Associations of Adipocytokines with The Development of Cardiovascular Events in Young People
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roth, G.A.; Huffman, M.D.; Moran, A.E.; Feigin, V.; Mensah, G.A.; Naghavi, M.; Murray, C.J. Global and regional patterns in cardiovascular mortality from 1990 to 2013. Circulation 2015, 132, 1667–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauchno-organizatsionnyi komitet proekta ÉSSE-RF. Epidemiology of cardiovascular diseases in different regions of Russia (esse-rf). The rationale for and design of the study. Profil. Meditsina 2013, 16, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Piepoli, M.F.; Hoes, A.W.; Agewall, S.; Albus, C.; Brotons, C.; Catapano, A.L.; Cooney, M.-T.; Corrà, U.; Cosyns, B.; Deaton, C.; et al. 2016 European Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice: The Sixth Joint Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and Other Societies on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Clinical Practice (constituted by representatives of 10 societies and by invited experts). Developed with the special contribution of the European Association for Cardiovascular Prevention & Rehabilitation (EACPR). Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 2315–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ural, D.; Karaaslan, D.; Kay, M.; Bar, C.; Abac, A.; Tokg, L. Data on prevalence of obesity and waist circumference in Turkey: Systematic Review, Meta-analysis and Meta-regression of Epidemiological Studies on Cardiovascular Risk Factors. Turk. Kardiyol. Dern. Ars. 2018, 46, 577–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chait, A.; den Hartigh, L.J. Adipose Tissue Distribution, Inflammation and Its Metabolic Consequences, Including Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwaifa, I.K.; Bahari, H.; Yong, Y.K.; Noor, S.M. Endothelial Dysfunction in Obesity-Induced Inflammation: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouchi, N.; Parker, J.L.; Lugus, J.J.; Walsh, K. Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, E.E.; Bauer, R.C. Emerging Roles for Adipose Tissue in Cardiovascular Disease. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, E137–E144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, S.; Canada, J.M.; Billingsley, H.E.; Siddiqui, M.S.; Elagizi, A.; Lavie, C.J. Obesity paradox in cardiovascular disease: Where do we stand? Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2019, 15, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutheil, F.; Gordon, B.A.; Naughton, G.; Crendal, E.; Courteix, D.; Chaplais, E.; Thivel, D.; Lac, G.; Benson, A.C. Cardiovascular risk of adipokines: A review. J. Int. Med. Res. 2017, 46, 2082–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2013, 3, 1–1507. [Google Scholar]
- Kouvari, M.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Chrysohoou, C.; Georgousopoulou, E.; Notara, V.; Tousoulis, D.; Pitsavos, C.; ATTICA & GREECS Studies Investigators. Gender-specific, Lifestyle-related Factors and 10-year Cardiovascular Disease Risk; the ATTICA and GREECS Cohort Studies. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2019, 17, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.U.A.; Browne, L.D.; Li, X.; Adeeb, F.; Perez-Ruiz, F.; Fraser, A.D.; Stack, A.G. Temporal trends in hyperuricaemia in the Irish health system from 2006–2014: A cohort study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, S.; Yu, X.-Y.; Li, Y. The Influence of Sex on Cardiac Physiology and Cardiovascular Diseases. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2019, 13, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koliaki, C.; Liatis, S.; Kokkinos, A. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: Revisiting an old relationship. Metabolism 2019, 92, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, A.L.; Cornoni, J.C.; Cassel, J.C.; Tyroler, H.A.; Heyden, S.; Hames, C.G. Influence of race, sex and weight on blood pressure behavior in young adults. Am. J. Cardiol. 1975, 35, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, F.B.; Lavie, C.J.; Blair, S.N. Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 1752–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, T.H. Pancreatic polypeptide: More than just another gut hormone? Gastroenterology 2003, 124, 1542–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, F.F.; Santos-Reis, T.; Marinho, T.S.; Aguila, M.B.; Mandarim-De-Lacerda, C.A. Hypothalamic anorexigenic signaling pathways (leptin, amylin, and proopiomelanocortin) are semaglutide (GLP-1 analog) targets in obesity control in mice. Life Sci. 2023, 313, 121268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergh, N.; Ulfhammer, E.; Glise, K.; Jern, S.; Karlsson, L. Influence of TNF-α and biomechanical stress on endothelial anti- and prothrombotic genes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 385, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Liu, X.; Tang, Y. HMGB1/Foxp1 regulates hypoxia-induced inflammatory response in macrophages. Cell Biol. Int. 2022, 46, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzálvez, M.; Ruiz-Ros, J.A.; Pérez-Paredes, M.; Lozano, M.L.; Almagro, F.J.G.; Martínez-Corbalán, F.; Giménez, D.M.; Carrillo, A.; Carnero, A.; Cubero, T.; et al. Valor pronóstico del factor de necrosis tumoral alfa en pacientes con infarto agudo de miocardio con elevación del segmento ST. [Prognostic value of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in patients with ST-segment elevation acute myocardial infarction]. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2007, 60, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paccalet, A.; Da Silva, C.C.; Mechtouff, L.; Amaz, C.; Varillon, Y.; de Bourguignon, C.; Cartier, R.; Prieur, C.; Tomasevic, D.; Genot, N.; et al. Serum Soluble Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptors 1 and 2 Are Early Prognosis Markers After ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 656928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Carter, P.; Bruzelius, M.; Vithayathil, M.; Kar, S.; Mason, A.M.; Lin, A.; Burgess, S.; Larsson, S.C. Effects of tumour necrosis factor on cardiovascular disease and cancer: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study. EBioMedicine 2020, 59, 102956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinbongard, P.; Schulz, R.; Heusch, G. TNFα in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion, remodeling and heart failure. Heart Fail. Rev. 2011, 16, 49–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Tanday, N.; Flatt, P.R.; Irwin, N. Pancreatic polypeptide revisited: Potential therapeutic effects in obesity-diabetes. Peptides 2023, 160, 170923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sam, A.H.; Sleeth, M.L.; Thomas, E.L.; Ismail, N.A.; Mat Daud, N.; Chambers, E.; Shojaee-Moradie, F.; Umpleby, M.; Goldstone, A.P.; Le Roux, C.W.; et al. Circulating pancreatic polypeptide concentrations predict visceral and liver fat content. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 1048–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjalmarsen, A.; Aasebø, U.; Aleksandersen, G.; Jorde, R. Cardiovascular responses to tests for autonomic dysfunction in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease with and without continuous long-term oxygen therapy. J. Auton. Nerv. Syst. 1996, 60, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathias, C.; da Costa, D.; Fosbraey, P.; Bannister, R.; Wood, S.; Bloom, S.; Christensen, N. Cardiovascular, biochemical and hormonal changes during food-induced hypotension in chronic autonomic failure. J. Neurol. Sci. 1989, 94, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Hoskins, A.; Verma, N.; Bers, D.M.; Despa, S.; Despa, F. Amylin and diabetic cardiomyopathy—Amylin-induced sarcolemmal Ca2+ leak is independent of diabetic remodeling of myocardium. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 1923–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F. Amylin in vasodilation, energy expenditure and inflammation. Front. Biosci. 2014, 19, 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kailasam, M.T.; Parmer, R.J.; Tyrell, E.A.; Henry, R.R.; O’connor, D.T. Circulating amylin in human essential hypertension: Heritability and early increase in individuals at genetic risk. J. Hypertens. 2000, 18, 1611–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
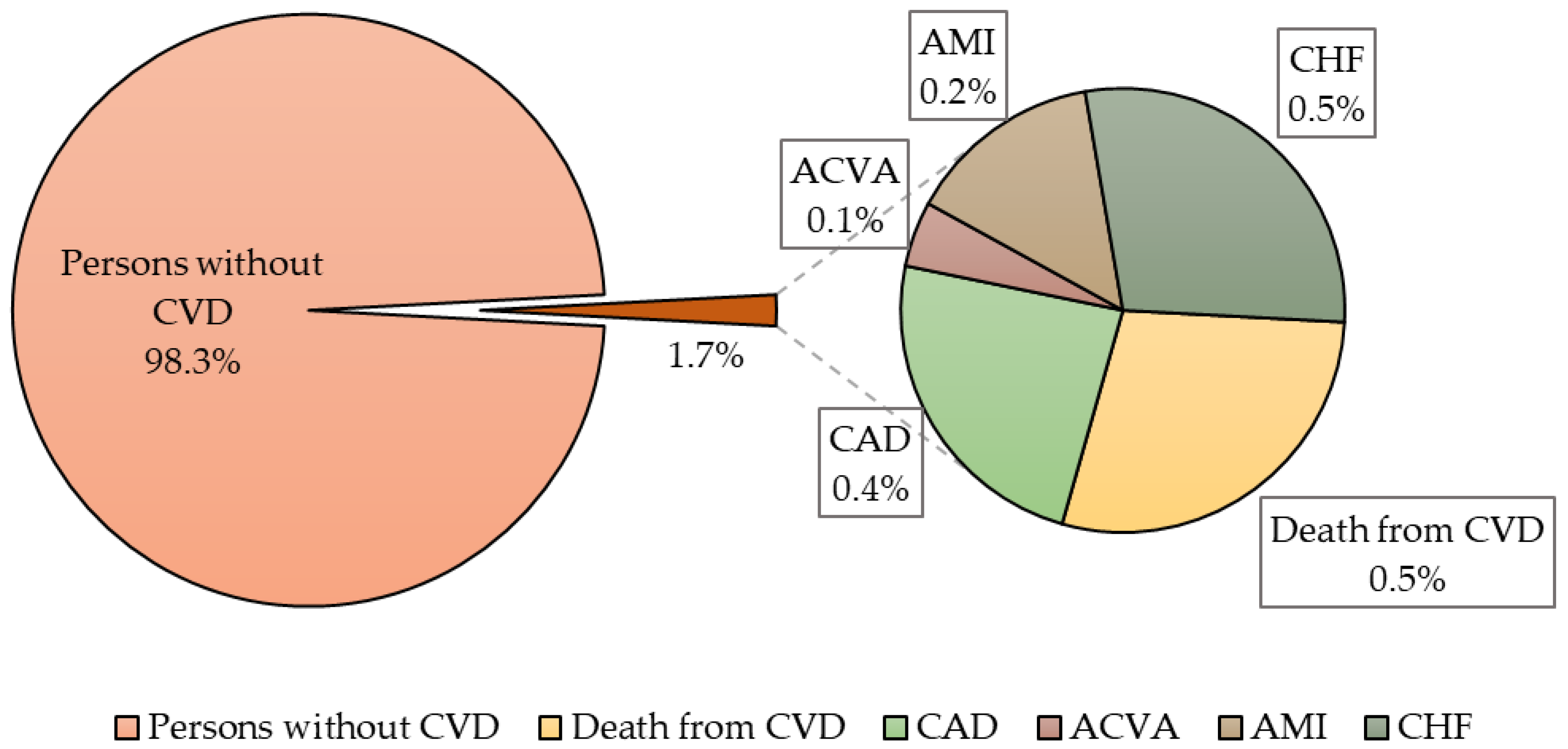

| Parameters | Individuals with Cardiovascular Events n = 21 | Persons without Cardiovascular Events n = 1219 | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 43.5 [39.8; 45.0] | 37.3 [31.8; 41.9] | 0.0001 |
| WC, cm | 99.0 [88.3; 107.6] | 86.0 [76.0; 96.0] | 0.0001 |
| SBP, mmHg | 128.5 [122.3; 147.0] | 120.0 [110.5; 130.0] | 0.0001 |
| DBP, mmHg | 91.5 [82.5; 98.8] | 78.5 [71.5; 87.0] | 0.0001 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 29.0 [25.2; 31.6] | 25.2 [22.1; 29.0] | 0.002 |
| TG, mmol/L | 1.4 [0.9; 2.6] | 1.0 [0.7; 1.4] | 0.002 |
| HDL-C, mmol/L | 1.3 [1.1; 1.5] | 1.1 [0.9; 1.5] | 0.066 |
| LDL-C, mmol/L | 4.0 [2.9; 4.6] | 3.2 [2.5; 3.7] | 0.005 |
| TCH, mmol/L | 5.9 [4.8; 6.8] | 5.0 [4.3; 5.7] | 0.002 |
| Non-HDL-C, mmol/L | 4.8 [3.7; 5.4] | 3.6 [3.0; 4.4] | 0.001 |
| GFRCKD-EPI, ml/min | 103.1 [80.4; 106.9] | 101.4 [90.4; 110.1] | 0.424 |
| Glucose, mmol/L | 6.4 [5.6; 6.8] | 5.7 [5.3; 6.0] | 0.001 |
| Parameters | Individuals with Cardiovascular Events n = 21; 1.7% | Persons without Cardiovascular Events n = 1219; 98.3% | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical activity less than 3 h/week (abs.; %) | 13; 65.0% | 812; 66.8% | 0.863 |
| Smoking (abs.; %) | 8; 40.0% | 413; 34% | 0.572 |
| AH (abs.; %) | 11; 52.4% | 244; 20.0% | 0.0001 |
| BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2 (abs.; %) | 16; 76.2% | 632; 51.9% | 0.027 |
| T2DM (abs.; %) | 4; 19.0% | 27; 2.2% | 0.0001 |
| Parameters | Individuals with Cardiovascular Events n = 21 | Persons without Cardiovascular Events n = 1219 | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Me [25%; 75%] | Me [25%; 75%] | ||
| Adiponectin, mcg/mL | 34.0 [26.3; 139.3] | 37.4 [25.7; 115.1] | 0.372 |
| Adipsin, mcg/mL | 11.4 [9.4; 14.5] | 11.7 [7.6; 14.1] | 0.372 |
| Lipocalin-2, ng/mL | 493.0 [215.3; 1223.5] | 379.2 [196.3; 1136.9] | 0.694 |
| Resistin, ng/mL | 539.0 [176.8; 690.0] | 170.9 [25.5; 598.0] | 0.090 |
| Amylin, pg/mL | 14.2 [7.1; 22.7] | 6.2 [3.4; 14.2] | 0.0001 |
| IL-6, pg/mL | 2.4 [1.1; 6.5] | 1.3 [0.6; 2.5] | 0.025 |
| PAI-1, ng/mL | 29.4 [18.4; 41.3] | 21.4 [13.0; 31.5] | 0.106 |
| C-peptide, ng/mL | 1.3 [0.7; 2.0] | 0.8 [0.3; 1.2] | 0.013 |
| Insulin, ng/mL | 498.4 [327.8; 1172.2] | 469.7 [296.0; 700.6] | 0.261 |
| Leptin, ng/mL | 4846.2 [1922.1; 9370.0] | 4382.7 [1689.3; 8271.9] | 0.808 |
| MCP-1, pg/mL | 220.1 [118.6; 360.2] | 238.3 [162.7; 319.6] | 0.721 |
| Ghrelin, pg/mL | 66.2 [18.6; 111.1] | 34.1 [18.6; 88.4] | 0.289 |
| TNFα, pg/mL | 3.3 [2.6; 5.9] | 4.7 [2.9; 7.3] | 0.046 |
| GIP, pg/mL | 46.8 [18.3; 65.6] | 26.1 [16.3; 51.4] | 0.084 |
| Glucagon, pg/mL | 21.25 [11.5; 40.6] | 11.5 [7.2; 20.9] | 0.012 |
| PP, pg/mL | 65.9 [53.5; 121.3] | 39.5 [22.8; 77.2] | 0.001 |
| GLP1, pg/mL | 321.1 [174.9; 470.6] | 283.8 [173.5; 492.7] | 0.800 |
| PYY, pg/mL | 66.3 [60.3; 114.8] | 56.1 [37.0; 74.3] | 0.027 |
| Secretin, pg/mL | 17.7 [8.8; 26.8] | 22.4 [16.0; 61.2] | 0.212 |
| Parameters | OR | 95% Confidence Interval (CI) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | |||
| C-peptide, per 1 ng/mL | 1.294 | 0.810 | 2.066 | 0.281 |
| GIP, per 1 pg/mL | 1.001 | 0.992 | 1.011 | 0.816 |
| GLP1, per 1 pg/mL | 0.999 | 0.997 | 1.001 | 0.186 |
| PAI-1, per 1 ng/mL | 1.019 | 0.990 | 1.050 | 0.201 |
| IL-6, per 1 pg/mL | 0.985 | 0.898 | 1.080 | 0.743 |
| Insulin, per 1 ng/mL | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.997 |
| Adipsin, per 1 mcg/mL | 0.994 | 0.947 | 1.044 | 0.820 |
| Lipocalin-2, per 1 ng/mL | 1.000 | 0.999 | 1.001 | 0.744 |
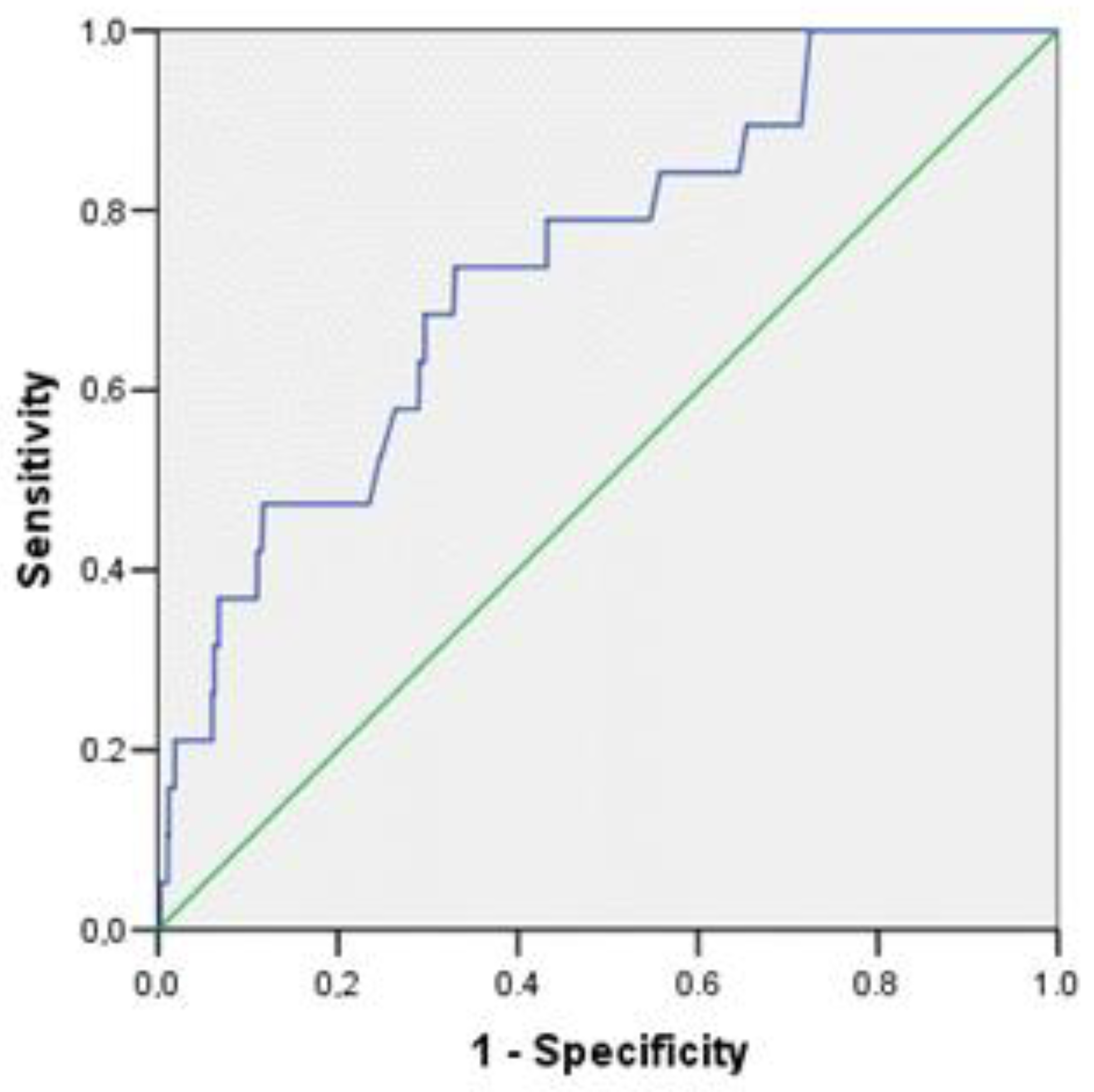
| Amylin, per 1 pg/mL | 1.033 | 1.006 | 1.062 | 0.018 |
| Ghrelin, per 1 pg/mL | 1.001 | 0.998 | 1.003 | 0.677 |
| Glucagon, per 1 pg/mL | 1.010 | 0.992 | 1.029 | 0.255 |
| Leptin, per 1 ng/mL | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.365 |
| MCP-1, per 1 pg/mL | 1.000 | 0.996 | 1.004 | 0.869 |
| PP, per 1 pg/mL | 1.006 | 1.000 | 1.013 | 0.056 |
| PYY, per 1 pg/mL | 1.006 | 0.995 | 1.017 | 0.283 |
| Secretin, per 1 pg/mL | 0.996 | 0.986 | 1.007 | 0.487 |
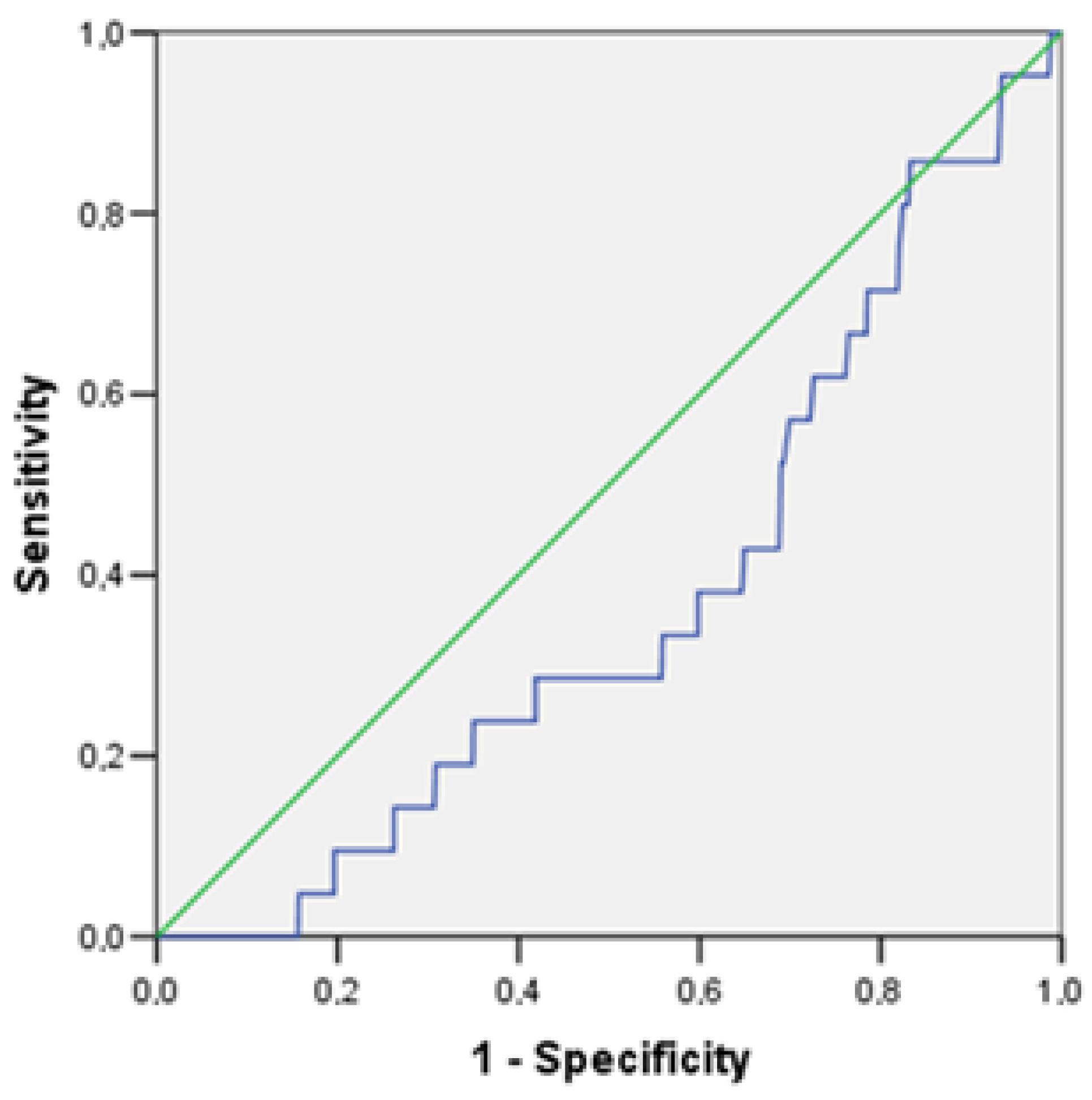
| TNFα, per 1 pg/mL | 0.833 | 0.699 | 0.992 | 0.040 |
| Adiponectin, per 1 mcg/mL | 1.000 | 0.993 | 1.006 | 0.918 |
| Resistin, per 1 mcg/mL | 1.000 | 0.999 | 1.001 | 0.943 |
| Parameters | OR | 95% Confidence Interval (CI) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | |||
| Age, for 1 year | 1.211 | 1.075 | 1.364 | 0.002 |
| Gender, female vs. male | 0.373 | 0.108 | 1.296 | 0.121 |
| DBP, per 1 mm Hg | 1.047 | 1.006 | 1.089 | 0.026 |
| Non-HDL-C, per 1 mmol/L | 1.365 | 0.939 | 1.985 | 0.103 |
| BMI, ≥25 kg/m2 vs. <25 kg/m2 | 0.668 | 0.191 | 2.339 | 0.528 |
| Amylin, per 1 pg/mL | 1.036 | 1.003 | 1.069 | 0.032 |
| PP, per 1 pg/mL | 1.009 | 1.001 | 1.016 | 0.024 |
| TNFα, per 1 pg/mL | 0.808 | 0.669 | 0.975 | 0.026 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khudiakova, A.D.; Polonskaya, Y.V.; Shramko, V.S.; Shcherbakova, L.V.; Garbuzova, E.V.; Kashtanova, E.V.; Ragino, Y.I. Associations of Adipocytokines with The Development of Cardiovascular Events in Young People. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1582. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13111582
Khudiakova AD, Polonskaya YV, Shramko VS, Shcherbakova LV, Garbuzova EV, Kashtanova EV, Ragino YI. Associations of Adipocytokines with The Development of Cardiovascular Events in Young People. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2023; 13(11):1582. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13111582
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhudiakova, Alena D., Yana V. Polonskaya, Victoria S. Shramko, Lilia V. Shcherbakova, Evgeniia V. Garbuzova, Elena V. Kashtanova, and Yulia I. Ragino. 2023. "Associations of Adipocytokines with The Development of Cardiovascular Events in Young People" Journal of Personalized Medicine 13, no. 11: 1582. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13111582
APA StyleKhudiakova, A. D., Polonskaya, Y. V., Shramko, V. S., Shcherbakova, L. V., Garbuzova, E. V., Kashtanova, E. V., & Ragino, Y. I. (2023). Associations of Adipocytokines with The Development of Cardiovascular Events in Young People. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 13(11), 1582. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13111582




.JPG)


