IL13Rα2 Is Involved in the Progress of Renal Cell Carcinoma through the JAK2/FOXO3 Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. RCC Patients and Tissue Samples
2.2. Immunohistochemical Staining and Scoring
2.3. Chemical Reagents, Antibodies, and Plasmid DNAs
2.4. Cell Culture
2.5. Transfection of siRNA and Plasmid DNA
2.6. WST-1 Assay
2.7. Cell Counting Assay
2.8. Colony Formation Assay
2.9. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.10. TUNEL Assay
2.11. Annexin V Staining Analysis
2.12. Western Blotting Analysis
2.13. Immunoprecipitation Analysis
2.14. JAK2 Kinase Inhibition Assay
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
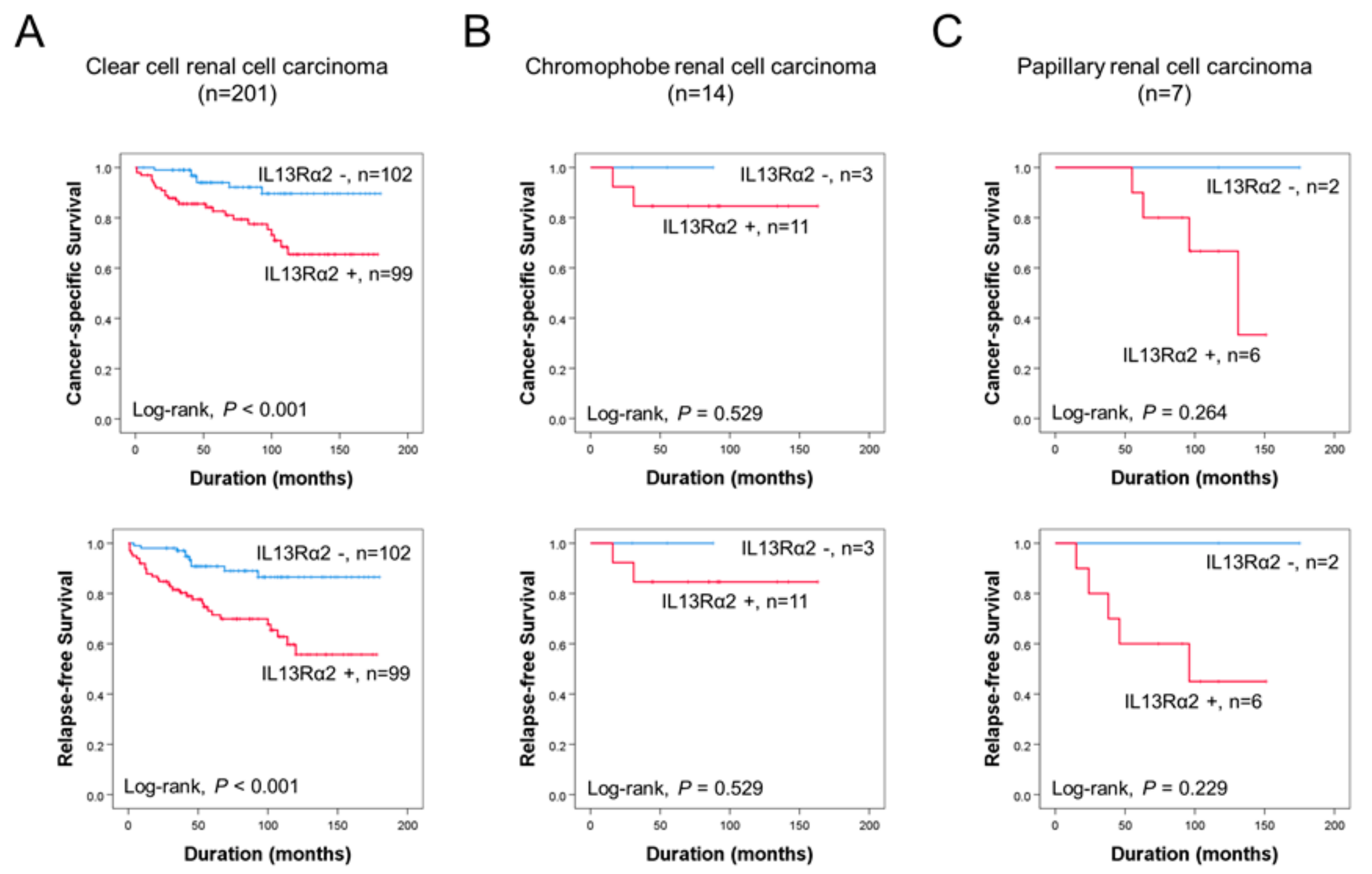
3.1. Immunohistochemical Expression of IL13Rα2 Is Associated with Poor Prognosis of RCC Patients
3.2. Knockdown of IL13Rα2 Displays the AntiProliferative Activity in A498, ACHN, Caki1, and Caki2 Cells
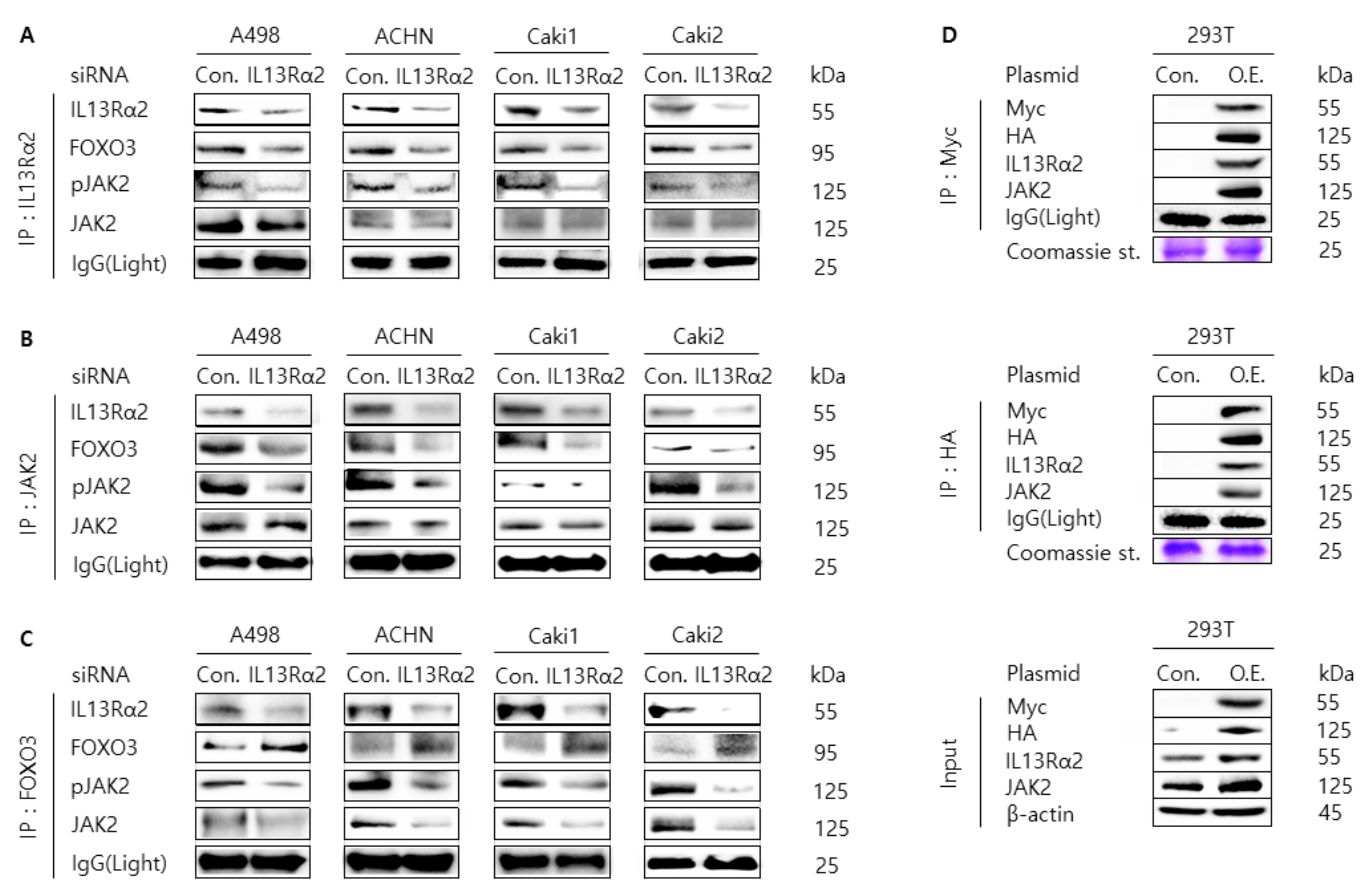
3.3. Knockdown of IL13Rα2 Attenuates the Protein Interaction Among IL13Rα2, pJAK2, and FOXO3 in A498, ACHN, Caki1, and Caki2 Cells
3.4. Telmisartan Suppresses Cell Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest in A498, ACHN, Caki1, and Caki2 Cells Via Inhibition of JAK2
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, R.; Gore, M.; Larkin, J. Current and future systemic treatments for renal cell carcinoma. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2013, 23, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escudier, B.; Eisen, T.; Stadler, W.M.; Szczylik, C.; Oudard, S.; Siebels, M.; Negrier, S.; Chevreau, C.; Solska, E.; Desai, A.A.; et al. Sorafenib in Advanced Clear-Cell Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choueiri, T.K.; Motzer, R.J. Systemic Therapy for Metastatic Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, D.Y.; Xie, W.; Regan, M.M.; Warren, M.A.; Golshayan, A.R.; Sahi, C.; Eigl, B.J.; Ruether, J.D.; Cheng, T.; North, S.; et al. Prognostic Factors for Overall Survival in Patients With Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Treated With Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor–Targeted Agents: Results From a Large, Multicenter Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5794–5799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, D.Y.; Xie, W.; Regan, M.M.; Harshman, L.C.; Bjarnason, G.; Vaishampayan, U.N.; Mackenzie, M.; Wood, L.; Donskov, F.; Tan, M.-H.; et al. External validation and comparison with other models of the International Metastatic Renal-Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium prognostic model: A population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, J.J.; Purdue, M.P.; Signoretti, S.; Swanton, C.; Albiges, L.; Schmidinger, M.; Heng, D.Y.; Larkin, J.; Ficarra, V. Renal cell carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.-X.; Huang, Y.-J.; Yao, Y.; Shen, Z.; Min, D.-L. Incidence and Risk of Treatment-Related Mortality with mTOR Inhibitors Everolimus and Temsirolimus in Cancer Patients: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudier, B.; Szczylik, C.; Porta, C.; Gore, M. Treatment selection in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: Expert consensus. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 9, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershey, G.K. IL-13 receptors and signaling pathways: An evolving web. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 111, 677–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, R.; Suzuki, A.; Leland, P.; Joshi, B.H.; Puri, R.K. Identification of a novel role of IL-13Rα2 in human Glioblastoma multiforme: Interleukin-13 mediates signal transduction through AP-1 pathway. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, H.; Yoshimatsu, Y.; Tomizawa, T.; Kunita, A.; Takayama, R.; Morikawa, T.; Komura, D.; Takahashi, K.; Oshima, T.; Sato, M.; et al. Interleukin-13 receptor α2 is a novel marker and potential therapeutic target for human melanoma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolomé, R.A.; Jaén, M.; Casal, J.I. An IL13Rα2 peptide exhibits therapeutic activity against metastatic colorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 119, 940–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgis, P.; Ozturk, S.; Lambert, A.W.; Neophytou, C.M.; Tzatsos, A.; Wong, C.K.; Thiagalingam, S.; Constantinou, A.I. Targeting IL13Ralpha2 activates STAT6-TP63 pathway to suppress breast cancer lung metastasis. Breast Cancer Res. 2015, 17, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-H.; Chung, Y.M.; Ma, J.; Yang, Q.; Berek, J.S.; Hu, M.C.-T. Pharmacological activation of FOXO3 suppresses triple-negative breast cancer in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 42110–42125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Hu, X.; Wang, Y.; Yao, X.; Zhang, W.; Yu, C.; Cheng, F.; Li, J.; Fang, Q. Ivermectin, a potential anticancer drug derived from an antiparasitic drug. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 163, 105207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borém, L.M.A.; Neto, J.F.R.; Brandi, I.V.; Lelis, D.F.; Santos, S.H.S. The role of the angiotensin II type I receptor blocker telmisartan in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A brief review. Hypertens. Res. 2018, 41, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moch, H.; Humphrey, P.A.; Ulbright, T.M. WHO Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs, 4th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 70, pp. 93–105. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, M.B.; American Joint Committee on Cancer; American Cancer Society. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual; Springer: Chicago, IL, USA, 2017; 1024p, p. xvii. [Google Scholar]
- Allred, D.C.; Harvey, J.M.; Berardo, M.; Clark, G.M. Prognostic and predictive factors in breast cancer by immunohistochemical analysis. Mod. Pathol. 1998, 11, 155–168. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, M.-A.; Lee, J.; Ha, S.H.; Lee, C.M.; Kim, K.M.; Jang, K.Y.; Park, S.-H. Interleukin4Rα (IL4Rα) and IL13Rα1 Are Associated with the Progress of Renal Cell Carcinoma through Janus Kinase 2 (JAK2)/Forkhead Box O3 (FOXO3) Pathways. Cancers 2019, 11, 1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.M.; Hussein, U.K.; Park, S.-H.; Kang, M.A.; Moon, Y.J.; Zhang, Z.; Song, Y.; Park, H.S.; Bae, J.S.; Park, B.-H.; et al. FAM83H is involved in stabilization of β-catenin and progression of osteosarcomas. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Bae, J.S.; Kim, K.M.; Moon, Y.J.; Park, S.-H.; Ha, S.H.; Hussein, U.K.; Zhang, Z.; Park, H.S.; Park, B.-H.; et al. The PARP inhibitor olaparib potentiates the effect of the DNA damaging agent doxorubicin in osteosarcoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.M.; Hussein, U.K.; Bae, J.S.; Park, S.-H.; Kwon, K.S.; Ha, S.H.; Park, H.S.; Lee, H.; Chung, M.J.; Moon, W.S.; et al. The Expression Patterns of FAM83H and PANX2 Are Associated with Shorter Survival of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Patients. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sai, K.K.S.; Sattiraju, A.; Almaguel, F.G.; Xuan, A.; Rideout, S.; Krishnaswamy, R.S.; Zhang, J.; Herpai, D.M.; Debinski, W.; Mintz, A. Peptide-based PET imaging of the tumor restricted IL13RA2 biomarker. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 50997–51007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartolomé, R.A.; Martín-Regalado, Á.; Jaén, M.; Zannikou, M.; Zhang, P.; Ríos, V.D.L.; Balyasnikova, I.V.; Casal, J.I. Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase-1B Inhibition Disrupts IL13Rα2-Promoted Invasion and Metastasis in Cancer Cells. Cancers 2020, 12, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa, T.; Shimamura, T.; Goto, K.; Nakagawa, R.; Muroyama, R.; Ino, Y.; Horiuchi, H.; Endo, I.; Maeda, S.; Harihara, Y.; et al. A Novel Role of Interleukin 13 Receptor alpha2 in Perineural Invasion and its Association with Poor Prognosis of Patients with Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, S.T.; Tan, K.M.; Kok, C.Y.L.; Guan, S.P.; Lai, S.H.; Lim, C.; Hu, J.; Sturgis, C.; Eng, C.; Lam, P.Y.P.; et al. IL13RA2 Is Differentially Regulated in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma vs Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 5573–5584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimamura, T.; Fujisawa, T.; Husain, S.R.; Joshi, B.H.; Puri, R.K. Interleukin 13 Mediates Signal Transduction through Interleukin 13 Receptor α2 in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Role of IL-13 Pseudomonas Exotoxin in Pancreatic Cancer Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Boesteanu, A.C.; Binder, Z.A.; Xu, C.; Reid, R.A.; Rodriguez, J.L.; Cook, D.R.; Thokala, R.; Blouch, K.; McGettigan-Croce, B.; et al. Checkpoint Blockade Reverses Anergy in IL-13Rα2 Humanized scFv-Based CAR T Cells to Treat Murine and Canine Gliomas. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2018, 11, 20–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibasaki, N.; Yamasaki, T.; Kanno, T.; Arakaki, R.; Sakamoto, H.; Utsunomiya, N.; Inoue, T.; Tsuruyama, T.; Nakamura, E.; Ogawa, O.; et al. Role of IL13RA2 in Sunitinib Resistance in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.A.; Torres, T. JAK/STAT inhibitors for the treatment of atopic dermatitis. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2019, 31, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotter, D.G.; Schairer, D.; Eichenfield, L. Emerging therapies for atopic dermatitis: JAK inhibitors. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2018, 78, S53–S62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanimoto, A.; Shinozaki, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Katsuda, Y.; Taniai-Riya, E.; Toyoda, K.; Kakimoto, K.; Kimoto, Y.; Amano, W.; Konishi, N.; et al. A novel JAK inhibitor JTE-052 reduces skin inflammation and ameliorates chronic dermatitis in rodent models: Comparison with conventional therapeutic agents. Exp. Dermatol. 2017, 27, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.S.; Howell, M.D.; Sun, K.; Papp, K.; Nasir, A.; Kuligowski, M.E. Treatment of atopic dermatitis with ruxolitinib cream (JAK1/JAK2 inhibitor) or triamcinolone cream. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 572–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malemud, C.J. The role of the JAK/STAT signal pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2018, 10, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Xia, N.; Zhang, W.; Wei, Y.; Huang, J.; Ren, Z.; Meng, F.; Yang, L. Anti-arthritic activity of ferulic acid in complete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA)-induced arthritis in rats: JAK2 inhibition. Inflammopharmacology 2019, 28, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhao, Q.; Zhong, L.; Li, Q.; Li, R.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Li, N.; Su, J.; Dhondrup, W.; et al. Tibetan medicine Ershiwuwei Lvxue Pill attenuates collagen-induced arthritis via inhibition of JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 270, 113820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollenberg, A.; Howell, M.D.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Silverberg, J.I.; Kell, C.; Ranade, K.; Moate, R.; van der Merwe, R. Treatment of atopic dermatitis with tralokinumab, an anti–IL-13 mAb. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marone, G.; Granata, F.; Pucino, V.; Pecoraro, A.; Heffler, E.; Loffredo, S.; Scadding, G.W.; Varricchi, G. The Intriguing Role of Interleukin 13 in the Pathophysiology of Asthma. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieber, T. Interleukin-13: Targeting an underestimated cytokine in atopic dermatitis. Allergy 2020, 75, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnarajah, K.; Le, M.; Muntyanu, A.; Mathieu, S.; Nigen, S.; Litvinov, I.V.; Jack, C.S.; Netchiporouk, E. Inhibition of IL-13: A New Pathway for Atopic Dermatitis. J. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2020, 10, 1203475420982553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, T.Y.; Hsiao, J.L.; Shi, V.Y. Therapeutic Potential of Lebrikizumab in the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis. J. Asthma Allergy 2020, 13, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.D.; Flanagan, M.E.; Telliez, J.-B. Discovery and Development of Janus Kinase (JAK) Inhibitors for Inflammatory Diseases. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 5023–5038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskoski, R. Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors in the treatment of inflammatory and neoplastic diseases. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 111, 784–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.; Ye, J.; Liu, Z.; Ren, Y.; He, W.; Xu, J.; He, Y.; Yuan, Y. Complement C3 overexpression activates JAK2/STAT3 pathway and correlates with gastric cancer progression. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.-T.; Liu, X.-F.; Yang, W.-T.; Zheng, P.-S. REX1 promotes EMT-induced cell metastasis by activating the JAK2/STAT3-signaling pathway by targeting SOCS1 in cervical cancer. Oncogene 2019, 38, 6940–6957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Gao, H.; Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, B.; Han, Z.; Chen, X.; Han, M.; Gao, M. Retracted: Hispidulin suppresses cell growth and metastasis by targeting PIM 1 through JAK 2/ STAT 3 signaling in colorectal cancer. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 1369–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Yan, T.; Huang, C.; Xu, Z.; Wang, L.; Jiang, E.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, K.; Shao, Z.; et al. Melanoma cell-secreted exosomal miR-155-5p induce proangiogenic switch of cancer-associated fibroblasts via SOCS1/JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, C.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Z.-X.; Yu, D.; Bai, Z.-M. Salidroside reduces renal cell carcinoma proliferation by inhibiting JAK2/STAT3 signaling. Cancer Biomark. 2016, 17, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, I.G.; Chun, K.-S. Abstract 4844: Thymoquinone induces apoptosis through inhibition of JAK2/STAT3 signaling via production of ROS in human renal cancer Caki cells. Cancer Chem. 2016, 76, 4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, E.L.; Macdonald, A. JAK2 Inhibition Impairs Proliferation and Sensitises Cervical Cancer Cells to Cisplatin-Induced Cell Death. Cancers 2019, 11, 1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Gautam, J.; Kim, J.; Kang, K.W. Inhibition of tumor growth and angiogenesis of tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells by ruxolitinib, a selective JAK2 inhibitor. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 3981–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.X.; Lian, Q.W.; Pan, J.D.; Xu, Z.L.; Zhou, T.M.; Ye, B. JAK2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor AG490 suppresses cell growth and invasion of gallbladder cancer cells via inhibition of JAK2/STAT3 signaling. J. Boil. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2017, 31, 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Cheon, J.H.; Kim, K.S.; Yadav, D.K.; Kim, M.; Kim, H.S.; Yoon, S. The JAK2 inhibitors CEP-33779 and NVP-BSK805 have high P-gp inhibitory activity and sensitize drug-resistant cancer cells to vincristine. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 490, 1176–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClellan, K.J.; Markham, A. Telmisartan. Drugs 1998, 56, 1039–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, M.; Jarvis, B.; Goa, K.L. Telmisartan. Drugs 2001, 61, 1501–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukumaran, V.; Veeraveedu, P.T.; Gurusamy, N.; Yamaguchi, K.; Lakshmanan, A.P.; Ma, M.; Suzuki, K.; Kodama, M.; Watanabe, K. Cardioprotective Effects of Telmisartan against Heart Failure in Rats Induced By Experimental Autoimmune Myocarditis through the Modulation of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme-2/Angiotensin 1-7/Mas Receptor Axis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 7, 1077–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarlane, S. Telmisartan and cardioprotection. Vasc. Heal. Risk Manag. 2011, 7, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, L.D.; Mafura, B.; Lauscher, J.C.; Seeliger, H.; Kreis, M.E.; Gröne, J. Antiproliferative and apoptotic effects of telmisartan in human colon cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 2014, 8, 2681–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuyama, M.; Funao, K.; Kuratsukuri, K.; Tanaka, T.; Kawahito, Y.; Sano, H.; Chargui, J.; Touraine, J.-L.; Yoshimura, N.; Yoshimura, R. Telmisartan inhibits human urological cancer cell growth through early apoptosis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2010, 1, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.T.-L.; Niu, H.-S.; Chen, L.-J.; Cheng, J.-T.; Tong, Y.-C. Increase of human prostate cancer cell (DU145) apoptosis by telmisartan through PPAR-delta pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 775, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheduzzaman, M.; Moon, J.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Nazim, U.M.; Park, S.-Y. Telmisartan generates ROS-dependent upregulation of death receptor 5 to sensitize TRAIL in lung cancer via inhibition of autophagy flux. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 102, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, N.; Nishida, Y.; Ishii, T.; Yoshida, T.; Furukawa, Y.; Narahara, H. Telmisartan Induces Growth Inhibition, DNA Double-Strand Breaks and Apoptosis in Human Endometrial Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Júnior, R.F.D.A.; Oliveira, A.L.C.L.; Silveira, R.F.D.M.; Rocha, H.A.D.O.; Cavalcanti, P.D.F.; De Araújo, A.A. Telmisartan induces apoptosis and regulates Bcl-2 in human renal cancer cells. Exp. Biol. Med. 2014, 240, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, N.; Fujita, K.; Iwama, H.; Kobara, H.; Fujihara, S.; Chiyo, T.; Namima, D.; Yamana, H.; Kono, T.; Takuma, K.; et al. Antihypertensive drug telmisartan suppresses the proliferation of gastric cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 44, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, T.; Chiyo, T.; Kobara, H.; Fujihara, S.; Fujita, K.; Namima, D.; Nakahara, M.; Kobayashi, N.; Nishiyama, N.; Yachida, T.; et al. Telmisartan Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Tumor Growth of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Inducing S-Phase Arrest In Vitro and In Vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrero, M.B.; Venema, V.J.; Ju, H.; Eaton, D.C.; Venema, R.C. Regulation of angiotensin II-induced JAK2 tyrosine phosphorylation: Roles of SHP-1 and SHP-2. Am. J. Physiol. Content 1998, 275, C1216–C1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McWhinney, C.D.; Dostal, D.; Baker, K. Angiotensin II Activates Stat5 Through Jak2 Kinase in Cardiac Myocytes. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 1998, 30, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, S.S.; Schmidt, A.M.; Banes, A.K.; Wang, X.; Stern, D.M.; Marrero, M.B. S100B-RAGE-Mediated Augmentation of Angiotensin II-Induced Activation of JAK2 in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Is Dependent on PLD2. Diabetes 2003, 52, 2381–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Banes-Berceli, A.K.L.; Ketsawatsomkron, P.; Ogbi, S.; Patel, B.; Pollock, D.M.; Marrero, M.B. Angiotensin II and endothelin-1 augment the vascular complications of diabetes via JAK2 activation. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2007, 293, H1291–H1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Ye, S.; Zou, C.; Chen, T.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Jiang, L.; Xu, J.; Huang, W.; Wang, Y.; et al. Angiotensin II Causes Biphasic STAT3 Activation Through TLR4 to Initiate Cardiac Remodeling. Hypertension 2018, 72, 1301–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wu, F.; Xu, Y.; Yan, J.-X.; Wu, Y.-D.; Li, S.-H.; Liao, X.; Liang, J.-X.; Li, Z.-H.; Liu, H.-W. A novel role of angiotensin II in epidermal cell lineage determination: Angiotensin II promotes the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into keratinocytes through the p38 MAPK, JNK and JAK2 signalling pathways. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 28, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, E.; Li, Y.; Anand-Srivastava, M.B. Role of JAK2/STAT3 pathway in angiotensin II-induced enhanced expression of Giα proteins and hyperproliferation of aortic vascular smooth muscle cells. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2021, 99, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.-Y.; Zhang, C.; Xiao, Q.-F.; Dou, H.; Chen, Y.; Gu, C.-M.; Cui, M.-J. Hepatocyte growth factor inhibits tubular epithelial-myofibroblast transdifferentiation by suppression of angiotensin II via the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 2737–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, S.G.; Phipps, R.P. The nuclear receptor PPAR gamma is expressed by mouse T lymphocytes and PPAR gamma agonists induce apoptosis. Eur. J. Immunol. 2001, 31, 1098–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.M.; Desouky, E.M.; Hozayen, W.G.; Bin-Jumah, M.; El-Nahass, E.-S.; Soliman, H.A.; Farghali, A.A. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Trigger Liver and Kidney Injury and Fibrosis Via Altering TLR4/NF-κB, JAK2/STAT3 and Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling in Rats. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Sun, K.; Wu, H.; Chen, X.; Tang, H.; Mao, J. PPARγ alleviated hepatocyte steatosis through reducing SOCS3 by inhibiting JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 498, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.X.; Lin, S.Y.; Lian, S.X.; Qiu, Y.R.; Li, Z.H.; Chen, Z.H.; Lu, W.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, L.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Inhibition of the breast cancer by PPARγ agonist pioglitazone through JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Neoplasma 2020, 67, 834–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Characteristics | Overall Renal Cell Carcinoma (n = 229) | Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma (n = 201) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | IL13Rα2 Positive | P | No. | IL13Rα2 Positive | P | ||
| Sex | Male | 156 | 86 (55%) | 0.411 | 140 | 71 (51%) | 0.530 |
| Female | 73 | 36 (49%) | 61 | 28 (46%) | |||
| Age, y | ≤55 | 95 | 46 (48%) | 0.215 | 82 | 35 (43%) | 0.122 |
| >55 | 134 | 76 (57%) | 119 | 64 (54%) | |||
| Tumor size, cm | ≤7 | 193 | 95 (49%) | 0.004 | 169 | 76 (45%) | 0.005 |
| >7 | 36 | 27 (75%) | 32 | 23 (72%) | |||
| TNM stage | I | 183 | 88 (48%) | 0.002 | 163 | 72 (44%) | 0.003 |
| II-IV | 46 | 34 (74%) | 38 | 27 (71%) | |||
| LN metastasis | Absence | 226 | 119 (53%) | 0.103 | 199 | 97 (49%) | 0.149 |
| Presence | 3 | 3 (100%) | 2 | 2 (100%) | |||
| Nuclear grade | 1 | 45 | 17 (38%) | <0.001 | 36 | 10 (28%) | <0.001 |
| 2 | 134 | 67 (50%) | 123 | 59 (48%) | |||
| 3 and 4 | 50 | 38 (76%) | 42 | 30 (71%) | |||
| Necrosis | Absence | 196 | 102 (52%) | 0.362 | 174 | 85 (49%) | 0.772 |
| Presence | 33 | 20 (61%) | 27 | 14 (52%) | |||
| Histologic type | Clear cell | 201 | 99 (49%) | 0.005 | |||
| Chromophobe | 16 | 13 (81%) | |||||
| Papillary | 12 | 10 (83%) | |||||
| Characteristics. | No. | CSS | RFS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | P | HR (95% CI) | P | ||
| Overall RCC (n = 229) | |||||
| Sex, male (vs. female) | 156/229 | 0.564 (0.258–1.234) | 0.152 | 0.513 (0.255–1.030) | 0.060 |
| Age, y, >55 (vs. ≤55) | 134/229 | 4.386 (1.828–10.524) | <0.001 | 2.537 (1.319–4.880) | 0.005 |
| Tumor size, >7 cm (vs. ≤7 cm) | 36/229 | 3.415 (1.736–6.715) | <0.001 | 3.984 (2.218–7.155) | <0.001 |
| TNM stage, I (vs. II-IV) | 46/229 | 4.231 (2.219–8.068) | <0.001 | 5.166 (2.930–9.018) | <0.001 |
| LN metastasis, presence (vs. absence) | 3/229 | 1.670 (0.226–12.308) | 0.615 | 17.410 (3.874–78.249) | <0.001 |
| Nuclear grade, 1 | 45/229 | 1 | 0.032 | 1 | 0.008 |
| 2 | 134/229 | 0.943 (0.347–2.564) | 0.909 | 1.172 (0.476–2.883) | 0.730 |
| 3 and 4 | 50/229 | 2.327 (0.836–6.476) | 0.106 | 2.846 (1.128–7.179) | 0.027 |
| Necrosis, presence (vs. absence) | 33/229 | 3.620 (1.842–7.114) | <0.001 | 2.542 (1.345–4.807) | 0.004 |
| Histologic type, clear cell | 201/229 | 1 | 0.654 | 1 | 0.328 |
| chromophobe | 16/229 | 0.808 (0.193–3.382) | 0.771 | 0.585 (0.141–2.421) | 0.460 |
| papillary | 12/229 | 1.570 (0.553–4.462) | 0.397 | 1.802 (0.711–4.565) | 0.214 |
| IL13Rα2, positive (vs. negative) | 122/229 | 3.726 (1.636–8.489) | 0.002 | 3.625 (1.806–7.278) | <0.001 |
| Clear cell RCC (n = 201) | |||||
| Sex, male (vs. female) | 140/201 | 0.541 (0.222–1.319) | 0.177 | 0.523 (0.241–1.132) | 0.100 |
| Age, y, >55 (vs. ≤55) | 119/201 | 4.152 (1.593–10.822) | 0.004 | 2.491 (1.220–5.084) | 0.012 |
| Tumor size, >7 cm (vs. ≤7 cm) | 32/201 | 3.977 (1.928–8.204) | <0.001 | 4.773 (2.560–8.900) | <0.001 |
| TNM stage, I (vs. II-IV) | 38/201 | 3.964 (1.953–8.049) | <0.001 | 5.199 (2.814–9.604) | <0.001 |
| LN metastasis, presence (vs. absence) | 2/201 | 0.049 (0.000–7.516 × 105) | 0.721 | 14.681 (1.841–117.039) | 0.011 |
| Nuclear grade, 1 | 36/201 | 1 | 0.170 | 1 | 0.028 |
| 2 | 123/201 | 1.028 (0.344–3.075) | 0.961 | 1.122 (0.423–2.978) | 0.817 |
| 3 and 4 | 42/201 | 2.111 (0.661–6.739) | 0.207 | 2.655 (0.955–7.380) | 0.061 |
| Necrosis, presence (vs. absence) | 27/201 | 3.044 (1.401–6.617) | 0.005 | 2.016 (0.962–4.225) | 0.063 |
| IL13Rα2, positive (vs. negative) | 99/201 | 3.591 (1.546–8.342) | 0.003 | 3.518 (1.724–7.181) | <0.001 |
| Characteristics | CSS | RFS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | P | HR (95% CI) | P | |
| Overall RCC (n = 229) * | ||||
| Age, y, >55 (vs. ≤55) | 2.941 (1.200–7.209) | 0.018 | ||
| TNM stage, I (vs. II-IV) | 2.600 (1.331–5.077) | 0.005 | 4.036 (2.260–7.209) | <0.001 |
| Necrosis, presence (vs. absence) | 2.686 (1.350–5.345) | 0.005 | 2.240 (1.172–4.278) | 0.015 |
| IL13Rα2, positive (vs. negative) | 2.627 (1.132–6.097) | 0.025 | 2.801 (1.379–5.688) | 0.004 |
| Clear cell RCC (n = 201) ** | ||||
| Age, y, >55 (vs. ≤55) | 2.779 (1.036–7.453) | 0.042 | ||
| TNM stage, I (vs. II-IV) | 2.616 (1.255–5.451) | 0.010 | 4.214 (2.257–7.867) | <0.001 |
| Necrosis, presence (vs. absence) | 3.002 (1.361–6.618) | 0.006 | 2.088 (0.988–4.414) | 0.054 |
| IL13Rα2, positive (vs. negative) | 2.792 (1.182–6.595) | 0.019 | 2.838 (1.372–5.870) | 0.005 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, M.-A.; Lee, J.; Lee, C.M.; Park, H.S.; Jang, K.Y.; Park, S.-H. IL13Rα2 Is Involved in the Progress of Renal Cell Carcinoma through the JAK2/FOXO3 Pathway. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11040284
Kang M-A, Lee J, Lee CM, Park HS, Jang KY, Park S-H. IL13Rα2 Is Involved in the Progress of Renal Cell Carcinoma through the JAK2/FOXO3 Pathway. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(4):284. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11040284
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Mi-Ae, Jongsung Lee, Chang Min Lee, Ho Sung Park, Kyu Yun Jang, and See-Hyoung Park. 2021. "IL13Rα2 Is Involved in the Progress of Renal Cell Carcinoma through the JAK2/FOXO3 Pathway" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 4: 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11040284
APA StyleKang, M.-A., Lee, J., Lee, C. M., Park, H. S., Jang, K. Y., & Park, S.-H. (2021). IL13Rα2 Is Involved in the Progress of Renal Cell Carcinoma through the JAK2/FOXO3 Pathway. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(4), 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11040284









