The SGLT-2 Inhibitors in Personalized Therapy of Diabetes Mellitus Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Mechanism of Action of SGLT-2i and Clinical Effects—A Brief Overview
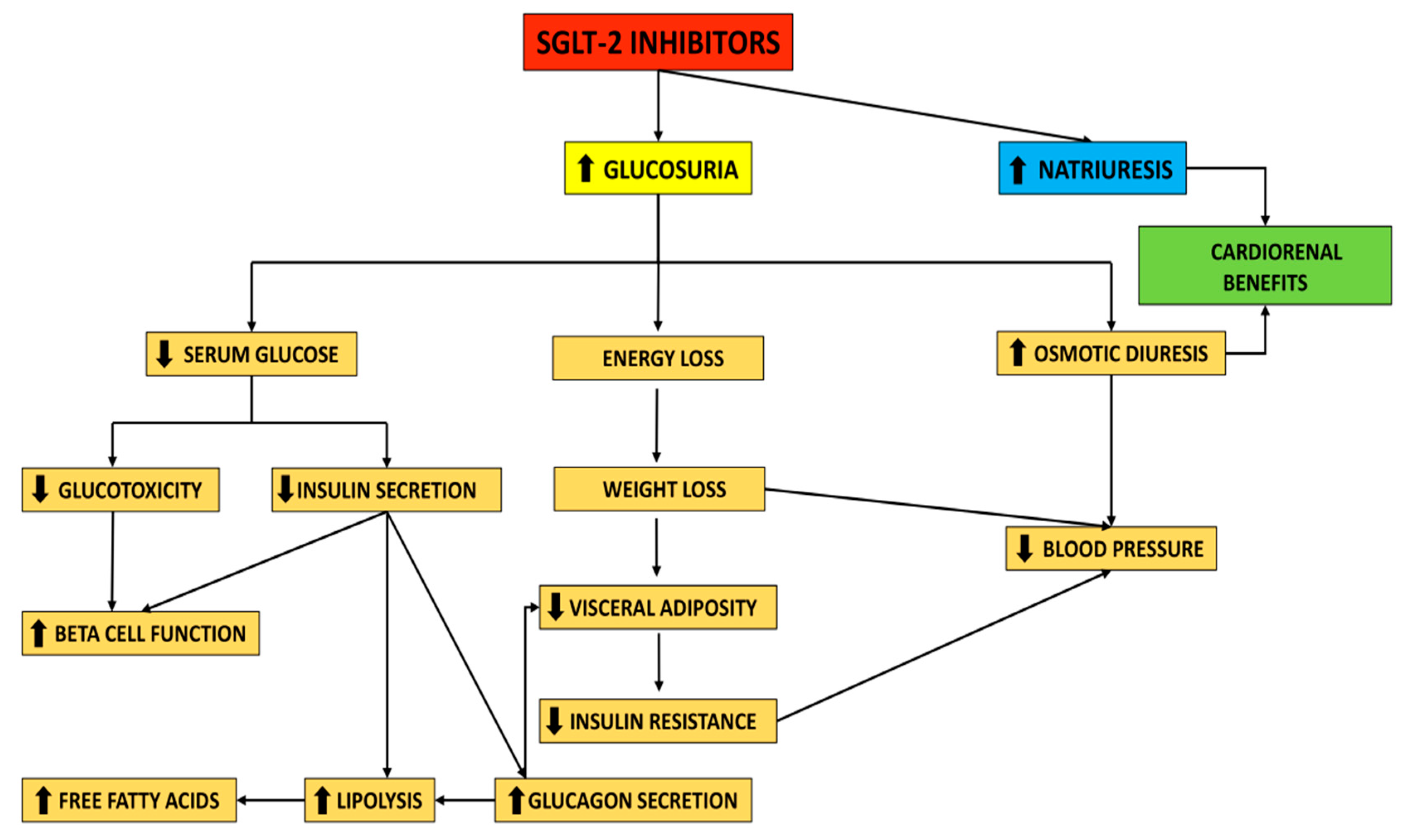
2.1. Mechanism of Action of SGLT-2i
2.2. Clinical Effects of SGLT-2i
3. SGLT-2i as Antidiabetic Agents
3.1. Improving Glycemic Control
3.2. Body Weight Reduction Benefits and Effects on Blood Pressure
3.3. SGLT-2i and Cardiorenal Continuum
3.3.1. The Era of SGLT-2i Benefits in Heart Failure
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas—9th Edition. 2019. Available online: http://www.diabetesatlas.org/ (accessed on 4 September 2021).
- Raghavan, S.; Vassy, J.L.; Ho, Y.L.; Song, R.J.; Gagnon, D.R.; Cho, K.; Wilson, P.W.F.; Phillips, L.S. Diabetes mellitus-related all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in a national cohort of adults. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e011295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, A.M. Diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 558–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, Y.; Xie, H.; Liu, Y.; Gao, P.; Yang, X.; Shen, Z. Effect of metformin on all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients with coronary artery diseases: A systematic review and an updated meta-analysis. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2019, 18, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Griffin, S.J.; Leaver, J.K.; Irving, G.J. Impact of metformin on cardiovascular disease: A meta-analysis of randomised trials among people with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1620–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marso, S.P.; Daniels, G.H.; Brown-Frandsen, K.; Kristensen, P.; Mann, J.F.; Nauck, M.A.; Nissen, S.E.; Pocock, S.; Poulter, N.R.; Ravn, L.S.; et al. Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marso, S.P.; Bain, S.C.; Consoli, A.; Eliaschewitz, F.G.; Jódar, E.; Leiter, L.A.; Lingvay, I.; Rosenstock, J.; Seufert, J.; Warren, M.L.; et al. Semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1834–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holman, R.R.; Bethel, M.A.; Mentz, R.J.; Thompson, V.P.; Lokhnygina, Y.; Buse, J.B.; Chan, J.C.; Choi, J.; Gustavson, S.M.; Iqbal, N.; et al. Effects of once-weekly exenatide on cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1228–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association. 9. Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2021. Diabetes Care 2021, 44 (Suppl. S1), S111–S124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guthrie, R. Canagliflozin and cardiovascular and renal events in type 2 diabetes. Postgrad. Med. 2018, 130, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pereira, M.J.; Eriksson, J.W. Emerging role of SGLT-2 inhibitors for the treatment of obesity. Drugs 2019, 79, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Briasoulis, A.; Al Dhaybi, O.; Bakris, G.L. SGLT2 inhibitors and mechanisms of hypertension. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2018, 20, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, J.A. SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes and renal disease: Overview of current evidence. Postgrad. Med. 2019, 131, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zelniker, T.A.; Wiviott, S.D.; Raz, I.; Im, K.; Goodrich, E.L.; Bonaca, M.P.; Mosenzon, O.; Kato, E.T.; Cahn, A.; Furtado, R.H.M.; et al. SGLT2 inhibitors for primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet 2019, 393, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurray, J.J.V.; Solomon, S.D.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Køber, L.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Martinez, F.A.; Ponikowski, P.; Sabatine, M.S.; Anand, I.S.; Bělohlávek, J.; et al. Dapagliflozin in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1995–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scheen, A.J. Pharmacodynamics, efficacy and safety of sodium-glucose co-transporter type 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Drugs 2015, 75, 33–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghezzi, C.; Loo, D.D.F.; Wright, E.M. Physiology of renal glucose handling via SGLT1, SGLT2 and GLUT2. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 2087–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, E.; Rajeev, S.P.; Cuthbertson, D.J.; Wilding, J.P.H. A review of the mechanism of action, metabolic profile and haemodynamic effects of sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2019, 21 (Suppl. S2), 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hummel, C.S.; Lu, C.; Loo, D.D.; Hirayama, B.A.; Voss, A.A.; Wright, E.M. Glucose transport by human renal Na+/D-glucose cotransporters SGLT1 and SGLT2. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2011, 300, C14–C21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wright, E.M.; Loo, D.D.; Hirayama, B.A. Biology of human sodium glucose transporters. Physiol. Rev. 2011, 91, 733–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moses, R.G.; Colagiuri, S.; Pollock, C. SGLT2 inhibitors: New medicines for addressing unmet needs in type 2 diabetes. Australas. Med. J. 2014, 7, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsia, D.S.; Grove, O.; Cefalu, W.T. An update on sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors for the treatment of diabetes mellitus. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2017, 24, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giugliano, D.; Longo, M.; Scappaticcio, L.; Caruso, P.; Esposito, K. Sodium-glucose transporter-2 inhibitors for prevention and treatment of cardiorenal complications of type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2021, 20, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatt, D.L.; Szarek, M.; Steg, P.G.; Cannon, C.P.; Leiter, L.A.; McGuire, D.K.; Lewis, J.B.; Riddle, M.C.; Voors, A.A.; Metra, M.; et al. Sotagliflozin in patients with diabetes and recent worsening heart failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrannini, E. Sodium-glucose co-transporters and their inhibition: Clinical physiology. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takahara, M.; Shiraiwa, T.; Matsuoka, T.A.; Katakami, N.; Shimomura, I. Ameliorated pancreatic β cell dysfunction in type 2 diabetic patients treated with a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor ipragliflozin. Endocr. J. 2015, 62, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Polidori, D.; Mari, A.; Ferrannini, E. Canagliflozin, a sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor, improves model-based indices of beta cell function in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 891–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saisho, Y. SGLT2 inhibitors: The star in the treatment of type 2 diabetes? Diseases 2020, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuen, B.L.; Young, T.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Neal, B.; Perkovic, V.; Billot, L.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Charytan, D.M.; Wheeler, D.C.; Arnott, C.; et al. SGLT2 inhibitors for the prevention of kidney failure in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardine, M.J.; Zhou, Z.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Oshima, M.; Agarwal, R.; Bakris, G.; Bajaj, H.S.; Bull, S.; Cannon, C.P.; Charytan, D.M.; et al. Renal, cardiovascular, and safety outcomes of canagliflozin by baseline kidney function: A secondary analysis of the CREDENCE randomized trial. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 31, 1128–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, W.H.H.; Chan, S.P.; Matawaran, B.J.; Deerochanawong, C.; Mithal, A.; Chan, J.; Suastika, K.; Khoo, C.M.; Nguyen, H.M.; Linong, J.; et al. Use of SGLT-2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and abdominal obesity: An Asian perspective and expert recommendations. Diabetes Metab. J. 2020, 44, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFronzo, R.A.; Norton, L.; Abdul-Ghani, M. Renal, metabolic and cardiovascular considerations of SGLT2 inhibition. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of medical care in diabetes—2021. Diabetes Care 2021, 44 (Suppl. S1), S15–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. 4. Comprehensive medical evaluation and assessment of comorbidities: Standards of medical care in diabetes—2021. Diabetes Care 2021, 44 (Suppl. S1), S40–S52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koye, D.N.; Magliano, D.J.; Nelson, R.G.; Pavkov, M.E. The global epidemiology of diabetes and kidney disease. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2018, 25, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilinca, M.C.; Tiuca, R.A.; Burlacu, A.; Varga, A. 2021 update on the use of liraglutide in the modern treatment of ‘diabesity’: A narrative review. Medicina 2021, 57, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilinca, M.C.; Tiuca, R.A.; Niculas, C.; Varga, A.; Tilea, I. Future perspectives in diabesity treatment: Semaglutide, a glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monami, M.; Nardini, C.; Mannucci, E. Efficacy and safety of sodium glucose co-transport-2 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2014, 16, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, C.J.; Gross, J.L.; Pieters, A.; Bastien, A.; List, J.F. Effect of dapagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes who have inadequate glycaemic control with metformin: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2010, 375, 2223–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilakou, D.; Karagiannis, T.; Athanasiadou, E.; Mainou, M.; Liakos, A.; Bekiari, E.; Sarigianni, M.; Matthews, D.R.; Tsapas, A. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors for type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 159, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenlöf, K.; Cefalu, W.T.; Kim, K.A.; Alba, M.; Usiskin, K.; Tong, C.; Canovatchel, W.; Meininger, G. Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin monotherapy in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled with diet and exercise. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2013, 15, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Søfteland, E.; Meier, J.J.; Vangen, B.; Toorawa, R.; Maldonado-Lutomirsky, M.; Broedl, U.C. Empagliflozin as Add-on Therapy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Inadequately Controlled with Linagliptin and Metformin: A 24-Week Randomized, Double-Blind, Parallel-Group Trial. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, S.; Krumins, T.; Zhou, H.; Huyck, S.; Johnson, J.; Golm, G.; Terra, S.G.; Mancuso, J.P.; Engel, S.S.; Lauring, B. Ertugliflozin and Sitagliptin Co-initiation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: The VERTIS SITA Randomized Study. Diabetes Ther. 2018, 9, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shyangdan, D.S.; Uthman, O.A.; Waugh, N. SGLT-2 receptor inhibitors for treating patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e009417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goring, S.; Hawkins, N.; Wygant, G.; Roudaut, M.; Townsend, R.; Wood, I.; Barnett, A.H. Dapagliflozin compared with other oral anti-diabetes treatments when added to metformin monotherapy: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2014, 16, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Lu, M.; Ma, L.; Zhou, Y.; Cui, Y. Efficacy and tolerability of canagliflozin as add-on to metformin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 71, 1325–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.N.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, X.; Che, W.S.; Leung, S.W. The efficacy of dapagliflozin combined with hypoglycaemic drugs in treating type 2 diabetes mellitus: Meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ Open 2014, 4, e004619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zaccardi, F.; Webb, D.R.; Htike, Z.Z.; Youssef, D.; Khunti, K.; Davies, M.J. Efficacy and safety of sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes mellitus: Systematic review and network meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2016, 18, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenstock, J.; Frias, J.; Páll, D.; Charbonnel, B.; Pascu, R.; Saur, D.; Darekar, A.; Huyck, S.; Shi, H.; Lauring, B.; et al. Effect of ertugliflozin on glucose control, body weight, blood pressure and bone density in type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled on metformin monotherapy (VERTIS MET). Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henry, R.R.; Strange, P.; Zhou, R.; Pettus, J.; Shi, L.; Zhuplatov, S.B.; Mansfield, T.; Klein, D.; Katz, A. Effects of dapagliflozin on 24-hour glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2018, 20, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kovacs, C.S.; Seshiah, V.; Swallow, R.; Jones, R.; Rattunde, H.; Woerle, H.J.; Broedl, U.C.; EMPA-REG PIOTM Trial Investigators. Empagliflozin improves glycaemic and weight control as add-on therapy to pioglitazone or pioglitazone plus metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: A 24-week, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2014, 16, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terauchi, Y.; Utsunomiya, K.; Yasui, A.; Seki, T.; Cheng, G.; Shiki, K.; Lee, J. Safety and efficacy of empagliflozin as add-on therapy to GLP-1 receptor agonist (Liraglutide) in japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomised, double-blind, parallel-group phase 4 study. Diabetes Ther. 2019, 10, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terra, S.G.; Focht, K.; Davies, M.; Frias, J.; Derosa, G.; Darekar, A.; Golm, G.; Johnson, J.; Saur, D.; Lauring, B.; et al. Phase III, efficacy and safety study of ertugliflozin monotherapy in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled with diet and exercise alone. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2017, 19, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolinder, J.; Ljunggren, Ö.; Kullberg, J.; Johansson, L.; Wilding, J.; Langkilde, A.M.; Sugg, J.; Parikh, S. Effects of dapagliflozin on body weight, total fat mass, and regional adipose tissue distribution in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus with inadequate glycemic control on metformin. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 1020–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fadini, G.P.; Bonora, B.M.; Zatti, G.; Vitturi, N.; Iori, E.; Marescotti, M.C.; Albiero, M.; Avogaro, A. Effects of the SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin on HDL cholesterol, particle size, and cholesterol efflux capacity in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized placebo-controlled trial. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2017, 16, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrannini, G.; Hach, T.; Crowe, S.; Sanghvi, A.; Hall, K.D.; Ferrannini, E. Energy balance after sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 1730–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, L.; Ma, J.; Li, H.; Mansfield, T.A.; T’joen, C.L.; Iqbal, N.; Ptaszynska, A.; List, J.F. Dapagliflozin as monotherapy in drug-naive Asian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized, blinded, prospective phase III study. Clin. Ther. 2014, 36, 84–100.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaku, K.; Kiyosue, A.; Inoue, S.; Ueda, N.; Tokudome, T.; Yang, J.; Langkilde, A.M. Efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin monotherapy in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled by diet and exercise. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2014, 16, 1102–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frías, J.P.; Guja, C.; Hardy, E.; Ahmed, A.; Dong, F.; Öhman, P.; Jabbour, S.A. Exenatide once weekly plus dapagliflozin once daily versus exenatide or dapagliflozin alone in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin monotherapy (DURATION-8): A 28 week, multicentre, double-blind, phase 3, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016, 4, 1004–1016. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Strojek, K.; Yoon, K.H.; Hruba, V.; Sugg, J.; Langkilde, A.M.; Parikh, S. Dapagliflozin added to glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus sustains glycemic control and weight loss over 48 weeks: A randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Ther. 2014, 5, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cefalu, W.T.; Stenlöf, K.; Leiter, L.A.; Wilding, J.P.; Blonde, L.; Polidori, D.; Xie, J.; Sullivan, D.; Usiskin, K.; Canovatchel, W.; et al. Effects of canagliflozin on body weight and relationship to HbA1c and blood pressure changes in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 1183–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgianos, P.I.; Agarwal, R. Ambulatory Blood Pressure Reduction With SGLT-2 Inhibitors: Dose-Response Meta-analysis and Comparative Evaluation with Low-Dose Hydrochlorothiazide. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wright, J.T., Jr.; Williamson, J.D.; Whelton, P.K.; Snyder, J.K.; Sink, K.M.; Rocco, M.V.; Reboussin, D.M.; Rahman, M.; Oparil, S.; Lewis, C.E.; et al. A Randomized Trial of Intensive versus Standard Blood-Pressure Control. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2103–2116. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, C.E.; Fine, L.J.; Beddhu, S.; Cheung, A.K.; Cushman, W.C.; Cutler, J.A.; Evans, G.W.; Johnson, K.C.; Kitzman, D.W.; Oparil, S.; et al. Final Report of a Trial of Intensive versus Standard Blood-Pressure Control. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1921–1930. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Buckley, L.F.; Dixon, D.L.; Wohlford, G.F., IV; Wijesinghe, D.S.; Baker, W.L.; Van Tassell, B.W. Intensive Versus Standard Blood Pressure Control in SPRINT-Eligible Participants of ACCORD-BP. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 1733–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oliva, R.V.; Bakris, G.L. Blood pressure effects of sodium-glucose co-transport 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2014, 8, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikkanen, I.; Narko, K.; Zeller, C.; Green, A.; Salsali, A.; Broedl, U.C.; Woerle, H.J. EMPA-REG BP Investigators. Empagliflozin reduces blood pressure in patients with type 2 diabetes and hypertension. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zanchi, A.; Burnier, M.; Muller, M.E.; Ghajarzadeh-Wurzner, A.; Maillard, M.; Loncle, N.; Milani, B.; Dufour, N.; Bonny, O.; Pruijm, M. Acute and Chronic Effects of SGLT2 Inhibitor Empagliflozin on Renal Oxygenation and Blood Pressure Control in Nondiabetic Normotensive Subjects: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e016173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontes-Carvalho, R.; Santos-Ferreira, D.; Raz, I.; Marx, N.; Ruschitzka, F.; Cosentino, F. Protective effects of SGLT-2 inhibitors across the cardiorenal continuum: Two faces of the same coin. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2021, zwab034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, A.; Abidi, E.; El-Yazbi, A.; Eid, A.; Booz, G.W.; Zouein, F.A. Direct cardiovascular impact of SGLT2 inhibitors: Mechanisms and effects. Heart Fail. Rev. 2018, 23, 419–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilgin, S.; Kurtkulagi, O.; Duman, T.T.; Tel, B.M.A.; Kahveci, G.; Kiran, M.; Erge, E.; Aktas, G. Sodium glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitor, Empagliflozin, is associated with significant reduction in weight, body mass index, fasting glucose, and A1c levels in Type 2 diabetic patients with established coronary heart disease: The SUPER GATE study. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannon, C.P.; Pratley, R.; Dagogo-Jack, S.; Mancuso, J.; Huyck, S.; Masiukiewicz, U.; Charbonnel, B.; Frederich, R.; Gallo, S.; Cosentino, F.; et al. Cardiovascular outcomes with ertugliflozin in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1425–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Zhang, M.; Suo, M.; Liu, D.; Wang, X.; Liu, M.; Pan, J.; Jin, T.; An, F. Dapagliflozin alleviates cardiac fibrosis through suppressing EndMT and fibroblast activation via AMPKα/TGF-β/Smad signalling in type 2 diabetic rats. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 7642–7659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Gallego, C.G.; Requena-Ibanez, J.A.; San Antonio, R.; Garcia-Ropero, A.; Ishikawa, K.; Watanabe, S.; Picatoste, B.; Vargas-Delgado, A.P.; Flores-Umanzor, E.J.; Sanz, J.; et al. Empagliflozin ameliorates diastolic dysfunction and left ventricular fibrosis/stiffness in nondiabetic heart failure: A multimodality study. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2021, 14, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saran, R.; Li, Y.; Robinson, B.; Abbot, K.C.; Agodoa, L.Y.C.; Ayanian, J.; Bragg-Gresham, J.; Balkrishnan, R.; Chen, J.L.; Cope, E.; et al. US Renal Data System 2015 Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 67, S1–S305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanner, C.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Zinman, B.; EMPA-REG OUTCOME Investigators. Empagliflozin and progression of kidney disease in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1801–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neal, B.; Perkovic, V.; Mahaffey, K.W.; de Zeeuw, D.; Fulcher, G.; Erondu, N.; Shaw, W.; Law, G.; Desai, M.; Matthews, D.R. Canagliflozin and cardiovascular and renal events in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 644–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiviott, S.D.; Raz, I.; Bonaca, M.P.; Mosenzon, O.; Kato, E.T.; Cahn, A.; Silverman, M.G.; Zelniker, T.A.; Kuder, J.F.; Murphy, S.A.; et al. Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Karasik, A.; Thuresson, M.; Melzer-Cohen, C.; Chodick, G.; Khunti, K.; Wilding, J.P.H.; Garcia Rodriguez, L.A.; Cea-Soriano, L.; Kohsaka, S.; et al. Kidney outcomes associated with use of SGLT2 inhibitors in real-world clinical practice (CVD-REAL 3): A multinational observational cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Stefánsson, B.V.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Chertow, G.M.; Greene, T.; Hou, F.F.; Mann, J.F.E.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Lindberg, M.; Rossing, P.; et al. Dapagliflozin in patients with chronic kidney disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkovic, V.; Jardine, M.J.; Neal, B.; Bompoint, S.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Charytan, D.M.; Edwards, R.; Agarwal, R.; Bakris, G.; Bull, S.; et al. Canagliflozin and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2295–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahaffey, K.W.; Neal, B.; Perkovic, V.; de Zeeuw, D.; Fulcher, G.; Erondu, N.; Shaw, W.; Fabbrini, E.; Sun, T.; Li, Q.; et al. Canagliflozin for primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular events: Results from the CANVAS program (Canagliflozin Cardiovascular Assessment Study). Circulation 2018, 137, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kenny, H.C.; Abel, E.D. Heart Failure in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, C.S.P.; Chandramouli, C.; Ahooja, V.; Verma, S. SGLT-2 Inhibitors in heart failure: Current management, unmet needs, and therapeutic prospects. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e013389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinman, B.; Wanner, C.; Lachin, J.M.; Fitchett, D.; Bluhmki, E.; Hantel, S.; Mattheus, M.; Devins, T.; Johansen, O.E.; Woerle, H.J.; et al. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2117–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitchett, D.; Zinman, B.; Wanner, C.; Lachin, J.M.; Hantel, S.; Salsali, A.; Johansen, O.E.; Woerle, H.J.; Broedl, U.C.; Inzucchi, S.E.; et al. Heart failure outcomes with empagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes at high cardiovascular risk: Results of the EMPA-REG OUTCOME® trial. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 1526–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neal, B.; Perkovic, V.; Matthews, D.R. Canagliflozin and cardiovascular and renal events in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosentino, F.; Grant, P.J.; Aboyans, V.; Bailey, C.J.; Ceriello, A.; Delgado, V.; Federici, M.; Filippatos, G.; Grobbee, D.E.; Hansen, T.B.; et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases developed in collaboration with the EASD. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 255–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Packer, M.; Anker, S.D.; Butler, J.; Filippatos, G.; Pocock, S.J.; Carson, P.; Januzzi, J.; Verma, S.; Tsutsui, H.; Brueckmann, M.; et al. Cardiovascular and renal outcomes with empagliflozin in heart failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1413–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anker, S.D.; Butler, J.; Filippatos, G.; Ferreira, J.P.; Bocchi, E.; Böhm, M.; Brunner-La Rocca, H.P.; Choi, D.J.; Chopra, V.; Chuquiure-Valenzuela, E.; et al. Empagliflozin in Heart Failure with a Preserved Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1451–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragagni, A.; Piani, F.; Borghi, C. Surprises in cardiology: Efficacy of gliflozines in heart failure even in the absence of diabetes. Eur. Heart J. Suppl. 2021, 23 (Suppl. E), E40–E44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargar, A.H.; Trailokya, A.A.; Ghag, S.; Pawar, R.; Aiwale, A.; Zalke, A. Current role of dapagliflozin in clinical practice. J. Assoc. Phys. India 2021, 69, 11–12. [Google Scholar]
- Solomon, S.D.; de Boer, R.A.; DeMets, D.; Hernandez, A.F.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Lam, C.S.P.; Martinez, F.; Shah, S.J.; Lindholm, D.; et al. Dapagliflozin in heart failure with preserved and mildly reduced ejection fraction: Rationale and design of the DELIVER trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2021, 23, 1217–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dapagliflozin and Effect on Cardiovascular Events in Acute Heart Failure -Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction 68 (DAPA ACT HF-TIMI 68). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04363697 (accessed on 6 September 2021).
- Cox, Z.L.; Collins, S.P.; Aaron, M.; Hernandez, G.A.; Iii, A.T.M.; Davidson, B.T.; Fowler, M.; Lindsell, C.J.; Harrel, F.E., Jr.; Jenkins, C.A.; et al. Efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin in acute heart failure: Rationale and design of the DICTATE-AHF trial. Am. Heart J. 2021, 232, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dapagliflozin Heart Failure Readmission. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04249778 (accessed on 6 September 2021).
- Dapagliflozin Effects on Cardiovascular Events in Patients with an Acute Heart Attack (DAPA-MI). Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04564742 (accessed on 6 September 2021).
- Effectiveness of Dapagliflozin for Weight Loss. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03968224 (accessed on 6 September 2021).

| Name | Available Doses (Milligrams) | Route of Administration |
|---|---|---|
| Canagliflozin (INVOKANA®) | 100, 300 | Oral, q.a.m |
| Dapagliflozin (FORXIGATM, FARXIGATM) | 5, 10 | Oral, q.a.m |
| Empagliflozin (JARDIANCE®) | 10, 25 | Oral, q.a.m |
| Ertugliflozin (STEGLATRO®) | 5, 15 | Oral, q.a.m |
| Sotagliflozin (ZYNQUISTA™) | 200 | Oral, q.a.m |
| Abbreviations | q.a.m, every morning | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tilinca, M.C.; Tiuca, R.A.; Tilea, I.; Varga, A. The SGLT-2 Inhibitors in Personalized Therapy of Diabetes Mellitus Patients. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11121249
Tilinca MC, Tiuca RA, Tilea I, Varga A. The SGLT-2 Inhibitors in Personalized Therapy of Diabetes Mellitus Patients. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(12):1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11121249
Chicago/Turabian StyleTilinca, Mariana Cornelia, Robert Aurelian Tiuca, Ioan Tilea, and Andreea Varga. 2021. "The SGLT-2 Inhibitors in Personalized Therapy of Diabetes Mellitus Patients" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 12: 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11121249
APA StyleTilinca, M. C., Tiuca, R. A., Tilea, I., & Varga, A. (2021). The SGLT-2 Inhibitors in Personalized Therapy of Diabetes Mellitus Patients. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(12), 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11121249








