Impact of AI Assistance in Pneumothorax Detection on Chest Radiographs Among Readers of Varying Experience
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
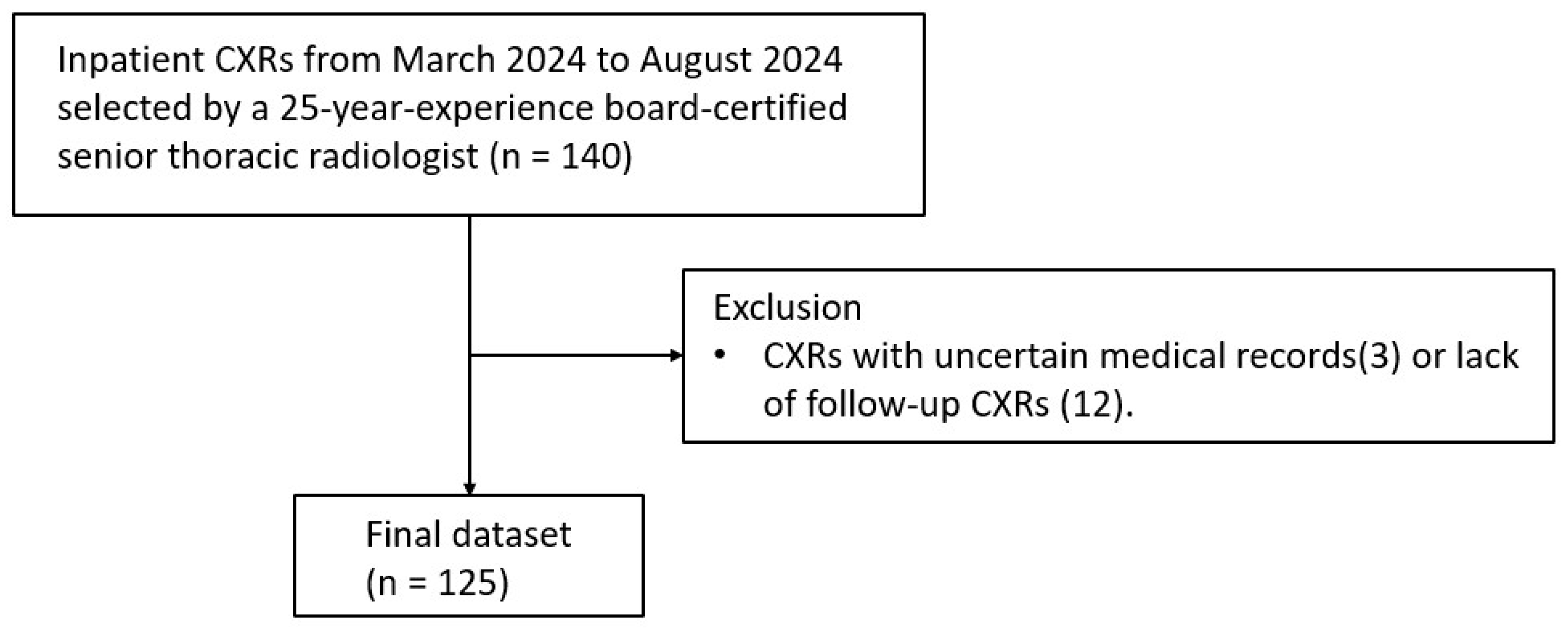
2.1. Image Dataset
2.2. AI Software
2.3. Readers
2.4. Scoring
2.5. Reference Standard
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Data Characteristics
3.2. Performance of AI Alone and Compared with Unassisted Readers
3.3. Readers’ Performance Without AI Assistance
3.4. Readers’ Performance with AI Assistance
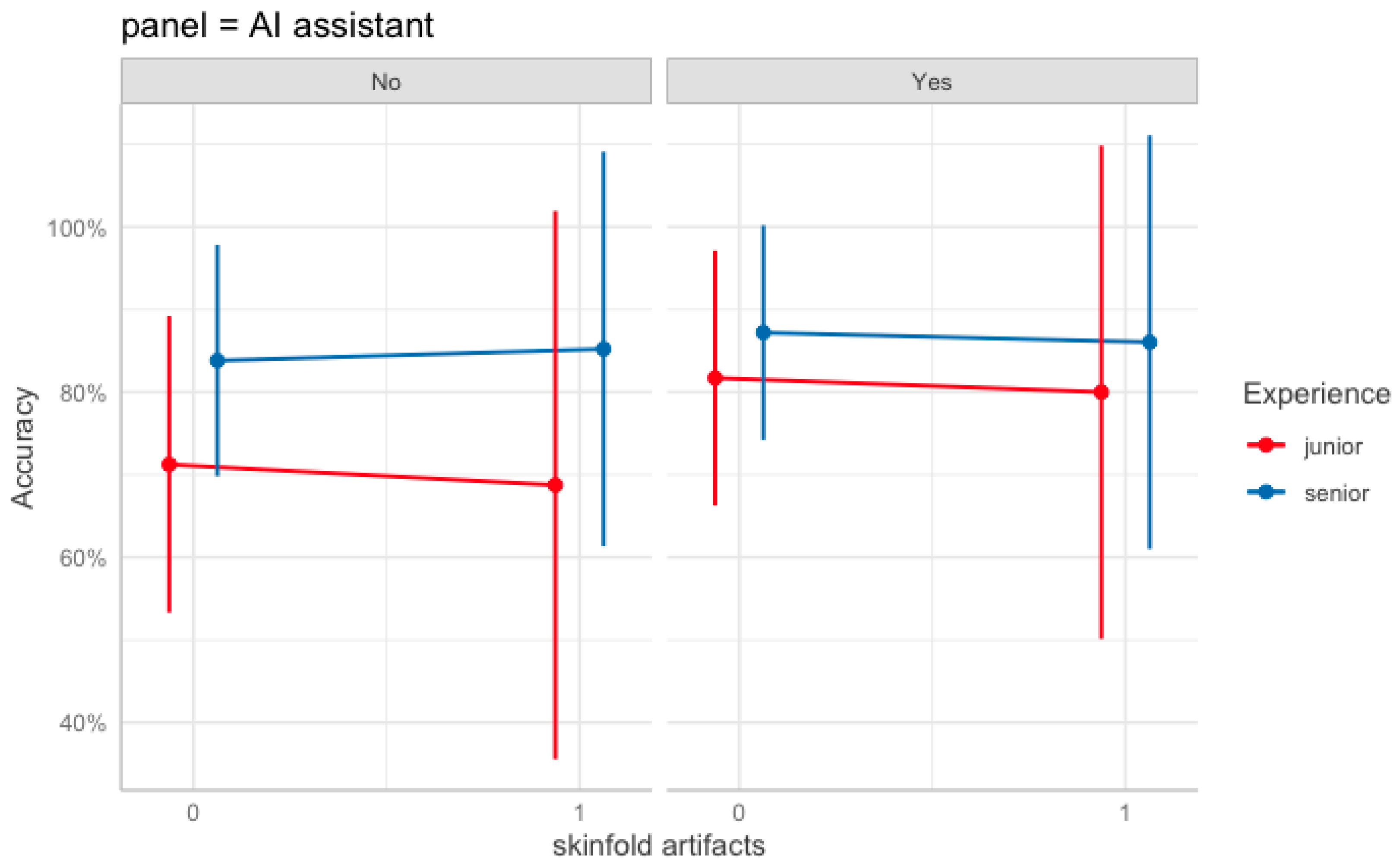
3.5. GEE Model of Pneumothorax Diagnostic Accuracy of Readers
3.5.1. Main Effects
3.5.2. Two-Way Interactions
3.5.3. Higher-Order Interactions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AUC | Area Under Curve |
| CXR | Chest Radiograph |
| FNR | False Negative Rate |
| FPR | False Positive Rate |
| PGY | Postgraduate Year Residents |
| PTX | Pneumothorax |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve |
| SF | Skin fold |
References
- Gefter, W.B.; Post, B.A.; Hatabu, H. Commonly Missed Findings on Chest Radiographs: Causes and Consequences. Chest 2023, 163, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaviani, P.; Kalra, M.K.; Digumarthy, S.R.; Gupta, R.V.; Dasegowda, G.; Jagirdar, A.; Gupta, S.; Putha, P.; Mahajan, V.; Reddy, B.; et al. Frequency of Missed Findings on Chest Radiographs (CXRs) in an International, Multicenter Study: Application of AI to Reduce Missed Findings. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, C.Y.; Lin, C.Y.; Chao, C.C.; Huang, H.S.; Lee, H.Y.; Chang, C.M.; Sung, K.; Chen, T.R.; Chiang, P.C.; Huang, L.T.; et al. Automated Radiology Alert System for Pneumothorax Detection on Chest Radiographs Improves Efficiency and Diagnostic Performance. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.G.; Mielke, C.; Mongan, J. Automated detection of moderate and large pneumothorax on frontal chest X-rays using deep convolutional neural networks: A retrospective study. PLoS Med. 2018, 15, e1002697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind Plesner, L.; Muller, F.C.; Brejnebol, M.W.; Laustrup, L.C.; Rasmussen, F.; Nielsen, O.W.; Boesen, M.; Brun Andersen, M. Commercially Available Chest Radiograph AI Tools for Detecting Airspace Disease, Pneumothorax, and Pleural Effusion. Radiology 2023, 308, e231236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mones Alamri, A. Artificial Intelligence in Radiology: Current Applications and Future Prospects. Kurd. Stud. 2021, 9, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, E.K.; Han, K.; Ryu, L.; Lee, E.H.; Shin, H.J. Factors for increasing positive predictive value of pneumothorax detection on chest radiographs using artificial intelligence. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 19624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueckel, J.; Trappmann, L.; Schachtner, B.; Wesp, P.; Hoppe, B.F.; Fink, N.; Ricke, J.; Dinkel, J.; Ingrisch, M.; Sabel, B.O. Impact of Confounding Thoracic Tubes and Pleural Dehiscence Extent on Artificial Intelligence Pneumothorax Detection in Chest Radiographs. Investig. Radiol. 2020, 55, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.N.; Kim, E.Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, G.P.; Kim, H.; Oh, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Han, J.H.; Cho, Y.J. Diagnostic effect of artificial intelligence solution for referable thoracic abnormalities on chest radiography: A multicenter respiratory outpatient diagnostic cohort study. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 3469–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, J.G.; Bera, K.; Shah, N.; Bukhari, S.M.A.; Marshall, C.; Caovan, D.; Rosipko, B.; Gupta, A. Real-World Performance of Pneumothorax-Detecting Artificial Intelligence Algorithm and its Impact on Radiologist Reporting Times. Acad. Radiol. 2024, 32, P1165–P1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennani, S.; Regnard, N.E.; Ventre, J.; Lassalle, L.; Nguyen, T.; Ducarouge, A.; Dargent, L.; Guillo, E.; Gouhier, E.; Zaimi, S.H.; et al. Using AI to Improve Radiologist Performance in Detection of Abnormalities on Chest Radiographs. Radiology 2023, 309, e230860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, A.; Ather, S.; Gill, A.; Aylward, P.; Maskell, G.; Cowell, G.W.; Espinosa Morgado, A.T.; Duggan, T.; Keevill, M.; Gamble, O.; et al. Evaluation of the impact of artificial intelligence-assisted image interpretation on the diagnostic performance of clinicians in identifying pneumothoraces on plain chest X-ray: A multi-case multi-reader study. Emerg. Med. J. 2024, 41, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDuff, A.; Arnold, A.; Harvey, J. Management of spontaneous pneumothorax: British Thoracic Society Pleural Disease Guideline 2010. Thorax 2010, 65 (Suppl. 2), ii18–ii31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, J.G.; Kim, M.; Park, J.; Hwang, E.J.; Lee, J.H.; Hong, J.H.; Goo, J.M.; Park, C.M. Development and validation of a deep learning algorithm detecting 10 common abnormalities on chest radiographs. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 57, 2003061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, S.; Song, H.; Shin, Y.J.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Lee, K.W.; Lee, S.S.; Lee, W.; Lee, S.; Lee, K.H. Deep Learning-based Automatic Detection Algorithm for Reducing Overlooked Lung Cancers on Chest Radiographs. Radiology 2020, 296, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chassagnon, G.; Soyer, P. Artificial Intelligence for the Detection of Pneumothorax on Chest Radiograph: Not yet the Panacea. Can. Assoc. Radiol. J. 2024, 75, 458–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillis, J.M.; Bizzo, B.C.; Mercaldo, S.; Chin, J.K.; Newbury-Chaet, I.; Digumarthy, S.R.; Gilman, M.D.; Muse, V.V.; Bottrell, G.; Seah, J.C.Y.; et al. Evaluation of an Artificial Intelligence Model for Detection of Pneumothorax and Tension Pneumothorax in Chest Radiographs. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2247172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugibayashi, T.; Walston, S.L.; Matsumoto, T.; Mitsuyama, Y.; Miki, Y.; Ueda, D. Deep learning for pneumothorax diagnosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2023, 32, 220259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thian, Y.L.; Ng, D.; Hallinan, J.; Jagmohan, P.; Sia, S.Y.; Tan, C.H.; Ting, Y.H.; Kei, P.L.; Pulickal, G.G.; Tiong, V.T.Y.; et al. Deep Learning Systems for Pneumothorax Detection on Chest Radiographs: A Multicenter External Validation Study. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2021, 3, e200190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, T.; Shaukat, A.; Akram, M.U.; Mustansar, Z.; Khan, A. Automatic Diagnosis of Pneumothorax from Chest Radiographs: A Systematic Literature Review. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 145817–145839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzman, B.D.; Alabousi, M.; Islam, N.; Zha, N.; Patlas, M.N. Deep Learning for Pneumothorax Detection on Chest Radiograph: A Diagnostic Test Accuracy Systematic Review and Meta Analysis. Can. Assoc. Radiol. J. 2024, 75, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.S.; Ebrahimian, S.; McDermott, S.; Lee, S.; Naccarato, L.; Di Capua, J.F.; Wu, M.Y.; Zhang, E.W.; Muse, V.; Miller, B.; et al. Association of Artificial Intelligence-Aided Chest Radiograph Interpretation with Reader Performance and Efficiency. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2229289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Beek, E.J.R.; Ahn, J.S.; Kim, M.J.; Murchison, J.T. Validation study of machine-learning chest radiograph software in primary and emergency medicine. Clin. Radiol. 2023, 78, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brealey, S.; Scally, A.; Hahn, S.; Thomas, N.; Godfrey, C.; Coomarasamy, A. Accuracy of radiographer plain radiograph reporting in clinical practice: A meta-analysis. Clin. Radiol. 2005, 60, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, T.; Harianto, H.; Spanger, M.; Young, A.; Wadhwa, V. Low accuracy and confidence in chest radiograph interpretation amongst junior doctors and medical students. Intern. Med. J. 2018, 48, 864–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisen, L.A.; Berger, J.S.; Hegde, A.; Schneider, R.F. Competency in chest radiography. A comparison of medical students, residents, and fellows. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2006, 21, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woznitza, N.; Ghimire, B.; Devaraj, A.; Janes, S.M.; Piper, K.; Rowe, S.; Bhowmik, A.; Hayes, N.; Togher, D.; Arumalla, N.; et al. Impact of radiographer immediate reporting of X-rays of the chest from general practice on the lung cancer pathway (radioX): A randomised controlled trial. Thorax 2023, 78, 890–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woznitza, N.; Piper, K.; Rowe, S.; Bhowmik, A. Immediate reporting of chest X-rays referred from general practice by reporting radiographers: A single centre feasibility study. Clin. Radiol. 2018, 73, 507.e1–507.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaf, A.; Alshammari, M.; Zayed, H.; Emnawer, M.; Esfahani, A. Exploring Radiographers’ Readiness for Artificial Intelligence in Kuwait: Insights and Applications. Health Sci. Rep. 2025, 8, e70465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Inpatient CXRs (n = 125, 125 CXRs from 125 Patients) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean age ± standard deviation | 66.36 ± 19.2 | ||
| Gender | |||
| Male | 88 (70.4%) | ||
| Female | 37 (29.6%) | ||
| Pneumothorax | |||
| Absent | 73 (58.4%) | ||
| Present | 52 (41.6%) | ||
| Small (<2 cm) | 30 (57.7%) | ||
| Large (≥2 cm) | 22 (42.3%) | ||
| Projection type | |||
| Upright PA | 48 (38.4%) | ||
| Upright AP | 16 (12.8%) | ||
| Supine AP | 61 (48.8%) | ||
| Skinfold artifacts | |||
| Present | 56 (44.8%) | ||
| No pneumothorax | 38 (67.9%) | ||
| Small pneumothorax | 12 (21.4%) | ||
| Large pneumothorax | 6 (10.7%) | ||
| Absent | 69 (55.2%) |
| (a) | |||||||
| AI | Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 | Group 4 | Group 5 | Group 6 | |
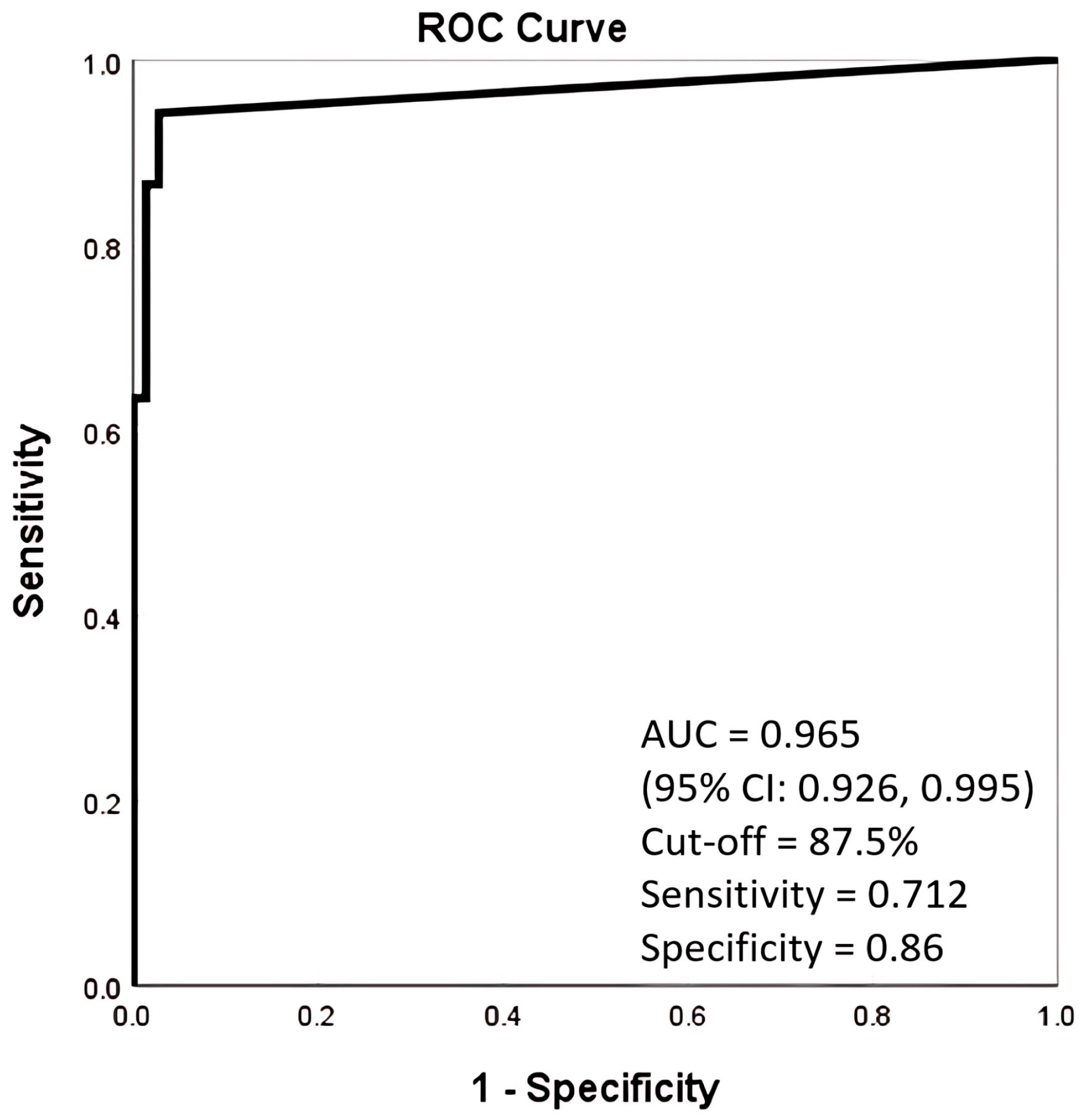
| AUC | 0.965 | 0.907 | 0.85 | 0.776 | 0.713 | 0.84 | 0.606 |
| p value | |||||||
| Group 1 | 0.14 | ||||||
| Group 2 | <0.01 | 0.14 | |||||
| Group 3 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.11 | ||||
| Group 4 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.15 | |||
| Group 5 | <0.01 | 0.09 | 0.71 | 0.15 | <0.01 | ||
| Group 6 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.04 | <0.01 | |
| (b) | |||||||
| Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 | Group 4 | Group 5 | Group 6 | ||
| AUC | 0.933 | 0.889 | 0.864 | 0.832 | 0.879 | 0.837 | |
| p value | |||||||
| Group 1 | |||||||
| Group 2 | 0.49 | ||||||
| Group 3 | 0.07 | >0.99 | |||||
| Group 4 | <0.01 | 0.40 | >0.99 | ||||
| Group 5 | 0.22 | >0.99 | >0.99 | 0.76 | |||
| Group 6 | <0.01 | 0.49 | >0.99 | >0.99 | 0.94 | ||
| Estimate | SE | Wald | Sig. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 0.65 | 0.12 | 30.0 | *** |
| AI assistance (Yes) | 0.76 | 0.14 | 31.2 | *** |
| Senior group | 0.94 | 0.13 | 49.5 | *** |
| No pneumothorax | 1.56 | 0.13 | 147.2 | *** |
| Small pneumothorax | −1.16 | 0.11 | 116.1 | *** |
| Skinfold artifacts | −0.16 | 0.19 | 0.7 | |
| Projection type: AP | 0.11 | 0.16 | 0.4 | |
| Projection type: portable | −0.33 | 0.10 | 9.9 | ** |
| AI assistance × Senior group | −0.43 | 0.2 | 4.7 | * |
| AI assistance × SF | 0.02 | 0.27 | 0.0 | |
| Senior group × SF | 0.29 | 0.27 | 1.2 | |
| AI assistance × Senior group × Skinfold artifacts | −0.27 | 0.40 | 0.4 |
| Seniority | AI Aid | Diagnosis Outcome | SF (−) | SF (+) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Senior | Yes | True negative | 27% | 30% |
| False negative | 7% | 4% | ||
| True positive | 20% | 10% | ||
| False positive | 1% | 1% | ||
| No | True negative | 27% | 30% | |
| False negative | 9% | 5% | ||
| True positive | 18% | 9% | ||
| False positive | 1% | 1% | ||
| Junior | Yes | True negative | 26% | 28% |
| False negative | 10% | 5% | ||
| True positive | 18% | 10% | ||
| False positive | 2% | 2% | ||
| No | True negative | 25% | 26% | |
| False negative | 15% | 7% | ||
| True positive | 13% | 8% | ||
| False positive | 3% | 5% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ho, C.-W.; Wu, Y.-L.; Chen, Y.-C.; Ju, Y.-J.; Wu, M.-T. Impact of AI Assistance in Pneumothorax Detection on Chest Radiographs Among Readers of Varying Experience. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2639. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15202639
Ho C-W, Wu Y-L, Chen Y-C, Ju Y-J, Wu M-T. Impact of AI Assistance in Pneumothorax Detection on Chest Radiographs Among Readers of Varying Experience. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(20):2639. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15202639
Chicago/Turabian StyleHo, Chen-Wei, Yu-Lun Wu, Yi-Chun Chen, Yu-Jeng Ju, and Ming-Ting Wu. 2025. "Impact of AI Assistance in Pneumothorax Detection on Chest Radiographs Among Readers of Varying Experience" Diagnostics 15, no. 20: 2639. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15202639
APA StyleHo, C.-W., Wu, Y.-L., Chen, Y.-C., Ju, Y.-J., & Wu, M.-T. (2025). Impact of AI Assistance in Pneumothorax Detection on Chest Radiographs Among Readers of Varying Experience. Diagnostics, 15(20), 2639. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15202639






