Diagnostic Accuracy of Methods for Detection of Antibodies against Type I Interferons in Patients with Endocrine Disorders
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients, Healthy Donors and Serum Samples
- -
- Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 2, n = 38;
- -
- Autoimmune thyropathies (autoimmune thyroiditis (AIT) and Graves’ disease), n = 23;
- -
- Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1D)/latent autoimmune diabetes in adults (LADA), n = 21;
- -
- Hypergonadotropic hypogonadism (HH) of autoimmune origin, n = 4;
- -
- Autoimmune adrenal insufficiency (AAI), n = 3.
- -
- Non-autoimmune thyroid diseases, n = 5;
- -
- Non-autoimmune diabetes, n = 5;
- -
- Non-autoimmune HH, n = 6;
- -
- Non-autoimmune adrenal insufficiency (AI), n = 17;
- -
- Non-autoimmune pathology of the parathyroid glands, n = 6;
- -
- Multiple endocrine pathology of non-autoimmune origin, n = 32.
2.2. Microarray-Based Assay
2.3. Anti-IFN-ω Cell-Based Autoantibody Assay
2.4. Anti-IFN-α Autoantibodies ELISA
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Autoantibodies against IFN-I among APS-1 Patients
3.2. Anti-IFN-I Autoantibodies among Control Groups
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meager, A.; Visvalingam, K.; Peterson, P.; Möll, K.; Murumägi, A.; Krohn, K.; Eskelin, P.; Perheentupa, J.; Husebye, E.; Kadota, Y.; et al. Anti-interferon autoantibodies in autoimmune polyendocrinopathy syndrome type 1. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, 1152–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Barker, J.M.; Babu, S.; Su, M.; Stenerson, M.; Cheng, M.; Shum, A.; Zamir, E.; Badolato, R.; Law, A.; et al. A robust immunoassay for anti-interferon autoantibodies that is highly specific for patients with autoimmune polyglandular syndrome type 1. Clin. Immunol. 2007, 125, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meloni, A.; Furcas, M.; Cetani, F.; Marcocci, C.; Falorni, A.; Perniola, R.; Pura, M.; Bøe Wolff, A.S.; Husebye, E.S.; Lilic, D.; et al. Autoantibodies against type I interferons as an additional diagnostic criterion for autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type I. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 4389–4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meager, A.; Wadhwa, M.; Dilger, P.; Bird, C.; Thorpe, R.; Newsom-Davis, J.; Willcox, N. Anti-cytokine autoantibodies in autoimmunity: Preponderance of neutralizing autoantibodies against interferon-alpha, interferon-omega and interleukin-12 in patients with thymoma and/or myasthenia gravis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2003, 132, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Tatouli, I.P.; Rosen, L.B.; Hasni, S.; Alevizos, I.; Manna, Z.G.; Rivera, J.; Jiang, C.; Siegel, R.M.; Holland, S.M.; et al. Distinct functions of autoantibodies against interferon in systemic lupus erythematosus: A comprehensive analysis of anticytokine autoantibodies in common rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 1677–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burbelo, P.D.; Browne, S.; Holland, S.M.; Iadarola, M.J.; Alevizos, I. Clinical features of Sjögren’s syndrome patients with autoantibodies against interferons. Clin. Transl. Med. 2019, 8, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bastard, P.; Rosen, L.B.; Zhang, Q.; Michailidis, E.; Hoffmann, H.H.; Zhang, Y.; Dorgham, K.; Philippot, Q.; Rosain, J.; Béziat, V.; et al. Autoantibodies against type I IFNs in patients with life-threatening COVID-19. Science 2020, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastard, P.; Michailidis, E.; Hoffmann, H.H.; Chbihi, M.; Le Voyer, T.; Rosain, J.; Philippot, Q.; Seeleuthner, Y.; Gervais, A.; Materna, M.; et al. Auto-antibodies to type I IFNs can underlie adverse reactions to yellow fever live attenuated vaccine. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 218, e20202486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastard, P.; Gervais, A.; Le Voyer, T.; Rosain, J.; Philippot, Q.; Manry, J.; Michailidis, E.; Hoffmann, H.-H.; Eto, S.; Garcia-Prat, M.; et al. Autoantibodies neutralizing type I IFNs are present in ~4% of uninfected individuals over 70 years old and account for ~20% of COVID-19 deaths. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, eabl4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troya, J.; Bastard, P.; Casanova, J.L.; Abel, L.; Pujol, A. Low lymphocytes and IFN-neutralizing autoantibodies as biomarkers of COVID-19 mortality. J. Clin. Immunol. 2022, 42, 738–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savvateeva, E.; Filippova, M.; Valuev-Elliston, V.; Nuralieva, N.; Yukina, M.; Troshina, E.; Baklaushev, V.; Ivanov, A.; Gryadunov, D. Microarray-based detection of antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 proteins, common respiratory viruses and type I interferons. Viruses 2021, 13, 2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schidlowski, L.; Iwamura, A.P.D.; Condino-Neto, A.; Prando, C. Diagnosis of APS-1 in two siblings following life-threatening COVID-19 pneumonia. J. Clin. Immunol. 2022, 42, 749–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisand, K.; Link, M.; Wolff, A.S.B.; Meager, A.; Tserel, L.; Org, T.; Murumägi, A.; Uibo, R.; Willcox, N.; Podkrajšek, K.T.; et al. Interferon autoantibodies associated with AIRE deficiency decrease the expression of IFN-stimulated genes. Blood 2008, 112, 2657–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puel, A.; Bastard, P.; Bustamante, J.; Casanova, J.L. Human autoantibodies underlying infectious diseases. J. Exp. Med. 2022, 219, e20211387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjøgren, T.; Bratland, E.; Røyrvik, E.C.; Grytaas, M.A.; Benneche, A.; Knappskog, P.M.; Kämpe, O.; Oftedal, B.E.; Husebye, E.S.; Wolff, A.S.B. Screening patients with autoimmune endocrine disorders for cytokine autoantibodies reveals monogenic immune deficiencies. J. Autoimmun. 2022, 133, 102917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oftedal, B.E.; Bøe Wolff, A.S.; Bratland, E.; Kämpe, O.; Perheentupa, J.; Myhre, A.G.; Meager, A.; Purushothaman, R.; Ten, S.; Husebye, E.S. Radioimmunoassay for autoantibodies against interferon omega; its use in the diagnosis of autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type I. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 129, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Mo, A.; Jutivorakool, K.; Pancholi, M.; Holland, S.M.; Browne, S.K. Determination of human anticytokine autoantibody profiles using a particle-based approach. J. Clin. Immunol. 2012, 32, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, J.M.; Price, J.V.; Barcenas-Morales, G.; Ceron-Gutierrez, L.; Davies, S.; Kumararatne, D.S.; Döffinger, R.; Utz, P.J. Protein microarrays identify disease-specific anti-cytokine autoantibody profiles in the landscape of immunodeficiency. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 204–213.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breivik, L.; Oftedal, B.E.V.; Bøe Wolff, A.S.; Bratland, E.; Orlova, E.M.; Husebye, E.S. A novel cell-based assay for measuring neutralizing autoantibodies against type I interferons in patients with autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 153, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlova, E.M.; Sozaeva, L.S.; Karmanov, M.E.; Breivik, L.E.; Husebye, E.S.; Kareva, M.A. The new immunological methods for diagnostics of type 1 autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome (the first experience in Russia). Probl. Endocrinol. 2015, 61, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sozaeva, L.S. The new immunological methods for diagnostics of type 1 autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome. Probl. Endocrinol. 2015, 61, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Savvateeva, E.N.; Yukina, M.Y.; Nuralieva, N.F.; Filippova, M.A.; Gryadunov, D.A.; Troshina, E.A. Multiplex autoantibody detection in patients with autoimmune polyglandular syndromes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervato, S.; Morlin, L.; Albergoni, M.P.; Masiero, S.; Greggio, N.; Meossi, C.; Chen, S.; Del Pilar Larosa, M.; Furmaniak, J.; Rees Smith, B.; et al. AIRE gene mutations and autoantibodies to interferon omega in patients with chronic hypoparathyroidism without APECED. Clin. Endocrinol. 2010, 73, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antonelli, G.; Currenti, M.; Turriziani, O.; Dianzani, F. Neutralizing antibodies to interferon-α: Relative frequency in patients treated with different interferon preparations. J. Infect. Dis. 1991, 163, 882–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, G.; Simeoni, E.; Currenti, M.; De Pisa, F.; Colizzi, V.; Pistello, M.; Dianzani, F. Interferon antibodies in patients with infectious diseases. Biotherapy 1997, 10, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.J.; Leung, P.S.C.; Zhang, W.; Ma, X.; Gershwin, M.E. The immunobiology and clinical features of type 1 autoimmune polyglandular syndrome (APS-1). Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlova, E.M.; Sozaeva, L.S.; Kareva, M.A.; Oftedal, B.E.; Wolff, A.S.B.; Breivik, L.; Zakharova, E.Y.; Ivanova, O.N.; Kämpe, O.; Dedov, I.I.; et al. Expanding the phenotypic and genotypic landscape of autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 3546–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
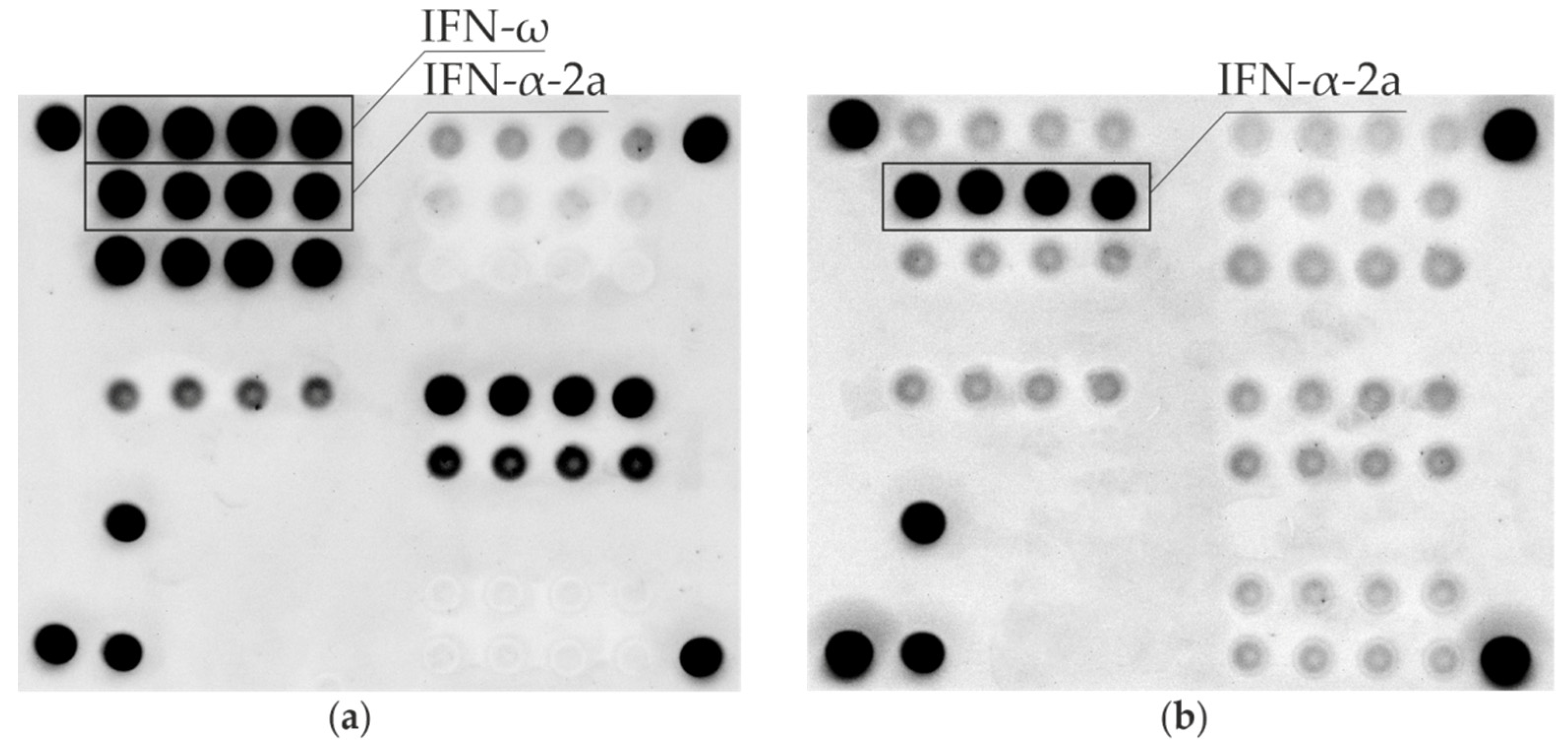
| Sample # | Age | Gender | AIRE Mutations | APS-1 Components | Anti-IFN-ω Auto-Abs | Anti-IFN-α Auto-Abs | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Endocrine | Non-Endocrine | |||||||||||||
| AAI * | Hypoparathyroidism | TD1/LADA | AIT | HH | CMC | Other pathology | Microarray | CBAA | Microarray | ELISA | ||||
| 3 | 49 | m | R257X/R257X | + | + | − | - | - | + | − | + | + | + | n/a |
| 49 | 20 | f | R257X/R257X | + | + | − | + | + | + | Malabsorption syndrome, tooth enamel hypoplasia, total alopecia, vitiligo | + | + | + | + |
| 51 | 18 | f | R257X/- | + | + | − | − | + | + | − | + | + | + | + |
| 64 | 29 | f | p.R257 */p.W78R | + | + | − | − | + | + | Atrophic gastritis, cataract | + | + | + | + |
| 103 | 18 | f | R257X/R257X | + | + | − | − | + | + | Atrophic gastritis, cataract | + | + | + | + |
| 115 | 30 | f | R257X/R257X | + | + | + | + | − | + | Total alopecia, atrophic gastritis | + | + | + | + |
| 124 | 18 | m | R257X/A58V | + | − | − | − | − | + | B12 deficiency anemia, malabsorption syndrome, tooth enamel hypoplasia, spleen hypoplasia | + | + | + | + |
| 125 | 45 | f | not studied | + | + | - | + | − | + | Atrophic gastroduodenitis, vitiligo, cataract, corneal dystrophy | + | + | + | + |
| 129 | 45 | m | not studied | + | + | − | − | − | + | Alopecia areata | + | + | + | + |
| 133 | 27 | m | − | + | + | − | + | − | + | Autoimmune fibrosing alveolitis, total alopecia | + | n/a | + | + |
| 135 | 30 | f | R257X/R257X | + | + | − | − | + | + | Vitiligo, malabsorption syndrome, corneal dystrophy, partial eyelid ptosis, asplenia, atrophic gastroduodenitis, autoimmune hepatitis | + | − | + | + |
| 136 | 28 | f | R257X/c.931delT | + | + | − | − | + | + | Corneal dystrophy, atrophic gastritis | + | + | + | + |
| 152 | 27 | f | R257X/- | + | + | − | − | + | + | Subtotal alopecia, tooth enamel dysplasia, chronic tubulointerstitial nephritis | + | + | + | + |
| 156 | 36 | m | not studied | + | + | − | − | − | + | − | + | + | + | + |
| 168 | 32 | f | R257X/R257X | + | + | − | − | + | + | Diffuse alopecia, vitiligo | + | + | + | + |
| 189 | 31 | f | R257X/R257X | + | + | − | − | + | + | Atrophic gastroduodenitis, malabsorption syndrome, tooth enamel hypoplasia, retinitis pigmentosa, cataract, strabismus | + | + | + | + |
| 191 | 44 | f | R257X/R257X | + | + | − | − | + | + | Cataract | + | + | + | + |
| 194 | 25 | f | R257X/c.821delG | + | + | − | + | + | + | Atrophic gastritis | + | + | + | + |
| Group | Anti-IFN-ω Auto-Abs Microarray | Anti-IFN-ω Auto-Abs CBAA | Anti-IFN-α Auto-Abs Microarray | Anti-IFN-α Auto-Abs ELISA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 18/18 | 16/17 | 18/18 | 17/17 |
| 2 | 0/89 | 0/87 | 0/89 | n/a |
| 3 | 1/71 | 0/68 | 2/71 | 2/2 |
| 4 | 0/28 | 0/28 | 0/28 | 0/10 |
| Total number of samples tested | 206 | 200 | 206 | 29 |
| Sensitivity, 95% CI | 100.0% [78.9%; 100.0%] | 94.1% [70.7%; 100.0%] | 100.0% [78.9%; 100.0%] | Not determined. The assay was used as a comparative test |
| Specificity, 95% CI | 99.5% [96.7%; 100.0%] | 100.0% [97.5%; 100.0%] | 98.9% [95.9%; 99.9%] | Not determined. The assay was used as a comparative test |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nuralieva, N.; Yukina, M.; Sozaeva, L.; Donnikov, M.; Kovalenko, L.; Troshina, E.; Orlova, E.; Gryadunov, D.; Savvateeva, E.; Dedov, I. Diagnostic Accuracy of Methods for Detection of Antibodies against Type I Interferons in Patients with Endocrine Disorders. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1948. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12121948
Nuralieva N, Yukina M, Sozaeva L, Donnikov M, Kovalenko L, Troshina E, Orlova E, Gryadunov D, Savvateeva E, Dedov I. Diagnostic Accuracy of Methods for Detection of Antibodies against Type I Interferons in Patients with Endocrine Disorders. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(12):1948. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12121948
Chicago/Turabian StyleNuralieva, Nurana, Marina Yukina, Leila Sozaeva, Maxim Donnikov, Liudmila Kovalenko, Ekaterina Troshina, Elizaveta Orlova, Dmitry Gryadunov, Elena Savvateeva, and Ivan Dedov. 2022. "Diagnostic Accuracy of Methods for Detection of Antibodies against Type I Interferons in Patients with Endocrine Disorders" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 12: 1948. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12121948
APA StyleNuralieva, N., Yukina, M., Sozaeva, L., Donnikov, M., Kovalenko, L., Troshina, E., Orlova, E., Gryadunov, D., Savvateeva, E., & Dedov, I. (2022). Diagnostic Accuracy of Methods for Detection of Antibodies against Type I Interferons in Patients with Endocrine Disorders. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(12), 1948. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12121948









