Utility of REMS-Derived Fragility Score and Trabecular Bone Score in Evaluating Bone Health in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
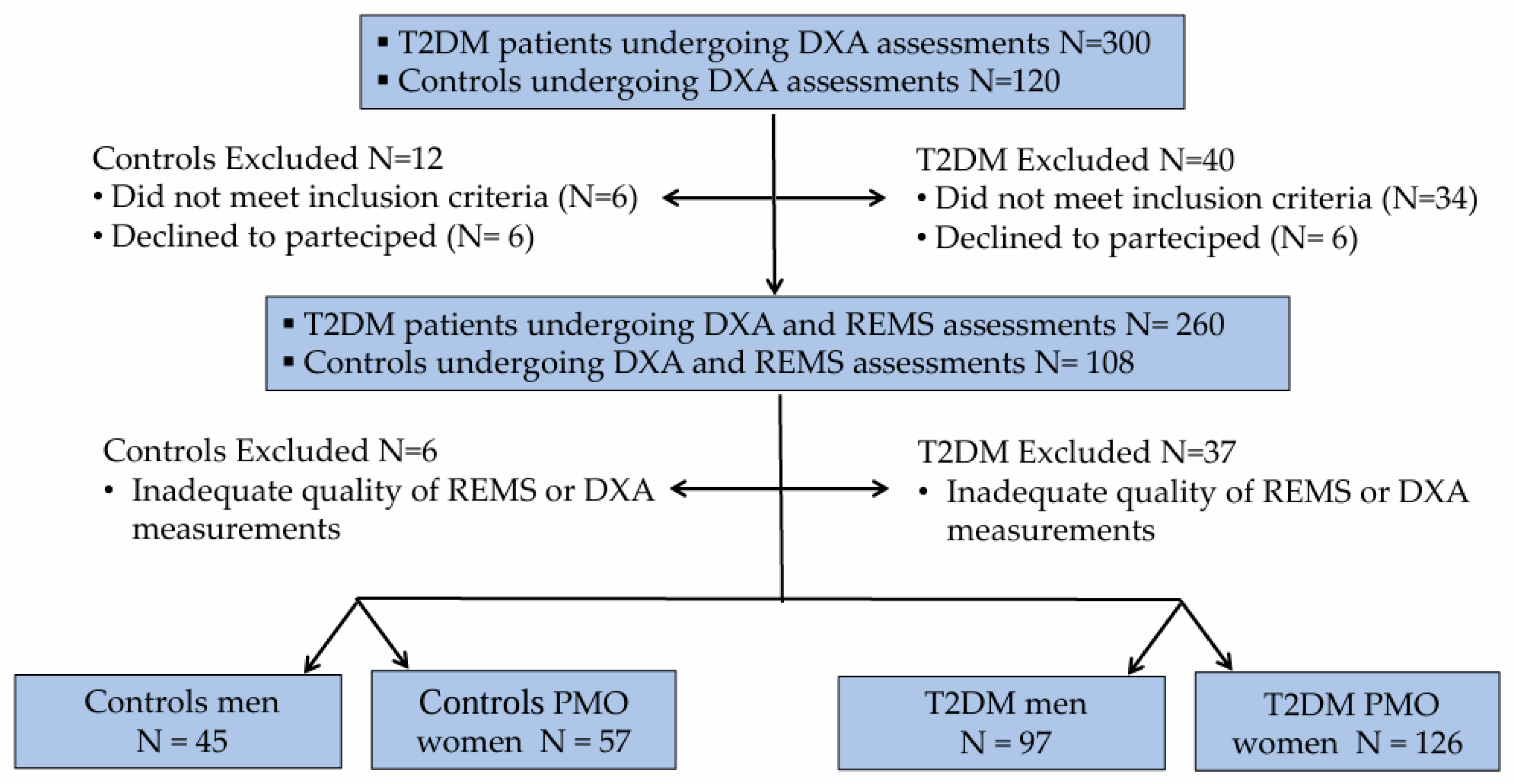
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA)
2.3. Radiofrequency Echographic MultiSpectrometry (REMS)
2.4. Laboratory Tests and Fractures Assessment
2.5. Fracture Assessment
2.6. Statistical Analysis
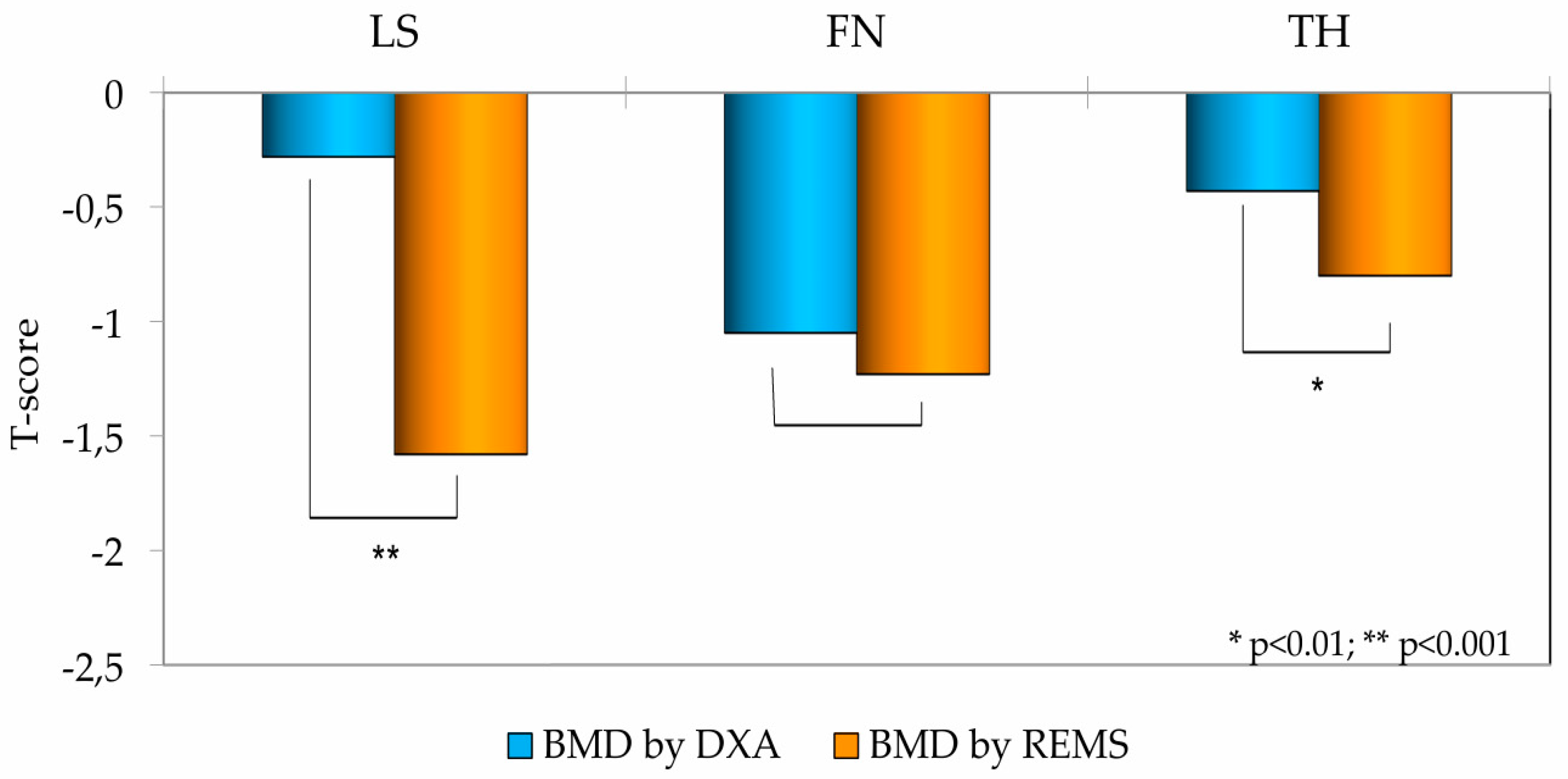
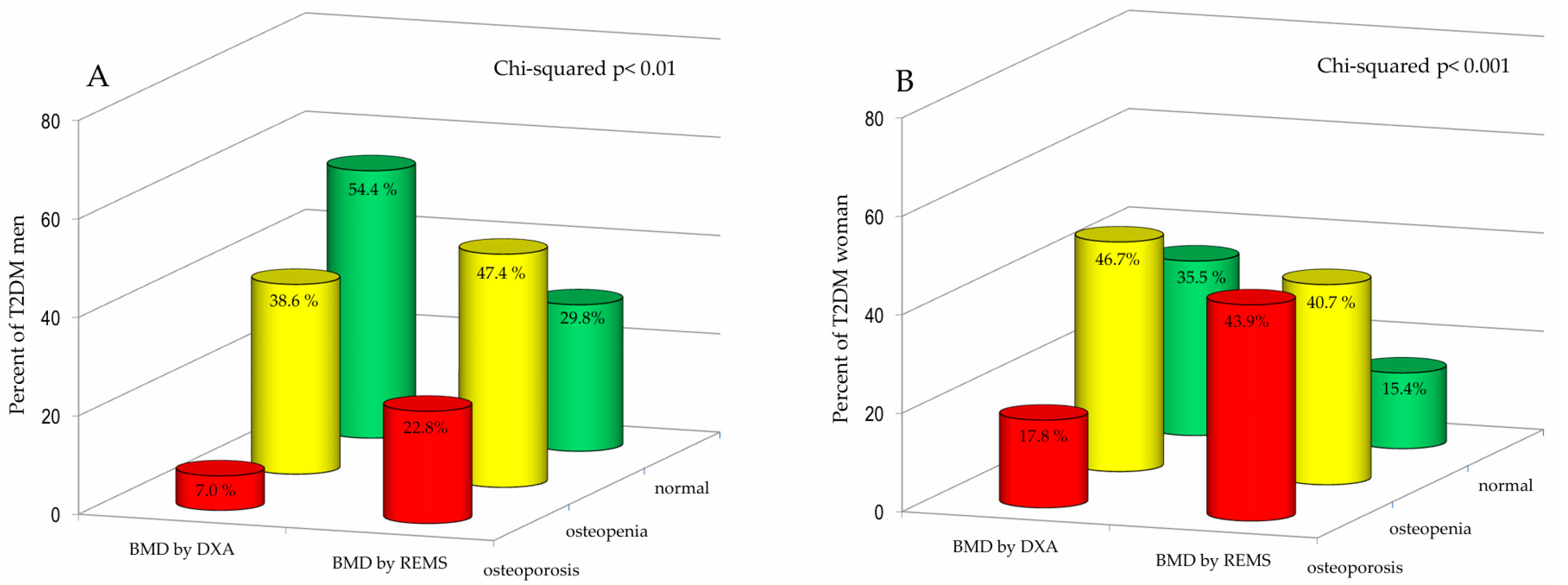
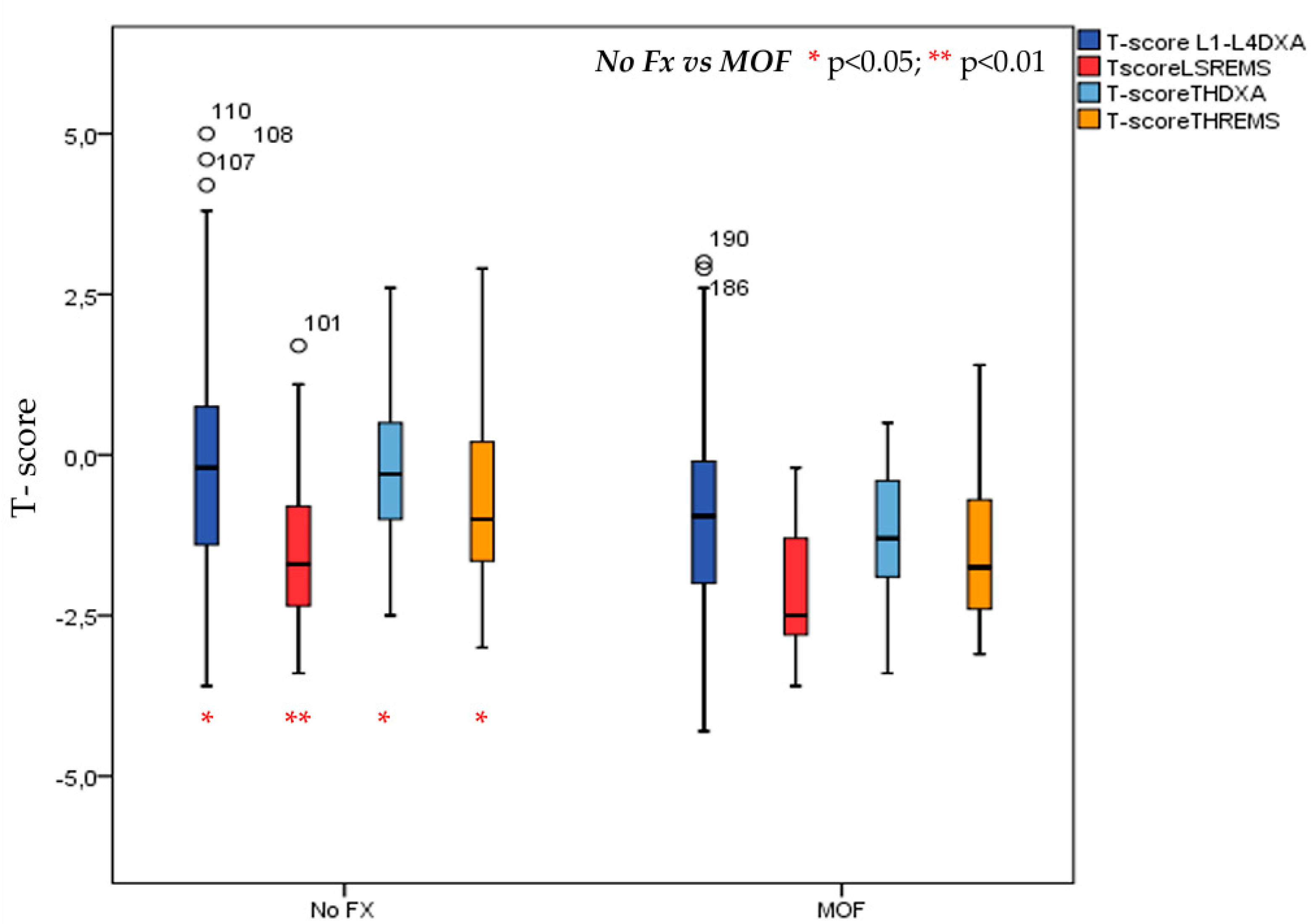
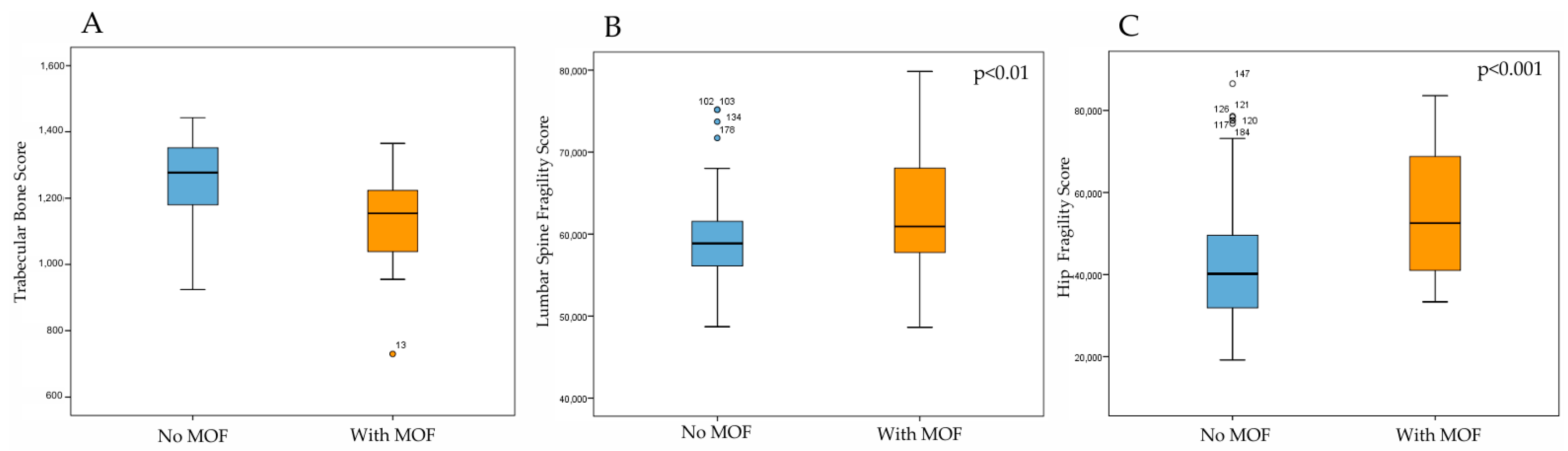
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| T2DM | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| BMD | Bone mineral density |
| TBS | Trabecular Bone Score |
| REMS | Radiofrequency echographic multispectrometry |
| LS | Lumbar spine |
| FN | Femoral neck |
| TH | Total hip |
| FS | Fragility score |
| DXA | Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry |
| MOF | Major osteoporotic fractures |
| DALYs | Disability-adjusted life years |
| AGEs | Advanced glycation end-products |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| HbA1c | Glycated hemoglobin |
| PTH | Parathyroid hormone |
| 25OHD | 25-hydroxyvitamin D |
| HR-pQCT | High-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography |
| QUS | Quantitative ultrasound |
References
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.N.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, A.V.; Sellmeyer, D.E.; Ensrud, K.E.; Cauley, J.A.; Tabor, H.K.; Schreiner, P.J.; Jamal, S.A.; Black, D.M.; Cummings, S.R.; Study of Osteoporotic Features Research Group. Older women with diabetes have an increased risk of fracture: A prospective study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vestergaard, P. Discrepancies in bone mineral density and fracture risk in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes—A meta-analysis. Osteoporos. Int. 2007, 18, 427–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napoli, N.; Chandran, M.; Pierroz, D.D.; Abrahamsen, B.; Schwartz, A.V.; Ferrari, S.L. Mechanisms of diabetes mellitus-induced bone fragility. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebé, C.; Martínez-Laguna, D.; Carbonell-Abella, C.; Reyes, C.; Moreno, V.; Diez-Perez, A.; Collins, G.S.; Prieto-Alhambra, D. The association between type 2 diabetes mellitus, hip fracture, and post-hip fracture mortality: A multi-state cohort analysis. Osteoporos. Int. 2019, 30, 2407–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schacter, G.I.; Leslie, W.D. Diabetes and Osteoporosis: Part I, Epidemiology and Pathophysiology. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 50, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giangregorio, L.M.; Leslie, W.D.; Lix, L.M.; Johansson, H.; Oden, A.; McCloskey, E.; Kanis, J.A. FRAX underestimates fracture risk in patients with diabetes. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2012, 27, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, S.L.; Abrahamsen, B.; Napoli, N.; Akesson, K.; Chandran, M.; Eastell, R.; El-Hajj Fuleihan, G.; Josse, R.; Kendler, D.L.; Kraenzlin, M.; et al. Diagnosis and management of bone fragility in diabetes: An emerging challenge. Osteoporos. Int. 2018, 29, 2585–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanbhogue, V.V.; Mitchell, D.M.; Rosen, C.J.; Bouxsein, M.L. Type 2 diabetes and the skeleton: New insights into sweet bones. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016, 4, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, M.; Petroianu, G.; Adem, A. Advanced Glycation End Products and Diabetes Mellitus: Mechanisms and Perspectives. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Xia, W. Assessment of bone quality in patients with diabetes mellitus. Osteoporos. Int. 2018, 29, 1721–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roux, J.P.; Wegrzyn, J.; Boutroy, S.; Bouxsein, M.L.; Hans, D.; Chapurlat, R. The predictive value of trabecular bone score (TBS) on whole lumbar vertebrae mechanics: An ex vivo study. Osteoporos. Int. 2013, 24, 2455–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, B.C.; Broy, S.B.; Boutroy, S.; Schousboe, J.T.; Shepherd, J.A.; Leslie, W.D. Fracture Risk Prediction by Non-BMD DXA Measures: The 2015 ISCD Official Positions Part 2: Trabecular Bone Score. J. Clin. Densitom. 2015, 18, 309–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shevroja, E.; Cafarelli, F.P.; Guglielmi, G.; Hans, D. DXA parameters, Trabecular Bone Score (TBS) and Bone Mineral Density (BMD), in fracture risk prediction in endocrine-mediated secondary osteoporosis. Endocrine 2021, 74, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, W.D.; Aubry-Rozier, B.; Lamy, O.; Hans, D.; Manitoba Bone Density Program. TBS (trabecular bone score) and diabetes-related fracture risk. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trandafir, A.I.; Sima, O.C.; Gheorghe, A.M.; Ciuche, A.; Cucu, A.P.; Nistor, C.; Carsote, M. Trabecular Bone Score (TBS) in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: An Updated Review. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez-Perez, A.; Brandi, M.L.; Al-Daghri, N.; Branco, J.C.; Bruyère, O.; Cavalli, L.; Cooper, C.; Cortet, B.; Dawson-Hughes, B.; Dimai, H.P.; et al. Radiofrequency echographic multi-spectrometry for the in-vivo assessment of bone strength: State of the art-outcomes of an expert consensus meeting organized by the European Society for Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis, Osteoarthritis and Musculoskeletal Diseases (ESCEO). Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 31, 1375–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caffarelli, C.; Tomai Pitinca, M.D.; Al Refaie, A.; Ceccarelli, E.; Gonnelli, S. Ability of radiofrequency echographic multispectrometry to identify osteoporosis status in elderly women with type 2 diabetes. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2022, 34, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisani, P.; Greco, A.; Conversano, F.; Renna, M.D.; Casciaro, E.; Quarta, L.; Costanza, D.; Muratore, M.; Casciaro, S. A quantitative ultra sound approach to estimate bone fragility: A first comparison with dual X-ray absorptiometry. Measurement 2017, 101, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, A.; Pisani, P.; Conversano, F.; Soloperto, G.; Renna, M.D.; Muratore, M.; Casciaro, S. Ultrasound Fragility Score: An innovative approach for the assessment of bone fragility. Measurement 2017, 101, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisani, P.; Conversano, F.; Muratore, M.; Adami, G.; Brandi, M.L.; Caffarelli, C.; Casciaro, E.; Di Paola, M.; Franchini, R.; Gatti, D.; et al. Fragility Score: A REMS-based indicator for the prediction of incident fragility fractures at 5 years. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2023, 35, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janghorbani, M.; Van Dam, R.M.; Willett, W.C.; Hu, F.B. Systematic review of type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus and risk of fracture. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2007, 166, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Wei, F.; Lang, Y.; Liu, Y. Diabetes mellitus and risk of hip fractures: A meta-analysis. Osteoporos. Int. 2016, 27, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eller-Vainicher, C.; Cairoli, E.; Grassi, G.; Grassi, F.; Catalano, A.; Merlotti, D.; Falchetti, A.; Gaudio, A.; Chiodini, I.; Gennari, L. Pathophysiology and Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Bone Fragility. J. Diabetes Res. 2020, 2020, 7608964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holloway-Kew, K.L.; Betson, A.; Rufus-Membere, P.G.; Gaston, J.; Diez-Perez, A.; Kotowicz, M.A.; Pasco, J.A. Impact microindentation in men with impaired fasting glucose and type 2 diabetes. Bone 2021, 142, 115685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, B.; Liu, J.M.; Zhao, H.Y.; Sun, L.H.; Wang, W.Q.; Li, X.Y.; Ning, G. Differences between measurements of bone mineral densities by quantitative ultrasound and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry in type 2 diabetic postmenopausal women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 1670–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Kanazawa, I.; Yamauchi, M.; Yano, S.; Tanaka, N.; Nitta, E.; Fukuma, A.; Uno, S.; Sho-no, T.; et al. Quantitative ultrasound and vertebral fractures in patients with type 2 diabetes. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2011, 29, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuggle, N.R.; Reginster, J.Y.; Al-Daghri, N.; Bruyere, O.; Burlet, N.; Campusano, C.; Cooper, C.; Perez, A.D.; Halbout, P.; Ghi, T.; et al. Radiofrequency echographic multi spectrometry (REMS) in the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis: State of the art. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2024, 36, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caffarelli, C.; Al Refaie, A.; Mondillo, C.; Manasse, G.; Versienti, A.; Tomai Pitinca, M.D.; Conticini, E.; Frediani, B.; Gonnelli, S. The Advantages of Radiofrequency Echographic MultiSpectrometry in the Evaluation of Bone Mineral Density in a Population with Osteoarthritis at the Lumbar Spine. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronese, N.; Cooper, C.; Reginster, J.Y.; Hochberg, M.; Branco, J.; Bruyère, O.; Chapurlat, R.; Al-Daghri, N.; Dennison, E.; Herrero-Beaumont, G.; et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and osteoarthritis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2019, 49, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adami, G.; Arioli, G.; Bianchi, G.; Brandi, M.L.; Caffarelli, C.; Cianferotti, L.; Gatti, D.; Girasole, G.; Gonnelli, S.; Manfredini, M.; et al. Radiofrequency echographic multi spectrometry for the prediction of incident fragility fractures: A 5-year follow-up study. Bone 2020, 134, 115297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Icătoiu, E.; Vlădulescu-Trandafir, A.I.; Groșeanu, L.M.; Berghea, F.; Cobilinschi, C.O.; Potcovaru, C.G.; Bălănescu, A.R.; Bojincă, V.C. Radiofrequency Echographic Multi Spectrometry-A Novel Tool in the Diagnosis of Osteoporosis and Prediction of Fragility Fractures: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho-Pham, L.T.; Nguyen, T.V. Association between trabecular bone score and type 2 diabetes: A quantitative update of evidence. Osteoporos. Int. 2019, 30, 2079–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J.; Ock, S.Y.; Chung, Y.S. Trabecular Bone Score (TBS) and TBS-Adjusted Fracture Risk Assessment Tool are Potential Supplementary Tools for the Discrimination of Morphometric Vertebral Fractures in Postmenopausal Women with Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Densitom. 2016, 19, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulivieri, F.M.; Silva, B.C.; Sardanelli, F.; Hans, D.; Bilezikian, J.P.; Caudarella, R. Utility of the trabecular bone score (TBS) in secondary osteoporosis. Endocrine 2014, 47, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amnuaywattakorn, S.; Sritara, C.; Utamakul, C.; Chamroonrat, W.; Kositwattanarerk, A.; Thamnirat, K.; Ongphiphadhanakul, B. Simulated increased soft tissue thickness artefactually decreases trabecular bone score: A phantom study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2016, 17, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevroja, E.; Aubry-Rozier, B.; Hans, G.; Gonzalez- Rodriguez, E.; Stoll, D.; Lamy, O.; Hans, D. Clinical Performance of the Updated Trabecular Bone Score (TBS) Algorithm, Which Accounts for the Soft Tissue Thickness: The OsteoLaus Study. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2019, 34, 2229–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalli, P.; Mautino, C.; Busso, C.; Bardesono, F.; Di Monaco, M.; Lippi, L.; Invernizzi, M.; Minetto, M.A. Reproducibility and Accuracy of the Radiofrequency Echographic Multi-Spectrometry for Femoral Mineral Density Estimation and Discriminative Power of the Femoral Fragility Score in Patients with Primary and Disuse-Related Osteoporosis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| T2DM Patients (N = 223) | Controls (N = 102) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| M/F | 97/126 | 45/57 | n.s. |
| Age (yrs) | 67.5 ± 9.1 | 68.7 ± 7.5 | n.s. |
| Weight (Kg) | 78.6 ± 15.7 | 74.1 ± 12.3 | 0.05 |
| Height (cm) | 164.0 ± 8.6 | 165.1 ± 6.7 | n.s. |
| BMI (Kg/m2) | 29.2 ± 5.1 | 27.6 ± 4.3 | 0.01 |
| HbA1c (%) | 6.8 ± 1.2 | -------- | |
| T2DM duration (yrs) | 12.8 ± 10.6 | --------- | |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.0 ± 0.3 | 0.9 ± 0.2 | n.s. |
| Calcium (mg/dL) | 9.4 ± 0.5 | 9.3 ± 0.4 | n.s. |
| Phosphate (mg/dL) | 3.6 ± 0.6 | 3.5 ± 0.6 | n.s. |
| 25OHD (ng/mL) | 21.6 ± 11.3 | 23.8 ± 9.4 | n.s. |
| PTH (pg/mL) | 35.5 ± 16.7 | 33.6 ± 15.8 | n.s. |
| DXA LS-BMD (g/cm2) | 1.070 ± 0.211 | 0.946 ± 0.189 | 0.01 |
| DXA FN-BMD (g/cm2) | 0.792 ± 0.162 | 0.730 ± 0.178 | 0.05 |
| DXA TH-BMD (g/cm2) | 0.936 ± 0.157 | 0.887 ± 0.178 | 0.05 |
| REMS LS-BMD (g/cm2) | 0.871 ± 0.119 | 0.893 ± 0.120 | 0.05 |
| REMS FN-BMD (g/cm2) | 0.724 ± 0.120 | 0.733 ± 0.099 | n.s. |
| REMS TH-BMD (g/cm2) | 0.865 ± 0.170 | 0.872 ± 0.117 | 0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al Refaie, A.; Mondillo, C.; Cavati, G.; Gonnelli, S.; Tomai Pitinca, M.D.; Ceccarelli, E.; Pisani, P.; Gennari, L.; Gonnelli, S.; Caffarelli, C. Utility of REMS-Derived Fragility Score and Trabecular Bone Score in Evaluating Bone Health in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2877. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15222877
Al Refaie A, Mondillo C, Cavati G, Gonnelli S, Tomai Pitinca MD, Ceccarelli E, Pisani P, Gennari L, Gonnelli S, Caffarelli C. Utility of REMS-Derived Fragility Score and Trabecular Bone Score in Evaluating Bone Health in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(22):2877. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15222877
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl Refaie, Antonella, Caterina Mondillo, Guido Cavati, Sara Gonnelli, Maria Dea Tomai Pitinca, Elena Ceccarelli, Paola Pisani, Luigi Gennari, Stefano Gonnelli, and Carla Caffarelli. 2025. "Utility of REMS-Derived Fragility Score and Trabecular Bone Score in Evaluating Bone Health in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus" Diagnostics 15, no. 22: 2877. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15222877
APA StyleAl Refaie, A., Mondillo, C., Cavati, G., Gonnelli, S., Tomai Pitinca, M. D., Ceccarelli, E., Pisani, P., Gennari, L., Gonnelli, S., & Caffarelli, C. (2025). Utility of REMS-Derived Fragility Score and Trabecular Bone Score in Evaluating Bone Health in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diagnostics, 15(22), 2877. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15222877










