Factors Influencing the Difficulty and Need for External Help during Laparoscopic Appendectomy: Analysis of 485 Procedures from the Resident-1 Multicentre Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
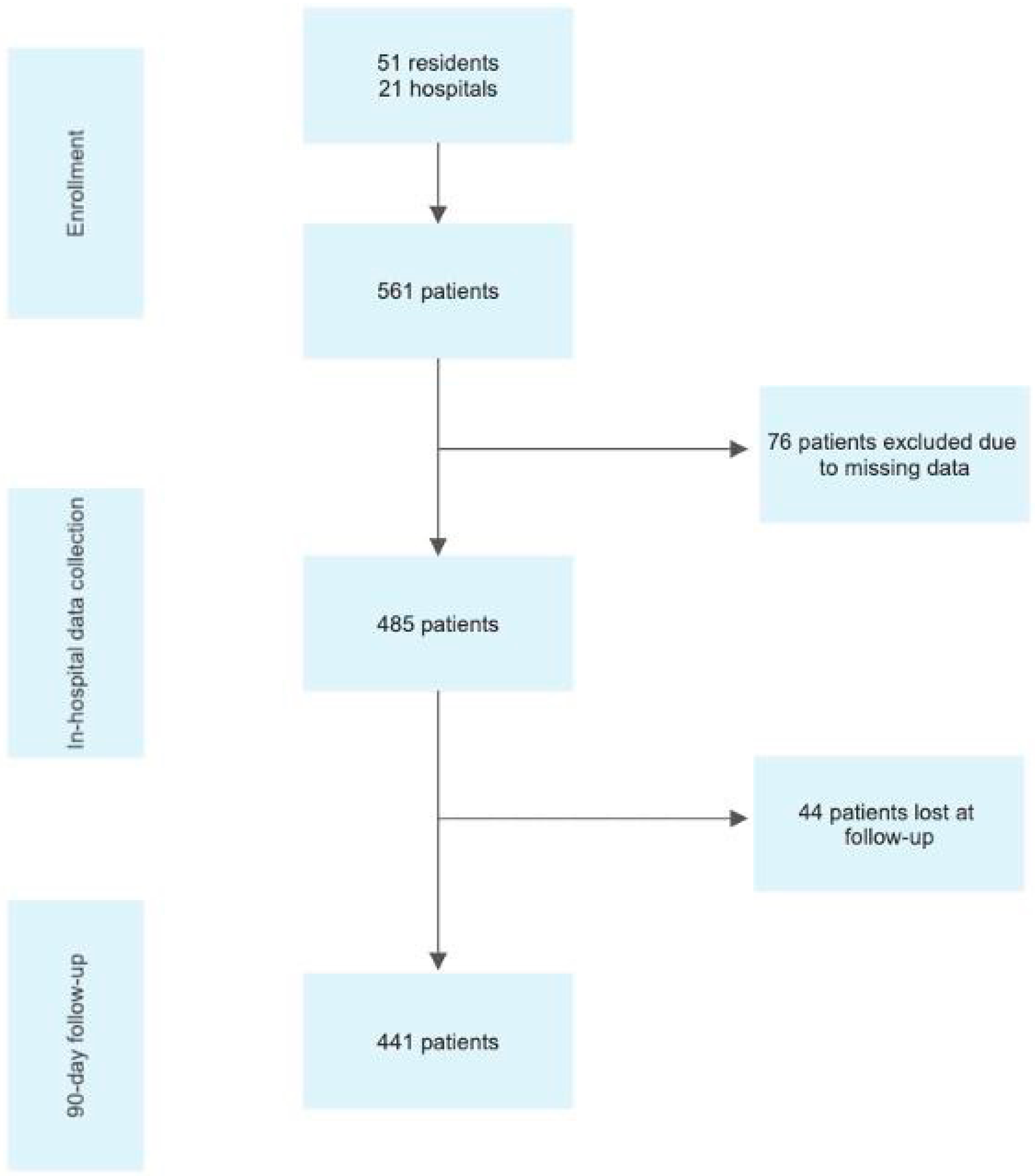
2. Materials and Methods
- Inclusion criteria:
- ○
- Patients younger than 18 years old.
- ○
- Surgical laparoscopic approach for AA.
- ○
- Intraoperative and histological diagnosis of AA.
- Exclusion criteria:
- ○
- Patients < 18 years old or > 80 years old.
- ○
- Previous appendicitis treated conservatively.
- ○
- Negative appendectomy.
- ○
- Open approach for surgery or intraoperative conversion.
- ○
- Coexistence of other intraabdominal infections (IAI).
- ○
- Patients with immunodeficiency.
- ○
- Patients treated with steroids, immunosuppressants, or CHT within the six previous months.
- A procedure performed by the first operator without any help from the assistant.
- The first surgeon can perform the procedure by seeking passive support from the assistant.
- The first surgeon can perform the procedure by seeking active support from the assistant.
- The procedure is technically demanding. The surgeon and the assistant can finish the procedure laparoscopically with the external support of a more expert nonscrubbed surgeon.
- The procedure is technically demanding and challenging. The surgeon and the assistant need the help of an external and more expert surgeon who scrubs in to safely finish the procedure laparoscopically.
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sartelli, M.; Chichom-Mefire, A.; Labricciosa, F.M.; Hardcastle, T.; Abu-Zidan, F.M.; Adesunkanmi, A.K.; Ansaloni, L.; Bala, M.; Balogh, Z.J.; Beltran, M.A.; et al. The management of intra-abdominal infections from a global perspective: 2017 WSES guidelines for the management of intra-abdominal infections. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2017, 12, 29. Available online: https://www.narcis.nl/publication/RecordID/oai:repository.ubn.ru.nl:2066%2F175669 (accessed on 15 July 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moris, D.; Paulson, E.K.; Pappas, T.N. Diagnosis and Management of Acute Appendicitis in Adults: A Review. JAMA 2021, 326, 2299–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krisher, S.L.; Browne, A.; Dibbins, A.; Tkacz, N.; Curci, M. Intra-Abdominal Abscess after Laparoscopic Appendectomy for Perforated Appendicitis. Arch. Surg. 2001, 136, 438–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cueto, J.; D’Allemagne, B.; Vazquez-Frias, J.; Gomez, S.; Delgado, F.; Trullenque, L.; Fajardo, R.; Valencia, S.; Poggi, L.; Balli, J.; et al. morbidity of laparoscopic surgery for complicated appendicitis: An international study. Surg. Endosc. 2006, 20, 717–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.W.; Jeon, S.Y.; Paik, B.; Bong, J.W.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, S.H. Resident Learning Curve for Laparoscopic Appendectomy According to Seniority. Ann. Coloproctol. 2020, 36, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.Y.; Shabbir, A.; So, J.B. Laparoscopic appendectomy by residents: Evaluating outcomes and learning curve. Surg. Endosc. 2010, 24, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ussia, A.; Vaccari, S.; Gallo, G.; Grossi, U.; Ussia, R.; Sartarelli, L.; Minghetti, M.; Lauro, A.; Barbieri, P.; Di Saverio, S.; et al. Laparoscopic appendectomy as an index procedure for surgical trainees: Clinical outcomes and learning curve. Updates Surg. 2021, 73, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Li, Y.; Ding, H.F.; Dong, D.H.; Zhang, X.F.; Liu, X.M.; Lv, Y.; Xiang, J.X. A novel preoperative scoring system to predict technical difficulty in laparoscopic splenectomy for non-traumatic diseases. Surg. Endosc. 2020, 34, 5360–5367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russolillo, N.; Maina, C.; Fleres, F.; Langella, S.; Lo Tesoriere, R.; Ferrero, A. Comparison and validation of three difficulty scoring systems in laparoscopic liver surgery: A retrospective analysis on 300 cases. Surg. Endosc. 2020, 34, 5484–5494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Huang, C.M.; Lin, J.X.; Zheng, C.H.; Xie, J.W.; Wang, J.B.; Lu, J.; Chen, Q.Y.; Cao, L.L.; Lin, M.; et al. A preoperatively predictive difficulty scoring system for laparoscopic spleen-preserving splenic hilar lymph node dissection for gastric cancer: Experience from a large-scale single center. Surg. Endosc. 2016, 30, 4092–4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioffi, S.P.B.; Altomare, M.; Spota, A.; Granieri, S.; Cimbanassi, S.; Chiara, O. REsiDENT 1 (re-assessment of appendicitis evaluation during laparoscopic appendectomy: Do we end a non-standardized treatment approach and habit?): Peritoneal irrigation during laparoscopic appendectomy—Does the grade of contamination matter? A prospective multicenter resident-based evaluation of a new classification system. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2019, 14, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likert, R. A Technique for the Measurement of Attitudes. Arch. Psychol. 1932, 140, 1–55. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, P.A.; Taylor, R.; Thielke, R.; Payne, J.; Gonzalez, N.; Conde, J.G. Research electronic data capture (REDCap)—A metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J. Biomed. Inform. 2009, 42, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, M.; Kolodziej, B.; Andersson, R.E. Validation of the Appendicitis Inflammatory Response (AIR) Score. World J. Surg. 2021, 45, 2081–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeşiltaş, M.; Karakaş, D.Ö.; Gökçek, B.; Hot, S.; Eğin, S. Can Alvarado and Appendicitis Inflammatory Response scores evaluate the severity of acute appendicitis? Turk. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2018, 24, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Saverio, S.; Podda, M.; De Simone, B.; Ceresoli, M.; Augustin, G.; Gori, A.; Boermeester, M.; Sartelli, M.; Coccolini, F.; Tarasconi, A.; et al. Diagnosis and treatment of acute appendicitis: 2020 update of the WSES Jerusalem guidelines. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2020, 15, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schildberg, C.W.; Reissig, K.; Hunger, R.; Paasch, C.; Stillger, R.; Mantke, R. Diagnostic, Therapy and Complications in Acute Appendicitis of 19,749 Cases Based on Routine Data: A Retrospective Multicenter Observational Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Park, J.H.; Lee, S.S.; Lee, W.J.; Ko, Y.; Andersson, R.E.; Lee, K.H. CT in Differentiating Complicated from Uncomplicated appendicitis: Presence of Any of 10 CT Features Versus Radiologists’ Gestalt Assessment. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2019, 213, W218–W227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahankali, S.K.; Ahamed, S.A.; Gupta, G.S.P.; Razek, A.A.K.A. CT based Acute Appendicitis Severity Index for acute appendicitis and validate its effectiveness in predicting. Emerg. Radiol. 2021, 28, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atema, J.J.; van Rossem, C.C.; Leeuwenburgh, M.M.; Stoker, J.; Boermeester, M.A. Scoring system to distinguish uncomplicated from complicated acute appendicitis. Br. J. Surg. 2015, 102, 979–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, A. A practical score for the early diagnosis of acute appendicitis. Ann. Emerg. Med. 1986, 15, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, M.E.; Pompei, P.; Ales, K.L.; MacKenzie, C.R. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: Development and validation. J. Chronic. Dis. 1987, 40, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Chen, G.; Wang, W.; Peng, K.; Xiao, W.; Yang, H. Outcome of rectal cancer surgery in obese and non-obese patients: A meta-analysis. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 14, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panteleimonitis, S.; Popeskou, S.; Harper, M.; Kandala, N.; Figueiredo, N.; Qureshi, T.; Parvaiz, A. Minimally invasive colorectal surgery in the morbid obese: Does size really matter? Surg. Endosc. 2018, 32, 3486–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, Y.; Ohue, M.; Sekimoto, M.; Takiguchi, S.; Takemasa, I.; Ikeda, M.; Yamamoto, H.; Monden, M. Evaluation of the technical difficulty performing laparoscopic resection of a rectosigmoid carcinoma: Visceral fat reflects technical difficulty more accurately than body mass index. Surg. Endosc. 2007, 21, 929–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, J.; Tatsumi, K.; Ota, M.; Suwa, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Watanabe, A.; Ishibe, A.; Watanabe, K.; Akiyama, H.; Ichikawa, Y.; et al. The impact of visceral obesity on surgical outcomes of laparoscopic surgery for colon cancer. Int. J. Colorectal. Dis. 2014, 29, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Yang, T.; Wu, Q.; Jin, C.; He, Y.; Wang, Z. The impact of general/visceral obesity on completion of mesorectum and perioperative outcomes of laparoscopic TME for rectal cancer: A STARD-compliant article. Medicine 2016, 95, e4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erestam, S.; Bock, D.; Erichsen Andersson, A.; Bjartell, A.; Carlsson, S.; Stinesen Kollberg, K.; Sjoberg, D.; Steineck, G.; Stranne, J.; Thorsteinsdottir, T.; et al. Associations between intraoperative factors and surgeons’ self-assessed operative satisfaction. Surg. Endosc. 2020, 34, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| (a) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | DG 1–3 | DG 4–5 | p-Value |
| N = 474 | N = 87 | ||
| Age | 34.86 (±16.15) | 46.47 (±18.25) | <0.001 |
| 95% CI: [33.4; 36.31] | 95% CI: [42.58; 50.36] | ||
| Range: (19.0; 91.0) | Range: (18; 87.0) | ||
| N = 474 | N = 87 | ||
| Sex | 0.607 | ||
| Female | 197 (41.56%) | 33 (37.93%) | |
| Male | 277 (58.44%) | 54 (62.07%) | |
| N = 474 | N = 87 | ||
| BMI > 30 kg/m2 | <0.001 | ||
| Yes | 32 (6.75%) | 21 (24.14%) | |
| No | 442 (93.25%) | 66 (75.86%) | |
| N = 474 | N = 87 | ||
| ASA | <0.001 | ||
| 1 | 293 (61.81%) | 28 (32.18%) | |
| 2 | 159 (33.54%) | 48 (55.17%) | |
| 3 | 21 (4.43%) | 10 (11.49%) | |
| 4 | 1 (0.21%) | 1 (1.15%) | |
| N = 474 | N = 87 | ||
| CCI | 0.403 (±1.02) | 1.14 (±1.59) | <0.001 |
| 95% CI: [0.311; 0.495] | 95% CI: [0.8; 1.48] | ||
| Range: (0.0; 11.0) | Range: (0.0; 7.0) | ||
| N = 474 | N = 87 | ||
| PIRO score | 0.173 (±0.599) | 0.632 (±1.26) | <0.001 |
| 95% CI: [0.119; 0.227] | 95% CI: [0.364; 0.9] | ||
| Range: (0.0; 8.0) | Range: (0.0; 9.0) | ||
| N = 474 | N = 87 | ||
| Alvarado score | 6.38 (±1.73) | 6.99 (±1.42) | 0.002 |
| 95% CI: [6.22; 6.53] | 95% CI: [6.69; 7.29] | ||
| Range: (1.0; 10.0) | Range: (3.0; 10.0) | ||
| N = 474 | N = 87 | ||
| AIR score | 5.73 (±1.94) | 6.68 (±1.9) | <0.001 |
| 95% CI: [5.55; 5.91] | 95% CI: [6.27; 7.09] | ||
| Range: (1.0; 11.0) | Range: (2.0; 12.0) | ||
| N = 444 | N = 85 | ||
| Preoperative exams | <0.001 | ||
| CT | 174 (39.82%) | 59 (74.68%) | |
| US | 263 (60.18%) | 20 (25.32%) | |
| N = 437 | N = 79 | ||
| (b) | |||
| Variable | DG 1–3 | DG 4–5 | p-Value |
| N = 474 | N = 87 | ||
| Operative time | 62.17 (±21.31) | 92.94 (±33.91) | <0.001 |
| 95% CI: [60.25; 64.1] | 95% CI: [85.72; 100.17] | ||
| Range: (15.0; 180.0) | Range: (40.0; 230.0) | ||
| N = 474 | N = 87 | ||
| Operator | 0.009 | ||
| Surgeon | 311 (65.61%) | 70 (80.46%) | |
| Resident | 163 (34.39%) | 17 (19.54%) | |
| N = 474 | N = 87 | ||
| Peritoneal contamination | <0.001 | ||
| No contamination | 273 (57.6%) | 8 (9.2%) | |
| Single abscess | 77 (16.24%) | 25 (28.74%) | |
| Multiple abscess | 4 (0.8%) | 2 (2.3%) | |
| Localised purulent peritonitis | 95 (20 %) | 33 (37.9%) | |
| Diffuse purulent peritonitis | 20 (4.2%) | 16 (18.4%) | |
| Localized faecal peritonitis | 3 (0.6%) | 2 (2.3%) | |
| Diffuse faecal peritonitis | 2 (0.4%) | 1 (1.2%) | |
| N = 474 | N = 87 | ||
| Appendix aspect | <0.001 | ||
| Erythematous | 90 (18.99%) | 3 (3.45%) | |
| Phlegmon | 274 (57.81%) | 19 (21.84%) | |
| Gangrene | 87 (18.35%) | 40 (45.98%) | |
| Perforation | 23 (4.85%) | 25 (28.74%) | |
| N = 474 | N = 87 | ||
| Peritoneal lavage | <0.001 | ||
| Yes | 332 (70.04%) | 84 (96.55%) | |
| No | 142 (29.96%) | 3 (3.45%) | |
| N = 474 | N = 87 | ||
| Drainage | <0.001 | ||
| Yes | 223 (47.05%) | 80 (91.95%) | |
| No | 251 (52.95%) | 7 (8.05%) | |
| N = 474 | N = 87 | ||
| (c) | |||
| Variable | DG 1–3 | DG 4–5 | p-Value |
| N = 474 | N = 87 | ||
| Length of stay | 4.03 (±3.44) | 6.14 (±3.07) | <0.001 |
| 95% CI: [3.72; 4.34] | 95% CI: [5.48; 6.79] | ||
| Range: (0.0; 21.0) | Range: (3.0; 21.0) | ||
| N = 474 | N = 87 | ||
| Superficial SSI | 0.397 | ||
| Yes | 2 (0.42%) | 1 (1.15%) | |
| No | 472 (99.58%) | 86 (98.85%) | |
| N = 474 | N = 87 | ||
| Deep SSI | 0.155 | ||
| Yes | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (1.15%) | |
| No | 474 (100.0%) | 86 (98.85%) | |
| N = 474 | N = 87 | ||
| Organ/space SSI | <0.001 | ||
| No | 467 (98.52%) | 74 (85.06%) | |
| Single abscess | 6 (1.27%) | 11 (12.64%) | |
| Multiple abscess | 0 (0.0%) | 2 (2.3%) | |
| Peritonitis | 1 (0.21%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| N = 474 | N = 87 | ||
| New hospitalisation—30 days | 0.099 | ||
| Yes | 9 (2.38%) | 4 (6.35%) | |
| No | 369 (97.62%) | 59 (93.65%) | |
| N = 378 | N = 63 | ||
| New hospitalisation—60 days | >0.999 | ||
| Yes | 1 (0.26%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| No | 377 (99.74%) | 63 (100.0%) | |
| N = 378 | N = 63 | ||
| Variable | Odds Ratio | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Constant | 0.0105 [0.00289;0.0384] | <0.001 |
| Age | 1.02 [0.995;1.05] | 0.108 |
| ASA | 0.653 [0.241;1.77] | 0.401 |
| CCI | 1.21 [0.851;1.73] | 0.285 |
| AIR score | 1.22 [1.06;1.4] | 0.0043 |
| Preoperative CT scan | 2.38 [1.24;4.57] | 0.009 |
| BMI > 30 kg/m2 | 2.61 [1.29;5.27] | 0.007 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cioffi, S.P.B.; Spota, A.; Altomare, M.; Granieri, S.; Bini, R.; Virdis, F.; Renzi, F.; Reitano, E.; Chiara, O.; Cimbanassi, S.; et al. Factors Influencing the Difficulty and Need for External Help during Laparoscopic Appendectomy: Analysis of 485 Procedures from the Resident-1 Multicentre Trial. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1904. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12111904
Cioffi SPB, Spota A, Altomare M, Granieri S, Bini R, Virdis F, Renzi F, Reitano E, Chiara O, Cimbanassi S, et al. Factors Influencing the Difficulty and Need for External Help during Laparoscopic Appendectomy: Analysis of 485 Procedures from the Resident-1 Multicentre Trial. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(11):1904. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12111904
Chicago/Turabian StyleCioffi, Stefano Piero Bernardo, Andrea Spota, Michele Altomare, Stefano Granieri, Roberto Bini, Francesco Virdis, Federica Renzi, Elisa Reitano, Osvaldo Chiara, Stefania Cimbanassi, and et al. 2022. "Factors Influencing the Difficulty and Need for External Help during Laparoscopic Appendectomy: Analysis of 485 Procedures from the Resident-1 Multicentre Trial" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 11: 1904. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12111904
APA StyleCioffi, S. P. B., Spota, A., Altomare, M., Granieri, S., Bini, R., Virdis, F., Renzi, F., Reitano, E., Chiara, O., Cimbanassi, S., & The Resident-1 Research Group. (2022). Factors Influencing the Difficulty and Need for External Help during Laparoscopic Appendectomy: Analysis of 485 Procedures from the Resident-1 Multicentre Trial. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(11), 1904. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12111904








