Brain Perfusion Scintigraphy in the Diagnostic Toolbox for the Confirmation of Brain Death: Practical Aspects and Examination Protocol
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Characteristics
2.2. Scintigraphic Method
2.3. Image Evaluation
2.4. Statistical Evaluation
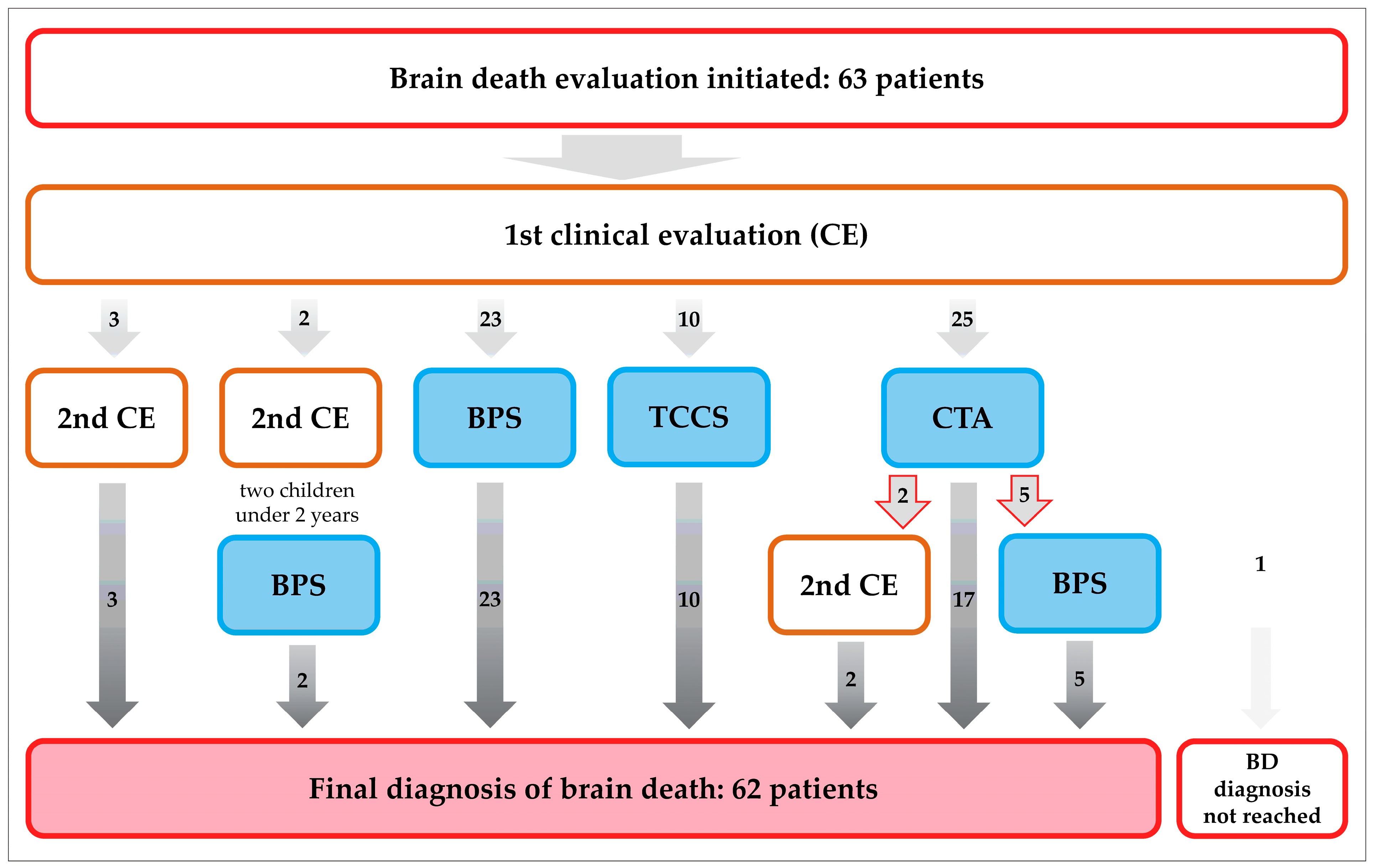
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
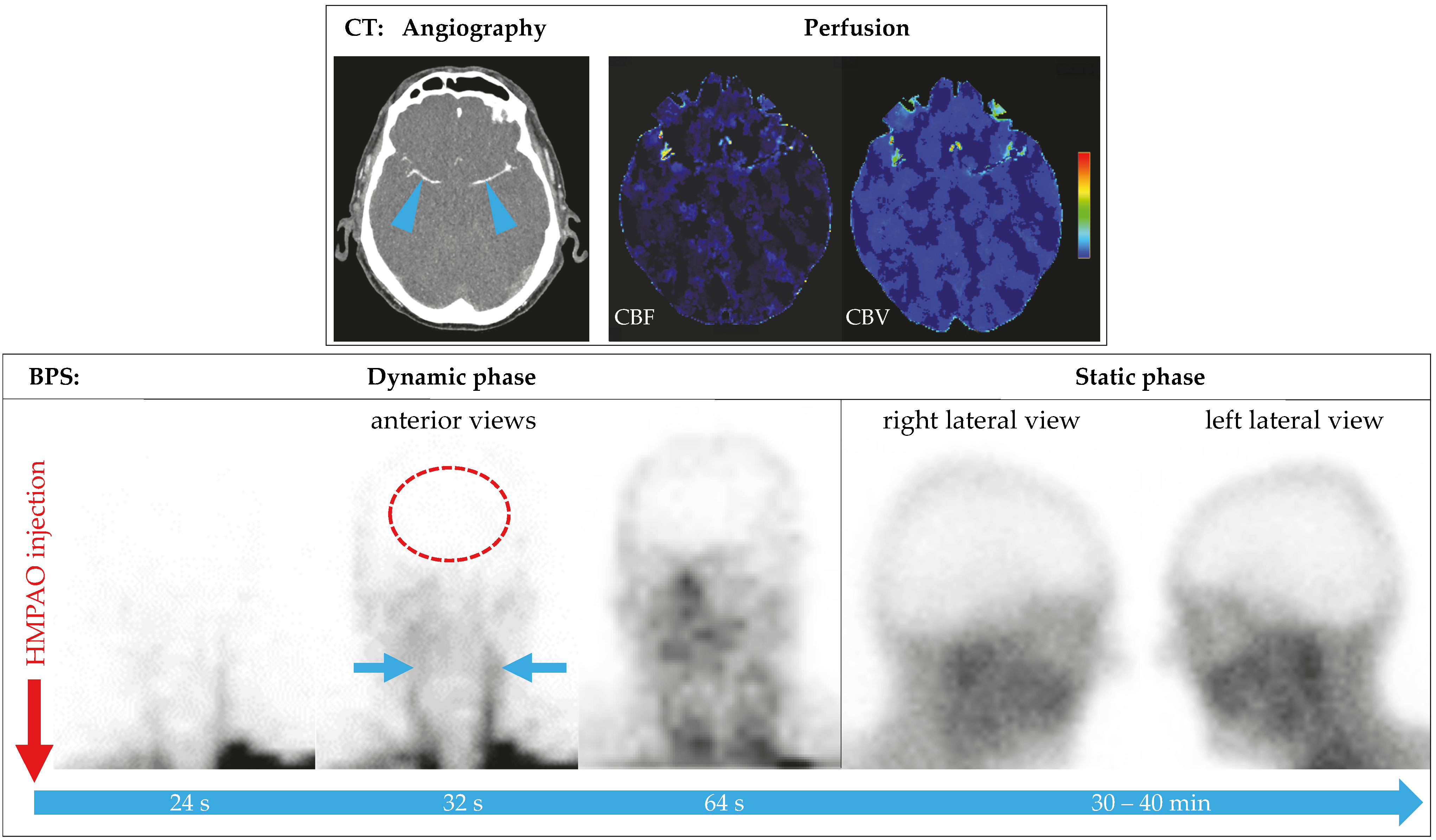
3.2. Brain Perfusion Scintigraphy
3.3. Semiquantitative Evaluation
4. Discussion
4.1. BPS in the Context of Guidelines
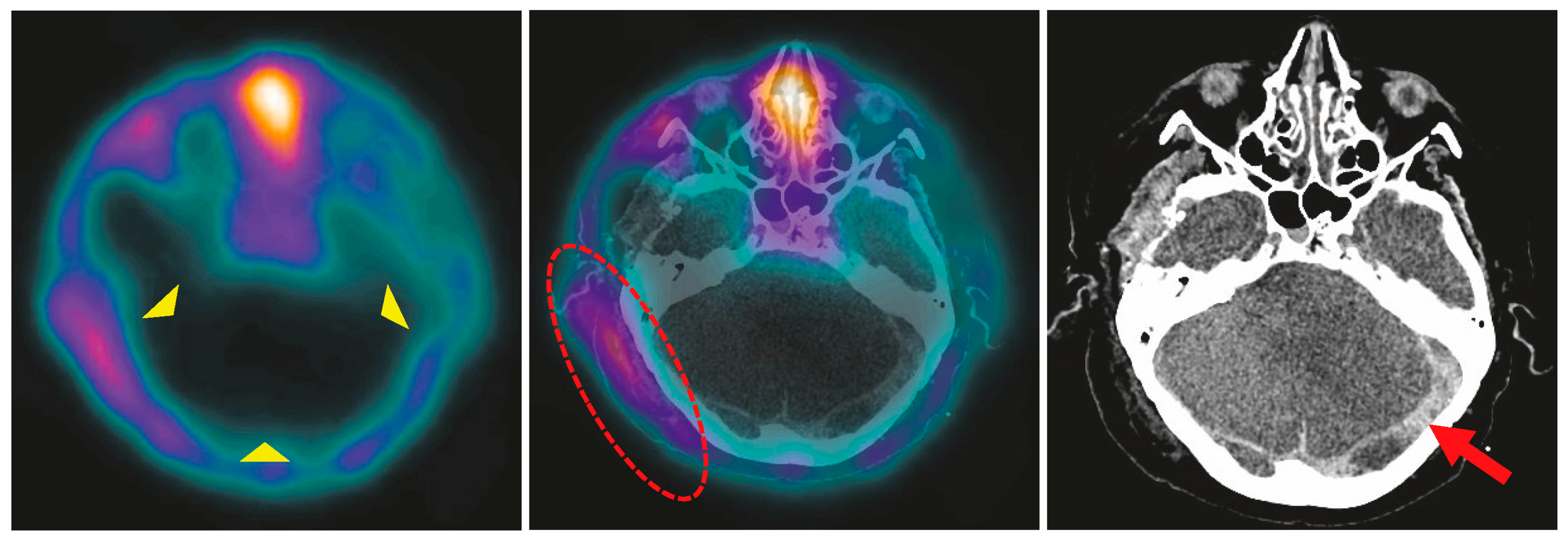
4.2. BPS in Infants and Children
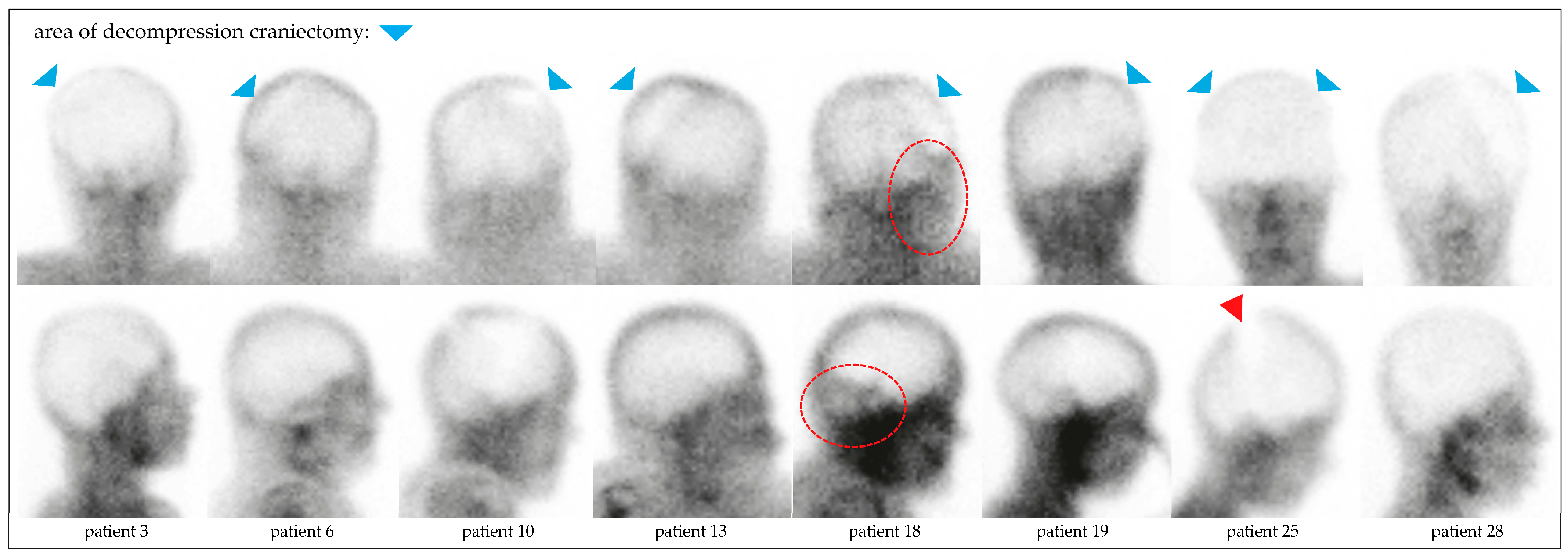
4.3. BPS in Hemicraniectomy
4.4. BPS in Patients on vaECMO or LVAD
4.5. BPS Compared with Other Ancillary Tests
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BD | brain death |
| BPS | brain perfusion scintigraphy |
| CPR | cardiopulmonary resuscitation |
| CTA | computed tomography angiography |
| DC | decompressive craniectomy |
| DGN | Deutsche Gesellschaft für Neurologie (German Neurological Society) |
| DGN | Deutsche Gesellschaft für Nuklearmedizin (German Society of Nuclear Medicine) |
| DSA | digital subtraction angiography |
| DUI | delayed uptake index |
| EANM | European Association of Nuclear Medicine |
| EDH/SDH/SAH/ICH | epidural/subdural/subarachnoid/intracerebral hemorrhage |
| EEG | electroencephalogram |
| EP | evoked potentials |
| HMPAO | hexamethylpropyleneamine oxime |
| ILBF | irreversible loss of brain function |
| IQR | interquartile range |
| LEHR | low energy high resolution |
| LVAD | left ventricular assist devices |
| NAHI | non-accidental head injury |
| e | regions of interest |
| SNMMI | Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging |
| SOP | standard operating procedure |
| SPECT | single-photon emission computed tomography |
| e | thin-layer chromatography |
| vaECMO | veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation |
References
- Pius, P., XII. The Prolongation of Life. Pope Speak. 1958, 4, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federal Medical Association Germany (Bundesärztekammer). Guideline for the determination of death and of irreversible loss of brain function, 5th edition (Richtlinie gemäß § 16 Abs. 1 S. 1 Nr. 1 TPG für die Regeln zur Feststellung des Todes nach § 3 Abs. 1 S. 1 Nr. 2 TPG und die Verfahrensregeln zur Feststellung des endgültigen, nicht behebbaren Ausfalls der Gesamtfunktion des Großhirns, des Kleinhirns und des Hirnstamms nach § 3 Abs. 2 Nr. 2 TPG, fünfte Fortschreibung). Dtsch. Ärzteblatt 2022, 119, A-1487–B-1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, D.M.; Shemie, S.D.; Lewis, A.; Torrance, S.; Varelas, P.; Goldenberg, F.D.; Bernat, J.L.; Souter, M.; Topcuoglu, M.A.; Alexandrov, A.W.; et al. Determination of Brain Death/Death by Neurologic Criteria: The World Brain Death Project. JAMA 2020, 324, 1078–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neves Briard, J.; Nitulescu, R.; Lemoine, E.; Titova, P.; McIntyre, L.; English, S.W.; Knoll, G.; Shemie, S.D.; Martin, C.; Turgeon, A.F.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of ancillary tests for death by neurologic criteria: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Can. J. Anaesth. 2023, 70, 736–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roine, R.O.; Launes, J.; Lindroth, L.; Nikkinen, P. 99mTc-hexamethylpropyleneamine oxime scans to confirm brain death. Lancet 1986, 2, 1223–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, R.H.; Gulenchyn, K.Y.; Ballinger, J.R. Clinical use of technetium-99m HM-PAO for determination of brain death. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 1989, 30, 1621–1626. [Google Scholar]
- Munari, M.; Zucchetta, P.; Carollo, C.; Gallo, F.; De Nardin, M.; Marzola, M.C.; Ferretti, S.; Facco, E. Confirmatory tests in the diagnosis of brain death: Comparison between SPECT and contrast angiography. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 33, 2068–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GE Healthcare. Ceretec (Tc-99m Exametazime) Prescribing Information. Available online: https://www.gehealthcare.com/-/jssmedia/GEHC/US/Files/Products/Molecular-Imaging/Ceretec-Cobalt/Ceretec-Cobalt-Prescribing-Information-092018-CERETEC-with-Cobalt-Chloride-BK (accessed on 5 May 2025).
- GE Healthcare. Ceretec (Tc-99m Exametazim) Fachinformation. Available online: https://www.gehealthcare.de/-/jssmedia/global/dach/files/pdx/spcdeff-stabilised-ceretec-september2018-clean.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2025).
- Zuckier, L.S.; Brendel, M.; Cecchin, D.; Donohoe, K.; Frey, K.; Klein, R.; Nadel, H.; Shemie, S.D.; Sinha, P. The SNMMI/EANM Practice Guideline for Radionuclide Brain Perfusion Scintigraphy in Suspected Death by Neurologic Criteria (Brain Death) 3.0 Updated from 2012. Available online: https://snmmi.org/common/Uploaded%20files/Web/Clinical%20Practice/Procedure%20Standards/2024/Brain%20Death%20Scintigraphy%203.0_FINAL_2025.pdf (accessed on 7 January 2025).
- Kranert, T.; Menzel, C.; Bartenstein, P.; Brust, P.; Coenen, H.H.; Krause, B.J.; Kuwert, T.; Sabri, O.; Schreckenberger, M.; Tatsch, K.; et al. [Perfusion brain imaging with SPECT-technique. German Guideline S1]. Nuklearmedizin Nucl. Med. 2013, 52, 157–162. [Google Scholar]
- German Society of Nuclear Medicine. Brain perfusion SPECT with Tc-99m radiopharmaceuticals (Hirnperfusions-SPECT mit Tc-99m-Radiopharmaka), S1 Guideline. Available online: https://register.awmf.org/de/leitlinien/detail/031-016 (accessed on 5 May 2025).
- European Association of Nuclear Medicine. EANM Dosage Card, Version 5.7.2016. Available online: https://eanm.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/EANM_Dosage_Card_040214.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2025).
- Mrhac, L.; Zakko, S.; Parikh, Y. Brain death: The evaluation of semi-quantitative parameters and other signs in HMPAO scintigraphy. Nucl. Med. Commun. 1995, 16, 1016–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, J.C. Quantitative SPECT: A survey of current practice in the UK Nuclear Medicine Community. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2019, 40, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, S.; Tan, Y.Z.; Ozturk, F.K.; Battal, F. Confirmation of Brain Death with Positron Emission Tomography. J. Pediatr. Intensive Care 2020, 9, 51–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M.A. Evaluating brain death with positron emission tomography: Case report on dynamic imaging of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose activity after intravenous bolus injection. J. Neuroimaging 1996, 6, 117–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proisy, M.; Mitra, S.; Uria-Avellana, C.; Sokolska, M.; Robertson, N.J.; Le Jeune, F.; Ferre, J.C. Brain Perfusion Imaging in Neonates: An Overview. AJNR. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2016, 37, 1766–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donohoe, K.J.; Frey, K.A.; Gerbaudo, V.H.; Mariani, G.; Nagel, J.S.; Shulkin, B. Procedure guideline for brain death scintigraphy. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 2003, 44, 846–851. [Google Scholar]
- Zuckier, L.S.; McKinnon, N.K. Ancillary radionuclide perfusion studies in the determination of death by neurologic criteria: Methods, interpretation, and lexicon-a user guide for the clinician. Can. J. Anaesth. 2023, 70, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, P.; Conrad, G.R.; Williams, B.L. Visualization of bullet track and bullet by radionuclide brain scintigraphy. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2005, 30, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohatyrewicz, R.; Pastuszka, J.; Walas, W.; Chamier-Cieminska, K.; Poncyljusz, W.; Dabrowski, W.; Wojczal, J.; Luchowski, P.; Guzinski, M.; Jurkiewicz, E.; et al. Implementation of Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) and Computed Tomography Perfusion (CTP) in Polish Guidelines for Determination of Cerebral Circulatory Arrest (CCA) during Brain Death/Death by Neurological Criteria (BD/DNC) Diagnosis Procedure. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinnon, N.K.; Maratta, C.; Zuckier, L.S.; Boyd, J.G.; Chasse, M.; Hornby, L.; Kramer, A.; Kromm, J.; Mooney, O.T.; Muthusami, P.; et al. Ancillary investigations for death determination in infants and children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Can. J. Anaesth. 2023, 70, 749–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coker, S.B.; Dillehay, G.L. Radionuclide cerebral imaging for confirmation of brain death in children: The significance of dural sinus activity. Pediatr. Neurol. 1986, 2, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, D.M.; Maia, A.C.M., Jr.; Boni, R.C.; da Rocha, A.J. Impact of Skull Defects on the Role of CTA for Brain Death Confirmation. AJNR. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2019, 40, 1177–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiyama, M.; Relyea-Chew, A.; Longstreth, W.T.; Lewis, D.H. Impact of decompressive craniectomy on brain perfusion scintigraphy as an ancillary test for brain death diagnosis. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2019, 33, 842–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, L.; Grus, T.; Balik, M.; Fichtl, J.; Kavan, J.; Belohlavek, J. Hemodynamic changes in patients with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) demonstrated by contrast-enhanced CT examinations—implications for image acquisition technique. Perfusion 2017, 32, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunther, A.; Werner, A.; Fritzenwanger, M.; Brauer, M.; Freesmeyer, M.; Schulze, P.C.; Salih, F.; Drescher, R. Determination of brain death using (99m)Tc-HMPAO scintigraphy and transcranial duplex sonography in a patient on veno-arterial ECMO. Neurol. Res. Pr. 2024, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berlit, P.; Wetzel, E.; Bethke, U.; Pohlmann-Eden, B. [Cerebral blood flow scintigraphy using 99mTc-HM-PAO in the diagnosis of brain death]. Wien. Med. Wochenschr. 1990, 140, 571–574. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Greer, D.M.; Strozyk, D.; Schwamm, L.H. False positive CT angiography in brain death. Neurocritical Care 2009, 11, 272–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petsanis, K.; Markou, P.; Chatzopoulos, D.; Tsolaki, M. The role of Tc-99m-HMPAO SPET perfusion neuroimaging and cerebrovascular reactivity to acetazolamide in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Ann. Gen. Psychiatry 2006, 5, S332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Patient * | Age | Initial Event | Initial Imaging Findings | DC | Brain Perfusion Scintigraphy | DUI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Years | Days After Event | Days After Event | Arterial Blood Pressure (mm Hg) | Perfusion Detected | ||||
| Traumatic (n = 6) | ||||||||
| 1 | 2.1 | NAHI | SDH, SAH, brain edema | - | 2 | 115/73 | no | 0.083 |
| 3 | 14.7 | traffic accident | EDH, SDH, contusion, axonal injuries, brain edema, spinal fractures | 0 | 2 | 130/74 | no | 0.194 |
| 4 | 0.1 | NAHI | axonal injuries, brain edema, SDH, SAH | - | 4 | 94/51 | no | 0.176 |
| 27 ** | 62.7 | gunshot injury | ICH, SAH | - | 1 | 123/79 | no | 0.304 |
| 28 | 15.0 | traffic accident | ICH, SDH, brain edema | 1 | 1 | 129/85 | no | 0.173 |
| 30 | 33.1 | cervical fractures, VA dissection | brain edema | - | 1 | 125/71 | no | 0.153 |
| Hemorrhagic (n = 10) | ||||||||
| 2 | 56.9 | spontaneous ICH | ICH, brain edema | - | 2 | 125/65 | no | 0.225 |
| 6 | 55.1 | aneurysm rupture | SAH, brain edema, brain ischemia | 0 | 14 | 90/60 | no | 0.226 |
| 7 ** | 62.1 | aneurysm rupture | SAH, brain edema, brain ischemia | - | 10 | 95/45 | no | 0.263 |
| 10 | 42.3 | aneurysm rupture | SAH, brain edema | 1 | 15 | 143/78 | no | 0.213 |
| 11 ** | 55.2 | aneurysm rupture | SAH, ICH, brain edema | - | 13 | 120/77 | no | 0.258 |
| 12 | 70.6 | basilar artery rupture | SAH | - | 2 | 146/62 | no | 0.187 |
| 13 | 48.1 | spontaneous ICH | ICH, brain edema, brain ischemia | 1 | 18 | 123/56 | no | 0.298 |
| 17 | 79.8 | spontaneous ICH | ICH, brain edema | - | 3 | 164/85 | no | 0.253 |
| 19 | 34.8 | aneurysm rupture | SAH | 1 | 11 | 122/66 | no | 0.172 |
| 26 | 62.2 | ICH after ischemia | brain ischemia, ICH | - | 5 | 123/78 (LVAD) | no | 0.239 |
| Hypoxic (n = 7) | ||||||||
| 5 ** | 62.2 | cardiac arrest, CPR | brain edema | - | 7 | 106/77 (vaECMO) | no | 0.158 |
| 8 ** | 39.3 | cardiac arrest, CPR | brain edema, ischemia, SAH | - | 16 | 154/90 | no | 0.271 |
| 14 | 55.8 | cardiac arrest, CPR | SAH, brain edema | - | 8 | 138/75 | no | 0.295 |
| 16 | 58.4 | cardiac arrest, CPR | anoxic brain injury, brain edema | - | 4 | 101/64 (vaECMO) | no | 0.198 |
| 21 | 14.0 | smoke inhalation | brain edema | - | 1 | 115/63 | no | 0.203 |
| 23 | 1.8 | non-diphtheric croup, cardiac arrest, CPR | brain edema | - | 2 | 95/51 | no | 0.083 |
| 29 | 72.6 | cardiac arrest | brain edema | - | 3 | 121/75 (vaECMO) | no | 0.286 |
| Ischemic stroke (n = 5) | ||||||||
| 9 | 79.6 | brain ischemia | ischemia, brain edema | - | 5 | 188/80 | no | 0.234 |
| 15 | 62.0 | brain ischemia | ischemia, SAH | - | 2 | 110/70 | no | 0.328 |
| 18 | 71.3 | brain ischemia | ischemia, ICH | 0 | 14 | 148/68 | no | 0.205 |
| 20 | 64.8 | brain ischemia | ischemia | - | 4 | 135/85 | no | 0.222 |
| 22 | 69.0 | brain ischemia | ischemia, brain edema | - | 3 | 115/62 | no | 0.196 |
| Infectious (n = 2) | ||||||||
| 24 | 13.9 | encephalitis | brain edema | - | 11 | 124/84 | no | 0.326 |
| 25 | 13.1 | pneumococcal meningitis | brain edema | 1 | 7 | 118/75 | no | 0.165 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Günther, A.; Gunkel, A.; Geis, C.; Brämer, D.; Brauer, M.; Doerfel, C.; Fritzenwanger, M.; Freesmeyer, M.; Winkens, T.; Drescher, R.; et al. Brain Perfusion Scintigraphy in the Diagnostic Toolbox for the Confirmation of Brain Death: Practical Aspects and Examination Protocol. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2734. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15212734
Günther A, Gunkel A, Geis C, Brämer D, Brauer M, Doerfel C, Fritzenwanger M, Freesmeyer M, Winkens T, Drescher R, et al. Brain Perfusion Scintigraphy in the Diagnostic Toolbox for the Confirmation of Brain Death: Practical Aspects and Examination Protocol. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(21):2734. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15212734
Chicago/Turabian StyleGünther, Albrecht, Anne Gunkel, Christian Geis, Dirk Brämer, Martin Brauer, Claus Doerfel, Michael Fritzenwanger, Martin Freesmeyer, Thomas Winkens, Robert Drescher, and et al. 2025. "Brain Perfusion Scintigraphy in the Diagnostic Toolbox for the Confirmation of Brain Death: Practical Aspects and Examination Protocol" Diagnostics 15, no. 21: 2734. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15212734
APA StyleGünther, A., Gunkel, A., Geis, C., Brämer, D., Brauer, M., Doerfel, C., Fritzenwanger, M., Freesmeyer, M., Winkens, T., Drescher, R., & Werner, A. (2025). Brain Perfusion Scintigraphy in the Diagnostic Toolbox for the Confirmation of Brain Death: Practical Aspects and Examination Protocol. Diagnostics, 15(21), 2734. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15212734





