Advanced Life Peaked Billions of Years Ago According to Black Holes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Black Hole Feedback on Stars across Space and Time
3. The Drake Equation Viewed Broadly
4. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haqq-Misra, J.; Baum, S.D. The sustainability solution to the Fermi Paradox. JBIS 2009, 62, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Savitch, E.; Frank, A.; Carroll-Nellenback, J.; Haqq-Nisra, J. Triggering a climate change dominated “anthropocene”: Is it common among exocivilizations? Astron. J. 2021, 162, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prantzos, N. A probabilistic analysis of the Fermi paradox in terms of the Drake formula: The role of the L factor. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 493, 3464–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, F. How can we detect radio transmissions from distant planetary systems? Sky Telesc. 1960, 19, 140. [Google Scholar]
- Magorrian, J.; Tremaine, S.; Richstone, D.; Bender, R.; Bower, G.; Dressler, A.; Faber, S.M.; Gebhardt, K.; Green, R.; Grillmair, C.; et al. The demography of massive dark objects in galaxy centers. Astron. J. 1998, 115, 2285–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebhardt, K.; Bender, R.; Bower, G.; Dressler, A.; Faber, S.M.; Filippenko, A.V.; Green, R.; Grillmair, C.; Ho, L.C.; Kormendy, J.; et al. A Relationship between Nuclear Black Hole Mass and Galaxy Velocity Dispersion. Astrophys. J. 2000, 539, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrarese, L.; Merritt, D. A Fundamental Relation between Supermassive Black Holes and Their Host Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2000, 539, L9–L12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakura, N.I.; Sunyaev, R.A. Black holes in binary systems. Observational appearance. Astron. Astrophys. 1973, 24, 337–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalfountzou, E.; Stevens, J.A.; Jarvis, M.J.; Hardcastle, M.J.; Smith, D.J.B.; Bourne, N.; Dunne, L.; Ibar, E.; Eales, S.; Ivison, R.J.; et al. Hertschel-ATLAS: Far-infrared properties of radio-loud and radio-quiet quasars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 442, 1181–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comerford, J.M.; Negus, J.; Müller-Sánchez, F.; Eracleous, M.; Wylezalek, D.; Storchi-Bergmann, T.; Greene, J.E.; Barrows, R.S.; Nevin, R.; Roy, N.; et al. A Catalog of 406 AGNs in MaNGA: A Connection between Radio-mode AGNs and Star Formation Quenching. Astrophys. J. 2020, 901, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.B.; Kulasiri, N.; North, M.; Garofalo, D. The Black Hole-star Formation Connection Over Cosmic Time. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2021, 133, 104101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, D.; Evans, D.A.; Sambruna, R.M. The evolution of radio-loud active galactic nuclei as a function of black hole spin. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 406, 975–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardeen, J.M.; Petterson, J.A. The Lense-Thirring Effect and Accretion Disks around Kerr Black Holes. Astrophys. J. 1975, 195, 65–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonuccio-Delogu, V.; Silk, J. Active galactic nuclei activity: Self-regulation from backflow. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 405, 1303–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neilsen, J.; Lee, J.C. Accretion disk winds as the jet suppression mechanism in the microquasar GRS 1915+105. Nature 2009, 458, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponti, G.; Fender, R.P.; Begelman, M.C.; Dunn, R.J.H.; Neilsen, J.; Coriat, M. Ubiquitous equatorial accretion disc winds in black hole soft states. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 2012, 422, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, D.; Moravec, E.; Macconi, D.; Singh, C.B. Is jet re-orientation the elusive trigger for star formation suppression in radio galaxies? Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2022, 134, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitmire, D.P. The habitability of large elliptical galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 494, 3048–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirasuolo, M.; Magliocchetti, M.; Celotti, A.; Danese, L. The radio-loud/radio-quiet dichotomy: News from the 2dF QSO Redshift Survey. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2003, 341, 993–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadhunter, C.; Dicken, D.; Morganti, R.; Könyves, V.; Ysard, N.; Nesvadba, N.; Almeida, C.R. The dust masses of powerful radio galaxies: Clues to the triggering of their activity. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 2014, 445, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.R.; Lubow, S.H.; Ogilvie, G.I.; Pringle, J.E. Aligning spinning black holes and accretion discs. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2005, 363, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, D.; Christian, D.J.; Jones, A.M. The Sub-Eddington Boundary for the Quasar Mass–Luminosity Plane: A Theoretical Perspective. Universe 2019, 5, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayal, P.; Cockell, C.S.; Rice, K.; Mazumdar, A. The quest for cradles of life: Using the fundamental metallicity relation to hunt for the most habitable type of galaxy. Astrophys. J. 2015, 810, L2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojković, N.; Vukotić, B.; Martinović, N.; Ćirković, M.M.; Micic, M. Galactic habitability re-examined: Indications of bimodality. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 490, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertone, S.; Conselice, C.J. A comparison of galaxy merger history observations and predictions from semi-analytic models. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2009, 396, 2345–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Jiang, J.H.; Fahy, K.A.; Yung, Y.L. A Statistical Estimation of the Occurrence of Extraterrestrial Intelligence in the Milky Way Galaxy. Galaxies 2021, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingam, M.; Loeb, A. Colloquium: Physical constraints for the evolution of life on exoplanets. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2019, 91, 021002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, H.J.; Miralda-Escude, J. Gaseous galactic halos and quasi-stellar object absorption-line systems. Astrophys. J. 1996, 469, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, D.; Joshi, R.; Yang, X.; Singh, C.B.; North, M.; Hopkins, M. A Unified Framework for X-shaped Radio Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2020, 889, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, R.; Krishna, G.; Yang, X.; Shi, J.; Yu, S.-Y.; Wiita, P.J.; Ho, L.C.; Wu, X.-B.; An, T.; Wang, R.; et al. X-shaped Radio Galaxies: Optical Properties, Large-scale Environment, and Relationship to Radio Structure. Astrophys. J. 2019, 887, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, G.; Brownlee, D.; Ward, P. The galactic habitable zone: Galactic chemical evolution. Icarus 2001, 152, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lineweaver, C.H.; Fenner, Y.; Gibson, B.K. The Galactic Habitable Zone and the Age Distribution of Complex Life in the Milky Way. Science 2004, 303, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, J.C.; Loeb, A. Evaporation of planetary atmospheres due to XUV illumination by quasars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 479, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbi, A.; Tombesi, F. The habitability of the Milky Way during the active phase of its central supermassive black hole. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Forbes, J.C.; Loeb, A. Habitable Evaporated Cores and the Occurrence of Panspermia Near the Galactic Center. Astrophys. J. 2018, 855, L1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisłocka, A.M.; Kovačević, A.B.; Balbi, A. Comparative analysis of the influence of Sgr A* and nearby active galactic nuclei on the mass loss of known exoplanets. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 624, A71–A88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chen, X.; Du, F. Impact of an Active Sgr A* on the Synthesis of Water and Organic Molecules throughout the Milky Way. Astrophys. J. 2020, 899, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacetti, E.; Balbi, A.; Lingam, M.; Tombesi, F.; Perlman, E. The impact of tidal disruption events on galactic habitability. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 498, 3153–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, S. On the relative importance of AGN winds for the evolution of exoplanet atmospheres. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 513, 4669–4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrifi, A.; Balbi, A.; Lingam, M.; Tombesi, F.; Perlman, E. The impact of AGN outflows on the surface habitability of terrestrial planets in the Milky Way. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 512, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.H.; Li, H.; Chong, M.; Jin, Q.; Rosen, P.E.; Jiang, X.; Fahy, K.A.; Taylor, S.F.; Kong, Z.; Hah, J.; et al. A Beacon in the Galaxy: Updated Arecibo Message for Potential FAST and SETI Projects. Galaxies 2022, 10, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
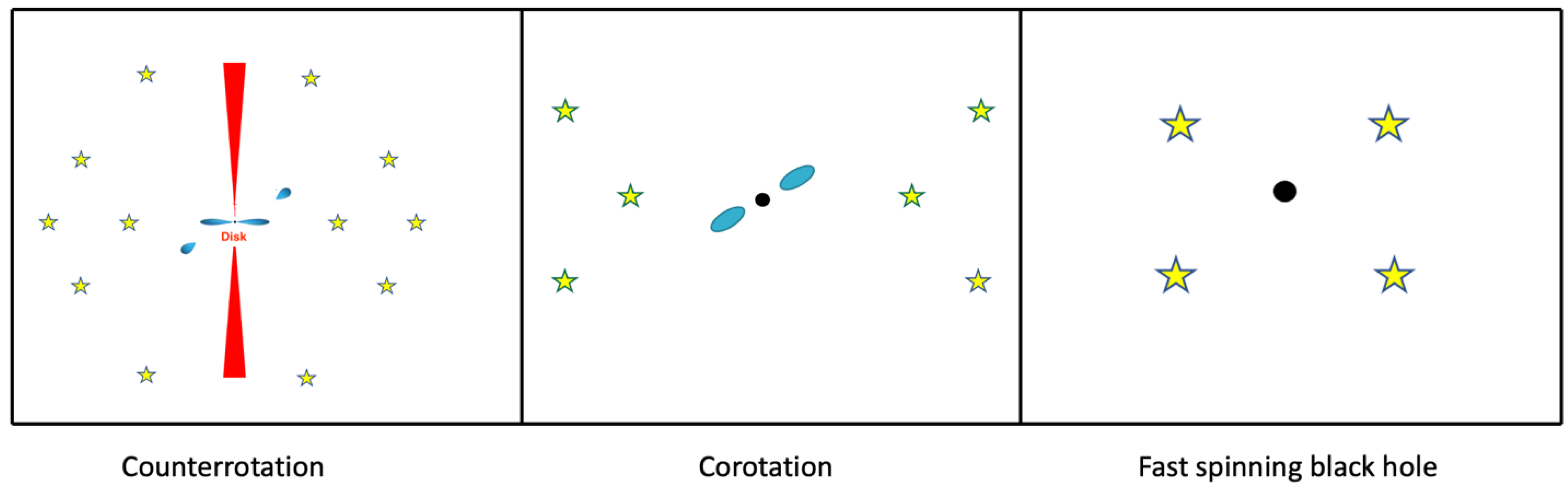
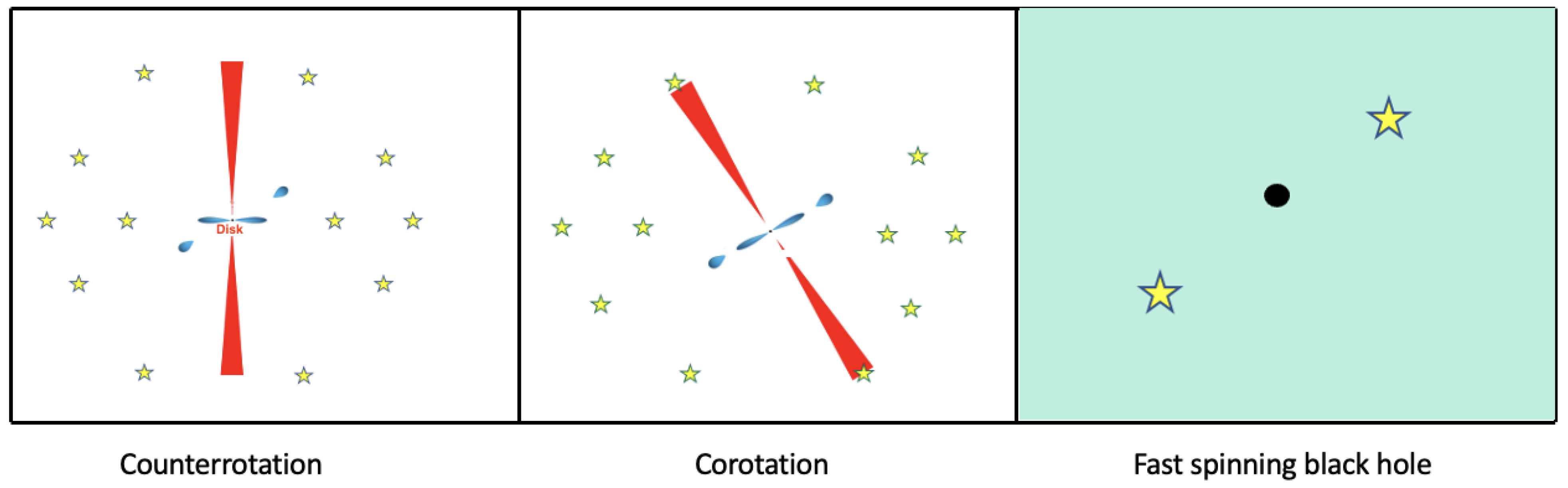
| Type | SFR | R | Dust Mass | μd | FDrake |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clusters | 200 | 66.7 | 7 × 104 | 2.2 × 10−3 | 0.15 |
| Groups | 40 | 13.3 | 2 × 105 | 6.2 × 10−3 | 0.08 |
| Fields | 15 | 5 | 2.6 × 108 | 8.125 | 40.63 |
| Milky Way | 3 | 1 | 3.2 × 107 | 1 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garofalo, D. Advanced Life Peaked Billions of Years Ago According to Black Holes. Galaxies 2023, 11, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies11030066
Garofalo D. Advanced Life Peaked Billions of Years Ago According to Black Holes. Galaxies. 2023; 11(3):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies11030066
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarofalo, David. 2023. "Advanced Life Peaked Billions of Years Ago According to Black Holes" Galaxies 11, no. 3: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies11030066
APA StyleGarofalo, D. (2023). Advanced Life Peaked Billions of Years Ago According to Black Holes. Galaxies, 11(3), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies11030066






