Phenotypes of Food Allergies in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis Aged Under 24 Months: A Multicenter Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data Acquisition and Patient Follow-Up
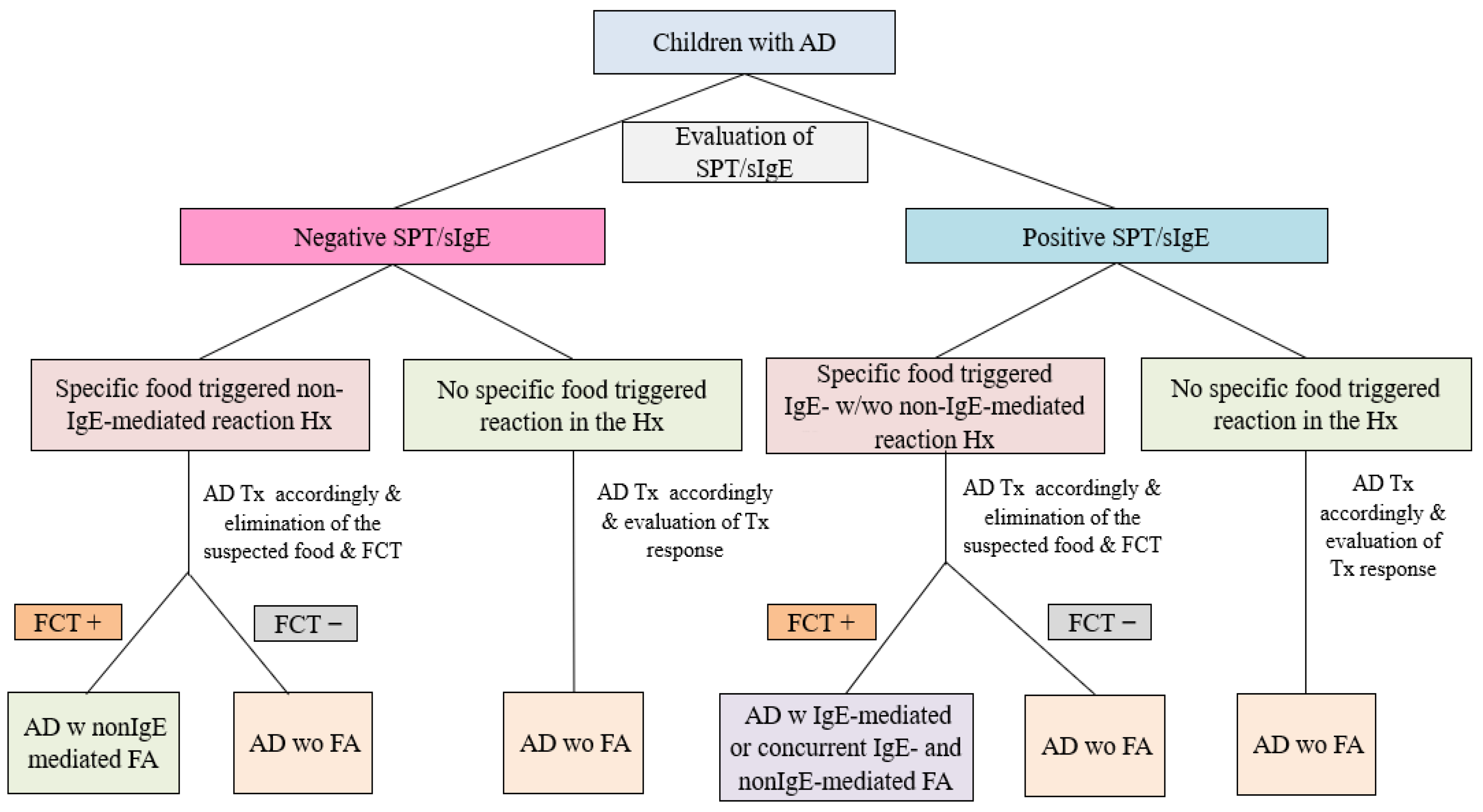
2.2. Classification of FA Phenotypes
- AD concomitant IgE-mediated FA
- AD concomitant non-IgE-mediated FA
- AD concomitant IgE- and non-IgE-mediated FA
- AD without FA
3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
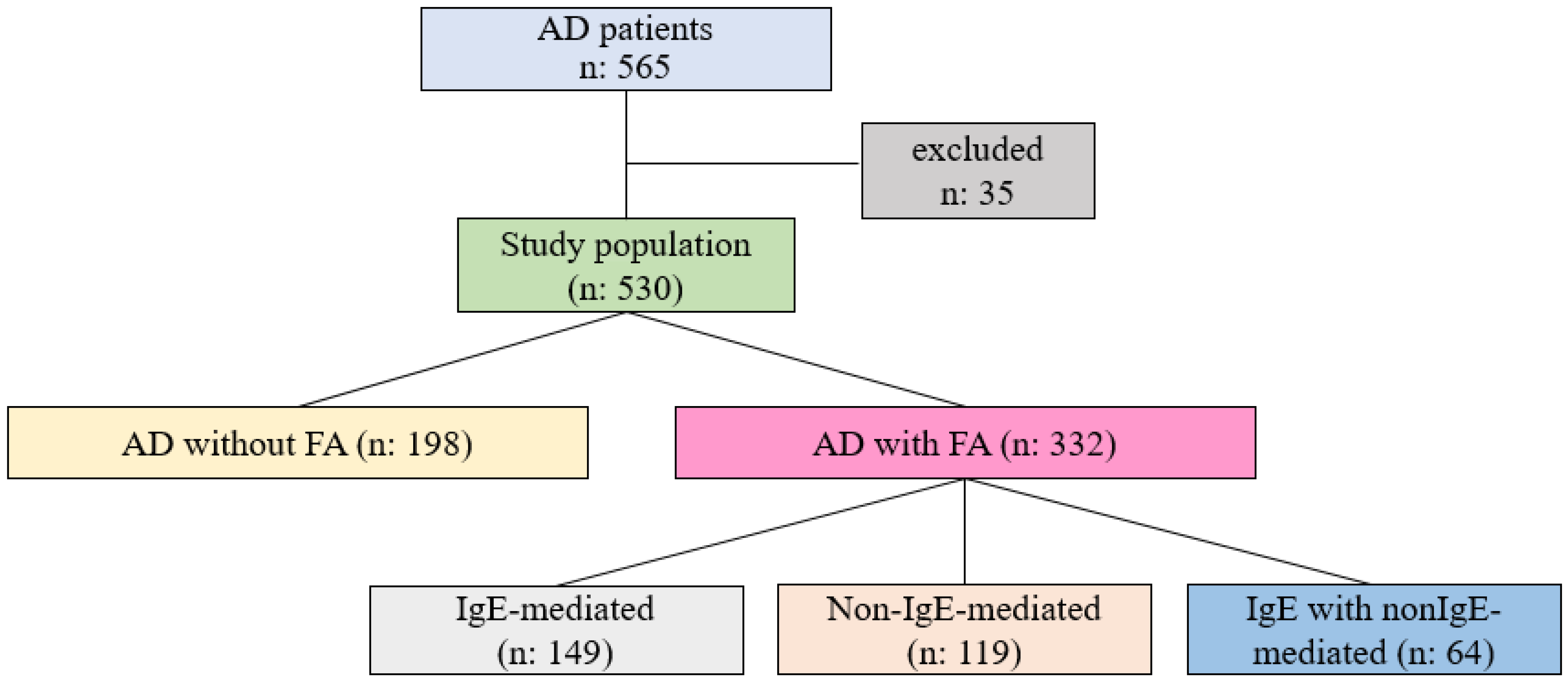
4.1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of AD Patients, with or Without FA
4.2. Clinical Characteristics of FA Phenotypes
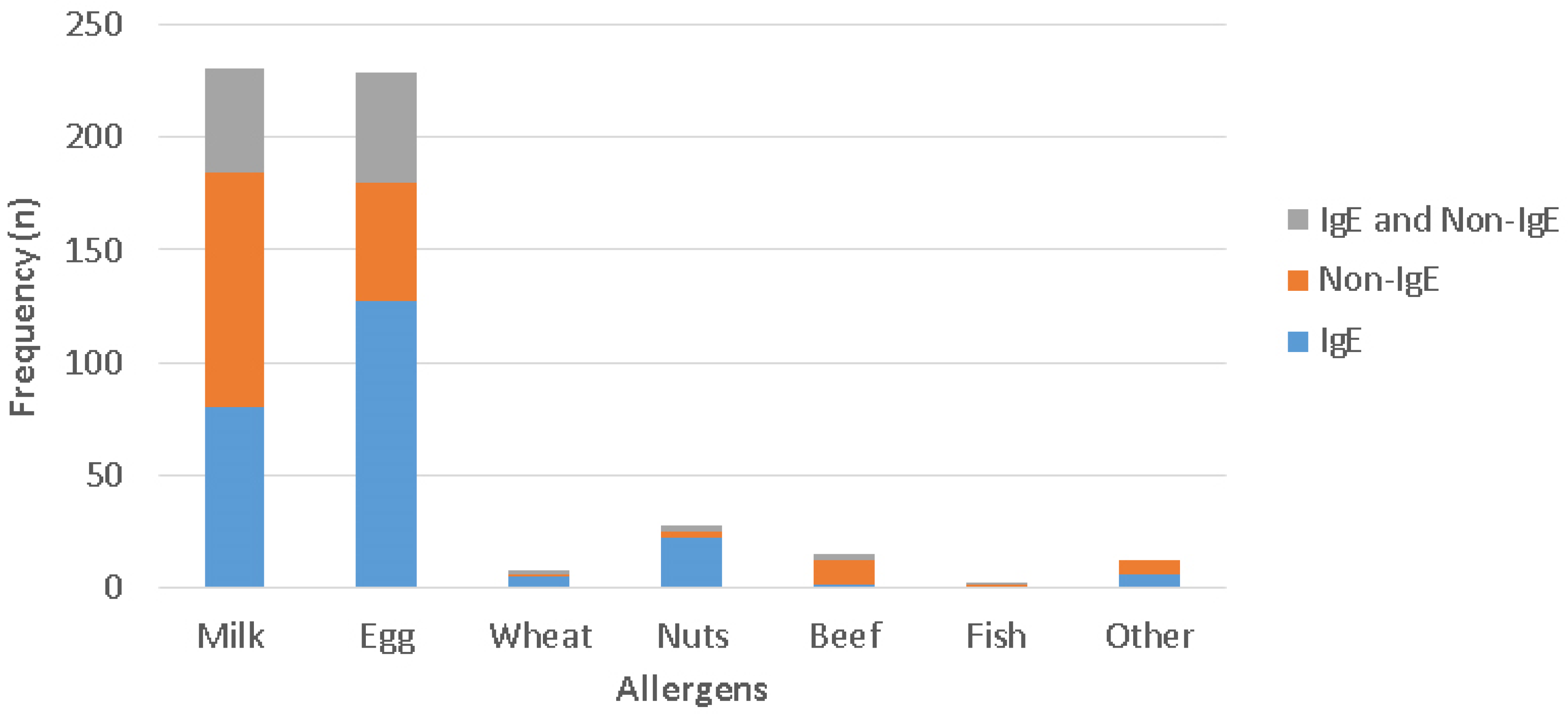
4.3. The Distribution of Triggering Foods for Different Phenotypes of FA
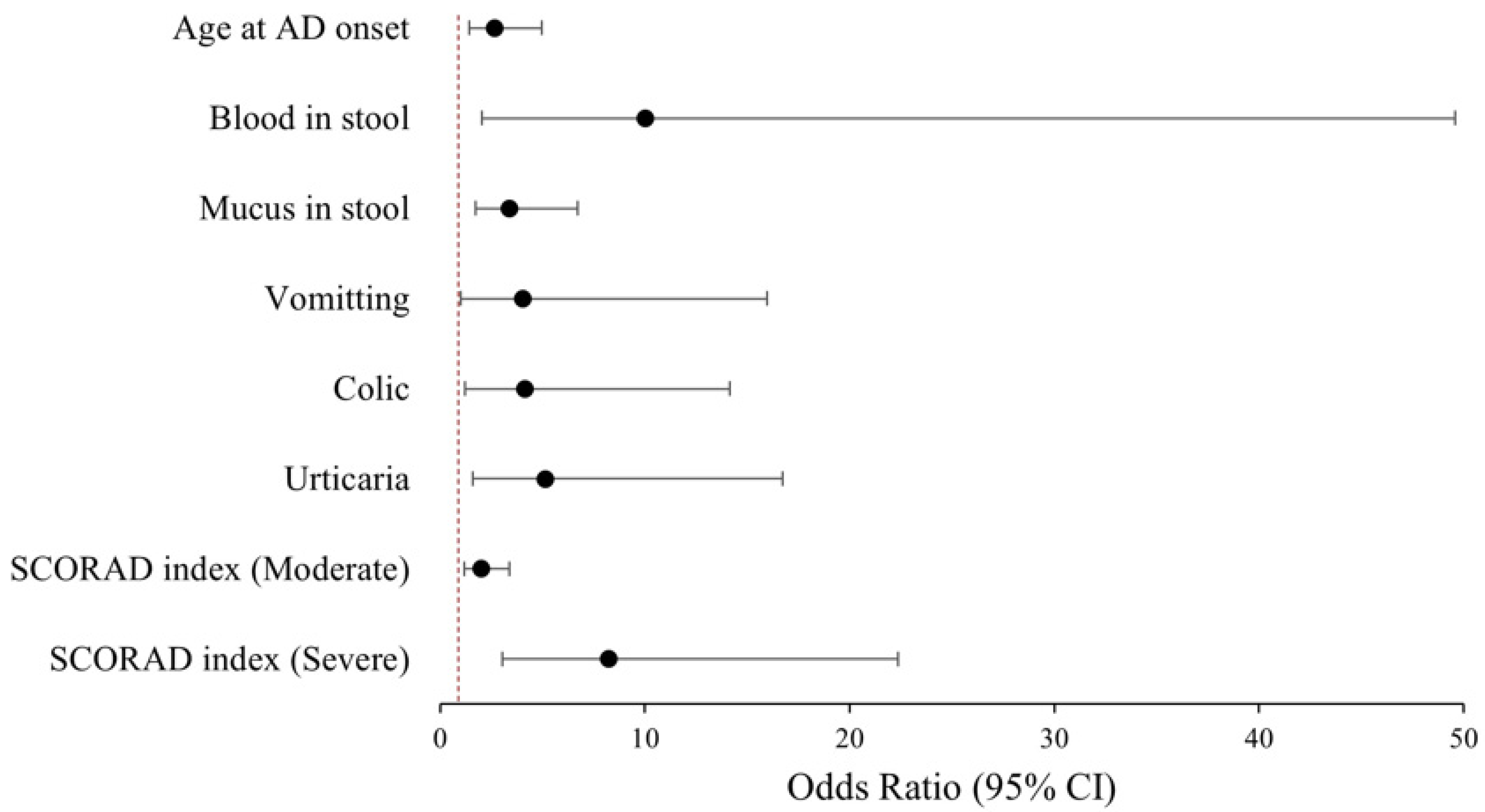
4.4. Clinic Predictors of FA Phenotypes
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Atopic Dermatitis |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| CM | Cow’s milk |
| CMA | Cow’s milk allergy |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| FA | Food Allergy |
| FCT | Food challenge test |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| ROC | The Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| SCORAD | Scoring of Atopic Dermatitis |
| SI | SCORAD Index |
| sIgE | Specific Immunoglobulin E |
| SPT | Skin prick test |
References
- Domínguez, O.; Plaza, A.M.; Alvaro, M. Relationship Between Atopic Dermatitis and Food Allergy. Curr. Pediatr. Rev. 2020, 16, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samady, W.; Warren, C.; Kohli, S.; Jain, R.; Bilaver, L.; Mancini, A.J.; Gupta, R. The prevalence of atopic dermatitis in children with food allergy. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019, 122, 647–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitarik, A.R.; Eapen, A.A.; Biagini, J.M.; Jackson, D.J.; Joseph, C.L.M.; Kim, H.; Martin, L.J.; Rivera-Spoljaric, K.; Schauberger, E.M.; Wegienka, G.; et al. Phenotypes of Atopic Dermatitis and Development of Allergic Diseases. JAMA Netw. Open 2025, 8, e2515094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tedner, S.G.; Asarnoj, A.; Thulin, H.; Westman, M.; Konradsen, J.R.; Nilsson, C. Food allergy and hypersensitivity reactions in children and adults—A review. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 291, 283–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AAAAI/ACAAI JTF Atopic Dermatitis Guideline Panel; Chu, D.K.; Schneider, L.; Asiniwasis, R.N.; Boguniewicz, M.; De Benedetto, A.; Ellison, K.; Frazier, W.T.; Greenhawt, M.; Huynh, J.; et al. Atopic dermatitis (eczema) guidelines: 2023 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology/American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology Joint Task Force on practice parameters GRADE– and Institute of Medicine–based recommendations. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2024, 132, 274–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venter, C.; Halken, S.; Toniolo, A.; Nowak-Wegrzyn, A.; Vlieg-Boerstra, B.; Nilsson, C.A.; Fleischer, D.M.; de Silva, D.; Barber, D.; Khaleva, E.; et al. Global Network of Centres of Excellence for Anaphylaxis & Food Allergy—ANAcare. Diagnosing IgE-mediated food allergy: How to apply the latest guidelines in clinical practice. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Glob. 2025, 4, 100556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, R.; Chebar Lozinsky, A.; Fleischer, D.M.; Vieira, M.C.; Du Toit, G.; Vandenplas, Y.; Dupont, C.; Knibb, R.; Uysal, P.; Cavkaytar, O.; et al. Diagnosis and management of Non-IgE gastrointestinal allergies in breastfed infants—An EAACI Position Paper. Allergy 2020, 75, 14–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langan, S.M.; Irvine, A.D.; Weidinger, S. Atopic dermatitis. Lancet 2020, 396, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak-Węgrzyn, A.; Katz, Y.; Mehr, S.S.; Koletzko, S. Non-IgE-mediated gastrointestinal food allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 1114–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugović-Mihić, L.; Meštrović-Štefekov, J.; Ferček, I.; Pondeljak, N.; Lazić-Mosler, E.; Gašić, A. Atopic Dermatitis Severity, Patient Perception of the Disease, and Personality Characteristics: How Are They Related to Quality of Life? Life 2021, 11, 1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansotegui, I.J.; Melioli, G.; Canonica, G.W.; Caraballo, L.; Villa, E.; Ebisawa, M.; Passalacqua, G.; Savi, E.; Ebo, D.; Gómez, R.M.; et al. IgE allergy diagnostics and other relevant tests in allergy, a World Allergy Organization position paper. World Allergy Organ. J. 2020, 13, 100080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.-Y.; Um, J.-Y.; Chung, B.-Y.; Lee, S.-Y.; Park, J.-S.; Kim, J.-C.; Park, C.-W.; Kim, H.-O. Moisturizer in Patients with Inflammatory Skin Diseases. Medicina 2022, 58, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, H.A.; Arasi, S.; Bahnson, H.T.; Ballmer-Webe, B.; Beyer, K.; Bindslev-Jensen, C.; Bird, J.A. AAAAI-EAACI PRACTALL: Standardizing oral food challenges—2024 Update. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2024, 35, e14276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrosse, R.; Graham, F.; Caubet, J.C. Non-IgE-Mediated Gastrointestinal Food Allergies in Children: An Update. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, C.L.; Levin, M.E.; Zar, H.J.; Potter, P.C.; Khumalo, N.P.; Volkwyn, L.; Fenemore, B.; du Toit, G. Food allergy in South African children with atopic dermatitis. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2014, 25, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailhol, C.; Giordano-Labadie, F.; Lauwers-Cances, V.; Ammoury, A.; Paul, C.; Rance, F. Point prevalence and risk factors for food allergy in a cohort of 386 children with atopic dermatitis attending a multidisciplinary dermatology/paediatric allergy clinic. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2014, 24, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flohr, C.; Perkin, M.; Logan, K.; Marrs, T.; Radulovic, S.; Campbell, L.E.; MacCallum, S.F.; McLean, W.I.; Lack, G. Atopic dermatitis and disease severity are the main risk factors for food sensitization in exclusively breastfed infants. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cansever, M.; Oruç, Ç. What plays a role in the severity of atopic dermatitis in children? Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 51, 2494–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Marín, H.A.; Singh, A.M.; Ong, P.Y.; Silverberg, J.I. Food allergy testing in atopic dermatitis. JAAD Int. 2022, 9, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, M.O.; Barakji, Y.A.; Loft, N.; Khatib, C.M.; Egeberg, A.; Thomsen, S.F.; Silverberg, J.I.; Flohr, C.; Maul, J.T.; Schmid-Grendelmeier, P.; et al. Prevalence of an association between atopic dermatitis and food sensitivity, food allergy and challenge-proven food allergy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2023, 37, 984–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, C.; Graham, F.; Fleischer, D.M.; Molloy, J.; Bégin, P.; Eigenmann, P. The Evolution of IgE-Based Allergy Testing in Atopic Dermatitis: Where Do We Stand? J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2025, 13, 1879–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muraro, A.; Werfel, T.; Hoffmann-Sommergruber, K.; Roberts, G.; Beyer, K.; Bindslev-Jensen, C.; Cardona, V.; Dubois, A.; duToit, G.; Eigenmann, P.; et al. EAACI Food Allergy and Anaphylaxis Guidelines Group EAACI food allergy and anaphylaxis guidelines: Diagnosis and management of food allergy. Allergy 2014, 69, 1008–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, M.; Leeds, S.; Nowak-Węgrzyn, A. Recent Update in Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Management. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2022, 14, 587–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uncuoğlu, A.; Aydoğan, M.; Şimşek, I.E.; Çöğürlü, M.T.; Uçak, K.; Acar, H.C. A Prospective Assessment of Clinical Characteristics and Responses to Dietary Elimination in Food Protein-Induced Allergic Proctocolitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2022, 10, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimen, S.S.; Guc, B.U.; Bulbul, L. Food sensitivity in children diagnosed with atopic dermatitis in the first 2 years: How many of these patients are truly allergic? Sisli Etfal Hast. Tip Bul. 2023, 57, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozanli, I.; Uluc, N.N.; Iskender, N.; Akin, T.Y.; Varli, Y.Z.; Balci, S.; Simsek, I.E.; Aydogan, M. Food allergy concurrent with atopic dermatitis: Correlation with age of onset and severity. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2025, 46, e137–e143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocanu, M.; Vâță, D.; Alexa, A.I.; Trandafir, L.; Patrașcu, A.I.; Hâncu, M.F.; Gheucă-Solovăstru, L. Atopic Dermatitis-Beyond the Skin. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepper, A.N. Atopic dermatitis and food allergy: To test or not to test. J. Food Allergy 2023, 5, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, P.E.; Eckert, J.K.; Koplin, J.J.; Lowe, A.J.; Gurrin, L.C.; Dharmage, S.C.; Vuillermin, P.; Tang, M.L.K.; Ponsonby, A.-L.; Matheson, M.; et al. HealthNuts Study Investigators. Which infants with eczema are at risk of food allergy? Results from a population-based cohort. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2015, 45, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverberg, J.; Simpson, E.L. Association between severe eczema in children and multiple comorbid conditions and increased healthcare utilization. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2013, 24, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| AD Without FA (n = 198) | AD with FA (n = 332) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (months) † | 7.5 (5.5–12.5) | 7 (5–10.8) | 0.008 * |
| Age at AD onset (months) † | 3 (2–6) | 2 (1–3.5) | <0.001 * |
| Sex (male), n (%) | 119 (60.1) | 196 (59) | 0.809 ** |
| SCORAD index † | 21.9 (15.5–31.1) | 31.3 (20.6–45) | <0.001 * |
| AD severity (n, %) | <0.001 ** | ||
| Mild | 116 (58.6) | 114 (34.3) | |
| Moderate | 75 (37.9) | 161 (48.5) | |
| Severe | 7 (3.5) | 57 (17.2) | |
| Parental history of AD, n (%) | 24 (12.1) | 54 (16.3) | 0.193 ** |
| AD Without FA (n = 198) | AD Concomitant IgE-Mediated (n = 149) | AD Concomitant Non-IgE-Mediated (n = 119) | AD Concomitant IgE with Non-IgE-Mediated (n = 64) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (months) † | 7.5 (5.5–12.5) | 7.5 (5.5–11.3) | 5.5 (4.5–8.5) | 6.5 (4.5–10.8) | <0.001 ‡ |
| Age at onset of AD (months) † | 3 (2–6) | 2 (1–4) | 2 (1–3) | 2 (1–3) | <0.001 § |
| Age at onset of AD ≤ 4 months, n (%) | 131 (66.2) | 126 (84.6) | 105 (88.2) | 61 (95.3) | <0.001 ¶ |
| Sex (male), n (%) | 119 (60.1) | 94 (63.1) | 61 (51.3) | 41 (64.1) | 0.193 ¶ |
| SCORAD index † | 21.8 (15.5–31.1) | 32.4 (21.2–48.5) | 26.9 (18.6–35.2) | 35.6 (28–49.8) | <0.001 * |
| AD severity, n (%) | <0.001 ¶ | ||||
| Mild | 116 (58.6) | 52 (34.9) | 50 (42.1) | 12 (18.8) | |
| Moderate | 75 (37.9) | 66 (44.3) | 58 (48.7) | 37 (57.8) | |
| Severe | 7 (3.5) | 31 (20.8) | 11 (9.2) | 15 (23.4) | |
| Feeding types at diagnosis, n (%) | |||||
| Breastfeeding | 140 (71.8) | 132 (90.4) | 106 (91.4) | 59 (95.2) | <0.001 ¶ |
| Formula feeding | 36 (18.6) | 22 (15.1) | 37 (31.9) | 17 (27.4) | 0.004 ¶ |
| Complementary feeding | 59 (30.3) | 35 (24.1) | 15 (12.9) | 5 (8.1) | <0.001 ¶ |
| Other FA related symptoms in the history, n (%) | |||||
| Blood in stool | 2 (1) | 2 (1.3) | 37 (31.1) | 17 (26.6) | <0.001 ¶ |
| Mucus in stool | 21 (10.6) | 26 (17.4) | 76 (63.9) | 30 (46.9) | <0.001 ¶ |
| Vomiting | 3 (1.5) | 12 (8.1) | 24 (20.2) | 12 (18.8) | <0.001 ¶ |
| Colic | 4 (2) | 13 (8.7) | 37 (31.1) | 14 (21.9) | <0.001 ¶ |
| Urticaria | 5 (2.5) | 26 (17.4) | 2 (1.7) | 9 (14.1) | <0.001 ¶ |
| Angioedema | 0 | 3 (2) | 0 | 2 (3.1) | 0.019 ** |
| Anaphylaxis | 0 | 5 (3.4) | 0 | 0 | 0.05 ** |
| OR | 95% CI | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age at AD onset (≤4 months) | 2.67 | 1.43–4.98 | 0.002 |
| Blood in stool | 10.04 | 2.03–49.59 | 0.005 |
| Mucus in stool | 3.39 | 1.72–6.71 | <0.001 |
| Vomitting | 4.02 | 1.01–15.98 | 0.048 |
| Colic | 4.14 | 1.21–14.15 | 0.024 |
| Urticaria | 5.14 | 1.58–16.72 | 0.007 |
| SCORAD index (referring mild AD) | |||
| Moderate | 2.01 | 1.19–3.39 | 0.009 |
| Severe | 8.25 | 3.04–22.39 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cogurlu, M.T.; Aydogan, M.; Cavkaytar, O.; Uysal, P.; Culpan, H.C.; Yakici, N.; Demirkale, Z.H.; Topal, E.; Yuksel, H.; Aydemir, S.; et al. Phenotypes of Food Allergies in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis Aged Under 24 Months: A Multicenter Study. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2656. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15202656
Cogurlu MT, Aydogan M, Cavkaytar O, Uysal P, Culpan HC, Yakici N, Demirkale ZH, Topal E, Yuksel H, Aydemir S, et al. Phenotypes of Food Allergies in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis Aged Under 24 Months: A Multicenter Study. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(20):2656. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15202656
Chicago/Turabian StyleCogurlu, Mujde Tuba, Metin Aydogan, Ozlem Cavkaytar, Pinar Uysal, Hazal Cansu Culpan, Nalan Yakici, Zeynep Hizli Demirkale, Erdem Topal, Hasan Yuksel, Sezin Aydemir, and et al. 2025. "Phenotypes of Food Allergies in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis Aged Under 24 Months: A Multicenter Study" Diagnostics 15, no. 20: 2656. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15202656
APA StyleCogurlu, M. T., Aydogan, M., Cavkaytar, O., Uysal, P., Culpan, H. C., Yakici, N., Demirkale, Z. H., Topal, E., Yuksel, H., Aydemir, S., Cigerci Gunaydin, N., Aydogmus, C., Cekic, S., Akkelle, E., Tuncel, T., Eser Simsek, I., Arga, M., Altinel, Z. Ü., Kaplan, F., ... Orhan, F. (2025). Phenotypes of Food Allergies in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis Aged Under 24 Months: A Multicenter Study. Diagnostics, 15(20), 2656. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15202656







