Are Parkinson’s Disease Patients the Ideal Preclinical Population for Alzheimer’s Disease Therapeutics?
Abstract
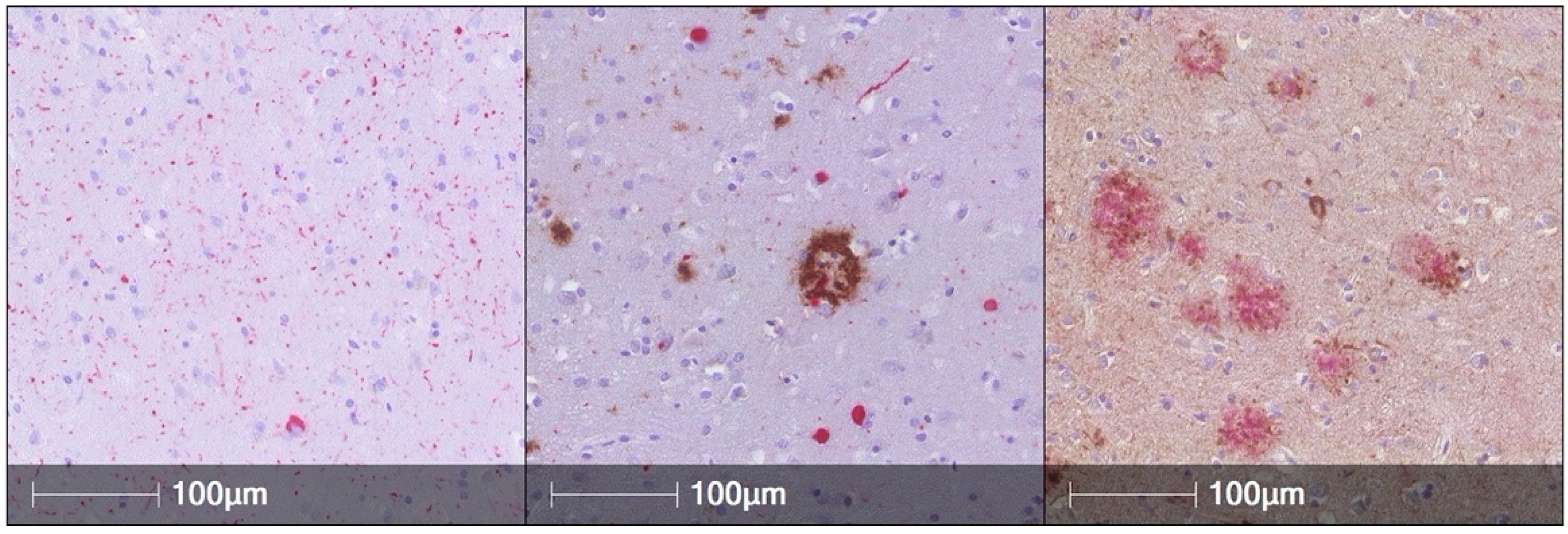
:1. AD Pathology Is Common in PD Brains and Is Associated with Worse Cognitive Performance during Life
2. AD Associated Biomarkers of Neurodegeneration, Tau, and Alpha-Synuclein Associate with Cognitive Performance in PD Cohorts
3. In Vitro, Cell-Based, and Animal Models Provide Evidence for AD Pathogenic Mechanisms in PD
4. Precision Medicine Approaches Can Enrich for Those PD Individuals Most Likely to Develop Concomitant AD Pathology
5. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tanner, C.M.; Goldman, S.M. Epidemiology of Movement-Disorders. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 1994, 7, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nussbaum, R.L.; Ellis, C.E. Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1356–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Lau, L.M.; Breteler, M.M. Epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2006, 5, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorsey, E.R.; Constantinescu, R.; Thompson, J.P.; Biglan, K.M.; Holloway, R.G.; Kieburtz, K.; Marshall, F.J.; Ravina, B.M.; Schifitto, G.; Siderowf, A.; et al. Projected number of people with Parkinson disease in the most populous nations, 2005 through 2030. Neurology 2007, 68, 384–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marras, C.; Beck, J.C.; Bower, J.H.; Roberts, E.; Ritz, B.; Ross, G.W.; Abbott, R.D.; Savica, R.; Van Den Eeden, S.K.; Willis, A.W.; et al. Prevalence of Parkinson’s disease across North America. NPJ Park. Dis. 2018, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Postuma, R.B.; Berg, D.; Stern, M.; Poewe, W.; Olanow, C.W.; Oertel, W.; Obeso, J.; Marek, K.; Litvan, I.; Lang, A.E.; et al. MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Martin, P.; Rodriguez-Blazquez, C.; Kurtis, M.M.; Chaudhuri, K.R. The impact of non-motor symptoms on health-related quality of life of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2011, 26, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudlicka, A.; Clare, L.; Hindle, J.V. Quality of life, health status and caregiver burden in Parkinson’s disease: Relationship to executive functioning. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2014, 29, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vossius, C.; Larsen, J.P.; Janvin, C.; Aarsland, D. The economic impact of cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2011, 26, 1541–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarsland, D.; Andersen, K.; Larsen, J.P.; Lolk, A.; Nielsen, H.; Kragh-Sørensen, P. Risk of dementia in Parkinson’s disease: A community-based, prospective study. Neurology 2001, 56, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hely, M.A.; Reid, W.G.J.; Adena, M.A.; Halliday, G.M.; Morris, J.G.L. The Sydney Multicenter Study of Parkinson’s disease: The inevitability of dementia at 20 years. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litvan, I.; Aarsland, D.; Adler, C.H.; Goldman, J.G.; Kulisevsky, J.; Mollenhauer, B.; Rodriguez-Oroz, M.C.; Tröster, A.I.; Weintraub, D. MDS task force on mild cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease: Critical review of PD-MCI. Mov. Disord. 2011, 26, 1814–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Goedert, M. Synucleinopathies: Past, present and future. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2016, 42, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robinson, J.L.; Lee, E.B.; Xie, S.X.; Rennert, L.; Suh, E.; Bredenberg, C.; Caswell, C.; Van Deerlin, V.M.; Yan, N.; Yousef, A.; et al. Neurodegenerative disease concomitant proteinopathies are prevalent, age-related and APOE4-associated. Brain 2018, 141, 2181–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, C.; Malek, N.; Grosset, K.; Cullen, B.; Gentleman, S.; Grosset, D.G. Neuropathology of dementia in patients with Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review of autopsy studies. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 1234–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alzheimer’s Disease International. World Alzheimer Report 2018—The State of the Art of Dementia Research: New Frontiers; Alzheimer’s Disease International: London, UK, 2018; pp. 1–82. [Google Scholar]
- Sperling, R.A.; Aisen, P.S.; Beckett, L.A.; Bennett, D.A.; Craft, S.; Fagan, A.M.; Iwatsubo, T.; Jack, C.R.; Kaye, J.; Montine, T.J.; et al. Toward defining the preclinical stages of Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2011, 7, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- 2021 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2021, 17, 327–406. [CrossRef]
- Montine, T.J.; Phelps, C.H.; Beach, T.G.; Bigio, E.H.; Cairns, N.J.; Dickson, D.W.; Duyckaerts, C.; Frosch, M.P.; Mirra, S.S.; Nelson, P.T.; et al. National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association guidelines for the neuropathologic assessment of Alzheimer’s disease: A practical approach NIH Public Access. Acta Neuropathol. 2012, 123, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, J.H.; Korecka, M.; Figurski, M.J.; Toledo, J.B.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Waligorska, T.; Brylska, M.; Fields, L.; Shah, N.; et al. The Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative 2 Biomarker Core: A review of progress and plans. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2015, 11, 772–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Novak, G.; Streffer, J.R.; Timmers, M.; Henley, D.; Brashear, H.R.; Bogert, J.; Russu, A.; Janssens, L.; Tesseur, I.; Tritsmans, L.; et al. Long-term safety and tolerability of atabecestat (JNJ-54861911), an oral BACE1 inhibitor, in early Alzheimer’s disease spectrum patients: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study and a two-period extension study. Alzheimers. Res. Ther. 2020, 12, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leoutsakos, J.-M.S.; Muthen, B.O.; Breitner, J.C.S.; Lyketsos, C.G. ADAPT Research Team Effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug treatments on cognitive decline vary by phase of pre-clinical Alzheimer disease: Findings from the randomized controlled Alzheimer’s Disease Anti-inflammatory Prevention Trial. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2012, 27, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Study of Crenezumab Versus Placebo to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety in Participants with Prodromal to Mild Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) (CREAD 2). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02670083 (accessed on 15 June 2021).
- Tariot, P.N.; Lopera, F.; Langbaum, J.B.; Thomas, R.G.; Hendrix, S.; Schneider, L.S.; Rios-Romenets, S.; Giraldo, M.; Acosta, N.; Tobon, C.; et al. The Alzheimer’s Prevention Initiative Autosomal-Dominant Alzheimer’s Disease Trial: A study of crenezumab versus placebo in preclinical PSEN1 E280A mutation carriers to evaluate efficacy and safety in the treatment of autosomal-dominant Alzheimer’s disease, including a placebo-treated noncarrier cohort. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2018, 4, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer Network Trial: An Opportunity to Prevent Dementia. A Study of Potential Disease Modifying Treatments in Individuals at Risk for or With a Type of Early Onset Alzheimer’s Disease Caused by a Genetic Mutation. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01760005 (accessed on 15 June 2021).
- Carlsson, C.M.; Gleason, C.E.; Hess, T.M.; Moreland, K.A.; Blazel, H.M.; Koscik, R.L.; Schreiber, N.T.N.; Johnson, S.C.; Atwood, C.S.; Puglielli, L.; et al. Effects of simvastatin on cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers and cognition in middle-aged adults at risk for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2008, 13, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sevigny, J.; Chiao, P.; Bussière, T.; Weinreb, P.H.; Williams, L.; Maier, M.; Dunstan, R.; Salloway, S.; Chen, T.; Ling, Y.; et al. The antibody aducanumab reduces Aβ plaques in Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 2016, 537, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmers, M.; Streffer, J.R.; Russu, A.; Tominaga, Y.; Shimizu, H.; Shiraishi, A.; Tatikola, K.; Smekens, P.; Börjesson-Hanson, A.; Andreasen, N.; et al. Pharmacodynamics of atabecestat (JNJ-54861911), an oral BACE1 inhibitor in patients with early Alzheimer’s disease: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Alzheimers. Res. Ther. 2018, 10, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frölich, L.; Wunderlich, G.; Thamer, C.; Roehrle, M.; Garcia, M.; Dubois, B. Evaluation of the efficacy, safety and tolerability of orally administered BI 409306, a novel phosphodiesterase type 9 inhibitor, in two randomised controlled phase II studies in patients with prodromal and mild Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2019, 11, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lowe, S.L.; Willis, B.A.; Hawdon, A.; Natanegara, F.; Chua, L.; Foster, J.; Shcherbinin, S.; Ardayfio, P.; Sims, J.R. Donanemab (LY3002813) dose-escalation study in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2021, 7, e12112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, S.Y.; Kaplow, J.; Zhao, J.; Dhadda, S.; Luthman, J.; Albala, B. P4-389: Elenbecestat, E2609, a bace inhibitor: Results from a phase-2 study in subjects with mild cognitive impairment and mild-to-moderate dementia due to alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2018, 14, P1623–P1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrowitzki, S.; Lasser, R.A.; Dorflinger, E.; Scheltens, P.; Barkhof, F.; Nikolcheva, T.; Ashford, E.; Retout, S.; Hofmann, C.; Delmar, P.; et al. A phase III randomized trial of gantenerumab in prodromal Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2017, 9, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Study of JNJ-63733657 in Participants With Early Alzheimer’s Disease—Full Text View—ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04619420?term=JNJ-63733657&draw=2&rank=1 (accessed on 15 June 2021).
- SEMA4D Blockade Safety and Brain Metabolic Activity in Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) (SIGNAL-AD). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04381468 (accessed on 15 June 2021).
- PRESS RELEASE AC Immune Reports Top Line Results from TAURIEL Phase 2 Trial Evaluating Semorinemab in Early Alzheimer’s Disease. Available online: https://ir.acimmune.com/static-files/7296e650-85ea-4151-aca5-6f63ec71653c (accessed on 15 June 2021).
- Serrano-Pozo, A.; Vega, G.L.; Lütjohann, D.; Locascio, J.J.; Tennis, M.K.; Deng, A.; Atri, A.; Hyman, B.T.; Irizarry, M.C.; Growdon, J.H. Effects of simvastatin on cholesterol metabolism and Alzheimer disease biomarkers. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2010, 24, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clinical Trial of Solanezumab for Older Individuals Who May be at Risk for Memory Loss—Full Text View—ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02008357?term=solanezumab&draw=2&rank=5 (accessed on 15 June 2021).
- A Study of Solanezumab (LY2062430) in Participants With Prodromal Alzheimer’s Disease—Full Text View—ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02760602?term=solanezumab&draw=2&rank=1 (accessed on 15 June 2021).
- Egan, M.F.; Kost, J.; Voss, T.; Mukai, Y.; Aisen, P.S.; Cummings, J.L.; Tariot, P.N.; Vellas, B.; van Dyck, C.H.; Boada, M.; et al. Randomized Trial of Verubecestat for Prodromal Alzheimer’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1408–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coughlin, D.; Xie, S.X.; Liang, M.; Williams, A.; Peterson, C.; Weintraub, D.; McMillan, C.T.; Wolk, D.A.; Akhtar, R.S.; Hurtig, H.I.; et al. Cognitive and Pathological Influences of Tau Pathology in Lewy Body Disorders. Ann. Neurol. 2019, 85, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colom-Cadena, M.; Gelpi, E.; Charif, S.; Belbin, O.; Blesa, R.; Martí, M.J.; Clarimon, J.; Lleó, A. Confluence of α-Synuclein, Tau, and β-Amyloid Pathologies in Dementia With Lewy Bodies. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 72, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, D.L.; Tropea, T.F.; Robinson, J.L.; Suh, E.; Hurtig, H.; Weintraub, D.; Van Deerlin, V.; Lee, E.B.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Chen-Plotkin, A.S. ADNC-RS, a clinical-genetic risk score, predicts Alzheimer’s pathology in autopsy-confirmed Parkinson’s disease and Dementia with Lewy bodies. Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 140, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorenzato, E.; Biundo, R.; Cecchin, D.; Frigo, A.C.; Kim, J.; Weis, L.; Strafella, A.P.; Antonini, A. Brain Amyloid Contribution to Cognitive Dysfunction in Early-Stage Parkinson’s Disease: The PPMI Dataset. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 66, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, R.O.; Aakre, J.A.; Kremers, W.K.; Vassilaki, M.; Knopman, D.S.; Mielke, M.M.; Alhurani, R.; Geda, Y.E.; Machulda, M.M.; Coloma, P.; et al. Prevalence and outcomes of amyloid positivity among persons without dementia in a longitudinal, population-based setting. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 970–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrou, M.; Dwamena, B.A.; Foerster, B.R.; Maceachern, M.P.; Bohnen, N.I.; Müller, M.L.; Albin, R.L.; Frey, K.A. Amyloid deposition in Parkinson’s disease and cognitive impairment: A systematic review. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irwin, D.J.; Grossman, M.; Weintraub, D.; Hurtig, H.I.; Duda, J.E.; Xie, S.X.; Lee, E.B.; Van Deerlin, V.M.; Lopez, O.L.; Kofler, J.K.; et al. Neuropathological and genetic correlates of survival and dementia onset in synucleinopathies: A retrospective analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lemstra, A.W.; De Beer, M.H.; Teunissen, C.E.; Schreuder, C.; Scheltens, P.; Van Der Flier, W.M.; Sikkes, S.A.M. Concomitant AD pathology affects clinical manifestation and survival in dementia with Lewy bodies. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2017, 88, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, E.; Irwin, D.J.; Rascovsky, K.; Nevler, N.; Shellikeri, S.; Tropea, T.F.; Spindler, M.; Deik, A.; Chen-Plotkin, A.; Siderowf, A.; et al. Cognitive Profile and Markers of Alzheimer Disease-Type Pathology in Patients With Lewy Body Dementias. Neurology 2021, 96, 1855–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peavy, G.M.; Edland, S.D.; Toole, B.M.; Hansen, L.A.; Galasko, D.R.; Mayo, A.M. Phenotypic differences based on staging of Alzheimer’s neuropathology in autopsy-confirmed dementia with Lewy bodies. Park. Relat. Disord. 2016, 31, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weiner, M.W.; Veitch, D.P.; Aisen, P.S.; Beckett, L.A.; Cairns, N.J.; Cedarbaum, J.; Green, R.C.; Harvey, D.; Jack, C.R.; Jagust, W.; et al. 2014 Update of the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative: A review of papers published since its inception. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2015, 11, e1–e120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wallin, Å.K.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Londos, E.; Minthon, L.; Hansson, O. CSF biomarkers predict a more malignant outcome in Alzheimer disease. Neurology 2010, 74, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zetterberg, H.; Skillbäck, T.; Mattsson, N.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Portelius, E.; Shaw, L.M.; Weiner, M.W.; Blennow, K. Association of cerebrospinal fluid neurofilament light concentration with Alzheimer disease progression. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, B.; Portelius, E.; Cullen, N.C.; Sandelius, Å.; Zetterberg, H.; Andreasson, U.; Höglund, K.; Irwin, D.J.; Grossman, M.; Weintraub, D.; et al. Association of Cerebrospinal Fluid Neurofilament Light Protein Levels with Cognition in Patients with Dementia, Motor Neuron Disease, and Movement Disorders. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strozyk, D.; Blennow, K.; White, L.R.; Launer, L.J. CSF Aß 42 levels correlate with amyloid-neuropathology in a population-based autopsy study. Neurology 2003, 60, 652–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, B.; Lautner, R.; Andreasson, U.; Öhrfelt, A.; Portelius, E.; Bjerke, M.; Hölttä, M.; Rosén, C.; Olsson, C.; Strobel, G.; et al. CSF and blood biomarkers for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.R.; Bennett, D.A.; Blennow, K.; Carrillo, M.C.; Dunn, B.; Haeberlein, S.B.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.; Jessen, F.; Karlawish, J.; et al. NIA-AA Research Framework: Toward a biological definition of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2018, 14, 535–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperling, R.A.; Rentz, D.M.; Johnson, K.A.; Karlawish, J.; Donohue, M.; Salmon, D.P.; Aisen, P. The A4 study: Stopping AD before symptoms begin? Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 228fs13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siderowf, A.; Xie, S.X.; Hurtig, H.; Weintraub, D.; Duda, J.; Chen-Plotkin, A.; Shaw, L.M.; Van Deerlin, V.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Clark, C. CSF amyloid β 1-42 predicts cognitive decline in Parkinson disease. Neurology 2010, 75, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terrelonge, M.; Marder, K.S.; Weintraub, D.; Alcalay, R.N. CSF β-Amyloid 1-42 Predicts Progression to Cognitive Impairment in Newly Diagnosed Parkinson Disease. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2016, 58, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hall, S.; Surova, Y.; Öhrfelt, A.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Hansson, O.; Hansson, O. L ongitudinal M easurements of C erebrospinal F luid B iomarkers in P arkinson’s D isease. Mov. Disord. 2016, 31, 898–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-H.; Li, C.-H.; Yang, K.-C.; Lin, F.-J.; Wu, C.-C.; Chieh, J.-J.; Chiu, M.-J. Blood NfL: A biomarker for disease severity and progression in Parkinson disease. Neurology 2019, 93, e1104–e1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tropea, T.F.; Xie, S.X.; Rick, J.; Chahine, L.M.; Dahodwala, N.; Doshi, J.; Davatzikos, C.; Shaw, L.M.; Van Deerlin, V.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; et al. APOE, thought disorder, and SPARE-AD predict cognitive decline in established Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2018, 33, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, F.-T.; Hou, X.-H.; Li, J.-Q.; Cao, X.-P.; Tan, L.; Wang, J.; Yu, J.-T. Predictors of cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 2713–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moussaud, S.; Jones, D.R.; Moussaud-Lamodière, E.L.; Delenclos, M.; Ross, O.A.; McLean, P.J. Alpha-synuclein and tau: Teammates in neurodegeneration? Mol. Neurodegener. 2014, 9, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, X.; Uronen, R.-L.; Huttunen, H.J. The interaction of α-synuclein and Tau: A molecular conspiracy in neurodegeneration? Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 99, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, P.H.; Hager, H.; Nielsen, M.S.; Hojrup, P.; Gliemann, J.; Jakes, R. alpha-synuclein binds to Tau and stimulates the protein kinase A-catalyzed tau phosphorylation of serine residues 262 and 356. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 25481–25489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giasson, B.I.; Forman, M.S.; Higuchi, M.; Golbe, L.I.; Graves, C.L.; Kotzbauer, P.T.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M.Y.M.-Y. Initiation and synergistic fibrillization of tau and alpha-synuctein. Science 2003, 300, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, J.L.; Lee, V.M.Y. Cell-to-cell transmission of pathogenic proteins in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bassil, F.; Meymand, E.S.; Brown, H.J.; Xu, H.; Cox, T.O.; Pattabhiraman, S.; Maghames, C.M.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, B.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; et al. α-Synuclein modulates tau spreading in mouse brains. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 218, e20192193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study Drug | Mechanism of Action | Sponsor | Enrollment Criteria | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Studies enrolling at-risk or preclinical stage human participants | ||||
| Atabecestat | BACE Inhibitor | Janssen | APOE E4 genotype. | [21] |
| Celecoxib | Selective COX-2 inhibitor | Pfizer | Cognitively normal with a family history of AD. | [22] |
| Crenezumab | Aβ monoclonal antibody | Hoffmann-La Roche | PSEN1 E280A mutation carriers. | [23,24] |
| Gantenerumab | Aβ monoclonal antibody | Hoffmann-La Roche | APP, presenilin-1, or presenilin-2 carriers. | [25] |
| Simvastatin | HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor | Merck | Cognitively normal with a family history of AD. | [26] |
| Solenezumab | Aβ monoclonal antibody | Eli Lilly | APP, presenilin-1, or presenilin-2 carriers. | [25] |
| Studies enrolling prodromal human participants | ||||
| Aducanumab | Aβ monoclonal antibody | Biogen | MCI with positive amyloid PET. | [27] |
| Atabecestat | BACE Inhibitor | Janssen | MCI with pathological CSF Aβ or positive amyloid PET. | [28] |
| BI 409306 | Phosphodiesterase-9A inhibitor | Boehringer Ingelheim | MCI. | [29] |
| Crenezumab | Aβ monoclonal antibody | Hoffmann-La Roche | Pathological CSF Aβ or positive amyloid PET. | [23,24] |
| Donanemab | Aβ monoclonal antibody | Eli Lilly | MCI with positive amyloid PET. | [30] |
| Elenbecestat | BACE inhibitor | Biogen, Eisai | MCI. | [31] |
| Exenatide | Glucagon-like peptide-1 agonist | Astra Zeneca | MCI. | NA |
| Gantenerumab | Aβ monoclonal antibody | Hoffmann-La Roche | MCI with pathological CSF Aβ. | [25,32] |
| JNJ-63733657 | Tau monoclonal antibody | Janssen | Subjective cognitive decline and positive tau PET. | [33] |
| Pepinemab | Semaphorin 4D monoclonal antibody | Vaccinex | MCI with pathological CSF Aβ or positive amyloid PET. | [34] |
| Semorinemab | Tau monocloncal antibody | Genentech | MCI with pathological CSF Aβ or positive amyloid PET. | [35] |
| Simvastatin | HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor | Merck | MCI. | [36] |
| Solenezumab | Aβ monoclonal antibody | Eli Lilly | MCI with positive amyloid PET. | [37,38] |
| Verubecestat | BACE inhibitor | Merck | MCI with positive amyloid PET. | [39] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tropea, T.F.; Chen-Plotkin, A. Are Parkinson’s Disease Patients the Ideal Preclinical Population for Alzheimer’s Disease Therapeutics? J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11090834
Tropea TF, Chen-Plotkin A. Are Parkinson’s Disease Patients the Ideal Preclinical Population for Alzheimer’s Disease Therapeutics? Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(9):834. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11090834
Chicago/Turabian StyleTropea, Thomas F., and Alice Chen-Plotkin. 2021. "Are Parkinson’s Disease Patients the Ideal Preclinical Population for Alzheimer’s Disease Therapeutics?" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 9: 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11090834
APA StyleTropea, T. F., & Chen-Plotkin, A. (2021). Are Parkinson’s Disease Patients the Ideal Preclinical Population for Alzheimer’s Disease Therapeutics? Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(9), 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11090834






