Polygenic Risk Score Associated with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in an AmericanIndian Population
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Approval and Participants
2.2. Genotyping
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Cohort
3.2. Univariate Associations
3.3. Multivariate Associations
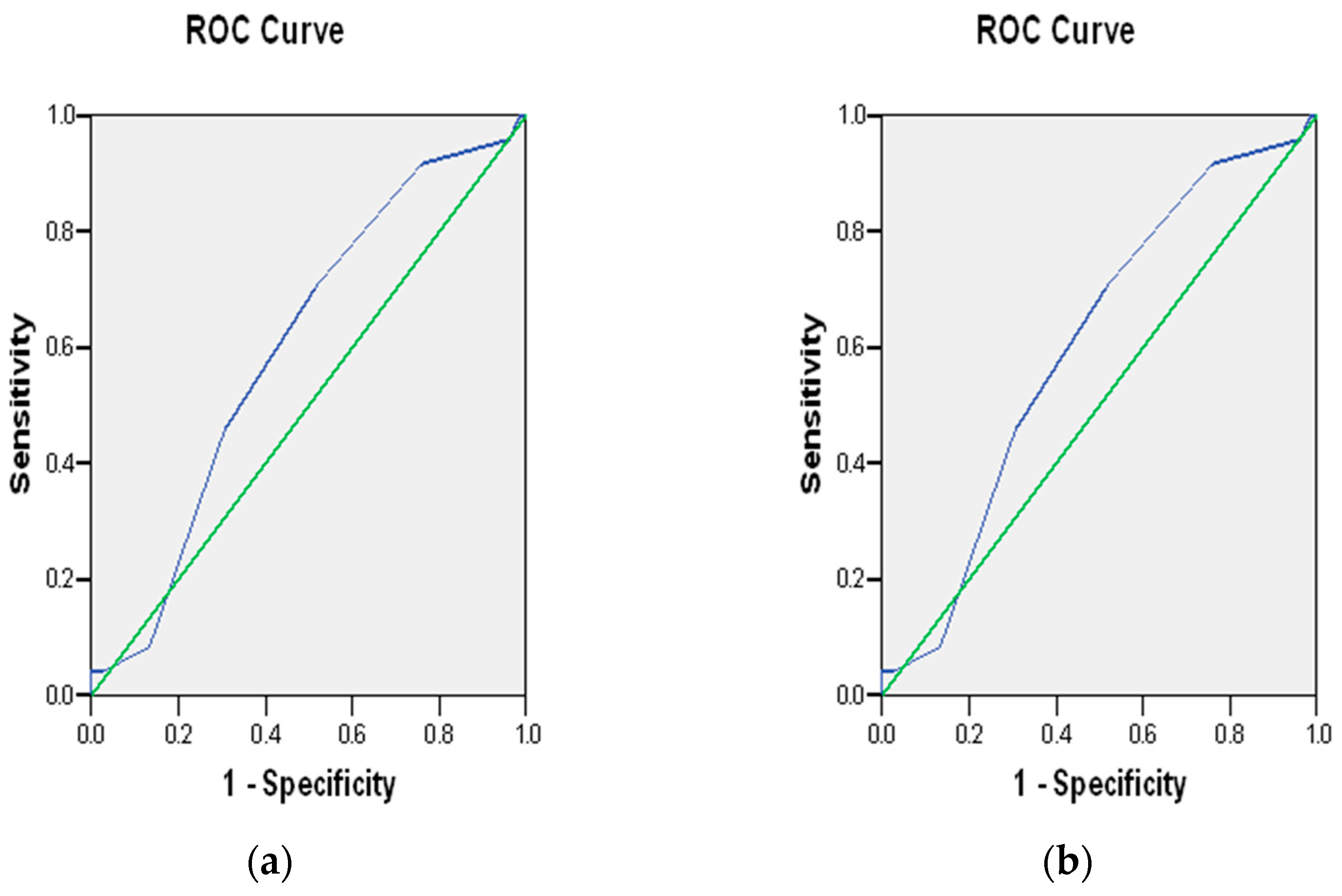
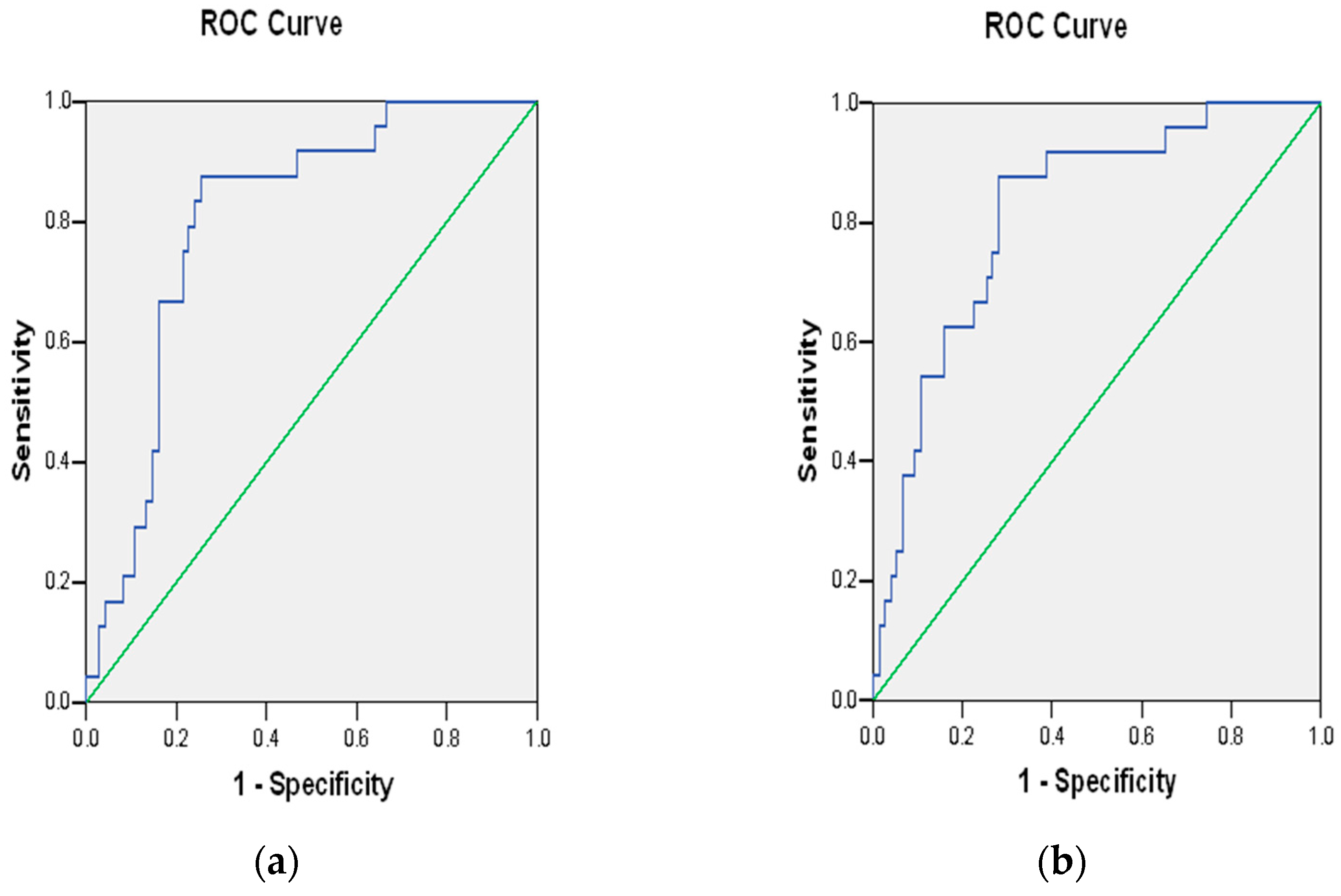
3.4. Polygenic Risk Scores
4. Discussion
4.1. Rationale for Variants Included in the Analysis
4.2. Functionality of the Variants Included
4.3. Implications of Individual Variant Results
4.4. Implications of Polygenic Risk Score Results
4.5. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Best, L.G.; Nadeau, M.; Davis, K.; Lamb, F.; Bercier, S.; Anderson, C.M. Genetic variants, immune function, and risk of pre-eclampsia among American Indians. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2012, 67, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Best, L.G.; Saxena, R.; Anderson, C.M.; Barnes, M.R.; Hakonarson, H.; Falcon, G.; Martin, C.; Castillo, B.A.; Karumanchi, A.; Keplin, K.; et al. Two variants of the C-reactive protein gene are associated with risk of pre-eclampsia in an American Indian population. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71231, Erratum in PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caughey, A.B.; Turrentine, M. ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 190: Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 131, e49–e64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modzelewski, R.; Stefanowicz-Rutkowska, M.M.; Matuszewski, W.; Bandurska-Stankiewicz, E.M. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus-Recent Literature Review. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dyck, R.; Klomp, H.; Tan, L.K.; Turnell, R.W.; Boctor, M.A. A comparison of rates, risk factors, and outcomes of gestational diabetes between aboriginal and non-aboriginal women in the Saskatoon health district. Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plows, J.F.; Stanley, J.L.; Baker, P.N.; Reynolds, C.M.; Vickers, M.H. The Pathophysiology of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Luo, M.; Wang, T.; Wei, J.; Zhang, S.; Shu, J.; Zhong, T.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhu, P.; et al. Effect of the interaction between advanced maternal age and pre-pregnancy BMI on pre-eclampsia and GDM in Central China. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2023, 11, e003324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannakou, K.; Evangelou, E.; Yiallouros, P.; Christophi, C.A.; Middleton, N.; Papatheodorou, E.; Papatheodorou, S.I. Risk factors for gestational diabetes: An umbrella review of meta-analyses of observational studies. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiao, C.M.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, X.Q.; Li, X.F.; Shao, R.Y.; Gao, Y.M. Factors Associated with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis. J. Diabetes Res. 2021, 2021, 6692695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, P.A.; Madi, J.M.; da Silva, E.R.; Vergani, D.O.P.; de Araújo, B.F.; Garcia, R.M.R. Gestational Diabetes in the Population Served by Brazilian Public Health Care. Prevalence and Risk Factors. Rev. Bras. Ginecol. Obstet. 2020, 42, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, J. Current perspectives on preeclampsia. J. Nurse Midwifery 1994, 39, 70–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powe, C.E.; Udler, M.S.; Hsu, S.; Allard, C.; Kuang, A.; Manning, A.K.; Perron, P.; Bouchard, L.; Lowe, W.L., Jr.; Scholtens, D.; et al. Genetic Loci and Physiologic Pathways Involved in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Implicated Through Clustering. Diabetes 2021, 70, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjørnland, T.; Langaas, M.; Grill, V.; Mostad, I.L. Assessing gene-environment interaction effects of FTO, MC4R and lifestyle factors on obesity using an extreme phenotype sampling design: Results from the HUNT study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Namjou, B.; Stanaway, I.B.; Lingren, T.; Mentch, F.D.; Benoit, B.; Dikilitas, O.; Niu, X.; Shang, N.; Shoemaker, A.H.; Carey, D.J. Evaluation of the MC4R gene across eMERGE network identifies many unreported obesity-associated variants. Int. J. Obes. (Lond.) 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulit, S.L.; Stoneman, C.; Morris, A.P.; Wood, A.R.; Glastonbury, C.A.; Tyrrell, J.; Yengo, L.; Ferreira, T.; Marouli, E.; Ji, Y.; et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies for body fat distribution in 694 649 individuals of European ancestry. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2019, 28, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, W.L., Jr.; Kuang, A.; Hayes, M.G.; Hivert, M.F.; Scholtens, D.M. Genetics of glucose homeostasis in pregnancy and postpartum. Diabetologia 2024, 67, 2726–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsay, A.; Wang, J.C. The Role of PIK3R1 in Metabolic Function and Insulin Sensitivity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, A.; Taliun, D.; Thurner, M.; Robertson, N.R.; Torres, J.M.; Rayner, N.W.; Payne, A.J.; Steinthorsdottir, V.; Scott, R.A.; Grarup, N.; et al. Fine-mapping type 2 diabetes loci to single-variant resolution using high-density imputation and islet-specific epigenome maps. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1505–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Levi, A.; Barabash, A.; Valerio, J.; García de la Torre, N.; Mendizabal, L.; Zulueta, M.; de Miguel, M.P.; Diaz, A.; Duran, A.; Familiar, C.; et al. Genetic variants for prediction of gestational diabetes mellitus and modulation of susceptibility by a nutritional intervention based on a Mediterranean diet. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2022, 13, 1036088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keating, B.J.; Tischfield, S.; Murray, S.S.; Bhangale, T.; Price, T.S.; Glessner, J.T.; Galver, L.; Barrett, J.C.; Grant, S.F.A.; Farlow, D.N.; et al. Concept, design and implementation of a cardiovascular gene-centric 50 k SNP array for large-scale genomic association studies. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.W.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/snp (accessed on 24 July 2025).
- Bai, Y.; Tang, L.; Li, L.; Li, L. The roles of ADIPOQ rs266729 and MTNR1B rs10830963 polymorphisms in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis. Gene 2020, 730, 144302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suleman, S.; Madsen, A.L.; Ängquist, L.H.; Schubert, M.; Linneberg, A.; Loos, R.J.F.; Hansen, T.; Grarup, N. Genetic Underpinnings of Fasting and Oral Glucose-stimulated Based Insulin Sensitivity Indices. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 109, 2754–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vejrazkova, D.; Vankova, M.; Vcelak, J.; Krejci, H.; Anderlova, K.; Tura, A.; Pacini, G.; Sumova, A.; Sladek, M.; Bendlova, B. The rs10830963 Polymorphism of the MTNR1B Gene: Association With Abnormal Glucose, Insulin and C-peptide Kinetics. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 868364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Accili, D.; Deng, Z.; Liu, Q. Insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2025, 21, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Hruby, V.J. MC4R biased signalling and the conformational basis of biological function selections. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 4125–4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claussnitzer, M.; Dankel, S.N.; Kim, K.H.; Quon, G.; Meuleman, W.; Haugen, C.; Glunk, V.; Sousa, I.S.; Beaudry, J.L.; Puviindran, V.; et al. FTO Obesity Variant Circuitry and Adipocyte Browning in Humans. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 895–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saucedo, R.; Valencia, J.; Gutierrez, C.; Basurto, L.; Hernandez, M.; Puello, E.; Rico, G.; Vega, G.; Zarate, A. Gene variants in the FTO gene are associated with adiponectin and TNF-alpha levels in gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2017, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, C.H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.C.; Yuen, L.Y.; Lim, C.K.; Leng, J.; Wu, L.; Ng, A.C.; Hou, Y.; Tsoi, K.Y.; et al. Identification and Potential Clinical Utility of Common Genetic Variants in Gestational Diabetes among Chinese Pregnant Women. Diabetes Metab. J. 2025, 49, 128–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kawai, V.K.; Levinson, R.T.; Adefurin, A.; Kurnik, D.; Collier, S.P.; Conway, D.; Stein, C.M. A genetic risk score that includes common type 2 diabetes risk variants is associated with gestational diabetes. Clin. Endocrinol. 2017, 87, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, Y.; Yang, M.; Yuan, L.; Li, T.; Zhong, X.; Guo, Y. Associations between a polygenic risk score and the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus in a Chinese population: A case-control study. Endocr. J. 2023, 70, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, M.; Liu, M.; Zhang, L.; Liang, Z.; Chen, D. An early prediction model for gestational diabetes mellitus based on genetic variants and clinical characteristics in China. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2022, 14, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cheng, J.; Meng, C.; Li, J.; Kong, Z.; Zhou, A. Integrating polygenic risk scores in the prediction of gestational diabetes risk in China. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1391296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ding, M.; Chavarro, J.; Olsen, S.; Lin, Y.; Ley, S.H.; Bao, W.; Rawal, S.; Grunnet, L.G.; Thuesen, A.C.B.; Mills, J.L.; et al. Genetic variants of gestational diabetes mellitus: A study of 112 SNPs among 8722 women in two independent populations. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 1758–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Perišić, M.M.; Vladimir, K.; Karpov, S.; Štorga, M.; Mostashari, A.; Khanin, R. Polygenic Risk Score and Risk Factors for Gestational Diabetes. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lamri, A.; Limbachia, J.; Schulze, K.M.; Desai, D.; Kelly, B.; de Souza, R.J.; Paré, G.; Lawlor, D.A.; Wright, J.; Anand, S.S. Born in Bradford and START investigators. The genetic risk of gestational diabetes in South Asian women. Elife 2022, 11, e81498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
| Gene | SNP * | Risk/Alternate Allele | Included in Current Analysis | Theorized Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MC4R | rs523288 | T/A | + | Obesity [12,13,14] |
| PURG | rs10954772 | T/C | + | Adiposity [12,15] |
| CRHR2 | rs917195 | C/T | + | Pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction [12] |
| FTO | rs1421085 | C/T | + | Obesity [12,13] |
| MTNR1B | rs10830963 | G/C | + | Insulin resistance Pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction [12,16] |
| PIK3R1 | rs4976033 | G/A | + | Insulin resistance [17] |
| SHQ1 | rs13085136 | C/T | + | Adiposity [12,18] |
| MRPS30 | rs6884702 | G/A | Unknown [12] | |
| GLP2R | rs7222481 | C/G | Pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction [12,19] | |
| SLC2A2 | rs9873618 | G/A | Hepatic glucose uptake [12] |
| GDM | Control | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number (N) | 38 | 296 | |
| Age at delivery mean (SD) | 28.0 (6.48) | 23.8 (5.73) | 3 × 10−5 |
| Parity, N (% nulliparous) | 16 (42.1%) | 151 (51.0%) | 0.301 |
| Body mass index (SD) | 34.8 (8.10) | 28.7 (7.15) | 1.4 × 10−6 |
| Pre-eclampsia, N (% yes) | 22 (57.9%) | 117 (39.5%) | 0.031 |
| Risk Allele * | Case Risk Allele Frequency (%) | Control Risk Allele Frequency (%) | Case vs. Control Risk Allele Frequency ** p Value | Hardy-Weinberg p Value *** | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs523288 | T | 11/66 (16.7) | 29/230 (12.6) | 0.518 | 0.621 |
| rs10954772 | T | 19/70 (27.1) | 96/312 (30.8) | 0.650 | 0.812 |
| rs917195 | C | 34/50 (68.0) | 170/236 (72.0) | 0.689 | 0.920 |
| rs1421085 | C | 13/76 (17.1) | 158/554 (28.5) | 0.050 | 0.361 |
| rs10830963 | G | 22/72 (30.6) | 151/538 (28.1) | 0.764 | 0.679 |
| rs4976033 | G | 30/50 (60.0) | 134/216 (62.0) | 0.916 | 0.871 |
| rs13085136 | C | 42/48 (87.5) | 240/272 (88.2) | 0.923 | 0.091 |
| Risk/Alt Allele * | Odds Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age at delivery | 1.114 | 1.06–1.17 | <0.001 | |
| Nulliparity | 0.698 | 0.35–1.38 | 0.303 | |
| Body mass index | 1.093 | 1.05–1.14 | <0.001 | |
| Pre-eclampsia | 2.104 | 1.06–4.18 | 0.033 | |
| rs523288, T-ADD | T/A | 1.408 | 0.65–3.06 | 0.388 |
| rs10954772, T-Rec | T/C | 0.240 | 0.03–1.87 | 0.173 |
| rs917195, C-Dom | C/T | 0.606 | 0.15–2.42 | 0.478 |
| rs1421085, C-ADD | C/T | 0.499 | 0.26–0.95 | 0.034 |
| rs10830963, G-Rec | G/C | 1.403 | 0.45–4.33 | 0.556 |
| rs4976033, G-Dom | G/A | 1.131 | 0.46–2.79 | 0.789 |
| rs13085136, C-ADD | C/T | 0.923 | 0.34–2.52 | 0.876 |
| PRS-7 ** | 1.266 | 0.92–1.74 | 0.144 | |
| PRS-7, weighted * | 1.201 | 0.89–1.62 | 0.232 | |
| PRS-3 *** | 1.673 | 1.08–2.59 | 0.021 |
| Risk/Alt Allele * | Odds Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age at delivery | 1.099 | 1.03–1.18 | 0.006 | |
| Body mass index | 1.079 | 1.02–1.14 | 0.005 | |
| Pre-eclampsia | 2.011 | 0.81–5.01 | 0.134 | |
| PC-1 ** | 0.032 | 0.00–146.8.8 | 0.423 | |
| PC-2 | 0.027 | 0.00–3432 | 0.548 | |
| PC-3 | 0.018 | 1.03–128.9 | 0.375 | |
| PC-4 | 0.152 | 0.00–2597 | 0.704 | |
| PC-5 | 0.299 | 0.00–3853 | 0.802 | |
| PC-6 | 0.001 | 0.00–115.7 | 0.230 | |
| PC-7 | 0.598 | 0.00–52,172 | 0.929 | |
| PC-8 | 0.276 | 0.00–10,894 | 0.812 | |
| PC-9 | 1.378 | 0.00–1310 | 0.927 | |
| PC-10 *** | 13,152 | 0.96–179,234,369 | 0.051 | |
| The above covariates included in analysis with each of the following independently | ||||
| rs523288, T-ADD | T/A | 1.523 | 0.51–4.55 | 0.451 |
| rs10954772, T-Rec | T/C | 0.970 | 0.84–11.15 | 0.981 |
| rs917195, C-Dom | C/T | 0.375 | 0.06–2.46 | 0.306 |
| rs1421085, C-ADD | C/T | 0.613 | 0.28–1.35 | 0.225 |
| rs10830963, G-Rec | G/C | 1.822 | 0.45–7.40 | 0.402 |
| rs4976033, G-Dom | G/A | 1.330 | 0.36–4.85 | 0.666 |
| rs13085136, C-ADD | C/T | 0.743 | 0.22–2.46 | 0.627 |
| PRS-7 **** | 1.569 | 0.96–2.56 | 0.070 | |
| PRS-7, weighted * | 1.437 | 0.92–2.26 | 0.114 | |
| PRS-3 ***** | 2.436 | 1.17–5.06 | 0.017 | |
| PRS-7 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Score | Number with Score | % |
| 0 | 1 | 1.0 |
| 1 | 3 | 3.0 |
| 2 | 16 | 16.2 |
| 3 | 23 | 23.2 |
| 4 | 22 | 22.2 |
| 5 | 22 | 22.2 |
| 6 | 9 | 9.1 |
| 7 | 2 | 2.0 |
| 8 | 1 | 1.0 |
| 9 | 1 | 1.0 |
| 10 | 3 | 3.0 |
| PRS-3 | ||
| 0 | 21 | 21.2 |
| 1 | 29 | 29.3 |
| 2 | 33 | 33.3 |
| 3 | 11 | 11.1 |
| 4 | 5 | 5.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peterson, K.; Powe, C.E.; Sun, Q.; Azure, C.; Azure, T.; Davis, H.; Gourneau, K.; LaRocque, S.; Poitra, C.; Poitra, S.; et al. Polygenic Risk Score Associated with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in an AmericanIndian Population. J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15, 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15090395
Peterson K, Powe CE, Sun Q, Azure C, Azure T, Davis H, Gourneau K, LaRocque S, Poitra C, Poitra S, et al. Polygenic Risk Score Associated with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in an AmericanIndian Population. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2025; 15(9):395. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15090395
Chicago/Turabian StylePeterson, Karrah, Camille E. Powe, Quan Sun, Crystal Azure, Tia Azure, Hailey Davis, Kennedy Gourneau, Shyanna LaRocque, Craig Poitra, Sabra Poitra, and et al. 2025. "Polygenic Risk Score Associated with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in an AmericanIndian Population" Journal of Personalized Medicine 15, no. 9: 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15090395
APA StylePeterson, K., Powe, C. E., Sun, Q., Azure, C., Azure, T., Davis, H., Gourneau, K., LaRocque, S., Poitra, C., Poitra, S., Standish, S., Parisien, T. J., Morin, K. J., & Best, L. G. (2025). Polygenic Risk Score Associated with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in an AmericanIndian Population. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 15(9), 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15090395









