The Accuracy of ChatGPT-4o in Interpreting Chest and Abdominal X-Ray Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
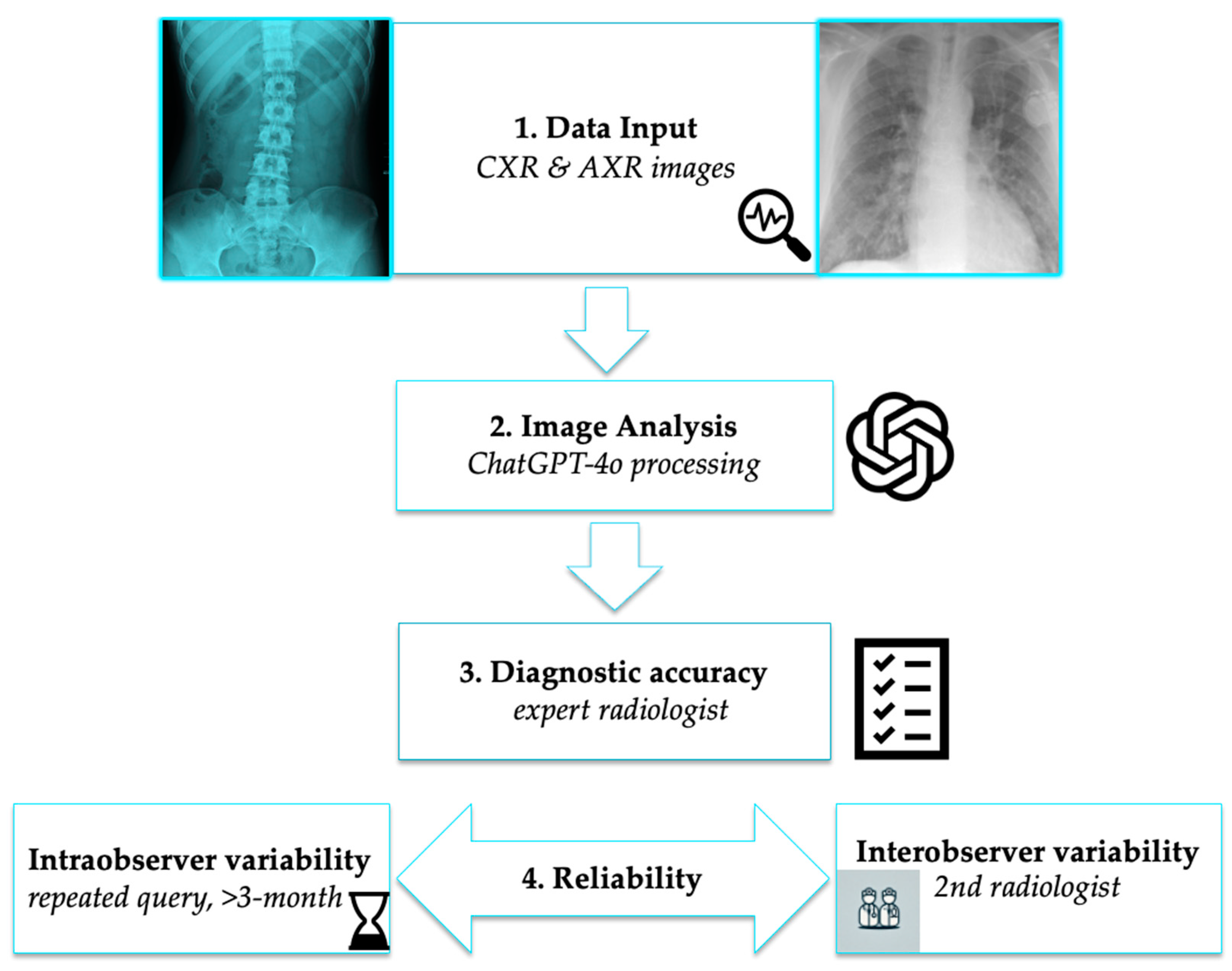
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. AI-Based Image Analysis
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
Diagnostic Accuracy
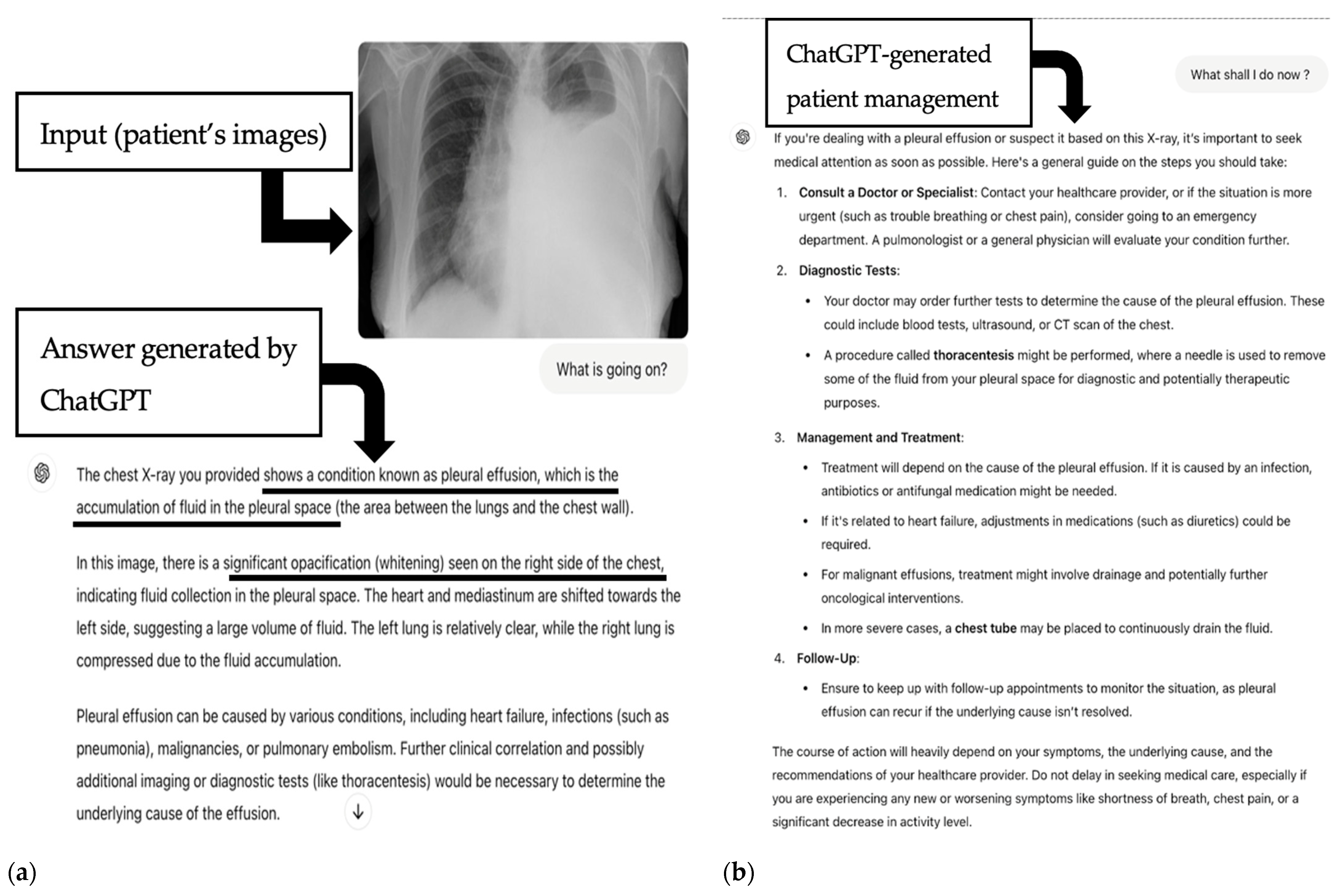
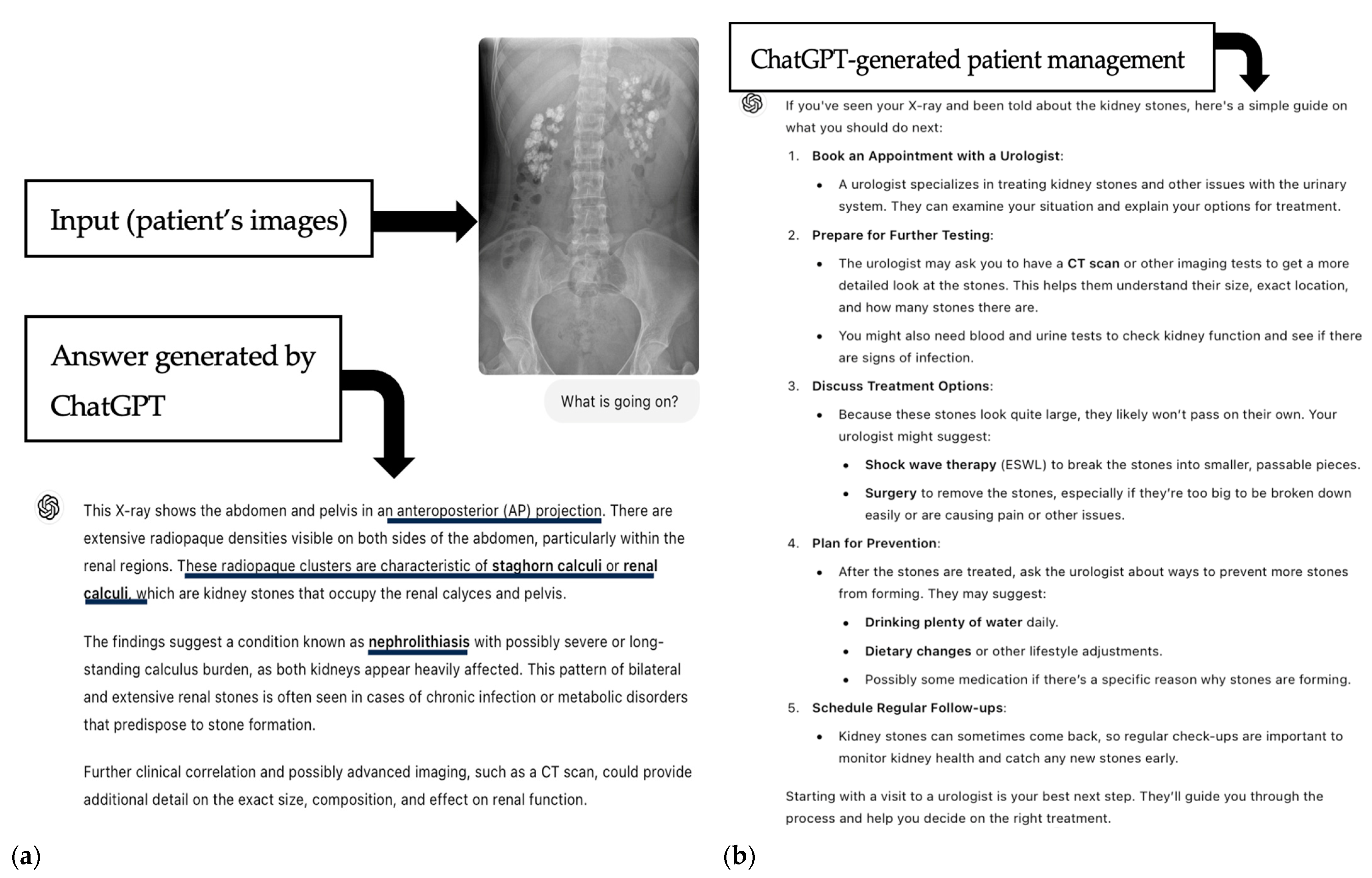
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| LLM | Large Language Model |
| CXR | Chest X-ray |
| AXR | Abdominal X-ray |
| ED | Emergency Department |
| ICU | Intensive Care Unit |
| GPT-4V | Generative Pretrained Transformer 4 Vision |
| GPT-4o | Generative Pretrained Transformer 4 omni |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| CTA | Computed Tomography Angiography |
| BO | Bowel Obstruction |
| R/U/B | Renal/Ureter/Bladder |
| CM | Cardiomegaly |
| Med. | Mediastinum |
| Fx | Fracture |
| Eff | Effusion |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| N | Number (of cases) |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| MACEs | Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events |
| ASCVD | Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease |
| USMLE | United States Medical Licensing Examination |
References
- Ou, X.; Chen, X.; Xu, X.; Xie, L.; Chen, X.; Hong, Z.; Bai, H.; Liu, X.; Chen, Q.; Li, L.; et al. Recent Development in X-Ray Imaging Technology: Future and Challenges. Research 2021, 2021, 9892152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Baratella, E.; Marrocchio, C.; Bozzato, A.M.; Roman-Pognuz, E.; Cova, M.A. Chest X-ray in intensive care unit patients: What there is to know about thoracic devices. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2021, 27, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Schneider, E.; Franz, W.; Spitznagel, R.; Bascom, D.A.; Obuchowski, N.A. Effect of computerized physician order entry on radiologic examination order indication quality. Arch. Intern. Med. 2011, 171, 1036–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, M.D.; Curtin, S.; Lee, R. Evaluation of the quality of radiology requisitions for intensive care unit patients. Acad. Radiol. 2006, 13, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waisberg, E.; Ong, J.; Masalkhi, M.; Kamran, S.A.; Zaman, N.; Sarker, P.; Lee, A.G.; Tavakkoli, A. GPT-4: A new era of artificial intelligence in medicine. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2023, 192, 3197–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Mou, W.; Lai, Y.; Chen, J.; Lin, S.; Xu, L.; Lin, J.; Guo, Z.; Yang, T.; Lin, A.; et al. Step into the era of large multimodal models: A pilot study on ChatGPT-4V(ision)’s ability to interpret radiological images. Int. J. Surg. 2024, 110, 4096–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kuzan, B.N.; Meşe, İ.; Yaşar, S.; Kuzan, T.Y. A retrospective evaluation of the potential of ChatGPT in the accurate diagnosis of acute stroke. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2025, 31, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, D.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, L.; Lu, X.; Xu, Y. The role of large language models in medical image processing: A narrative review. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2024, 14, 1108–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mihalache, A.; Huang, R.S.; Popovic, M.M.; Patil, N.S.; Pandya, B.U.; Shor, R.; Pereira, A.; Kwok, J.M.; Yan, P.; Wong, D.T.; et al. Accuracy of an Artificial Intelligence Chatbot’s Interpretation of Clinical Ophthalmic Images. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2024, 142, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rogasch, J.M.; Jochens, H.V.; Metzger, G.; Wetz, C.; Kaufmann, J.; Furth, C.; Amthauer, H.; Schatka, I. Keeping Up With ChatGPT: Evaluating Its Recognition and Interpretation of Nuclear Medicine Images. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2024, 49, 500–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, N.; Gilbert, S.; Poisson, L.M.; Griffith, B.; Klochko, C. Performance of GPT-4 with Vision on Text- and Image-based ACR Diagnostic Radiology In-Training Examination Questions. Radiology 2024, 312, e240153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.J.; Sobol, K.; Hickey, C.; Raphael, J. The Comparative Performance of Large Language Models on the Hand Surgery Self-Assessment Examination. Hand, 2024; Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, Q.; Tan, J.; Zapadka, M.E.; Ponnatapura, J.; Niu, C.; Myers, K.J.; Wang, G.; Whitlow, C.T. Translating radiology reports into plain language using ChatGPT and GPT-4 with prompt learning: Results, limitations, and potential. Vis. Comput. Ind. Biomed. Art. 2023, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ueda, D.; Mitsuyama, Y.; Takita, H.; Horiuchi, D.; Walston, S.L.; Tatekawa, H.; Miki, Y. ChatGPT’s Diagnostic Performance from Patient History and Imaging Findings on the Diagnosis Please Quizzes. Radiology 2023, 308, e231040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suthar, P.P.; Kounsal, A.; Chhetri, L.; Saini, D.; Dua, S.G. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Radiology: A Deep Dive Into ChatGPT 4.0’s Accuracy with the American Journal of Neuroradiology’s (AJNR) “Case of the Month”. Cureus 2023, 15, e43958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Horiuchi, D.; Tatekawa, H.; Shimono, T.; Walston, S.L.; Takita, H.; Matsushita, S.; Oura, T.; Mitsuyama, Y.; Miki, Y.; Ueda, D. Accuracy of ChatGPT generated diagnosis from patient’s medical history and imaging findings in neuroradiology cases. Neuroradiology 2024, 66, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaki, H.A.; Mai, M.; Abdel-Megid, H.; Liew, S.Q.R.; Kidanemariam, S.; Omar, A.S.; Tiwari, U.; Hamze, J.; Ahn, S.H.; Maxwell, A.W.P. Using ChatGPT to Improve Readability of Interventional Radiology Procedure Descriptions. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2024, 47, 1134–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truhn, D.; Weber, C.D.; Braun, B.J.; Bressem, K.; Kather, J.N.; Kuhl, C.; Nebelung, S. A pilot study on the efficacy of GPT-4 in providing orthopedic treatment recommendations from MRI reports. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 20159, Erratum in Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5431. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-56029-x. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Horiuchi, D.; Tatekawa, H.; Oura, T.; Shimono, T.; Walston, S.L.; Takita, H.; Matsushita, S.; Mitsuyama, Y.; Miki, Y.; Ueda, D. ChatGPT’s diagnostic performance based on textual vs. visual information compared to radiologists’ diagnostic performance in musculoskeletal radiology. Eur. Radiol. 2024; Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, S.; Saban, M. Evaluating the reliability of ChatGPT as a tool for imaging test referral: A comparative study with a clinical decision support system. Eur. Radiol. 2024, 34, 2826–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barash, Y.; Klang, E.; Konen, E.; Sorin, V. ChatGPT-4 Assistance in Optimizing Emergency Department Radiology Referrals and Imaging Selection. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2023, 20, 998–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, A.; Li, H.; Trout, A.T. Large language models can help with biostatistics and coding needed in radiology research. Acad. Radiol. 2024, 14, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mongan, J.; Moy, L.; Kahn, C.E. Checklist for Artificial Intelligence in Medical Imaging (CLAIM): A Guide for Authors and Reviewers. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2020, 2, e200029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bhayana, R. Chatbots and Large Language Models in Radiology: A Practical Primer for Clinical and Research Applications. Radiology 2024, 310, e232756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehdab, R.; Brendlin, A.; Werner, S.; Almansour, H.; Gassenmaier, S.; Brendel, J.M.; Nikolaou, K.; Afat, S. Evaluating ChatGPT-4V in chest CT diagnostics: A critical image interpretation assessment. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2024, 42, 1168–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mitsuyama, Y.; Tatekawa, H.; Takita, H.; Sasaki, F.; Tashiro, A.; Oue, S.; Walston, S.L.; Nonomiya, Y.; Shintani, A.; Miki, Y.; et al. Comparative analysis of GPT-4-based ChatGPT’s diagnostic performance with radiologists using real-world radiology reports of brain tumors. Eur. Radiol. 2024, 35, 1938–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javan, R.; Kim, T.; Mostaghni, N. GPT-4 Vision: Multi-Modal Evolution of ChatGPT and Potential Role in Radiology. Cureus 2024, 16, e68298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, H.; Moon, J.T.; Iyer, D.; Balthazar, P.; Krupinski, E.A.; Bercu, Z.L.; Newsome, J.M.; Banerjee, I.; Gichoya, J.W.; Trivedi, H.M. Decoding radiology reports: Potential application of OpenAI ChatGPT to enhance patient understanding of diagnostic reports. Clin. Imaging 2023, 101, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Gomaa, A.; Semrau, S.; Haderlein, M.; Lettmaier, S.; Weissmann, T.; Grigo, J.; Ben Tkhayat, H.; Frey, B.; Gaipl, U.; et al. Benchmarking ChatGPT-4 on a radiation oncology in-training exam and Red Journal Gray Zone cases: Potentials and challenges for ai-assisted medical education and decision making in radiation oncology. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1265024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Patil, N.S.; Huang, R.S.; van der Pol, C.B.; Larocque, N. Using Artificial Intelligence Chatbots as a Radiologic Decision-Making Tool for Liver Imaging: Do ChatGPT and Bard Communicate Information Consistent With the ACR Appropriateness Criteria? J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2023, 20, 1010–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derevianko, A.; Pizzoli, S.F.M.; Pesapane, F.; Rotili, A.; Monzani, D.; Grasso, R.; Cassano, E.; Pravettoni, G. The Use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the Radiology Field: What Is the State of Doctor-Patient Communication in Cancer Diagnosis? Cancers 2023, 15, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sim, Y.; Chung, M.J.; Kotter, E.; Yune, S.; Kim, M.; Do, S.; Han, K.; Kim, H.; Yang, S.; Lee, D.-J.; et al. Deep Convolutional Neural Network-based Software Improves Radiologist Detection of Malignant Lung Nodules on Chest Radiographs. Radiology 2020, 294, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castiglioni, I.; Ippolito, D.; Interlenghi, M.; Monti, C.B.; Salvatore, C.; Schiaffino, S.; Polidori, A.; Gandola, D.; Messa, C.; Sardanelli, F. Machine learning applied on chest x-ray can aid in the diagnosis of COVID-19: A first experience from Lombardy, Italy. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2021, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zandehshahvar, M.; van Assen, M.; Maleki, H.; Kiarashi, Y.; De Cecco, C.N.; Adibi, A. Toward understanding COVID-19 pneumonia: A deep-learning-based approach for severity analysis and monitoring the disease. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Akter, S.; Shamrat, F.M.J.M.; Chakraborty, S.; Karim, A.; Azam, S. COVID-19 Detection Using Deep Learning Algorithm on Chest X-ray Images. Biology 2021, 10, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Oh, Y.; Park, S.; Ye, J.C. Deep learning COVID-19 features on CXR using limited training data sets. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging. 2020, 39, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, Y.; Shukla, P.; Tiwari, A.; Stalin, S.; Singh, S. Deep transfer learning based classification model for COVID-19 disease. Ing. Rech. Biomed. 2022, 43, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minaee, S.; Kafieh, R.; Sonka, M.; Yazdani, S.; Soufi, G.J. Deep-COVID: Predicting COVID-19 from chest X-ray images using deep transfer learning. Med. Image. Anal. 2020, 65, 101794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, J.; Raghu, V.K.; Paruchuri, K.; Zinzuwadia, A.; Natarajan, P.; Aerts, H.J.; Lu, M.T. Deep Learning to Estimate Cardiovascular Risk From Chest Radiographs: A Risk Prediction Study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2024, 177, 409–417, Erratum in Ann. Intern. Med. 2024, 178, 1. https://doi.org/10.7326/ANNALS-24-03386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nakaura, T.; Ito, R.; Ueda, D.; Nozaki, T.; Fushimi, Y.; Matsui, Y.; Yanagawa, M.; Yamada, A.; Tsuboyama, T.; Fujima, N.; et al. The impact of large language models on radiology: A guide for radiologists on the latest innovations in AI. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2024, 42, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shieh, A.; Tran, B.; He, G.; Kumar, M.; Freed, J.A.; Majety, P. Assessing ChatGPT 4.0’s test performance and clinical diagnostic accuracy on USMLE STEP 2 CK and clinical case reports. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 9330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Goh, E.; Gallo, R.; Hom, J.; Strong, E.; Weng, Y.; Kerman, H.; Cool, J.A.; Kanjee, Z.; Parsons, A.S.; Ahuja, N.; et al. Large Language Model Influence on Diagnostic Reasoning: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw. Open. 2024, 7, e2440969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kochanek, M.; Cichecki, I.; Kaszyca, O.; Szydło, D.; Madej, M.; Jędrzejewski, D.; Kazienko, P.; Kocoń, J. Improving Training Dataset Balance with ChatGPT Prompt Engineering. Electronics 2024, 13, 2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunes, Y.C.; Cesur, T. The Diagnostic Performance of Large Language Models and General Radiologists in Thoracic Radiology Cases: A Comparative Study. J. Thorac. Imaging. 2025, 40, e0805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, P.G.; Russe, M.F.; Bamberg, F.; Emrich, T.; Vecsey-Nagy, M.; Ashi, A.; Kravchenko, D.; Varga-Szemes, Á.; Soschynski, M.; Rau, A.; et al. Performance of large language models for CAD-RADS 2.0 classification derived from cardiac CT reports. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2025; Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Ding, X.; Huai, T.; Liu, S.; Chen, Q.; Xie, Y.; He, L. Recent Advances of Foundation Language Models-based Continual Learning: A Survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2025, 57, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochanek, K.; Skarzynski, H.; Jedrzejczak, W.W. Accuracy and Repeatability of ChatGPT Based on a Set of Multiple-Choice Questions on Objective Tests of Hearing. Cureus 2024, 16, e59857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen, Q.; Sun, H.; Liu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Ran, T.; Jin, X.; Xiao, X.; Lin, Z.; Chen, H.; Niu, Z. An extensive benchmark study on biomedical text generation and mining with ChatGPT. Bioinformatics 2023, 39, btad557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sounderajah, V.; Ashrafian, H.; Rose, S.; Shah, N.H.; Ghassemi, M.; Golub, R.; Kahn, C.E., Jr.; Esteva, A.; Karthikesalingam, A.; Mateen, B.; et al. A quality assessment tool for artificial intelligence-centered diagnostic test accuracy studies: QUADAS-AI. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1663–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mongan, J.; Moy, L.; Kahn, C.E. Checklist for Artificial Intelligence in Medical Imaging (CLAIM): 2024 Update. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2024, 6, e220159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
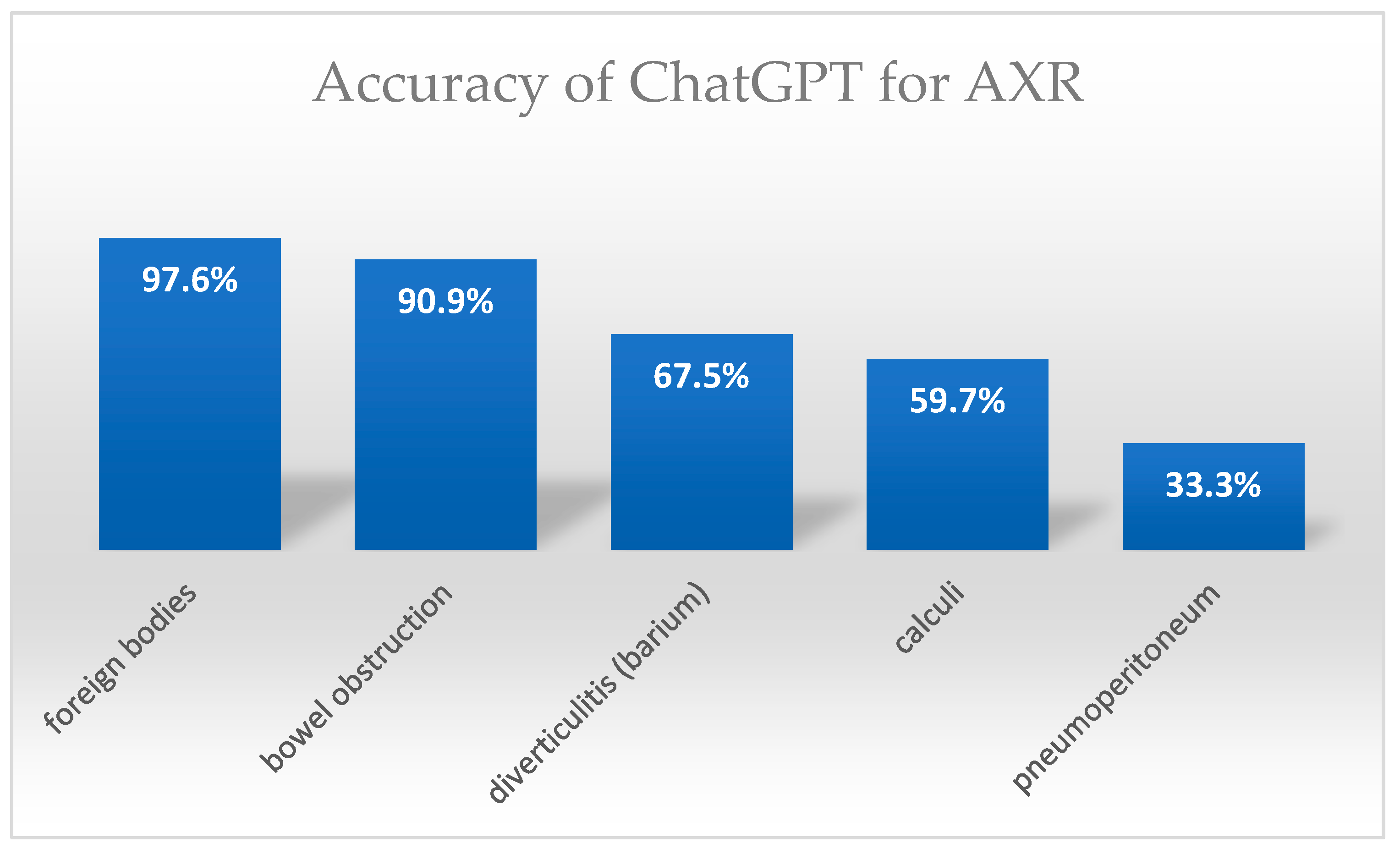

| CXR Pathology | N | Detection Rate N/N (%) | Confidence Score Median (IQR) | AXR Pathology | N | Detection Rate N/N (%) | Confidence Score Median (IQR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pneumonia | 50 | 37/50 (74%) | 3 (IQR 2) | Small/Large BO | 60 | 54/60 (90.9%) | 3.5 (IQR 2) |
| Pulmonary edema | 30 | 30/30 (100%) | 3 (IQR 0.5) | Pneumoperitoneum | 30 | 10/30 (33.3%) | 4 (IQR 0) |
| Pleural effusion | 30 | 21/30 (70%) | 2.5 (IQR 1) | R/U/B calculi or gallstones | 73 | 43/73 (59.7%) | 4 (IQR 1) |
| Lung tumors | 10 | 9/10 (90%) | 3.5 (IQR 0.75) | Diverticulitis (Barium) | 40 | 27/40 (67.5%) | 4 (IQR 1) |
| Emphysma | 11 | 9/11 (81.8%) | 4 (IQR 1) | Foreign bodies | 41 | 40/41 (97.6%) | 4 (IQR 0) |
| Cardiomegaly | 44 | 32/44 (72.7%) | 3 (IQR 2) | Total | 243 | 175/243 (72.02%) 95% CI: 66.06–77.28 | Median 4 (IQR 1) Mean 3.45 ± 1.1 |
| Enlarged mediastinum | 11 | 6/11 (54.5%) | 3 (IQR 1.25) | ||||
| Rib fracture | 20 | 0/20 (0%) | 3.5 (IQR 2) | ||||
| Pneumothorax | 51 | 21/51 (41.2%) | 3 (IQR 1) | ||||
| Total | 257 | 170/257 (66.15%) 95%CI:60.16–71.66 | Median 4 (IQR 3) Mean 2.48 ± 1.45 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lacaita, P.G.; Galijasevic, M.; Swoboda, M.; Gruber, L.; Scharll, Y.; Barbieri, F.; Widmann, G.; Feuchtner, G.M. The Accuracy of ChatGPT-4o in Interpreting Chest and Abdominal X-Ray Images. J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15, 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050194
Lacaita PG, Galijasevic M, Swoboda M, Gruber L, Scharll Y, Barbieri F, Widmann G, Feuchtner GM. The Accuracy of ChatGPT-4o in Interpreting Chest and Abdominal X-Ray Images. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2025; 15(5):194. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050194
Chicago/Turabian StyleLacaita, Pietro G., Malik Galijasevic, Michael Swoboda, Leonhard Gruber, Yannick Scharll, Fabian Barbieri, Gerlig Widmann, and Gudrun M. Feuchtner. 2025. "The Accuracy of ChatGPT-4o in Interpreting Chest and Abdominal X-Ray Images" Journal of Personalized Medicine 15, no. 5: 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050194
APA StyleLacaita, P. G., Galijasevic, M., Swoboda, M., Gruber, L., Scharll, Y., Barbieri, F., Widmann, G., & Feuchtner, G. M. (2025). The Accuracy of ChatGPT-4o in Interpreting Chest and Abdominal X-Ray Images. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 15(5), 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050194






