Anatomically Precise Microsurgical Resection of a Posterior Fossa Cerebellar Metastasis in an Elderly Patient with Preservation of Venous Outflow, Dentate Nucleus, and Cerebrospinal Fluid Pathways
Abstract
1. Introduction
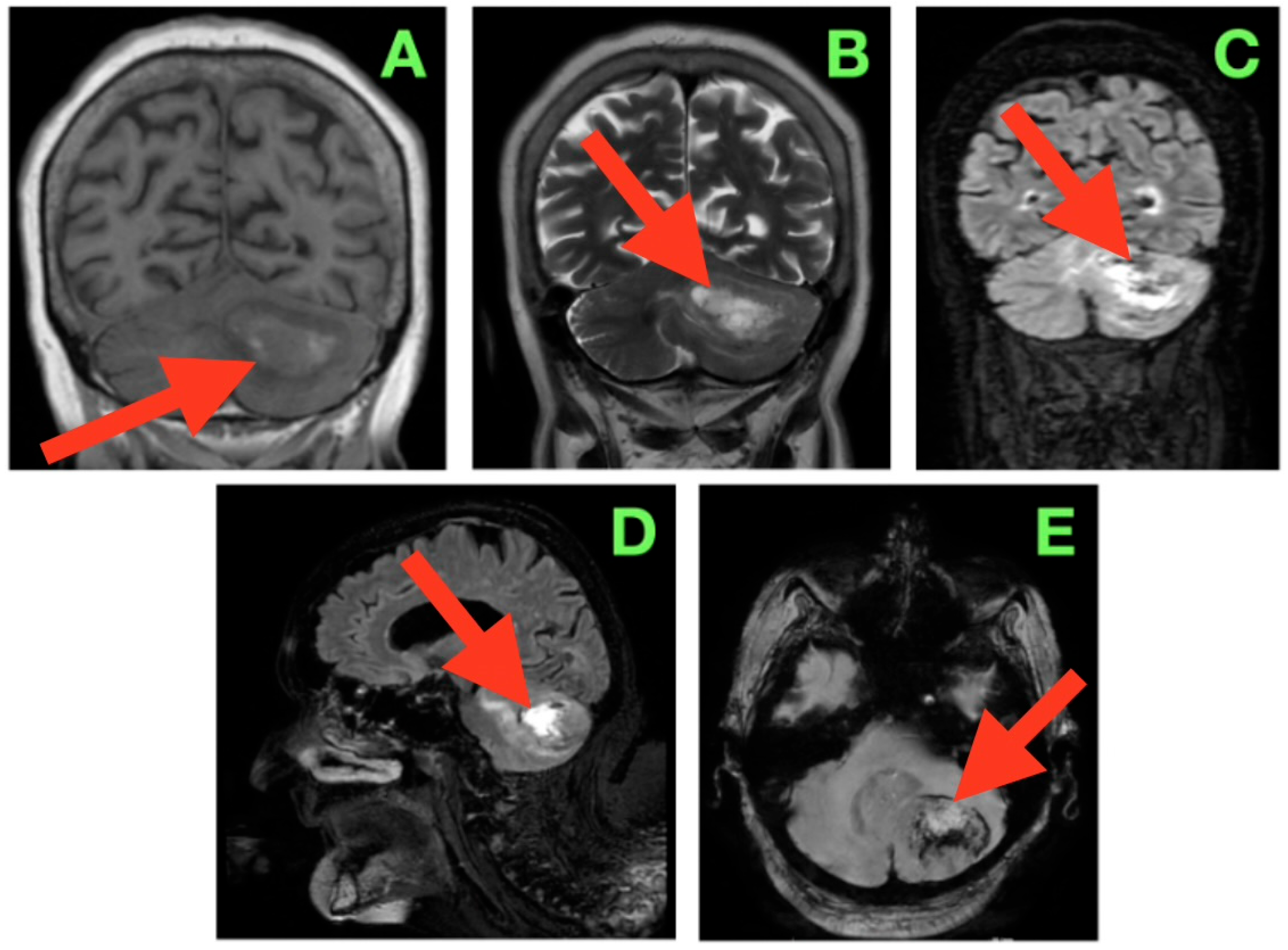
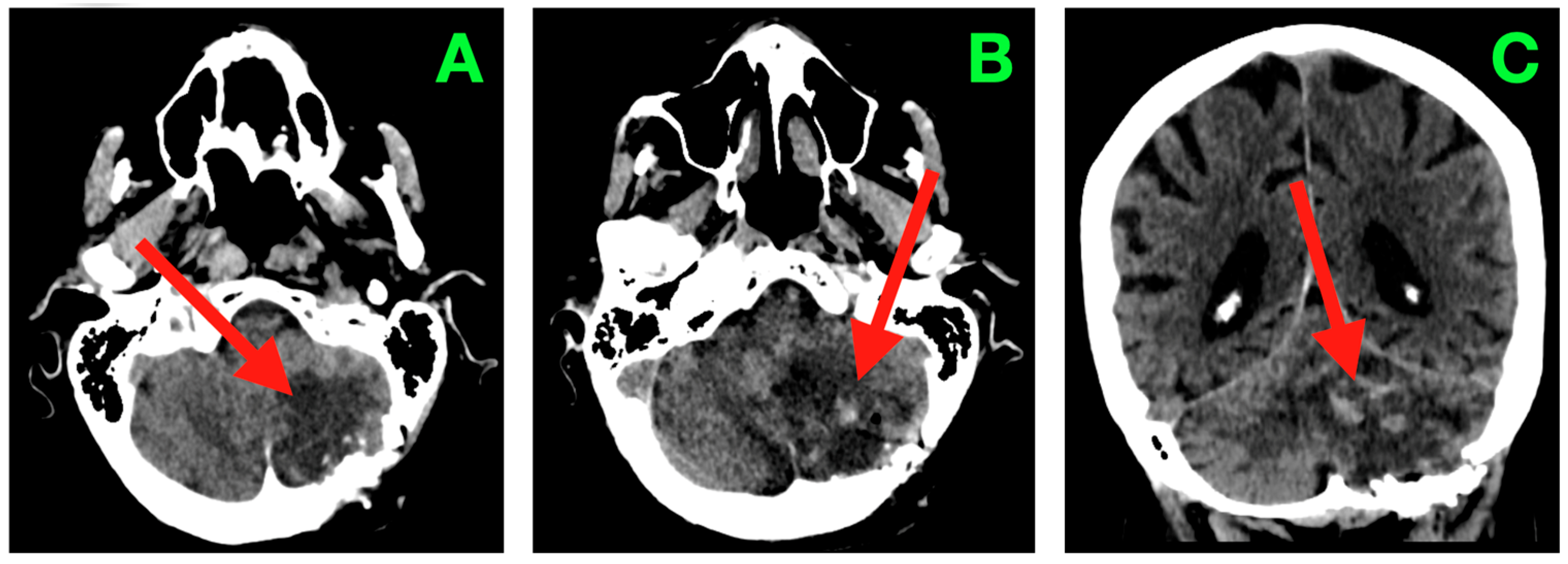
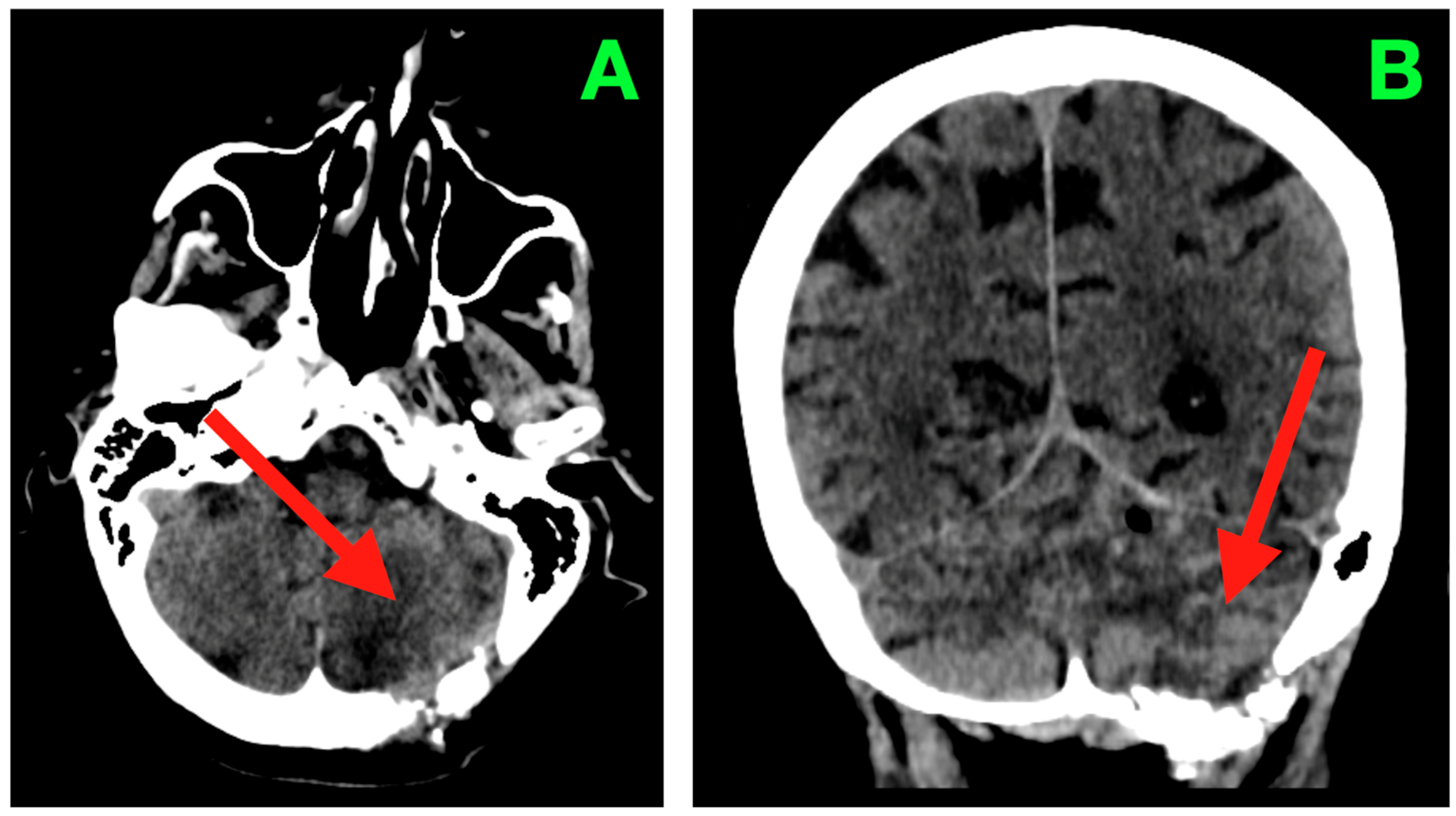
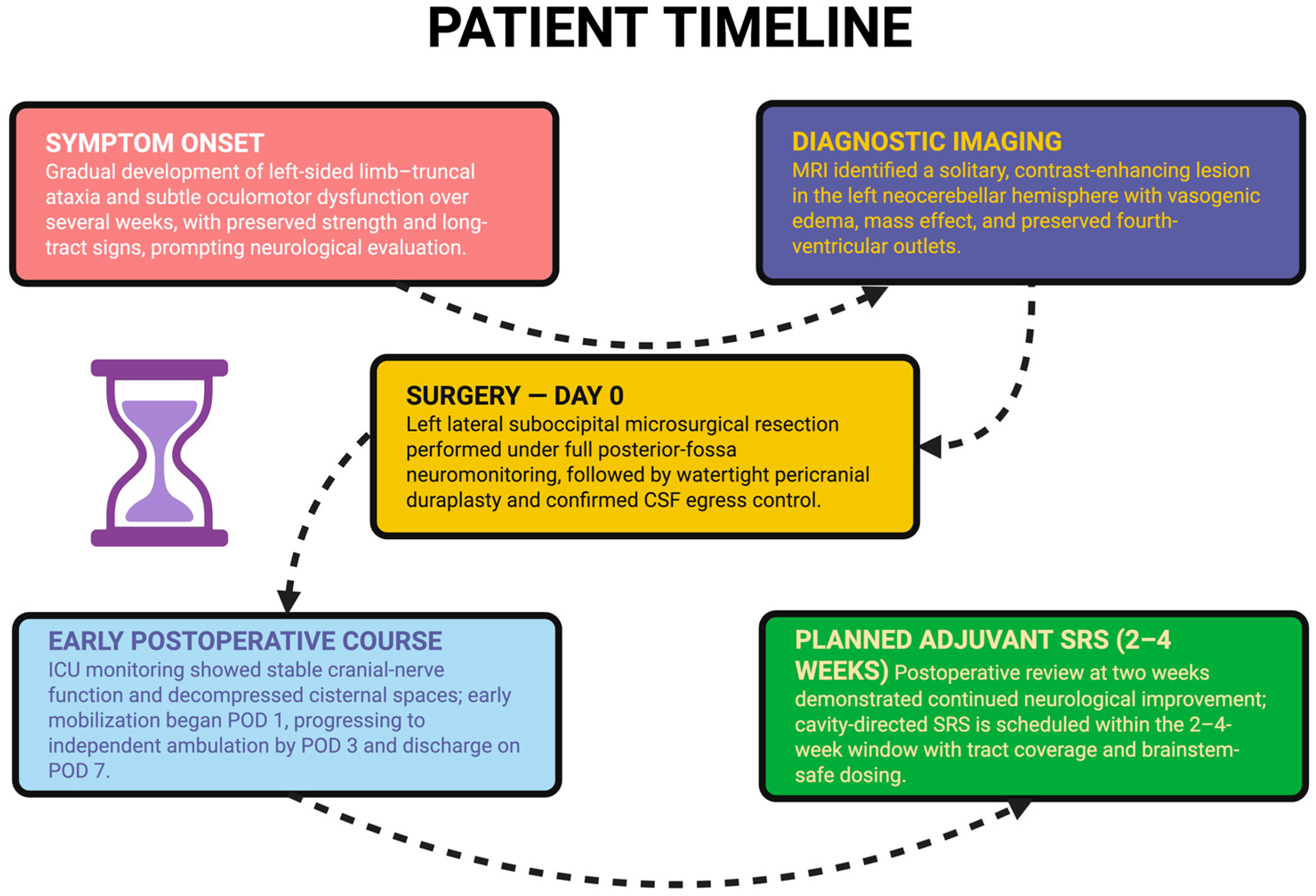
2. Case Presentation
- Posterior pole decompression created space for inward collapse.
- Lateral wall mobilization allowed the hemisphere to fall medially under gravity, widening the operative corridor without retractor use.
- Superior surface dissection along the tentorial undersurface preserved bridging veins to the tentorial sinus.
- Medial surface separation from the paravermian zone and dentate nucleus was performed millimeter-by-millimeter, using cottonoid countertraction and sharp dissection to preserve dentatothalamocortical fibers.
- Anteromedial pole detachment from the middle cerebellar peduncle was conducted with microdissectors alone, avoiding bipolar contact with the densely packed pontocerebellar fibers.
- Smooth medial wall, following the vermian contour without midline violation.
- Superior wall in continuity with tentorial dura, bridging veins intact.
- Anterior wall respecting the middle cerebellar peduncle contour.
- Inferior wall terminating above the foramen magnum, preserving cisterna magna.
3. Discussion
3.1. Epidemiology, Infratentorial Predilection, and Clinical Risks
3.2. Patient-Specific Indication for Resection
3.3. Adjuvant Radiation: Cavity SRS, Timing, and Pre- vs. Post-Operative Sequence
3.4. Systemic Therapy with CNS Activity: The Implications for Lung-Primary Suspicion
3.5. Peri-Operative and Geriatric Considerations: Frailty, Cognition, and Delirium
3.6. Venous Infarction, Hydrocephalus, and Posterior Fossa Specific Technical Challenges
3.7. Radiotherapy and Cognition in Patients with Pre-Existing Neurocognitive Disorders
3.8. Economics, Access, and Patterns of Practice
3.9. How This Case May Inform Clinical Practice
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.L.; Walker, E.V.; Paudel, Y.R.; Davis, F.G.; Yuan, Y. Brain Metastases among Cancer Patients Diagnosed from 2010–2017 in Canada: Incidence Proportion at Diagnosis and Estimated Lifetime Incidence. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 2091–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacome, M.A.; Wu, Q.; Chen, J.; Mohamed, Z.S.; Mokhtari, S.; Piña, Y.; Etame, A.B. Molecular Underpinnings of Brain Metastases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobar, L.E.; Farnsworth, R.H.; Stacker, S.A. Brain Vascular Microenvironments in Cancer Metastasis. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, T.; Hendizadeh, M.-S.; Vankina, R.; Park, S.; Kim, P. Combined Cerebellar and Spinal Cord Deficits Caused by an Underlying Gynecologic Malignancy. Case Rep. Oncol. Med. 2020, 2020, 9021843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadimi, K.; Abbas, I.; Karandish, A.; Crisman, C.; Eskandar, E.N.; Kobets, A.J. Cognitive Decline in Glioblastoma (GB) Patients with Different Treatment Modalities and Insights on Untreated Cases. Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersoy, T.F.; Mokhtari, N.; Brainman, D.; Berger, B.; Salay, A.; Schütt, P.; Weissinger, F.; Grote, A.; Simon, M. Surgical Treatment of Cerebellar Metastases: Survival Benefits, Complications and Timing Issues. Cancers 2021, 13, 5263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasilewski, D.; Shaked, Z.; Fuchs, A.; Roohani, S.; Xu, R.; Schlaak, M.; Frost, N.; Misch, M.; Capper, D.; Kaul, D.; et al. Re-resection of brain metastases—Outcomes of an institutional cohort study and literature review. BMC Cancer 2025, 25, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altieri, R.; Corvino, S.; La Rocca, G.; Cofano, F.; Melcarne, A.; Garbossa, D.; Barbarisi, M. Clinical Implication of Brain Metastases En-Bloc Resection: Surgical Technique Description and Literature Review. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowal, M.R.; Ibrahim, M.; Mihaljević, A.L.; Kron, P.; Lodge, P. Technological Advances in Pre-Operative Planning. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, A.B.; Wen, P.Y.; Polley, M.-Y.C. Molecular Profiling in Neuro-Oncology: Where We Are, Where We’re Heading, and How We Ensure Everyone Can Come Along. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2023, 43, e389322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, S.; von Bonin, M.; Bornhäuser, M.; Beste, C.; Ziemssen, T. Neurological complications in oncology and their monitoring and management in clinical practice: A narrative review. Support. Care Cancer 2024, 32, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-P.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Cheng, Y.-T.; Li, B.; Teng, X.-Z.; Zhang, J.; Lam, S.; Zhou, T.; Ma, Z.-R.; Sheng, J.-B.; et al. Artificial intelligence-driven radiomics study in cancer: The role of feature engineering and modeling. Mil. Med. Res. 2023, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, R.; Gutierrez-Valencia, E.; Santiago, A.; Lai, C.; Ahmed, D.B.; Habibi, P.; Laperriere, N.; Conrad, T.; Millar, B.-A.; Bernstein, M.; et al. Surgical Resection Followed by Stereotactic Radiosurgery (S+SRS) Versus SRS Alone for Large Posterior Fossa Brain Metastases: A Comparative Analysis of Outcomes and Factors Guiding Treatment Modality Selection. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Bao, J.; Wei, S. Optimizing outcomes in intracranial ependymoma: A contemporary review. Front. Oncol. 2025, 15, 1617169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoghbi, M.; Moussa, M.J.; Dagher, J.; Haroun, E.; Qdaisat, A.; Singer, E.D.; Karam, Y.E.; Yeung, S.-C.J.; Chaftari, P. Brain Metastasis in the Emergency Department: Epidemiology, Presentation, Investigations, and Management. Cancers 2024, 16, 2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, T.; Miyakita, Y.; Ohno, M.; Takahashi, M.; Yanagisawa, S.; Omura, T.; Tamura, Y.; Kikuchi, M.; Hosoya, T.; Narita, Y. MET-14 Outcome of Metastatic Cerebellar Tumor: A Single-Center Study. Neuro-Oncol. Adv. 2022, 4 (Suppl. S4), iii23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telera, S.; Gazzeri, R.; Villani, V.; Raus, L.; Giordano, F.R.; Costantino, A.; Delfinis, C.P.; Piludu, F.; Sperduti, I.; Pace, A. Surgical treatment of cerebellar metastases in elderly patients: A threshold that moves forward? World Neurosurg. X 2023, 18, 100164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, S.; Schwyzer, L.; Lomax, N.; Alonso, S.; Lazeroms, T.; Gomez, S.; Diahovets, K.; Fischer, I.; Schwenne, S.; Ademaj, A.; et al. Preoperative radiosurgery for brain metastases (PREOP-1): A feasibility trial. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 47, 100798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahnemann, L.; Krämer, A.; Fink, C.; Jungk, C.; Thomas, M.; Christopoulos, P.; Lischalk, J.; Meis, J.; Hörner-Rieber, J.; Eichkorn, T.; et al. Fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy of intracranial postoperative cavities after resection of brain metastases—Clinical outcome and prognostic factors. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 46, 100782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; McWilliams, T.; Belal, Z.; Lebow, E.; Hubbeling, H.; Kolker, J.; Nagda, S.; Kurtz, G.; Alonso-Basanta, M. Outcomes of Palliative Whole Posterior Fossa Radiotherapy for Adult Brain Metastases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 120 (Suppl. S2), e241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, D.F.; Wong, D.H.; Forshaw, M.M.; May, D.C.; Shenoy, D.A.; Mehta, D.S. Analysing the Rate of Recurrence and Leptomeningeal Disease in Posterior Fossa Brain Metastases Following Postoperative Radiotherapy-Single Centre Experience. Neuro-Oncology 2024, 26 (Suppl. S7), vii14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, C.; Haghighi, N.; Phillips, C.; Udovicich, C.; Li, M.P.; Drummond, K.; Dimou, J.; Davidson, A.S.; Sia, J. A feasibility trial of delayed resection for brain metastases following pre-operative stereotactic radiosurgery. J. Neurooncol. 2025, 174, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivers, C.I.; Mix, M.D.; Wang, K.; Godwin, W.; Takacs, I.; Chera, B. Postoperative Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Resected Brain Metastases: Targeting of the Surgical Tract. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2025, 15, 525–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Pino, I.; Chen, C.C. Stereotactic Radiosurgery as Treatment for Brain Metastases: An Update. Asian J. Neurosurg. 2023, 18, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretzschmar, L.; Gabrys, H.; Joye, A.; Kraft, J.; Guckenberger, M.; Andratschke, N. Postoperative stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) vs hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy (SRT) for resected brain metastases—a single centre analysis. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2025, 42, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotecha, R.; Tonse, R.; Menendez, M.A.R.; Williams, A.; Diaz, Z.; Tom, M.C.; Hall, M.D.; Mehta, M.P.; Alvarez, R.; Siomin, V.; et al. Evaluation of the impact of pre-operative stereotactic radiotherapy on the acute changes in histopathologic and immune marker profiles of brain metastases. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Faruqi, S.; Nordal, R.; Starreveld, Y.; Kelly, J.; Bowden, G.; Amanie, J.; Fairchild, A.; Lim, G.; Loewen, S.; et al. A phase III, multicenter, randomized controlled trial of preoperative versus postoperative stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with surgically resectable brain metastases. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrasheed, A.S.; Aleid, A.M.; Alharbi, R.A.; Alamer, M.A.; Alomran, K.A.; Bin Maan, S.A.; Almalki, S.F. Stereotactic radiosurgery versus whole-brain radiotherapy for intracranial metastases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2025, 16, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Miao, E.; Pike, L.R.G. Osimertinib-chemotherapy synergy in EGFR-mutant NSCLC: Advancing central nervous system control amidst toxicity considerations. Transl. Cancer Res. 2025, 14, 2188–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper-Vallillo, A.; Rotow, J.K.; Aredo, J.V.; Shaverdashvili, K.; Luo, J.; Carlisle, J.W.; Husain, H.; Muzikansky, A.; Heist, R.S.; Rangachari, D.; et al. High-Dose Osimertinib for CNS Progression in EGFR+ NSCLC: A Multi-Institutional Experience. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2022, 3, 100328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, T.A.; Wang, N. Targeting lung cancer brain metastases: A narrative review of emerging insights for anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-positive disease. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2023, 12, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurgeon, L.; Mitchell, C.; Cook, N.; Conway, A.-M. Cancer of unknown primary: The hunt for its elusive tissue-of-origin—is it time to call off the search? Br. J. Cancer 2025, 133, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.-B.; Lin, Y.-X.; Li, G.-Y.; Meng, T.-T.; Tian, P.; Chen, J.-L.; Zhang, X.-H.; Xu, W.-H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; et al. Associations of frailty and cognitive impairment with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in older adults: A prospective cohort study from NHANES 2011–2014. BMC Geriatr. 2025, 25, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mart, M.F.; Roberson, S.W.; Salas, B.; Pandharipande, P.P.; Ely, E.W. Prevention and Management of Delirium in the Intensive Care Unit. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 42, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, S.M.R.M.; Yadav, D.K.M.; Mehdi, H.M.; Baig, M.S.A.M.; Raza, M.M.; Abbas, J.M.; Mehdi, A.M.; Anjum, A.S.F. Unveiling the hidden danger: A rachnoid cyst in the fourth ventricle: A rare case report and review of the literature. Ann. Med. Surg. 2025, 87, 1759–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.D.; Gondi, V.; Pugh, S.; Tome, W.A.; Wefel, J.S.; Armstrong, T.S.; Bovi, J.A.; Robinson, C.; Konski, A.; Khuntia, D.; et al. Hippocampal Avoidance During Whole-Brain Radiotherapy Plus Memantine for Patients with Brain Metastases: Phase III Trial NRG Oncology CC001. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1019–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scampoli, C.; Cammelli, S.; Galietta, E.; Siepe, G.; Buwenge, M.; Macchia, G.; Deodato, F.; Cilla, S.; Strigari, L.; Chiesa, S.; et al. Memantine in the Prevention of Radiation-Induced Brain Damage: A Narrative Review. Cancers 2022, 14, 2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perlow, H.K.; Nalin, A.P.; Ritter, A.R.; Addington, M.; Ward, A.; Liu, M.; Nappi, C.; Blakaj, D.M.; Beyer, S.J.; Thomas, E.M.; et al. Advancing Beyond the Hippocampus to Preserve Cognition for Patients with Brain Metastases: Dosimetric Results from a Phase 2 Trial of Memory-Avoidance Whole Brain Radiation Therapy. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 9, 101337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlachos, N.; Lampros, M.G.; Filis, P.; Voulgaris, S.; Alexiou, G.A. Stereotactic radiosurgery versus whole-brain radiotherapy after resection of solitary brain metastasis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World Neurosurg. X 2023, 18, 100170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, J.; Rajkumar, S.; Shepard, M.J.; Wegner, R.E. National Trends in Radiation Treatment for Small Cell Lung Cancer Brain Metastases in the Modern Era. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2025, 10, 101720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| References | Design/Cohort | Key Population | Therapy | Outcomes | Practice-Relevant Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [6] | Retrospective surgical cohort | 73 cerebellar mets; lung/breast/GI common | Microsurgery; hydrocephalus relief | Median OS 9.2 mo; hydrocephalus worsened survival | Posterior fossa surgery yields outcomes comparable to supratentorial disease when selected carefully |
| [16] | Retrospective surgical series | 57 cerebellar mets; NSCLC/CRC/breast | Resection; multimodal care | IC-PFS 4.5 mo; OS 11.6 mo | Underscores early planning for cavity SRS given infratentorial recurrence risk |
| [17] | Comparative cohort | Elderly cerebellar mets | Tailored microsurgery | Functional recovery achievable | Frailty > age in determining safety—supports surgery in older adults |
| [18] | Prospective feasibility (pre-op SRS) | Resectable mets incl. posterior fossa | Pre-op SRS 24–72 h before surgery | Feasible; early cavity control; exploratory LMD signal | Concept of sterilizing tumor–CSF interface informs sequencing debate |
| [19] | Clinical series (post-op SRT) | Post-resection cavities | Fractionated SRT (e.g., 24 Gy/3 fx) | High LC; low brainstem toxicity | Fractionation mitigates posterior fossa dose-constraint limitations |
| [20] | Real-world palliative cohort | Predominant posterior fossa disease | Whole posterior fossa RT | Symptom relief | Useful when multifocal PF disease precludes focal SRS |
| [21] | Institutional posterior fossa experience | Post-op cavities | PORT/cavity RT | Higher LR/LMD with large volumes or pseudomeningocele | Highlights importance of cavity geometry and timing for SRS |
| [22] | Feasibility (delayed resection) | Resectable mets | Pre-op SRS with delayed surgery | Safe; immunologic interest | Extends pre-op SRS concept where PF logistics delay immediate surgery |
| [23] | Contemporary SRS practice update | Deep/large cavities | Cavity SRS with tract inclusion | LC tempered by dose-constraint adaptations | Directly relevant: brainstem constraints often require fractionation + tract coverage |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dobrin, N.; Brehar, F.-M.; Costea, D.; Dumitru, A.V.; Ciurea, A.V.; Munteanu, O.; Munteanu, L.V. Anatomically Precise Microsurgical Resection of a Posterior Fossa Cerebellar Metastasis in an Elderly Patient with Preservation of Venous Outflow, Dentate Nucleus, and Cerebrospinal Fluid Pathways. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 3131. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15243131
Dobrin N, Brehar F-M, Costea D, Dumitru AV, Ciurea AV, Munteanu O, Munteanu LV. Anatomically Precise Microsurgical Resection of a Posterior Fossa Cerebellar Metastasis in an Elderly Patient with Preservation of Venous Outflow, Dentate Nucleus, and Cerebrospinal Fluid Pathways. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(24):3131. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15243131
Chicago/Turabian StyleDobrin, Nicolaie, Felix-Mircea Brehar, Daniel Costea, Adrian Vasile Dumitru, Alexandru Vlad Ciurea, Octavian Munteanu, and Luciana Valentina Munteanu. 2025. "Anatomically Precise Microsurgical Resection of a Posterior Fossa Cerebellar Metastasis in an Elderly Patient with Preservation of Venous Outflow, Dentate Nucleus, and Cerebrospinal Fluid Pathways" Diagnostics 15, no. 24: 3131. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15243131
APA StyleDobrin, N., Brehar, F.-M., Costea, D., Dumitru, A. V., Ciurea, A. V., Munteanu, O., & Munteanu, L. V. (2025). Anatomically Precise Microsurgical Resection of a Posterior Fossa Cerebellar Metastasis in an Elderly Patient with Preservation of Venous Outflow, Dentate Nucleus, and Cerebrospinal Fluid Pathways. Diagnostics, 15(24), 3131. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15243131





