Link-Level Functional Connectivity Neuroalterations in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Developmental Resting-State fMRI Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects and Image Acquisition
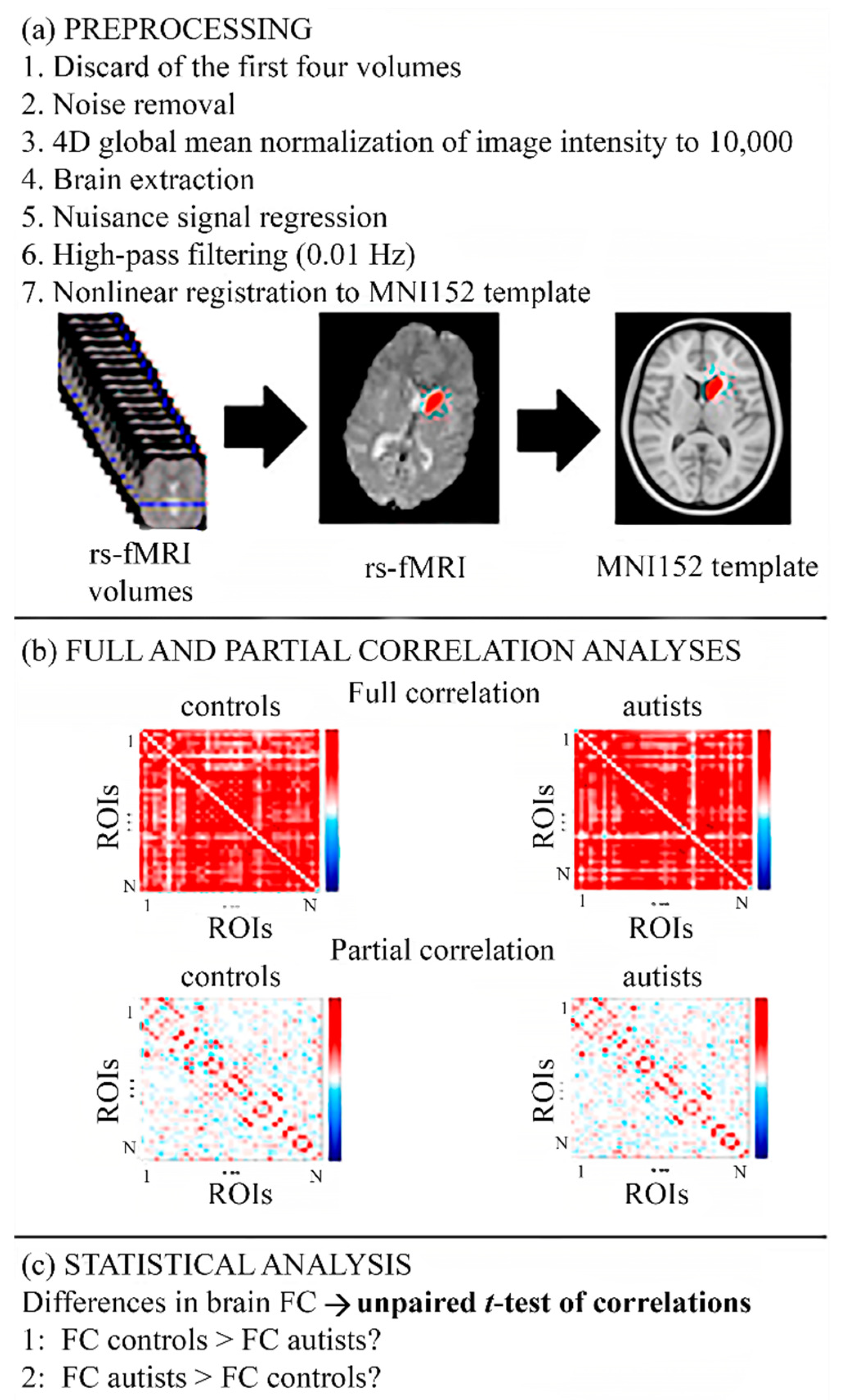
2.2. Preprocessing
2.3. rs-fMRI Time Series Extraction
2.4. Full and Partial Correlation Analyses
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
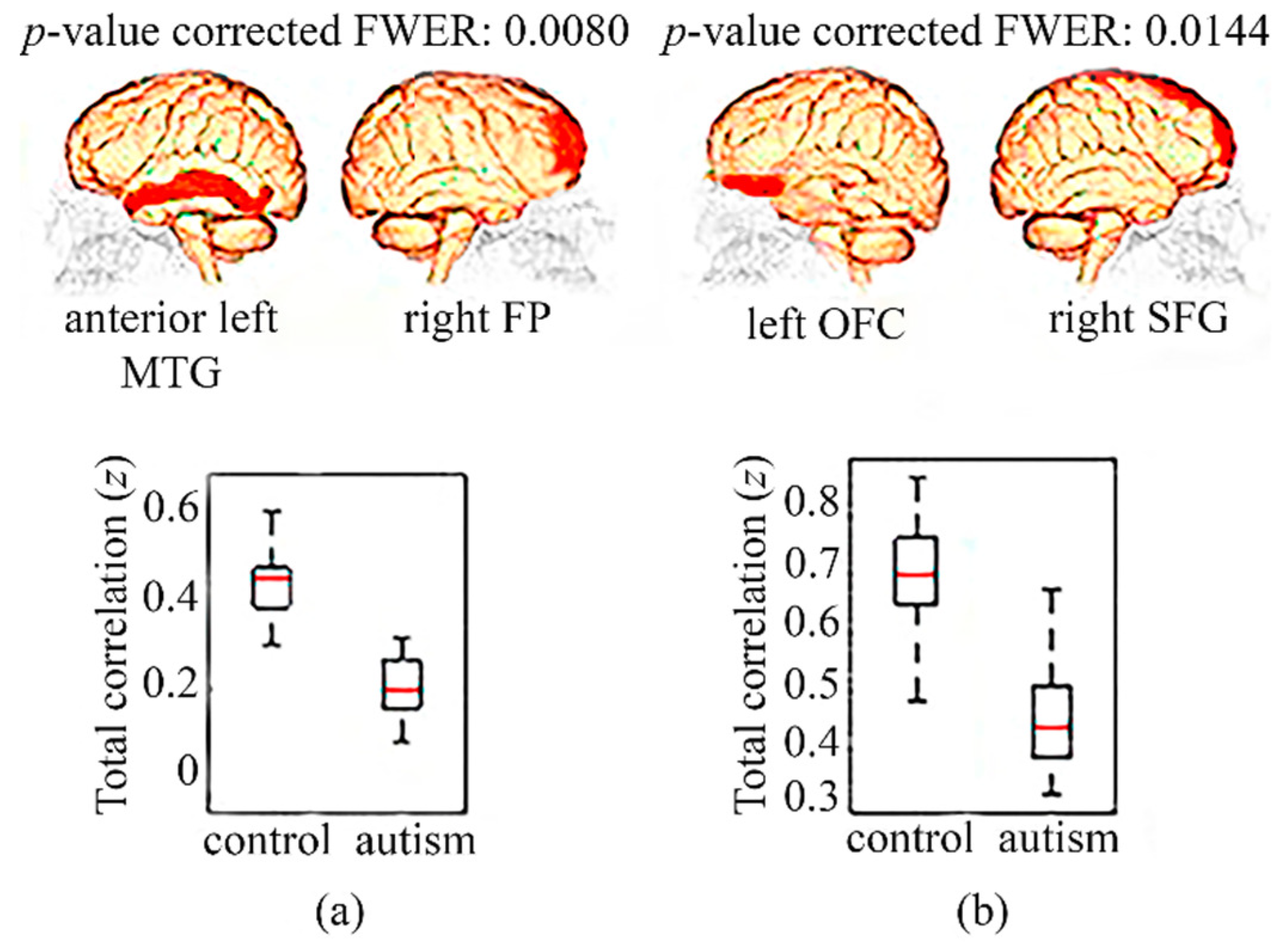
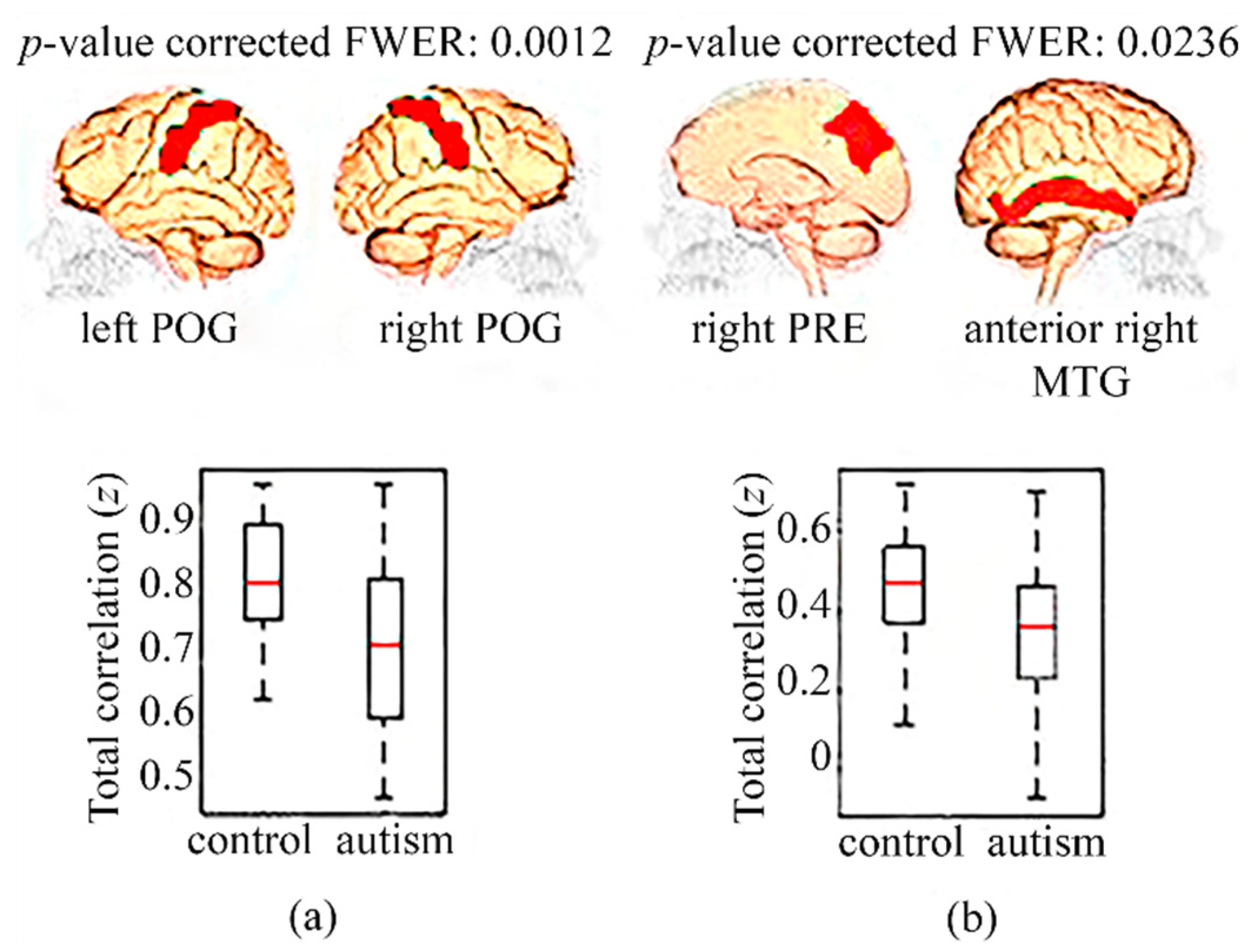
3.1. Functional Connectivity in Children
3.2. Functional Connectivity in Adolescents
3.3. Functional Connectivity in Adults
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hull, J.V.; Jacokes, Z.J.; Torgerson, C.M.; Irimia, A.; Van Horn, J.D. Resting-state functional connectivity in autism spectrum disorders: A review. Front. Psychiatry 2017, 7, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertz, L. Sharing data to solve the autism riddle: An interview with Adriana Di Martino and Michael Milham of ABIDE. IEEE Pulse 2017, 8, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Publishing: Arlington, VA, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-0-89042-554-1. [Google Scholar]
- Cociu, B.A.; Das, S.; Billeci, L.; Jamal, W.; Maharatna, K.; Calderoni, S.; Narzisi, A.; Muratori, F. Multimodal functional and structural brain connectivity analysis in autism: A preliminary integrated approach with EEG, fMRI and DTI. IEEE Trans. Cognit. Dev. Syst. 2018, 10, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekhil, O.; Hajjdiab, H.; Shalaby, A.; Ali, M.T.; Ayinde, B.; Switala, A.; Elshamekh, A.; Ghazal, M.; Keynton, R.; Barnes, G.; et al. Using resting state functional MRI to build a personalized autism diagnosis system. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, 1381–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, B.P.; Morgan, V.L.; Newton, A.T.; Gore, J.C. Assessing functional connectivity in the human brain by fMRI. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2007, 25, 1347–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.; Rolls, E.T.; Gu, H.; Zhang, J.; Feng, J. Autism: Reduced connectivity between cortical areas involved in face expression, theory of mind, and the sense of self. Brain 2015, 138, 1382–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, C.J.; Uddin, L.Q.; Supekar, K.; Khouzam, A.; Phillips, J.; Menon, V. Default mode network in childhood autism: Posteromedial cortex heterogeneity and relationship with social deficits. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 74, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uddin, L.Q.; Supekar, K.; Lynch, C.J.; Khouzam, A.; Phillips, J.; Feinstein, C.; Ryali, S.; Menon, V. Salience network-based classification and prediction of symptom severity in children with autism. JAMA Psychiatry 2013, 70, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martino, A.; Kelly, C.; Grzadzinski, R.; Zuo, X.-N.; Mennes, M.; Mairena, M.A.; Lord, C.; Castellanos, F.X.; Milham, M.P. Aberrant striatal functional connectivity in children with autism. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 69, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washington, S.D.; Gordon, E.M.; Brar, J.; Warburton, S.; Sawyer, A.T.; Wolfe, A.; Mease-Ference, E.R.; Girton, L.; Hailu, A.; Mbwana, J.; et al. Dysmaturation of the default mode network in autism. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2014, 35, 1284–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudie, J.D.; Hernandez, L.M.; Brown, J.A.; Beck-Pancer, D.; Colich, N.L.; Gorrindo, P.; Thompson, P.M.; Geschwind, D.H.; Bookheimer, S.Y.; Levitt, P.; et al. Autism-associated promoter variant in MET impacts functional and structural brain networks. Neuron 2012, 75, 904–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaf, M.; Jagannathan, K.; Calhoun, V.D.; Miller, L.; Stevens, M.C.; Sahl, R.; Boyle, J.G.O.; Schultz, R.T.; Pearlson, G.D. Abnormal functional connectivity of default mode sub-networks in autism spectrum disorder patients. Neuroimage 2010, 53, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weng, S.; Wiggins, J.L.; Peltier, S.J.; Carrasco, M.; Risi, S.; Lord, C.; Monk, C.S. Alterations of resting state functional connectivity in the default network in adolescents with autism spectrum disorders. Brain Res. 2010, 1313, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, D.P.; Courchesne, E. The intrinsic functional organization of the brain is altered in autism. Neuroimage 2008, 39, 1877–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, S.; Keeser, D.; Samson, A.C.; Kirsch, V.; Blautzik, J.; Grothe, M.; Erat, O.; Hegenloh, M.; Coates, U.; Reiser, M.F.; et al. Convergent findings of altered functional and structural brain connectivity in individuals with high functioning autism: A multimodal MRI study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von dem Hagen, E.A.H.; Stoyanova, R.S.; Baron-Cohen, S.; Calder, A.J. Reduced functional connectivity within and between ‘social’ resting state networks in autism spectrum conditions. Soc. Cognit. Affect. Neurosci. 2013, 8, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, L.Q.; Supekar, K.; Menon, V. Reconceptualizing functional brain connectivity in autism from a developmental perspective. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kana, R.K.; Uddin, L.Q.; Kenet, T.; Chugani, D.; Müller, R.-A. Brain connectivity in autism. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckmann, C.F.; Smith, S.M. Probabilistic independent component analysis for functional magnetic resonance imaging. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2004, 23, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, D.M.; Smith, S.M.; Beckmann, C.F. Advances and pitfalls in the analysis and interpretation of resting-state FMRI data. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2010, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etzel, J.A.; Gazzola, V.; Keysers, C. An introduction to anatomical ROI-based fMRI classification analysis. Brain Res. 2009, 1282, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Martino, A.; Yan, C.-G.; Li, Q.; Denio, E.; Castellanos, F.X.; Alaerts, K.; Anderson, J.S.; Assaf, M.; Bookheimer, S.Y.; Dapretto, M.; et al. The autism brain imaging data exchange: Towards a large-scale evaluation of the intrinsic brain architecture in autism. Mol. Psychiatry 2014, 19, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craddock, C.; Benhajali, Y.; Chu, C.; Chouinard, F.; Evans, A.; Jakab, A.; Khundrakpam, B.S.; Lewis, J.D.; Li, Q.; Milham, M.; et al. The neuro bureau preprocessing initiative: Open sharing of preprocessed neuroimaging data and derivatives. Front. Neuroinform. 2013, 41, 1662–5196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Yang, Z.; Jiang, L.; Xing, X.X.; Zuo, X.N. A connectome computation system for discovery science of brain. Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desikan, R.S.; Segonne, F.; Fischl, B.; Quinn, B.T.; Dickerson, B.C.; Blacker, D.; Buckner, R.L.; Dale, A.M.; Maguire, R.P.; Hyman, B.T.; et al. An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. Neuroimage 2006, 31, 968–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, M.W.; Yang, G.J.; Murray, J.D.; Repovs, G.; Anticevic, A. Functional connectivity change as shared signal dynamics. J. Neurosci. Methods 2016, 259, 22–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, J. Generalized Tikhonov Regularization. Basic Theory and Comprehensive Results on Convergence Rates. Ph.D. Thesis, Chemnitz University of Technology, Chemnitz, Germany, October 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, S.M.; Jenkinson, M.; Woolrich, M.W.; Beckmann, C.F.; Behrens, T.E.J.; Johansen-Berg, H.; Bannister, P.R.; De Luca, M.; Drobnjak, I.; Flitney, D.E.; et al. Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. Neuroimage 2004, 23, S208–S219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jenkinson, M.; Beckmann, C.F.; Behrens, T.E.J.; Woolrich, M.W.; Smith, S.M. FSL. Neuroimage 2012, 62, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutner, M.H.; Nachtsheim, C.J.; Neter, J.; Li, W. Applied Linear Statistical Models, 5th ed.; McGraw-Hill Irwin: Boston, MA, USA, 2005; pp. 623–640. ISBN 0-07-238688-6. [Google Scholar]
- Winkler, A.M.; Ridgway, G.R.; Webster, M.A.; Smith, S.M.; Nichols, T.E. Permutation inference for the general linear model. Neuroimage 2014, 92, 381–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhaumik, R.; Pradhan, A.; Das, S.; Bhaumik, D.K. Predicting autism spectrum disorder using domain-adaptive cross-site evaluation. Neuroinformatics 2018, 2, 1539–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavanna, A.E.; Trimble, M.R. The precuneus: A review of its functional anatomy and behavioural correlates. Brain 2006, 129, 564–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolls, E.T. The functions of the orbitofrontal cortex. Brain Cognit. 2004, 55, 11–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, J.S.; John, O.P.; Scabini, D.; Knight, R.T. Orbitofrontal cortex and social behavior: Integrating self-monitoring and emotion-cognition interactions. J. Cognit. Neurosci. 2006, 18, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Qin, W.; Liu, H.; Fan, L.; Wang, J.; Jiang, T.; Yu, C. Subregions of the human superior frontal gyrus and their connections. Neuroimage 2013, 78, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, T.; Liang, X.; He, Y.; Zang, Y.; Han, Z.; Caramazza, A.; Bi, Y. Predicting conceptual processing capacity from spontaneous neuronal activity of the left middle temporal gyrus. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martino, A.; O’Connor, D.; Chen, B.; Alaerts, K.; Anderson, J.S.; Assaf, M.; Balsters, J.H.; Baxter, L.; Beggiato, A.; Bernaerts, S.; et al. Enhancing studies of the connectome in autism using the autism brain imaging data exchange II. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 170010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Age Range | Number of Individuals (Controls/Autists) | Average Age ± Standard Deviation | Universities or Research Centers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Children (<12 years old) | 25/25 11/11 | 10.63 ± 0.86 10.47 ± 0.86 | NYU, UCLA, UM, NYU |
| Adolescents (12–18 years old) | 49/49 | 14.35 ± 1.77 | Leuven, NYU, Pitt, Trinity, UCLA, UM |
| Adults (>18 years old) | 16/16 | 23.41 ± 3.76 | CMU, Leuven, NYU, Pitt |
| 19 Anatomical ROIs in Each Cerebral Hemisphere | ||
|---|---|---|
| Amygdala (AMG) | Inferior frontal gyrus “pars triangularis” (IFGpt) | Hippocampus (HIP) |
| Insular cortex (INC) | Middle frontal gyrus (MFG) | Frontal pole (FP) |
| Orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) | Superior frontal gyrus (SFG) | Caudate nucleus (CAN) |
| Precuneus (PRE) | Postcentral gyrus (POG) | Putamen (PUT) |
| Anterior cingulate gyrus (aCG) | Precentral gyrus (PRG) | Thalamus (THL) |
| Posterior cingulate gyrus (pCG) | Anterior middle temporal gyrus (aMTG) | |
| Inferior frontal gyrus “pars opercularis” (IFGpo) | Posterior middle temporal gyrus (pMTG) | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borràs-Ferrís, L.; Pérez-Ramírez, Ú.; Moratal, D. Link-Level Functional Connectivity Neuroalterations in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Developmental Resting-State fMRI Study. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics9010032
Borràs-Ferrís L, Pérez-Ramírez Ú, Moratal D. Link-Level Functional Connectivity Neuroalterations in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Developmental Resting-State fMRI Study. Diagnostics. 2019; 9(1):32. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics9010032
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorràs-Ferrís, Lluis, Úrsula Pérez-Ramírez, and David Moratal. 2019. "Link-Level Functional Connectivity Neuroalterations in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Developmental Resting-State fMRI Study" Diagnostics 9, no. 1: 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics9010032
APA StyleBorràs-Ferrís, L., Pérez-Ramírez, Ú., & Moratal, D. (2019). Link-Level Functional Connectivity Neuroalterations in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Developmental Resting-State fMRI Study. Diagnostics, 9(1), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics9010032






