Abstract
Introduction: X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA) is a prototypical inborn error of immunity (IEI) caused by mutations in the BTK gene, leading to a profound deficiency of mature B cells and severe pan-hypogammaglobulinemia. The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), which primarily infects B lymphocytes, is believed to be unable to establish persistence in these patients due to the lack of its natural reservoir. Indeed, current evidence supports that EBV infection is typically refractory in individuals with XLA. Methods: We describe the clinical and molecular characterization of a 10-year-old male patient with genetically confirmed XLA who developed EBV viremia, hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH), and EBV-positive cutaneous T cell lymphoma. Diagnosis was supported by flow cytometry, serology, quantitative PCR, EBER in situ hybridization, histopathology, and whole-exome sequencing. Results: Despite the complete absence of peripheral B cells, EBV was detected in leukocytes and multiple tissues, indicating active infection. The patient developed HLH and a T cell lymphoma with EBER-positive infiltrates. Genetic analysis revealed a nonsense mutation in BTK (1558C>T, R520*), confirming XLA. The clinical course included multiple episodes of neutropenia, viral and bacterial infections, and severe systemic inflammation. Conclusions: This is the first documented case of an XLA patient with confirmed BTK mutation presenting with clinical features more consistent with chronic active EBV infection. These findings challenge the prevailing paradigm that XLA confers protection against EBV-related diseases and further support the possibility of EBV noncanonical reservoirs leading to immune dysregulation. EBV should also be considered in the differential diagnosis of XLA patients presenting with systemic inflammation or lymphoproliferative disease.
1. Introduction
Inborn errors of immunity (IEI) are a group of genetic disorders that impair the development, function, and/or number of immune cells. With 500+ defective genes identified to date, these disorders display considerable clinical and immunological heterogeneity, ranging from severe combined immunodeficiency, where patients lack a functional immune system, to milder forms that may go unnoticed until later in life. Depending on the affected gene, IEIs can compromise nearly all immune cell lineages or selectively impair lymphoid, myeloid, or even a single immune cell type, such as B cells [1].
XLA is caused by mutations in the BTK gene, located on the X chromosome. BTK contains multiple conserved domains that mediate its function in B cell signaling. The pleckstrin homology (PH) domain allows membrane localization through binding to PIP3. The TEC homology (TH) domain contributes to protein stability via a zinc finger motif. The SH3 and SH2 domains mediate protein–protein interactions, recognizing proline-rich sequences and phosphotyrosine motifs, respectively. Together, these domains regulate BTK activation and its downstream signaling essential for the development of B lymphocytes. BTK deficiency arrests their maturation at the pre-B cell stage in the bone marrow, preventing the formation of functional peripheral mature B cells [2,3,4,5,6]. Consequently, XLA patients exhibit profoundly reduced peripheral blood B cell counts (CD19+ cells < 2%) and severely reduced or absent immunoglobulin levels due to the lack of antibody-producing plasma cells [7,8]. XLA is one of the most common IEIs, with affected individuals primarily suffering from recurrent pyogenic infections such as pneumonia, conjunctivitis, otitis media, and bacteremia [9].
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), discovered in 1964 by Anthony Epstein, Bert Achong, and Yvonne Barr, represents the first human oncogenic virus to be identified. EBV is a ubiquitous human herpesvirus, infecting approximately 95% of the world’s population [10,11,12]. During its infection cycle, EBV enters the host through the lymphoepithelial tissue of the oropharynx, primarily targeting B cells, where it establishes latent, lifelong infection within the memory B cell compartment. Reactivation from latency leads to viral replication and shedding, with newly formed virions infecting additional B lymphocytes or being transmitted to new hosts via the oral cavity. EBV is associated with a wide spectrum of malignancies, including B cell, T cell, and NK cell lymphomas, as well as gastric and nasopharyngeal carcinomas. EBV is also implicated in severe inflammatory and autoimmune diseases [13]. Despite its pathogenic potential, most individuals maintain EBV in control, exhibiting no obvious clinical symptoms.
There is a subset of IEIs characterized by a loss of immune control over EBV infection, leading to high circulating viral loads and severe, often life-threatening complications, in which malignancy, inflammation, and autoimmunity often can coexist. These IEIs generally affect the function of cytotoxic T cells and/or NK cells, the primary immune effectors responsible for EBV control [14]. Given that EBV resides in B cells, conditions that impair B cell development, such as XLA, are generally thought to protect against EBV-driven diseases by eliminating its natural reservoir. Nevertheless, EBV-related disease has been previously reported in patients with hypogammaglobulinemia. For instance, Kleinman et al. described an EBV-positive mucocutaneous ulcer in a patient with low levels of all immunoglobulins, yet with normal B cell numbers [15]. Interestingly, a previous study conducted on XLA patients concluded that they are refractory to EBV infection, proposing that their markedly low B cell numbers prevent EBV infection [16,17,18]. However, such conclusions are not absolute and may be challenged by exceptional cases that help to reveal the full complexity of EBV infection in immunodeficient hosts.
Here, we describe a pediatric patient with XLA caused by a BTK mutation who, despite lacking circulating mature B cells, developed active EBV viremia, hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH), and an EBV-positive cutaneous T cell lymphoma. Despite the complete absence of peripheral B cells, EBV was detected in leukocytes and multiple tissues, with EBER-ISH confirming its presence in neoplastic T cells, indicating active infection in noncanonical cellular reservoirs. The clinical and virological features of this case overlap with chronic active EBV (CAEBV) disease, a rare T/NK cell lymphoproliferative syndrome usually seen in individuals with functional immune cells. This report highlights a rare and clinically significant presentation and is, to our knowledge, the first to describe EBV-associated lymphoma and HLH in a patient with genetically confirmed XLA. We further provide a focused review of the literature on EBV-related disease in patients with agammaglobulinemia and IEIs. This manuscript adheres to CARE guidelines (http://www.care-statement.org/ accessed on 17 February 2025) for reporting case reports.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Evaluation and Record Review
The patient underwent a comprehensive clinical evaluation on admission, including a history of recurrent infections, physical examination, and family history of immunodeficiency. Initial laboratory tests included a complete blood count, leukocyte differential, and serum chemistry. Immunologic testing included quantification of serum immunoglobulin levels (IgG, IgA, IgM, and IgE) by nephelometry and flow cytometry to analyze lymphocyte subsets (CD3+, CD4+, CD8+, CD16+/CD56+, and CD19+ cells).
Additionally, histopathological evaluation of skin biopsies was performed. Hematoxylin and eosin staining was used for general histology. Immunohistochemistry with chromogenic detection was performed using antibodies against CD3, CD4, CD8, CD20, CD30, CD79, and Ki67 to characterize lymphoid phenotype and assess proliferation. Serological testing for EBV antigens (VCA, EA, and EBNA), CMV, HHV-6, HHV-7, and HHV-8 were conducted using standard commercial kits.
Diagnostic criteria for HLH were evaluated according to the HLH-2004 protocol. All patient clinical information, except for EBV viral load detection and EBER-ISH, was obtained from the medical record.
2.2. EBV Detection and Viral Load
The viral load of EBV was determined according to the protocol of Morales-Sánchez A et al., 2018 [19]. Briefly, DNA was purified from 1 × 106 PBMCs and 400 µL plasma using the QIAamp DNA Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The DNA concentration was quantified using a NanoDrop 1000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), and quality was assessed by optical density (260/280 ratio) and amplification of the endogenous β-actin gene. EBV detection was performed using 100 ng of PBMCs DNA or 5 µL of plasma DNA per qPCR reaction. Results were expressed as viral copies per microgram of DNA or calculated and reported as copies per milliliter of plasma. Quantification was based on standard curves and all samples were analyzed in triplicate.
2.3. Genetic Analysis
Genomic DNA was extracted from peripheral blood mononuclear cells as described in the previous section. Whole-exome sequencing was performed to identify pathogenic variants associated with IEI. Bioinformatic analysis included alignment to the GRCh37/hg19 reference genome, variant calling, and annotation using clinically relevant databases. Sanger sequencing and Western blotting of BTK were performed in the index patient and affected relatives.
2.4. EBER-Based In Situ Hybridization (EBER-ISH)
Detection of EBV-infected cells in tissue samples was performed by EBER-ISH. Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) sections from lung, brain, and bone marrow were hybridized with digoxigenin-labeled oligonucleotide probes specific to EBV-encoded small RNAs (EBERs). The hybridization signal was visualized using an anti-digoxigenin antibody and chromogenic detection system. Positive nuclear staining confirmed the presence of EBV-infected cells.
2.5. Review of Literature
We searched the PubMed database for the terms (“XLA manifestations”, “CAEBV clinical manifestations” OR “XLA and CAEBV” and we selected articles published in English between 2014 and 2025. We summarized the most relevant clinical features reported for both conditions.
2.6. Ethical Compliance
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics and Biosafety Committees of the Hospital Infantil de México Federico Gómez (Protocol Registration HIM-2020-017, SSA 1649). Written informed consent was obtained from the patient’s legal guardian for diagnostic and research purposes.
3. Results
3.1. Case Presentation
A patient was initially admitted at 4 years of age with vesicular dermatosis on the right lower extremity, progressing to severe cellulitis accompanied by persistent fever (38.7 °C), limited mobility, and pain. Hematological evaluation revealed pancytopenia, with CD19+ B cell counts at 0.4%, and low levels of neutrophils (neutropenia), eosinophils, and immunoglobulins (Table 1). Initial treatment included Dicloxacillin and monthly subcutaneous immunoglobulin infusions (545 mg/kg). This therapeutic approach resulted in an improvement of the patient’s cutaneous lesion.

Table 1.
Patient laboratory results.
A few days later, the patient experienced sudden neurological deterioration and right hemiparesis. Computed tomography (CT) revealed early-stage bilateral cerebritis with left-sided predominance. A fronto-temporo-parietal decompressive craniectomy was performed, resulting in patient improvement. Mydriasis and lesions compatible with varicella (chickenpox) infection were also noted. A subsequent CT scan showed multiple pulmonary lesions and lung collapse (atelectasis) consistent with a fungal infection, which was treated with voriconazole. Bronchoalveolar aspirate cytology revealed epithelial cells, an inflammatory infiltrate with polymorphonuclear cells (PMNs), and bacterial colonies.
Unexplained facial dermal lesions raised suspicion of a lymphoproliferative process, prompting a skin biopsy for histopathologic and immunophenotypic analysis. The biopsy revealed a dense lymphocytic infiltrate and a lymphoproliferative process positive for Ki67, CD3 (100%), CD8 (40%), and CD4 (60.5%), and negative for CD20, CD30, CD19, and CD79 (Table 2). These findings were interpreted as cutaneous T cell lymphoma, and the patient was immediately started on systemic chemotherapy according to the pediatric protocol: intravenous vincristine (VCR; 2 mg/m2) and daunorubicin (DNR; 25 mg/m2) every seven days for four doses, followed by intravenous etoposide and cytarabine (Ara-C; 300 mg/m2) every seven days for two months.

Table 2.
Chronological presentation of clinical manifestations.
A positron emission tomography (PET) scan showed bilateral cervical lymphadenopathy, mediastinal adenopathy, and infra- and supra-diaphragmatic pulmonary infiltration involving the liver, spleen, and muscle. During chemotherapy, the patient was admitted twice to the emergency department: first for neutropenic colitis and septic shock, and second for papulovesicular lesions on the left forearm and necrotic lesions on the right forearm. A Tzanck test for herpes simplex virus (HSV) was positive, and acyclovir (1500 mg/day) was administered. Subsequent admissions revealed pneumonia caused by bocavirus (HBoV) and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), along with at least two episodes of febrile neutropenia. The clinical course and therapeutic interventions are summarized in Table 2.
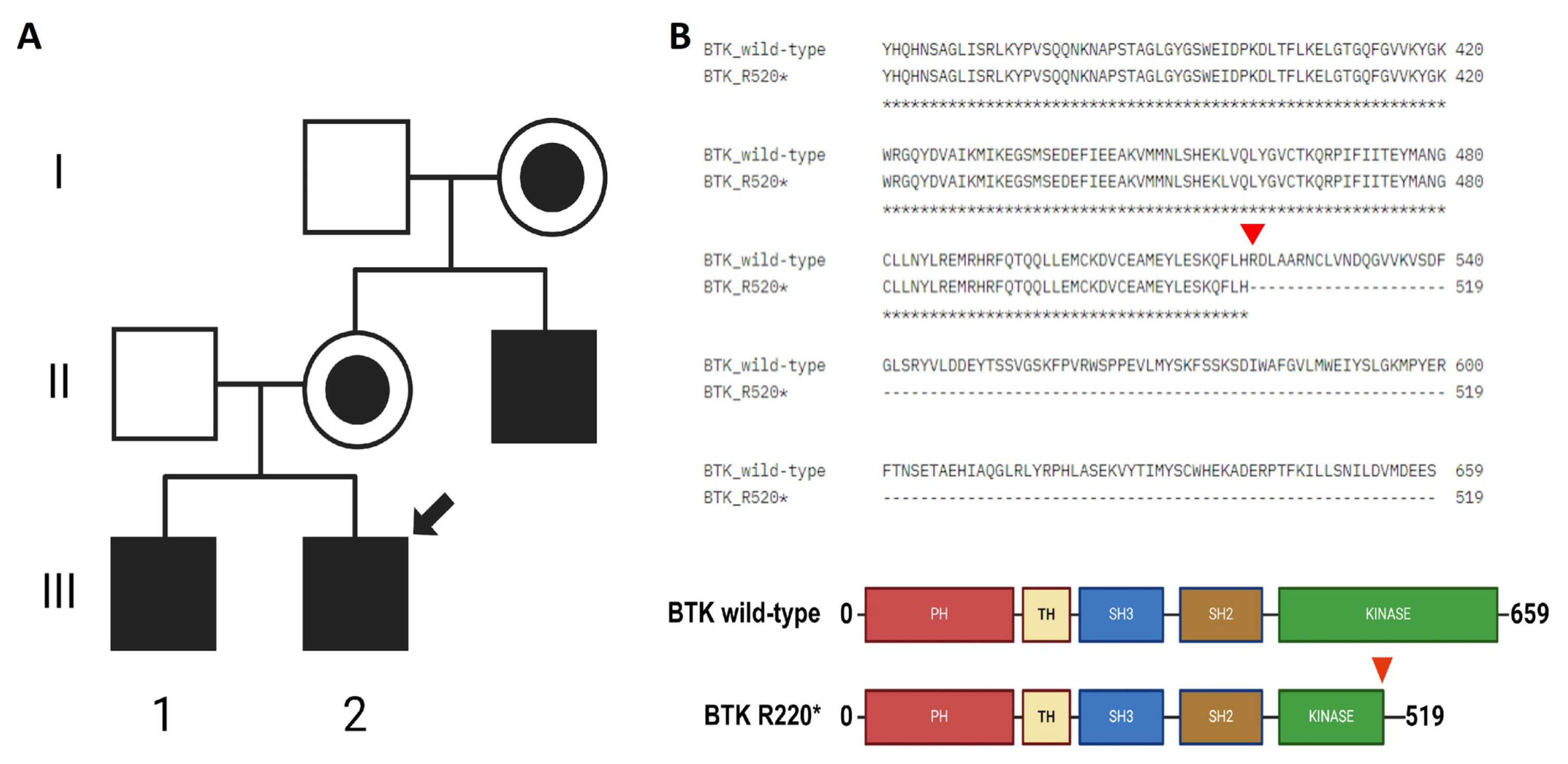
The patient had a family history of XLA, with an older brother and a maternal uncle also diagnosed with the condition (Figure 1A). A BTK mutation was confirmed by whole-exome sequencing (WES) in all three cases and validated by Sanger sequencing and Western blotting for the uncle (Supplementary Figure S1). The sequencing analysis identified a single-nucleotide variant(SNV) (1558C>T) in the three patients, resulting in a premature stop codon (Arg520*) in the kinase domain of the BTK protein (Figure 1B and Supplementary Figure S1). This mutation is expected to impair kinase activity and therefore disrupt BTK function. Importantly, this was the only pathogenic variant of clinical significance detected in our patient, and its classification as pathogenic was confirmed based on available evidence from variant databases such as ClinVar and Franklin, as well as according to the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG) guidelines. This variant was first reported in 1994 during mutational screening of unrelated XLA patients, with two additional unrelated cases described in 1998. Codons 520 and 525 are considered mutational hotspots in the BTK gene, with both nonsense and missense variants previously reported [3,4,20]. At the age of 10 years, the patient developed HLH, further complicating the clinical course (Table 2). HLH is a life-threatening hyperinflammatory syndrome characterized by non-remitting fever, hepatosplenomegaly, cytopenias, coagulopathy, lipid abnormalities, and multiple organ failure. It results from immune dysregulation involving cytotoxic T cells, NK cells, and histiocytes. EBV infection has been implicated as a major trigger of HLH [21]. The patient was treated according to the HLH-2004 protocol and included etoposide, dexamethasone and cyclosporine A [7,22,23,24].
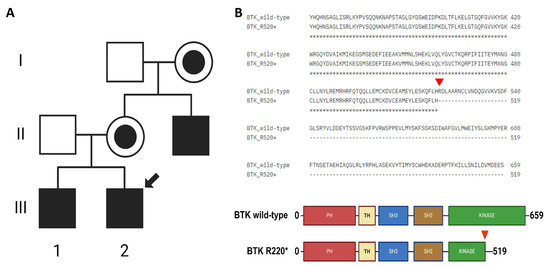
Figure 1.
Family background and identification of BTK mutation. (A) Maternal male relatives have been diagnosed with XLA. Filled squares indicate the affected patients, the one marked with a black arrow indicates the proband, healthy members are indicated by empty squares, and women carriers of the mutation are indicated by black filled circles. (B) The 1558C>T changein BTK results in a premature stop codon R520* (red arrow).
Due to the patient’s history of immunodeficiency and EBV-associated conditions, including HLH and cutaneous T cell lymphoma, EBV load was analyzed by qPCR. The first test, conducted while the patient was receiving chemotherapy, showed no detectable EBV in whole blood. However, a subsequent EBV load assay performed four years later, coinciding with the onset of HLH, revealed the presence of EBV exclusively in leukocytes (640 copies/µg of DNA), with no detectable virus in plasma. This result was consistent with the observed lymphoproliferative activity. EBV infection was confirmed in multiple tissues with lymphoproliferative infiltrate, including lung nodules, brain parenchyma, and bone marrow, by EBER-based in situ hybridization (EBER-ISH) (Figure 2). Serological tests for EBV lytic (VCA and EAD) and latent (EBNA1) antigens were negative, likely reflecting the absence of plasma cells (Table 1). The patient tested negative for other herpesviruses, including CMV, HHV-6, HHV-7, and HHV-8, by qPCR. The most recent hospital admission of the patient was due to neutropenia and SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) infection.
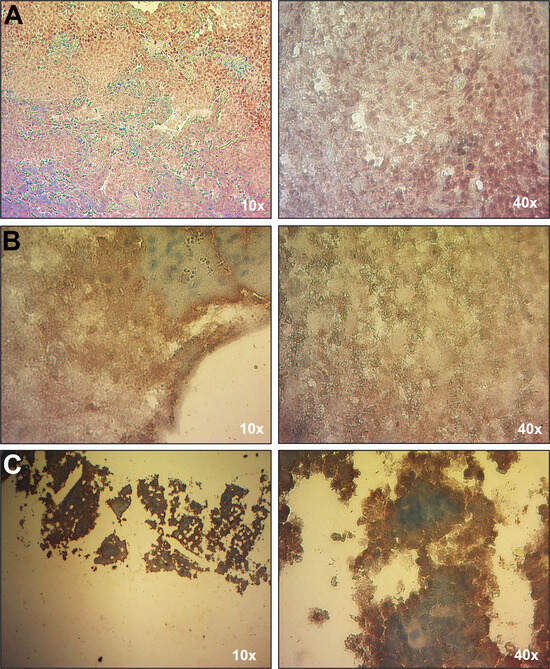
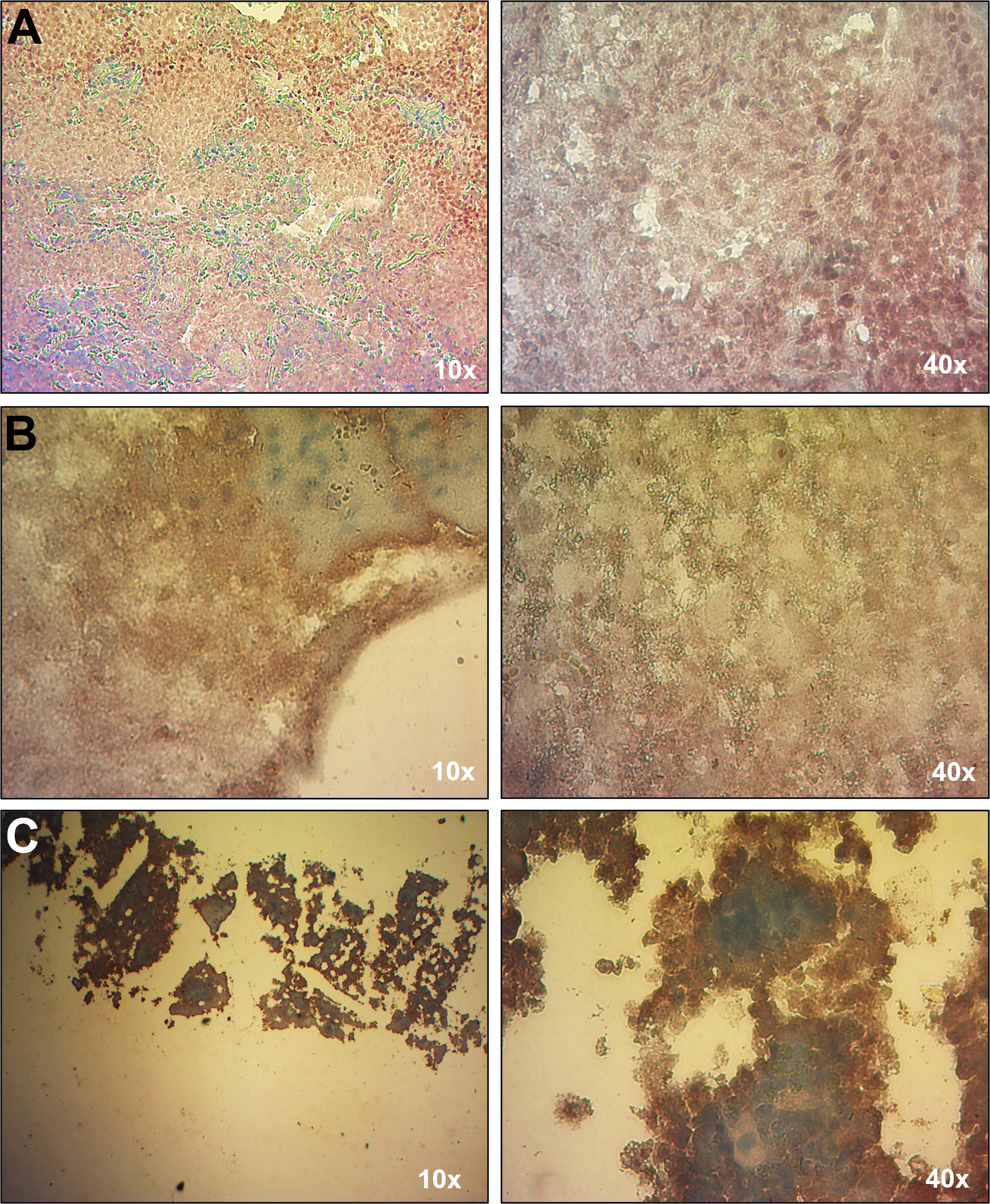
Figure 2.
Detection of EBV in tissues with EBER-ISH. An EBER-ISH assay was performed to determine the presence of EBV in the following tissues: (A) lung nodule; (B) brain parenchyma, and (C) bone marrow. All tissues showed a positive signal for EBV (brown signal), indicative of EBV infection.
3.2. Review of the Literature
XLA and CAEBV are two distinct immunological disorders that differ markedly in genetic origin, immunopathogenesis, and clinical course. XLA is a well-characterized IEI caused by germline mutations in the BTK gene, resulting in impaired B cell development, profound hypogammaglobulinemia, and increased susceptibility to bacterial infections, predominantly affecting males and manifesting in early infancy [25]. In contrast, CAEBV is a chronic, EBV-driven lymphoproliferative disorder characterized by persistent infection of T or NK cells [26,27,28]. It is not classified as a primary immunodeficiency per se, but may arise in the context of acquired somatic mutations (e.g., STAT3, DDX3X, or BCOR) or immune dysregulation affecting EBV control. CAEBV affects both sexes and is notably more prevalent in East Asian and Latin American populations, including Mexico, with cases ranging from pediatric to adult at onset.
In XLA, classical manifestations include recurrent sinopulmonary infections such as otitis media, sinusitis, and pneumonia. Gastrointestinal symptoms, including chronic diarrhea and IBD-like enteropathy, are also frequent [29,30,31]. Less common complications include enteroviral meningoencephalitis, pericarditis, or pulmonary alveolar proteinosis [32,33,34]. Additional atypical features reported in case series include allergic rhinitis, Mohr–Tranebjaerg syndrome, and hepatocellular carcinoma [30,31]. In contrast, CAEBV typically manifests with prolonged fever, hepatosplenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, cytopenia, rash, lymphoproliferation, and HLH. NK/T lymphoproliferation and HLH are common and often defining complications. Atypical features include coronary artery aneurysms, generalized myositis, pulmonary hypertension, and CNS involvement [27,35,36,37]. Misdiagnosis is frequently reported due to overlapping symptoms with autoimmune and systemic inflammatory conditions.
XLA tends to manifest in early childhood with infection-driven pathology resulting from severe antibody deficiency, whereas CAEBV is characterized by chronic systemic inflammation and tissue infiltration driven by clonal expansion of EBV-infected T and/or NK cells. HLH is a hallmark of CAEBV, but it is very rare in XLA, where it is typically triggered by bacterial infections [38,39].
3.2.1. Susceptibility to Microbial Infections
XLA patients are highly susceptible to encapsulated bacteria, including Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Staphylococcus aureus, due to impaired antibody-mediated opsonization. The broader infectious spectrum includes Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Campylobacter jejuni, Salmonella spp., Giardia lamblia, rotavirus, and SARS-CoV-2 [32,38,40,41,42]. In contrast, CAEBV is primarily driven by persistent EBV infection, which sometimes also confers an increased susceptibility to other opportunistic pathogens: viral (CMV, HHV-3, and HHV-6 ), bacterial (e.g., Pseudomonas spp.), and fungal (Candida spp.). This susceptibility is mainly due to immune dysregulation and cytopenias (Supplementary Tables S1 and S2) [37,38,43,44].
3.2.2. Immunological and Cellular Deficiencies
In XLA, some patients exhibit a “leaky” phenotype, retaining low but detectable B-cell numbers and partial immunoglobulin synthesis. Neutropenia occurs in approximately 10–25% of cases, possibly resulting from defective Fc receptor signaling in BTK-dependent myeloid cells [42,45].
In contrast, CAEBV is characterized by complex and progressive pan-lymphocyte abnormalities, including reduced numbers of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, B cells, and NK cells. A common immunological feature is the inversion of the CD4/CD8 ratio, observed in 32.1% of adult CAEBV patients in one study [28]. This inversion is often accompanied by concurrent decreases in both CD4+ and CD8+ T cell subsets, reflecting widespread T-cell dysregulation (Supplementary Table S2).
In summary, XLA is a genetically determined, B-cell intrinsic immunodeficiency, whereas CAEBV is driven by chronic immune activation and clonal expansion of EBV-infected T or NK cells.
3.2.3. BTK Mutations and Genotype–Phenotype Correlation
XLA is caused by over 2400 different mutations in the BTK gene, including missense, nonsense, and splice-site changes (https://databases.lovd.nl/shared/genes/BTK (accessed on 30 May 2025)). Large deletions involving BTK and adjacent genes, such as TIMM8A, cause syndromic forms, such as Mohr-Tranebjaerg syndrome [33], which includes neurodegeneration and hearing loss [33].
In contrast, CAEBV involves somatic mutations arising in EBV-infected T or NK cells, often affecting genes such as DDX3X, TET2, and BCOR [46,47]. Clonal T-cell receptor (TCR) gene rearrangements are also frequently observed, supporting both the diagnosis of CAEBV and the associated risk of lymphoproliferation (Supplementary Table S2) [35,38,46,48,49]. Thus, while XLA is a monogenic, inherited disorder principally affecting bone marrow B cell progenitor cells, CAEBV arises from somatic mutations in mature T and/or NK cells and is more closely related to clonal lymphoproliferative disease.
3.2.4. Atypical Manifestations in CAEBV and XLA Related to EBV
Atypical manifestations in XLA include inflammatory enteropathy, pulmonary conditions such as alveolar proteinosis, Mohr–Tranebjaerg syndrome, and HLH-like episodes mainly triggered by bacterial infection [30,31,32,34]. In CAEBV, atypical presentations include cerebral aneurysm rupture, systemic myositis, and gastrointestinal perforation [35,36,37,50]. Additionally, several reports describe cytokine storm-like syndromes and macrophage hyperactivation as central features of disease severity. Elevated inflammatory cytokines, particularly in the context of activated CD8+ T cells and persistent EBV infection, have been implicated in systemic inflammation and multiorgan damage [26,28,43,45].
Both XLA and CAEBV disorders display an aggressive, potentially fatal course if untreated. However, XLA morbidity is manageable by treating recurrent infections and regular immunoglobulin replacement therapy, in contrast to CAEBV, where hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) offers curative potential.
3.2.5. Differential Biomarker Patterns in CAEBV and XLA
Laboratory findings clearly delineate the distinct pathophysiological profiles of CAEBV and XLA. Patients with CAEBV consistently exhibit elevated liver transaminases (ALT and AST), indicative of hepatic inflammation or multi-organ involvement. Ferritin levels, a surrogate marker of inflammation and macrophage activation, are also profoundly elevated in CAEBV. Other laboratory abnormalities include markedly elevated soluble IL-2 receptor alpha (sIL-2Rα), hypertriglyceridemia, increased lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), and inversion of the CD4/CD8 ratio, which together support a hyperinflammatory state and lymphoproliferative activity (Supplementary Table S3) [51].
In contrast, patients with XLA typically display profound B cell lymphopenia and pan-hypogammaglobulinemia. Unlike CAEBV, where vaccine responses can range from partial to intact, XLA patients consistently fail to mount effective humoral responses owing to their intrinsic B cell deficiency. Notably, as CAEBV progresses, gradual B cell depletion and waning antibody titers have also been observed in advanced stages of disease.
4. Discussion
The interaction between EBV and IEI has been widely explored in the context of cytotoxic T cell and NK cell deficiencies [13,14,21,24]. However, the relationship between EBV and humoral immunodeficiencies such as XLA remains poorly characterized. Traditionally, XLA patients have been considered resistant to EBV infection due to the absence of mature B cells, the virus’s primary latent reservoir [17,18,52]. This case report challenges that paradigm by documenting EBV persistence in peripheral leukocytes and tissues, despite a complete lack of circulating B cells. The clinical course, which includes EBV-positive T cell lymphoma and HLH, reveals a pathologic trajectory more commonly associated with CAEBV.
The comparative literature review in this study underscores key distinctions between XLA and CAEBV in terms of genetic architecture, immunopathogenesis, and clinical features [3,7,48]. Importantly, this case reopens the question of how EBV might enter and persist in the absence of B cells. Canonically, EBV latency is maintained in memory B cells, with reactivation occurring at mucosal sites, where epithelial cells are infected in a basolateral fashion [53,54]. The absence of this reservoir in XLA patients was previously thought to prevent persistent EBV infection [17,18,52]. Supporting this model, allogeneic bone marrow transplant studies have shown that transplanted patients acquire the donor’s EBV strain, reinforcing the role of B cells in viral persistence [55].
However, the detection of EBV in CD3+ T cells and in multiple tissues in our patient suggests alternative routes of viral entry and latency. One proposed mechanism is the transient infection of T or NK cells during the acute phase, as observed in infectious mononucleosis [56], where such infected cells typically undergo apoptosis, although rare conditions may permit their survival. Alternatively, trogocytosis has been suggested as a mechanism whereby T or NK cells acquire the EBV receptor CD21 from B cells at immunological synapses, thus enabling direct viral entry [57,58]. Although speculative, these mechanisms may help explain how EBV persists in non–B cell compartments, particularly in immunodeficient hosts.
Another notable feature is the persistent neutropenia, present at diagnosis and during subsequent hospitalizations. This complication, observed in 10–25% of XLA patients, has been attributed to BTK-related defects in myeloid cells or immune-mediated destruction [25,45,59,60,61]. It is noteworthy that neutropenia was resolved partially with immunoglobulin replacement, but recurred in the context of systemic inflammation and chemotherapy. Recent data on BTK inhibitors such as pirtobrutinib and zanub Tranebjaerg rutinib support the idea that BTK has broader roles in neutrophil survival and Fc receptor signaling, highlighting its relevance beyond B cell maturation [6,62,63].
What renders this case truly unique is the convergence of CAEBV-like features, HLH, EBV-positive T cell lymphoma, systemic EBV tissue infiltration, EBV peripheral load, and immune dysregulation within the well-defined genetic framework of XLA. To our knowledge, no other report has demonstrated EBV persistence by both qPCR and EBER-ISH in a patient with a confirmed BTK mutation and complete absence of mature B cells. This challenges current assumptions about EBV biology and extends the clinical spectrum of XLA. Clinicians should consider EBV in the differential diagnosis of XLA patients presenting with unexplained inflammation, cytopenias, or lymphoproliferative symptoms, even in the absence of classical serologic markers or plasma viral load. Further studies are warranted to elucidate noncanonical reservoirs and mechanisms of immune evasion in the context of humoral immunodeficiency.
5. Conclusions
This case challenges long-standing assumptions about the biology of EBV infection in the context of primary humoral immunodeficiencies. Despite the absence of mature B cells, the patient with genetically confirmed XLA developed EBV-positive T-cell lymphoma and HLH, demonstrating that EBV can persist and drive lymphoproliferative disease through noncanonical mechanisms. While EBV latency has classically been attributed to memory B cells, this report suggests that alternative reservoirs such as CD3+ T cells may sustain infection and pathogenesis in profoundly B cell-deficient hosts. These findings not only expand the clinical phenotype of XLA but also provoke reconsideration of EBV tropism, immune evasion, and viral-host dynamics in IEIs.
In summary, this case illustrates how clinical and laboratory features classically attributed to CAEBV can emerge in patients with underlying IEIs like XLA, challenging current classifications. Ultimately, this case illustrates the biological adaptability of EBV and highlights the importance of maintaining high clinical suspicion for EBV-related pathology in XLA patients with systemic inflammation or lymphoid abnormalities. It reinforces the need for further mechanistic studies to elucidate viral behavior in non-classical immune contexts and to guide future therapeutic strategies.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jpm15080365/s1, Figure S1: Sanger sequencing and Western blotting. (A) Sanger sequencing of the index patient identifying the single nucleotide variant (CGA>TGA) in codon 520 of the BTK gene, consistent with the exome sequencing results. The patient marked with R520* corresponds to a sample of the uncle of our index patient and XLA1-6 to other individuals with XLA diagnosis. (B) Western blot shows no expression of BTK protein in a cohort of patients with X-linked agammaglobulinemia. GAPDH was used as a housekeeping gene. Table S1: Clinical spectrum and immunological characteristics of patients with XLA: case reports and cohort evidence (2014–2025). The table includes both classical and atypical presentations, including HLH and EBV-associated findings. BTK mutation types and therapeutic responses are listed when available. Table S2: Clinical spectrum and immunological characteristics of patients with CAEBV: case reports and cohort evidence (2014–2025). Table S3: Representative Laboratory Abnormalities Associated with CAEBV and XLA [64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73].
Author Contributions
J.H.P.-O.: Conceptualization; investigation; writing—original draft. E.M.-C.: Conceptualization; investigation. J.J.M.-O.: Investigation, visualization. J.A.-H., P.B.-C., and G.F.G.-Z.: Formal analysis; investigation, data curation. G.L.-H.: Investigation; formal analysis, data curation. M.A.Y.-N.: Conceptualization; investigation. O.J.S.-R.: Investigation. L.C.B.: Supervision; funding acquisition. E.M.F.-P.: Investigation; writing—review and editing; supervision; funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Council for Humanities, Science and Technology (CONAHCYT FORDECYT-PRONACES (CIENCIA DE FRONTERA) 10869/2020), and by the Hospital Infantil de México “Federico Gómez” Fondo de Apoyo a la Investigación (HIM-2020-017, SSA 1649).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board and Ethics and Biosafety Committees of the Hospital Infantil de México Federico Gómez (protocol registration (HIM-2020-017, SSA 1649) approval date: 17 June 2020).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study and they all gave informed consent for publication.
Data Availability Statement
All weighted de-identified data used here are included in this study. The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. This literature review did not generate or analyze any new datasets. The study synthesized findings from existing published literature, all of which are cited within the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
JHPO gratefully acknowledges the support of this research by a CONAHCYT postdoctoral fellowship (I1200/320/2022), “Estancias Postdoctorales por México 2022 (1)”, with CVU 417968. JJMO acknowledges the scholarship of the comisión interinstitucional para la formación de recursos humanos (CIFRHS) from SSA, and Universidad Anáhuac Veracruz, campus Xalapa. We also want to acknowledge the support from the Dirección de Investigación from Hospital Infantil de México “Federico Gómez”.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Poli, M.C.; Aksentijevich, I.; Bousfiha, A.A.; Cunningham-Rundles, C.; Hambleton, S.; Klein, C.; Morio, T.; Picard, C.; Puel, A.; Rezaei, N.; et al. Human inborn errors of immunity: 2024 update on the classification from the International Union of Immunological Societies Expert Committee. J. Hum. Immun. 2025, 1, e20250003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinicola, B.; Uva, A.; Leonardi, L.; Moratto, D.; Giliani, S.; Carsetti, R.; Ferrari, S.; Zicari, A.M.; Duse, M. Case Report: A Case of X-Linked Agammaglobulinemia with High Serum IgE Levels and Allergic Rhinitis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 582376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holinski-Feder, E.; Weiss, M.; Brandau, O.; Jedele, K.B.; Nore, B.; Bäckesjö, C.M.; Vihinen, M.; Hubbard, S.R.; Belohradsky, B.H.; Smith, C.E.; et al. Mutation screening of the BTK gene in 56 families with X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA): 47 unique mutations without correlation to clinical course. Pediatrics 1998, 101, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagemann, T.L.; Chen, Y.; Rosen, F.S.; Kwan, S.P. Genomic organization of the Btk gene and exon scanning for mutations in patients with x-linked agammaglobulinemia. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1994, 3, 1743–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozkiewicz, D.; Hermanowicz, J.M.; Kwiatkowska, I.; Krupa, A.; Pawlak, D. Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (BTKIs): Review of Preclinical Studies and Evaluation of Clinical Trials. Molecules 2023, 28, 2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alu, A.; Lei, H.; Han, X.; Wei, Y.; Wei, X. BTK Inhibitors in the Treatment of Hematological Malignancies and Inflammatory Diseases: Mechanisms and Clinical Studies. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.P.; Lin, Y.F.; Weng, H.Y.; Tsai, S.F.; Fu, L.S. A novel BTK gene mutation in a child with atypical X-linked agammaglobulinemia and recurrent hemophagocytosis: A case report. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graziani, S.; Di Matteo, G.; Benini, L.; Di Cesare, S.; Chiriaco, M.; Chini, L.; Chianca, M.; De Iorio, F.; La Rocca, M.; Iannini, R.; et al. Identification of a Btk mutation in a dysgammaglobulinemic patient with reduced B cells: XLA diagnosis or not? Clin. Immunol. 2008, 128, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedaiwy, N.; Alhamdi, S.; Al Suwairi, W.; Alsalamah, M. Case report of a novel mutation in Bruton’s tyrosine kinase gene with confirmed agammaglobulinemia and absent B lymphocytes. LymphoSign J. 2022, 9, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin-Drubin, M.E.; Munger, K. Viruses associated with human cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Basis Dis. 2008, 1782, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, D.A.; Tayyar, Y.; Idris, A.; McMillan, N.A.J. A “hit-and-run” affair—A possible link for cancer progression in virally driven cancers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Rev. Cancer 2021, 1875, 188476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, M.A.; Achong, B.G.; Barr, Y.M. Virus Particles in Cultured Lymphoblasts from Burkitt’s Lymphoma. Lancet 1964, 1, 702–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latour, S.; Winter, S. Inherited immunodeficiencies with high predisposition to Epstein-Barr Virus-driven lymphoproliferative diseases. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 364381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojdani, A.; Koksoy, S.; Vojdani, E.; Engelman, M.; Benzvi, C.; Lerner, A. Natural Killer Cells and Cytotoxic T Cells: Complementary Partners against Microorganisms and Cancer. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinman, S.; Jhaveri, D.; Caimi, P.; Cameron, R.; Lemonovich, T.; Meyerson, H.; Hostoffer, R.; Tcheurekdjian, H. A rare presentation of EBV+ mucocutaneous ulcer that led to a diagnosis of hypogammaglobulinemia. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2014, 2, 810–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatton, O.L.; Harris-Arnold, A.; Schaffert, S.; Krams, S.M.; Martinez, O.M. The Interplay Between Epstein Barr Virus and B Lymphocytes: Implications for Infection, Immunity, and Disease. Immunol. Res. 2014, 58, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, G.C.; Burrows, S.R.; Khanna, R.; Moss, D.J.; Bird, A.G.; Crawford, D.H. X-Linked agammaglobulinemia patients are not infected with Epstein-Barr virus: Implications for the biology of the virus. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 1555–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grammatikos, A.; Donati, M.; Johnston, S.L.; Gompels, M.M. Peripheral B Cell Deficiency and Predisposition to Viral Infections: The Paradigm of Immune Deficiencies. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 731643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Ponce, Y.; Varela-Fascinetto, G.; Romo-Vázquez, J.C.; López-Martínez, B.; Sánchez-Huerta, J.L.; Parra-Ortega, I.; Fuentes-Pananá, E.M.; Morales-Sánchez, A. Simultaneous Detection of Beta and Gamma Human Herpesviruses by Multiplex qPCR Reveals Simple Infection and Coinfection Episodes Increasing Risk for Graft Rejection in Solid Organ Transplantation. Viruses 2018, 10, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Zhang, M.; Winkelstein, J.; Chen, S.H.; Ochs, H.D. Unique mutations of bruton’s tyrosine kinase in fourteen unrelated x-linked agammaglobulinemia families. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1994, 3, 1899–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.Y.; Montes-Mojarro, I.A.; Fend, F.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L. Epstein-barr virus-associated T and NK-cell lymphoproliferative diseases. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 433291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mallawany, N.K.; Curry, C.V.; Allen, C.E. Haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and Epstein–Barr virus: A complex relationship with diverse origins, expression and outcomes. Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 196, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehr, B.; Brannock, K.; Wyma, R.; Kahwash, S.B. Differentiating fulminant EBV infection complicated by HLH from Lymphoma: Report of a case and a brief literature review. Diagn. Pathol. 2023, 18, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, R.A. Epstein-Barr virus and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 8, 1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanegane, H.; Taneichi, H.; Nomura, K.; Futatani, T.; Miyawaki, T. Severe Neutropenia in Japanese Patients with X-Linked Agammaglobulinemia. J. Clin. Immunol. 2005, 25, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Wu, H.; Gu, L.; Wu, X.; Su, M.; Lin, H.; Liu, B.; Zheng, J.; Mei, X.; Li, D. Clinicopathologic findings of chronic active Epstein–Barr virus infection in adults: A single-center retrospective study in China. Clin. Exp. Med. 2021, 21, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Hu, B.; Luo, R.; Hu, H.; Zhang, J.; Kuang, W.; Zhang, R.; Li, L.; Liu, G. Chronic active Epstein–Barr virus infection manifesting as coronary artery aneurysm and uveitis. Virol. J. 2020, 17, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Wang, H.; Fan, H.; Xie, J.; Qiu, Z.; Li, T. The clinical characteristics and the features of immunophenotype of peripheral lymphocytes of adult onset chronic active Epstein-Barr virus disease at a Tertiary Care Hospital in Beijing. Medicine 2018, 97, e9854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pac, M.M.; Bernatowska, E.A.; Kierkuś, J.; Ryżko, J.P.; Cielecka-Kuszyk, J.; Jackowska, T.; Mikołuć, B. Gastrointestinal disorders next to respiratory infections as leading symptoms of X-linked agammaglobulinemia in children—34-year experience of a single center. Arch. Med. Sci. 2017, 13, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barmettler, S.; Otani, I.M.; Minhas, J.; Abraham, R.S.; Chang, Y.; Dorsey, M.J.; Ballas, Z.K.; Bonilla, F.A.; Ochs, H.D.; Walter, J.E. Gastrointestinal Manifestations in X-linked Agammaglobulinemia. J. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 37, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Person, H.; Dekio, F.; Ogawa, M.; Ho, H.E.; Dunkin, D.; Secord, E.; Cunningham-Rundles, C.; Ward, S.C. Crohn’s-like Enteritis in X-Linked Agammaglobulinemia: A Case Series and Systematic Review. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 3466–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bearden, D.; Collett, M.; Quan, P.L.; Costa-Carvalho, B.T.; Sullivan, K.E. Enteroviruses in X-Linked Agammaglobulinemia: Update on Epidemiology and Therapy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2016, 4, 1059–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martignani, C.; Massaro, G.; Bruno, A.G.; Biffi, M.; Ziacchi, M.; Diemberger, I. Acute primary purulent pericarditis in an adult patient with unknown X-linked agammaglobulinemia. Immunobiology 2020, 225, 151861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Li, M.; Tan, L.; Li, X. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis induced by X-linked agammaglobulinemia: A case report. World J. Clin. Cases 2024, 12, 1644–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, K.; Shuai, X.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, T.; Niu, T.; Ma, H. Chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection involving gastrointestinal tract with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Ann. Hematol. 2023, 102, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Li, L.; Pan, C.; Yang, Y.; Chen, G.; He, Y. Case report: Systemic muscle involvement as the primary clinical manifestation of chronic active Epstein–Barr virus infection: A case-based review. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1027859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, T.; Steinberg, J.; Olson, S.; El-Said, H.; Mo, J.; Anderson, E.; Gloude, N.; Schiff, D. Chronic active Epstein–Barr virus and hydroa vacciniforme-like lymphoproliferative disorder in a pediatric patient complicated by fatal ruptured cerebral artery aneurysm. Clin. Case Rep. 2023, 11, e7436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, Y.H.; Hsieh, M.Y.; Lee, W.I.; Huang, J.L.; Chen, L.C.; Yeh, K.W.; Ou, L.S.; Yao, T.C.; Wu, C.Y.; Lin, S.J. Distinct Clinical Features and Novel Mutations in Taiwanese Patients With X-Linked Agammaglobulinemia. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dávila Saldaña, B.J.; John, T.; Bonifant, C.; Buchbinder, D.; Chandra, S.; Chandrakasan, S.; Chang, W.; Chen, L.; Elfassy, H.L.; Geerlinks, A.V.; et al. High risk of relapsed disease in patients with NK/T-cell chronic active Epstein-Barr virus disease outside of Asia. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadden, D.; Fowler, G.; Engel, E.; Logan, C.; Marathe, K.; Gosdin, C. Streptococcal pneumonia meningitis as an initial presentation of X-linked agammaglobulinemia: A case report and discussion. JACEP Open 2021, 2, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chear, C.T.; Ismail, I.H.; Chan, K.C.; Noh, L.M.; Kassim, A.; Latiff, A.H.A.; Gill, S.S.; Ramly, N.H.; Tan, K.K.; Sundaraj, C.; et al. Clinical features and mutational analysis of X-linked agammaglobulinemia patients in Malaysia. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1252765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markocsy, A.; Kapustová, D.; Čereš, A.; Froňkova, E.; Jeseňák, M. Atypical Manifestation of X-linked Agammaglobulinemia—the Importance of Genetic Testing. Acta Medica 2024, 67, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, Y.; Albogami, M.; Alsaedy, A.; Khubrani, R.; Al Ahmadi, B. A Lethal Manifestation of Chronic Active Epstein-Barr Virus Infection: A Case Report. Cureus 2022, 14, e30158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.C.; Chiang, B.L.; Lee, Y.J.; Chang, Y.T.; Fang, S.B. Pseudomonas aeruginosa sepsis presenting as oral ecthyma gangrenosum in identical twins with Bruton tyrosine kinase gene mutation: Two case reports and review of the literature. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2020, 53, 1030–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Lanlokun, M.; Borden, A.; Nieves, D.; Walter, J.E.; Albright, D. X-Linked Agammaglobulinemia Presenting as Neutropenia: Case Report and an Overview of Literature. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 633692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Gu, Z.H.; Yan, Z.X.; Zhao, X.; Xie, Y.Y.; Zhang, Z.G.; Pan, C.M.; Hu, Y.; Cai, C.P.; Dong, Y.; et al. Exome sequencing identifies somatic mutations of DDX3X in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1061–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, A. Advances in the study of Chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection: Clinical features under the 2016 WHO classification and mechanisms of development. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuno, Y.; Murata, T.; Sato, Y.; Muramatsu, H.; Ito, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Okuno, T.; Murakami, N.; Yoshida, K.; Sawada, A.; et al. Defective Epstein–Barr virus in chronic active infection and haematological malignancy. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saburi, M.; Ogata, M.; Satou, T.; Yoshida, N.; Nagamatsu, K.; Nashimoto, Y.; Moroga, Y.; Takano, K.; Kohno, K.; Shirao, K. Successful cord blood stem cell transplantation for an adult case of chronic active epstein-barr virus infection. Intern. Med. 2016, 55, 3499–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Xiao, H.J.; Li, J.; Song, H.M.; Li, Z.H.; Dong, M.; Zhou, X.G. Epstein-Barr virus-positive T/NK-cell lymphoproliferative disorders manifested as gastrointestinal perforations and skin lesions a case report. Medicine 2016, 95, e2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, A.; Ma, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, D.; Lian, H.; Zhang, R.; Wang, T. Clinical analysis of chronic active EBV infection with coronary artery dilatation and a matched case–control study. Orphanet. J. Rare Dis. 2021, 16, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochs, H.D.; Smith, C.I.E. X-Linked Agammaglobulinemia A Clinical and Molecular Analysis. Rev. Med. Virol. 1996, 75, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.L.; Streuli, C.H. Integrins and epithelial cell polarity. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127, 3217–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Kenyon, W.J.; Li, Q.; Müllberg, J.; Hutt-Fletcher, L.M. Epstein-Barr Virus Uses Different Complexes of Glycoproteins gH and gL To Infect B Lymphocytes and Epithelial Cells. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 5552–5558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gratama, J.W.; Oosterveer, M.A.; Zwaan, F.E.; Lepoutre, J.; Klein, G.; Ernberg, I. Eradication of Epstein-Barr virus by allogeneic bone marrow transplantation: Implications for sites of viral latency. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 8693–8696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anagnostopoulos, L.; Hummel, M.; Kreschel, C.; Stein, H. Morphology, Immunophenotype, and Distribution of Latently and/or Productively Epstein-Barr Virus-Infected Cells in Acute Infectious Mononucleosis: Implications for the Interindividual Infection Route of Epstein-Barr Virus. Blood 1995, 85, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, A.; Yamaguchi, T.; Komatsu, H.; Imadome, K.I.; Kurata, M.; Nagata, K.; Miura, O. Infectious mononucleosis accompanied by clonal proliferation of EBV-infected cells and infection of CD8-positive cells. Int. J. Hematol. 2014, 99, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabiasco, J.; Vercellone, A.; Meggetto, F.; Hudrisier, D.; Brousset, P.; Fournié, J.J. Acquisition of Viral Receptor by NK Cells Through Immunological Synapse. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 5993–5998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.; Guedes, M.; Vasconcelos, J.; Neves, E.; Fernandes, S.; Marques, L. Agammaglobulinemia ligada al cromosoma X: Experiencia en un hospital portugués. An. Pediatr. (Engl. Ed.) 2015, 82, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, Z.D.; Guajardo, J.R.; Anderson, K.M. XLA-associated Neutropenia Treatment. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2008, 30, 631–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrar, J.E.; Rohrer, J.; Conley, M.E. Neutropenia in X-linked agammaglobulinemia. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1996, 81, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierda, W.G.; Shah, N.N.; Cheah, C.Y.; Lewis, D.; Hoffmann, M.S.; Coombs, C.C.; Lamanna, N.; Ma, S.; Jagadeesh, D.; Munir, T.; et al. Pirtobrutinib, a highly selective, non-covalent (reversible) BTK inhibitor in patients with B-cell malignancies: Analysis of the Richter transformation subgroup from the multicentre, open-label, phase 1/2 BRUIN study. Lancet Haematol 2024, 11, e682–e692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhou, K.; Zou, D.; Zhou, J.; Hu, J.; Yang, H.; Zhang, H.; Ji, J.; Xu, W.; Jin, J.; et al. Zanubrutinib in relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma: Long-term efficacy and safety results from a phase 2 study. Blood 2022, 139, 3148–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, S.; Cao, M.; Zou, J.; Bai, Y.; Shi, M.; Jiang, H. Case report of renal manifestations in X-linked agammaglobulinemia. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1376258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, F.; Wang, H.; Wang, X. Chronic Diarrhea with Villous Blunting of the Small Intestine Under Capsule Endoscopy in Common Variable Immunodeficiency and X-Linked Agammaglobulinemia: A Case Series. J. Asthma Allergy 2023, ume 16, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rise, N.; Touborg, T.; Lundsted, D.H.; Dalager-Pedersen, M.; Mogensen, T.H. Case report: Evolution of pulmonary manifestations and virological markers in critical COVID-19 infection in Bruton’s agammaglobulinemia. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1057065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, E.; Kikuchi, K.; Sasahara, Y.; Kono, M.; Akiyama, M.; Aiba, S. Atopic dermatitis without serum immunoglobulin E elevation or loss-of-function filaggrin gene mutation in a patient with X-linked agammaglobulinemia. J. Dermatol. 2020, 47, 58–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-F.; Wang, W.-F.; Zhang, Y.-D.; Zhao, W.; Wu, J.; Chen, T.-X. Clinical characteristics and genetic profiles of 174 patients with X-linked agammaglobulinemia. Medicine 2016, 95, e4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Qu, J. Chronic active Epstein–Barr virus colitis, a rare cause of recurrent diarrhea in an immunocompetent female: A case report. BMC Infect. Dis. 2025, 25, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, K.; Hiejima, E.; Nihira, H.; Kato, K.; Honda, Y.; Izawa, K.; Kawabata, N.; Kato, I.; Ogawa, E.; Sonoda, M.; et al. Case Report: A Case of Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Acute Liver Failure Requiring Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation After Emergent Liver Transplantation. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 825806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.-H.; Yang, J.; Wei, A.; Zhu, G.-H.; Wang, B.; Zhang, R.; Jia, C.-G.; Yan, Y.; Wang, K.; Li, S.; et al. Haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for pediatric patients with chronic active Epstein–Barr virus infection: A retrospective analysis of a single center. World J. Pediatr. 2021, 17, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ba, H.; Xu, L.; Peng, H.; Lin, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Qin, Y.; Wang, X. Chronic Active Epstein-Barr Virus Infection With Systemic Vasculitis and Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in a Child. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, H.; Taniwaki, M.; Matsumoto, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Shimura, K.; Fujino, T.; Uchiyama, H.; Kuroda, J. An adult-onset case of chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection with fulminant clinical course. J. Infect. Chemother. 2018, 24, 479–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).