Genomic Profiling on an Unselected Solid Tumor Population Reveals a Highly Mutated Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Associated with Oncogenic EGFR Mutations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
2.1. Classification of a Mutant EGFR Containing Cancer Cohort
2.2. Functional Analysis and Mapping of the Variants in the AE Group
2.2.1. Receptors
2.2.2. Genes Involved in Genomic and Epigenomic Stability
2.2.3. Wnt/Β-Catenin Pathway
2.2.4. TP53/Apoptosis and RB/Cell Cycle Pathways
2.2.5. PI3K–AKT–mTOR and RAS–RAF–MEK–ERK Pathways
2.2.6. Kinase and Phosphatase
2.2.7. NOTCH
2.2.8. Others (Hedgehog, NF-κB, TGF-β)
2.3. The Mutation Types of the Top Three Mutated Genes and Their Enrichment in AE Cases
2.4. Mutation Distribution of Top Three Mutated Genes between EGFR L858R and EGFR Exon 19del
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Patient Samples
3.2. CANCERPLEX
3.3. Functional Mapping of the Variants to Their Respective Pathways
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paez, J.G.; Janne, P.A.; Lee, J.C.; Tracy, S.; Greulich, H.; Gabriel, S.; Herman, P.; Kaye, F.J.; Lindeman, N.; Boggon, T.J.; et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: Correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science 2004, 304, 1497–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, T.J.; Bell, D.W.; Sordella, R.; Gurubhagavatula, S.; Okimoto, R.A.; Brannigan, B.W.; Harris, P.L.; Haserlat, S.M.; Supko, J.G.; Haluska, F.G.; et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 2129–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troiani, T.; Napolitano, S.; Della Corte, C.M.; Martini, G.; Martinelli, E.; Morgillo, F.; Ciardiello, F. Therapeutic value of EGFR inhibition in CRC and NSCLC: 15 years of clinical evidence. ESMO Open 2016, 1, e000088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Greulich, H.; Janne, P.A.; Sellers, W.R.; Meyerson, M.; Griffin, J.D. Epidermal growth factor-independent transformation of Ba/F3 cells with cancer-derived epidermal growth factor receptor mutants induces gefitinib-sensitive cell cycle progression. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 8968–8974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, D.L.; Dunn, E.F.; Harari, P.M. Understanding resistance to EGFR inhibitors-impact on future treatment strategies. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 7, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, D.L.; Huang, S.; Kruser, T.J.; Nechrebecki, M.M.; Armstrong, E.A.; Benavente, S.; Gondi, V.; Hsu, K.T.; Harari, P.M. Mechanisms of acquired resistance to cetuximab: Role of HER (ERBB) family members. Oncogene 2008, 27, 3944–3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Li, X.; Liang, K.; Luwor, R.; Siddik, Z.H.; Mills, G.B.; Mendelsohn, J.; Fan, Z. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) ubiquitination as a mechanism of acquired resistance escaping treatment by the anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody cetuximab. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 8240–8247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, D.L.; Iida, M.; Kruser, T.J.; Nechrebecki, M.M.; Dunn, E.F.; Armstrong, E.A.; Huang, S.; Harari, P.M. Epidermal growth factor receptor cooperates with SRC family kinases in acquired resistance to cetuximab. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2009, 8, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lievre, A.; Bachet, J.B.; Le Corre, D.; Boige, V.; Landi, B.; Emile, J.F.; Cote, J.F.; Tomasic, G.; Penna, C.; Ducreux, M.; et al. KRAS mutation status is predictive of response to cetuximab therapy in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 3992–3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erjala, K.; Sundvall, M.; Junttila, T.T.; Zhang, N.; Savisalo, M.; Mali, P.; Kulmala, J.; Pulkkinen, J.; Grenman, R.; Elenius, K. Signaling via ErbB2 and ErbB3 associates with resistance and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) amplification with sensitivity to EGFR inhibitor gefitinib in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 4103–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelman, J.A.; Zejnullahu, K.; Mitsudomi, T.; Song, Y.; Hyland, C.; Park, J.O.; Lindeman, N.; Gale, C.M.; Zhao, X.; Christensen, J.; et al. MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science 2007, 316, 1039–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, E.L.; Tan, S.Z.; Liu, G.; Tsao, M.S. Known and putative mechanisms of resistance to EGFR targeted therapies in NSCLC patients with EGFR mutations—A review. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2015, 4, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Togashi, Y.; Hayashi, H.; Terashima, M.; de Velasco, M.A.; Sakai, K.; Fujita, Y.; Tomida, S.; Nakagawa, K.; Nishio, K. Inhibition of β-catenin enhances the anticancer effect of irreversible EGFR-TKI in EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer with a T790M mutation. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakata, A.; Yoshida, R.; Yamaguchi, R.; Yamauchi, M.; Tamada, Y.; Fujita, A.; Shimamura, T.; Imoto, S.; Higuchi, T.; Nomura, M.; et al. Elevated β-catenin pathway as a novel target for patients with resistance to EGF receptor targeting drugs. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casas-Selves, M.; Kim, J.; Zhang, Z.; Helfrich, B.A.; Gao, D.; Porter, C.C.; Scarborough, H.A.; Bunn, P.A., Jr.; Chan, D.C.; Tan, A.C.; et al. Tankyrase and the canonical Wnt pathway protect lung cancer cells from EGFR inhibition. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 4154–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sholl, L.M.; Do, K.; Shivdasani, P.; Cerami, E.; Dubuc, A.M.; Kuo, F.C.; Garcia, E.P.; Jia, Y.; Davineni, P.; Abo, R.P.; et al. Institutional implementation of clinical tumor profiling on an unselected cancer population. JCI Insight 2016, 1, e87062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richer, A.L.; Friel, J.M.; Carson, V.M.; Inge, L.J.; Whitsett, T.G. Genomic profiling toward precision medicine in non-small cell lung cancer: Getting beyond EGFR. Pharmgenom. Pers. Med. 2015, 8, 63–79. [Google Scholar]
- Eifert, C.; Pantazi, A.; Sun, R.; Xu, J.; Cingolani, P.; Heyer, J.; Russell, M.; Lvova, M.; Ring, J.; Tse, J.Y.; et al. Clinical application of a cancer genomic profiling assay to guide precision medicine decisions. Personal. Med. 2017, 14, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsudomi, T.; Yatabe, Y. Epidermal growth factor receptor in relation to tumor development: EGFR gene and cancer. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, Q.; Guo, H.; Zhang, K.; Zheng, R.; Xiao, C. PKHD1 gene silencing may cause cell abnormal proliferation through modulation of intracellular calcium in autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 40, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, C.J.; Wu, Y.; Johnson, R.A.; Woollard, J.R.; Bergstralh, E.J.; Cicek, M.S.; Bakeberg, J.; Rossetti, S.; Heyer, C.M.; Petersen, G.M.; et al. Germline PKHD1 mutations are protective against colorectal cancer. Hum. Genet. 2011, 129, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spano, J.P.; Lagorce, C.; Atlan, D.; Milano, G.; Domont, J.; Benamouzig, R.; Attar, A.; Benichou, J.; Martin, A.; Morere, J.F.; et al. Impact of EGFR expression on colorectal cancer patient prognosis and survival. Ann. Oncol. 2005, 16, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, K.D.; Mahale, S.; Astling, D.P.; Aisner, D.L.; Le, A.T.; Hinz, T.K.; Vaishnavi, A.; Bunn, P.A., Jr.; Heasley, L.E.; Tan, A.C.; et al. Resistance to ros1 inhibition mediated by EGFR pathway activation in non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.C.; Xu, C.W.; Ye, X.Q.; Yin, M.X.; Zhang, J.X.; Du, K.Q.; Zhang, Z.H.; Hu, J. Lung cancer with concurrent EGFR mutation and ros1 rearrangement: A case report and review of the literature. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 9, 4301–4305. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Y.; Wu, S. ALK and ROS1 concurrent with EGFR mutation in patients with lung adenocarcinoma. OncoTargets Ther. 2017, 10, 3399–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chang, H.; Sung, J.H.; Moon, S.U.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, J.S. EGF induced ret inhibitor resistance in ccdc6-ret lung cancer cells. Yonsei Med. J. 2017, 58, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhinge, K.; Yang, L.; Terra, S.; Nasir, A.; Muppa, P.; Aubry, M.C.; Yi, J.; Janaki, N.; Kovtun, I.V.; Murphy, S.J.; et al. EGFR mediates activation of ret in lung adenocarcinoma with neuroendocrine differentiation characterized by ASCL1 expression. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 27155–27165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Klempner, S.J.; Bazhenova, L.A.; Braiteh, F.S.; Nikolinakos, P.G.; Gowen, K.; Cervantes, C.M.; Chmielecki, J.; Greenbowe, J.R.; Ross, J.S.; Stephens, P.J.; et al. Emergence of ret rearrangement co-existing with activated EGFR mutation in EGFR-mutated NSCLC patients who had progressed on first- or second-generation EGFR TKI. Lung Cancer 2015, 89, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadakis, A.I.; Sun, C.; Knijnenburg, T.A.; Xue, Y.; Grernrum, W.; Holzel, M.; Nijkamp, W.; Wessels, L.F.; Beijersbergen, R.L.; Bernards, R.; et al. Smarce1 suppresses EGFR expression and controls responses to MET and ALK inhibitors in lung cancer. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imielinski, M.; Berger, A.H.; Hammerman, P.S.; Hernandez, B.; Pugh, T.J.; Hodis, E.; Cho, J.; Suh, J.; Capelletti, M.; Sivachenko, A.; et al. Mapping the hallmarks of lung adenocarcinoma with massively parallel sequencing. Cell 2012, 150, 1107–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, S.; Davoli, T.; Leng, Y.; Li, M.Z.; Xu, Q.; Elledge, S.J. A genetic interaction analysis identifies cancer drivers that modify EGFR dependency. Genes Dev. 2017, 31, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Getz, G.; Wheeler, D.A.; Mardis, E.R.; McLellan, M.D.; Cibulskis, K.; Sougnez, C.; Greulich, H.; Muzny, D.M.; Morgan, M.B.; et al. Somatic mutations affect key pathways in lung adenocarcinoma. Nature 2008, 455, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.; Kipps, T.; Kurzrock, R. ATM mutations in cancer: Therapeutic implications. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 1781–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Lan, L.; Peng, G.; Chang, W.C.; Hsu, M.C.; Wang, Y.N.; Cheng, C.C.; Wei, L.; Nakajima, S.; Chang, S.S.; et al. Tyrosine 370 phosphorylation of ATM positively regulates DNA damage response. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marks, J.L.; Golas, B.; Kirchoff, T.; Miller, V.A.; Riely, G.J.; Offit, K.; Pao, W. EGFR mutant lung adenocarcinomas in patients with germline BRCA mutations. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2008, 3, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Waard WIQ, V.D.B.D.; Monkhorst, K.; Vessies, D.C.L.; Vis, D.J.; van den Heuvel, M.M. EGFR and BRCA2 mutations in metastasized adenocarcinoma of the lung. SM Lung Cancer Res. Ther. 2017, 1, 1001. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, X.; Gu, P.; Zhou, C.; Liang, A.; Ren, S.; Liu, F.; Zeng, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, B.; et al. β-catenin overexpression is associated with gefitinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 28, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, D.J. Wnt signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, T.; Li, C. Convergence between Wnt-β-catenin and EGFR signaling in cancer. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, M.; Shigematsu, H.; Nakajima, T.; Kubo, R.; Motohashi, S.; Sekine, Y.; Shibuya, K.; Iizasa, T.; Hiroshima, K.; Nakatani, Y.; et al. Synchronous alterations of Wnt and epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathways through aberrant methylation and mutation in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 6087–6092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, S.; Sng, N.; Carretero, J.; Welner, R.; Hayashi, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Tan, A.J.; Yamaguchi, N.; Yasuda, H.; Li, D.; et al. β-catenin contributes to lung tumor development induced by EGFR mutations. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 5891–5902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickering, C.R.; Zhang, J.; Yoo, S.Y.; Bengtsson, L.; Moorthy, S.; Neskey, D.M.; Zhao, M.; Ortega Alves, M.V.; Chang, K.; Drummond, J.; et al. Integrative genomic characterization of oral squamous cell carcinoma identifies frequent somatic drivers. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 770–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, Y.; Miyazaki, T.; Nakashiro, K.; Yamagata, H.; Isokane, M.; Goda, H.; Tanaka, H.; Oka, R.; Hamakawa, H. Human fat1 cadherin controls cell migration and invasion of oral squamous cell carcinoma through the localization of β-catenin. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 26, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Morris, L.G.; Kaufman, A.M.; Gong, Y.; Ramaswami, D.; Walsh, L.A.; Turcan, S.; Eng, S.; Kannan, K.; Zou, Y.; Peng, L.; et al. Recurrent somatic mutation of FAT1 in multiple human cancers leads to aberrant Wnt activation. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bock, C.E.; Ardjmand, A.; Molloy, T.J.; Bone, S.M.; Johnstone, D.; Campbell, D.M.; Shipman, K.L.; Yeadon, T.M.; Holst, J.; Spanevello, M.D.; et al. The FAT1 cadherin is overexpressed and an independent prognostic factor for survival in paired diagnosis-relapse samples of precursor B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2012, 26, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Pan, S.; Hsieh, M.H.; Ng, N.; Sun, F.; Wang, T.; Kasibhatla, S.; Schuller, A.G.; Li, A.G.; Cheng, D.; et al. Targeting Wnt-driven cancer through the inhibition of porcupine by LGK974. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 20224–20229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loregger, A.; Grandl, M.; Mejias-Luque, R.; Allgauer, M.; Degenhart, K.; Haselmann, V.; Oikonomou, C.; Hatzis, P.; Janssen, K.P.; Nitsche, U.; et al. The E3 ligase RNF43 inhibits Wnt signaling downstream of mutated β-catenin by sequestering TCF4 to the nuclear membrane. Sci. Signal 2015, 8, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bond, C.E.; McKeone, D.M.; Kalimutho, M.; Bettington, M.L.; Pearson, S.A.; Dumenil, T.D.; Wockner, L.F.; Burge, M.; Leggett, B.A.; Whitehall, V.L. RNF43 and ZNRF3 are commonly altered in serrated pathway colorectal tumorigenesis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 70589–70600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, T.; Rindtorff, N.; Boutros, M. Wnt signaling in cancer. Oncogene 2017, 36, 1461–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordero, J.B.; Stefanatos, R.K.; Myant, K.; Vidal, M.; Sansom, O.J. Non-autonomous crosstalk between the JAK/stat and EGFR pathways mediates APC1-driven intestinal stem cell hyperplasia in the Drosophila adult midgut. Development 2012, 139, 4524–4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, A.E.; Hunt, D.H.; Javid, S.H.; Redston, M.; Carothers, A.M.; Bertagnolli, M.M. APC deficiency is associated with increased EGFR activity in the intestinal enterocytes and adenomas of C57BL/6J-min/+ mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 43261–43272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salahshor, S.; Woodgett, J.R. The links between axin and carcinogenesis. J. Clin. Pathol. 2005, 58, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.Q.; Brabletz, T.; Fearon, E.; Willis, A.L.; Hu, C.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Weiss, S.J. Canonical Wnt suppressor, axin2, promotes colon carcinoma oncogenic activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 11312–11317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamb, R.; Ablett, M.P.; Spence, K.; Landberg, G.; Sims, A.H.; Clarke, R.B. Wnt pathway activity in breast cancer sub-types and stem-like cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Jin, K.; van Pelt, G.W.; van Dam, H.; Yu, X.; Mesker, W.E.; Ten Dijke, P.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, L. c-Myb enhances breast cancer invasion and metastasis through the Wnt/β-catenin/Axin2 pathway. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 3364–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jho, E.H.; Zhang, T.; Domon, C.; Joo, C.K.; Freund, J.N.; Costantini, F. Wnt/β-catenin/Tcf signaling induces the transcription of Axin2, a negative regulator of the signaling pathway. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 1172–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgopoulos, N.T.; Kirkwood, L.A.; Southgate, J. A novel bidirectional positive-feedback loop between Wnt-β-catenin and EGFR-ERK plays a role in context-specific modulation of epithelial tissue regeneration. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127, 2967–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hognason, T.; Chatterjee, S.; Vartanian, T.; Ratan, R.R.; Ernewein, K.M.; Habib, A.A. Epidermal growth factor receptor induced apoptosis: Potentiation by inhibition of RAS signaling. FEBS Lett. 2001, 491, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, S.; Hidalgo, M.; Perez-Soler, R. EGFR inhibitor-mediated apoptosis in solid tumors. J. Exp. Ther. Oncol. 2007, 6, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bheda, A.; Creek, K.E.; Pirisi, L. Loss of p53 induces epidermal growth factor receptor promoter activity in normal human keratinocytes. Oncogene 2008, 27, 4315–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yallowitz, A.R.; Li, D.; Lobko, A.; Mott, D.; Nemajerova, A.; Marchenko, N. Mutant p53 amplifies epidermal growth factor receptor family signaling to promote mammary tumorigenesis. Mol. Cancer Res. 2015, 13, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Benavente, S.; Armstrong, E.A.; Li, C.; Wheeler, D.L.; Harari, P.M. p53 modulates acquired resistance to EGFR inhibitors and radiation. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 7071–7079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Wang, D.; Su, C.; Rong, T.; Guo, A. Combined detection of p53, p16, Rb, and EGFR mutations in lung cancer by suspension microarray. Genet. Mol. Res. 2009, 8, 1509–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niederst, M.J.; Sequist, L.V.; Poirier, J.T.; Mermel, C.H.; Lockerman, E.L.; Garcia, A.R.; Katayama, R.; Costa, C.; Ross, K.N.; Moran, T.; et al. Rb loss in resistant EGFR mutant lung adenocarcinomas that transform to small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.K.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.; Youk, J.; Park, S.; An, Y.; Keam, B.; Kim, D.W.; Heo, D.S.; et al. Clonal history and genetic predictors of transformation into small-cell carcinomas from lung adenocarcinomas. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3065–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza, M.C.; Er, E.E.; Blenis, J. The RAS-ERK and PI3K-mtor pathways: Cross-talk and compensation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2011, 36, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pines, G.; Kostler, W.J.; Yarden, Y. Oncogenic mutant forms of EGFR: Lessons in signal transduction and targets for cancer therapy. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 2699–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, F.; Kato, A.; Gonez, L.J.; Hibbs, M.L.; Pouliot, N.; Levitzki, A.; Burgess, A.W. Activation of the ras/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway by kinase-defective epidermal growth factor receptors results in cell survival but not proliferation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998, 18, 7192–7204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, Y.; Shi, C.; Inge, L.; Hibner, M.; Balducci, J.; Huang, Y. Differential roles of ERK and AKT pathways in regulation of EGFR-mediated signaling and motility in prostate cancer cells. Oncogene 2010, 29, 4947–4958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faber, A.C.; Li, D.; Song, Y.; Liang, M.C.; Yeap, B.Y.; Bronson, R.T.; Lifshits, E.; Chen, Z.; Maira, S.M.; Garcia-Echeverria, C.; et al. Differential induction of apoptosis in HER2 and EGFR addicted cancers following PI3K inhibition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19503–19508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makinoshima, H.; Takita, M.; Saruwatari, K.; Umemura, S.; Obata, Y.; Ishii, G.; Matsumoto, S.; Sugiyama, E.; Ochiai, A.; Abe, R.; et al. Signaling through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) axis is responsible for aerobic glycolysis mediated by glucose transporter in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mutated lung adenocarcinoma. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 17495–17504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bononi, A.; Agnoletto, C.; De Marchi, E.; Marchi, S.; Patergnani, S.; Bonora, M.; Giorgi, C.; Missiroli, S.; Poletti, F.; Rimessi, A.; et al. Protein kinases and phosphatases in the control of cell fate. Enzyme Res. 2011, 2011, 329098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cully, M.; You, H.; Levine, A.J.; Mak, T.W. Beyond PTEN mutations: The PI3K pathway as an integrator of multiple inputs during tumorigenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.C.; Qi, R.Z.; Paudel, H.; Zhu, H.J. Regulation and function of protein kinases and phosphatases. Enzyme Res. 2011, 2011, 794089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smoly, I.; Shemesh, N.; Ziv-Ukelson, M.; Ben-Zvi, A.; Yeger-Lotem, E. An asymmetrically balanced organization of kinases versus phosphatases across eukaryotes determines their distinct impacts. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitkreutz, A.; Choi, H.; Sharom, J.R.; Boucher, L.; Neduva, V.; Larsen, B.; Lin, Z.Y.; Breitkreutz, B.J.; Stark, C.; Liu, G.; et al. A global protein kinase and phosphatase interaction network in yeast. Science 2010, 328, 1043–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguirre, A.; Rubio, M.E.; Gallo, V. Notch and EGFR pathway interaction regulates neural stem cell number and self-renewal. Nature 2010, 467, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pancewicz-Wojtkiewicz, J. Epidermal growth factor receptor and notch signaling in non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 3572–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Li, A.; Wang, J.; Weber, J.D.; Michel, L.S. Synthetic lethality through combined notch-epidermal growth factor receptor pathway inhibition in basal-like breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 5465–5474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Fu, W.; Li, T.; Yuan, Q.; Wang, F.; Lv, G.; Lv, Y.; Fan, X.; Shen, Y.; Lin, F.; et al. Antagonism of EGFR and notch limits resistance to EGFR inhibitors and radiation by decreasing tumor-initiating cell frequency. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, 0339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, Y.; Tanaka, N. The hedgehog signaling networks in lung cancer: The mechanisms and roles in tumor progression and implications for cancer therapy. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 7969286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.Y.; Zhang, X.C.; Yang, S.Q.; An, S.J.; Chen, Z.H.; Su, J.; Xie, Z.; Gou, L.Y.; Wu, Y.L. Blockade of hedgehog signaling synergistically increases sensitivity to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancer cell lines. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Corte, C.M.; Malapelle, U.; Vigliar, E.; Pepe, F.; Troncone, G.; Ciaramella, V.; Troiani, T.; Martinelli, E.; Belli, V.; Ciardiello, F.; et al. Efficacy of continuous EGFR-inhibition and role of hedgehog in EGFR acquired resistance in human lung cancer cells with activating mutation of EGFR. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 23020–23032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgillo, F.; Della Corte, C.M.; Fasano, M.; Ciardiello, F. Mechanisms of resistance to EGFR-targeted drugs: Lung cancer. ESMO Open 2016, 1, e000060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.; Maitah, M.Y.; Ginnebaugh, K.R.; Li, Y.; Bao, B.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Sarkar, F.H. Inhibition of hedgehog signaling sensitizes NSCLC cells to standard therapies through modulation of EMT-regulating mirnas. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2013, 6, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tornatore, L.; Thotakura, A.K.; Bennett, J.; Moretti, M.; Franzoso, G. The nuclear factor κB signaling pathway: Integrating metabolism with inflammation. Trends Cell Biol. 2012, 22, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, D.; Jiang, C.; Ma, Z.; Blonska, M.; You, M.J.; Lin, X. MALT1 is required for EGFR-induced NF-κB activation and contributes to EGFR-driven lung cancer progression. Oncogene 2016, 35, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bivona, T.G.; Hieronymus, H.; Parker, J.; Chang, K.; Taron, M.; Rosell, R.; Moonsamy, P.; Dahlman, K.; Miller, V.A.; Costa, C.; et al. Fas and NF-KAPPAB signalling modulate dependence of lung cancers on mutant EGFR. Nature 2011, 471, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blakely, C.M.; Pazarentzos, E.; Olivas, V.; Asthana, S.; Yan, J.J.; Tan, I.; Hrustanovic, G.; Chan, E.; Lin, L.; Neel, D.S.; et al. NF-κB-activating complex engaged in response to EGFR oncogene inhibition drives tumor cell survival and residual disease in lung cancer. Cell Rep. 2015, 11, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, C.F.; Chang, Y.W.; Kuo, K.T.; Shen, Y.S.; Liu, C.Y.; Yu, Y.H.; Cheng, C.C.; Lee, K.Y.; Chen, F.C.; Hsu, M.K.; et al. NF-KAPPAB-driven suppression of FOXO3a contributes to EGFR mutation-independent gefitinib resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E2526–E2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Gu, X.; Yue, J.; Zhao, Q.; Lv, D.; Chen, H.; Xu, L. Acquisition of EGFR TKI resistance and EMT phenotype is linked with activation of IGF1R/NF-κB pathway in EGFR-mutant NSCLC. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 92240–92253. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Lamouille, S.; Derynck, R. TGF-β-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Cell Res. 2009, 19, 156–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Z.; Fenoglio, S.; Gao, D.C.; Camiolo, M.; Stiles, B.; Lindsted, T.; Schlederer, M.; Johns, C.; Altorki, N.; Mittal, V.; et al. TGF-β IL-6 axis mediates selective and adaptive mechanisms of resistance to molecular targeted therapy in lung cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 15535–15540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakobsen, K.R.; Demuth, C.; Sorensen, B.S.; Nielsen, A.L. The role of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2016, 5, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
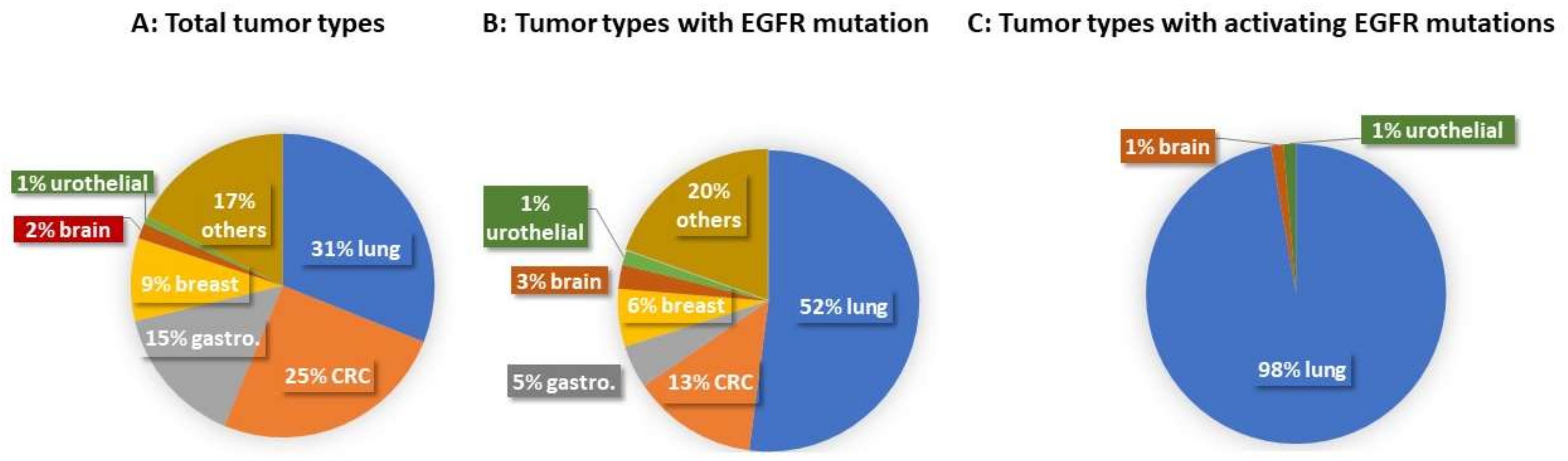
| Case Type | Total Case (Number) | Lung Cancer | CRC | Gastroesophageal Adenocarcinoma | Breast Cancer | Brain Tumor | Urothelial Carcinoma | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total tumor types | 1565 | 486 | 395 | 234 | 138 | 26 | 12 | 274 |
| Tumor types with EGFR mutations | 194 | 101 | 26 | 9 | 12 | 5 | 3 | 38 |
| Tumor types with activating EGFR mutations | 74 | 72 | 1 | 1 |
| EGFR Mutation Types | Case Number | Tumor Types (Case Number) |
|---|---|---|
| EGFR exon 21 p.L858R | 24 | NSCLC (8 adeno + 15 NOS) + 1 Lung cancer (Historical) |
| EGFR exon 21 p.L858R + exon 18 p.E709K | 1 | NSCLC (1 adeno) |
| EGFR Exon 19 p.746_750del | 25 | NSCLC (10 adeno + 3 sequam + 10 NOS) + 2 Lung cancer (Hisorical) |
| EGFR Exon 19 p.746_750del + Exon 20 p.T790M | 2 | NSCLC (2 adeno) |
| EGFR Exon 19 p.746_751del | 4 | NSCLC (3 adeno + 1 NOS) |
| EGFR exon 19 p.746_752del | 1 | NSCLC (1 adeno) |
| EGFR exon 19 p.746_748del | 2 | NSCLC (2 adeno) |
| EGFR exon 19 p.L747_T751del | 1 | NSCLC (1 adeno) |
| EGFR exon 19 p.747_752del | 1 | NSCLC (1 adeno) |
| EGFR Exon 19 p.747_753del | 4 | NSCLC (3 adeno + 1NOS) |
| EGFR exon 17 p.S645C | 1 | 1 Brain tumor: Glioblastoma |
| EGFR Exon 18 p.G719A | 1 | NSCLC (1 adeno) |
| EGFR Exon 18 p.G719A + exon 20 p.R776H | 1 | NSCLC (1 adeno) |
| EGFR Exon 20 p.A767delinsASVD | 3 | NSCLC (1 adeno + 1 sequam) + 1 Urothelial carcinoma |
| EGFR exon 20 p.N771delinsNPHVC | 1 | NSCLC (1 adeno) |
| EGFR exon 20 p.M766delinsMASV | 1 | NSCLC (1 adeno) |
| EGFR exon 21 p.L861Q | 1 | NSCLC (1 adeno) |
| Total Case | 74 |
| Associated Case Number | Pathway/Biological Function | Total Variant Number | TOP 1 Mutated Gene (Variant Number) | TOP 2 Mutated Gene (Variant Number) | TOP 3 Mutated Gene (Variant Number) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 69 | Receptors | 189 | PKHD1 (21) | ROS1 (18) | RET (9) |
| 65 | Genome and Epigenome | 182 | ARID1A (17) | ATM (13) | BRCA2 (11) |
| 34 | Wnt/β-catenin | 48 | FAT1 (12) | APC, RNF43, (7) | AXIN2 (6) |
| 33 | TP53/apoptosis | 40 | TP53 (27) | NUMA1 (5) | NLRP1 (3) |
| 31 | PI3K-AKT-mTOR | 40 | PIK3CA (10) | RICTOR (5) | PIK3R2, TSC2, (3) |
| 26 | NOTCH | 34 | NOTCH2, NOTCH4, (8) | SPEN (7) | MAML2 (6) |
| 25 | Kinase | 32 | TNK2, TYK2, (8) | ABL1, JAK3, (4) | JAK2 (3) |
| 18 | Rb1/cell cycle | 19 | Rb, NUP214, (4) | CDKN2A, CDK12, (2) | CCND1, 2, 3, et al., (1) |
| 18 | RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK | 19 | NF1, RASA1, (5) | KIAA1804 (3) | RPS6KA2 (2) |
| 11 | Hedgehog | 12 | PTCH1 (4) | SMO, ETV4, (3) | STK36, SUFU, (1) |
| 9 | NF-κB | 10 | IKBKE, CARD11, (2) | IKBKB, REL, et al., (1) | |
| 8 | TGF-β | 9 | TGFBR2 (3) | TFE3, SMAD4, ACVR2A, (2) | |
| 4 | Phosphatases | 5 | PTPRT (4) | PTPRD (1) |
| Pathway/Biological Function | Gene | Variant (AA Change) | Variant Number in Total 1565 Cases | Variant Number in 74 AE Cases | Fold Change of Variant Frequency in AE Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Receptors | PKHD1 | p.V3934I | 3 | 1 | 7 |
| p.T2869K | 21 | 1 | 1 | ||
| p.G2648S | 10 | 1 | 2 | ||
| p.W2280X | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.T1615M | 2 | 1 | 10.6 | ||
| p.R4036W | 5 | 1 | 4 | ||
| p.R3772Q | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.S3505R | 10 | 1 | 2 | ||
| p.G448R | 7 | 1 | 3 | ||
| p.G2285E | 4 | 1 | 5.3 | ||
| p.T36M | 3 | 1 | 7 | ||
| p.D220N | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.E3769D | 2 | 1 | 10.6 | ||
| p.I2364N | 35 | 2 | 1 | ||
| p.R559W | 14 | 1 | 1.5 | ||
| p.V1701I | 2 | 1 | 10.6 | ||
| p.S3210C | 35 | 1 | 0.6 | ||
| p.F2779V | 11 | 1 | 2 | ||
| p.T2082I | 8 | 1 | 2.6 | ||
| p.Q1610K | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| Total | 176 | 21 | 2.5 | ||
| ROS1 | p.Q412E | 1 | 1 | 21 | |
| p.G2121V | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.K934M | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.P224S | 55 | 4 | 1.5 | ||
| p.E1902K | 44 | 3 | 1.4 | ||
| p.D618G | 4 | 2 | 10.6 | ||
| p.T326R | 9 | 1 | 2.3 | ||
| p.K461E | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.L590P | 4 | 1 | 5.3 | ||
| p.A887V | 2 | 1 | 10 | ||
| p.R2039H | 5 | 1 | 4 | ||
| p.D839E | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| Total | 128 | 18 | 3 | ||
| RET | p.T278N | 18 | 2 | 2.3 | |
| p.L410V | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.D489N | 71 | 4 | 1 | ||
| p.L56M | 16 | 1 | 1 | ||
| p.T1038A | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| Total | 107 | 9 | 1.8 | ||
| Genome and Epigenome | ARID1A | p.P21del | 53 | 1 | 0.4 |
| p.K1795N | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.A52V | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.339_343del | 4 | 1 | 5.3 | ||
| p.L117P | 108 | 1 | 0.2 | ||
| p.Q288P | 49 | 11 | 4.7 | ||
| p.N756fs | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| Total | 217 | 17 | 1.7 | ||
| ATM | p.S49C | 19 | 1 | 1 | |
| p.T935R | 6 | 1 | 3.5 | ||
| p.I1740V | 2 | 1 | 10.6 | ||
| p.R1730Q | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.T2640I | 2 | 1 | 10.6 | ||
| p.G1586A | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.L1450P | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.S1691R | 6 | 1 | 3.5 | ||
| p.T1756S | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.K2318Q | 2 | 1 | 10.6 | ||
| p.D1853V | 26 | 1 | 0.8 | ||
| p.I2683fs | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.G509X | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| Total | 69 | 13 | 4 | ||
| BRCA2 | p.A895T | 1 | 1 | 21 | |
| p.V746G | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.D1902N | 5 | 1 | 4 | ||
| p.N2436I | 10 | 1 | 2 | ||
| p.K2729N | 16 | 1 | 1 | ||
| p.V2109I | 10 | 1 | 2 | ||
| p.K322Q | 21 | 1 | 1 | ||
| p.M784V | 104 | 1 | 0.2 | ||
| p.G2044V | 21 | 1 | 1 | ||
| p.T3013I | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.A2351T | 2 | 1 | 10.6 | ||
| Total | 192 | 11 | 1.2 | ||
| Wnt/β-catenin | FAT1 | p.M1149T | 21 | 1 | 1 |
| p.V912I | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.P509S | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.S1565F | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.I2004M | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.H1850Y | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.S2353A | 13 | 1 | 1.6 | ||
| p.D1113N | 6 | 1 | 3.5 | ||
| p.T1679I | 7 | 1 | 3 | ||
| p.E1141D | 9 | 1 | 2.3 | ||
| p.I1228V | 4 | 1 | 5.3 | ||
| p.R4208W | 4 | 1 | 5.3 | ||
| Total | 69 | 12 | 3.7 | ||
| APC | p.V1099I | 1 | 1 | 21 | |
| p.F1840C | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.G253S | 4 | 1 | 5.3 | ||
| p.S1545X | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.K603X | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.T1585fs | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.H1845fs | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| Total | 10 | 7 | 14.8 | ||
| RNF43 | p.E170K | 6 | 1 | 3.5 | |
| p.A365T | 23 | 3 | 2.8 | ||
| p.R519Q | 15 | 1 | 1.4 | ||
| p.L214V | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.R145X | 2 | 1 | 10.6 | ||
| Total | 47 | 7 | 3 | ||
| AXIN2 | p.T673P | 34 | 1 | 0.6 | |
| p.H474del | 13 | 2 | 3.3 | ||
| p.A761D | 5 | 2 | 8.5 | ||
| p.G755V | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| Total | 53 | 6 | 2.4 | ||
| TP53/apoptosis | TP53 | p.V31I | 8 | 1 | 2.6 |
| p.P58fs | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.S241F | 2 | 1 | 10.6 | ||
| p.V216M | 2 | 1 | 10.6 | ||
| p.R273H | 39 | 1 | 0.5 | ||
| p.Q165X | 4 | 1 | 5.3 | ||
| p.C176F | 10 | 3 | 6.3 | ||
| p.252_254del | 2 | 1 | 10.6 | ||
| p.Q144P | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.V272M | 5 | 1 | 4 | ||
| p.P72fs | 2 | 1 | 10.6 | ||
| p.P92fs | 2 | 1 | 10.6 | ||
| p.R273P | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.G154V | 7 | 2 | 6 | ||
| p.R158L | 7 | 1 | 3 | ||
| p.C135Y | 3 | 1 | 7 | ||
| p.P89fs | 3 | 1 | 7 | ||
| p.I232F | 2 | 1 | 10.6 | ||
| p.D281V | 2 | 1 | 10.6 | ||
| p.E258K | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.V274F | 2 | 1 | 10.6 | ||
| p.Q136X | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.H179L | 3 | 1 | 7 | ||
| p.K132M | 2 | 1 | 10.6 | ||
| Total | 112 | 27 | 5 | ||
| NUMA1 | p.R972Q | 16 | 1 | 1.3 | |
| p.L1346M | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.P1117Q | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.Y1836H | 8 | 1 | 2.6 | ||
| p.M108I | 8 | 1 | 2.6 | ||
| Total | 34 | 5 | 3 | ||
| NLRP1 | p.P233L | 1 | 1 | 21 | |
| p.V1231I | 12 | 2 | 3.5 | ||
| Total | 13 | 3 | 4.9 | ||
| PI3K–AKT–mTOR | PIK3CA | p.H1048R | 1 | 1 | 21 |
| p.I816V | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.S405F | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.E545K | 44 | 2 | 1 | ||
| p.E542K | 21 | 1 | 1 | ||
| p.9_18del | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.G1049R | 3 | 1 | 7 | ||
| p.Y1021C | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.R108delinsREEKILS | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| Total | 74 | 10 | 2.9 | ||
| RICTOR | p.G1584V | 1 | 1 | 21 | |
| p.T258fs | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.D1182G | 4 | 1 | 5.3 | ||
| p.P1668L | 13 | 1 | 1.6 | ||
| p.I518T | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| Total | 20 | 5 | 5.3 | ||
| PIK3R2 | p.F381L | 1 | 1 | 21 | |
| p.P723L | 4 | 1 | 5.3 | ||
| p.P4S | 47 | 1 | 0.4 | ||
| Total | 52 | 3 | 1 | ||
| TSC2 | p.A460T | 4 | 1 | 5.3 | |
| p.G1787S | 2 | 1 | 10.6 | ||
| p.A678T | 8 | 1 | 2 | ||
| Total | 14 | 3 | 4.5 | ||
| NOTCH | NOTCH2 | p.P1591L | 1 | 1 | 21 |
| p.D182N | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.R91L | 9 | 1 | 2.3 | ||
| p.Q466K | 2 | 1 | 10.6 | ||
| p.F1209V | 12 | 1 | 1.8 | ||
| p.I1698M | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.I681N | 43 | 2 | 1 | ||
| Total | 69 | 8 | 2.5 | ||
| NOTCH4 | p.L16delinsLLLL | 11 | 1 | 2 | |
| p.G487R | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.1536_1537del | 3 | 1 | 7 | ||
| p.A439P | 2 | 1 | 10.6 | ||
| p.E513D | 19 | 1 | 1 | ||
| p.R1410H | 25 | 3 | 2.5 | ||
| Total | 61 | 8 | 2.8 | ||
| SPEN | p.D2007E | 11 | 1 | 2 | |
| p.V1022M | 6 | 1 | 3.5 | ||
| p.N2957D | 3 | 1 | 7 | ||
| p.S286N | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.R277K | 3 | 1 | 7 | ||
| p.P2240L | 36 | 1 | 0.6 | ||
| p.A2777V | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| Total | 61 | 7 | 2.4 | ||
| MAML2 | p.I480M | 35 | 2 | 1 | |
| p.R422Q | 3 | 2 | 14 | ||
| p.605_607del | 13 | 1 | 1.6 | ||
| p.603_613del | 3 | 1 | 7 | ||
| Total | 54 | 6 | 2.3 | ||
| Kinase | TNK2 | p.P506R | 1 | 1 | 21 |
| p.T829N | 4 | 1 | 5.3 | ||
| p.P584S | 4 | 1 | 5.3 | ||
| p.P887H | 2 | 1 | 10.6 | ||
| p.A701T | 4 | 1 | 5.3 | ||
| p.A104T | 5 | 1 | 4 | ||
| p.R748W | 6 | 1 | 3.5 | ||
| p.R382W | 13 | 1 | 1.6 | ||
| Total | 39 | 8 | 4.3 | ||
| TYK2 | p.E1163G | 5 | 1 | 4 | |
| p.S418L | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.R703W | 23 | 4 | 3.7 | ||
| p.R231W | 11 | 1 | 2 | ||
| p.R124H | 2 | 1 | 10.6 | ||
| Total | 42 | 8 | 4 | ||
| ABL1 | p.K247R | 2 | 1 | 10.6 | |
| p.M237V | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.K609del | 94 | 2 | 0.4 | ||
| Total | 97 | 4 | 0.9 | ||
| JAK3 | p.R687M | 1 | 1 | 21 | |
| p.A919S | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.I688F | 2 | 1 | 10.6 | ||
| p.Q501H | 2 | 1 | 10.6 | ||
| Total | 6 | 4 | 14 | ||
| JAK2 | p.Y1099C | 1 | 1 | 21 | |
| p.S797C | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.Q955R | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| Total | 3 | 3 | 21 | ||
| Rb1/cell cycle | RB1 | p.L171fs | 1 | 1 | 21 |
| p.F482fs | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.K192E | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.A538fs | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| Total | 4 | 4 | 21 | ||
| NUP214 | p.S492C | 1 | 1 | 21 | |
| p.A109V | 5 | 1 | 4 | ||
| p.R741L | 12 | 1 | 1.8 | ||
| p.V1638I | 7 | 1 | 3 | ||
| Total | 25 | 4 | 3.4 | ||
| CDKN2A | p.R144C | 5 | 1 | 4 | |
| p.H66R | 16 | 1 | 1.3 | ||
| Total | 21 | 2 | 2 | ||
| CDK12 | p.P1275L | 16 | 2 | 2.6 | |
| Total | 16 | 2 | 2.6 | ||
| CCND1 | p.276_276del | 5 | 1 | 4 | |
| Total | 5 | 1 | 4 | ||
| CCND2 | p.R262H | 3 | 1 | 7 | |
| Total | 3 | 1 | 7 | ||
| CCND3 | p.E253D | 25 | 1 | 0.8 | |
| Total | 25 | 1 | 0.8 | ||
| AURKA | p.G173R | 1 | 1 | 21 | |
| Total | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| CDKN1A | p.P4L | 7 | 1 | 3 | |
| Total | 7 | 1 | 3 | ||
| CHEK1 | p.V46I | 2 | 1 | 10.6 | |
| Total | 2 | 1 | 10.6 | ||
| BUB1B | p.R550Q | 8 | 1 | 2.6 | |
| Total | 8 | 1 | 2.6 | ||
| RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK | NF1 | p.Q83L | 1 | 1 | 21 |
| p.V1753I | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.P678T | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.F2634C | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.R1958fs | 2 | 1 | 10.6 | ||
| Total | 6 | 5 | 17.6 | ||
| RASA1 | p.E70G | 35 | 4 | 2.4 | |
| p.G75A | 6 | 1 | 3.5 | ||
| Total | 41 | 5 | 2.6 | ||
| KIAA1804 | p.E563D | 11 | 1 | 2 | |
| p.I941T | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.A695V | 6 | 1 | 3.5 | ||
| Total | 18 | 3 | 3.5 | ||
| RPS6KA2 | p.H371Y | 5 | 1 | 4 | |
| p.R500Q | 3 | 1 | 7 | ||
| Total | 8 | 2 | 5.3 | ||
| Hedgehog | PTCH1 | p.P1441L | 1 | 1 | 21 |
| p.P813A | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.R893H | 16 | 1 | 1.3 | ||
| p.S649G | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| Total | 19 | 4 | 4.5 | ||
| SMO | p.K575M | 12 | 1 | 1.8 | |
| p.P698R | 6 | 1 | 3.5 | ||
| p.16_17del | 4 | 1 | 5.3 | ||
| Total | 22 | 3 | 2.9 | ||
| ETV4 | p.H175N | 4 | 2 | 10.6 | |
| p.V448I | 7 | 1 | 3 | ||
| Total | 11 | 3 | 5.8 | ||
| STK36 | p.H713Y | 1 | 1 | 21 | |
| Total | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| SUFU | p.R239W | 1 | 1 | 21 | |
| Total | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| NF-κB | IKBKE | p.V418M | 2 | 1 | 10.6 |
| p.T483M | 9 | 1 | 2.3 | ||
| Total | 11 | 2 | 3.8 | ||
| CARD11 | p.N191S | 5 | 1 | 4 | |
| p.M551T | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| Total | 6 | 2 | 7 | ||
| IKBKB | p.M83V | 2 | 1 | 10.6 | |
| Total | 2 | 1 | 10.6 | ||
| REL | p.L331S | 32 | 1 | 0.7 | |
| Total | 32 | 1 | 0.7 | ||
| TNFAIP3 | p.C590S | 1 | 1 | 21 | |
| Total | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| BCL11B | p.D122N | 1 | 1 | 21 | |
| Total | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| BLNK | p.I308T | 2 | 1 | 10.6 | |
| Total | 2 | 1 | 10.6 | ||
| BIRC3 | p.R202S | 11 | 1 | 2 | |
| Total | 11 | 1 | 2 | ||
| TGF-β | TGFBR2 | p.T315M | 12 | 3 | 5.3 |
| Total | 12 | 3 | 5.3 | ||
| TFE3 | p.A139V | 2 | 1 | 10.6 | |
| p.A484T | 4 | 1 | 5.3 | ||
| Total | 6 | 2 | 7 | ||
| SMAD4 | p.H92Y | 2 | 1 | 10.6 | |
| p.M447fs | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| Total | 3 | 2 | 14 | ||
| ACVR2A | p.M148T | 1 | 1 | 21 | |
| p.A151V | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| Total | 2 | 2 | 21 | ||
| Phosphatases | PTPRT | p.V1017A | 9 | 1 | 2.3 |
| p.Q1188fs | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.S1290F | 1 | 1 | 21 | ||
| p.N1167K | 5 | 1 | 4 | ||
| Total | 16 | 4 | 5.3 | ||
| PTPRD | p.R1088H1 | 1 | 1 | 21 | |
| Total | 1 | 1 | 21 |
| Pathway/Biological Function | Gene | Variant Number in AE Cases | Variant Number in EGFR L858R Cases | Variant Number in EGFR Exon 19del Cases | Variant Frequency in L858R Cases (%) | Variant Frequency in Exon 19del Cases (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Receptors | PKHD1 | 21 | 6 | 10 | 28 | 47 |
| ROS1 | 18 | 3 | 13 | 16 | 72 | |
| RET | 9 | 4 | 3 | 44 | 33 | |
| Genome and Epigenome | ARID1A | 17 | 7 | 7 | 41 | 41 |
| ATM | 13 | 6 | 6 | 46 | 46 | |
| BRCA2 | 11 | 5 | 4 | 45 | 36 | |
| Wnt/β-catenin | FAT1 | 12 | 5 | 5 | 41 | 41 |
| APC | 7 | 4 | 2 | 57 | 28 | |
| RNF43 | 7 | 4 | 3 | 57 | 42 | |
| AXIN2 | 6 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 50 | |
| TP53/apoptosis | TP53 | 27 | 9 | 13 | 33 | 48 |
| NUMA1 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 40 | 40 | |
| NLRP1 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 66 | |
| PI3K-AKT-mTOR | PIK3CA | 10 | 1 | 8 | 10 | 80 |
| RICTOR | 5 | 2 | 3 | 40 | 60 | |
| PIK3R2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 66 | 33 | |
| TSC2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 33 | 66 | |
| NOTCH | NOTCH2 | 8 | 3 | 4 | 37 | 50 |
| NOTCH4 | 8 | 3 | 4 | 37 | 50 | |
| SPEN | 7 | 3 | 2 | 42 | 28 | |
| MAML2 | 6 | 2 | 3 | 33 | 50 | |
| Kinase | TNK2 | 8 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 62 |
| TYK2 | 8 | 3 | 4 | 37 | 50 | |
| ABL1 | 4 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 75 | |
| JAK3 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 50 | 25 | |
| JAK2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 33 | 33 | |
| Rb1/cell cycle | RB1 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 25 | 75 |
| NUP214 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 25 | 50 | |
| CDKN2A | 2 | 1 | 0 | 50 | 0 | |
| CDK12 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 50 | 0 | |
| CCND1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 100 | |
| CCND2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 100 | |
| CCND3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 100 | |
| AURKA | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 100 | |
| CDKN1A | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 100 | |
| CHEK1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | 0 | |
| BUB1B | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | 0 | |
| RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK | NF1 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 20 | 40 |
| RASA1 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 60 | 40 | |
| KIAA1804 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 66 | 33 | |
| RPS6KA2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Hedgehog | PTCH1 | 4 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 100 |
| SMO | 3 | 2 | 1 | 66 | 33 | |
| ETV4 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 66 | |
| STK36 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 100 | |
| SUFU | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 100 | |
| NF-κB | IKBKE | 2 | 2 | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| CARD11 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 50 | 0 | |
| IKBKB | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 100 | |
| REL | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 100 | |
| TNFAIP3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 100 | |
| BCL11B | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | 0 | |
| BLNK | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | 0 | |
| BIRC3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 100 | |
| TGF-β | TGFBR2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 33 | 33 |
| TFE3 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 100 | |
| SMAD4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 50 | 0 | |
| ACVR2A | 2 | 1 | 1 | 50 | 50 | |
| Phosphatases | PTPRT | 4 | 1 | 3 | 25 | 75 |
| PTPRD | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 100 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, J.; Protopopov, A.; Sun, R.; Lyle, S.; Russell, M. Genomic Profiling on an Unselected Solid Tumor Population Reveals a Highly Mutated Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Associated with Oncogenic EGFR Mutations. J. Pers. Med. 2018, 8, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm8020013
Jiang J, Protopopov A, Sun R, Lyle S, Russell M. Genomic Profiling on an Unselected Solid Tumor Population Reveals a Highly Mutated Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Associated with Oncogenic EGFR Mutations. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2018; 8(2):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm8020013
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Jingrui, Alexei Protopopov, Ruobai Sun, Stephen Lyle, and Meaghan Russell. 2018. "Genomic Profiling on an Unselected Solid Tumor Population Reveals a Highly Mutated Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Associated with Oncogenic EGFR Mutations" Journal of Personalized Medicine 8, no. 2: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm8020013
APA StyleJiang, J., Protopopov, A., Sun, R., Lyle, S., & Russell, M. (2018). Genomic Profiling on an Unselected Solid Tumor Population Reveals a Highly Mutated Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Associated with Oncogenic EGFR Mutations. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 8(2), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm8020013





