Cross-Cultural Validation of the Short Version of the Questionnaire of Olfactory Disorders—Negative Statements into Italian: Towards Personalized Patient Care
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Damm, M.; Temmel, A.; Welge-Lüssen, A.; Eckel, H.E.; Kreft, M.-P.; Klussmann, J.P.; Gudziol, H.; Hüttenbrink, K.-B.; Hummel, T. Olfactory dysfunctions. Epidemiology and therapy in Germany, Austria and Switzerland. HNO 2004, 52, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mott, A.E.; Leopold, D.A. Disorders in Taste and Smell. Med. Clin. N. Am. 1991, 75, 1321–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cullen, M.M.; Leopold, D.A. Disorders of Smell and Taste. Med. Clin. N. Am. 1999, 83, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkes, C.H.; Shephard, B.C.; E Daniel, S. Olfactory dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1997, 62, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Úbeda-Bañón, I.; Saiz-Sanchez, D.; Flores-Cuadrado, A.; Rioja-Corroto, E.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, M.; Villar-Conde, S.; Astillero-Lopez, V.; Cabello-De La Rosa, J.P.; Gallardo-Alcañiz, M.J.; Vaamonde-Gamo, J.; et al. The human olfactory system in two proteinopathies: Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Transl. Neurodegener. 2020, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercante, G.; Ferreli, F.; de Virgilio, A.; Gaino, F.; di Bari, M.; Colombo, G.; Russo, E.; Costantino, A.; Pirola, F.; Cugini, G. Prevalence of Taste and Smell Dysfunction in Coronavirus Disease 2019. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2020, 146, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitcroft, K.L.; Hummel, T. Olfactory Dysfunction in COVID-19: Diagnosis and Management. JAMA 2020, 323, 2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedaghat, A.R.; Gengler, I.; Speth, M.M. Olfactory Dysfunction: A Highly Prevalent Symptom of COVID-19 with Public Health Significance. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2020, 163, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ascanio, L.; Pandolfini, M.; Cingolani, C.; Latini, G.; Gradoni, P.; Capalbo, M.; Frausini, G.; Maranzano, M.; Brenner, M.J.; Di Stadio, A. Olfactory Dysfunction in COVID-19 Patients: Prevalence and Prognosis for Recovering Sense of Smell. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2020, 164, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiardini, I.; Paoletti, G.; Mariani, A.; Malvezzi, L.; Pirola, F.; Spriano, G.; Mercante, G.; Puggioni, F.; Racca, F.; Melone, G.; et al. Nasal Polyposis Quality of Life (NPQ): Development and Validation of the First Specific Quality of Life Questionnaire for Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps. Healthcare 2022, 10, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philpott, C.; Boak, D. The Impact of Olfactory Disorders in the United Kingdom. Chem. Senses 2014, 39, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Corso, E.; Bilò, M.B.; Matucci, A.; Seccia, V.; Braido, F.; Gelardi, M.; Heffler, E.; Latorre, M.; Malvezzi, L.; Pelaia, G.; et al. Personalized Management of Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps in Clinical Practice: A Multidisciplinary Consensus Statement. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seccia, V.; D’Amato, M.; Scioscia, G.; Bagnasco, D.; Di Marco, F.; Fadda, G.; Menzella, F.; Pasquini, E.; Pelaia, G.; Tremante, E.; et al. Management of Patients with Severe Asthma and Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps: A Multidisciplinary Shared Approach. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardi, C.; Asero, R.; Bagnasco, D.; Blasi, F.; Bonini, M.; Bussi, M.; Canevari, R.F.; Canonica, G.W.; Castelnuovo, P.; Cecchi, L.; et al. ARIA-ITALY multidisciplinary consensus on nasal polyposis and biological treatments. World Allergy Organ. J. 2021, 14, 100592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Wei, J.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Jin, X.; Chaib, L. Psychometric validity of the 22-item Sinonasal Outcome Test. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2009, 34, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.G.; Oh, J.-H.; Na Choi, H.; Park, S.Y. Simple assessment of olfaction in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2015, 135, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frasnelli, J.; Hummel, T. Olfactory dysfunction and daily life. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2004, 262, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattos, J.L.; Schlosser, R.J.; DeConde, A.S.; Hyer, M.; Mace, J.C.; Smith, T.L.; Soler, Z.M. Factor analysis of the questionnaire of olfactory disorders in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2018, 8, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillemin, F.; Bombardier, C.; Beaton, D. Cross-cultural adaptation of health-related quality of life measures: Literature review and proposed guidelines. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1993, 46, 1417–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iavarone, A.; The Working Group; Mazzi, M.C.; Russo, G.; D’Anna, F.; Peluso, S.; Mazzeo, P.; De Luca, V.; De Michele, G.; Iaccarino, G.; et al. The Italian version of the quick mild cognitive impairment (Qmci-I) screen: Normative study on 307 healthy subjects. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2018, 31, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjelland, I.; Dahl, A.A.; Haug, T.T.; Neckelmann, D. The validity of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale The validity of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale. An updated literature review. J. Psychosom. Res. 2002, 52, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechien, J.R.; Chiesa-Estomba, C.M.; De Siati, D.R.; Horoi, M.; Le Bon, S.D.; Rodriguez, A.; Dequanter, D.; Blecic, S.; El Afia, F.; Distinguin, L.; et al. Olfactory and gustatory dysfunctions as a clinical presentation of mild-to-moderate forms of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19): A multicenter European study. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2020, 277, 2251–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puxeddu, I.; Petrelli, F.; Cristofani-Mencacci, L.; Scarano, M.; Latorre, M.; De Rosa, A.; Dallan, I.; Manca, M.L.; Berrettini, S.; Migliorini, P.; et al. Component-Resolved Diagnosis for Endotyping Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2022, 183, 770–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattos, J.L.; Ba, C.E.; Schlosser, R.J.; Hyer, M.; Mace, J.C.; Smith, T.L.; Soler, Z.M. A brief version of the questionnaire of olfactory disorders in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2019, 9, 1144–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiesa-Estomba, C.M.; Lechien, J.R.; Calvo-Henríquez, C.; Mayo, M.; Maldonado, B.; Maza, J.; Tucciarone, M.; Villareal, I.; Vaira, L.A.; Izquierdo-Dominguez, A.; et al. Translation and validation of the short version of the Questionnaire of Olfactory Disorders–Negative Statements to Spanish. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2020, 42, 102775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leclercq, C.; Chiesa-Estomba, C.M.; Horoi, M.; Le Bon, S.D.; Hans, S.; Distinguin, L.; Chekkoury-Idrissi, Y.; Circiu, M.P.; Khalife, M.; Saussez, S.; et al. Validity and reliability of the french short version of the questionnaire of olfactory disorders-negative statements (sQOD-NS). Ear Nose Throat J. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alobid, I.; Benitez, P.; Bernal-Sprekelsen, M.; Roca, J.; Alonso, J.; Picado, C.; Mullol, J. Nasal polyposis and its impact on quality of life: Comparison between the effects of medical and surgical treatments. Allergy 2005, 60, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brämerson, A.; Nordin, S.; Bende, M. Clinical experience with patients with olfactory complaints, and their quality of life. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2007, 127, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Kang, T.W.; Kim, K.R.; Jang, D.P.; Kim, I.Y.; Cho, S.H. Altered Quality of Life and Psychological Health (SCL-90-R) in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2015, 124, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valsamidis, K.; Printza, A.; Titelis, K.; Constantinidis, J.; Triaridis, S. Olfaction and quality of life in patients with nasal septal deviation treated with septoplasty. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2019, 40, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akay, H.G.; Muluk, N.B.; Inal, M.; Simsek, G.; Kiliç, R. Evaluation of Olfactory Sensation, Acoustic Rhinometry, and Quality of Life of the Patients with Nasal Septal Deviation. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2019, 30, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haytoğlu, S.; Dengiz, R.; Muluk, N.B.; Kuran, G.; Arikan, O.K. Effects of Septoplasty on Olfactory Function Evaluated by the Brief Smell Identification Test: A Study of 116 Patients. Ear Nose Throat J. 2017, 96, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philpott, C.M.; Wolstenholme, C.R.; Goodenough, P.C.; Clark, A.; Murty, G.E. Comparison of Subjective Perception with Objective Measurement of Olfaction. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2006, 134, 488–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, D.H.; Reiter, E.R.; Budd, S.G.; Shin, Y.; Kons, Z.A.; Costanzo, R.M. Quality of life and safety impact of COVID-19 asso-ciated smell and taste disturbances. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2021, 42, 103001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmquist, E.; Larsson, M.; Olofsson, J.K.; Seubert, J.; Bäckman, L.; Laukka, E.J. A Prospective Study on Risk Factors for Olfactory Dysfunction in Aging. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2019, 75, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

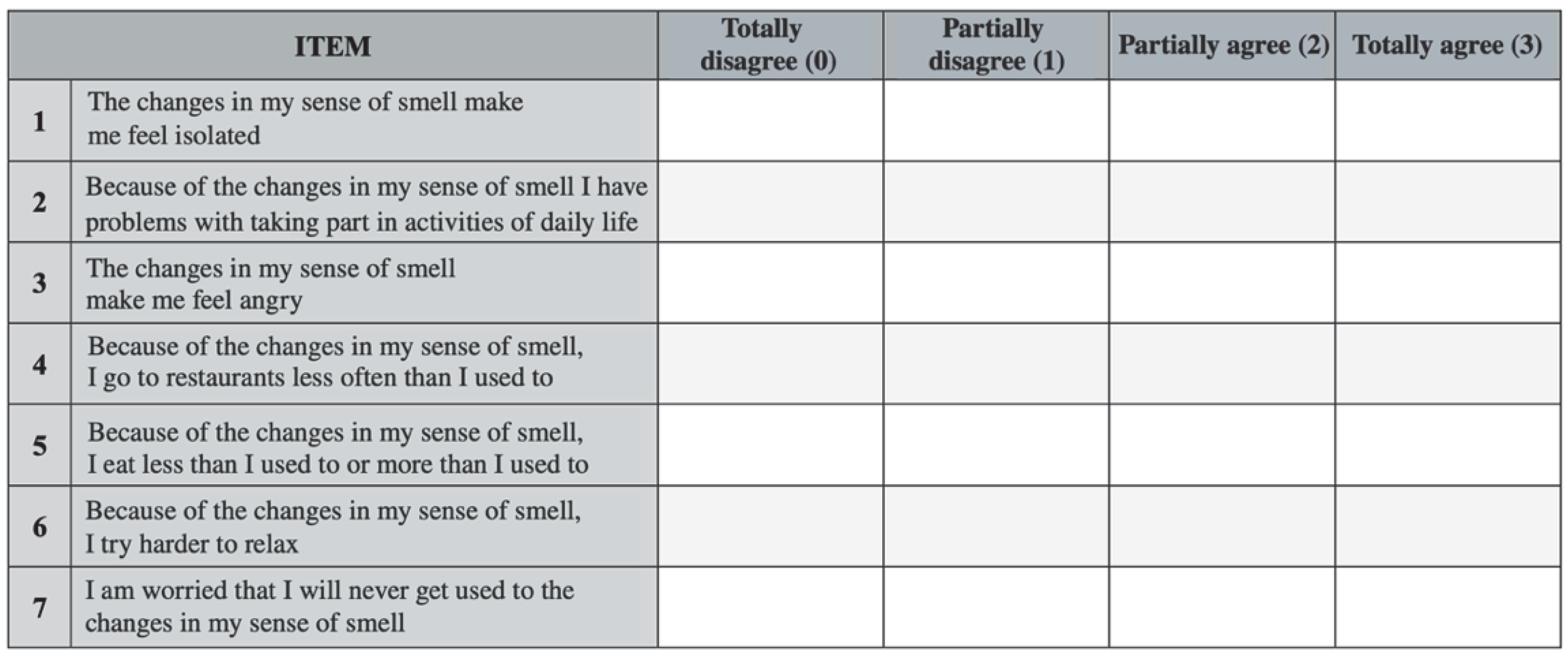

| Cases | Controls | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | females (%) | 21 (42) | 26 (52) |
| males (%) | 29 (58) | 24 (48) | |
| Age | mean ± sd | 44.1 ± 13.9 | 43.0 ± 15.1 |
| Disease | CRSwNP (%) | 25 (50) | / |
| septal deviation (%) | 25 (50) | / | |
| NPS | mean ± sd | 4.7 ± 2.3 | / |
| Comorbidities | asthma (%) | 13 (26) | 4 (8) |
| allergy (%) | 22 (44) | 6 (12) | |
| Smoking | yes (%) | 10 (20) | 12 (24) |
| no (%) | 40 (80) | 38 (76) |
| Timepoint | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Questionnaire | T0 (±sd) | T1 (±sd) | T2 (±sd) |
| ITA svQOD-NS | 8.58 ± 5.70 | 2.33 ± 3.11 | 1.49 ± 1.72 |
| SNOT-22 | 46.46 ± 19.11 | 19.42 ± 12.63 | 10.88 ± 8.12 |
| VAS | 6.10 ± 3.10 | 2.02 ± 2.56 | 0.98 ± 1.12 |
| HADS | 9.32 ± 6.92 | 6.02 ± 6.29 | 3.86 ± 3.31 |
| ITEM of the ITA svQOD-NS | Item-to-Total Correlation | Cronbach’s α if Item Deleted |
|---|---|---|
| item#1 | 0.646 | 0.922 |
| item#2 | 0.780 | 0.909 |
| item#3 | 0.789 | 0.908 |
| item#4 | 0.767 | 0.911 |
| item#5 | 0.744 | 0.913 |
| item#6 | 0.850 | 0.902 |
| item#7 | 0.757 | 0.913 |
| ITA svQOD-NS | Cases + Controls | CRSwNP | Septal Deviation | Healthy Controls |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| item#1 | 0.96 ± 1.05 | 1.45 ± 1.06 | 0.43 ± 0.34 | 0.04 ± 0.03 |
| item#2 | 1.61 ± 1.11 | 2.18 ± 0.80 | 0.97 ± 0.76 | 0.06 ± 0.04 |
| item#3 | 1.43 ± 1.17 | 2.00 ± 0.99 | 0.83 ± 0.73 | 0.08 ± 0.05 |
| item#4 | 0.70 ± 1.00 | 1.18 ± 1.14 | 0.19 ± 0.14 | 0.02 ± 0.02 |
| item#5 | 0.86 ± 1.08 | 1.34 ± 1.10 | 0.35 ± 0.29 | 0.02 ± 0.01 |
| item#6 | 1.39 ± 1.16 | 1.92 ± 1.00 | 0.81 ± 0.67 | 0.06 ± 0.04 |
| item#7 | 1.54 ± 1.13 | 2.16 ± 0.92 | 0.95 ± 0.81 | 0.08 ± 0.05 |
| TOTAL | 4.47 ± 5.80 | 12.23 ± 5.31 | 4.53 ± 4.34 | 0.37 ± 0.32 |
| ITA svQOD-NS | Score Difference | 95%CI | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| in CRSwNP | vs. SD | +7.7 | 3.82–8.75 | <0.001 |
| vs. Controls | +11.86 | 9.26–13.62 | <0.001 | |
| in SD | vs. Controls | +4.16 | 3.06–7.34 | <0.001 |
| Questionnaire | Difference of the Means (±sd) | 95%CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| ITA svQOD-NS | |||
| T0 vs. T1 | 6.14 ± 5.28 | 4.64–7.64 | <0.001 |
| T1 vs. T2 | 0.84 ± 1.41 | 0.44–1.24 | <0.001 |
| T0 vs. T2 | 6.98 ± 5.27 | 5.48–8.48 | <0.001 |
| SNOT-22 | |||
| T0 vs. T1 | 27.04 ± 17.90 | 21.95–32.12 | <0.001 |
| T1 vs. T2 | 8.54 ± 7.73 | 6.34–10.74 | <0.001 |
| T0 vs. T2 | 35.58 ± 18.58 | 30.30–40.86 | <0.001 |
| VAS | |||
| T0 vs. T1 | 4.08 ± 3.15 | 3.19–4.97 | <0.001 |
| T1 vs. T2 | 1.04 ± 1.47 | 0.62–1.46 | <0.001 |
| T0 vs. T2 | 5.12 ± 2.90 | 4.29–5.95 | <0.001 |
| HADS | |||
| T0 vs. T1 | 3.30 ± 5.40 | 1.77–4.83 | <0.001 |
| T1 vs. T2 | 2.16 ± 2.35 | 1.49–2.83 | <0.001 |
| T0 vs. T2 | 5.46 ± 5.20 | 3.98–6.94 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pirola, F.; Giombi, F.; Ferreli, F.; Costantino, A.; Mercante, G.; Paoletti, G.; Heffler, E.; Canonica, G.W.; Settimi, S.; De Corso, E.; et al. Cross-Cultural Validation of the Short Version of the Questionnaire of Olfactory Disorders—Negative Statements into Italian: Towards Personalized Patient Care. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 2010. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12122010
Pirola F, Giombi F, Ferreli F, Costantino A, Mercante G, Paoletti G, Heffler E, Canonica GW, Settimi S, De Corso E, et al. Cross-Cultural Validation of the Short Version of the Questionnaire of Olfactory Disorders—Negative Statements into Italian: Towards Personalized Patient Care. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(12):2010. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12122010
Chicago/Turabian StylePirola, Francesca, Francesco Giombi, Fabio Ferreli, Andrea Costantino, Giuseppe Mercante, Giovanni Paoletti, Enrico Heffler, Giorgio Walter Canonica, Stefano Settimi, Eugenio De Corso, and et al. 2022. "Cross-Cultural Validation of the Short Version of the Questionnaire of Olfactory Disorders—Negative Statements into Italian: Towards Personalized Patient Care" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 12: 2010. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12122010
APA StylePirola, F., Giombi, F., Ferreli, F., Costantino, A., Mercante, G., Paoletti, G., Heffler, E., Canonica, G. W., Settimi, S., De Corso, E., Spriano, G., & Malvezzi, L. (2022). Cross-Cultural Validation of the Short Version of the Questionnaire of Olfactory Disorders—Negative Statements into Italian: Towards Personalized Patient Care. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(12), 2010. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12122010












