Risk of Vestibulocochlear Disorders in Patients with Migraine or Non-Migraine Headache
Abstract
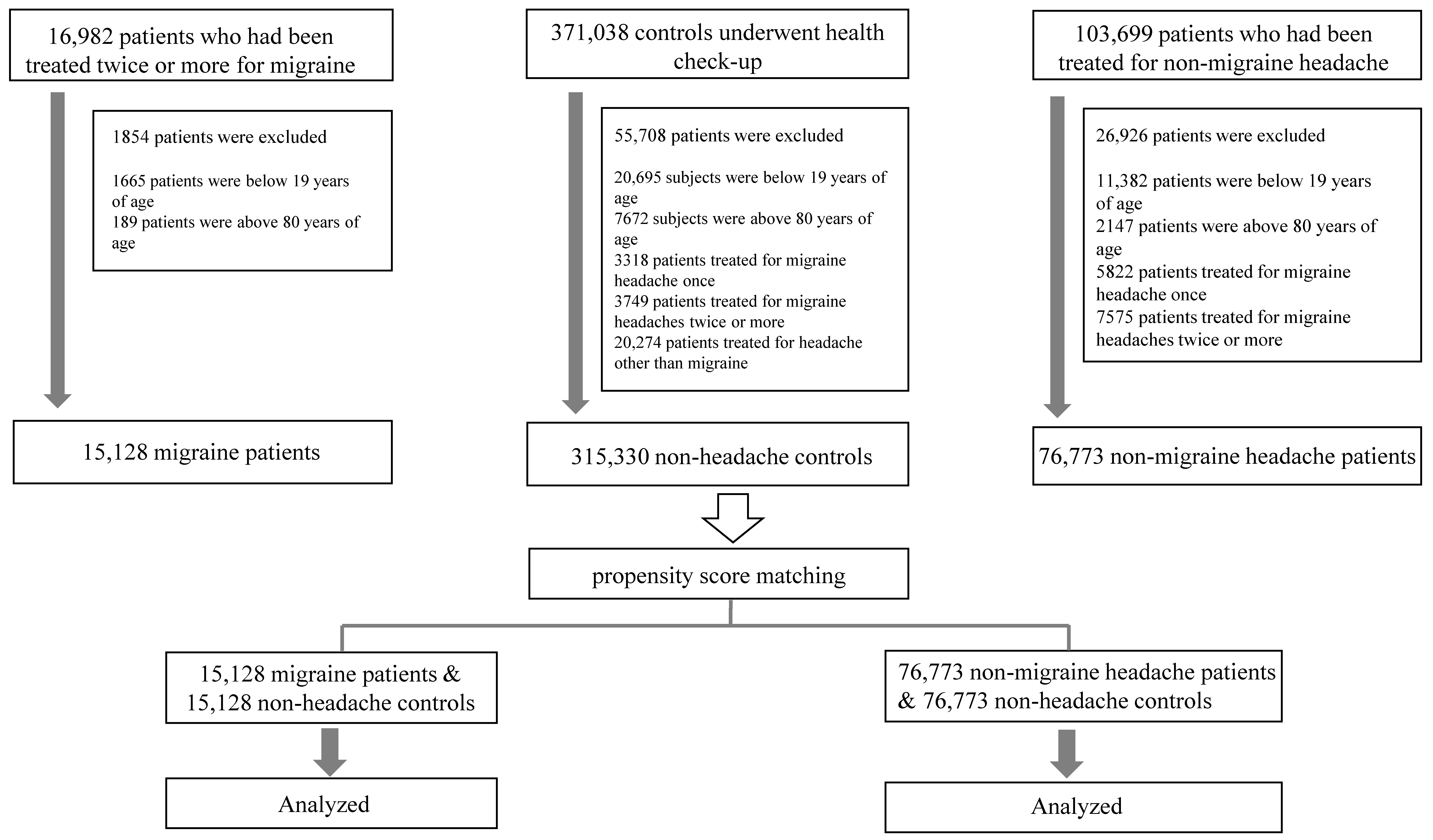
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Migraine/Non-Migraine Headache, Vestibulocochlear Disorders, and Covariates
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Subject Characteristics
3.2. ORs for Vestibulocochlear Disorders in Migraineurs
3.3. ORs for Vestibulocochlear Disorders in Non-Migraine Headaches
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bisdorff, A.; Andrée, C.; Vaillant, M.; Sándor, P.S. Headache-associated dizziness in a headache population: Prevalence and impact. Cephalalgia 2010, 30, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdal, G.; Ozge, A.; Ergör, G. The prevalence of vestibular symptoms in migraine or tension-type headache. J. Vestib. Res. 2013, 23, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuković, V.; Plavec, D.; Galinović, I.; Lovrencić-Huzjan, A.; Budisić, M.; Demarin, V. Prevalence of vertigo, dizziness, and migrainous vertigo in patients with migraine. Headache 2007, 47, 1427–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bisdorff, A. Migraine and dizziness. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2014, 27, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldingh, M.I.; Ljøstad, U.; Mygland, Å.; Monstad, P. Comparison of interictal vestibular function in vestibular migraine vs. migraine without vertigo. Headache 2013, 53, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Brevern, M.; Neuhauser, H. Epidemiological evidence for a link between vertigo and migraine. J. Vestibu. Res. 2011, 21, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asai, M.; Aoki, M.; Hayashi, H.; Yamada, N.; Mizuta, K.; Ito, Y. Subclinical deviation of the subjective visual vertical in patients affected by a primary headache. Acta Otolaryngol. 2009, 129, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Sohn, S.I.; Jung, D.K.; Cho, Y.W.; Lim, J.G.; Yi, S.D.; Yi, H.A. Migraine and isolated recurrent vertigo of unknown cause. Neurol. Res. 2002, 24, 663–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizaki, K.; Mori, N.; Takeshima, T.; Fukuhara, Y.; Ijiri, T.; Kusumi, M.; Yasui, K.; Kowa, H.; Nakashima, K. Static stabilometry in patients with migraine and tension-type headache during a headache-free period. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2002, 56, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, C.H.; Kim, Y.; Yoo, M.H.; Kim, T.S.; Park, J.W.; Kang, B.C.; Park, H.J. Management of Ménière’s Disease: How Does the Coexistence of Vestibular Migraine Affect Outcomes? Otol. Neurotol. 2019, 40, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyykkö, I.; Manchaiah, V.; Färkkilä, M.; Kentala, E.; Zou, J. Association between Ménière’s disease and vestibular migraine. Auris Nasus Larynx 2019, 46, 724–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abouzari, M.; Abiri, A.; Djalilian, H.R. Successful treatment of a child with definite Meniere’s disease with the migraine regimen. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2019, 40, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Diao, T.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, L. The clinical characteristics and audiogram in 103 Meniere’s disease patients with and without vestibular migraine. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2018, 43, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghavami, Y.; Mahboubi, H.; Yau, A.Y.; Maducdoc, M.; Djalilian, H.R. Migraine features in patients with Meniere’s disease. Laryngoscope 2016, 126, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murofushi, T.; Tsubota, M.; Kitao, K.; Yoshimura, E. Simultaneous Presentation of Definite Vestibular Migraine and Definite Ménière’s Disease: Overlapping Syndrome of Two Diseases. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, J.T.; Liu, T.C. Proposal for a New Diagnosis for Cochlear Migraine. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 144, 185–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Lopez, I.; Ishiyama, A.; Baloh, R.W. Can migraine damage the inner ear? Arch. Neurol. 2000, 57, 1631–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, J.H.; Tsai, S.J.; Liu, T.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Lai, J.T. Association of Tinnitus and Other Cochlear Disorders With a History of Migraines. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 144, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.H.; Liu, C.J.; Fuh, J.L.; Shiao, A.S.; Chen, T.J.; Wang, S.J. Migraine is a risk factor for sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A nationwide population-based study. Cephalalgia 2013, 33, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.C.; Tsai, S.J.; Chen, J.C.; Hwang, J.H. Risks of tinnitus, sensorineural hearing impairment, and sudden deafness in patients with non-migraine headache. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michiels, S.; Van de Heyning, P.; Truijen, S.; Hallemans, A.; De Hertogh, W. Prognostic indicators for decrease in tinnitus severity after cervical physical therapy in patients with cervicogenic somatic tinnitus. Musculoskelet. Sci. Pract. 2017, 29, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langguth, B.; Hund, V.; Landgrebe, M.; Schecklmann, M. Tinnitus Patients with Comorbid Headaches: The Influence of Headache Type and Laterality on Tinnitus Characteristics. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ralli, M.; Altissimi, G.; Turchetta, R.; Mazzei, F.; Salviati, M.; Cianfrone, F.; Orlando, M.P.; Testugini, V.; Cianfrone, G. Somatosensory Tinnitus: Correlation between Cranio-Cervico-Mandibular Disorder History and Somatic Modulation. Audiol. Neurootol. 2016, 21, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzoli, M.; Ugolini, A.; Rota, E.; Ferrero, L.; Milani, C.; Pezzoli, L.; Pecorari, G.; Mongini, F. Tinnitus and its relationship with muscle tenderness in patients with headache and facial pain. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2015, 129, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farri, A.; Enrico, A.; Lacilla, M.; Sartoris, A. Tinnitus during headache: Clinical-instrumental evaluation. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 1999, 19, 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- Neuhauser, H.K.; Radtke, A.; von Brevern, M.; Feldmann, M.; Lezius, F.; Ziese, T.; Lempert, T. Migrainous vertigo: Prevalence and impact on quality of life. Neurology 2006, 67, 1028–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furman, J.M.; Marcus, D.A.; Balaban, C.D. Migrainous vertigo: Development of a pathogenetic model and structured diagnostic interview. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2003, 16, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieterich, M.; Obermann, M.; Celebisoy, N. Vestibular migraine: The most frequent entity of episodic vertigo. J. Neurol. 2016, 263 (Suppl. 1), 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsiao, P.C.; Hu, H.Y.; Yang, T.H.; Lee, F.P.; Huang, H.M. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss associated with tension-type headache: A population-based study. Audiol. Neurootol. 2015, 20, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, D.H.; Drummond, P.D. Head pain referral during examination of the neck in migraine and tension-type headache. Headache 2012, 52, 1226–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.Y.; Fernández-de-las-Peñas, C.; Arendt-Nielsen, L. Sympathetic facilitation of hyperalgesia evoked from myofascial tender and trigger points in patients with unilateral shoulder pain. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2006, 117, 1545–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mongini, F.; Ciccone, G.; Deregibus, A.; Ferrero, L.; Mongini, T. Muscle tenderness in different headache types and its relation to anxiety and depression. Pain 2004, 112, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, R.; Rasmussen, B.K.; Pedersen, B.; Olesen, J. Muscle tenderness and pressure pain thresholds in headache. A population study. Pain 1993, 52, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura-Craig, M.; Smith, T.W. Substance P and peripheral inflammatory hyperalgesia. Pain 1989, 38, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, S.N.; Meyer, R.A.; Campbell, J.N. Peripheral mechanisms of somatic pain. Anesthesiology 1988, 68, 571–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Gonzalez, M.A.; Lopez-Lorente, C.; Abrante, A.; Benaixa, P.; Esteban, F. Sudden Deafness Caused by Lifestyle Stress: Pathophysiological Mechanisms and New Therapeutic Perspectives. Open Otorhinolaryngol. J. 2009, 3, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, M.; Kanzaki, S.; Minami, S.; Kikuchi, J.; Kanzaki, J.; Sato, H.; Ogawa, K. Correlations of inflammatory biomarkers with the onset and prognosis of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otol. Neurotol. 2012, 33, 1142–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guichard, E.; Montagni, I.; Tzourio, C.; Kurth, T. Association Between Headaches and Tinnitus in Young Adults: Cross-Sectional Study. Headache 2016, 56, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akdal, G.; Özge, A.; Ergör, G. Vestibular symptoms are more frequent in migraine than in tension type headache patients. J. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 357, 295–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marano, E.; Marcelli, V.; Di Stasio, E.; Bonuso, S.; Vacca, G.; Manganelli, F.; Marciano, E.; Perretti, A. Trigeminal stimulation elicits a peripheral vestibular imbalance in migraine patients. Headache 2005, 45, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buisseret-Delmas, C.; Compoint, C.; Delfini, C.; Buisseret, P. Organisation of reciprocal connections between trigeminal and vestibular nuclei in the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 1999, 409, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.K.; Balaban, C.D. Distribution of 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D receptors in the inner ear. Brain Res. 2010, 1346, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Usman, H.O.; Balaban, C.D. Distribution of 5-HT(1F) Receptors in Monkey Vestibular and Trigeminal Ganglion Cells. Front. Neurol. 2016, 7, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shore, S.E.; Vass, Z.; Wys, N.L.; Altschuler, R.A. Trigeminal ganglion innervates the auditory brainstem. J. Comp. Neurol. 2000, 419, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viirre, E.S.; Baloh, R.W. Migraine as a cause of sudden hearing loss. Headache 1996, 36, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolay, H.; Bayazit, Y.A.; Gündüz, B.; Ugur, A.K.; Akçali, D.; Altunyay, S.; Ilica, S.; Babacan, A. Subclinical dysfunction of cochlea and cochlear efferents in migraine: An otoacoustic emission study. Cephalalgia 2008, 28, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neff, B.A.; Staab, J.P.; Eggers, S.D.; Carlson, M.L.; Schmitt, W.R.; Van Abel, K.M.; Worthington, D.K.; Beatty, C.W.; Driscoll, C.L.; Shepard, N.T. Auditory and vestibular symptoms and chronic subjective dizziness in patients with Meniere’s disease, vestibular migraine, and Meniere’s disease with concomitant vestibular migraine. Otol. Neurotol. 2012, 33, 1235–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Escamez, J.A.; Dlugaiczyk, J.; Jacobs, J.; Lempert, T.; Teggi, R.; von Brevern, M.; Bisdorff, A. Accompanying symptoms overlap during attacks in Meniere’s Disease and vestibular migraine. Front. Neurol. 2014, 15, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radtke, A.; Lempert, T.; Gresty, M.A.; Brookes, G.B.; Bronstein, A.M.; Neuhauser, H. Migraine and Meniere’s disease: Is there a link? Neurology 2002, 10, 1700–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Before PSM | After PSM | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Migraine (n = 15,128) | Control (n = 315,330) | ASD | Migraine (n = 15,128) | Control (n = 15,128) | ASD | |
| Age, years (min, SD) | 44.0 (14.3) | 46.6 (15.4) | 0.18 | 44 (14.3) | 45 (14.6) | 0.04 |
| Female (n, %) | 11,247 (74.3) | 150,593 (47.8) | 0.61 | 11,247 (74.3) | 11,243 (74.3) | <0.01 |
| DM (n, %) | 686 (4.5) | 17,655 (5.6) | 0.05 | 686 (4.5) | 690 (4.6) | <0.01 |
| HTN (n, %) | 1657 (11) | 26,579 (8.4) | 0.08 | 1657 (11) | 1703 (11.3) | <0.01 |
| Dyslipidemia (n, %) | 959 (6.3) | 19,032 (6) | 0.01 | 959 (6.3) | 923 (6.1) | <0.01 |
| Angina (n, %) | 726 (4.8) | 10,792 (3.4) | 0.06 | 726 (4.8) | 717 (4.7) | <0.01 |
| AF (n, %) | 9 (4.6) | 3346 (1.1) | 0.06 | 94 (0.6) | 82 (0.5) | 0.01 |
| Heart disease (n, %) | 518 (3.4) | 9202 (2.9) | 0.03 | 518 (3.4) | 497 (3.3) | <0.01 |
| Cerebrovascular disease (n, %) | 1756 (11.6) | 14,888 (4.7) | 0.21 | 1756 (11.6) | 1840 (12.2) | 0.02 |
| Chronic pulmonary disease (n, %) | 1075 (7.1) | 17,797 (5.6) | 0.06 | 1075 (7.1) | 1097 (7.3) | <0.01 |
| Renal failure (n, %) | 145 (1) | 4355 (1.4) | 0.04 | 145 (1) | 142 (0.9) | <0.01 |
| Chronic hepatitis (n, %) | 583 (3.9) | 17,223 (5.5) | 0.08 | 583 (3.9) | 559 (3.7) | <0.01 |
| Anxiety (n, %) | 641 (4.2) | 3607 (1.1) | 0.15 | 641 (4.2) | 636 (4.2) | <0.01 |
| Depression (n, %) | 1874 (12.4) | 7581 (2.4) | 0.3 | 1874 (12.4) | 1931 (12.8) | 0.01 |
| Sleep disorder (n, %) | 912 (6) | 5230 (1.7) | 0.18 | 912 (6) | 907 (6) | <0.01 |
| Menopause (n, %) | 584 (3.9) | 7128 (2.3) | 0.08 | 584 (3.9) | 590 (3.9) | <0.01 |
| Before PSM | After PSM | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NMH (n = 76,773) | Control (n = 315,330) | ASD | NMH (n = 14,606) | Control (n = 14,606) | ASD | |
| Age, years (min, SD) | 49.1 (14.6) | 46.6 (15.4) | 0.17 | 49 (14.6) | 50 (14.9) | 0.03 |
| Female (n, %) | 45,148 (58.8) | 150,593 (47.8) | 0.22 | 45,148 (58.8) | 44,649 (58.2) | 0.01 |
| DM (n, %) | 4471 (5.8) | 17,655 (5.6) | <0.01 | 4471 (5.8) | 4700 (6.1) | 0.01 |
| HTN (n, %) | 9737 (12.7) | 26,579 (8.4) | 0.13 | 9737 (12.7) | 10,361 (13.5) | 0.02 |
| Dyslipidemia (n, %) | 5622 (7.3) | 19,032 (6) | 0.05 | 5622 (7.3) | 5865 (7.6) | 0.01 |
| Angina (n, %) | 4394 (5.7) | 10,792 (3.4) | 0.1 | 4394 (5.7) | 4393 (5.7) | <0.01 |
| AF (n, %) | 911 (1.2) | 3346 (1.1) | 0.01 | 911 (1.2) | 914 (1.2) | <0.01 |
| Heart disease (n, %) | 3014 (3.9) | 9202 (2.9) | 0.05 | 3014 (3.9) | 3104 (4) | <0.01 |
| Cerebrovascular disease (n, %) | 9743 (12.7) | 14,888 (4.7) | 0.24 | 9743 (12.7) | 9739 (12.7) | <0.01 |
| Chronic pulmonary disease (n, %) | 5871 (7.6) | 17,797 (5.6) | 0.08 | 5871 (7.6) | 6085 (7.9) | 0.01 |
| Renal failure (n, %) | 1070 (1.4) | 4355 (1.4) | <0.01 | 1070 (1.4) | 1095 (1.4) | <0.01 |
| Chronic hepatitis (n, %) | 3523 (4.6) | 17,223 (5.5) | 0.04 | 3523 (4.6) | 3488 (4.5) | <0.01 |
| Anxiety (n, %) | 2679 (3.5) | 3607 (1.1) | 0.13 | 2679 (3.5) | 2502 (3.3) | 0.01 |
| Depression (n, %) | 4497 (5.9) | 7581 (2.4) | 0.15 | 4497 (5.9) | 4636 (6) | <0.01 |
| Sleep disorder (n, %) | 2700 (3.5) | 5230 (1.7) | 0.1 | 2700 (3.5) | 2782 (3.6) | <0.01 |
| Menopause (n, %) | 2602 (3.4) | 7128 (2.3) | 0.06 | 2602 (3.4) | 2549 (3.3) | <0.01 |
| OR (95% CI) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MD | BPPV | VN | SNHL | Tinnitus | |
| UA | 2.519 (1.988–3.192) | 1.941 (1.728–2.182) | 2.838 (2.518–3.200) | 1.647 (1.331–2.038) | 1.867 (1.574–2.215) |
| AVA | 2.597 (2.047–3.295) | 2.045 (1.816–2.302) | 2.976 (2.636–3.360) | 1.740 (1.404–2.156) | 1.972 (1.659–2.343) |
| AVPA | 2.597 (2.047–3.295) | 2.045 (1.816–2.302) | 2.976 (2.636–3.360) | 1.739 (1.404–2.155) | 1.970 (1.658–2.341) |
| ORs in the Migraine Group Taking Triptans (95% CI) | |||||
| MD | BPPV | VN | SNHL | Tinnitus | |
| UA | 2.781 (1.943–3.960) | 2.222 (1.853–2.664) | 2.683 (2.228–3.230) | 1.749 (1.250–2.448) | 1.732 (1.350–2.224) |
| AVA | 2.930 (2.040–4.209) | 2.365 (1.965–2.845) | 2.883 (2.385–3.484) | 1.821 (1.298–2.556) | 1.859 (1.443–2.394) |
| AVPA | 2.928 (2.038–4.206) | 2.359 (1.960–2.838) | 2.882 (2.385–3.483) | 1.812 (1.291–2.543) | 1.862 (1.446–2.399) |
| ORs in the Migraine Group Using NSAIDs (95% CI) | |||||
| MD | BPPV | VN | SNHL | Tinnitus | |
| UA | 1.746 (1.315–2.318) | 2.314 (1.997–2.683) | 3.190 (2.743–3.711) | 1.568 (1.228–2.048) | 1.841 (1.490–2.275) |
| AVA | 1.809 (1.360–2.408) | 2.434 (2.095–2.827) | 3.364 (2.887–3.921) | 1.649 (1.275–2.134) | 1.984 (1.572–2.414) |
| AVPA | 1.809 (1.360–2.408) | 2.433 (2.095–2.826) | 3.365 (2.887–3.921) | 1.649 (1.274–2.133) | 1.941 (1.566–2.405) |
| OR (95% CI) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MD | BPPV | VN | SNHL | Tinnitus | |
| UA | 1.749 (1.541–1.984) | 1.681 (1.590–1.777) | 1.990 (1.881–2.105) | 1.339 (1.222–1.468) | 1.640 (1.521–1.768) |
| AVA | 1.774 (1.562–2.014) | 1.731 (1.637–1.831) | 2.048 (1.935–2.168) | 1.395 (1.272–1.530) | 1.693 (1.569–1.827) |
| AVPA | 1.771 (1.560–2.011) | 1.731 (1.637–1.831) | 2.048 (1.935–2.168) | 1.396 (1.273–1.531) | 1.693 (1.569–1.826) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Kwon, Y.-S.; Lee, J.-J.; Sohn, J.-H. Risk of Vestibulocochlear Disorders in Patients with Migraine or Non-Migraine Headache. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1331. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11121331
Lee S-H, Kim J-H, Kwon Y-S, Lee J-J, Sohn J-H. Risk of Vestibulocochlear Disorders in Patients with Migraine or Non-Migraine Headache. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(12):1331. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11121331
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Sang-Hwa, Jong-Ho Kim, Young-Suk Kwon, Jae-June Lee, and Jong-Hee Sohn. 2021. "Risk of Vestibulocochlear Disorders in Patients with Migraine or Non-Migraine Headache" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 12: 1331. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11121331
APA StyleLee, S.-H., Kim, J.-H., Kwon, Y.-S., Lee, J.-J., & Sohn, J.-H. (2021). Risk of Vestibulocochlear Disorders in Patients with Migraine or Non-Migraine Headache. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(12), 1331. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11121331






