Virtual Surgical Planning, 3D-Printing and Customized Bone Allograft for Acute Correction of Severe Genu Varum in Children
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
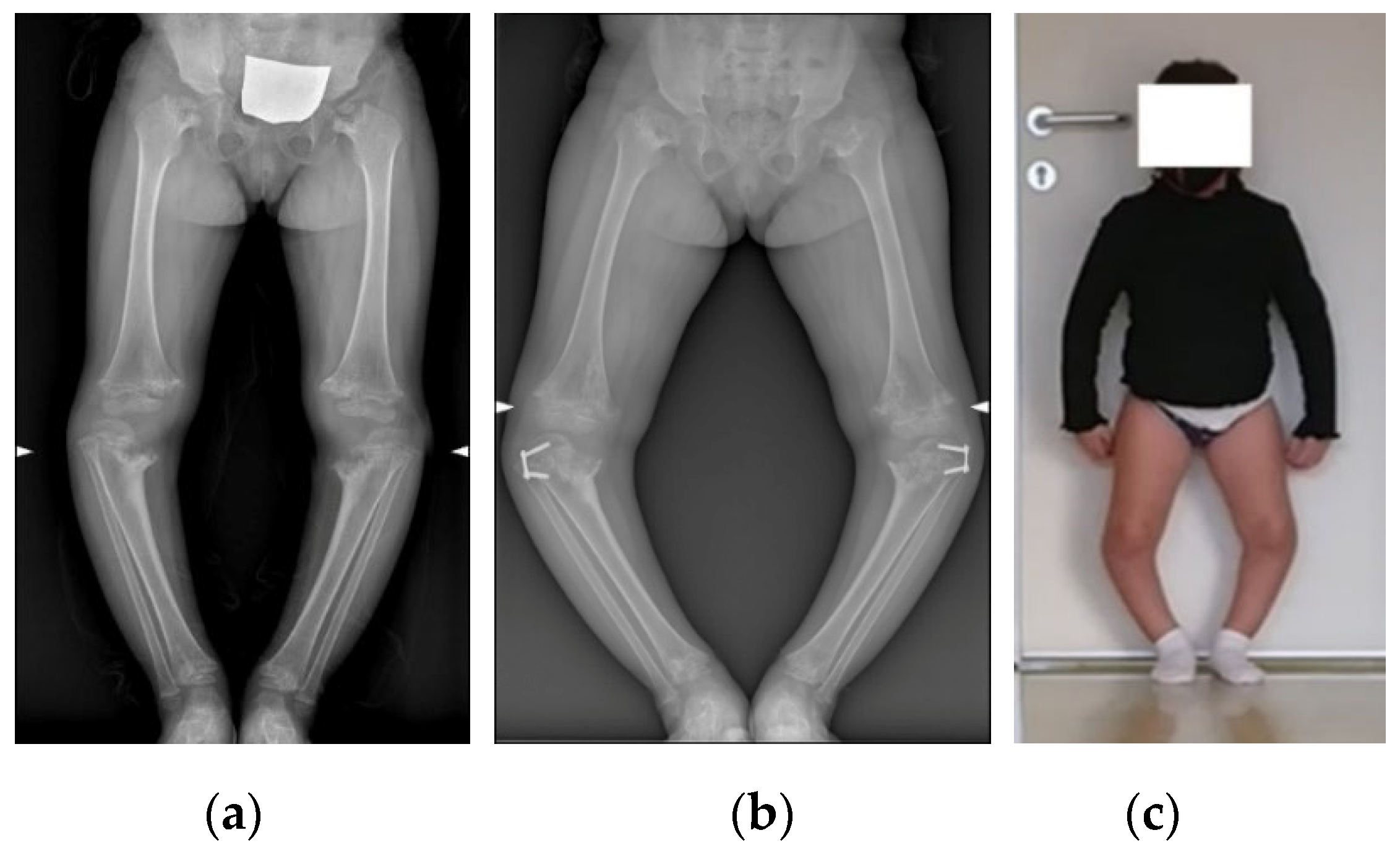
2.1. Case Presentation
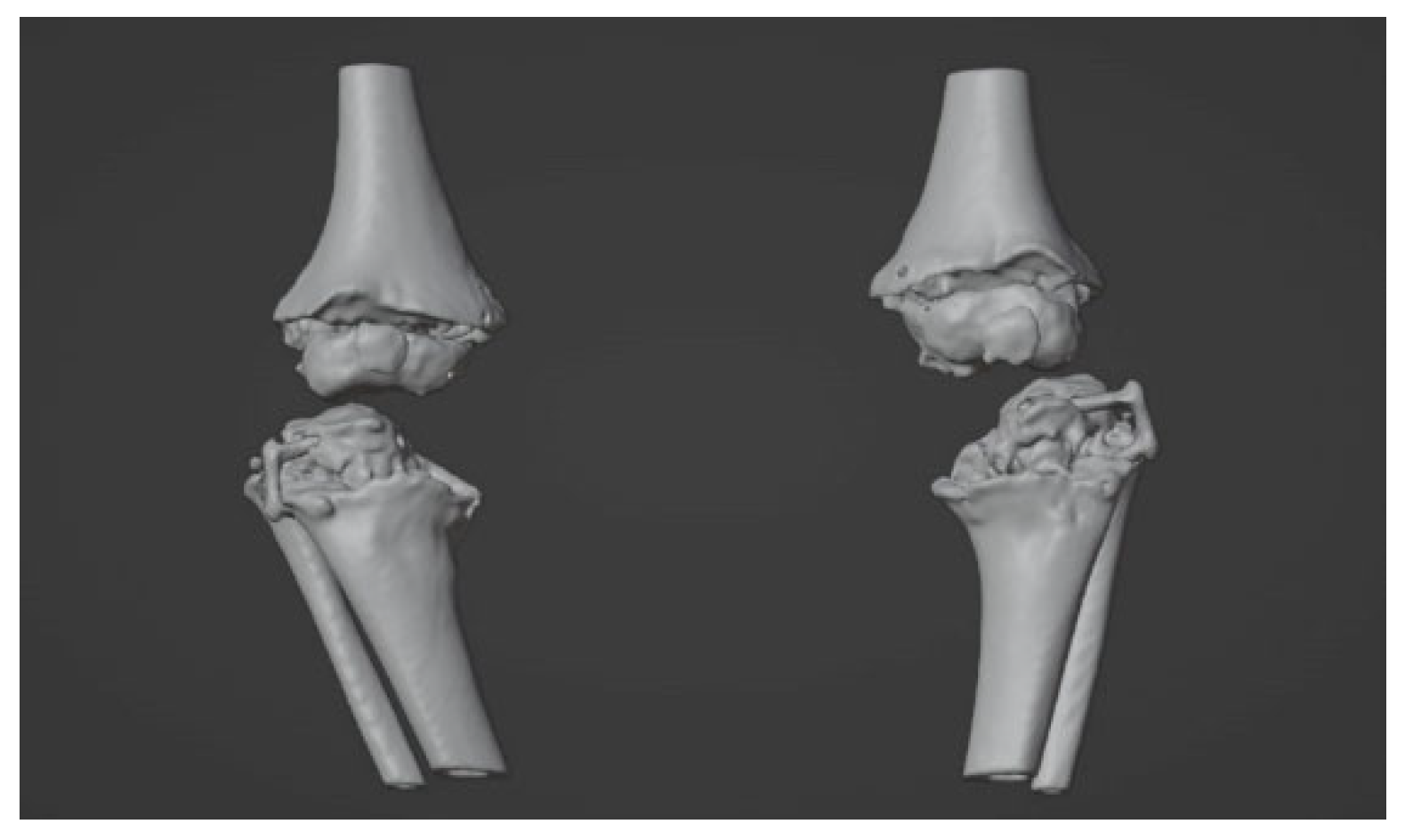
2.2. Image Acquisition and Reconstruction of 3D Model
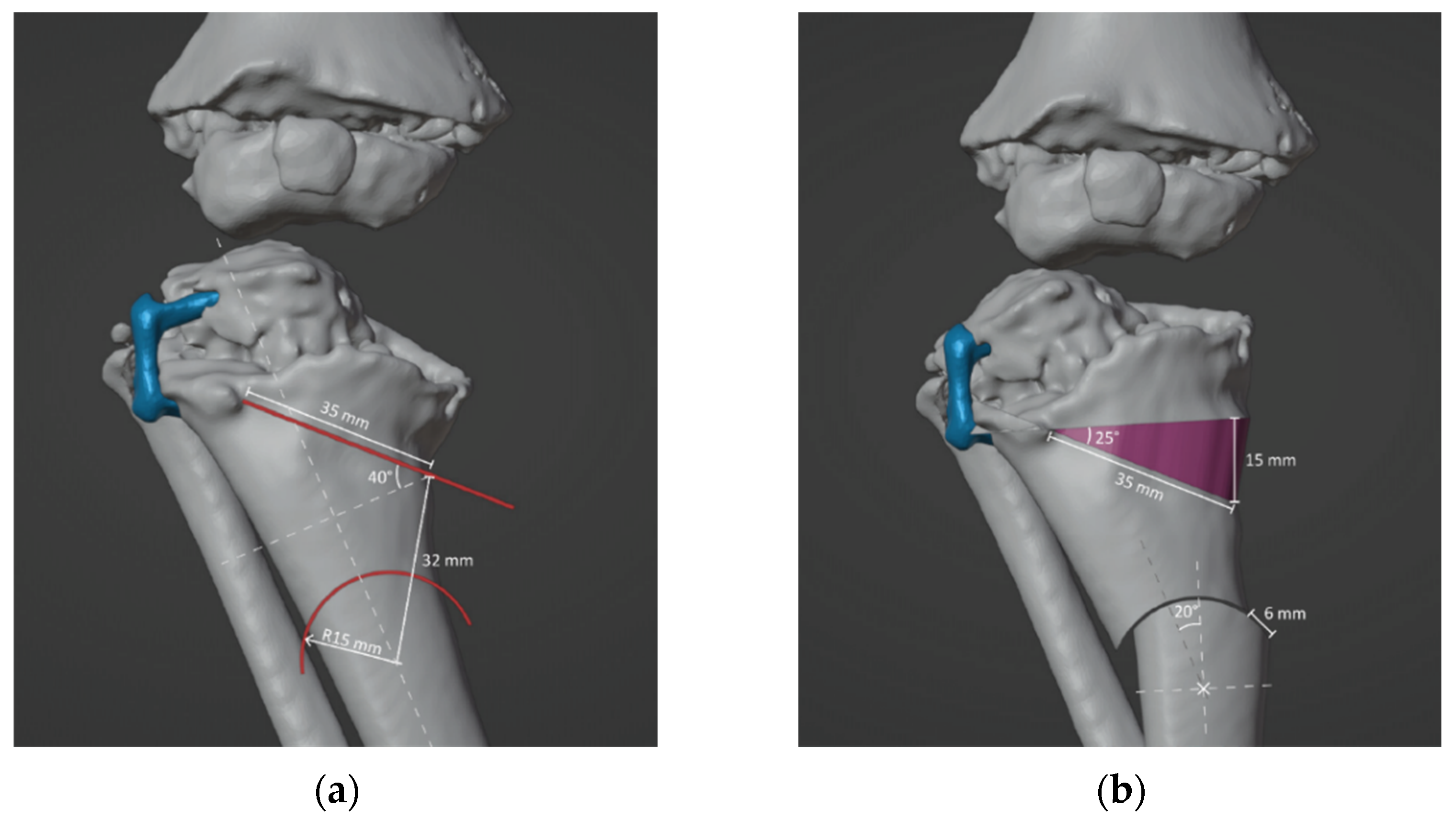
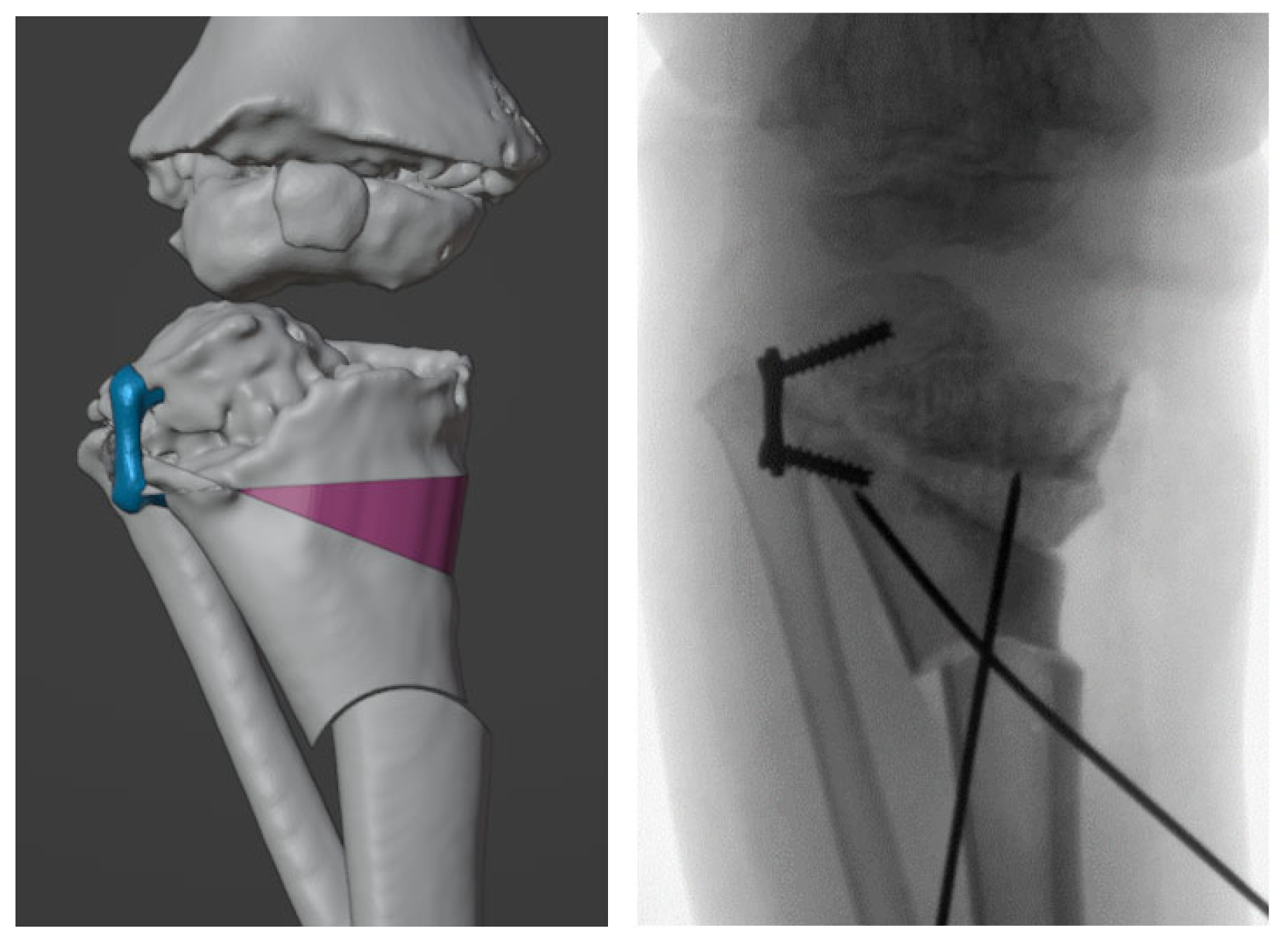
2.3. Surgical Simulation and Planning
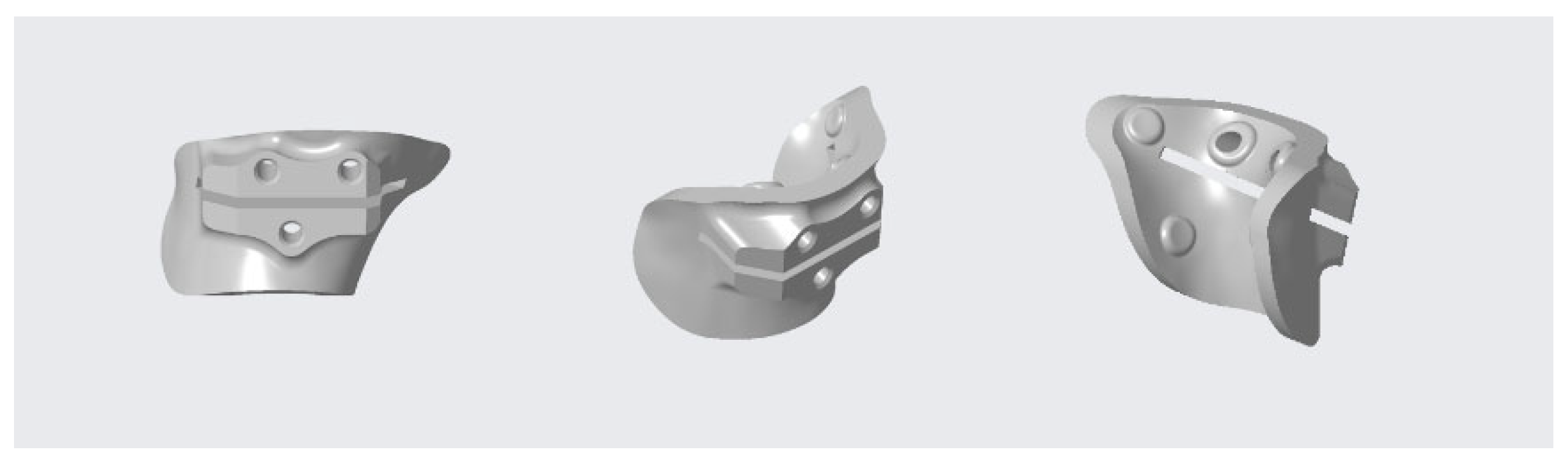
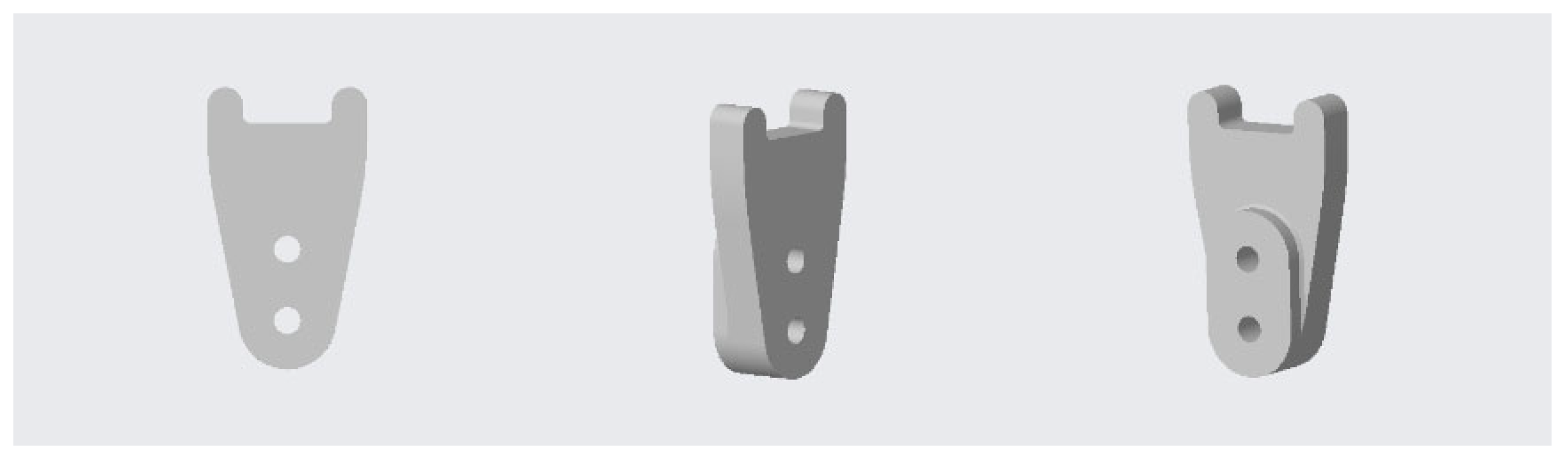
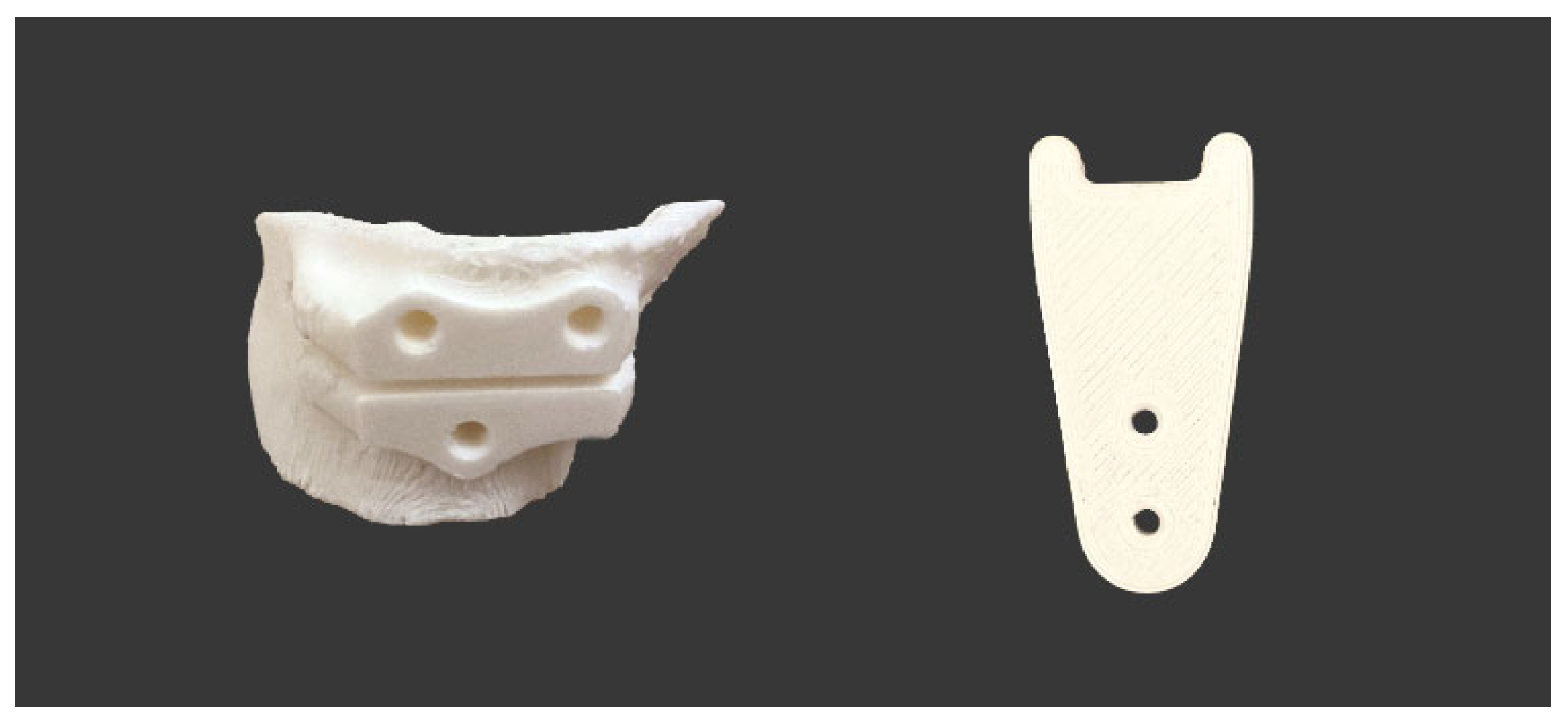
2.4. Design and 3D-printing of the Patient-Specific Surgical Instrument
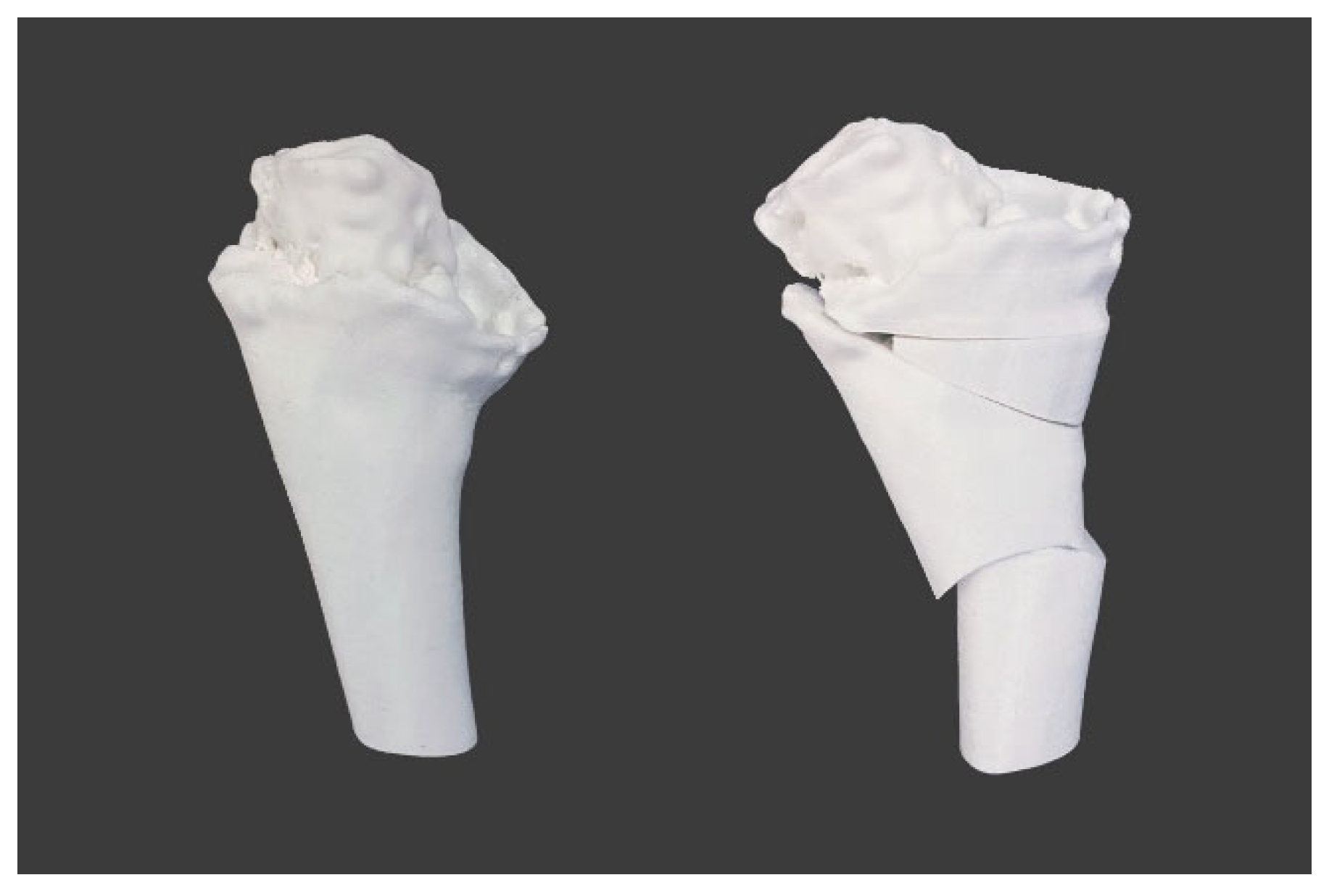
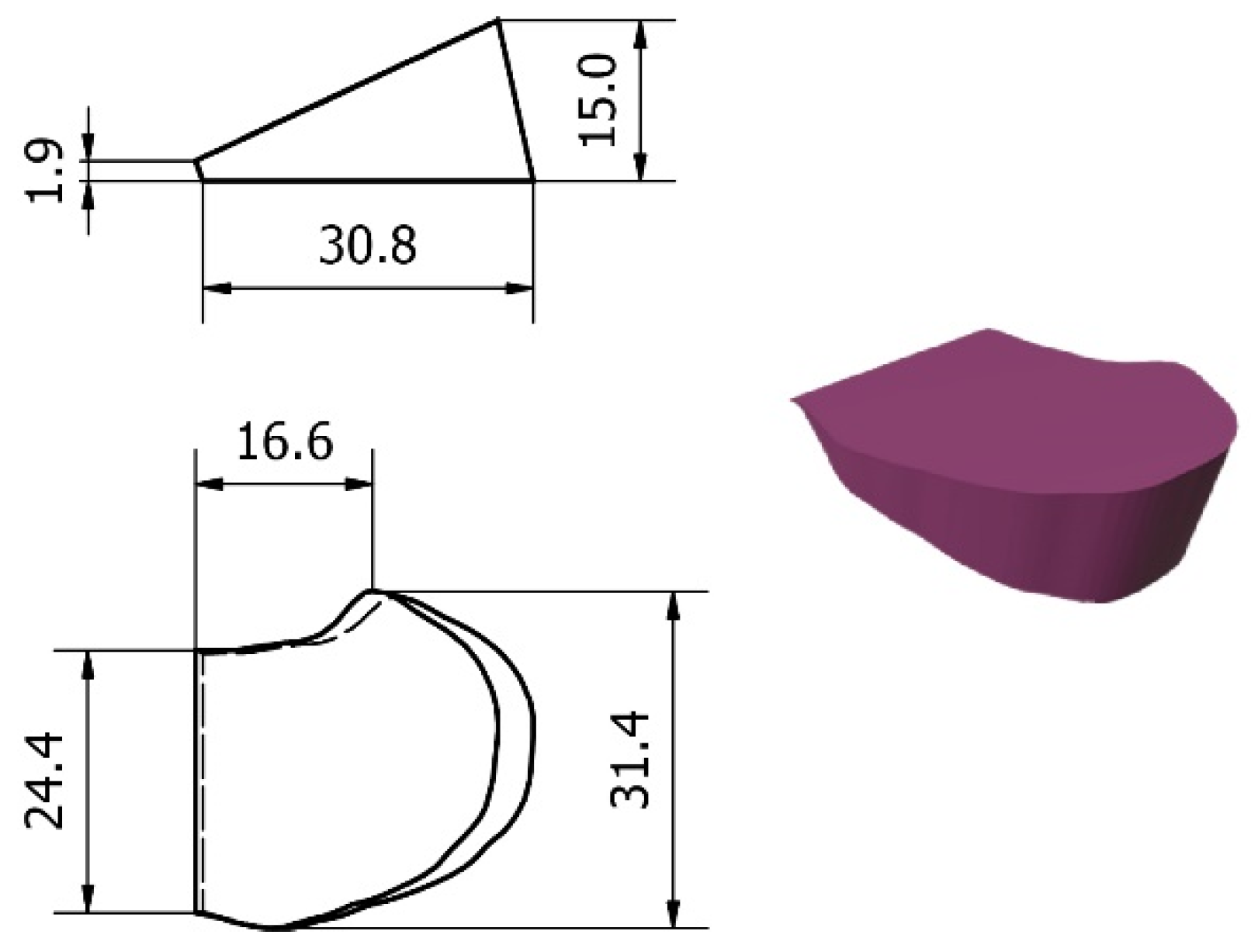
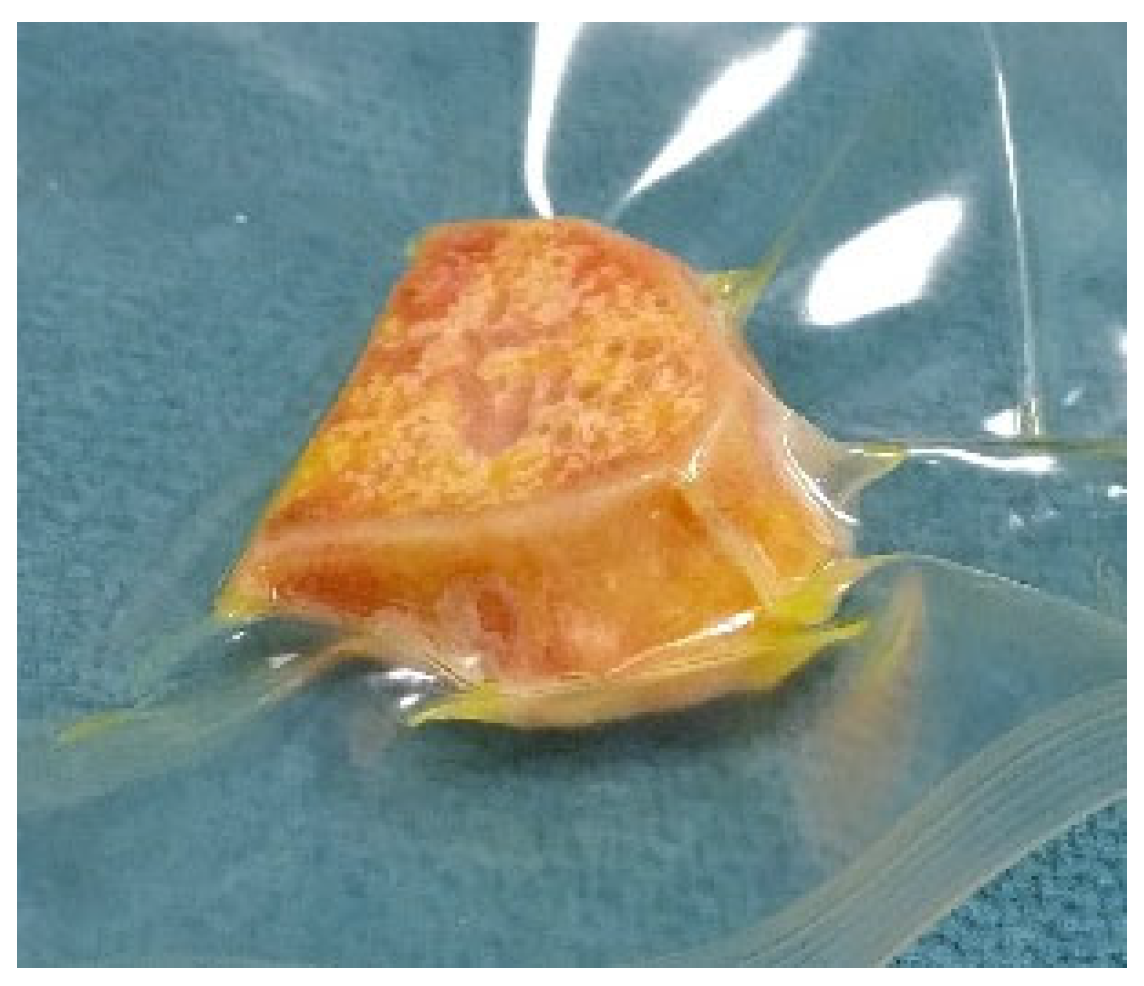
2.5. Design and Processing of the Patient-Specific Bone Allograft
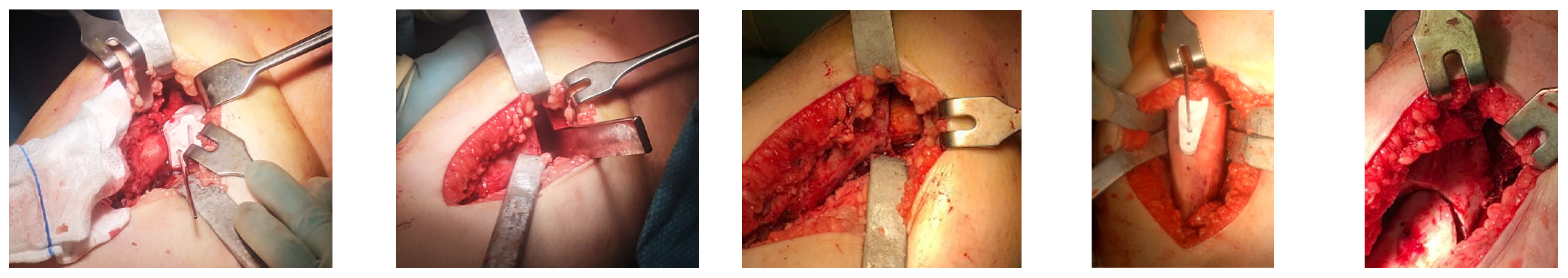
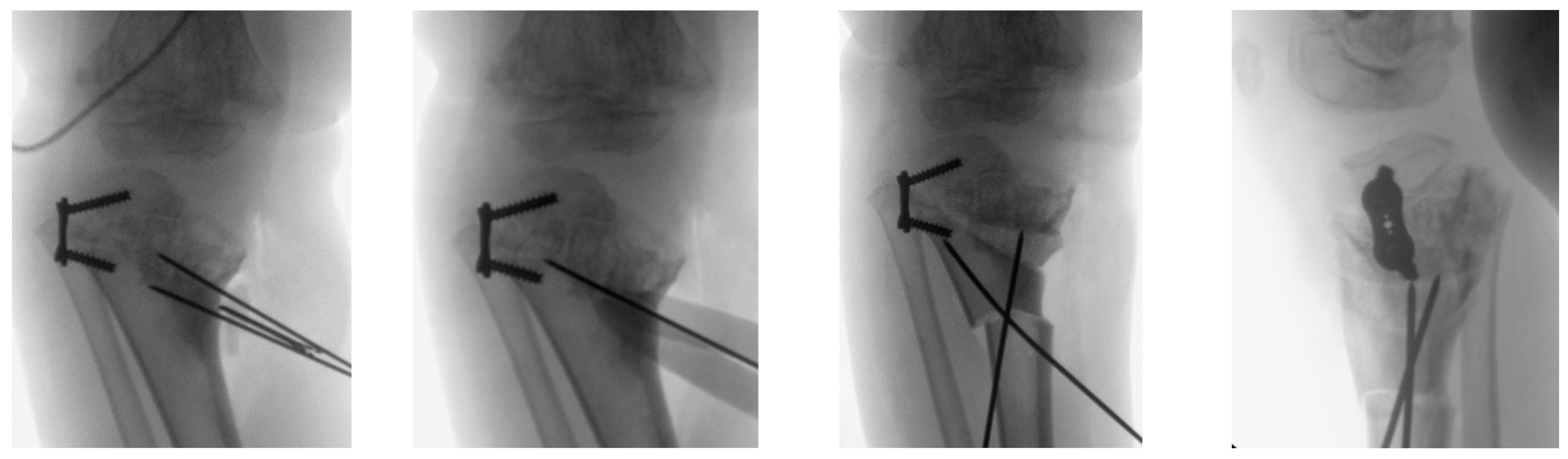
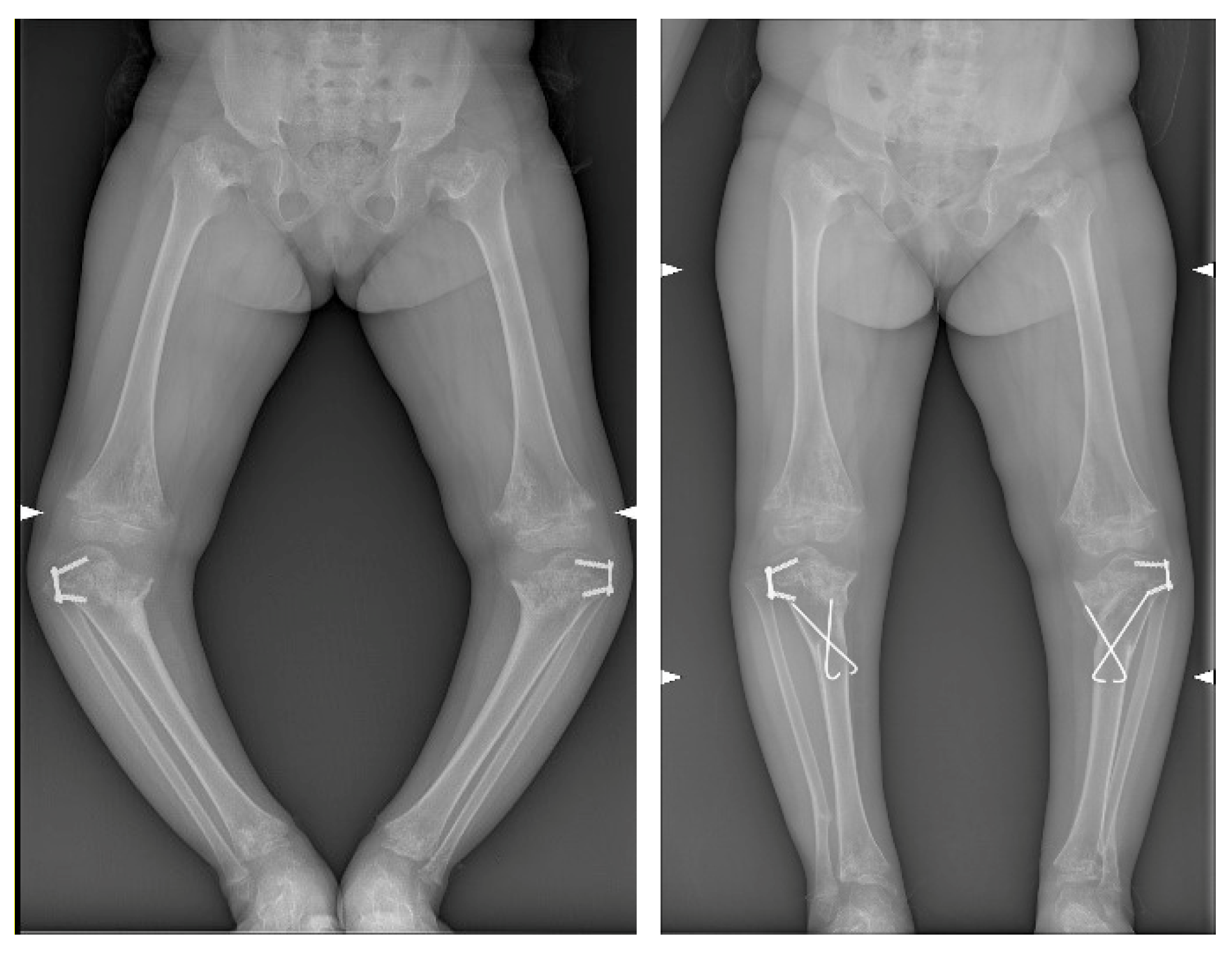
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herring, J.A. Tachdjian’s Pediatric Orthopaedics, 6th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; ISBN 9780323567695. [Google Scholar]
- Michaels, R.; Witsberger, C.A.; Powell, A.R.; Koka, K.; Cohen, K.; Nourmohammadi, Z.; Green, G.E.; Zopf, D.A. 3D Printing in Surgical Simulation: Emphasized Importance in the COVID-19 Pandemic Era. J. 3D Print. Med. 2021, 5, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauel, L.; Valls-Esteve, A.; Tejo-Otero, A.; Fenollosa-Artés, F. 3D-Printing in Surgery: Beyond Bone Structures. A Review. Ann. 3D Print. Med. 2021, 4, 100039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee AK, X.; Lin, T.L.; Hsu, C.J.; Fong, Y.C.; Chen, H.T.; Tsai, C.H. Three-Dimensional Printing and Fracture Mapping in Pelvic and Acetabular Fractures: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Zhou, P.; He, C. Clinical Efficacy and Safety of Surgery Combined with 3D Printing for Tibial Plateau Fractures: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2022, 10, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aman, Z.S.; DePhillipo, N.N.; Peebles, L.A.; Familiari, F.; LaPrade, R.F.; Dekker, T.J. Improved Accuracy of Coronal Alignment Can Be Attained Using 3D-Printed Patient-Specific Instrumentation for Knee Osteotomies: A Systematic Review of Level III and IV Studies. Arthroscopy 2022, 38, 2741–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girolami, M.; Boriani, S.; Bandiera, S.; Barbanti-Bródano, G.; Ghermandi, R.; Terzi, S.; Tedesco, G.; Evangelisti, G.; Pipola, V.; Gasbarrini, A. Biomimetic 3D-Printed Custom-Made Prosthesis for Anterior Column Reconstruction in the Thoracolumbar Spine: A Tailored Option Following En Bloc Resection for Spinal Tumors. Eur. Spine J. 2018, 27, 3073–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paolis, M.; Sambri, A.; Zucchini, R.; Frisoni, T.; Spazzoli, B.; Taddei, F.; Donati, D.M. Custom-Made 3D-Printed Prosthesis in Periacetabular Resections Through a Novel Ileo-Adductor Approach. Orthopedics 2022, 45, e110–e114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, G.; Benedetti, M.G.; Paolis, M.; De Sambri, A.; Frisoni, T.; Leardini, A.; Donati, D.M.; Taddei, F. Long-Term Functional Recovery in Patients with Custom-Made 3D-Printed Anatomical Pelvic Prostheses Following Bone Tumor Excision. Gait Posture 2022, 97, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.; Murphy, D.; Gelfer, Y. The Effect of Three-Dimensional (3D) Printing on Quantitative and Qualitative Outcomes in Paediatric Orthopaedic Osteotomies: A Systematic Review. EFORT Open Rev. 2021, 6, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, N.; Massaad, E.; Shankar, G.M.; Shin, J.H. Structural Allograft versus Polyetheretherketone Implants in Patients Undergoing Spinal Fusion Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2020, 136, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivarelli, L.; Govoni, M.; Attala, D.; Zoccali, C.; Biagini, R.; Dallari, D. Custom Massive Allograft in a Case of Pelvic Bone Tumour: Simulation of Processing with Computerised Numerical Control vs. Robotic Machining. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delloye, C.; Cornu, O.; Druez, V.; Barbier, O. Bone allografts: What they can offer and what they cannot. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2007, 89, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, L.; Docquier, P.L.; Cartiaux, O.; Cornu, O.; Delloye, C.; Banse, X. Selection of Massive Bone Allografts Using Shape-Matching 3-Dimensional Registration. Acta Orthop. 2010, 81, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, P.L.; Mericli, A.F.; Largo, R.D.; Garvey, P.B. Computer-Aided Design and Manufacturing versus Conventional Surgical Planning for Head and Neck Reconstruction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2021, 148, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Mo, S.; Fan, X.; You, Y.; Ye, G.; Zhou, N. A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review Comparing the Effectiveness of Traditional and Virtual Surgical Planning for Orthognathic Surgery: Based on Randomized Clinical Trials. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 79, 471.e1–471.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papotto, G.; Testa, G.; Mobilia, G.; Perez, S.; Dimartino, S.; Giardina, S.M.C.; Sessa, G.; Pavone, V. Use of 3D Printing and Pre-Contouring Plate in the Surgical Planning of Acetabular Fractures: A Systematic Review. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2022, 108, 103111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, F.R.; Grassi, R.; Vivarelli, L.; Dallari, D.; Govoni, M.; Nardi, G.M.; Kalemaj, Z.; Ballini, A. Design Techniques to Optimize the Scaffold Performance: Freeze-Dried Bone Custom-Made Allografts for Maxillary Alveolar Horizontal Ridge Augmentation. Materials 2020, 6, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frizziero, L.; Trisolino, G.; Santi, G.M.; Alessandri, G.; Agazzani, S.; Liverani, A.; Menozzi, G.C.; Di Gennaro, G.L.; Farella, G.M.G.; Abbruzzese, A.; et al. Computer-Aided Surgical Simulation through Digital Dynamic 3D Skeletal Segments for Correcting Torsional Deformities of the Lower Limbs in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Mou, X. Image Quality Guided Iterative Reconstruction for Low-Dose CT Based on CT Image Statistics. Phys. Med. Biol. 2021, 66, 185018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, Y.; Kaga, T.; Kawai, N.; Miyoshi, T.; Kawada, H.; Hyodo, F.; Kambadakone, A.; Matsuo, M. Low-Dose Whole-Body CT Using Deep Learning Image Reconstruction: Image Quality and Lesion Detection. Br. J. Radiol. 2021, 94, 20201329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zheng, H.; Liang, D.; Hu, Z. Low-Dose CT Reconstruction Method Based on Prior Information of Normal-Dose Image. J. Xray. Sci. Technol. 2020, 28, 1091–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorov, A.; Beichel, R.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Finet, J.; Fillion-Robin, J.C.; Pujol, S.; Bauer, C.; Jennings, D.; Fennessy, F.; Sonka, M.; et al. 3D Slicer as an Image Computing Platform for the Quantitative Imaging Network. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 30, 1323–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frizziero, L.; Santi, G.M.; Liverani, A.; Giuseppetti, V.; Trisolino, G.; Maredi, E.; Stilli, S. Paediatric Orthopaedic Surgery with 3D Printing: Improvements and Cost Reduction. Symmetry 2019, 11, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frizziero, L.; Liverani, A.; Donnici, G.; Osti, F.; Neri, M.; Maredi, E.; Trisolino, G.; Stilli, S. New Methodology for Diagnosis of Orthopedic Diseases through Additive Manufacturing Models. Symmetry 2019, 11, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- blender.com Blender.Org- Home of the Blender Project- Free and Open 3D Creation Software. Available online: https://www.blender.org/ (accessed on 30 November 2022).
- van Huyssteen, A.L.; Hastings, C.J.; Olesak, M.; Hoffman, E.B. Double-Elevating Osteotomy for Late-Presenting Infantile Blount’s Disease: The Importance of Concomitant Lateral Epiphysiodesis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2005, 87, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, E.; Toby, D.; Welborn, M.C.; Helder, C.W.; Murphy, A. New Single-Stage Double Osteotomy for Late-Presenting Infantile Tibia Vara: A Comprehensive Approach. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2019, 39, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, J.J.; MacIntyre, N.R.; Hooks, B.; Davidson, R.S. Double Osteotomy for the Treatment of Severe Blount Disease. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2009, 29, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraka, M.M.; Hefny, H.M.; Mahran, M.A.; Fayyad, T.A.; Abdelazim, H.; Nabil, A. Single-Stage Medial Plateau Elevation and Metaphyseal Osteotomies in Advanced-Stage Blount’s Disease: A New Technique. J. Child. Orthop. 2021, 15, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osti, F.; Santi, G.; Neri, M.; Liverani, A.; Frizziero, L.; Stilli, S.; Maredi, E.; Zarantonello, P.; Gallone, G.; Stallone, S.; et al. CT Conversion Workflow for Intraoperative Usage of Bony Models: From DICOM Data to 3D Printed Models. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frizziero, L.; Santi, G.M.; Leon-Cardenas, C.; Ferretti, P.; Sali, M.; Gianese, F.; Crescentini, N.; Donnici, G.; Liverani, A.; Trisolino, G.; et al. Heat Sterilization Effects on Polymeric, FDM-Optimized Orthopedic Cutting Guide for Surgical Procedures. J. Funct. Biomater. 2021, 12, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, P.; Leon-Cardenas, C.; Santi, G.M.; Sali, M.; Ciotti, E.; Frizziero, L.; Donnici, G.; Liverani, A. Relationship between Fdm 3d Printing Parameters Study: Parameter Optimization for Lower Defects. Polymers 2021, 13, 2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzotti, A.; Arceri, A.; Zielli, S.; Bonelli, S.; Viglione, V.; Faldini, C. Patient-Specific Instrumentation in Total Ankle Arthroplasty. World J. Orthop. 2022, 13, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amelio, A.; Van Lieshout, E.M.M.; Wakker, A.M.; Verhofstad, M.H.J.; Van Vledder, M.G. 3D-Printed Patient Specific Instruments for Corrective Osteotomies of the Lower Extremity. Injury 2022, 53 (Suppl. S3), S53–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.H.; Samuel, L.T.; Acuña, A.J.; Kamath, A.F. Patient-Specific High Tibial Osteotomy for Varus Malalignment: 3D-Printed Plating Technique and Review of the Literature. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2022, 32, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Home|BTM. Available online: https://btm.ior.it/ (accessed on 29 November 2022).
- Bennardo, F.; Antonelli, A.; Ostas, D.; Almăs, O.; Iles, R.R.; Andrei, V.; Thieringer, F.M.; Hedes, M.; Rotar, H. Point-of-Care Virtual Surgical Planning and 3D Printing in Oral and Cranio-Maxillofacial Surgery: A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sananta, P.; Santoso, J.; Sugiarto, M.A. Osteotomy Treatments and Post-Operative Fixations for Blount Disease: A Systematic Review. Ann. Med. Surg. 2022, 78, 103784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Greunen, E.; Firth, G.B. Recurrence in Infantile Tibia Vara (Blount Disease) after High Tibia and Fibula Osteotomy. J. Pediatr. Orthop. B 2022, 31, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mare, P.H.; Marais, L.C. Gradual Deformity Correction with a Computer-Assisted Hexapod External Fixator in Blount’s Disease. Strateg. Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2022, 17, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Printing (Nozzle) Temperature | 200 °C |
| Heated Bed Temperature | 60 °C |
| Nozzle Diameter | 0.4 mm |
| Layer Thickness | 0.2 mm |
| Printing Speed | 60 mm/s |
| Infill Density | 100 (%) |
| Flow | 100 (%) |
| Support | Yes |
| Material | FiloAlfa® PLA |
| MAD | aTFA | FC-TS Angle | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| preop | postop | preop | postop | preop | postop | |
| right | −100 mm | −39 mm | −45° | −3° | 49° | 86° |
| left | −100 mm | −51 mm | −44° | −15° | 55° | 72° |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alessandri, G.; Frizziero, L.; Santi, G.M.; Liverani, A.; Dallari, D.; Vivarelli, L.; Di Gennaro, G.L.; Antonioli, D.; Menozzi, G.C.; Depaoli, A.; et al. Virtual Surgical Planning, 3D-Printing and Customized Bone Allograft for Acute Correction of Severe Genu Varum in Children. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12122051
Alessandri G, Frizziero L, Santi GM, Liverani A, Dallari D, Vivarelli L, Di Gennaro GL, Antonioli D, Menozzi GC, Depaoli A, et al. Virtual Surgical Planning, 3D-Printing and Customized Bone Allograft for Acute Correction of Severe Genu Varum in Children. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(12):2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12122051
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlessandri, Giulia, Leonardo Frizziero, Gian Maria Santi, Alfredo Liverani, Dante Dallari, Leonardo Vivarelli, Giovanni Luigi Di Gennaro, Diego Antonioli, Grazia Chiara Menozzi, Alessandro Depaoli, and et al. 2022. "Virtual Surgical Planning, 3D-Printing and Customized Bone Allograft for Acute Correction of Severe Genu Varum in Children" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 12: 2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12122051
APA StyleAlessandri, G., Frizziero, L., Santi, G. M., Liverani, A., Dallari, D., Vivarelli, L., Di Gennaro, G. L., Antonioli, D., Menozzi, G. C., Depaoli, A., Rocca, G., & Trisolino, G. (2022). Virtual Surgical Planning, 3D-Printing and Customized Bone Allograft for Acute Correction of Severe Genu Varum in Children. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(12), 2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12122051











