Expression of Selected Genes Involved in Neurogenesis in the Etiopathogenesis of Depressive Disorders
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects and Data Collection
2.2. Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HDRS)
2.3. Collection and Storage of Blood Samples
2.4. Determination of mRNA Gene Expression
2.4.1. Total RNA Isolation
2.4.2. Quality Analysis of Isolated RNA
2.4.3. RT-PCR Reverse Transcription
2.4.4. Real-Time PCR Reaction
2.5. Determination of NGF, BDNF, GDNF and REST (NRSF) Protein Expression
2.5.1. Determining Protein Concentration
2.5.2. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Mean Gene Expression
3.2. Correlation with Depression Severity
3.3. Correlation with Gender and Age
4. Discussion
4.1. Nerve Growth Factor (NGF)
4.2. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF)
4.3. Glial-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (GDNF)
4.4. RE1-Silencing Transcription Factor (REST)/Neuron-Restrictive Silencer Factor (NRSF)
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miller, B.R.; Hen, R. The current state of the neurogenic theory of depression and anxiety. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2015, 30, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schloesser, R.J.; Manji, H.K.; Martinowich, K. Suppression of adult neurogenesis leads to an increased hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis response. NeuroReport 2009, 20, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Diorio, J.; Tannenbaum, B.; Caldji, C.; Francis, D.; Freedman, A.; Sharma, S.; Pearson, D.; Plotsky, P.M.; Meaney, M.J. Maternal Care, Hippocampal Glucocorticoid Receptors, and Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Responses to Stress. Science 1997, 277, 1659–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suri, D.; Vaidya, V. Glucocorticoid regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor: Relevance to hippocampal structural and functional plasticity. Neuroscience 2013, 239, 196–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Numakawa, T.; Odaka, H.; Adachi, N. Actions of Brain-Derived Neurotrophin Factor in the Neurogenesis and Neuronal Function, and Its Involvement in the Pathophysiology of Brain Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belleau, E.L.; Treadway, M.T.; Pizzagalli, D.A. The Impact of Stress and Major Depressive Disorder on Hippocampal and Medial Prefrontal Cortex Morphology. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 85, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, S.E.; Scheinost, D.; Finnema, S.J.; Naganawa, M.; Davis, M.T.; DellaGioia, N.; Nabulsi, N.; Matuskey, D.; Angarita, G.A.; Pietrzak, R.H.; et al. Lower synaptic density is associated with depression severity and network alterations. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacQueen, G.M.; Yucel, K.; Taylor, V.H.; Macdonald, K.; Joffe, R. Posterior Hippocampal Volumes Are Associated with Remission Rates in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 64, 880–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duman, R.S.; Shinohara, R.; Fogaça, M.V.; Hare, B. Neurobiology of rapid-acting antidepressants: Convergent effects on GluA1-synaptic function. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 1816–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machaliński, B.; Łażewski-Banaszak, P.; Dąbkowska, E.; Paczkowska, E.; Gołąb-Janowska, M.; Nowacki, P. Rola czynników neurotroficznych w procesach regeneracji układu nerwowego. Neurol. Neurochir. Polska 2012, 46, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldelli, P.; Meldolesi, J. The Transcription Repressor REST in Adult Neurons: Physiology, Pathology, and Diseases. Eneuro 2015, 2, 0010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozzi, A.; Guerini, F.R.; Forni, D.; Costa, A.S.; Nemni, R.; Baglio, F.; Cabinio, M.; Riva, S.; Pontremoli, C.; Clerici, M.; et al. REST, a master regulator of neurogenesis, evolved under strong positive selection in humans and in non human primates. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems; 10th ed.; World Health Organization: Genewa, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, M. A RATING SCALE FOR DEPRESSION. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1960, 23, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demyttenaere, K.; De Fruyt, J. Getting What You Ask for: On the Selectivity of Depression Rating Scales. Psychother. Psychosom. 2003, 72, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.W.; Lin, P.Y.; Tu, K.Y.; Cheng, Y.S.; Wu, C.K.; Tseng, P.T. Significantly lower nerve growth factor levels in patients with major depressive disorder than in healthy subjects: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2015, 11, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, T.; He, S.; Hong, B.; Peng, D.; Su, H.; Li, F.; Tang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Fang, Y.; et al. Nerve growth factor variations in patients with mood disorders: No changes in eight weeks of clinical treatment. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2014, 10, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pariante, C.M.; Miller, A.H. Glucocorticoid receptors in major depression: Relevance to pathophysiology and treatment. Biol. Psychiatry 2001, 49, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, J.; Uys, J.D.K.; Marais, L.; Stein, D.J.; Daniels, W.M.U. Early maternal separation followed by later stressors leads to dysregulation of the HPA-axis and increases in hippocampal NGF and NT-3 levels in a rat model. Metab. Brain Dis. 2006, 21, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aisa, B.; Gil-Bea, F.J.; Marcos, B.; Tordera, R.; Lasheras, B.; Del Río, J.; Ramirez, M.J. Neonatal stress affects vulnerability of cholinergic neurons and cognition in the rat: Involvement of the HPA axis. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2009, 34, 1495–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirulli, F.; Alleva, E. The NGF saga: From animal models of psychosocial stress to stress-related psychopathology. Front. Neuroendocr. 2009, 30, 379–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiener, C.D.; Ferreira, S.D.M.; Moreira, F.P.; Bittencourt, G.; De Oliveira, J.F.; Molina, M.L.; Jansen, K.; Souza, L.D.D.M.; Lara, D.R.; Portela, L.V.; et al. Serum levels of nerve growth factor (NGF) in patients with major depression disorder and suicide risk. J. Affect. Disord. 2015, 184, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martocchia, A.; Sigala, S.; Proietti, A.; D’Urso, R.; Spano, P.; Missale, C.; Falaschi, P. Sex-related variations in serum nerve growth factor concentration in humans. Neuropeptides 2002, 36, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terry, A.V.; Kutiyanawalla, A.; Pillai, A. Age-dependent alterations in nerve growth factor (NGF)-related proteins, sortilin, and learning and memory in rats. Physiol. Behav. 2011, 102, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortress, A.M.; Buhusi, M.; Helke, K.L.; Granholm, A.-C.E. Cholinergic Degeneration and Alterations in the TrkA and p75NTR Balance as a Result of Pro-NGF Injection into Aged Rats. J. Aging Res. 2011, 2011, 460543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linker, R.; Gold, R.; Luhder, F. Function of Neurotrophic Factors Beyond the Nervous System: Inflammation and Autoimmune Demyelination. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 29, 43–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubera, M.; Obuchowicz, E.; Goehler, L.; Brzeszcz, J.; Maes, M. In animal models, psychosocial stress-induced (neuro)inflammation, apoptosis and reduced neurogenesis are associated to the onset of depression. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 35, 744–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, C.; Jesse, C.; Donato, F.; Giacomeli, R.; Del Fabbro, L.; Antunes, M.D.S.; De Gomes, M.; Goes, A.; Boeira, S.; Prigol, M.; et al. Chronic unpredictable mild stress decreases BDNF and NGF levels and Na+, K+-ATPase activity in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex of mice: Antidepressant effect of chrysin. Neuroscience 2015, 289, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, T.; Ishikawa, M.; Niitsu, T.; Nakazato, M.; Watanabe, H.; Shiraishi, T.; Shiina, A.; Hashimoto, T.; Kanahara, N.; Hasegawa, T.; et al. Decreased Serum Levels of Mature Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF), but Not Its Precursor proBDNF, in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bus, B.A.A.; Molendijk, M.L.; Tendolkar, I.; Penninx, B.W.J.H.; Prickaerts, J.; Elzinga, B.M.; Voshaar, R.C.O. Chronic depression is associated with a pronounced decrease in serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor over time. Mol. Psychiatry 2015, 20, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molendijk, M.; Bus, B.A.; Spinhoven, P.; Penninx, B.W.; Kenis, G.; Prickaerts, J.; Voshaar, R.O.; Elzinga, B. Serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in major depressive disorder: State–trait issues, clinical features and pharmacological treatment. Mol. Psychiatry 2010, 16, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, S.; Duman, R.; Sanacora, G. Serum Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor, Depression, and Antidepressant Medications: Meta-Analyses and Implications. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 64, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karege, F.; Vaudan, G.; Schwald, M.; Perroud, N.; La Harpe, R. Neurotrophin levels in postmortem brains of suicide victims and the effects of antemortem diagnosis and psychotropic drugs. Mol. Brain Res. 2005, 136, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacón-Fernández, P.; Säuberli, K.; Colzani, M.; Moreau, T.; Ghevaert, C.; Barde, Y.-A. Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor in Megakaryocytes*. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 9872–9881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimura, H.; Altar, C.A.; Chen, R.; Nakamura, T.; Nakahashi, T.; Kambayashi, J.; Sun, B.; Tandon, N.N. Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor Is Stored in Human Platelets and Released by Agonist Stimulation. Thromb. Haemost. 2002, 87, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Banks, W.A.; Fasold, M.B.; Bluth, J.; Kastin, A.J. Transport of brain-derived neurotrophic factor across the blood–brain barrier. Neuropharmacology 1998, 37, 1553–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Li, W.; Lv, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhan, X. BDNF as a biomarker in diagnosis and evaluation of treatment for schizophrenia and depression. Discov. Med. 2018, 26, 127–136. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Du, X.-D.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, G.; Zhang, B.-S.; Soares, J.C.; Zhang, X.Y. Association of low serum BDNF with depression in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2017, 41, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jevtović, S.; Karlović, D.; Mihaljević-Peleš, A.; Šerić, V.; Vrkić, N.; Jakšić, N. Serum Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF): The severity and symptomatic dimensions of depression. Psychiatr. Danub. 2011, 23, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Caldieraro, M.A.; Vares, E.A.; Souza, L.H.; Spanemberg, L.; Guerra, T.A.; Wollenhaupt-Aguiar, B.; Ferrari, P.; Nierenberg, A.A.; Fleck, M.P. Illness severity and biomarkers in depression: Using a unidimensional rating scale to examine BDNF. Compr. Psychiatry 2017, 75, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, A.B.; Frey, B.N.; Andreazza, A.C.; Goi, J.D.; Rosa, A.R.; Gonçalves, C.A.; Santin, A.; Kapczinski, F. Serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor is decreased in bipolar disorder during depressive and manic episodes. Neurosci. Lett. 2006, 398, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marano, C.M.; Phatak, P.; Vemulapalli, U.R.; Sasan, A.; Nalbandyan, M.R.; Ramanujam, S.; Soekadar, S.R.; Demosthenous, M.; Regenold, W.T. Increased Plasma Concentration of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor with Electroconvulsive Therapy. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2007, 68, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimura, R.; Mitoma, M.; Sugita, A.; Hori, H.; Okamoto, T.; Umene, W.; Ueda, N.; Nakamura, J. Effects of paroxetine or milnacipran on serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor in depressed patients. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 31, 1034–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filuś, J.; Rybakowski, J. Serum BDNF levels and intensity of depressive symptoms. Neuropsychiatr. Neuropsychol. 2010, 5, 155–162. [Google Scholar]
- E Lang, U.; Hellweg, R.; Gallinat, J. BDNF Serum Concentrations in Healthy Volunteers are Associated with Depression-Related Personality Traits. Neuropsychopharmacology 2004, 29, 795–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lommatzsch, M.; Zingler, D.; Schuhbaeck, K.; Schloetcke, K.; Zingler, C.; Schuff-Werner, P.; Virchow, J.C. The impact of age, weight and gender on BDNF levels in human platelets and plasma. Neurobiol. Aging 2005, 26, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.B.; Ye, K. Sex differences in brain-derived neurotrophic factor signaling and functions. J. Neurosci. Res. 2017, 95, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Sun, L.H.; Yang, W.; Cui, R.J.; Xu, S.B. The Role of BDNF in the Neuroimmune Axis Regulation of Mood Disorders. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.-Y.; Tseng, P.-T. Decreased glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor levels in patients with depression: A meta-analytic study. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2015, 63, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.-M.; Lee, B.-H. Alterations in Serum BDNF and GDNF Levels after 12 Weeks of Antidepressant Treatment in Female Outpatients with Major Depressive Disorder. Psychiatry Investig. 2018, 15, 818–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.N.; Silva, B.F.B.D.C.E.; Soares, J.C.; Carvalho, A.F.; Quevedo, J. Role of trophic factors GDNF, IGF-1 and VEGF in major depressive disorder: A comprehensive review of human studies. J. Affect. Disord. 2016, 197, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Hou, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Hou, G.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z. Association study between plasma GDNF and cognitive function in late-onset depression. J. Affect. Disord. 2011, 132, 418–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, T.M.; Frangou, S.; Camara, S.; Thiemeyer, D.; Jecel, J.; Tatschner, T.; Zoechling, R.; Grünblatt, E. Altered glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) concentrations in the brain of patients with depressive disorder: A comparative post-mortem study. Eur. Psychiatry 2008, 23, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelucci, F.; Aloe, L.; Jiménez-Vasquez, P.; Mathé, A.A. Lithium treatment alters brain concentrations of nerve growth factor, brain-derived neurotrophic factor and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in a rat model of depression. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2003, 6, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.-Y.; Zukin, R.S. REST, a master transcriptional regulator in neurodegenerative disease. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2018, 48, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsuki, K.; Uchida, S.; Wakabayashi, Y.; Matsubara, T.; Hobara, T.; Funato, H.; Watanabe, Y. Aberrant REST-mediated transcriptional regulation in major depressive disorder. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2010, 44, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderone, A.; Jover, T.; Noh, K.-M.; Tanaka, H.; Yokota, H.; Lin, Y.; Grooms, S.Y.; Regis, R.; Bennett, M.V.L.; Zukin, R.S. Ischemic Insults Derepress the Gene Silencer REST in Neurons Destined to Die. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 2112–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formisano, L.; Noh, K.-M.; Miyawaki, T.; Mashiko, T.; Bennett, M.V.L.; Zukin, R.S. Ischemic insults promote epigenetic reprogramming of opioid receptor expression in hippocampal neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 4170–4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noh, K.-M.; Hwang, J.-Y.; Follenzi, A.; Athanasiadou, R.; Miyawaki, T.; Greally, J.M.; Bennett, M.V.L.; Zukin, R.S. Repressor element-1 silencing transcription factor (REST)-dependent epigenetic remodeling is critical to ischemia-induced neuronal death. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E962–E971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.-Y.; Kaneko, N.; Noh, K.-M.; Pontarelli, F.; Zukin, R.S. The Gene Silencing Transcription Factor REST Represses miR-132 Expression in Hippocampal Neurons Destined to Die. J. Mol. Biol. 2014, 426, 3454–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, N.; Hwang, J.-Y.; Gertner, M.; Pontarelli, F.; Zukin, R.S. Casein kinase 1 suppresses activation of REST in insulted hippocampal neurons and halts ischemia-induced neuronal death. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 6030–6039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, K.; Belluardo, N.; Metsis, M.; Timmusk, T. Õnis Neuronal Expression of Zinc Finger Transcription Factor REST/NRSF/XBR Gene. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 1280–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garriga-Canut, M.; Schoenike, B.; Qazi, R.; Bergendahl, K.; Daley, T.J.; Pfender, R.M.; Morrison, J.F.; Ockuly, J.; Stafstrom, C.; Sutula, T.; et al. 2-Deoxy-D-glucose reduces epilepsy progression by NRSF-CtBP–dependent metabolic regulation of chromatin structure. Nat. Neurosci. 2006, 9, 1382–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClelland, S.; Flynn, C.; Dubé, C.; Richichi, C.; Zha, Q.; Ghestem, A.; Esclapez, M.; Bernard, C.; Baram, T.Z. Neuron-restrictive silencer factor-mediated hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide gated channelopathy in experimental temporal lobe epilepsy. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 70, 454–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClelland, S.; Brennan, G.; Dubé, C.; Rajpara, S.; Iyer, S.; Richichi, C.; Bernard, C.; Baram, T.Z. The transcription factor NRSF contributes to epileptogenesis by selective repression of a subset of target genes. eLife 2014, 3, e01267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.; Aron, L.; Zullo, J.; Pan, Y.; Kim, H.; Chen, Y.; Yang, T.-H.; Kim, H.-M.; Drake, D.; Liu, X.S.; et al. REST and stress resistance in ageing and Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 507, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorostowicz, A.; Psychiatrii, U.J.K.; Siwek, M.; Afektywnych, K.P.Z.Z. Difficulties in the diagnosis of bipolar affective disorder. Psychiatr. Psychol. Klin. 2018, 18, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, P.F.; Fan, C.; Perou, C.M. Evaluating the comparability of gene expression in blood and brain. Am. J. Med Genet. Part B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2006, 141, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, J.A.; García-Suárez, O.; Hannestad, J.; Pérez-Pérez, M.; Germanà, A. Neurotrophins and the immune system. J. Anat. 2003, 203, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

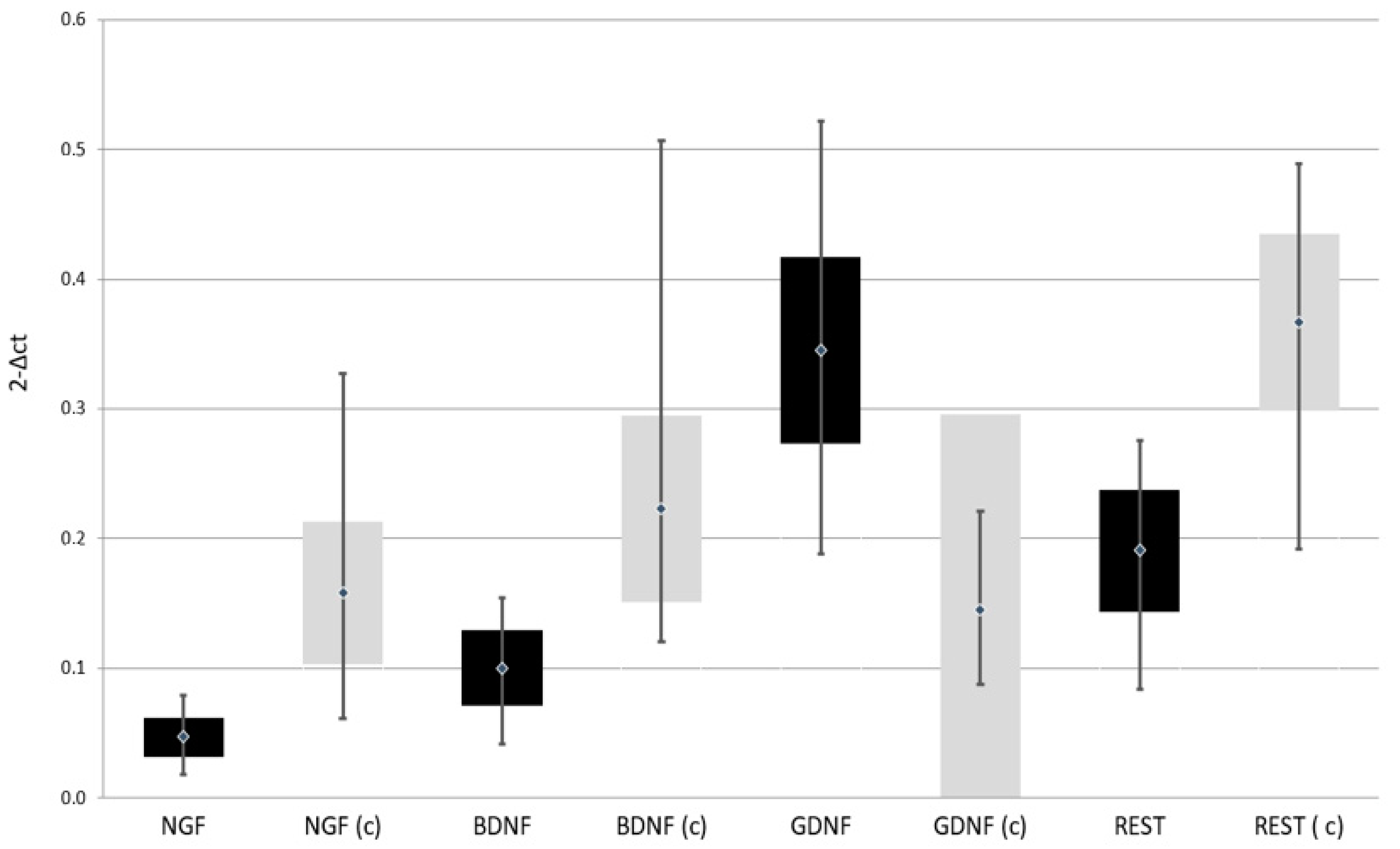
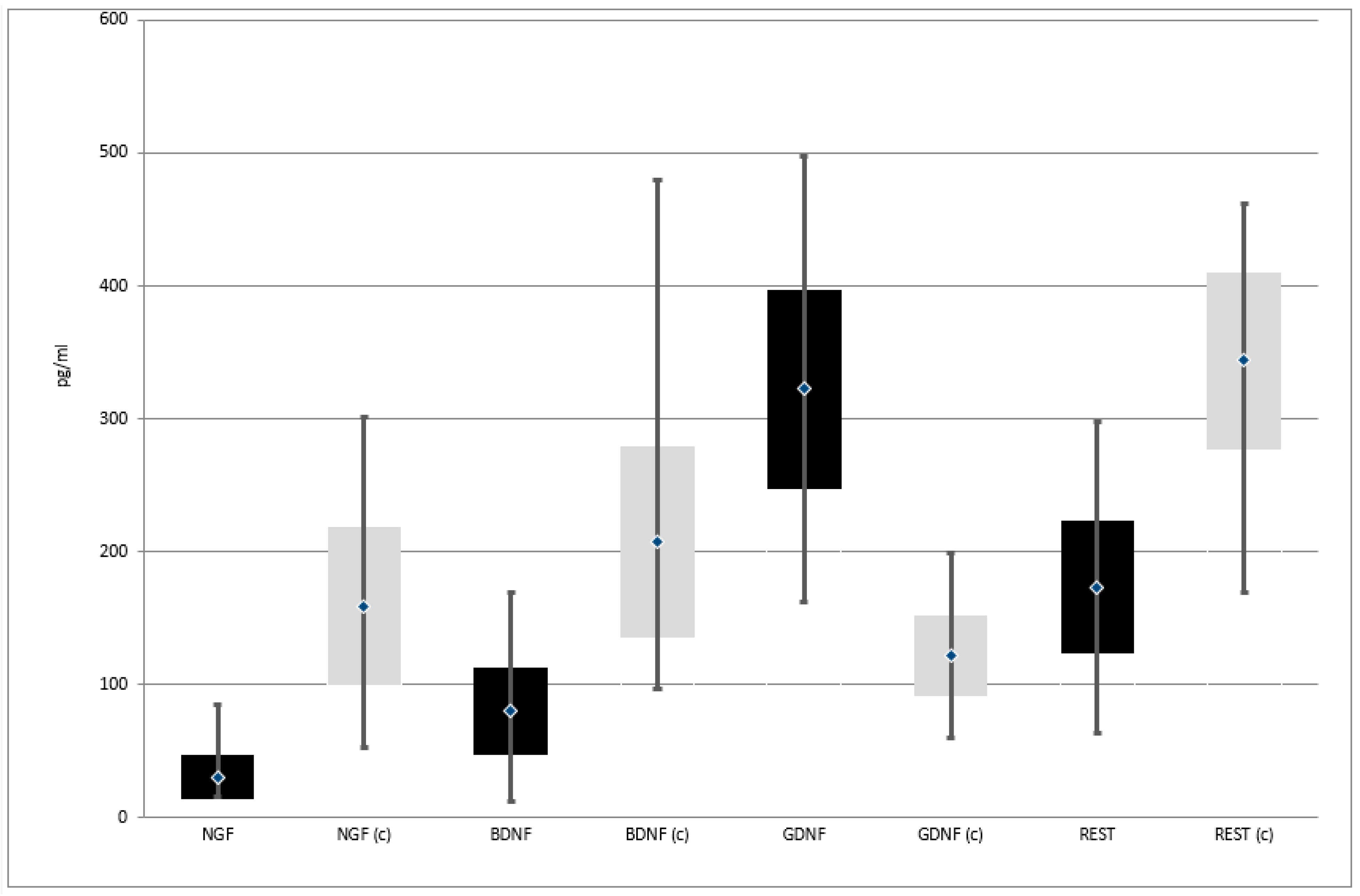
| Variable | Group | Means Comparison | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | Control | |||||||||||
| Gender | n | % | n | % | ||||||||
| M | 28 | 29.5 | 28 | 29.8 | chi2 = 0.002; p = 0.962; | |||||||
| F | 67 | 70.5 | 66 | 70.2 | ||||||||
| min | max | SD | V(%) | min | max | SD | V(%) | |||||
| Age (years) | 18 | 65 | 43.1 | 14.1 | 32.6 | 22 | 63 | 34.6 | 10.4 | 30.0 | Z = 3.961; p = 0.0001 * | |
| HDRS score (points) | M | 8 | 28 | 18.9 | 4.87 | 25.7 | Z = 2.751; p = 0.0059 * (between genders) | |||||
| F | 11 | 32 | 22.3 | 4.96 | 22.2 | |||||||
| Factor | Expression | Group | Mean Comparison | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | Control | |||||||||
| min | max | SD | min | max | SD | |||||
| NGF | mRNA (2−Δct) | 0.018 | 0.079 | 0.047 | 0.015 | 0.061 | 0.327 | 0.158 | 0.055 | Z = 3.961; p = 0.0000 * |
| protein (pg/mL) | 16 | 85 | 30.3 | 16.7 | 52 | 301 | 159.0 | 59.2 | Z = 11.787; p = 0.0000 * | |
| BDNF | mRNA (2−Δct) | 0.042 | 0.154 | 0.100 | 0.029 | 0.121 | 0.507 | 0.223 | 0.072 | Z = 11.453; p = 0.0000 * |
| protein (pg/mL) | 12 | 169 | 79.6 | 32.4 | 97 | 479 | 206.9 | 71.6 | Z = 11.787; p = 0.0000 * | |
| GDNF | mRNA (2−Δct) | 0.188 | 0.522 | 0.345 | 0.072 | 0.088 | 0.221 | 0.145 | 0.030 | Z = 11.817; p = 0.0000 * |
| protein (pg/mL) | 162 | 497 | 322.2 | 75.0 | 60 | 199 | 121.3 | 30.3 | Z = 11.791; p = 0.0000 * | |
| REST | mRNA (2−Δct) | 0.084 | 0.276 | 0.191 | 0.047 | 0.192 | 0.489 | 0.367 | 0.068 | Z = 11.656; p = 0.0000 * |
| protein (pg/mL) | 63 | 297 | 172.8 | 49.9 | 169 | 461 | 343.7 | 66.6 | Z = 11.530; p = 0.0000 * | |
| Correlation Between HDRS Score and | Spearman’s Rank Correlation Coefficient | Student’s t-Test Value | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| NGF mRNA expression (2−Δct) | −0.051 | 0.490 | 0.625 |
| NGF protein expression (pg/mL) | −0.058 | 0.561 | 0.576 |
| BDNF mRNA expression (2−Δct) | 0.002 | 0.023 | 0.981 |
| BDNF protein expression (pg/mL) | −0.071 | 0.688 | 0.493 |
| GDNF mRNA expression (2−Δct) | −0.037 | 0.357 | 0.722 |
| GDNF protein expression (pg/mL) | 0.006 | 0.058 | 0.954 |
| REST mRNA expression (2−Δct) | 0.072 | 0.693 | 0.490 |
| REST protein expression (pg/mL) | 0.031 | 0.295 | 0.768 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bliźniewska-Kowalska, K.; Gałecki, P.; Szemraj, J.; Talarowska, M. Expression of Selected Genes Involved in Neurogenesis in the Etiopathogenesis of Depressive Disorders. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11030168
Bliźniewska-Kowalska K, Gałecki P, Szemraj J, Talarowska M. Expression of Selected Genes Involved in Neurogenesis in the Etiopathogenesis of Depressive Disorders. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(3):168. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11030168
Chicago/Turabian StyleBliźniewska-Kowalska, Katarzyna, Piotr Gałecki, Janusz Szemraj, and Monika Talarowska. 2021. "Expression of Selected Genes Involved in Neurogenesis in the Etiopathogenesis of Depressive Disorders" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 3: 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11030168
APA StyleBliźniewska-Kowalska, K., Gałecki, P., Szemraj, J., & Talarowska, M. (2021). Expression of Selected Genes Involved in Neurogenesis in the Etiopathogenesis of Depressive Disorders. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(3), 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11030168








