Association between Genetic Variants and Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity: A Genome-Wide Approach and Validation Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patients
2.1.1. Discovery Cohort
2.1.2. Validation Cohort
2.2. Clinical Data Collection
2.3. Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity Phenotype
2.4. Genotyping and Imputation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.5.1. Genome-Wide Approach: Discovery Cohort
2.5.2. Candidate Gene Approach: Validation Cohort
2.5.3. Sensitivity Analysis in the Discovery Cohort
2.5.4. Association of Previously Investigated SNPs Based on the Systematic Review
2.5.5. Population Impact Measures
3. Results
3.1. Population Characteristics of Discovery and Validation Cohorts
3.2. Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity in the Discovery and Validation Cohorts
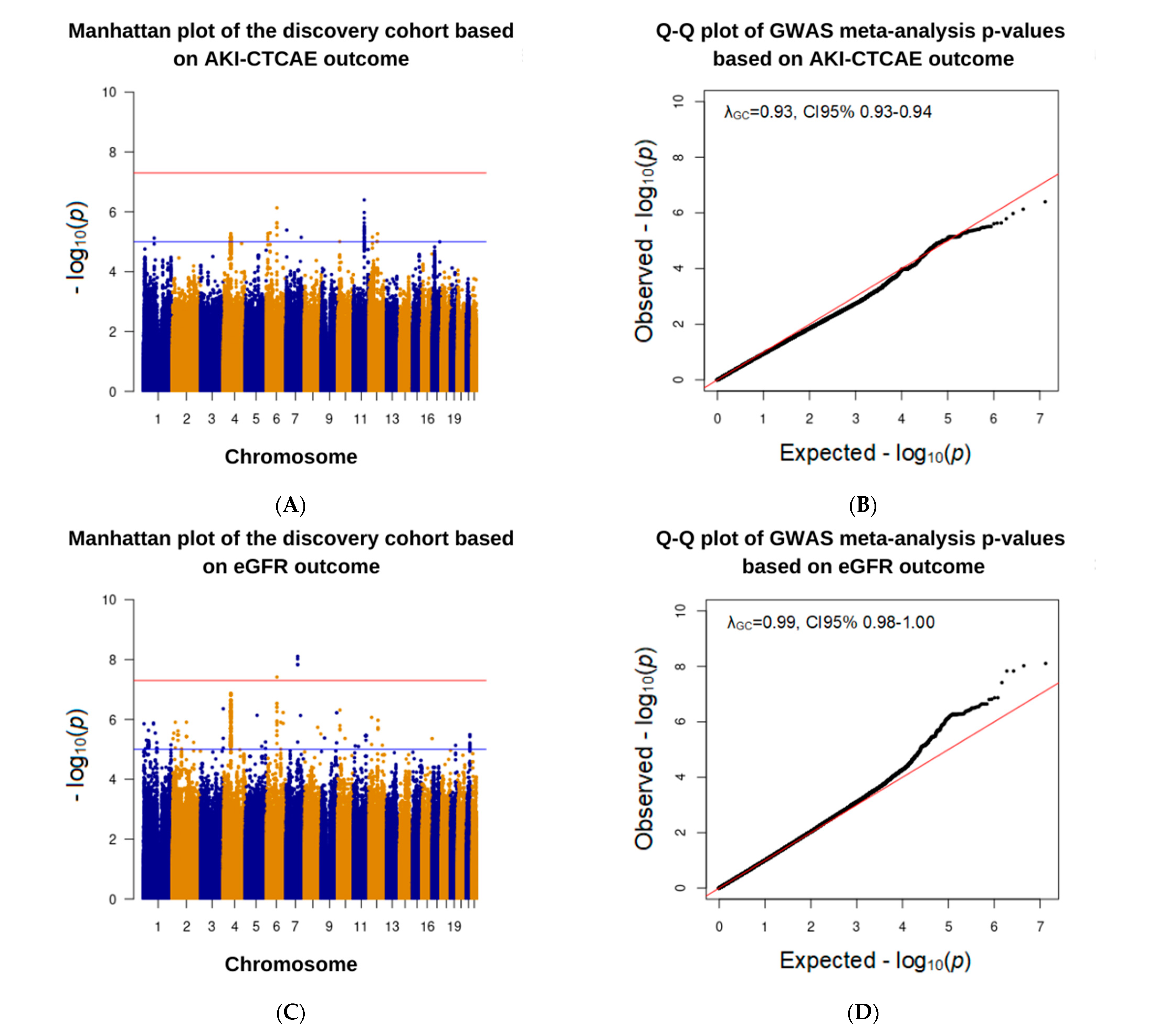
3.3. Association Analysis in the Discovery Cohort
3.4. Association Analysis in the Validation Cohort Based on GWAS Results
3.5. Association of Previously Investigated SNPs with Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity Based on the Systematic Review
3.6. BACH2 rs4388268 and Risk of Nephrotoxicity
4. Discussion
4.1. Main Findings
4.2. Potential Clinical Relevance
4.3. Strengths and Limitations
4.4. Future Research
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kelland, L. The resurgence of platinum-based cancer chemotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, S.; Tchounwou, P.B. Cisplatin in cancer therapy: Molecular mechanisms of action. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 740, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsimberidou, A.M.; Braiteh, F.; Stewart, D.J.; Kurzrock, R. Ultimate fate of oncology drugs approved by the us food and drug administration without a randomized Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 6243–6250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manohar, S.; Leung, N. Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: A review of the literature. J. Nephrol. 2018, 31, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volarevic, V.; Djokovic, B.; Jankovic, M.G.; Harrell, C.R.; Fellabaum, C.; Djonov, V.; Arsenijevic, N. Molecular mechanisms of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity: A balance on the knife edge between renoprotection and tumor toxicity. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 26, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fennell, D.A.; Summers, Y.; Cadranel, J.; Benepal, T.; Christoph, D.C.; Lal, R.; Das, M.; Maxwell, F.; Visseren-Grul, C.; Ferry, D. Cisplatin in the modern era: The backbone of first-line chemotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2016, 44, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pabla, N.; Dong, Z. Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: Mechanisms and renoprotective strategies. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 994–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lajer, H.; Daugaard, G. Cisplatin and hypomagnesemia. Cancer Treat. Rev. 1999, 25, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.P.; Tadagavadi, R.K.; Ramesh, G.; Reeves, W.B. Mechanisms of Cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Toxins 2010, 2, 2490–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Odutayo, A.; Wong, C.X.; Farkouh, M.; Altman, D.G.; Hopewell, S.; Emdin, C.A.; Hunn, B.H. AKI and Long-Term Risk for Cardiovascular Events and Mortality. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkok, A.; Edelstein, C.L. Pathophysiology of cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 967826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crona, D.J.; Faso, A.; Nishijima, T.F.; McGraw, K.A.; Galsky, M.D.; Milowsky, M.I. A Systematic Review of Strategies to Prevent Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity. Oncologist 2017, 22, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zazuli, Z.; Vijverberg, S.; Slob, E.; Liu, G.; Carleton, B.; Veltman, J.; Baas, P.; Masereeuw, R.; Maitland-van der Zee, A.H. Genetic Variations and Cisplatin Nephrotoxicity: A Systematic Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goekkurt, E.; Al-Batran, S.E.; Hartmann, J.T.; Mogck, U.; Schuch, G.; Kramer, M.; Jaeger, E.; Bokemeyer, C.; Ehninger, G.; Stoehlmacher, J. Pharmacogenetic analyses of a phase III trial in metastatic gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma with fluorouracil and leucovorin plus either oxaliplatin or cisplatin: A study of the arbeitsgemeinschaft internistische onkologie. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 2863–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powrozek, T.; Mlak, R.; Krawczyk, P.; Homa, I.; Ciesielka, M.; Koziol, P.; Prendecka, M.; Milanowski, J.; Malecka-Massalska, T. The relationship between polymorphisms of genes regulating DNA repair or cell division and the toxicity of platinum and vinorelbine chemotherapy in advanced NSCLC patients. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2016, 18, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KimCurran, V.; Zhou, C.; Schmid-Bindert, G.; Shengxiang, R.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J. Lack of correlation between ERCC1 (C8092A) single nucleotide polymorphism and efficacy/toxicity of platinum based chemotherapy in Chinese patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Adv. Med. Sci. 2011, 56, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motsinger-Reif, A.A.; Jorgenson, E.; Relling, M.V.; Kroetz, D.L.; Weinshilboum, R.; Cox, N.J.; Roden, D.M. Genome-wide association studies in pharmacogenomics: Successes and lessons. Pharm. Genom. 2013, 23, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirschhorn, J.N.; Daly, M.J. Genome-wide association studies for common diseases and complex traits. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005, 6, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, S.K.; Takahashi, A.; Mushiroda, T.; Kubo, M. Genome-wide association study: A useful tool to identify common genetic variants associated with drug toxicity and efficacy in cancer pharmacogenomics. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 2541–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Relling, M.V.; Evans, W.E. Pharmacogenomics in the clinic. Nature 2015, 526, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Jong, C.; Herder, G.J.M.; Deneer, V.H.M. Genetic variants as predictors of toxicity and response in patients with non-small cell lung cancer undergoing first-line platinum-based chemotherapy: Design of the multicenter PGxLUNG study. Thorac. Cancer 2020, 11, 3634–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Cancer Institute. Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) v4.03; National Cancer Institute: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2010.
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A. Estimating GFR using the CKD Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) creatinine equation: More accurate GFR estimates, lower CKD prevalence estimates, and better risk predictions. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2010, 55, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Acute Kidney Injury Work Group. Kidney Disease: Improving Global, Outcomes (KDIGO), KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Kidney Injury. Kidney Inter. Suppl. 2012, 2, 1–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, S.; Forer, L.; Schonherr, S.; Sidore, C.; Locke, A.E.; Kwong, A.; Vrieze, S.I.; Chew, E.Y.; Levy, S.; McGue, M.; et al. Next-generation genotype imputation service and methods. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1284–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, C.C.; Chow, C.C.; Tellier, L.C.; Vattikuti, S.; Purcell, S.M.; Lee, J.J. Second-generation PLINK: Rising to the challenge of larger and richer datasets. Gigascience 2015, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.; Chang, C.C. PLINK 1.9. Available online: www.cog-genomics.org/plink/1.9/ (accessed on 21 November 2020).
- Johnson, J.L. GAS Power Calculator. Available online: http://csg.sph.umich.edu/abecasis/gas_power_calculator/index.html (accessed on 21 November 2020).
- Willer, C.J.; Li, Y.; Abecasis, G.R. METAL: Fast and efficient meta-analysis of genomewide association scans. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2190–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlson, M.E.; Pompei, P.; Ales, K.L.; MacKenzie, C.R. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: Development and validation. J. Chronic Dis. 1987, 40, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Buchner, A.; Lang, A.G. Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1: Tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behav. Res. Methods 2009, 41, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tonk, E.C.M.; Gurwitz, D.; Maitland-van der Zee, A.H.; Janssens, A. Assessment of pharmacogenetic tests: Presenting measures of clinical validity and potential population impact in association studies. Pharm. J. 2017, 17, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Information, N.C.f.B. dbSNP Short Genetic Variations. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/snp/ (accessed on 2 December 2020).
- Howe, K.L.; Achuthan, P.; Allen, J.; Allen, J.; Alvarez-Jarreta, J.; Amode, M.R.; Armean, I.M.; Azov, A.G.; Bennett, R.; Bhai, J.; et al. Ensembl 2021. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2021, 49, D884–D891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GTEx Portal. Available online: https://gtexportal.org/home/ (accessed on 20 December 2020).
- Boyle, A.P.; Hong, E.L.; Hariharan, M.; Cheng, Y.; Schaub, M.A.; Kasowski, M.; Karczewski, K.J.; Park, J.; Hitz, B.C.; Weng, S.; et al. Annotation of functional variation in personal genomes using RegulomeDB. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1790–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pazderska, A.; Oftedal, B.E.; Napier, C.M.; Ainsworth, H.F.; Husebye, E.S.; Cordell, H.J.; Pearce, S.H.; Mitchell, A.L. A Variant in the BACH2 Gene Is Associated With Susceptibility to Autoimmune Addison’s Disease in Humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab 2016, 101, 3865–3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruiz-Larranaga, O.; Uribarri, M.; Alcaro, M.C.; Escorza-Trevino, S.; Del Amo, J.; Iriondo, M.; Manzano, C.; Migliorini, P.; Lorand, V.; Estonba, A. Genetic variants associated with rheumatoid arthritis patients and serotypes in European populations. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2016, 34, 236–241. [Google Scholar]
- Klasic, M.; Markulin, D.; Vojta, A.; Samarzija, I.; Birus, I.; Dobrinic, P.; Ventham, N.T.; Trbojevic-Akmacic, I.; Simurina, M.; Stambuk, J.; et al. Promoter methylation of the MGAT3 and BACH2 genes correlates with the composition of the immunoglobulin G glycome in inflammatory bowel disease. Clin. Epigenetics 2018, 10, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medici, M.; Porcu, E.; Pistis, G.; Teumer, A.; Brown, S.J.; Jensen, R.A.; Rawal, R.; Roef, G.L.; Plantinga, T.S.; Vermeulen, S.H.; et al. Identification of novel genetic Loci associated with thyroid peroxidase antibodies and clinical thyroid disease. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, H.N.; Gu, Z.H.; Yang, S.Y.; Ye, X.P.; Pan, C.M.; Zhao, S.X.; Xue, L.Q.; Xie, H.J.; Yu, S.S.; et al. Identification of BACH2 as a susceptibility gene for Graves′ disease in the Chinese Han population based on a three-stage genome-wide association study. Hum. Genet. 2014, 133, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thul, P.J.; Lindskog, C. The human protein atlas: A spatial map of the human proteome. Protein. Sci. 2018, 27, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uittenboogaard, L.M.; Payan-Gomez, C.; Pothof, J.; van Ijcken, W.; Mastroberardino, P.G.; van der Pluijm, I.; Hoeijmakers, J.H.; Tresini, M. BACH2: A marker of DNA damage and ageing. DNA Repair 2013, 12, 982–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, M.; Yang, F.; Peng, C.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, C. Bach2 Deficiency Leads to Spontaneous Expansion of IL-4-Producing T Follicular Helper Cells and Autoimmunity. Front Immunol. 2019, 10, 2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Altman, D.G.; Royston, P. The cost of dichotomising continuous variables. BMJ 2006, 332, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tzvetkov, M.V.; Behrens, G.; O′Brien, V.P.; Hohloch, K.; Brockmoller, J.; Benohr, P. Pharmacogenetic analyses of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity indicate a renoprotective effect of ERCC1 polymorphisms. Pharmacogenomics 2011, 12, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khrunin, A.V.; Moisseev, A.; Gorbunova, V.; Limborska, S. Genetic polymorphisms and the efficacy and toxicity of cisplatin-based chemotherapy in ovarian cancer patients. Pharmacogenomics J. 2010, 10, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cell Fraction eQTL. Available online: https://susztaklab.com/eQTLci/eQTL.php (accessed on 15 November 2021).
- Trendowski, M.R.; El-Charif, O.; Ratain, M.J.; Monahan, P.; Mu, Z.; Wheeler, H.E.; Dinh, P.C., Jr.; Feldman, D.R.; Ardeshir-Rouhani-Fard, S.; Hamilton, R.J.; et al. Clinical and Genome-Wide Analysis of Serum Platinum Levels after Cisplatin-Based Chemotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 5913–5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazuli, Z.; Otten, L.S.; Drogemoller, B.I.; Medeiros, M.; Monzon, J.G.; Wright, G.E.B.; Kollmannsberger, C.K.; Bedard, P.L.; Chen, Z.; Gelmon, K.A.; et al. Outcome Definition Influences the Relationship Between Genetic Polymorphisms of ERCC1, ERCC2, SLC22A2 and Cisplatin Nephrotoxicity in Adult Testicular Cancer Patients. Genes 2019, 10, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perazella, M.A.S.M. UpToDate: Cisplatin Nephrotoxicity. Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/cisplatin-nephrotoxicity?search=cisplatin%20induced%20nephrotoxicity&source=search_result&selectedTitle=1~150&usage_type=default&display_rank=1#H620040972 (accessed on 24 November 2020).
- Kraft, P.; Zeggini, E.; Ioannidis, J.P. Replication in genome-wide association studies. Stat. Sci. 2009, 24, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Griffin, B.R.; Faubel, S.; Edelstein, C.L. Biomarkers of Drug-Induced Kidney Toxicity. Ther. Drug Monit. 2019, 41, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zazuli, Z.; Duin, N.; Jansen, K.; Vijverberg, S.J.H.; Maitland-van der Zee, A.H.; Masereeuw, R. The Impact of Genetic Polymorphisms in Organic Cation Transporters on Renal Drug Disposition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.E.; Chang, C.; Hu, Y.; Hogan, S.L.; Mercke, N.; Gomez, M.; O′Bryant, C.L.; Bowles, D.W.; George, B.; Wen, X.; et al. Pharmacokinetic determinants of cisplatin-induced subclinical kidney injury in oncology patients. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 75, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Hu, Y.; Hogan, S.L.; Mercke, N.; Gomez, M.; O′Bryant, C.; Bowles, D.W.; George, B.; Wen, X.; Aleksunes, L.M.; et al. Pharmacogenomic Variants May Influence the Urinary Excretion of Novel Kidney Injury Biomarkers in Patients Receiving Cisplatin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Characteristics | Discovery Cohort (n = 608) | Validation Cohort (n = 149) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age at cisplatin initiation in years, mean ± SD | 57.9 ± 7.9 | 62.8 ± 9.4 | <0.01 * |
| Male, n (%) | 500 (82.2) | 71 (47.7) | <0.01 * |
| Cardiovascular disease, n (%) | 156 (25.7) | NA | NA |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 44 (7.2) | NA | NA |
| Charlson Comorbidity Index #, n (%) | |||
| 2–3 | 206 (40.5) | 71 (47.7) | <0.01 * |
| 4–5 | 247 (48.5) | 43 (28.9) | |
| ≥6 | 56 (11.0) | 35 (23.4) | |
| Missing data | 99 | 0 | |
| Chronic NSAID users, n (%) | 42 (6.9) | NA | NA |
| Concurrent administration of other antineoplastics, n (%) | 138 (22.7) | 149 (100) | <0.01 * |
| Received radiotherapy, n (%) | 534 (87.8) | 87 (58.4) | <0.01 * |
| Albumin baseline, median mmol/L (IQR) | 42 (40–44) | 39.0 (33.0–42.0) | <0.01 * |
| Baseline eGFR, median mL/min/1.73 m2 (IQR) | 94.0 (83.4–101.4) | 90.0 (80.0–90.0) | <0.01 * |
| Characteristics | Discovery Cohort (n = 608) | Validation Cohort (n = 149) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cumulative dose of cisplatin, median mg/m2 (IQR) | 196.7 (173.0–248.0) | 224.5 (150.1–274.8) | 0.297 |
| Cycles of cisplatin-based chemotherapy, n (%) | <0.01 * | ||
| 1 | 50 (8.2) | 28 (18.8) | |
| 2 | 313 (51.5) | 23 (15.4) | |
| 3 | 201 (33.1) | 55 (36.9) | |
| ≥4 | 44 (7.2) | 43 (28.9) | |
| AKI-CTCAE, n (%) # | <0.01 * | ||
| Grade 0 (no nephrotoxicity) | 515 (84.7) | 109 (73.2) | |
| Grade 1 | 71 (11.7) | 33 (22.1) | |
| Grade 2 | 17 (2.8) | 4 (2.7) | |
| Grade 3 | 5 (0.8) | 3 (2.0) | |
| Grade 4 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| Any grade | 93 (15.3) | 40 (26.8) | |
| Reduction in eGFR, median, mL/min/1.73 m2 (IQR) $ | 7.0 (0.6–18.9) | 11.0 (1.0–25.5) | <0.01 * |
| Patients without nephrotoxicity | 5.5 (0.0–14.3) | 7.0 (0.0–16.0) | 0.502 |
| Patients with grade 1 or higher AKI-CTCAE | 30.6 (15.3–42.9) | 34.5 (25.3–41.5) | 0.173 |
| Chromosome: Location: Allele a | Functional Consequences | Outcome | Effect Size (95% CI) b | p-Value | Direction c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6:90734908:G:A | Intron variant | AKI–CTCAE | 3.9 (2.3–6.7) | 7.4 × 10−7 | + + + |
| eGFR reduction | −8.4 (−11.4–−5.4) | 3.9 × 10−8 | − − − |
| RsID | Genes | Chromosome: Location: Allele a | Effect Size (95% CI) b | Unadjusted p-Value | Adjusted p-Value | Functional Consequences |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analysis of SNPs that meet at least the suggestive association threshold in the discovery cohort | ||||||
| AKI-CTCAE phenotypec | ||||||
| rs4388268 | BACH2 | 6:90734908:G:A | 1.7 (0.8–3.5) | 0.19 | 0.70 | Intron variant |
| eGFR phenotypec | ||||||
| rs17161766 | TMEM225B | 7:99177716:G:A | NA | NA | NA | Intron variant |
| NA | NA | 7:98951080:C:CTTAT | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| rs199659233 | ARPC1A | 7:98959960:T:C | NA | NA | NA | Intron variant |
| rs556958738 | ARPC1A | 7:98959961:T:C | NA | NA | NA | Intron variant |
| rs4388268 | BACH2 | 6:90734908:G:A | −1.5 (−5.3–2.4) | 0.45 | 0.99 | Intron variant |
| Analysis of known SNPs from systematic review | ||||||
| AKI-CTCAE phenotype | ||||||
| rs316019 | SLC22A2 | 6:160670282:A:C | 1.2 (0.4–3.6) | 0.73 | 0.82 | Missense variant |
| rs13181 | ERCC2 | 19:45854919:T:G | 0.6 (0.38–1.1) | 0.095 | 0.24 | Stop gained |
| rs1799793 | ERCC2 | 19:45867259:C:T | 0.5 (0.3–1.1) | 0.075 | 0.24 | Missense variant |
| rs3212986 | ERCC1 | 19:45912736:C:A | 0.9 (0.4–1.9) | 0.82 | 0.82 | 3 prime UTR variant |
| rs11615 | ERCC1 | 19:45923653:A:G | 1.4 (0.7–2.5) | 0.35 | 0.59 | Synonymous variant |
| eGFR phenotype | ||||||
| rs316019 | SLC22A2 | 6:160670282:A:C | 1.9 (−3.4–7.2) | 0.49 | 0.82 | Missense variant |
| rs13181 | ERCC2 | 19:45854919:T:G | 0.09 (−3.2–3.4) | 0.96 | 0.96 | Stop gained |
| rs1799793 | ERCC2 | 19:45867259:C:T | −0.3 (−3.8–3.3) | 0.89 | 0.96 | Missense variant |
| rs3212986 | ERCC1 | 19:45912736:C:A | −4.4 (−8.1–−0.7) | 0.02 | 0.10 | 3 prime UTR variant |
| rs11615 | ERCC1 | 19:45923653:A:G | −1.7 (−4.8–1.5) | 0.31 | 0.77 | Synonymous variant |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zazuli, Z.; de Jong, C.; Xu, W.; Vijverberg, S.J.H.; Masereeuw, R.; Patel, D.; Mirshams, M.; Khan, K.; Cheng, D.; Ordonez-Perez, B.; et al. Association between Genetic Variants and Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity: A Genome-Wide Approach and Validation Study. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11111233
Zazuli Z, de Jong C, Xu W, Vijverberg SJH, Masereeuw R, Patel D, Mirshams M, Khan K, Cheng D, Ordonez-Perez B, et al. Association between Genetic Variants and Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity: A Genome-Wide Approach and Validation Study. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(11):1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11111233
Chicago/Turabian StyleZazuli, Zulfan, Corine de Jong, Wei Xu, Susanne J. H. Vijverberg, Rosalinde Masereeuw, Devalben Patel, Maryam Mirshams, Khaleeq Khan, Dangxiao Cheng, Bayardo Ordonez-Perez, and et al. 2021. "Association between Genetic Variants and Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity: A Genome-Wide Approach and Validation Study" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 11: 1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11111233
APA StyleZazuli, Z., de Jong, C., Xu, W., Vijverberg, S. J. H., Masereeuw, R., Patel, D., Mirshams, M., Khan, K., Cheng, D., Ordonez-Perez, B., Huang, S., Spreafico, A., Hansen, A. R., Goldstein, D. P., de Almeida, J. R., Bratman, S. V., Hope, A., Knox, J. J., Wong, R. K. S., ... Liu, G. (2021). Association between Genetic Variants and Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity: A Genome-Wide Approach and Validation Study. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(11), 1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11111233








