Risk Stratification of Local Flaps and Skin Grafting in Skin Cancer-Related Facial Reconstruction: A Retrospective Single-Center Study of 607 Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Patient Demographics
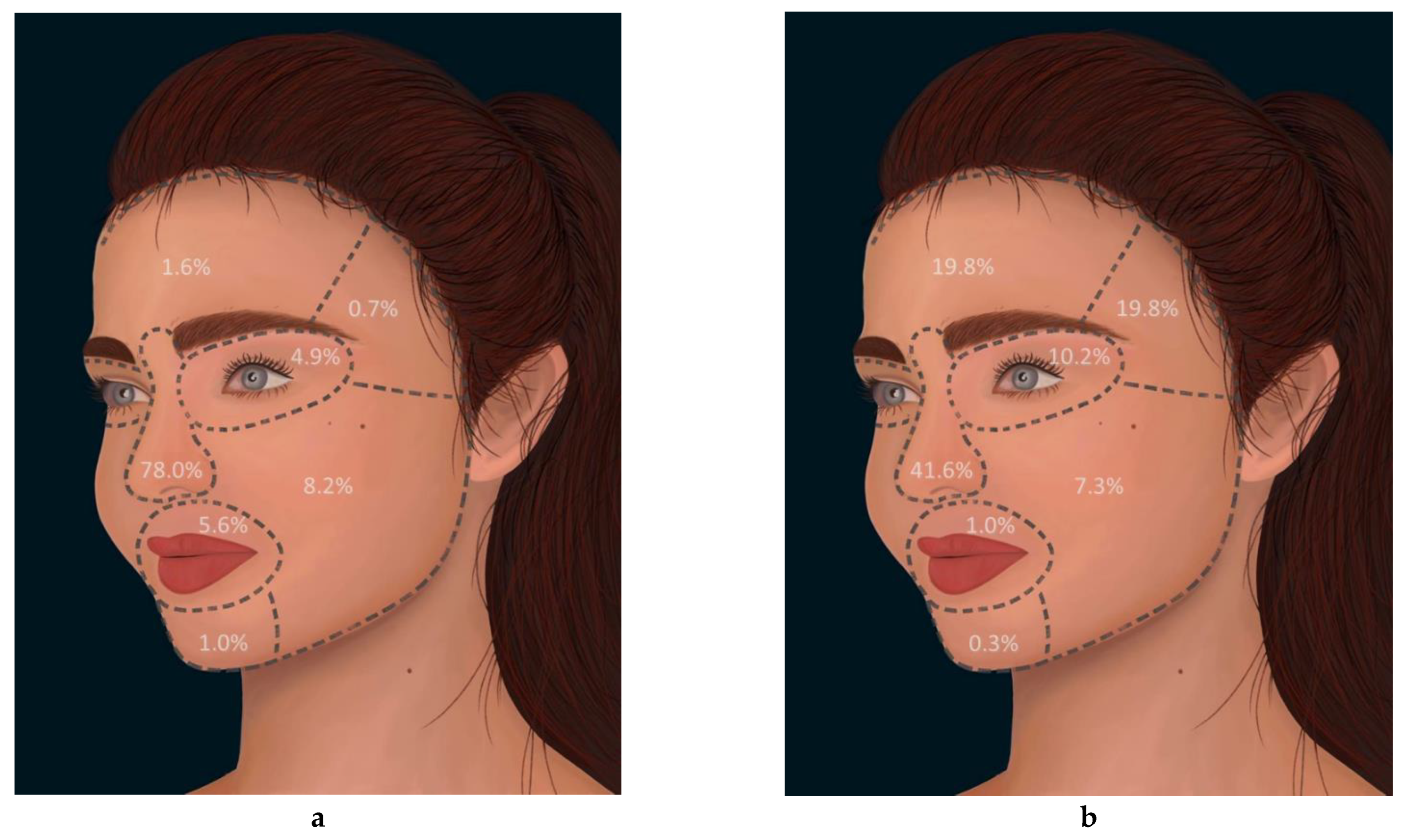
3.2. Facial Distribution of Surgery
3.3. Facial Flap Variability
3.4. Complications
3.4.1. Flap Surgery and FTSG
3.4.2. Flap Type-Associated Complications
3.4.3. Patient Age and Complications
3.4.4. Facial Region and Complications
3.4.5. Complications Related to Patient Demographics and Comorbidities
3.4.6. Tumor Size
3.4.7. Level of Surgical Experience
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lomas:, A.; Leonardi-Bee, J.; Bath-Hextall, F. A systematic review of worldwide incidence of nonmelanoma skin cancer. Br. J. Dermatol. 2012, 166, 1069–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badash, I.; Shauly, O.; Lui, C.G.; Gould, D.J.; Patel, K.M. Nonmelanoma Facial Skin Cancer: A Review of Diagnostic Strategies, Surgical Treatment, and Reconstructive Techniques. Clin. Med. Insights Ear Nose Throat 2019, 12, 117955061986527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Gorgojo, A.; Descalzo-Gallego, M.Á.; Arias-Santiago, S.; Molina-Leyva, A.; Gilaberte, Y.; Fernández-Crehuet, P.; Husein-ElAhmed, H.; Viera-Ramírez, A.; Fernández-Peñas, P.; Taberner, R.; et al. What Proportion of the Caseload at Dermatology Outpatient Clinics in Spain Do Skin Tumors Account for? Results from the DIADERM National Random Sampling Project. Actas Dermo-Sifiliogr. (Engl. Ed. ) 2021, 112, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadevan, K.; Sruthi, S.; Sridevi, S.; Vivek, R. Fourth dimension in reconstruction of defects following excision of basal cell carcinoma of head and neck! J. Cutan. Aesthet. Surg. 2018, 11, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, F.; Linares, M.; Iglesias, M.E.; Martínez-Amo, J.L.; Cabo, F.; Tercedor, J.; Costa-Vieira, R.; Toledo-Pastrana, T.; Ródenas, J.M.; Leis, V. Reconstruction Techniques of Choice for the Facial Cosmetic Units. Actas Dermo-Sifiliogr. (Engl. Ed. ) 2017, 108, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskiizmir, G.; Baker, S.; Cingi, C. Nonmelanoma Skin Cancer of the Head and Neck. Facial Plast. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 20, 493–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsey, M.; Walker, B.; Patel, B. Full Thickness Skin Grafts; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahimi, A.; Ashayeri, M.; Rasouli, H. Comparison of local flaps and skin grafts to repair cheek skin defects. J. Cutan. Aesthet. Surg. 2015, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnabl, S.M.; Breuninger, H.; Iordanou, E.; Scheu, A.; Kofler, L.; Häfner, H.-M.; Eberle, F.C. Patient satisfaction in 1,827 patients following various methods of facial reconstruction based on age, defect size and site: Patient satisfaction after facial reconstruction. JDDG J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2018, 16, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leibovitch, I.; Huilgol, S.C.; Richards, S.; Paver, R.; Selva, D. The Australian Mohs Database: Short-Term Recipient-Site Complications in Full-Thickness Skin Grafts. Derm. Surg 2006, 32, 1364–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keh, S.M.; Giblett, N.; Ahsan, S.F. Through-and-Through Mattress Suturing Versus Tie-Over Dressing in Full-Thickness Skin Graft Reconstruction. Turk. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 55, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, P.; Knabel, P.; Fleischer, A.B. United States burden of melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancer from 1990 to 2019. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 85, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghdassi, S.J.S.; Schröder, C.; Gastmeier, P. Gender-related risk factors for surgical site infections. Results from 10 years of surveillance in Germany. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2019, 8, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rustemeyer, J.; Günther, L.; Bremerich, A. Complications after nasal skin repair with local flaps and full-thickness skin grafts and implications of patients’ contentment. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2009, 13, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erkul, E.; Patel, K.G.; Day, T. Surgical Planning for Resection and Reconstruction of Facial Cutaneous Malignancies. Int. J. Head Neck Surg. 2016, 7, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.S.; Kim, J.O.; Kim, N.G.; Lee, Y.J.; Park, Y.J.; Kim, J.S. A Comparison of the Local Flap and Skin Graft by Location of Face in Reconstruction after Resection of Facial Skin Cancer. Arch. Craniofac. Surg. 2017, 18, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Kim, Y.; Choi, Y. Locoregional flaps versus skin grafts in the nose: Aesthetic considerations after cancer ablation. Arch. Aesthetic. Plast. Surg. 2022, 28, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Term | Definition of the Collected Data |
|---|---|
| BMI | Body mass index measured ≤30 days before surgery. |
| Autoimmune disease | Has an autoimmune diagnosis code in their medical journal. Including the following:
|
| Hypertension | Has the diagnosis code in their medical journal both well-regulated and unregulated? Including the following:
|
| Other cancer | Has a cancer diagnosis or previous cancer diagnosis, and still in follow-up, other than NMSC. |
| Heart disease | Has a heart disease diagnosis code in their medical journal, both well treated and untreated. Including following:
|
| Blood thinners | Take blood thinners regularly. The patients are advised to pause their medication prior to surgery. However, comorbidities may have led to the patients continuing due to the risk of pause. |
| Alcoholic drink | One substance contains 8 g of alcohol. |
| Previous smoker | Quit smoking ≥30 days before the surgery. |
| Infection | Clinically observed and required antibiotic treatment. |
| Cellulitis | Clinically observed. |
| Minor hematoma | No surgical revision required. |
| Major hematoma | Required surgical revision. |
| Edge necrosis | ≤5% of the transplant or flap. |
| Partial necrosis | >5% to 66% of the transplant or flap. |
| Total necrosis | >66.6% of the transplant or flap. |
| Major complication | Hematoma, partial necrosis, total necrosis, wound dehiscence, and infection. |
| FTSG (n) | Flap (n) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | 303 | 304 | |
| Age, (mean [a SD]) | 76.7 (10.1) | 73.4 (10.0) | <0.001 |
| Sex = Male (%) | 161 (53.1) | 144 (47.4) | 0.168 |
| BMI (mean [a SD]) | 26.24 (4.9) | 26.74 (4.8) | 0.263 |
| Autoimmune disease (%) | 31 (10.2) | 27 (8.9) | 0.584 |
| Hypertension (%) | 171 (56.4) | 170 (55.9) | 0.935 |
| Other cancer (%) | 72 (23.8) | 43 (14.1) | 0.003 |
| Diabetes (%) | 40 (13.2) | 42 (13.8) | 0.906 |
| Heart condition (%) | 107 (35.3) | 107 (35.2) | 1.000 |
| Blood thinners (%) | 0.043 | ||
| No | 155 (51.2) | 178 (58.6) | |
| Acetylic Acid | 48 (15.8) | 29 (9.5) | |
| Other blood thinners | 100 (33.0) | 97 (31.9) | |
| b Alcohol (%) | 0.736 | ||
| <7 units per week | 142 (46.9) | 154 (50.7) | |
| 7–14 units per week | 43 (14.2) | 41 (13.5) | |
| >14 units per week | 16 (5.3) | 18 (5.9) | |
| Not reported | 102 (33.7) | 91 (29.9) | |
| Smoking (%) | 0.950 | ||
| No | 127 (41.9) | 124 (40.8) | |
| Active smoker | 40 (13.2) | 39 (12.8) | |
| Former smoker | 56 (18.5) | 62 (20.4) | |
| Not reported | 80 (26.4) | 79 (26.0) |
| Flap Type | Number = n |
|---|---|
| Nasolabial | 90 |
| Hatchet | 5 |
| Frontonasal | 25 |
| Unspecified transposition | 6 |
| Paramedian Forehead | 9 |
| Random | 3 |
| Rhomboid | 35 |
| Unspecified rotation | 14 |
| Shark island | 3 |
| Spear | 3 |
| Bilobed | 58 |
| Trilobed | 4 |
| V-Y | 12 |
| Unspecified | 37 |
| Total | 304 |
| Complication | FTSG | Flaps | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Infection (%) | 25 (8.3) | 28 (9.2) | 0.774 |
| Cellulitis (%) | 7 (2.3) | 5 (1.6) | 0.577 |
| Hematoma (%) | 0.003 | ||
| No | 271 (89.4) | 291 (95.7) | |
| Minor hematoma | 31 (10.2) | 12 (3.9) | |
| Major hematoma | 1 (0.3) | 1 (0.3) | |
| Wound dehiscence (%) | 28 (9.2) | 20 (6.6) | 0.233 |
| Necrosis (%) | <0.001 | ||
| No | 247 (81.5) | 293 (96.4) | |
| Edge necrosis | 11 (3.6) | 9 (3.0) | |
| Partial necrosis | 22 (7.3) | 2 (0.7) | |
| Total necrosis | 23 (7.6) | 0 (0.0) |
| Advancement | Rotation | Transposition | Unspecified | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 15 | 47 | 209 | 33 | |
| Infection (%) | 1 (6.7) | 4 (8.5) | 20 (9.6) | 3 (9.1) | 1.000 |
| Cellulitis (%) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (1.4) | 2 (6.1) | 0.259 |
| Hematoma (%) | 0.436 | ||||
| No | 15 (100.0) | 45 (95.7) | 200 (95.7) | 31 (93.9) | |
| Minor hematoma | 0 (0.0) | 2 (4.3) | 9 (4.3) | 1 (3.0) | |
| Major hematoma | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (3.0) | |
| Wound dehiscence (%) | 1 (6.7) | 2 (4.3) | 15 (7.2) | 2 (6.1) | 0.971 |
| Necrosis (%) | 0.893 | ||||
| No | 15 (100.0) | 45 (95.7) | 200 (95.7) | 33 (100.0) | |
| Edge necrosis | 0 (0.0) | 2 (4.3) | 7 (3.3) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Partial necrosis | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (1.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Total necrosis | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Region | Frontal | Mental | Nasal | Perioral | Periorbital | Temporal | Zygomatic/Buccal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 65 | - | 363 | 20 | 46 | 62 | 47 |
| Risk of partial necrosis, total necrosis, or hematoma | 26.1% | - | 13% | 10.0% | 8.7% | 35.5% | 19.2% |
| Characteristic | Flaps | FTSG | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR 1 | 95% CI 1 | p-Value | OR 1 | 95% CI 1 | p-Value | |
| Age | 1.02 | 0.98, 1.06 | 0.4 | 01.06 | 1.02, 1.11 | 0.007 |
| Sex | ||||||
| Female | — | — | — | — | ||
| Male | 1.33 | 0.60, 2.96 | 0.5 | 3.72 | 1.72, 8.43 | 0.001 |
| BMI | 0.93 | 0.84, 1.02 | 0.12 | 0.96 | 0.88, 1.04 | 0.4 |
| Autoimmune disease | ||||||
| No | — | — | — | — | ||
| Yes | 2.13 | 0.57, 7.20 | 0.2 | 1.90 | 0.60, 5.91 | 0.3 |
| Hypertension | ||||||
| No | — | — | — | — | ||
| Yes | 0.57 | 0.24, 1.37 | 0.2 | 1.92 | 0.80, 4.82 | 0.2 |
| Other cancer | ||||||
| No | — | — | — | — | ||
| Yes | 0.39 | 0.08, 1.42 | 0.2 | 0.87 | 0.36, 2.01 | 0.7 |
| Diabetes | ||||||
| No | — | — | — | — | ||
| Yes | 2.38 | 0.80, 6.86 | 0.11 | 0.54 | 0.18, 1.54 | 0.3 |
| Heart disease | ||||||
| No | — | — | — | — | ||
| Yes | 2.67 | 0.93, 7.97 | 0.071 | 0.59 | 0.23, 1.46 | 0.3 |
| Blood thinners | ||||||
| ASA | — | — | — | — | ||
| Others | 0.46 | 0.11, 2.19 | 0.3 | 0.80 | 0.26, 2.43 | 0.7 |
| No | 0.74 | 0.18, 3.58 | 0.7 | 0.61 | 0.18, 2.05 | 0.4 |
| Flaps | FTSG | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Size of the tumors, mm (median, [IQR]) | 9.0 [6.0, 13.0] | 14.0 [9.0, 20.0] | 10.0 [7.0, 17.0] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mamsen, F.P.W.; Kiilerich, C.H.; Hesselfeldt-Nielsen, J.; Saltvig, I.; Remvig, C.L.-N.; Trøstrup, H.; Schmidt, V.-J. Risk Stratification of Local Flaps and Skin Grafting in Skin Cancer-Related Facial Reconstruction: A Retrospective Single-Center Study of 607 Patients. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 2067. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12122067
Mamsen FPW, Kiilerich CH, Hesselfeldt-Nielsen J, Saltvig I, Remvig CL-N, Trøstrup H, Schmidt V-J. Risk Stratification of Local Flaps and Skin Grafting in Skin Cancer-Related Facial Reconstruction: A Retrospective Single-Center Study of 607 Patients. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(12):2067. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12122067
Chicago/Turabian StyleMamsen, Frederik Penzien Wainer, Claes Hannibal Kiilerich, Jørgen Hesselfeldt-Nielsen, Iselin Saltvig, Celine Lund-Nielsen Remvig, Hannah Trøstrup, and Volker-Jürgen Schmidt. 2022. "Risk Stratification of Local Flaps and Skin Grafting in Skin Cancer-Related Facial Reconstruction: A Retrospective Single-Center Study of 607 Patients" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 12: 2067. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12122067
APA StyleMamsen, F. P. W., Kiilerich, C. H., Hesselfeldt-Nielsen, J., Saltvig, I., Remvig, C. L.-N., Trøstrup, H., & Schmidt, V.-J. (2022). Risk Stratification of Local Flaps and Skin Grafting in Skin Cancer-Related Facial Reconstruction: A Retrospective Single-Center Study of 607 Patients. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(12), 2067. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12122067








