Central Nervous System Metastases from Primary Lung Carcinoma: Significance of RNA Fusion Testing and Early Versus Late Metastases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Targeted NGS and Sequencing Data Processing
2.2. RNA NGS and Sequencing Data Processing
2.3. MET Exon Skipping Mutations
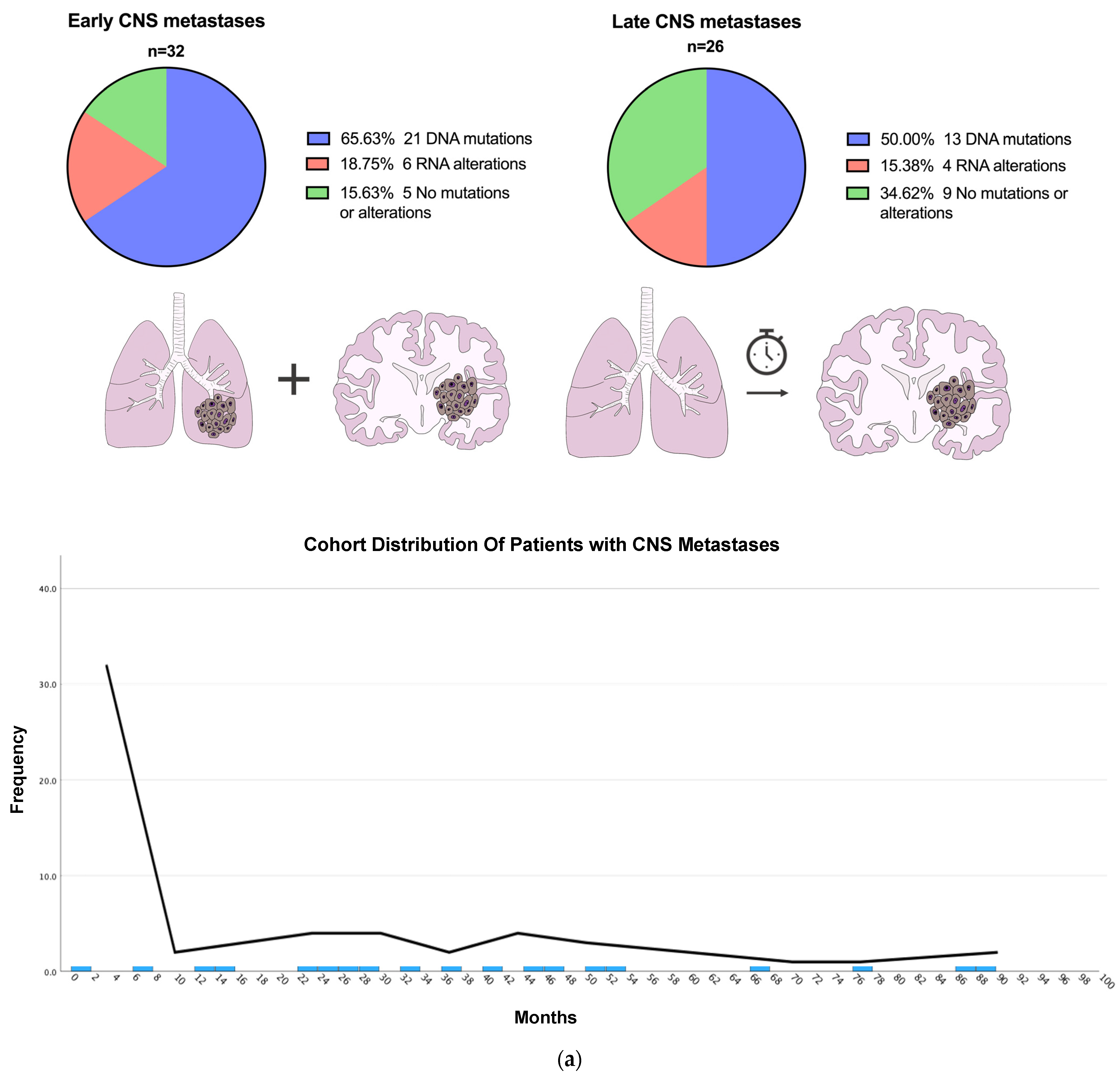
2.4. Early vs. Late CNS Metastases
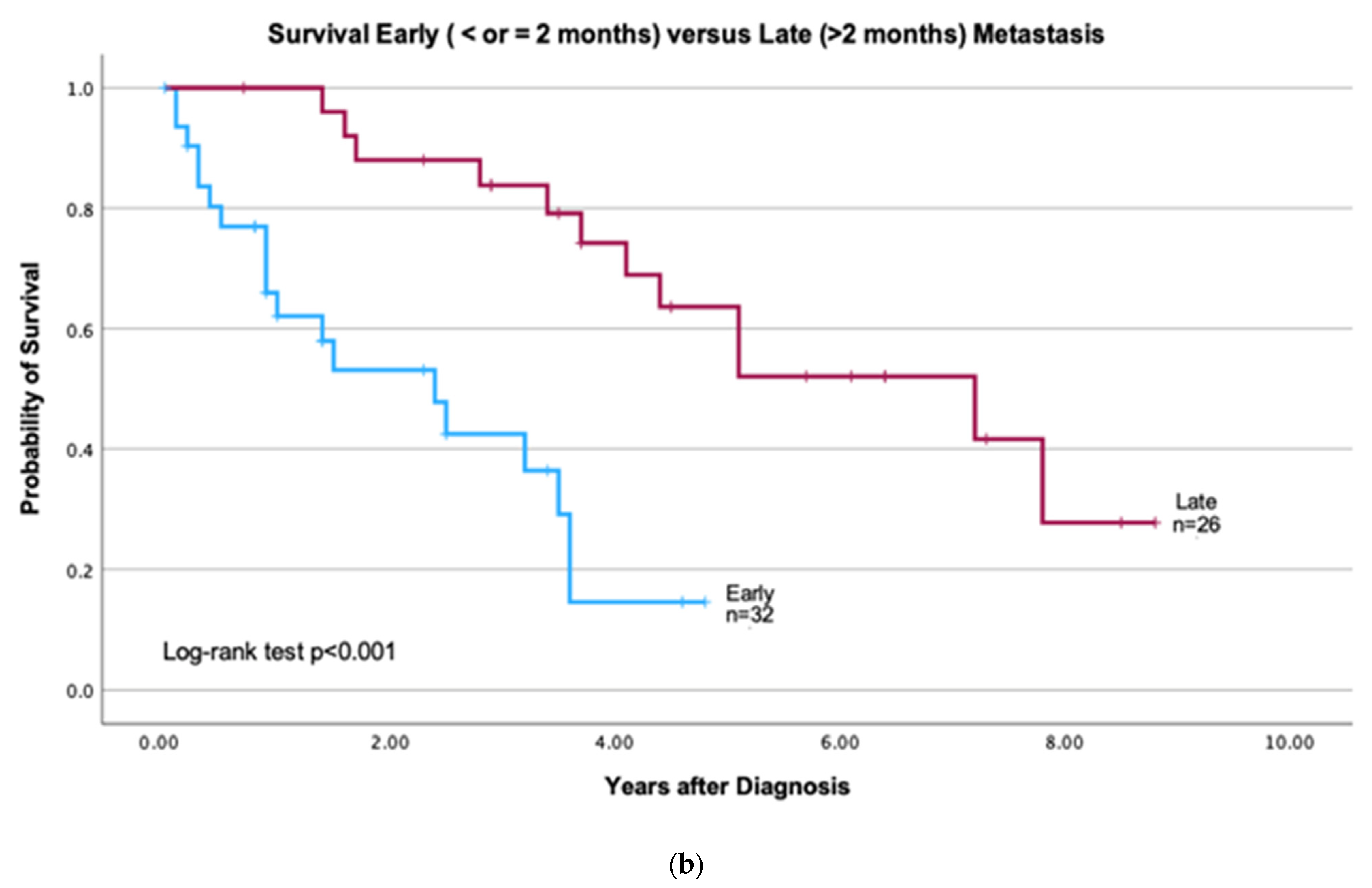
2.5. Clinical Characteristics and Survival
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients with Driver Mutations
3.2. Patients with Early vs. Late CNS Metastasis
3.3. Mutational Profile of Primary Lung Compared to CNS Metastatic Carcinomas and Additional Variants
4. Discussion
4.1. Mutational Profiles of Lung Carcinoma with CNS Metastases
4.2. Significance of Combined DNA NGS and RNA NGS
4.3. Early vs. Late CNS Metastases
4.4. Limitations
4.5. Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NSCLC | Non-small cell lung carcinoma |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| NGS | Next-generation sequencing |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| FISH | Fluorescent in situ hybridization |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| KRAS | Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog |
| ALK | Anaplastic lymphoma kinase |
| MET | MET proto-oncogene, receptor tyrosine kinase |
| ROS1 | c-ros oncogene 1 |
| RET | Rearranged during transfection proto-oncogene |
| ERBB2 | Erb-B2 receptor tyrosine kinase 2 (also known as HER2) |
| STK11 | Serine/threonine kinase 11 (also known as LKB1) |
| CDKN2A | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A |
| ARL9 | ADP-ribosylation factor-like 9 |
| MYC | MYC proto-oncogene, BHLH transcription factor |
| YAP1 | Yes-associated protein 1 |
| MMP13 | Matrix metallopeptidase 13 |
| SMARCA2 | SWI/SNF-related, matrix-associated, actin-dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily A, member 2 |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
References
- Lin, Y.-Y.; Wang, Y.-C.; Yeh, D.-W.; Hung, C.-Y.; Yeh, Y.-C.; Ho, H.-L.; Mon, H.-C.; Chen, M.-Y.; Wu, Y.-C.; Chou, T.-Y. Gene Expression Profile in Primary Tumor Is Associated with Brain-Tropism of Metastasis from Lung Adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howlader, N.; Forjaz, G.; Mooradian, M.J.; Meza, R.; Kong, C.Y.; Cronin, K.A.; Mariotto, A.B.; Lowy, D.R.; Feuer, E.J. The Effect of Advances in Lung-Cancer Treatment on Population Mortality. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skakodub, A.; Walch, H.; Tringale, K.R.; Eichholz, J.; Imber, B.S.; Vasudevan, H.N.; Li, B.T.; Moss, N.S.; Yu, K.K.H.; Mueller, B.A.; et al. Genomic analysis and clinical correlations of non-small cell lung cancer brain metastasis. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Planchard, D.; Cho, B.C.; Gray, J.E.; Ohe, Y.; Zhou, C.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Cheng, Y.; Chewaskulyong, B.; et al. Overall Survival with Osimertinib in Untreated, EGFR-Mutated Advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.T.; Bauer, T.M.; de Marinis, F.; Felip, E.; Goto, Y.; Liu, G.; Mazieres, J.; Kim, D.-W.; Mok, T.; Polli, A.; et al. First-Line Lorlatinib or Crizotinib in Advanced ALK-Positive Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2018–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, S.; Camidge, D.R.; Shaw, A.T.; Gadgeel, S.; Ahn, J.S.; Kim, D.W.; Ou, S.H.I.; Pérol, M.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Rosell, R.; et al. Alectinib versus Crizotinib in Untreated ALK-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarty, D.; Johnson, A.; Sklar, J.; Lindeman, N.I.; Moore, K.; Ganesan, S.; Lovly, C.M.; Perlmutter, J.; Gray, S.W.; Hwang, J.; et al. Somatic Genomic Testing in Patients With Metastatic or Advanced Cancer: ASCO Provisional Clinical Opinion. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 1231–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedlaender, A.; Perol, M.; Banna, G.L.; Parikh, K.; Addeo, A. Oncogenic alterations in advanced NSCLC: A molecular super-highway. Biomark. Res. 2024, 12, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, N.J.; Espirito, J.L.; Chen, L.; Nwokeji, E.; Karhade, M.; Evangelist, M.; Spira, A.; Neubauer, M.; Bullock, S.; Walberg, J.; et al. Biomarker testing and tissue journey among patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer receiving first-line therapy in The US Oncology Network. Lung Cancer 2022, 166, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadik, H.; Pritchard, D.; Keeling, D.-M.; Policht, F.; Riccelli, P.; Stone, G.; Finkel, K.; Schreier, J.; Munksted, S. Impact of Clinical Practice Gaps on the Implementation of Personalized Medicine in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2022, 6, e2200246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benayed, R.; Offin, M.; Mullaney, K.; Sukhadia, P.; Rios, K.; Desmeules, P.; Ptashkin, R.; Won, H.; Chang, J.; Halpenny, D.; et al. High Yield of RNA Sequencing for Targetable Kinase Fusions in Lung Adenocarcinomas with No Mitogenic Driver Alteration Detected by DNA Sequencing and Low Tumor Mutation Burden. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 4712–4722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, D.; Ben-Shachar, R.; Feliciano, J.; Gai, L.; Beauchamp, K.A.; Rivers, Z.; Hockenberry, A.J.; Harrison, G.; Guittar, J.; Catela, C.; et al. Actionable Structural Variant Detection via RNA-NGS and DNA-NGS in Patients With Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2442970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Parker, M.; Materi, J.; Azad, T.D.; Kamson, D.O.; Kleinberg, L.; Ye, X.; Rincon-Torroella, J.; Bettegowda, C. Epidemiology and survival outcomes of synchronous and metachronous brain metastases: A retrospective population-based study. Neurosurg. Focus 2023, 55, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, A.J.; Rock, J.P.; Johnson, C.C.; Weiss, L.; Jacobsen, G.; Rosenblum, M.L. Survival of patients with synchronous brain metastases: An epidemiological study in southeastern Michigan. J. Neurosurg. 2000, 93, 927–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibahara, I.; Kanamori, M.; Watanabe, T.; Utsunomiya, A.; Suzuki, H.; Saito, R.; Sonoda, Y.; Jokura, H.; Uenohara, H.; Tominaga, T. Clinical Features of Precocious, Synchronous, and Metachronous Brain Metastases and the Role of Tumor Resection. World Neurosurg. 2018, 113, e1–e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkinson, M.D.; Haylock, B.; Shenoy, A.; Husband, D.; Javadpour, M. Management of cerebral metastasis: Evidence-based approach for surgery, stereotactic radiosurgery and radiotherapy. Eur. J. Cancer 2011, 47, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barua, S.; Hsiao, S.; Clancy, E.; Freeman, C.; Mansukhani, M.; Fernandes, H. Quality metrics for enhanced performance of an NGS panel using single-vial amplification technology. J. Clin. Pathol. 2023, 77, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurkiewicz, M.; Yeh, R.; Shu, C.A.; Hsiao, S.J.; Mansukhani, M.M.; Saqi, A.; Fernandes, H. Challenges in Amplicon-Based DNA NGS Identification of MET Exon 14 Skipping Events in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancers. J. Mol. Pathol. 2025, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, A.C.; Itchins, M.; Khasraw, M. Brain Metastases in Lung Cancers with Emerging Targetable Fusion Drivers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, C.S.; Mustafa, M.A.; Richardson, G.E.; Alam, A.M.; Lee, K.S.; Hughes, D.M.; Escriu, C.; Zakaria, R. Genomic Alterations and the Incidence of Brain Metastases in Advanced and Metastatic NSCLC: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2023, 18, 1703–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canterbury, C.R.; Fernandes, H.; Crapanzano, J.P.; Murty, V.V.; Mansukhani, M.M.; Shu, C.A.; Szabolcs, M.; Saqi, A. ALK Gene Rearrangements in Lung Adenocarcinomas: Concordance of Immunohistochemistry, Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization, RNA In Situ Hybridization, and RNA Next-Generation Sequencing Testing. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2021, 2, 100223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demleitner, M.; Erlenbach-Wünsch, K.; Coras, R.; Erber, R.; Polifka, I.; Eyüpoğlu, I.; Fuchs, F.; Hartmann, A.; Agaimy, A. Lung cancer presenting with central nervous system metastasis: Clinicopathological and molecular analysis of 171 cases. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2023, 63, 152082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, D.J.H.; Nayyar, N.; Bihun, I.; Dagogo-Jack, I.; Gill, C.M.; Aquilanti, E.; Bertalan, M.; Kaplan, A.; D’andrea, M.R.; Chukwueke, U.; et al. Genomic characterization of human brain metastases identifies drivers of metastatic lung adenocarcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Ou, Q.; Li, D.; Qin, T.; Bao, H.; Hou, X.; Wang, K.; Wang, F.; Deng, Q.; Liang, J.; et al. Genes associated with increased brain metastasis risk in non-small cell lung cancer: Comprehensive genomic profiling of 61 resected brain metastases versus primary non-small cell lung cancer (Guangdong Association Study of Thoracic Oncology 1036). Cancer 2019, 125, 3535–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.K.; Han, J.; Kwon, G.Y.; Yeo, M.K.; Bae, G.E. Patterns of Extrathoracic Metastasis in Lung Cancer Patients. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 8794–8801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Yan, Y.; Zhou, K.; Su, C.; Ren, S.; Li, N.; Hou, L.; Guo, X.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, H.; et al. Characterization of evolution trajectory and immune profiling of brain metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma. npj Precis. Oncol. 2021, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
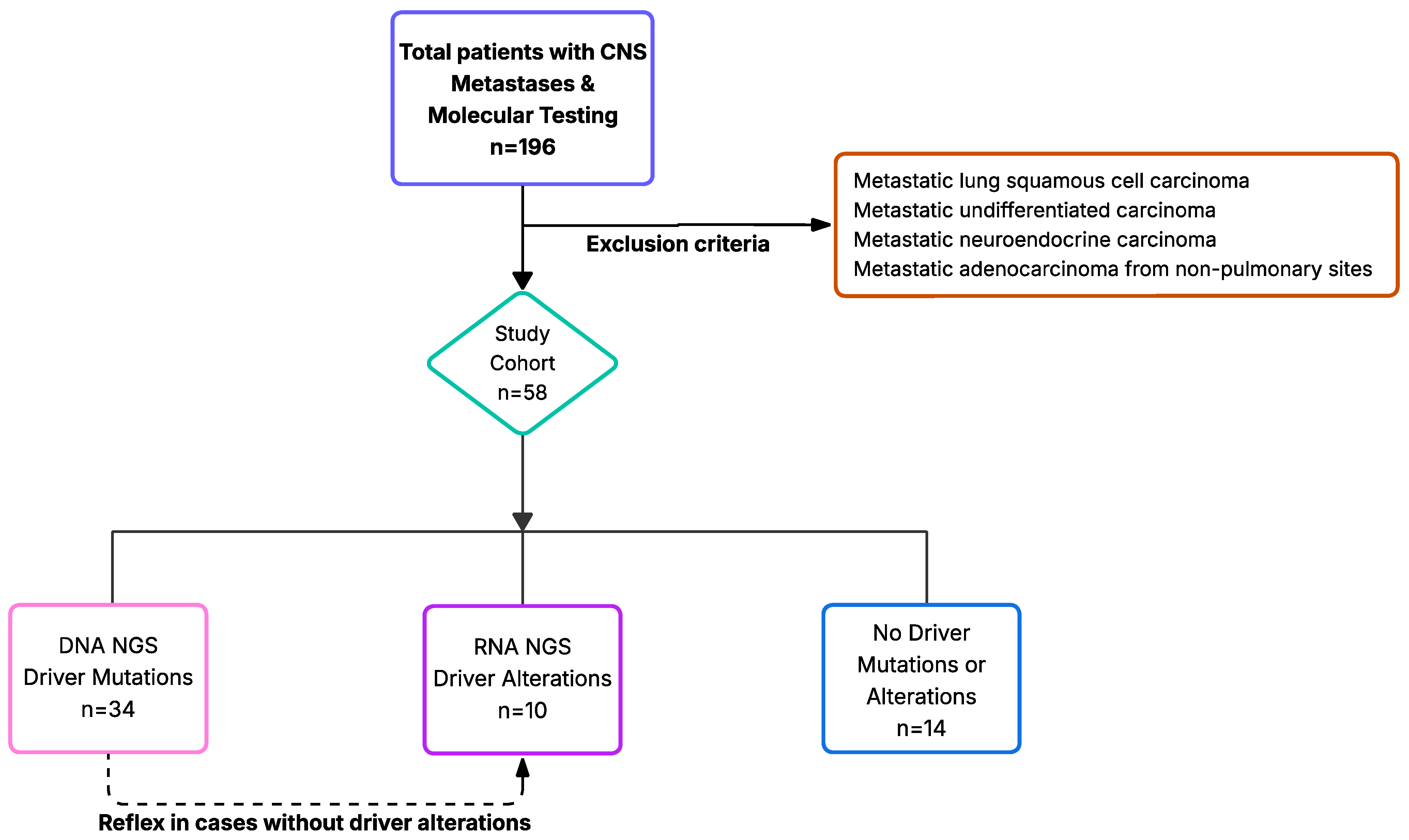
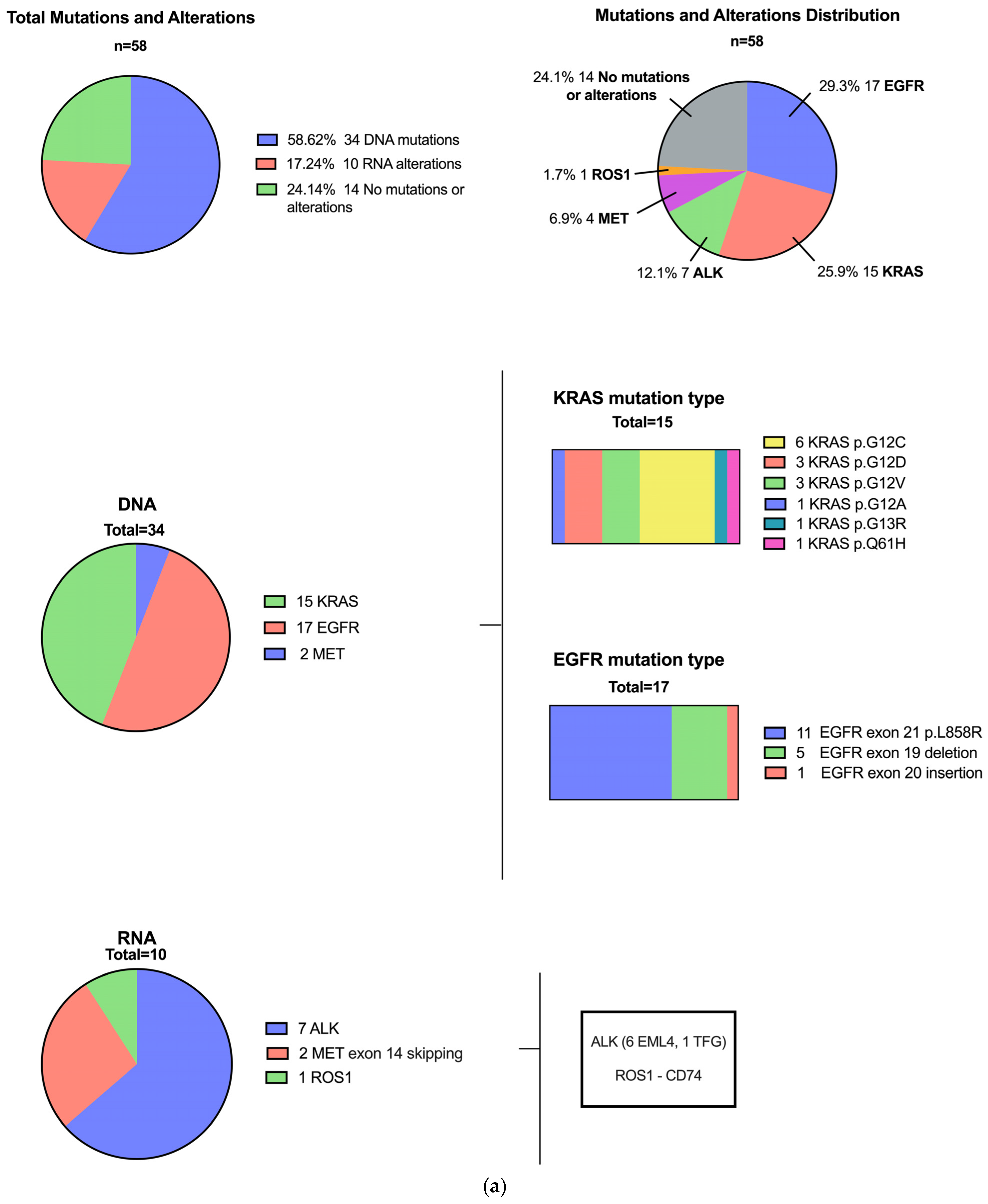


| Variable | Total n = 58 | Driver Mutation (DNA NGS) n = 34 (58.6%) | Driver Alterations (RNA NGS) n = 10 (17.2%) | No Driver Mutation or Alteration n = 14 (24.1%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean (SD) | 66.9 (10.9) | 68.7 (8.9) | 63.5 (16.3) | 64.8 (10.6) | 0.30 |
| Male | 31 (53.4%) | 14 (41.2) | 8 (80.0) | 9 (64.3) | 0.06 |
| Smoking 1 | 40 (72.7%) | 23 (69.7) | 4 (50.0) | 13 (92.9) | 0.08 |
| White race 2 | 26 (51.0%) | 15 (46.9) | 2 (28.6) | 9 (75.0) | 0.11 |
| Hispanic 3 | 18 (40.9%) | 13 (43.3) | 2 (33.3) | 3 (37.5) | 0.88 |
| History of other cancer types—total number 4 | 18 (32.7) | 12 (36.4) | 1 (12.5) | 5 (35.7) | 0.42 |
| Variable | Total (n = 58) | Early CNS Metastasis (n = 32) | Late CNS Metastasis (n = 26) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Any Alteration | 44 (75.9%) | 27 (84.4%) | 17 (65.4%) | 0.093 |
| DNA | 34 (58.6%) | 21 (65.6%) | 13 (50.0%) | 0.36 |
| EGFR L858R 1 Exon 19 del Exon 20 ins | 17 11 5 1 | 11 8 1 2 1 | 6 3 2 3 | |
| KRAS G12C G12D G12V G12A G13R Q61H | 15 6 3 3 1 1 1 | 8 3 2 2 1 1 | 7 3 1 1 1 - - | |
| MET 14 skipping | 2 | 2 | ||
| RNA | 10 (17.2%) | 6 | 4 | 0.74 |
| ALK | 7 | 4 ALK::EML4 | 3 ALK::EML4 (2) ALK::TFG (1) | |
| MET 14 skipping | 2 | 2 | 0 | |
| ROS1 | 1 | 1 ROS1::CD74 | ||
| No driver alterations | 14 (24.1%) | 5 (15.6%) | 9 (34.6%) | 0.093 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garlin Politis, M.; Mansukhani, M.; Herzberg, B.O.; Chen, L.N.; Stoopler, M.; Saliba, M.; Siegelin, M.; Zhu, Z.; Sonett, J.; Henick, B.S.; et al. Central Nervous System Metastases from Primary Lung Carcinoma: Significance of RNA Fusion Testing and Early Versus Late Metastases. J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15, 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050181
Garlin Politis M, Mansukhani M, Herzberg BO, Chen LN, Stoopler M, Saliba M, Siegelin M, Zhu Z, Sonett J, Henick BS, et al. Central Nervous System Metastases from Primary Lung Carcinoma: Significance of RNA Fusion Testing and Early Versus Late Metastases. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2025; 15(5):181. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050181
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarlin Politis, Michelle, Mahesh Mansukhani, Benjamin O. Herzberg, Lanyi N. Chen, Mark Stoopler, Maelle Saliba, Markus Siegelin, Zhe Zhu, Joshua Sonett, Brian S. Henick, and et al. 2025. "Central Nervous System Metastases from Primary Lung Carcinoma: Significance of RNA Fusion Testing and Early Versus Late Metastases" Journal of Personalized Medicine 15, no. 5: 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050181
APA StyleGarlin Politis, M., Mansukhani, M., Herzberg, B. O., Chen, L. N., Stoopler, M., Saliba, M., Siegelin, M., Zhu, Z., Sonett, J., Henick, B. S., Cheng, S. K., Acharyya, S., Shu, C. A., Miller, M. L., Izar, B., Fernandes, H., Hsiao, S., & Saqi, A. (2025). Central Nervous System Metastases from Primary Lung Carcinoma: Significance of RNA Fusion Testing and Early Versus Late Metastases. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 15(5), 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050181








