The Role of Oxidative Stress in the Relationship Between Periodontitis and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Review of the Literature
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Scope and Literature Selection
3. Overview of Alzheimer’s Disease and Its Systemic Context
4. Epidemiological Evidence Linking Periodontitis and AD
5. Mechanisms Underlying the Association
5.1. Neuroinflammation and Systemic Inflammatory Mediators
5.2. Direct Bacterial Invasion into the Brain
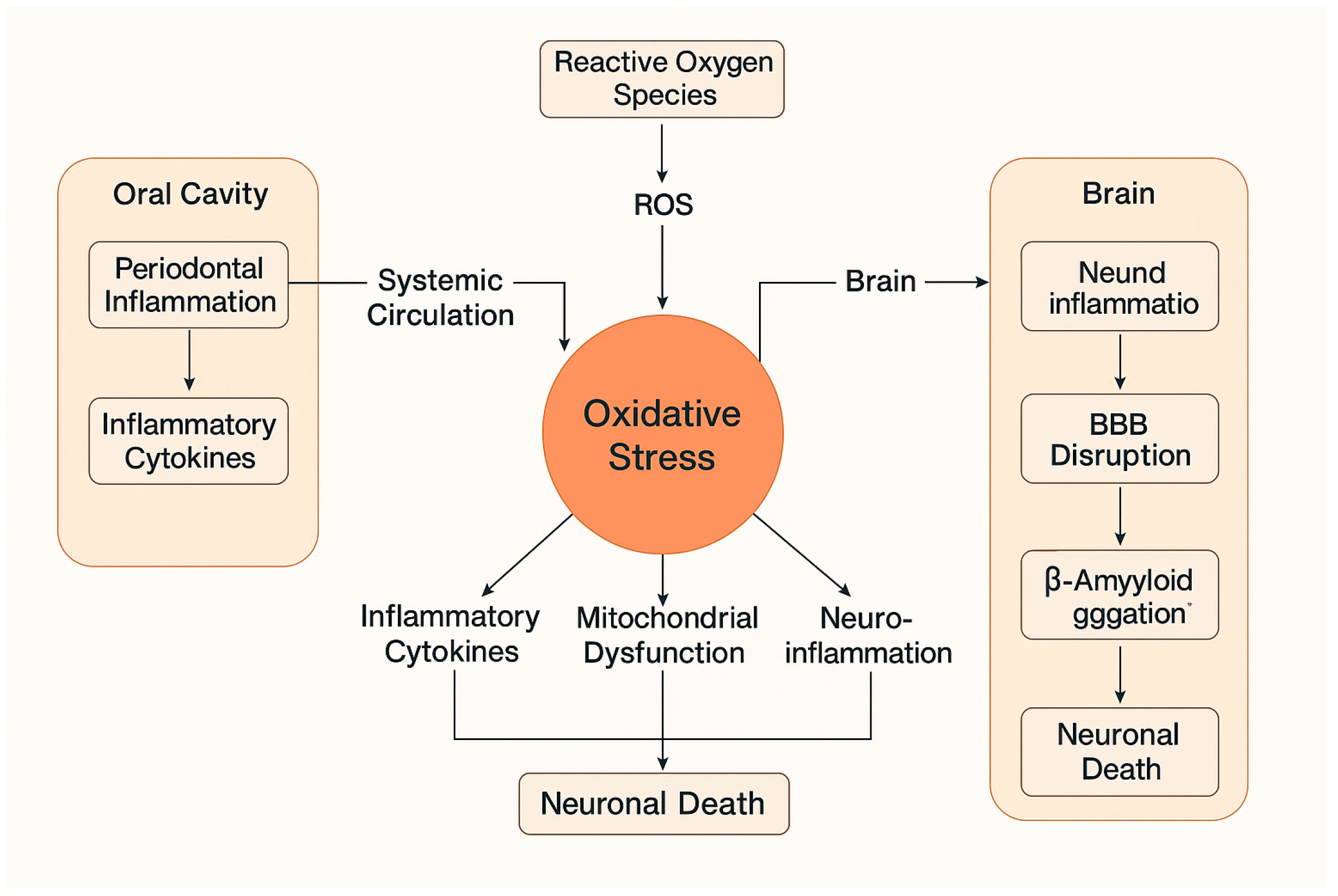
5.3. Oxidative Stress: Biological Basis and Relevance
6. The Relationship Between Saliva and the Brain
7. Periodontitis-Induced Oxidative Stress
7.1. Studies in Animals
7.2. Studies in Humans
8. Discussion
9. Conclusions
10. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Verma, A.; Azhar, G.; Zhang, X.; Patyal, P.; Kc, G.; Sharma, S.; Che, Y.; Wei, J.Y. P. gingivalis-LPS Induces Mitochondrial Dysfunction Mediated by Neuroinflammation through Oxidative Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, M.; Marco del Castillo, A.; Jepsen, S.; Gonzalez-Juanatey, J.R.; D’Aiuto, F.; Bouchard, P.; Chapple, I.; Dietrich, T.; Gotsman, I.; Graziani, F.; et al. Periodontitis and Cardiovascular Diseases. Consensus Report. Glob. Heart 2020, 15, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caton, J.G.; Armitage, G.; Berglundh, T.; Chapple, I.L.C.; Jepsen, S.; Kornman, K.S.; Mealey, B.L.; Papapanou, P.N.; Sanz, M.; Tonetti, M.S. A new classification scheme for periodontal and peri-implant diseases and conditions—Introduction and key changes from the 1999 classification. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89 (Suppl. 1), S1–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, W.; Qian, W. Identification the Low Oxidative Stress Subtype of Periodontitis. Int. Dent. J. 2024, 74, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, D.; Sanz, M.; Kebschull, M.; Jepsen, S.; Sculean, A.; Berglundh, T.; Papapanou, P.N.; Chapple, I.; Tonetti, M.S.; EFP Workshop Participants and Methodological Consultant. Treatment of stage IV periodontitis: The EFP S3 level clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2022, 49, 4–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Dementia in the Aged. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6121426/ (accessed on 9 February 2025).
- Knopman, D.S.; Petersen, R.C.; Jack, C.R. A brief history of “Alzheimer disease”: Multiple meanings separated by a common name. Neurology 2019, 92, 1053–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, L.N.C.; van Maurik, I.S.; Bouwman, F.H.; Staekenborg, S.; Vreeswijk, R.; Hempenius, L.; de Beer, M.H.; Roks, G.; Boelaarts, L.; Kleijer, M.; et al. Clinicians’ communication with patients receiving a MCI diagnosis: The ABIDE project. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.G.; March, Z.M.; Stephenson, R.A.; Narayan, P.S. Apolipoprotein E in lipid metabolism and neurodegenerative disease. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 34, 430–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canevelli, M.; Piscopo, P.; Talarico, G.; Vanacore, N.; Blasimme, A.; Crestini, A.; Tosto, G.; Troili, F.; Lenzi, G.L.; Confaloni, A.; et al. Familial Alzheimer’s disease sustained by presenilin 2 mutations: Systematic review of literature and genotype-phenotype correlation. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2014, 42, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dintica, C.S.; Yaffe, K. Epidemiology and Risk Factors for Dementia. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2022, 45, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, J.C.; Ibrahim-Verbaas, C.A.; Harold, D.; Naj, A.C.; Sims, R.; Bellenguez, C.; DeStafano, A.L.; Bis, J.C.; Beecham, G.W.; Grenier-Boley, B.; et al. Meta-analysis of 74,046 individuals identifies 11 new susceptibility loci for Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1452–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunkle, B.W.; Grenier-Boley, B.; Sims, R.; Bis, J.C.; Damotte, V.; Naj, A.C.; Boland, A.; Vronskaya, M.; van der Lee, S.J.; Amlie-Wolf, A.; et al. Genetic meta-analysis of diagnosed Alzheimer’s disease identifies new risk loci and implicates Aβ, tau, immunity and lipid processing. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 414–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marioni, R.E.; Harris, S.E.; Zhang, Q.; McRae, A.F.; Hagenaars, S.P.; Hill, W.D.; Davies, G.; Ritchie, C.W.; Gale, C.R.; Starr, J.M.; et al. GWAS on family history of Alzheimer’s disease. Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastrogiacomo, F.; Bergeron, C.; Kish, S.J. Brain α-Ketoglutarate Dehydrotenase Complex Activity in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neurochem. 1993, 61, 2007–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kish, S.J. Brain energy metabolizing enzymes in Alzheimer’s disease: Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex and cytochrome oxidase. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1997, 826, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ablinger, I.; Dressel, K.; Rott, T.; Lauer, A.A.; Tiemann, M.; Batista, J.P.; Taddey, T.; Grimm, H.S.; Grimm, M.O.W. Interdisciplinary Approaches to Deal with Alzheimer’s Disease—From Bench to Bedside: What Feasible Options Do Already Exist Today? Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheltens, P.; De Strooper, B.; Kivipelto, M.; Holstege, H.; Chételat, G.; Teunissen, C.E.; Cummings, J.; van der Flier, W.M. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 1577–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kametani, F.; Hasegawa, M. Reconsideration of Amyloid Hypothesis and Tau Hypothesis in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Pozo, A.; Frosch, M.P.; Masliah, E.; Hyman, B.T. Neuropathological alterations in Alzheimer disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2011, 1, a006189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Manis, M.; Long, J.; Wang, K.; Sullivan, P.M.; Serrano, J.R.; Hoyle, R.; Holtzman, D.M. Microglia drive APOE-dependent neurodegeneration in a tauopathy mouse model. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 2546–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Blazey, T.M.; Holtzman, D.M.; Cruchaga, C.; Su, Y.; Morris, J.C.; Benzinger, T.L.S.; A Gordon, B. Longitudinal brain imaging in preclinical Alzheimer disease: Impact of APOE ε4 genotype. Brain 2018, 141, 1828–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campion, D.; Charbonnier, C.; Nicolas, G. SORL1 genetic variants and Alzheimer disease risk: A literature review and meta-analysis of sequencing data. Acta Neuropathol. 2019, 138, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellenguez, C.; Charbonnier, C.; Grenier-Boley, B.; Quenez, O.; Le Guennec, K.; Nicolas, G.; Chauhan, G.; Wallon, D.; Rousseau, S.; Richard, A.C.; et al. Contribution to Alzheimer’s disease risk of rare variants in TREM2, SORL1, and ABCA7 in 1779 cases and 1273 controls. Neurobiol. Aging 2017, 59, 220.e1–220.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Deyn, L.; Sleegers, K. The impact of rare genetic variants on Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2025, 21, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.K.; Wu, Y.T.; Chang, Y.C. Association between chronic periodontitis and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease: A retrospective, population-based, matched-cohort study. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2017, 9, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamer, A.R.; Craig, R.G.; Niederman, R.; Fortea, J.; de Leon, M.J. Periodontal disease as a possible cause for Alzheimer’s disease. Periodontol 2000 2020, 83, 242–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, G.G.; Leite, F.R.; Mesquita, C.M.; Vidigal, M.T.C.; Borges, G.H.; Paranhos, L.R. Confounding in observational studies evaluating the association between Alzheimer’s disease and periodontal disease: A systematic review. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swerdlow, R.H. Mitochondria and Mitochondrial Cascades in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 62, 1403–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirnic, J.; Djuric, M.; Brkic, S.; Gusic, I.; Stojilkovic, M.; Tadic, A.; Veljovic, T. Pathogenic Mechanisms That May Link Periodontal Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus—The Role of Oxidative Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meli, A.C. The impact of cardiovascular diseases and new gene variants in swaying Alzheimer’s disease. Cardiovasc Res. 2019, 115, E102–E104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-García, M.; Hernández-Lemus, E. Periodontal Inflammation and Systemic Diseases: An Overview. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 709438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Wang, Y.Y.; Li, B.H.; Wu, L.; Xie, W.Z.; Zhou, X.; Ma, B. Association between periodontal disease and systemic diseases: A cross-sectional analysis of current evidence. Mil. Med. Res. 2024, 11, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ide, M.; Harris, M.; Stevens, A.; Sussams, R.; Hopkins, V.; Culliford, D.; Fuller, J.; Ibbett, P.; Raybould, R.; Thomas, R.; et al. Periodontitis and Cognitive Decline in Alzheimer’s Disease. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhrao, S.K.; Olsen, I. Assessing the role of Porphyromonas gingivalis in periodontitis to determine a causative relationship with Alzheimer’s disease. J. Oral Microbiol. 2019, 11, 1563405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhodehouse, B.C.; Erickson, M.A.; Banks, W.A.; Bearden, S.E. Hyperhomocysteinemic mice show cognitive impairment without features of Alzheimer’s disease phenotype. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2013, 35, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilievski, V.; Zuchowska, P.K.; Green, S.J.; Toth, P.T.; Ragozzino, M.E.; Le, K.; Aljewari, H.W.; O’bRien-Simpson, N.M.; Reynolds, E.C.; Watanabe, K.; et al. Chronic oral application of a periodontal pathogen results in brain inflammation, neurodegeneration and amyloid beta production in wild type mice. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Andrukhov, O.; Rausch-Fan, X. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant System in Periodontitis. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chistiakov, D.A.; Sobenin, I.A.; Revin, V.V.; Orekhov, A.N.; Bobryshev, Y.V. Mitochondrial aging and age-related dysfunction of mitochondria. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 238463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, H.; Barger, S.; Barnum, S.; Bradt, B.; Bauer, J.; Cole, G.M.; Cooper, N.R.; Eikelenboom, P.; Emmerling, M.; Fiebich, B.L.; et al. Inflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2000, 21, 383–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.Q.; Kosten, T.R.; Zhang, X.Y. Free radicals, antioxidant defense systems, and schizophrenia. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 46, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccellato, F.R.; D’anca, M.; Fenoglio, C.; Scarpini, E.; Galimberti, D.; Barone, E. Role of Oxidative Damage in Alzheimer’s Disease and Neurodegeneration: From Pathogenic Mechanisms to Biomarker Discovery. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McManus, L.J.; Dawes, P.J.D.; Stringer, M.D. Clinical anatomy of the chorda tympani: A systematic review. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2011, 125, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, H.E.; Tio, D.L.; Rahman, S.U.; Chiappelli, F.; Taylor, A.N. The glossopharyngeal nerve as a novel pathway in immune-to-brain communication: Relevance to neuroimmune surveillance of the oral cavity. J. Neuroimmunol. 2001, 115, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forner, L.; Larsen, T.; Kilian, M.; Holmstrup, P. Incidence of bacteremia after chewing, tooth brushing and scaling in individuals with periodontal inflammation. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2006, 33, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominy, S.S.; Lynch, C.; Ermini, F.; Benedyk, M.; Marczyk, A.; Konradi, A.; Nguyen, M.; Haditsch, U.; Raha, D.; Griffin, C.; et al. Porphyromonas gingivalis in Alzheimer’s disease brains: Evidence for disease causation and treatment with small-molecule inhibitors. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaau3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yang, J.; Liu, T.; Shi, Y. Role of the gut-microbiota-metabolite-brain axis in the pathogenesis of preterm brain injury. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 115243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganya, K.; Koo, B.S. Gut–brain axis: Role of gut microbiota on neurological disorders and how probiotics/prebiotics beneficially modulate microbial and immune pathways to improve brain functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedelnikova, O.A.; Redon, C.E.; Dickey, J.S.; Nakamura, A.J.; Georgakilas, A.G.; Bonner, W.M. Role of oxidatively induced DNA lesions in human pathogenesis. Mutat. Res. 2010, 704, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Q.; Tammineni, P. Mitochondrial Aspects of Synaptic Dysfunction in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2017, 57, 1087–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhol, N.K.; Bhanjadeo, M.M.; Singh, A.K.; Dash, U.C.; Ojha, R.R.; Majhi, S.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Jena, A.B. The interplay between cytokines, inflammation, and antioxidants: Mechanistic insights and therapeutic potentials of various antioxidants and anti-cytokine compounds. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 178, 117177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvath, S.; Raj, K. DNA methylation-based biomarkers and the epigenetic clock theory of ageing. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 19, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattei, A.L.; Bailly, N.; Meissner, A. DNA methylation: A historical perspective. Trends Genet. 2022, 38, 676–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Ye, W.; Ding, H.; Li, P.; Aung, L.H.H. Role of RNA Oxidation in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunomura, A.; Hofer, T.; Moreira, P.I.; Castellani, R.J.; Smith, M.A.; Perry, G. RNA oxidation in Alzheimer disease and related neurodegenerative disorders. Acta Neuropathol. 2009, 118, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kose, O.; Altin, A.; Kurt Bayrakdar, S.; Bostan, S.A.; Mercantepe, T.; Akyildiz, K.; Tumkaya, L.; Yilmaz, A.; Kose, S.; Yemenoglu, H.; et al. Influences of periodontitis on hippocampal inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in rats. J. Periodontal Res. 2021, 56, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, C.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Dong, J.; Lu, W.; Song, Z.; Zhou, W. Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide induces cognitive dysfunction, mediated by neuronal inflammation via activation of the TLR4 signaling pathway in C57BL/6 mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnusson, A.; Wu, R.; Demirel, I. Porphyromonas gingivalis triggers microglia activation and neurodegenerative processes through NOX4. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1451683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Lin, Q.; Liang, Y. Plant-Derived Antioxidants Protect the Nervous System From Aging by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakin, S.G.; Dudhia, J.; Werling, N.J.; Werling, D.; Abayasekara, D.R.E.; Smith, R.K.W. Inflamm-aging and arachadonic acid metabolite differences with stage of tendon disease. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakovcevski, M.; Akbarian, S. Epigenetic mechanisms in neurological disease. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1194–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liccardo, D.; Marzano, F.; Carraturo, F.; Guida, M.; Femminella, G.D.; Bencivenga, L.; Agrimi, J.; Addonizio, A.; Melino, I.; Valletta, A.; et al. Potential Bidirectional Relationship Between Periodontitis and Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loughman, A.; Adler, C.J.; MacPherson, H. Unlocking Modifiable Risk Factors for Alzheimer’s Disease: Does the Oral Microbiome Hold Some of the Keys? J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2023, 92, 1111–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilkaite, G.; Vogel, J.; Mattsson-Carlgren, N. Integrating amyloid and tau imaging with proteomics and genomics in Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Rep. Med. 2024, 5, 101735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squier, T.C. Oxidative stress and protein aggregation during biological aging. Exp. Gerontol. 2001, 36, 1539–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study | Association | Mechansism | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| [26] | Statistical | Link between AD and PD | |
| [27] | Risk for developing AD | Matched-cohort | Patients with PD have a 1.7-fold increased risk of developing AD |
| [28] | Review | Review of the literature | Overall relative risk for patients with PD to develop AD is 1.5–2 |
| Study | Model | Periodontitis Induction Method | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| [56] | Rats | Ligature-induced periodontitis | -Increased hippocampal TNFa, IL-1β levels and oxidative stress marker 8-OHdG. -Limited apoptotic changes and neurodegenerative signs. |
| [37] | Mice | Oral infection with Pophyromonas gingivals | -Increase hippocampal TNFa, IL-1β, IL-6 expression. -Neurodegenaration, microgliosis, astrogliosis, and extracellular amyloid-beta (Aβ) accumulation. -Elevated tau phospholylation and cognitive impairment. |
| [57] | Mice | Administration of Porphyromonas gingivalis LPS | -Impaired spatial learning, memory, and cognitive functions. -Activated microglia and astrocytes in cortex and hippocampus. -Increased TNF- a, IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-8 expression via TLR4 signalling pathway activation. |
| [58] | Human Microglia Cells | Porphyromonas gingivalis LPS stimulation | -NOX4-mediated reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and increased IL-6 and IL-8 secretion. -Reduced neuronal viability and elevated phosphorylated tau levels. -Enhanced neuroinflammatory response, potentially contributing to Alzheimer’s pathology. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Papadakis, K.A.; Doufexi, A.-E.; Kalamaki, M.S.; Bourazanas, E.; Lymperaki, E. The Role of Oxidative Stress in the Relationship Between Periodontitis and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Review of the Literature. J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15, 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15080384
Papadakis KA, Doufexi A-E, Kalamaki MS, Bourazanas E, Lymperaki E. The Role of Oxidative Stress in the Relationship Between Periodontitis and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Review of the Literature. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2025; 15(8):384. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15080384
Chicago/Turabian StylePapadakis, Konstantinos Antonios, Aikaterini-El Doufexi, Mary S. Kalamaki, Evangelos Bourazanas, and Evgenia Lymperaki. 2025. "The Role of Oxidative Stress in the Relationship Between Periodontitis and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Review of the Literature" Journal of Personalized Medicine 15, no. 8: 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15080384
APA StylePapadakis, K. A., Doufexi, A.-E., Kalamaki, M. S., Bourazanas, E., & Lymperaki, E. (2025). The Role of Oxidative Stress in the Relationship Between Periodontitis and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Review of the Literature. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 15(8), 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15080384






