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mguda, Z.; Faltenbacher, A.; Heyden, K.v.d.; Gottlöber, S.; Cress, C.; Vaisanen, P.; Yepes, G. Ram pressure statistics for bent tail radio galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 446, 3310–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proctor, D.D. Morphological Annotations for Groups in the First Database. Astrophys. J.Suppl. Ser. 2011, 194, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croston, J.H.; Hardcastle, M.J.; Mingo, B.; Best, P.N.; Sabater, J.; Shimwell, T.M.; Williams, W.L.; Duncan, K.J.; Röttgering, H.J.A.; Brienza, M.; et al. The environments of radio-loud AGN from the LOFAR Two-Metre Sky Survey (LoTSS). Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 622, A10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proctor, D.D. Comparing Pattern Recognition Feature Sets for Sorting Triples in the FIRST Database. Astrophys. J.Suppl. Ser. 2006, 165, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, J.O.; Gregory, S.A. The structure of 4C radio galaxies in poor clusters. Astron. J. 1982, 87, 1245–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardcastle, M.J.; Sakelliou, I.; Worrall, D.M. A Chandra and XMM-Newton study of the wide-angle tail radio galaxy 3C465. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2005, 359, 1007–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dea, C.P.; Owen, F.N. VLA observations of 57 sources in clusters of galaxies. Astron. J. 1985, 90, 927–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dea, C.P.; Owen, F.N. Multifrequency VLA Observations of the Prototypical Narrow-Angle Tail Radio Source, NGC 1265. Astrophys. J. 1986, 301, 841–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, M.L.; Burns, J.O.; Sulkanen, M.E. Disruption of galactic radio jets by shocks in the ambient medium. Nature 1988, 335, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loken, C.; Roettiger, K.; Burns, J.O.; Norman, M. Radio Jet Propagation and Wide-Angle Tailed Radio Sources in Merging Galaxy Cluster Environments. Astrophys. J. 1995, 445, 80–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appl, S.; Lery, T.; Baty, H. Current-driven instabilities in astrophysical jets. Linear analysis. Astron. Astrophys. 2000, 355, 818–828. [Google Scholar]
- Hardee, P.E. The stability of astrophysical jets. In Proceedings of the Jets at All Scales, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 13–17 September 2010; Romero, G.E., Sunyaev, R.A., Belloni, T., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011; Volume 275, pp. 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaglia, S.; Bodo, G.; Rossi, P.; Capetti, S.; Mignone, A. Making Faranoff-Riley I radio sources. II. The effects of jet magnetization. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 621, A132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martí, J.M. Numerical Simulations of Jets from Active Galactic Nuclei. Galaxies 2019, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barniol Duran, R.; Tchekhovskoy, A.; Giannios, D. Simulations of AGN jets: Magnetic kink instability versus conical shocks. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 469, 4957–4978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaglia, S.; Bodo, G.; Rossi, P.; Capetti, A.; Mignone, A. Making Fanaroff-Riley I radio sources. III. The effects of the magnetic field on relativistic jets’ propagation and source morphologies. Astron. Astrophys. 2022, 659, A139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Heinz, S.; Hooper, E. A Numerical Study of the Impact of Jet Magnetic Topology on Radio Galaxy Evolution. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.03863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Z.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Yuan, F. Three-dimensional Magnetohydrodynamical Simulations of the Morphology of Head-Tail Radio Galaxies Based on the Magnetic Tower Jet Model. Astrophys. J. 2017, 839, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardee, P.E. Spatial Stability of Relativistic Jets: Application to 3C 345. Astrophys. J. 1987, 318, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkinshaw, M. The Kelvin-Helmholtz instability for relativistic particle beams—II. Flows bounded by a simple shear layer. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1991, 252, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkinshaw, M. Instabilities in Astrophysical Jets. Astrophys. Space Sci. 1996, 242, 17–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamlin, N.D.; Newman, W.I. Role of the Kelvin-Helmholtz instability in the evolution of magnetized relativistic sheared plasma flows. Phys. Rev. E 2013, 87, 043101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal-Krishna; Wiita, P.J. The expansion and cosmological evolution of powerful radio sources. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1987, 226, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooda, J.S.; Wiita, P.J. Three-dimensional Simulations of Extragalactic Jets Crossing Interstellar Medium/Intracluster Medium Interfaces. Astrophys. J. 1996, 470, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.M.; Koide, S.; Sakai, J.I. Two-Dimensional Simulations of Relativistic Extragalactic Jets Crossing an ISM/ICM Interface. PASJ 1999, 51, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardee, P.E.; White, R.E.I.; Norman, M.L.; Cooper, M.A.; Clarke, D.A. Asymmetric Morphology of the Propagating Jet. II. The Effect of Atmospheric Gradients. Astrophys. J. 1992, 387, 460–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, S.W.; O’Brien, T.J.; Dunlop, J.S. Structures produced by the collision of extragalactic jets with dense clouds. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1999, 309, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wiita, P.J.; Hooda, J.S. Radio Jet Interactions with Massive Clouds. Astrophys. J. 2000, 534, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiita, P.J. Jet Propagation Through Irregular Media and the Impact of Lobes on Galaxy Formation. ApSS 2004, 293, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dea, C.P.; Owen, F.N.; Keel, W.C. Optical spectroscopy of radio jets in 3C 31, 3C 75, 3C 83.1B, and 3C 465. Can. J. Phys. 1986, 64, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dea, C.P.; Saikia, D.J. Compact steep-spectrum and peaked-spectrum radio sources. AA Rev. 2021, 29, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gull, S.F.; Northover, K.J.E. Bubble Model of Extragalactic Radio Sources. Nature 1973, 244, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowie, L.L.; McKee, C.F. A dynamical model of the tailed radio galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. 1975, 43, 337–343. [Google Scholar]
- Worrall, D.M.; Birkinshaw, M.; Cameron, R.A. The X-ray Environment of the Dumbbell Radio Galaxy NGC 326. Astrophys. J. 1995, 449, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laing, R.A. Magnetic fields in extragalactic radio sources. Astrophys. J. 1981, 248, 87–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benford, G. Current-carrying beams in astrophysics: Models for double radio sources and jets. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1978, 183, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.L.; Henriksen, R.N. On the supersonic dynamics of magnetized jets of thermal gas in radio galaxies. Astrophys. J. 1980, 241, 534–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyvaerts, J.; Norman, C. The Collimation of Magnetized Winds. Astrophys. J. 1989, 347, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynden-Bell, D. On why discs generate magnetic towers and collimate jets. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2003, 341, 1360–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabuzda, D. Evidence for Helical Magnetic Fields Associated with AGN Jets and the Action of a Cosmic Battery. Galaxies 2018, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fendt, C.; Zinnecker, H. Possible bending mechanisms of protostellar jets. Astron. Astrophys. 1998, 334, 750–755. [Google Scholar]
- Burns, J.O.; Loken, C.; Roettiger, K.; Rizza, E.; Bryan, G.; Norman, M.L.; Gómez, P.; Owen, F.N. Stormy weather and cluster radio galaxies. New A Rev. 2002, 46, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendygral, P.J.; Jones, T.W.; Dolag, K. MHD Simulations of Active Galactic Nucleus Jets in a Dynamic Galaxy Cluster Medium. Astrophys. J. 2012, 750, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, L.D.; Lifshitz, E.M. Fluid Mechanics; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Patnaik, A.R.; Banhatti, D.G.; Subrahmanya, C.R. VLA observations of the wide-angle tailed radio source 1313+073. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1984, 211, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
O’Dea, C.P.; Baum, S.A. Wide-Angle-Tail (WAT) Radio Sources. Galaxies 2023, 11, 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies11030067
O’Dea CP, Baum SA. Wide-Angle-Tail (WAT) Radio Sources. Galaxies. 2023; 11(3):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies11030067
Chicago/Turabian StyleO’Dea, Christopher P., and Stefi A. Baum. 2023. "Wide-Angle-Tail (WAT) Radio Sources" Galaxies 11, no. 3: 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies11030067
APA StyleO’Dea, C. P., & Baum, S. A. (2023). Wide-Angle-Tail (WAT) Radio Sources. Galaxies, 11(3), 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies11030067






