The Role of Age at Onset on the Clinical Course and Biochemical Parameters of Anorexia Nervosa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample and Study Design
2.2. Assessment
2.3. Blood Collection
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Study Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AN | Anorexia Nervosa |
| AAO | Age at Onset |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| CBT | Cognitive Behavioral Therapy |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| DUI | Duration of Untreated Illness |
| HDL | High-Density Lipoprotein |
| K | Potassium Ion |
| LDL | Low-Density Lipoprotein |
| Na | Sodium Ion |
| Na/K | Sodium-to-Potassium Ratio |
| NLR | Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| PLR | Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio |
| SPSS | Statistical Package for the Social Sciences |
| TC | Total Cholesterol |
References
- Yu, Z.; Muehleman, V. Eating Disorders and Metabolic Diseases. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Hoeken, D.; Hoek, H.W. Review of the Burden of Eating Disorders: Mortality, Disability, Costs, Quality of Life, and Family Burden. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2020, 33, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eeden, A.E.; van Hoeken, D.; Hoek, H.W. Incidence, Prevalence and Mortality of Anorexia Nervosa and Bulimia Nervosa. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2021, 34, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artoni, P.; Chierici, M.L.; Arnone, F. Body Perception Treatment, a Possible Way to Treat Body Image Disturbance in Eating Disorders: A Case–Control Efficacy Study. Eat. Weight. Disord. 2021, 26, 499–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H.; Tonoike, T.; Muroya, T.; Yoshida, K.; Ozaki, N. Age of Onset Has Limited Association with Body Mass Index at Time of Presentation for Anorexia Nervosa: Comparison of Peak-Onset and Late-Onset Anorexia Nervosa Groups. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2007, 61, 646–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buoli, M.; Esposito, C.M.; Ceresa, A.; Di Paolo, M.; Legnani, F.; Pan, A.; Ferrari, L.; Bollati, V.; Monti, P. Biomarkers Associated with Antidepressant Response and Illness Severity in Major Depressive Disorder: A Pilot Study. Pharmacol. Rep. 2025, 77, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 3rd ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Schorr, M.; Thomas, J.J.; Eddy, K.T.; Dichtel, L.E.; Lawson, E.A.; Meenaghan, E.; Paskal, M.L.; Fazeli, P.K.; Faje, A.T.; Misra, M.; et al. Bone density, body composition, and psychopathology of anorexia nervosa spectrum disorders in DSM-IV vs DSM-5. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2017, 50, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Affaticati, L.M.; Capuzzi, E.; Zuliani, T.; Legnani, F.; Vaccaro, N.; Manzo, F.; Scalia, A.; La Tegola, D.; Nicastro, M.; Colmegna, F.; et al. The Role of Duration of Untreated Illness (DUI) on the Course and Biochemical Parameters of Female Patients Affected by Anorexia Nervosa. Brain Behav. 2025, 15, e70584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasofer, D.R.; Muratore, A.F.; Attia, E.; Wu, P.; Wang, Y.; Minkoff, H.; Rufin, T.; Walsh, B.T.; Steinglass, J.E. Predictors of Illness Course and Health Maintenance Following Inpatient Treatment among Patients with Anorexia Nervosa. J. Eat. Disord. 2020, 8, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resmark, G.; Herpertz, S.; Herpertz-Dahlmann, B.; Zeeck, A. Treatment of Anorexia Nervosa—New Evidence-Based Guidelines. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himmerich, H.; Lewis, Y.D.; Conti, C.; Mutwalli, H.; Karwautz, A.; Sjögren, J.M.; Uribe Isaza, M.M.; Tyszkiewicz-Nwafor, M.; Aigner, M.; McElroy, S.L.; et al. World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry (WFSBP) Guidelines Update 2023 on the Pharmacological Treatment of Eating Disorders. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2023, 1–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipfel, S.; Giel, K.E.; Bulik, C.M.; Hay, P.; Schmidt, U. Anorexia Nervosa: Aetiology, Assessment, and Treatment. Lancet Psychiatry 2015, 2, 1099–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treasure, J.; Zipfel, S.; Micali, N.; Wade, T.; Stice, E.; Claudino, A.; Schmidt, U.; Frank, G.K.; Bulik, C.M.; Wentz, E. Anorexia Nervosa. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayrolles, A.; Clarke, J.; Godart, N.; André-Carletti, C.; Barbe, C.; Bargiacchi, A.; Blanchet, C.; Bergametti, F.; Bertrand, V.; Caldagues, E.; et al. Early-Onset Anorexia Nervosa: A Scoping Review and Management Guidelines. J. Eat. Disord. 2024, 12, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budde, L.I.; Wilms, S.; Föcker, M.; Dalhoff, A.; Müller, J.M.; Wessing, I. Influence of Identity Development on Weight Gain in Adolescent Anorexia Nervosa. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 887588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewlings, S.J. Eating Disorders and Dietary Supplements: A Review of the Science. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puckett, L. Renal and electrolyte complications in eating disorders: A comprehensive review. J. Eat. Disord. 2023, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savino, G.; Valenti, L.; D’Alisera, R.; Pinelli, M.; Persi, Y.; Trenti, T. Dietary Supplements, Drugs and Doping in the Sport Society. Ann. Ig. 2019, 31, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, O.; Tamai, H.; Fujita, M.; Kobayashi, N.; Komaki, G.; Matsubayashi, S.; Nakagawa, T. Vascular Responses to Angiotensin II in Anorexia Nervosa. Biol. Psychiatry 1993, 34, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, O.; Tamai, H.; Fujita, M.; Kobayashi, N.; Komaki, G.; Matsubayashi, S.; Nakagawa, T. Aldosterone responses to angiotensin II in anorexia nervosa. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 1992, 86, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torosyan, N.; Visrodia, P.; Torbati, T.; Minissian, M.B.; Shufelt, C.L. Dyslipidemia in Midlife Women: Approach and Considerations during the Menopausal Transition. Maturitas 2022, 166, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hundemer, G.L.; Clarke, A.; Akbari, A.; Bugeja, A.; Massicotte-Azarniouch, D.; Knoll, G.; Myran, D.T.; Tanuseputro, P.; Sood, M.M. Analysis of Electrolyte Abnormalities in Adolescents and Adults and Subsequent Diagnosis of an Eating Disorder. JAMA Net. Open 2022, 5, e2240809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohwada, R.; Hotta, M.; Oikawa, S.; Takano, K. Etiology of Hypercholesterolemia in Patients with Anorexia Nervosa. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2006, 39, 598–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantuti-Castelvetri, L.; Fitzner, D.; Bosch-Queralt, M.; Weil, M.T.; Su, M.; Sen, P.; Ruhwedel, T.; Mitkovski, M.; Trendelenburg, G.; Lütjohann, D.; et al. Defective Cholesterol Clearance Limits Remyelination in the Aged Central Nervous System. Science 2018, 359, 684–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertile, R.A.N.; Brigden, R.; Raman, V.; Cui, X.; Du, Z.; Eyles, D. Vitamin D: A Potent Regulator of Dopaminergic Neuron Differentiation and Function. J. Neurochem. 2023, 166, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.A.; Hübel, C.; Hindborg, M.; Lindkvist, E.; Kastrup, A.M.; Yilmaz, Z.; Støving, R.K.; Bulik, C.M.; Sjögren, J.M. Increased lipid and lipoprotein concentrations in anorexia nervosa: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2019, 52, 611–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jáuregui-Garrido, B.; Bolaños-Ríos, P.; Santiago-Fernández, M.J.; Jaúregui-Lobera, I. Lipid profile and cardiovascular risk in anorexia nervosa; the effect of nutritional treatment. Nutr. Hosp. 2012, 27, 908–913. [Google Scholar]
- Bevione, F.; Martini, M.; Longo, P.; Toppino, F.; Musetti, A.; Amodeo, L.; Abbate-Daga, G.; Panero, M. Role of Parental Educational Level as Psychosocial Factor in a Sample of Inpatients with Anorexia Nervosa and Bulimia Nervosa. Front. Psychol. 2024, 15, 1408695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panero, M.; Marzola, E.; Tamarin, T.; Brustolin, A.; Abbate-Daga, G. Comparison between Inpatients with Anorexia Nervosa with and without Major Depressive Disorder: Clinical Characteristics and Outcome. Psychiatry Res. 2021, 297, 113734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westmoreland, P.; Krantz, M.J.; Mehler, P.S. Medical Complications of Anorexia Nervosa and Bulimia. Am. J. Med. 2016, 129, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumitrașcu, M.C.; Șandru, F.; Carsote, M.; Petca, R.C.; Gheorghisan-Galateanu, A.A.; Petca, A.; Valea, A. Anorexia Nervosa: COVID-19 Pandemic Period. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagielska, G.; Kacperska, I. Outcome, Comorbidity and Prognosis in Anorexia Nervosa. Psychiatr. Pol. 2017, 51, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldiroli, A.; La Tegola, D.; Manzo, F.; Scalia, A.; Affaticati, L.M.; Capuzzi, E.; Colmegna, F.; Argyrides, M.; Giaginis, C.; Mendolicchio, L.; et al. The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Binge Eating Disorder: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nexo, E.; Parkner, T. Vitamin B12-Related Biomarkers. Food Nutr. Bull. 2024, 45 (Suppl. 1), S28–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedosov, S.N.; Brito, A.; Miller, J.W.; Green, R.; Allen, L.H. Combined Indicator of Vitamin B12 Status: Modification for Missing Biomarkers and Folate Status and Recommendations for Revised Cut-Points. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2015, 53, 1215–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakanalis, A.; Clerici, M.; Carrà, G.; Riva, G. Dysfunctional Bodily Experiences in Anorexia Nervosa: Where Are We? Eat. Weight Disord. 2016, 21, 731–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodan, S.C.; Bryant, E.; Le, A.; Maloney, D.; Touyz, S.; McGregor, I.S.; Maguire, S.; National Eating Disorder Research Consortium. Pharmacotherapy, Alternative and Adjunctive Therapies for Eating Disorders: Findings from a Rapid Review. J. Eat. Disord. 2023, 11, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Márquez, M.C.; Sánchez, J.M.; Salazar, A.M.; Martínez, C.V.; Valderrama, F.; Rojas-Gualdrón, D.F. Efficacy and Safety of Antipsychotics and Antidepressants in the Treatment of Anorexia Nervosa: A Systematic Review. Rev. Colomb. Psiquiatr. 2022, 51, 227–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovinazzo, S.; Sukkar, S.G.; Rosa, G.M.; Zappi, A.; Bezante, G.P.; Balbi, M.; Brunelli, C. Anorexia Nervosa and Heart Disease: A Systematic Review. Eat. Weight Disord. 2019, 24, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buoli, M.; Legnani, F.; Mastroianni, M.; Affaticati, L.M.; Capuzzi, E.; Clerici, M.; Caldiroli, A. Effectiveness of Yoga as a Complementary Therapy for Anorexia Nervosa: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Yoga 2024, 17, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakers, A.; Cimolai, V. Complementary and Integrative Medicine and Eating Disorders in Youth: Traditional Yoga, Virtual Reality, Light Therapy, Neurofeedback, Acupuncture, Energy Psychology Techniques, Art Therapies, and Spirituality. Child Adolesc. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2023, 32, 421–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variables | Total Sample n = 76 | Early Onset (<18 Years) n = 42 | Late Onset (≥18 Years) n = 34 | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age Missing n = 0 | 23.12 ± 8.32 | 20.69 ± 6.48 | 26.12 ± 9.40 | 2.86 | <0.01 |
| DUI (years) Missing n = 0 | 2.11 ± 2.71 | 2.26 ± 2.27 | 1.92 ± 3.15 | 0.54 | 0.59 |
| Duration of illness (years) Missing n = 0 | 4.17 ± 5.81 | 5.28 ± 7.01 | 2.80 ± 3.45 | 1.88 | 0.06 |
| Educational status (years) Missing n = 4 | 12.21 ± 3.04 | 11.26 ± 3.05 | 13.33 ± 2.64 | 3.10 | 0.01 |
| BMI Missing n = 4 | 17.23 ± 2.23 | 17.25 ± 1.92 | 17.21 ± 2.57 | 0.07 | 0.95 |
| Na+ (mmol/L) Missing n = 52 | 140.33 ± 2.78 | 140.99 ± 2.58 | 139.56 ± 2.91 | 1.08 | 0.29 |
| K+ (mmol/L) Missing n = 53 | 4.33 ± 0.35 | 4.55 ± 0.28 | 4.12 ± 0.29 | 3.63 | <0.01 |
| Na+/K+ Missing n = 53 | 32.66 ± 2.68 | 31.03 ± 1.84 | 34.15 ± 2.49 | 3.39 | <0.01 |
| Red blood cells (106/mm3) Missing n = 50 | 4.27 ± 0.44 | 4.19 ± 0.42 | 4.32 ± 0.46 | 0.76 | 0.45 |
| MCV (fL) Missing n = 50 | 90.82 ± 5.47 | 90.39 ± 4.50 | 91.14 ± 6.21 | 0.34 | 0.74 |
| Hb (g/dL) Missing n = 50 | 13.05 ± 1.26 | 12.80 ± 1.44 | 13.23 ± 1.13 | 0.85 | 0.41 |
| Leukocytes (109/L) Missing n = 2 | 5.67 ± 1.76 | 5.80 ± 1.81 | 5.51 ± 1.71 | 0.71 | 0.48 |
| Lymphocytes (109/L) Missing n = 3 | 2.13 ± 0.75 | 2.23 ± 0.81 | 2.00 ± 0.64 | 1.28 | 0.20 |
| Neutrophils (109/L) Missing n = 29 | 3.23 ± 1.70 | 3.25 ± 1.77 | 3.20 ± 1.63 | 0.11 | 0.91 |
| Platelets (109/L) Missing n = 2 | 227.66 ± 49.34 | 232.53 ± 45.76 | 221.94 ± 53.37 | 0.92 | 0.36 |
| NLR Missing n = 29 | 1.55 ± 0.94 | 1.37 ± 0.69 | 1.83 ± 1.20 | 1.49 | 0.15 |
| PLR Missing n = 3 | 117.06 ± 41.06 | 114.04 ± 38.26 | 120.72 ± 44.54 | 0.69 | 0.49 |
| Iron (μg/dL) Missing n = 20 | 106.60 ± 74.72 | 110.73 ± 87.67 | 101.82 ± 57.64 | 0.64 | 0.66 |
| Vitamin D (ng/mL) Missing n = 34 | 30.58 ± 14.24 | 29.92 ± 14.41 | 31.46 ± 14.39 | 0.34 | 0.73 |
| Folate (ng/mL) Missing n = 21 | 8.86 ± 6.24 | 7.91 ± 3.69 | 10.00 ± 8.29 | 1.17 | 0.25 |
| Vitamin B12 (pg/mL) Missing n = 26 | 529.42 ± 325.68 | 553.03 ± 376.15 | 500.92 ± 256.90 | 0.58 | 0.57 |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) Missing n = 28 | 172.10 ± 34.94 | 167.57 ± 28.13 | 178.45 ± 42.69 | 1.07 | 0.29 |
| Variables | Total Sample n = 76 | Early Onset (<18 Years) n = 42 | Late Onset (≥18 Years) n = 34 | χ2 | OR (95% CI) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current partner Missing n = 10 | No | 47 (71.2%) | 21 (63.6%) | 26 (78.8%) | 1.85 | 0.47 (0.16–1.41) | 0.28 |
| Yes | 19 (28.8%) | 12 (36.4%) | 7 (21.2%) | ||||
| Work status Missing n = 3 | Unemployed | 13 (17.8%) | 10 (25%) | 3 (9.1%) | 12.23 | / * | 0.02 |
| Student | 49 (67.1%) | 29 (72.5%) | 20 (60.6%) | ||||
| Worker | 11 (15.1%) | 1 (2.5%) | 10 (30.3%) | ||||
| Lifetime substance use disorders Missing n = 2 | No | 65 (87.8%) | 36 (90.0%) | 29 (85.3%) | 0.38 | 1.55 (0.38–6.31) | 0.72 |
| Yes | 9 (12.2%) | 4 (10.0%) | 5 (14.7%) | ||||
| Lifetime poly-substance use disorders Missing n = 3 | No | 70 (95.9%) | 38 (95.0%) | 32 (97.0%) | 0.51 | 2.38 (0.21–27.42) | 0.59 |
| Yes | 3 (4.1%) | 2 (5.0%) | 1 (3.0%) | ||||
| Psychiatric family history Missing n = 2 | No | 49 (66.2%) | 25 (62.5%) | 24 (70.6%) | 0.54 | 0.69 (0.26–1.84) | 0.62 |
| Yes | 25 (33.8%) | 15 (37.5%) | 10 (29.4%) | ||||
| Current psychotherapy Missing n = 14 | No | 58 (93.5%) | 32 (97%) | 26 (89.7%) | 1.37 | 3.69 (0.36–37.63) | 0.33 |
| Yes | 4 (6.5%) | 1 (3.0%) | 3 (10.3%) | ||||
| Psychiatric comorbidity Missing n = 0 | No | 51 (67.1%) | 29 (69.0%) | 22 (64.7%) | 0.16 | 1.22 (0.47–3.18) | 0.80 |
| Yes | 25 (32.9%) | 13 (31.0%) | 12 (35.3%) | ||||
| Type of psychiatric comorbidity Missing n = 0 | None | 51 (67.1%) | 29 (69.0%) | 22 (64.7%) | 10.84 | / * | 0.03 |
| Depression | 10 (13.2%) | 2 (4.8%) | 8 (23.5%) | ||||
| Anxiety disorders | 8 (10.5%) | 4 (9.5%) | 4 (11.8%) | ||||
| OCD | 2 (2.6%) | 2 (4.8%) | 0 (0.0%) | ||||
| Other | 5 (6.6%) | 5 (11.5%) | 0 (0.0%) | ||||
| Psychiatric poly-comorbidity Missing n = 0 | No | 68 (89.5%) | 37 (88.1%) | 31 (91.2%) | 0.19 | 0.72 (0.16–3.24) | 0.73 |
| Yes | 8 (10.5%) | 5 (11.9%) | 3 (8.8%) | ||||
| Personality disorder Missing n = 4 | None | 63 (87.4%) | 32 (84.3%) | 31 (91.2%) | 8.82 | / * | 0.06 |
| Schizoid | 1 (1.4%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (2.9%) | ||||
| Schizotypal | 2 (2.8%) | 0 (0.0%) | 2 (5.9%) | ||||
| Borderline | 4 (5.6%) | 4 (10.5%) | 0 (0.0%) | ||||
| OCD | 1 (1.4%) | 1 (2.6%) | 0 (0.0%) | ||||
| PD-NOS | 1 (1.4%) | 1 (2.6%) | 0 (0.0%) | ||||
| Thyroid disorders Missing n = 10 | No | 65 (98.5%) | 38 (97.4%) | 27 (100%) | 0.70 | 0.58 (0.48–0.72) | 1.00 |
| Yes | 1 (1.5%) | 1 (2.6%) | 0 (0%) | ||||
| Hypercholesterolemia Missing n = 7 | No | 66 (95.7%) | 37 (94.9%) | 29 (96.7%) | 0.31 | 0.64 (0.06–7.39) | 1.00 |
| Yes | 3 (4.3%) | 2 (5.1%) | 1 (3.3%) | ||||
| Diabetes Missing n = 8 | No | 68 (100%) | 39 (100%) | 29 (100%) | / ** | / ** | / ** |
| Yes | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | ||||
| Current medical poly-comorbidity Missing n = 4 | No | 69 (95.8%) | 40 (97.6%) | 29 (93.5%) | 0.71 | 2.76 (0.24–31.89) | 0.57 |
| Yes | 3 (4.2%) | 1 (2.4%) | 2 (6.5%) | ||||
| Type of current medical comorbidity Missing n = 27 | None | 37 (75.6%) | 26 (86.7%) | 11 (57.9%) | 13.63 | / * | 0.02 |
| CRF | 1 (2.0%) | 1 (3.3%) | 0 (0.0%) | ||||
| GERD | 2 (4.1%) | 0 (0.0%) | 2 (10.5%) | ||||
| Hyperthyroidism | 1 (2.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (5.3%) | ||||
| Thalassemia | 2 (4.1%) | 2 (6.7%) | 0 (0.0%) | ||||
| Endocrine disorders | 3 (6.2%) | 1 (3.3%) | 2 (10.5%) | ||||
| Blood disorders | 1 (2.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (5.3%) | ||||
| Others | 2 (4.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 2 (10.5%) | ||||
| Variables | B | SE | p Value | OR | 95% CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inferior | Superior | |||||
| Duration of illness | −0.17 | 0.19 | 0.36 | 0.84 | 0.58 | 1.21 |
| Sodium/Potassium | 0.80 | 0.37 | 0.03 | 2.23 | 1.1 | 4.57 |
| Variables Correlated with Age at Onset | r | p |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 0.66 | <0.01 |
| Education level (years) | 0.30 | <0.01 |
| K+ (mmol/L) | −0.75 | <0.01 |
| Na+/K+ | 0.78 | <0.01 |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 0.57 | <0.01 |
| Variable | B | SE | β | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
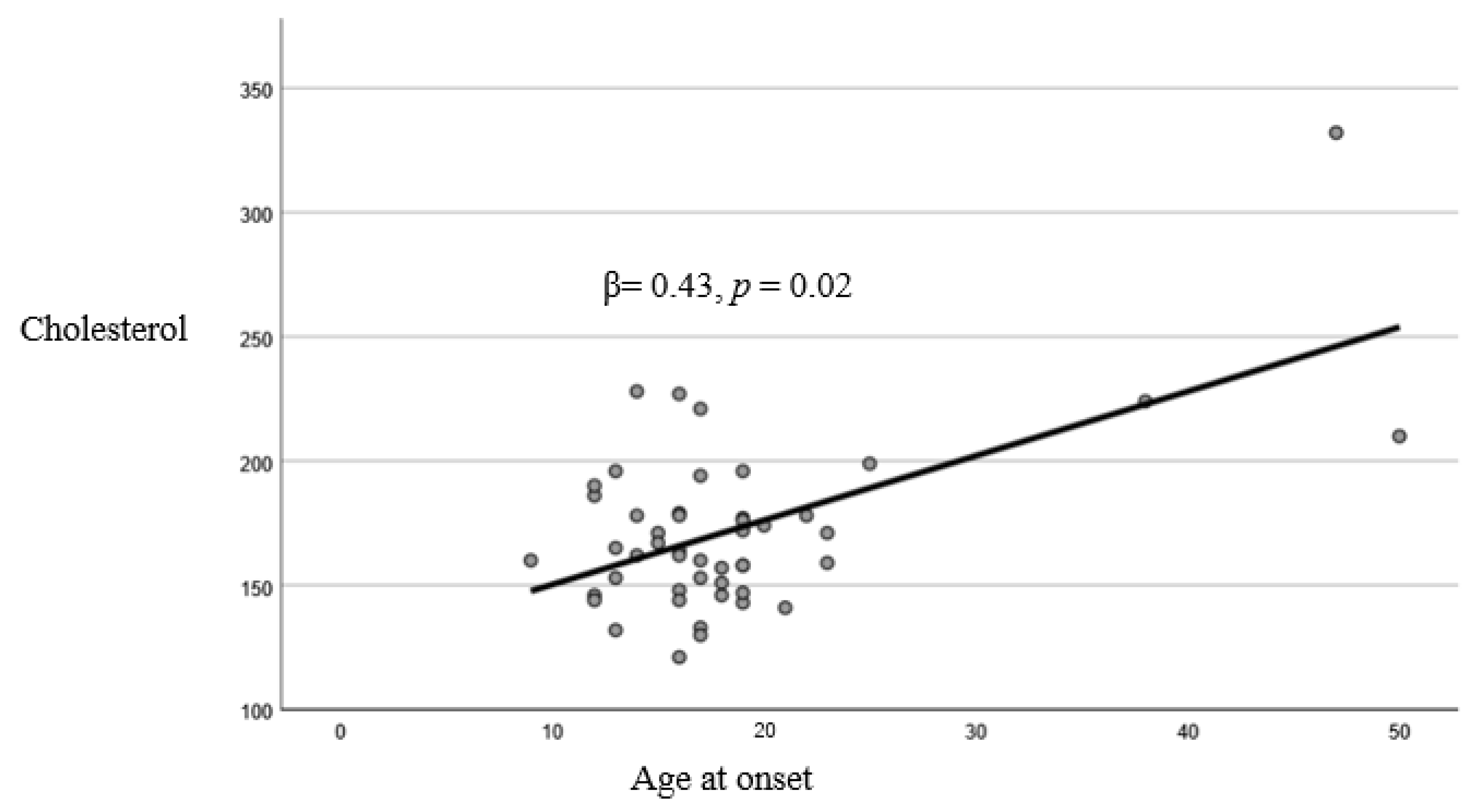
| Cholesterol | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.43 | 0.02 |
| NA+/K+ | 1.68 | 0.31 | 0.64 | <0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferrario, L.; Costantino, A.; Affaticati, L.M.; Clerici, M.; Dakanalis, A.; Capuzzi, E.; Buoli, M. The Role of Age at Onset on the Clinical Course and Biochemical Parameters of Anorexia Nervosa. J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15, 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15090442
Ferrario L, Costantino A, Affaticati LM, Clerici M, Dakanalis A, Capuzzi E, Buoli M. The Role of Age at Onset on the Clinical Course and Biochemical Parameters of Anorexia Nervosa. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2025; 15(9):442. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15090442
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerrario, Lorenzo, Andrea Costantino, Letizia Maria Affaticati, Massimo Clerici, Antonios Dakanalis, Enrico Capuzzi, and Massimiliano Buoli. 2025. "The Role of Age at Onset on the Clinical Course and Biochemical Parameters of Anorexia Nervosa" Journal of Personalized Medicine 15, no. 9: 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15090442
APA StyleFerrario, L., Costantino, A., Affaticati, L. M., Clerici, M., Dakanalis, A., Capuzzi, E., & Buoli, M. (2025). The Role of Age at Onset on the Clinical Course and Biochemical Parameters of Anorexia Nervosa. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 15(9), 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15090442












