Reappraisal of the Prognostic Factors of Outcome and Recovery Time in Patients with Idiopathic Bell’s Palsy: A Retrospective Single-Center Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holland, N.J.; Bernstein, J.M. Bell’s Palsy. BMJ Clin. Evid. 2014, 2014, 1204. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peitersen, E. Bell’s Palsy: The Spontaneous Course of 2500 Peripheral Facial Nerve Palsies of Different Etiologies. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2009, 122, 4–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.Y.; Byun, J.Y.; Park, M.S.; Yeo, S.G. Effect of Aging on the Prognosis of Bell’s Palsy. Otol. Neurotol. 2013, 34, 766–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanazawa, A.; Haginomori, S.-I.; Takamaki, A.; Nonaka, R.; Araki, M.; Takenaka, H. Prognosis for Bell’s palsy: A comparison of diabetic and nondiabetic patients. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2007, 127, 888–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillman, G.S.; Schaitkin, B.M.; May, M.; Klein, S.R. Bell’s Palsy in Pregnancy: A Study of Recovery Outcomes. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2002, 126, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khedr, E.M.; El-Fetoh, N.A.; El-Hammady, D.H.; Ghandour, A.M.; Osama, K.; Zaki, A.F.; Gamea, A. Prognostic Role of Neurophysiological Testing 3–7 Days after Onset of Acute Unilateral Bell’s Palsy. Neurophysiol. Clin. 2018, 48, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hah, Y.M.; Kim, S.H.; Jung, J.; Kim, S.S.; Byun, J.Y.; Park, M.S.; Yeo, S.G. Prognostic value of the blink reflex test in Bell’s palsy and Ramsay-Hunt syndrome. Auris Nasus Larynx 2018, 45, 966–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Almeida, J.R.; Guyatt, G.H.; Sud, S.; Dorion, J.; Hill, M.D.; Kolber, M.R.; Lea, J.; Reg, S.L.; Somogyi, B.K.; Westerberg, B.D.; et al. Management of Bell palsy: Clinical practice guideline. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2014, 186, 917–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baugh, R.F.; Basura, G.J.; Ishii, L.E.; Schwartz, S.R.; Drumheller, C.M.; Burkholder, R.; Deckard, N.A.; Dawson, C.; Driscoll, C.; Gillespie, M.B.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline: Bell’s Palsy. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2013, 149 (Suppl. S3), S1–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, C.-H.; Chang, K.-H.; Wu, Y.-M.; Chen, Y.-L.; Lyu, R.-K.; Chang, H.-S.; Wu, Y.-R.; Chen, C.-M.; Huang, C.-C.; Chu, C.-C.; et al. A comparison of benign and inflammatory manifestations of Tolosa-Hunt syndrome. Cephalalgia 2013, 33, 842–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulson, S.E.; Croxson, G.R.; Adams, R.D.; O’Dwyer, N.J. Reliability of the “Sydney,” “Sunnybrook,” and “House Brackmann” Facial Grading Systems to Assess Voluntary Movement and Synkinesis after Facial Nerve Paralysis. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2005, 132, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, M.C.; Soh, Y.; Chon, J.; Lee, J.H.; Jung, J.; Kim, S.S.; You, M.-W.; Byun, J.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Yeo, S.G. Evaluation of Factors Associated With Favorable Outcomes in Adults With Bell Palsy. JAMA Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2020, 146, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Oh, D.J.; Park, B.; Choi, H.G. Bell’s palsy and obesity, alcohol consumption and smoking: A nested case-control study using a national health screening cohort. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takemoto, N.; Horii, A.; Sakata, Y.; Inohara, H. Prognostic Factors of Peripheral Facial Palsy: Multivariate Analysis Followed by Receiver Operating Characteristic and Kaplan-Meier Analyses. Otol. Neurotol. 2011, 32, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riga, M.; Kefalidis, G.; Danielides, V. The Role of Diabetes Mellitus in the Clinical Presentation and Prognosis of Bell Palsy. J. Am. Board Fam. Med. 2012, 25, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, S.W.; Lee, D.H.; Jun, B.C.; Chang, K.H.; Park, Y.S. Analysis of Prognostic Factors in Bell’s Palsy and Ramsay Hunt Syndrome. Auris Nasus Larynx 2007, 34, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, I.M.; Maynard, C.; Mountain, R.E.; Barr-Hamilton, R.; Armstrong, M.; Murray, J.A. The Prognostic Value of Facial Electroneurography in Bell’s Palsy. Clin. Otolaryngol. Allied Sci. 1994, 19, 201–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Niu, X.; Ni, P.; Zhang, W.; Shao, B. Prognostic Factors of Bell’s Palsy and Ramsay Hunt Syndrome. Medicine 2017, 96, e5898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, F.M.; Swan, I.R.; Donnan, P.T.; Morrison, J.M.; Smith, B.H.; McKinstry, B.; Davenport, R.J.; Vale, L.D.; Clarkson, J.E.; Hammersley, V.; et al. Early Treatment with Prednisolone or Acyclovir in Bell’s Palsy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 1598–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engström, M.; Berg, T.; Stjernquist-Desatnik, A.; Axelsson, S.; Pitkäranta, A.; Hultcrantz, M.; Kanerva, M.; Hanner, P.; Jonsson, L. Prednisolone and Valaciclovir in Bell’s Palsy: A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Multicentre Trial. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 993–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
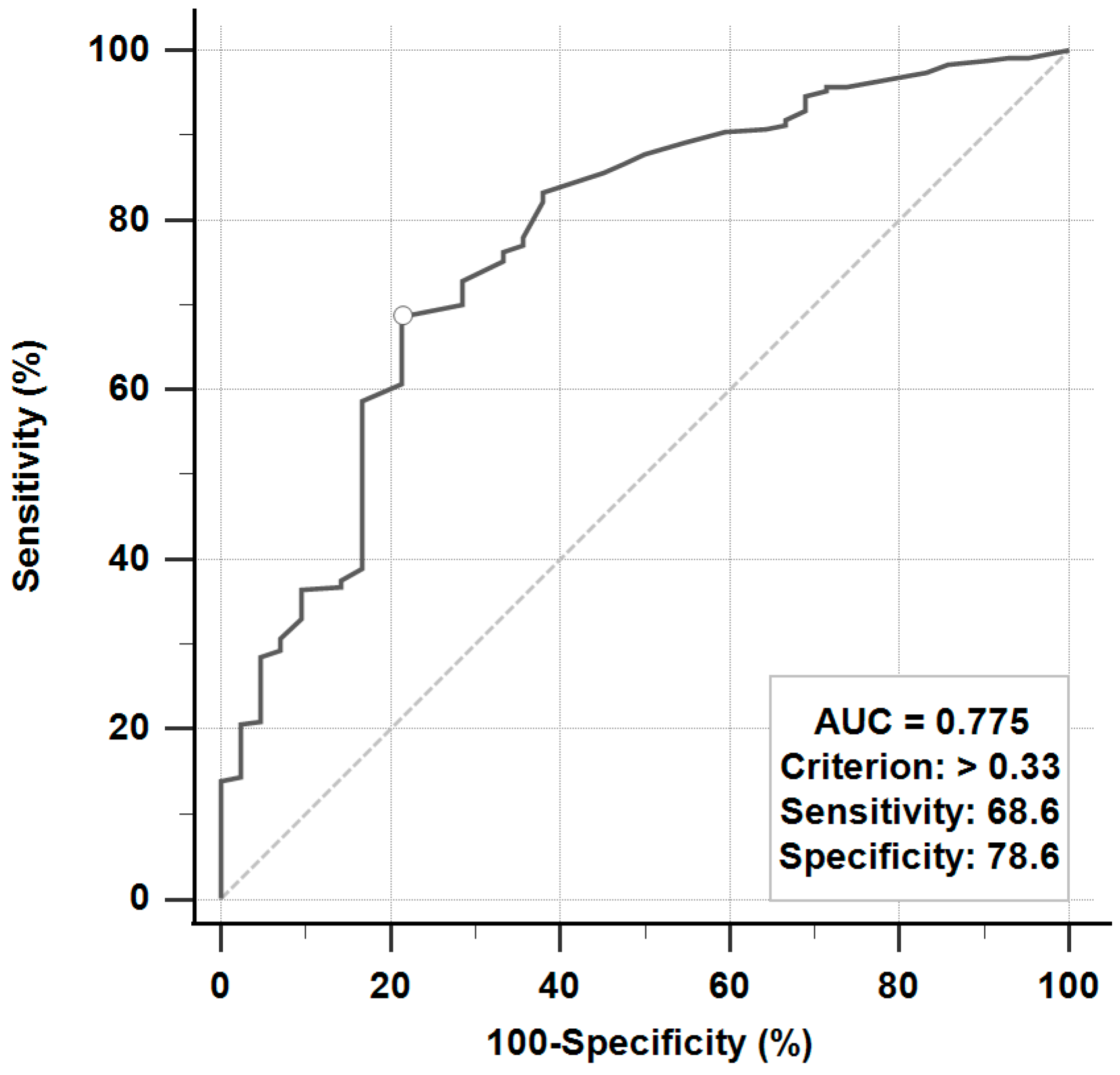
| Variable | All, n (%) | Favorable Outcome, n (%) | Unfavorable Outcome, n (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients, n | 396 (100) | 354 (89.4) | 42 (10.6) | |
| Age, years | 0.354 | |||
| <60 | 314 (79.3) | 283 (79.9) | 31 (73.8) | |
| ≥60 | 82 (20.7) | 71 (20.1) | 11 (26.2) | |
| Sex | 0.103 | |||
| Female | 179 (45.2) | 165 (46.6) | 14 (33.3) | |
| Male | 217 (54.8) | 189 (53.4) | 28 (66.7) | |
| Affected site | 0.279 | |||
| Right | 195 (50.8) | 183 (51.7) | 18 (42.9) | |
| Left | 201 (49.2) | 171 (48.3) | 24 (57.1) | |
| Smoking | 0.208 | |||
| No | 329 (83.1) | 297 (83.9) | 32 (76.2) | |
| Yes | 67 (16.9) | 57 (16.1) | 10 (23.8) | |
| Alcohol drinking | 0.226 | |||
| No | 352 (88.9) | 317 (89.5) | 35 (83.3) | |
| Yes | 44 (11.1) | 37 (10.5) | 7 (16.7) | |
| Betel nut chewing | 0.074 | |||
| No | 373 (94) | 336 (94.9) | 37 (88.1) | |
| Yes | 23 (6) | 18 (5.1) | 5 (11.9) | |
| Diabetes | 0.364 | |||
| No | 339 (85.6) | 305 (86.2) | 34 (81) | |
| Yes | 57 (14.4) | 49 (13.8) | 8 (19) | |
| Hypertension | 0.849 | |||
| No | 334 (84.3) | 299 (84.5) | 35 (83.3) | |
| Yes | 62 (15.7) | 55 (15.5) | 7 (16.7) | |
| Hyperlipidemia | 0.489 | |||
| No | 384 (97) | 344 (97.2) | 40 (95.2) | |
| Yes | 12 (3) | 10 (28.2) | 2 (4.8) | |
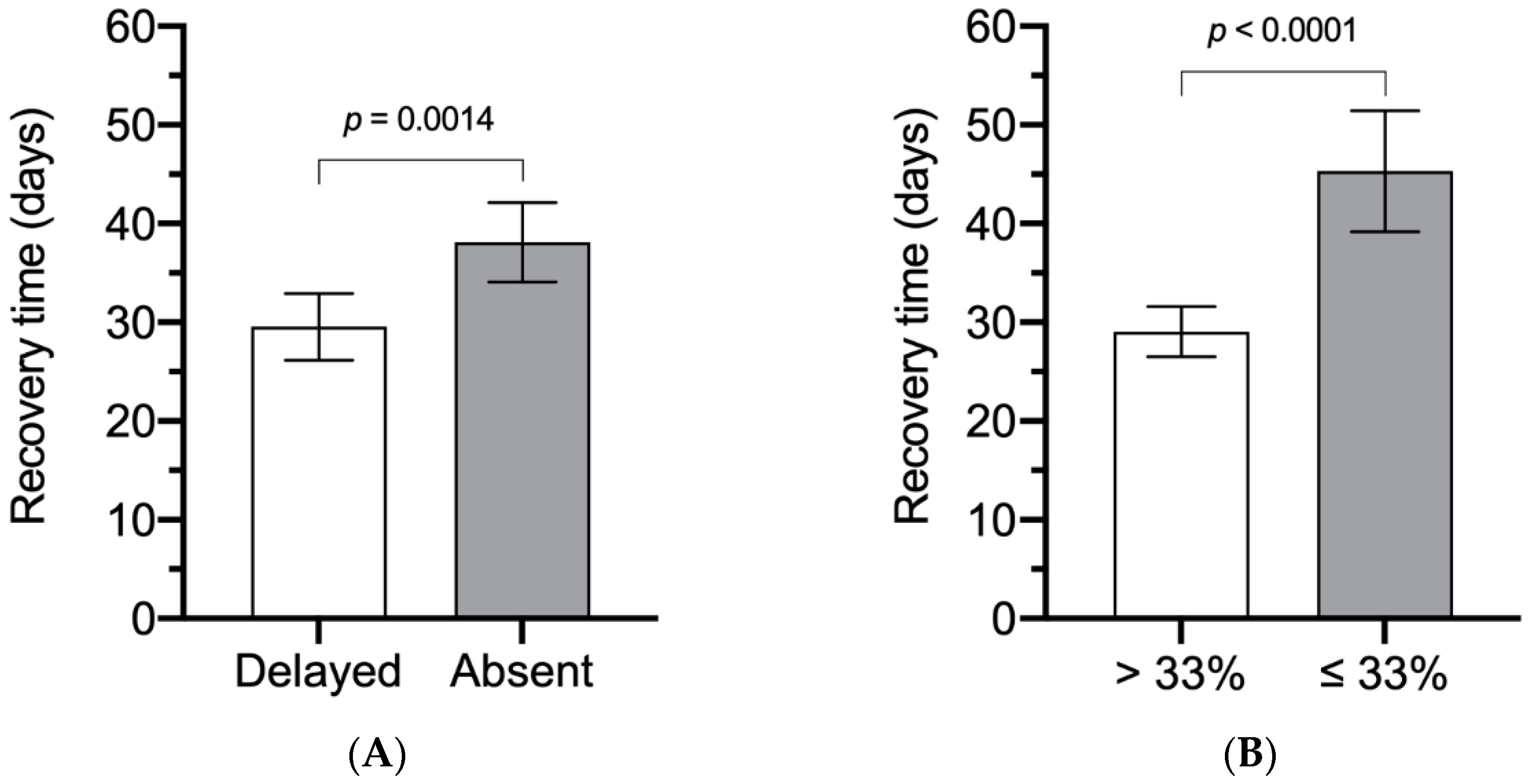
| Blink reflex | 0.0001 * | |||
| Delayed | 149 (37.6) | 145 (41) | 4 (9.5) | |
| Absent | 247 (62.4) | 209 (59) | 38 (90.5) | |
| Electroneurography | <0.0001 * | |||
| >33% | 254 (64.1) | 244 (68.9) | 10 (23.8) | |
| ≤33% | 142 (35.9) | 110 (31.1) | 32 (76.2) | |
| Treatment | 0.719 | |||
| Supportive care | 14 (3.5) | 12 (3.4) | 2 (4.8) | |
| Low-dose steroid a | 249 (62.9) | 221 (62.4) | 28 (66.7) | |
| High-dose steroid b | 133 (33.6) | 121 (34.2) | 12 (28.6) |
| Variable | Odds Ratio (95% CI) |
|---|---|
| Age, years | |
| <60 | 1.23 (0.51 to 2.97) |
| ≥60 | 1 (Reference) |
| Sex | |
| Female | 1.53 (0.70 to 3.36) |
| Male | 1 (Reference) |
| Smoking | |
| No | 1.28 (0.35 to 3.92) |
| Yes | 1 (Reference) |
| Alcohol drinking | |
| No | 1.41 (0.34 to 5.88) |
| Yes | 1 (Reference) |
| Betel nut chewing | |
| No | 1.36 (0.28 to 6.55) |
| Yes | 1 (Reference) |
| Diabetes | |
| No | 1.21 (0.43 to 3.39) |
| Yes | 1 (Reference) |
| Hypertension | |
| No | 1 (Reference) |
| Yes | 1.42 (0.44 to 4.54) |
| Hyperlipidemia | |
| No | 2.52 (0.41 to 15.55) |
| Yes | 1 (Reference) |
| Blink reflex | |
| Delayed | 5.38 (1.82 to 15.90) * |
| Absent | 1 (Reference) |
| Electroneurography | |
| >33% | 6.67 (3.02 to 14.71) * |
| ≤33% | 1 (Reference) |
| Treatment | |
| Supportive care | 1 (Reference) |
| Low-dose steroid a | 1.45 (0.22 to 9.72) |
| High-dose steroid b | 0.93 (0.13 to 6.60) |
| Duration | |
| ≤7 days | 2.41 (0.88 to 6.65) |
| >7 days | 1 (Reference) |
| Independent Variables | Coefficient | Standard Error | t-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Constant) | 52.93 | |||
| Age | −8.02 | 3.40 | −2.36 | 0.019 * |
| Blink reflex | −5.76 | 2.88 | −2.00 | 0.046 * |
| Electroneurography | −14.84 | 2.90 | −5.11 | <0.0001 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, C.-H.; Chen, J.-L.; Liao, M.-F.; Hsu, J.-L.; Hsu, H.-C.; Ro, L.-S. Reappraisal of the Prognostic Factors of Outcome and Recovery Time in Patients with Idiopathic Bell’s Palsy: A Retrospective Single-Center Analysis. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11030171
Peng C-H, Chen J-L, Liao M-F, Hsu J-L, Hsu H-C, Ro L-S. Reappraisal of the Prognostic Factors of Outcome and Recovery Time in Patients with Idiopathic Bell’s Palsy: A Retrospective Single-Center Analysis. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(3):171. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11030171
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Chi-Hao, Jiun-Liang Chen, Ming-Feng Liao, Jung-Lung Hsu, Hui-Ching Hsu, and Long-Sun Ro. 2021. "Reappraisal of the Prognostic Factors of Outcome and Recovery Time in Patients with Idiopathic Bell’s Palsy: A Retrospective Single-Center Analysis" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 3: 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11030171
APA StylePeng, C.-H., Chen, J.-L., Liao, M.-F., Hsu, J.-L., Hsu, H.-C., & Ro, L.-S. (2021). Reappraisal of the Prognostic Factors of Outcome and Recovery Time in Patients with Idiopathic Bell’s Palsy: A Retrospective Single-Center Analysis. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(3), 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11030171







