Neck Management in Malignant Parotid Tumors: A Retrospective Analysis of Elective Neck Dissection Indications and Outcomes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Data Collection and Analysis
2.3. Surgical Procedures
- Partial Parotidectomy: This procedure involves the removal of the superficial lobe of the parotid gland while preserving the facial nerve.
- Total Parotidectomy: This procedure consists of a superficial parotidectomy followed by a deep parotidectomy, ensuring the preservation of the facial nerve.
- Radical Parotidectomy: This procedure entails a total parotidectomy with complete removal of the facial nerve, typically necessitated by either clinical evidence of nerve involvement or tumor extension into the nerve pathway.
- Extended Parotidectomy: This technique is applied when there is extensive tumor involvement, necessitating wider resections beyond the confines of the parotid gland to achieve clear margins.
2.4. Neck Dissection
- Therapeutic Neck Dissection: This procedure is performed when there is clinical or radiological evidence of lymphatic involvement, ensuring thorough excision of affected lymph nodes.
- Elective Neck Dissection: Conducted on patients considered at elevated risk for occult metastatic disease, this approach aims to pre-emptively address potential nodal involvement. Patients considered at elevated risk were those with locally advanced (cT3-T4) tumors and high-grade histology (in this context, high-risk histologies predominantly include squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma, undifferentiated carcinoma, high-grade mucoepidermoid carcinoma, salivary duct carcinoma, and adenoid cystic carcinoma) [11,12,13].
2.5. Pathological Staging
2.6. Follow-Up
3. Results
3.1. Patient Demographics and Tumor Characteristics
3.2. Preoperative Diagnostic Procedures
3.3. Surgical Management
3.4. Histological Types and Grading
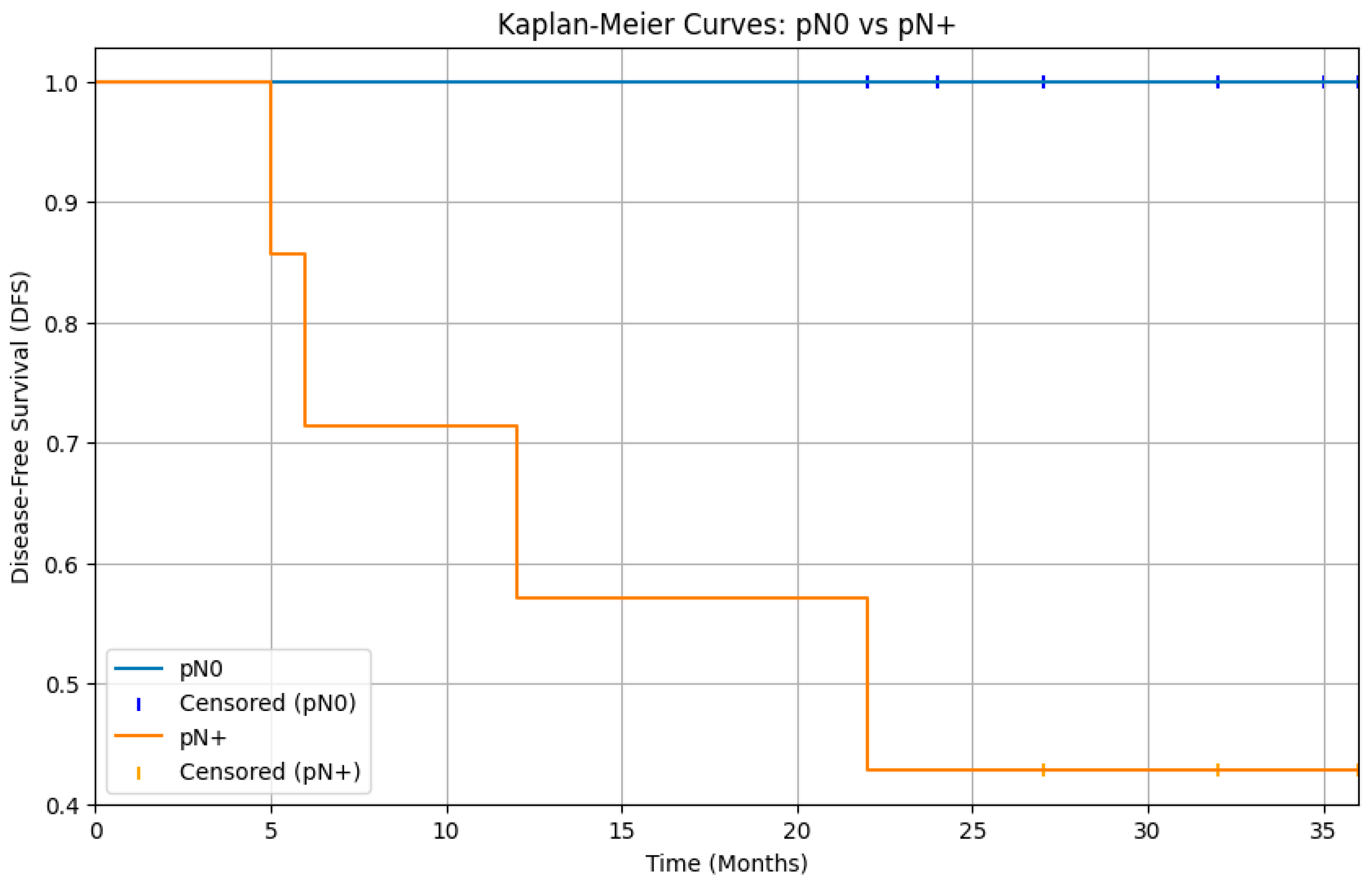
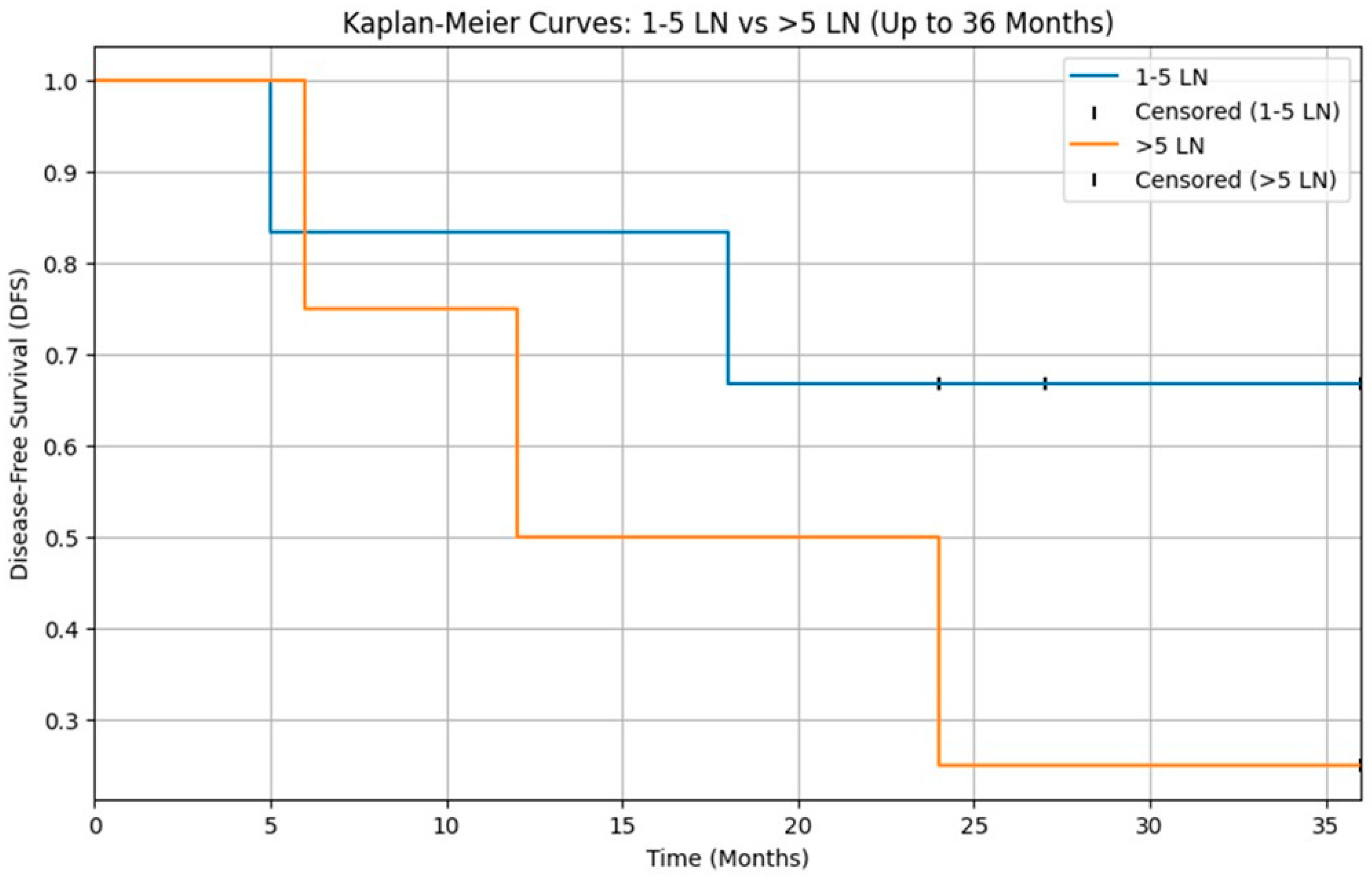
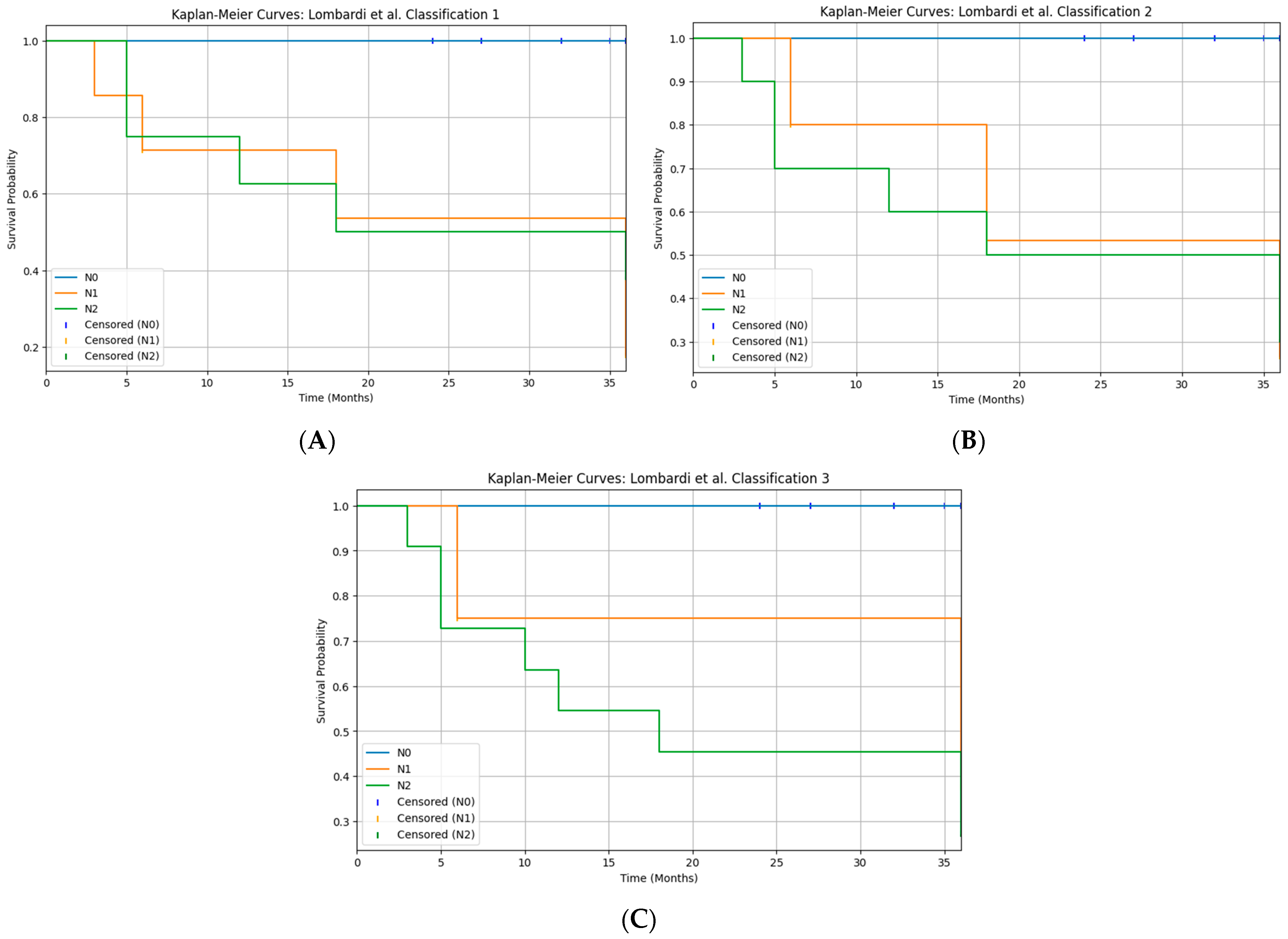
3.5. Pathological Features and Nodal Metastasis
3.6. Recurrences
4. Discussion
Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACC | Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma |
| AdCC | Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma |
| AJCC | American Joint Committee on Cancer |
| CHT | Chemotherapy |
| cN0 | Clinically Node-Negative |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| DFS | Disease-Free Survival |
| END | Elective Neck Dissection |
| FNAB | Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy |
| FNAC | Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology |
| IGLN | Intraglandular Lymph Node |
| LN | Lymph Node |
| MEC | Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| NCCN | National Comprehensive Cancer Network |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| OS | Overall Survival |
| PET | Positron Emission Tomography |
| pN+ | Pathologically Node-Positive |
| pN0 | Pathologically Node-Negative |
| RT | Radiotherapy |
| RT-CHT | Radiotherapy plus Chemotherapy |
| SCC | Squamous Cell Carcinoma |
| SGC | Salivary Gland Cancer |
| SGT | Salivary Gland Tumor |
| TND | Therapeutic Neck Dissection |
References
- Batsakis, J.G.; Regezi, J.A. The pathology of head and neck tumors: Salivary glands, part 1. Head Neck Surg. 1978, 1, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speight, P.M.; Barrett, A.W. Salivary gland tumours. Oral Dis. 2002, 8, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettl, T.; Schwarz-Furlan, S.; Gosau, M.; Reichert, T.E. Salivary gland carcinomas. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2012, 16, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; Ervik, M.; Lam, F.; Laversanne, M.; Colombet, M.; Mery, L.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Soerjomataram, I.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2024; Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today (accessed on 6 April 2025).
- Nagliati, M.; Bolner, A.; Vanoni, V.; Tomio, L.; Lay, G.; Murtas, R.; Deidda, M.A.; Madeddu, A.; Delmastro, E.; Verna, R.; et al. Surgery and radiotherapy in the treatment of malignant parotid tumors: A retrospective multicenter study. Tumori 2009, 95, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Lao, W.P.; Nguyen, S.A.; Sharma, A.K.; Day, T.A. Elective neck dissection in salivary gland malignancies: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Head Neck 2022, 44, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warshavsky, A.; Rosen, R.; Muhanna, N.; Ungar, O.; Nard-Carmel, N.; Abergel, A.; Fliss, D.M.; Horowitz, G. Rate of occult neck nodal metastasis in parotid cancer: A meta-analysis. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 28, 3664–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borsetto, D.; Iocca, O.; De Virgilio, A.; Boscolo-Rizzo, P.; Phillips, V.; Nicolai, P.; Spriano, G.; Fussey, J.; Di Maio, P. Elective neck dissection in primary parotid carcinomas: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2021, 50, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisong, A. Building Machine Learning and Deep Learning Models on Google Cloud Platform; O’Reilly Media: Sebastopol, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Google Colaboratory. Available online: https://research.google.com/colaboratory/ (accessed on 6 April 2025).
- Seethala, R.R. Histologic grading and prognostic biomarkers in salivary gland carcinomas. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2011, 18, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Herpen, C.; Vander Poorten, V.; Skalova, A.; Terhaard, C.; Maroldi, R.; van Engen, A.; Baujat, B.; Locati, L.D.; Jensen, A.D.; Smeele, L.; et al. Salivary gland cancer: ESMO–European Reference Network on Rare Adult Solid Cancers (EURACAN) Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. ESMO Open 2022, 7, 100602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pou, J.D.; Barton, B.M.; Lawlor, C.M.; Frederick, C.H.; Moore, B.A.; Hasney, C.P. Minimum lymph node yield in elective level I–III neck dissection. Laryngoscope 2017, 127, 2070–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander Poorten, V.; Bradley, P.J.; Takes, R.P.; Rinaldo, A.; Woolgar, J.A.; Ferlito, A. Diagnosis and management of parotid carcinoma with a special focus on recent advances in molecular biology. Head Neck 2012, 34, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasudevan, G.; Bishnu, A.; Singh, B.M.K.; Singh, V.K. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma of salivary gland: Limitations and pitfalls on FNA. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2017, 11, ER04–ER06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakaguro, M. Diagnostic clues and pitfalls in salivary gland fine-needle aspiration cytology. Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 2024, 41, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.N.; Onenerk, M.; Krane, J.F.; Rossi, E.D.; Baloch, Z.; Barkan, G.; Bongiovanni, M.; Callegari, F.; Canberk, S.; Dixon, G.; et al. Cytologic grading of primary malignant salivary gland tumors: A blinded review by an international panel. Cancer Cytopathol. 2020, 128, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagnani, G.; Palma, A.; Bozza, F.; Marsigli Rossi Lombardi, C.; Becelli, R. Systematic review and case report on the surgical management of pleomorphic adenomas: Lessons on recurrence and error prevention. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westergaard-Nielsen, M.; Möller, S.; Godballe, C.; Eriksen, J.G.; Larsen, S.R.; Kiss, K.; Agander, T. Prognostic scoring models in parotid gland carcinoma. Head Neck 2021, 43, 2081–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westergaard-Nielsen, M.; Rosenberg, T.; Gerke, O.; Dyrvig, A.-K.; Godballe, C.; Bjørndal, K. Elective neck dissection in patients with salivary gland carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2020, 49, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zbären, P.; Schüpbach, J.; Nuyens, M.; Stauffer, E. Elective neck dissection versus observation in primary parotid carcinoma. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2005, 132, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Liu, F.; Cheng, G.; Fang, Q.; Niu, X.; He, W. Significance of intraparotid node metastasis in predicting local control in primary parotid cancer. Laryngoscope 2019, 129, 2309–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aro, K.; Ho, A.S.; Luu, M.; Kim, S.; Tighiouart, M.; Clair, J.M.; Yoshida, E.J.; Shiao, S.L.; Leivo, I.; Zumsteg, Z.S. Development of a novel salivary gland cancer lymph node staging system. Cancer 2018, 124, 3171–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketterer, M.C.; Konrad Dahlem, K.K.; Häussler, S.M.; Jakob, T.F.; Pfeiffer, J.; Becker, C. Clinical significance and indication for surgical treatment of occult cervical and intraglandular nodal involvement in parotid malignancy. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 77, 2355–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Chen, M.M.; Divi, V.; Megwalu, U.C. Impact of lymph node sampling on survival in cN0 major salivary gland adenoid cystic carcinoma. Head Neck 2019, 41, 1903–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, D.; Tomasoni, M.; Missale, F.; Smeele, L.E.; Van Lierde, C.; Van Eecke, M.; Pellini, R.; Mazzola, F.; Ravanelli, M.; Farina, D.; et al. Nodal status in major salivary gland cancer: External validation of a novel N-classification. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2025, 51, 110006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, D.; Tomasoni, M.; Paderno, A.; Mattavelli, D.; Ferrari, M.; Battocchio, S.; Missale, F.; Mazzola, F.; Peretti, G.; Mocellin, D.; et al. The impact of nodal status in major salivary gland carcinoma: A multicenter experience and proposal of a novel N-classification. Oral Oncol. 2021, 112, 105076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shi, W. Metastatic lymph node burden impacts overall survival in submandibular gland cancer. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1229493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stennert, E.; Kisner, D.; Jungehuelsing, M.; Guntinas-Lichius, O.; Schröder, U.; Eckel, H.E.; Klussmann, J.P. High incidence of lymph node metastasis in major salivary gland cancer. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2003, 129, 720–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tofanelli, M.; Rigo, S.; Polesel, J.; Zanconati, F.; Bonazza, D.; Marcuzzo, A.V.; Gardenal, N.; Boscolo-Rizzo, P.; Tirelli, G. Accuracy of fine-needle aspiration and frozen section for the detection of squamous metastasis in cystic masses of the lateral neck. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 60, 1261–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Felice, F.; de Vincentiis, M.; Valentini, V.; Musio, D.; Mezi, S.; Lo Mele, L.; Della Monaca, M.; D’Aguanno, V.; Terenzi, V.; Di Brino, M.; et al. Management of salivary gland malignant tumor: The Policlinico Umberto I, “Sapienza” University of Rome Head and Neck Unit clinical recommendations. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2017, 120, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Modality | No. of Procedures, n (%) Among Patients with Preoperative Diagnosis * | Incorrect Diagnoses, n (%) | Nondiagnostic Results, n (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| FNAC | 31 (55.4%) | 15 (48.4%) | 3 (9.7%) |
| FNAB | 5 (8.9%) | 1 (20.0%) | 2 (40.0%) |
| Open Biopsy | 20 (35.7%) | - | - |
| Treatment Modality | Patients (n) | Patients (Rate) |
|---|---|---|
| Surgical treatment | ||
| Partial parotidectomy | 31 | 41.9% |
| Total parotidectomy | 23 | 31.1% |
| Radical Parotidectomy | 16 | 21.6% |
| Extended Parotidectomy | 4 | 5.4% |
| Neck dissection | ||
| Yes | 30 | 40.5% |
| No | 44 | 59.5% |
| Type of Neck dissection | ||
| TND | 13 | 17.6% |
| END | 17 | 23.0% |
| Treatment modality | ||
| Surgery alone | 36 | 48.6% |
| Surgery and postoperative RT | 15 | 20.3% |
| Surgery and postoperative RT-CHT | 12 | 16.2% |
| Histology | Absolute Number | Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Acinic cell Carcinoma | 6 | 8.1% |
| AdCC | 7 | 9.5% |
| Adenocarcinoma | 2 | 2.7% |
| Basal cell Adenocarcinoma | 1 | 1.4% |
| Carcinoma ex pleomorphic | 1 | 1.4% |
| Epithelial-Myoepithelial | 4 | 5.4% |
| MEC | 24 | 32.4% |
| Secretory Carcinoma | 4 | 5.4% |
| Myoepithelial carcinoma | 4 | 5.4% |
| Pleomorphic adenocarcinoma | 0 | 0.0% |
| Salivary duct carcinoma | 13 | 17.6% |
| SCC | 6 | 8.1% |
| Undifferentiated Carcinoma | 2 | 2.7% |
| Grading | Patients (n) | Patients (Rate) |
|---|---|---|
| High/intermediate | 46 | 62.2% |
| Low | 20 | 27.0% |
| Unknown/not specified | 8 | 10.8% |
| Pathological Features | Patients (n) | Patients (Rate) |
|---|---|---|
| T-classification | ||
| T1/T2 | 48 | 64.9% |
| T3/T4 | 26 | 35.1% |
| N-classification | ||
| N0 | 60 | 81.1% |
| N+ | 14 | 18.9% |
| Perineural invasion | ||
| Yes | 16 | 21.6% |
| No | 58 | 78.4% |
| Lymphovascular invasion | ||
| Yes | 11 | 14.9% |
| No | 63 | 85.1% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Battisti, A.; Pagnani, G.; Scivoletto, G.; Della Monaca, M.; Fatiga, M.; Cassoni, A.; Valentini, V. Neck Management in Malignant Parotid Tumors: A Retrospective Analysis of Elective Neck Dissection Indications and Outcomes. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 3194. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15243194
Battisti A, Pagnani G, Scivoletto G, Della Monaca M, Fatiga M, Cassoni A, Valentini V. Neck Management in Malignant Parotid Tumors: A Retrospective Analysis of Elective Neck Dissection Indications and Outcomes. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(24):3194. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15243194
Chicago/Turabian StyleBattisti, Andrea, Giulio Pagnani, Giulia Scivoletto, Marco Della Monaca, Matteo Fatiga, Andrea Cassoni, and Valentino Valentini. 2025. "Neck Management in Malignant Parotid Tumors: A Retrospective Analysis of Elective Neck Dissection Indications and Outcomes" Diagnostics 15, no. 24: 3194. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15243194
APA StyleBattisti, A., Pagnani, G., Scivoletto, G., Della Monaca, M., Fatiga, M., Cassoni, A., & Valentini, V. (2025). Neck Management in Malignant Parotid Tumors: A Retrospective Analysis of Elective Neck Dissection Indications and Outcomes. Diagnostics, 15(24), 3194. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15243194







