A Pilot Study of Exploring miRNA–Protein Interaction Networks in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Patients: Implications for Diagnosis and Prognosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collecting
2.2. Isolation of miRNA
2.3. Quantitative Analysis of miRNA Expression
2.4. In Silico Prediction and Network-Based Functional Analysis of miRNA Target Genes
2.5. Determination of Target Protein Levels by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics and Clinicopathological Characteristics
3.2. Expression Analyses of Selected miRNAs
3.2.1. Biomarker Potentials of Selected miRNAs and Their Combinations
3.2.2. Correlation of Selected miRNA Expression Levels with Clinical Parameters
3.3. In Silico Functional Analysis of miRNA Target Genes
3.4. Quantitative Analysis of Targeted Protein Expression Levels
3.4.1. Biomarker Potentials of Target Proteins and Their Combinations
3.4.2. Correlation of Targeted Protein Levels with Clinical Parameters
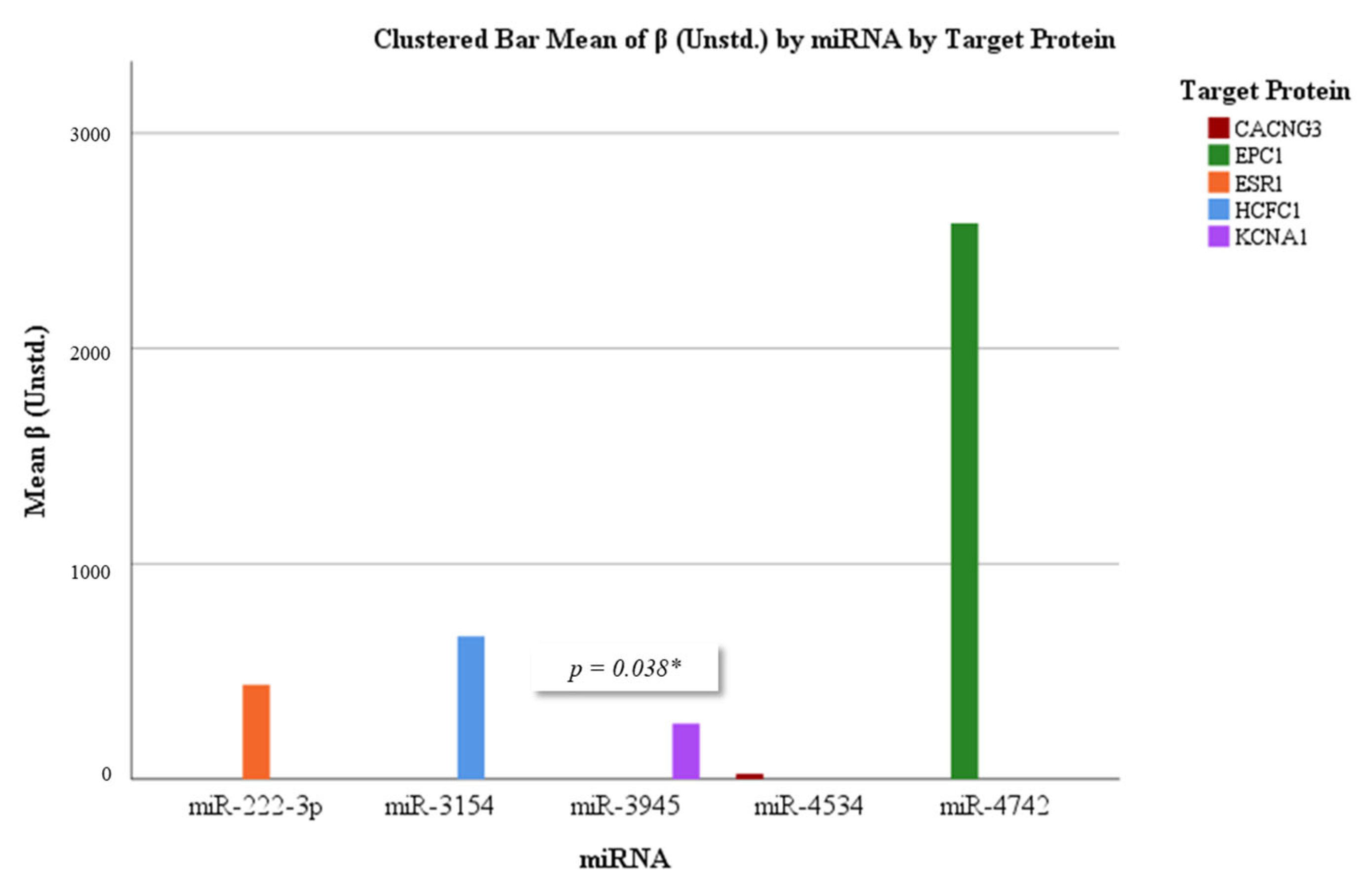
3.5. Correlation and Regression Analyses
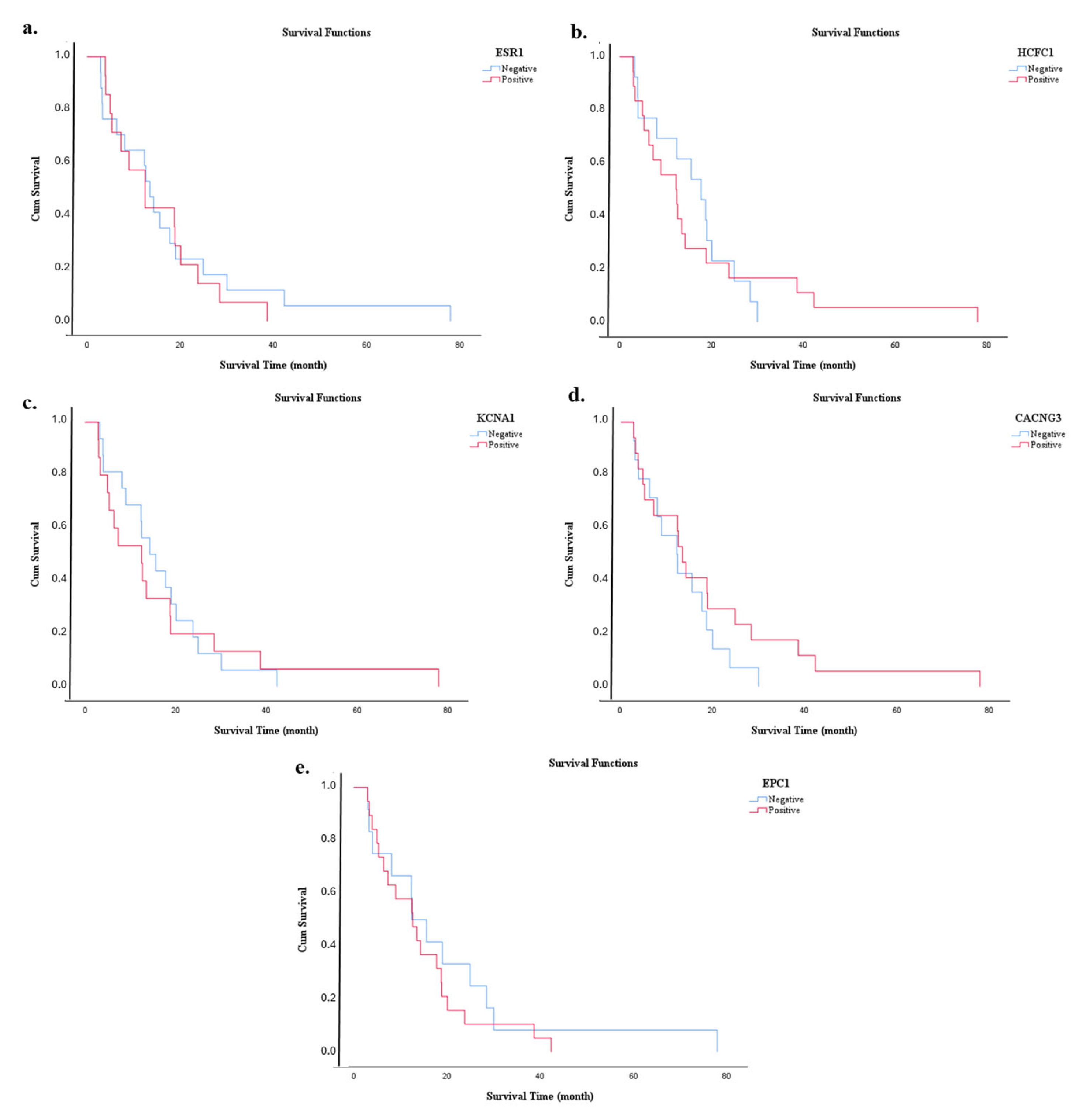
3.6. Survival Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haeberle, L.; Esposito, I. Pathology of pancreatic cancer. Transl. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 4, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neureiter, D.; Jager, T.; Ocker, M.; Kiesslich, T. Epigenetics and pancreatic cancer: Pathophysiology and novel treatment aspects. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 7830–7848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakaran, R.; Thamarai, R.; Sivasamy, S.; Dhandayuthapani, S.; Batra, J.; Kamaraj, C.; Karthik, K.; Shah, M.A.; Mallik, S. Epigenetic frontiers: miRNAs, long non-coding RNAs and nanomaterials are pioneering to cancer therapy. Epigenetics Chromatin 2024, 17, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capasso, M.; Franceschi, M.; Rodriguez-Castro, K.I.; Crafa, P.; Cambie, G.; Miraglia, C.; Barchi, A.; Nouvenne, A.; Leandro, G.; Meschi, T.; et al. Epidemiology and risk factors of pancreatic cancer. Acta Biomed. 2018, 89, 141–146. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, X. The roles of microRNAs in epigenetic regulation. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2019, 51, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volinia, S.; Calin, G.A.; Liu, C.G.; Ambs, S.; Cimmino, A.; Petrocca, F.; Visone, R.; Iorio, M.; Roldo, C.; Ferracin, M.; et al. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 2257–2261. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rawat, M.; Kadian, K.; Gupta, Y.; Kumar, A.; Chain, P.S.G.; Kovbasnjuk, O.; Kumar, S.; Parasher, G. MicroRNA in Pancreatic Cancer: From Biology to Therapeutic Potential. Genes 2019, 10, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolarz, B.; Durczynski, A.; Romanowicz, H.; Hogendorf, P. The Role of microRNA in Pancreatic Cancer. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, E.T.Y.; Chitty, J.L.; Cox, T.R. miRNAs in pancreatic cancer progression and metastasis. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2024, 41, 163–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madadjim, R.; An, T.; Cui, J. MicroRNAs in Pancreatic Cancer: Advances in Biomarker Discovery and Therapeutic Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortunato, O.; Gasparini, P.; Boeri, M.; Sozzi, G. Exo-miRNAs as a New Tool for Liquid Biopsy in Lung Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarantis, P.; Koustas, E.; Papadimitropoulou, A.; Papavassiliou, A.G.; Karamouzis, M.V. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: Treatment hurdles, tumor microenvironment and immunotherapy. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2020, 12, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, F.; Allen-Coyle, T.J.; Roche, S.; Meiller, J.; Conlon, N.T.; Swan, N.; Straubinger, R.M.; Geoghegan, J.; Straubinger, N.L.; Conlon, K.; et al. Alteration in Levels of Specific miRNAs and Their Potential Protein Targets between Human Pancreatic Cancer Samples, Adjacent Normal Tissue, and Xenografts Derived from These Tumors. Life 2023, 13, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helsinki WDo. WMA Declaration of Helsinki—Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Participants. 2024. Available online: https://www.wma.net/policies-post/wma-declaration-of-helsinki/ (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, X. miRDB: An online database for prediction of functional microRNA targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D127–D131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groot, V.P.; Rezaee, N.; Wu, W.; Cameron, J.L.; Fishman, E.K.; Hruban, R.H.; Weiss, M.J.; Zheng, L.; Wolfgang, C.L.; He, J. Patterns, Timing, and Predictors of Recurrence Following Pancreatectomy for Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Ann. Surg. 2018, 267, 936–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.M.; Thomassian, S.; Gong, J.; Hendifar, A.; Osipov, A. Advances in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Treatment. Cancers 2021, 13, 5510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, X.Q.; Wang, Z.F.; Wu, X.L.; Zhou, C.H.; Yan, J.Y.; Hu, B.Y.; et al. The molecular biology of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: Translational challenges and clinical perspectives. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitorino, R. Transforming Clinical Research: The Power of High-Throughput Omics Integration. Proteomes 2024, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, A.; Chen, Y.; Qiao, S.; Dong, J.; Li, Y.; Cao, B.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, R. Analysis of microRNAs and the microRNA-messengerRNA regulatory network in chronic alcohol exposure. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1377501. [Google Scholar]
- Tiraboschi, R.B.; Neto, F.S.L.; da Cunha Tirapelli, D.P.; de Bessa, J., Jr.; Miranda, E.P.; de Assis Cirino, M.L.; Tirapelli, L.F.; Tucci, S., Jr.; Molina, C.A.F. Expression of MicroRNAs (miR-15b, miR-16, miR-138, miR-221, and miR-222) as Biomarkers of Endothelial Corpus Cavernosum Dysfunction in a Diabetic Alcoholic Murine Model. Sex. Med. 2021, 9, 100326. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Wu, Q.; Lei, W.; Wu, D.; Sheng, J.; Liang, G.; Hou, G.; Fan, D. miR-3154 promotes glioblastoma proliferation and metastasis via targeting TP53INP1. Cell Div. 2024, 19, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Fu, X.; Liu, D.; Yang, M.; Yang, J.; Huo, Y.; Liu, W.; Hua, R.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J. Molecular markers associated with perineural invasion in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nip, H.; Dar, A.A.; Saini, S.; Colden, M.; Varahram, S.; Chowdhary, H.; Yamamura, S.; Mitsui, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Kato, T.; et al. Oncogenic microRNA-4534 regulates PTEN pathway in prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 68371–68384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmi, A.S.; Beck, F.W.; Bao, B.; Mohammad, R.M.; Sarkar, F.H. Aberrant epigenetic grooming of miRNAs in pancreatic cancer: A systems biology perspective. Epigenomics 2011, 3, 747–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Munoz, L.J.; Ulloa, E.V.; Sahlgren, C.; Lizano, M.; De La Cruz-Hernandez, E.; Contreras-Paredes, A. Modulating epigenetic modifications for cancer therapy (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2023, 49, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.D.; Shen, H.Z. Advances in pancreatic cancer epigenetics: From the mechanism to the clinic. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2025, 17, 106238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbatenko, A.; Sokilde, R.; Sorensen, E.E.; Newie, I.; Persson, H.; Morancho, B.; Arribas, J.; Litman, T.; Rovira, C.; Pedersen, S.F. HER2 and p95HER2 differentially regulate miRNA expression in MCF-7 breast cancer cells and downregulate MYB proteins through miR-221/222 and miR-503. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liao, X.; Huang, K.; Zeng, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, X.; Yu, T.; Yang, C.; Yu, L.; Wang, Q.; et al. Clustered microRNAs hsa-miR-221-3p/hsa-miR-222-3p and their targeted genes might be prognostic predictors for hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 2520–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Lou, W. Bioinformatic analysis shows the correlation of hsa_circ_0006220-miR-221/222-3p-ESR1/KDR axis with sorafenib resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma. Noncoding RNA Res. 2024, 9, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.; Zhao, C.; Guo, X.; Ding, H.; Cui, Y.; Shen, R.; Liu, J. Differential expression of microRNAs in omental adipose tissue from gestational diabetes mellitus subjects reveals miR-222 as a regulator of ERalpha expression in estrogen-induced insulin resistance. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 1982–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, X.; Liu, Y.; Lin, X.; Wang, R.; Dai, Z.; Chen, Y.; Ma, M.; Tasiheng, Y.; Yan, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Characterization of Estrogen Receptors in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma with Tertiary Lymphoid Structures. Cancers 2023, 15, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyagi, S.; Chabes, A.L.; Wysocka, J.; Herr, W. E2F activation of S phase promoters via association with HCF-1 and the MLL family of histone H3K4 methyltransferases. Mol. Cell 2007, 27, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Wei, L.; Han, T.; Ding, S. miR-3154 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via suppressing HNF4alpha. Carcinogenesis 2022, 43, 1002–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevarskaya, N.; Skryma, R.; Shuba, Y. Ion channels and the hallmarks of cancer. Trends Mol. Med. 2010, 16, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhan, S.; Zidar, N.; Tomazic, A.; Hauptman, N. Hypermethylated promoters of genes UNC5D and KCNA1 as potential novel diagnostic biomarkers in colorectal cancer. Epigenomics 2020, 12, 1677–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, C. Silencing of KCNA1 suppresses the cervical cancer development via mitochondria damage. Channels 2019, 13, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, J.L., 3rd. The voltage-gated calcium channel gamma subunits: A review of the literature. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2003, 35, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, E.; Cao, Y.N.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Ren, X.; Zhu, S.; Xi, X.; Mu, S.; Ma, M.; Zhi, T.; et al. Integrated profiling identifies CACNG3 as a prognostic biomarker for patients with glioma. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Bai, L.; Liang, J.; Li, M. Diagnostic value and clinical significance of serum miR-4534 combined with transvaginal color Doppler ultrasound in cervical cancer. Discov. Oncol. 2024, 15, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Alla, V.; Goody, D.; Gupta, S.K.; Spitschak, A.; Wolkenhauer, O.; Putzer, B.M.; Engelmann, D. Epigenetic factor EPC1 is a master regulator of DNA damage response by interacting with E2F1 to silence death and activate metastasis-related gene signatures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidalgo, M. Pancreatic cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1605–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilici, A. Prognostic factors related with survival in patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 10802–10812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loehrer, P.J., Sr.; Feng, Y.; Cardenes, H.; Wagner, L.; Brell, J.M.; Cella, D.; Flynn, P.; Ramanathan, R.K.; Crane, C.H.; Alberts, S.R.; et al. Gemcitabine alone versus gemcitabine plus radiotherapy in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer: An Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 4105–4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaconstantinou, I.G.; Manta, A.; Gazouli, M.; Lyberopoulou, A.; Lykoudis, P.M.; Polymeneas, G.; Voros, D. Expression of microRNAs in patients with pancreatic cancer and its prognostic significance. Pancreas 2013, 42, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islami, F.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global trends of lung cancer mortality and smoking prevalence. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2015, 4, 327–338. [Google Scholar]
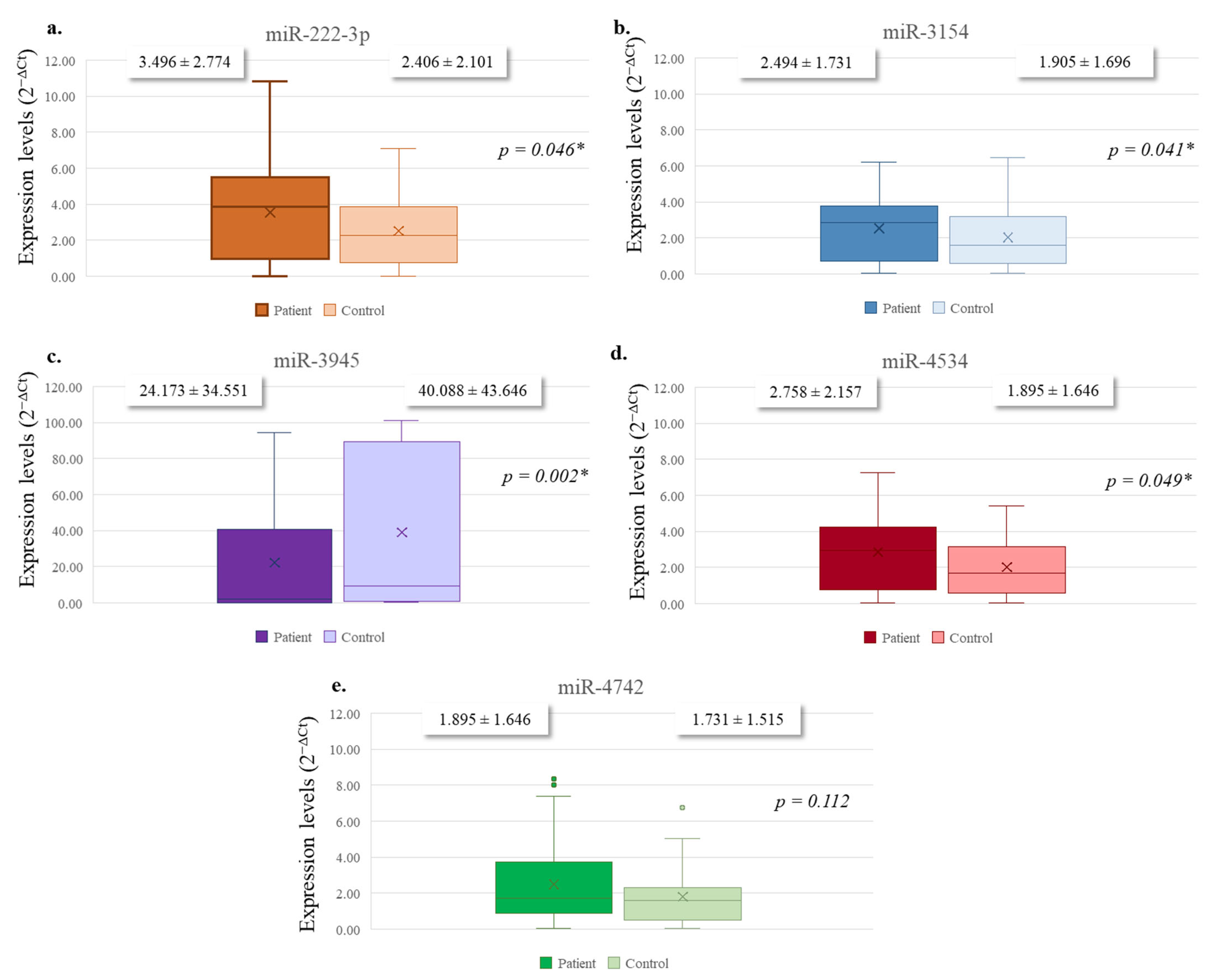

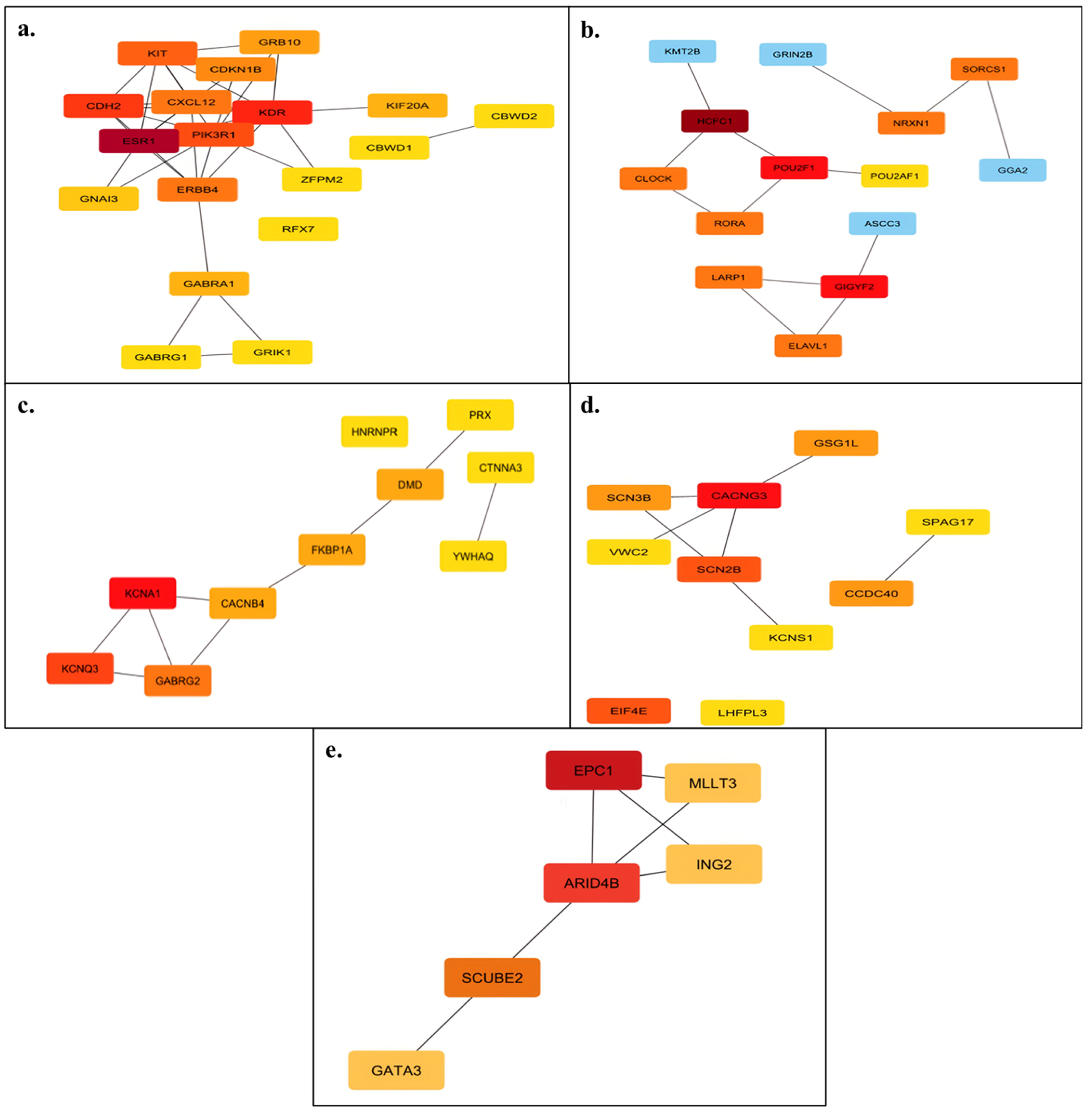
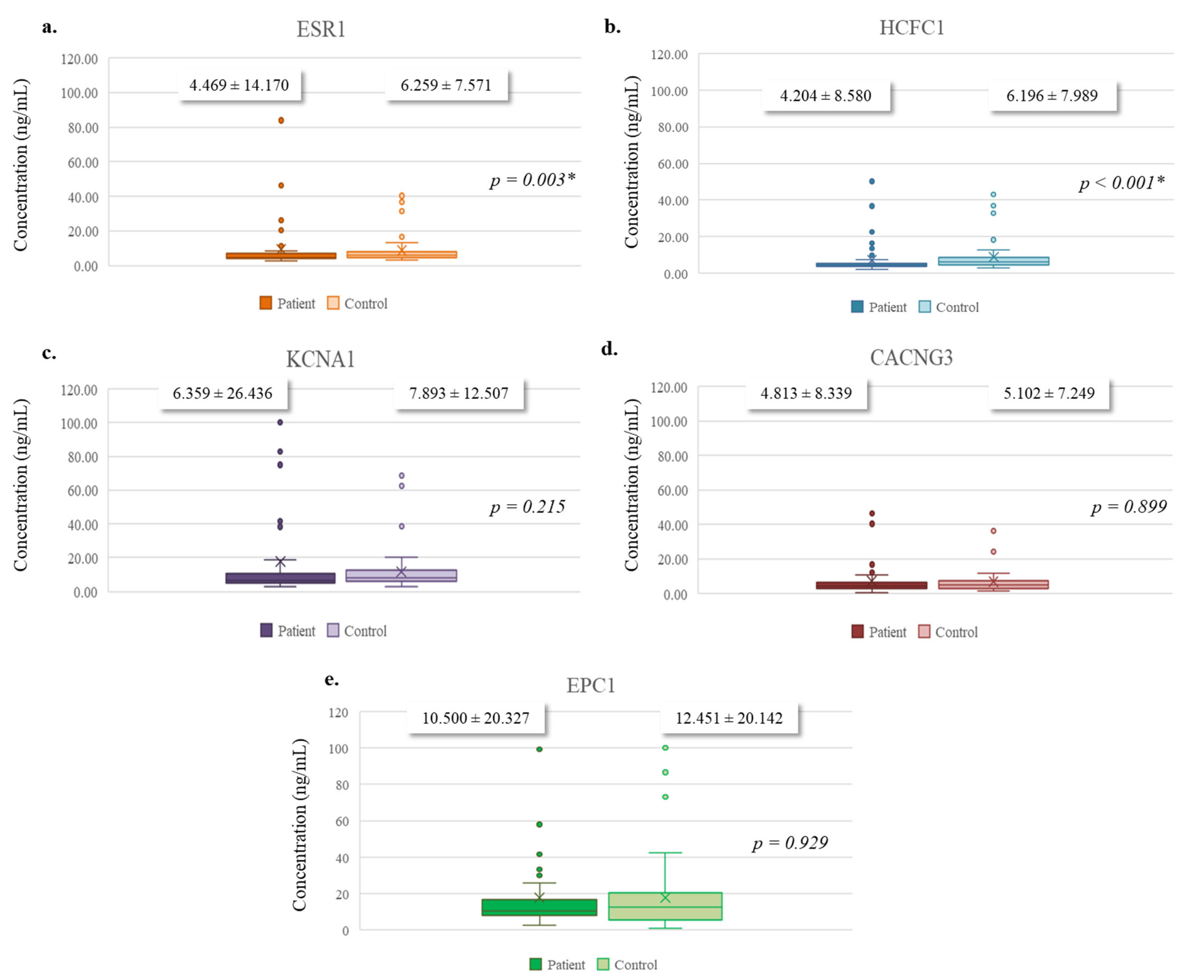
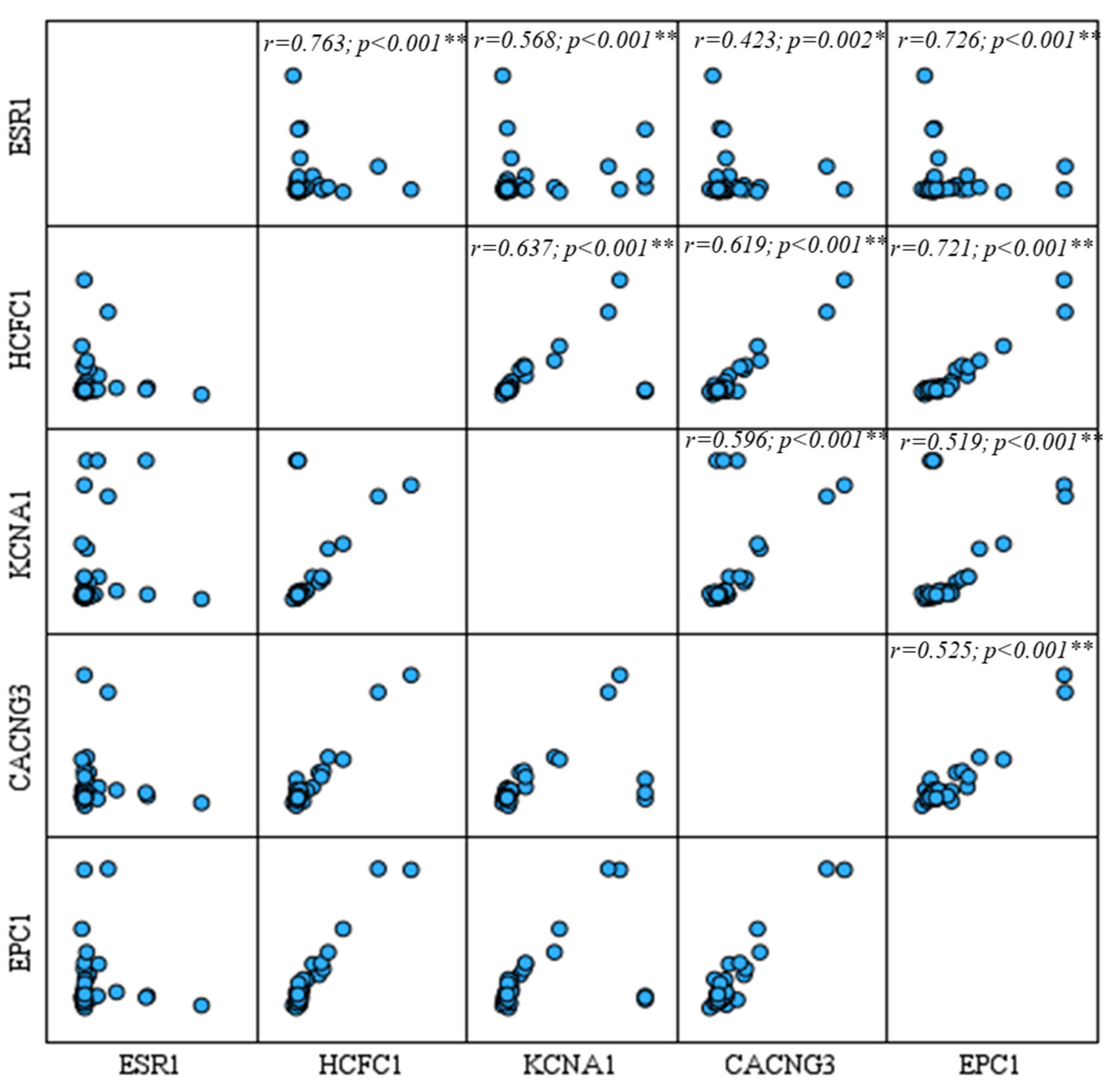


| miRNA | Primer (Forward) Sequence (5′→3′) | Stem-Loop Sequence (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| hsa-miR-222-3p (F) | AACGCCATTATCACACTAAATA | GAAAGAAGGCGAGGAGCAGATCGAGGAAGAAGACGGAAGAATGTGCGTCTCGCCTTCTTTCTATTTAGT |
| hsa-miR-3154 (F) | CAGAAGGGGAGTTGGGAGCAGA | GAAAGAAGGCGAGGAGCAGATCGAGGAAGAAGACGGAAGAATGTGCGTCTCGCCTTCTTTCTCTGCTCC |
| hsa-miR-3945 (F) | AGGGCATAGGAGAGGGTTGATAT | GAAAGAAGGCGAGGAGCAGATCGAGGAAGAAGACGGAAGAATGTGCGTCTCGCCTTCTTTCATATCAAC |
| hsa-miR-4534 (F) | GGATGGAGGAGGGGTCT | GAAAGAAGGCGAGGAGCAGATCGAGGAAGAAGACGGAAGAATGTGCGTCTCGCCTTCTTTCAGACCCCT |
| hsa-miR-4742-3p (F) | TCTGTATTCTCCTTTGCCTGCAG | GAAAGAAGGCGAGGAGCAGATCGAGGAAGAAGACGGAAGAATGTGCGTCTCGCCTTCTTTCCTGCAGGC |
| Universal Reverse (UR) | CGAGGAAGAAGACGGAAGAAT | |
| U6 | GCTTCGGCAGCACATATACTAAAAT |
| Clinical Parameters | N | % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age—median (minimum–maximum): | 53.5 (34–90) | ||
| Gender | Female | 22 | 47.8 |
| Male | 24 | 52.2 | |
| Smoking | No | 20 | 43.5 |
| Yes | 26 | 56.5 | |
| Alcohol | No | 36 | 78.3 |
| Yes | 10 | 21.7 | |
| Family history of malignancy | No | 21 | 45.7 |
| Yes | 25 | 54.3 | |
| Diabetes mellitus | No | 26 | 56.5 |
| Yes | 20 | 43.5 | |
| Comorbidity | No | 12 | 26.1 |
| Yes | 34 | 73.9 | |
| Anatomical involvement | Head | 28 | 60.9 |
| Corpus | 10 | 21.7 | |
| Tail | 8 | 17.4 | |
| Degree of differentiation | High | 0 | |
| Medium | 36 | 78.3 | |
| Low | 10 | 21.7 | |
| Surgical margin | Negative | 24 | 52.2 |
| Positive | 22 | 47.8 | |
| Lymphovascular invasion | No | 8 | 17.4 |
| Yes | 38 | 82.6 | |
| Perineural invasion | No | 13 | 28.3 |
| Yes | 33 | 71.7 | |
| T-stage | II | 17 | 37.0 |
| III | 21 | 45.7 | |
| IV | 8 | 17.4 | |
| Lymph node involvement (N) | No | 11 | 23.9 |
| Yes | 35 | 76.1 | |
| Metastasis (M) | No | 25 | 54.3 |
| Yes | 21 | 46.7 | |
| WHO stage | Ib | 5 | 10.9 |
| IIa | 4 | 8.7 | |
| IIb | 11 | 23.9 | |
| III | 5 | 10.9 | |
| IV | 21 | 45.7 | |
| Locally advanced status | No | 9 | 19.6 |
| Yes | 37 | 80.4 | |
| Treatment | No | 1 | 2.2 |
| CT | 27 | 58.7 | |
| CRT | 18 | 39.1 | |
| Recurrence | No | 39 | 84.8 |
| Yes | 7 | 15.2 | |
| Distant metastasis | No | 33 | 71.7 |
| Yes | 13 | 28.3 | |
| Current status | Alive | 15 | 32.6 |
| Ex | 31 | 67.4 | |
| Clinic Parameters | miR-222-3p | miR-3154 | miR-3945 | miR-4534 | miR-4742 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Median | p | Median | p | Median | p | Median | p | Median | p | ||
| Gender | Female | 22 | 23.20 | 0.886 | 24.27 | 0.709 | 26.05 | 0.218 | 22.82 | 0.741 | 21.18 | 0.262 |
| Male | 24 | 23.77 | 22.79 | 21.17 | 24.13 | 25.63 | ||||||
| Smoking | No | 20 | 23.00 | 0.825 | 25.85 | 0.298 | 25.15 | 0.465 | 25.60 | 0.352 | 24.10 | 0.790 |
| Yes | 26 | 23.88 | 21.69 | 22.23 | 21.88 | 23.04 | ||||||
| Alcohol | No | 36 | 21.28 | 0.033 | 22.71 | 0.448 | 22.33 | 0.263 | 21.97 | 0.143 | 22.08 | 0.164 |
| Yes | 10 | 31.50 | 26.35 | 27.70 | 29.00 | 28.60 | ||||||
| Family history of malignancy | No | 21 | 24.57 | 0.620 | 24.29 | 0.716 | 24.48 | 0.651 | 26.55 | 0.158 | 26.86 | 0.120 |
| Yes | 25 | 22.60 | 22.84 | 22.68 | 20.94 | 20.68 | ||||||
| Diabetes mellitus | No | 26 | 21.81 | 0.330 | 22.40 | 0.528 | 23.77 | 0.877 | 22.85 | 0.706 | 23.38 | 0.947 |
| Yes | 20 | 25.70 | 24.93 | 23.15 | 24.35 | 23.65 | ||||||
| Comorbidity | No | 12 | 26.75 | 0.329 | 26.83 | 0.317 | 25.54 | 0.540 | 26.21 | 0.416 | 31.67 | 0.014 |
| Yes | 34 | 22.35 | 22.32 | 22.78 | 22.54 | 20.62 | ||||||
| Anatomical involvement | Head | 28 | 21.61 | 0.255 | 20.46 | 0.083 | 21.82 | 0.594 | 21.45 | 0.070 | 22.07 | 0.268 |
| Corpus | 10 | 29.75 | 31.40 | 26.15 | 32.05 | 29.60 | ||||||
| Tail | 8 | 22.31 | 24.25 | 26.06 | 20.00 | 20.88 | ||||||
| Degree of differentiation | Medium | 36 | 23.32 | 0.863 | 22.68 | 0.432 | 23.85 | 0.739 | 23.40 | 0.926 | 23.08 | 0.690 |
| Low | 10 | 24.15 | 26.45 | 22.25 | 23.85 | 25.00 | ||||||
| Surgical margin | No | 24 | 21.35 | 0.257 | 19.81 | 0.050 | 20.67 | 0.135 | 20.33 | 0.095 | 19.46 | 0.033 |
| Yes | 22 | 25.84 | 27.52 | 26.59 | 26.95 | 27.91 | ||||||
| LVI | No | 8 | 23.25 | 0.963 | 28.13 | 0.291 | 26.06 | 0.578 | 26.69 | 0.470 | 24.25 | 0.875 |
| Yes | 38 | 23.55 | 22.53 | 22.96 | 22.83 | 23.34 | ||||||
| PNI | No | 13 | 17.46 | 0.055 | 19.88 | 0.252 | 23.19 | 0.922 | 22.04 | 0.643 | 22.38 | 0.724 |
| Yes | 33 | 25.88 | 24.92 | 23.62 | 24.08 | 23.94 | ||||||
| T-stage | II | 17 | 22.62 | 0.155 | 19.35 | 0.004 | 20.26 | 0.434 | 20.06 | 0.142 | 20.76 | 0.198 |
| III | 21 | 21.14 | 21.67 | 25.86 | 23.29 | 22.86 | ||||||
| IV | 8 | 31.56 | 37.13 | 24.19 | 31.38 | 31.00 | ||||||
| Lymph Node | Negative | 11 | 29.82 | 0.073 | 28.73 | 0.139 | 26.18 | 0.447 | 31.55 | 0.023 | 28.55 | 0.153 |
| Positive | 35 | 21.51 | 21.86 | 22.66 | 20.97 | 21.91 | ||||||
| M stage | No | 25 | 24.08 | 0.749 | 23.90 | 0.825 | 25.66 | 0.234 | 23.28 | 0.903 | 22.72 | 0.667 |
| Yes | 21 | 22.81 | 23.02 | 20.93 | 23.76 | 24.43 | ||||||
| WHO grade | Ib | 5 | 35.80 | 0.120 | 27.20 | 0.435 | 24.40 | 0.210 | 31.00 | 0.079 | 31.40 | 0.315 |
| IIa | 4 | 26.63 | 34.13 | 37.00 | 35.50 | 29.00 | ||||||
| IIb | 11 | 17.09 | 19.68 | 25.50 | 16.45 | 18.09 | ||||||
| III | 5 | 25.70 | 21.70 | 18.20 | 20.80 | 19.20 | ||||||
| IV | 21 | 22.81 | 23.02 | 20.93 | 23.76 | 24.43 | ||||||
| Locally advanced status | No | 9 | 31.72 | 0.035 | 30.28 | 0.092 | 30.00 | 0.106 | 33.00 | 0.013 | 30.33 | 0.090 |
| Yes | 37 | 21.50 | 21.85 | 21.92 | 21.19 | 21.84 | ||||||
| Treatment | Yok | 1 | 11.00 | 0.721 | 4.00 | 0.277 | 13.00 | 0.356 | 22.00 | 13.00 | ||
| CT | 27 | 23.70 | 22.74 | 21.61 | 21.72 | 24.67 | ||||||
| CRT | 18 | 23.89 | 25.72 | 26.92 | 26.25 | 22.33 | ||||||
| Recurrence | No | 39 | 23.96 | 0.590 | 23.32 | 0.834 | 24.68 | 0.165 | 23.22 | 0.742 | 23.87 | 0.682 |
| Yes | 7 | 20.93 | 24.50 | 16.93 | 25.07 | 21.43 | ||||||
| Distant metastasis | No | 33 | 25.91 | 0.050 | 26.14 | 0.034 | 25.98 | 0.045 | 24.88 | 0.267 | 25.09 | 0.200 |
| Yes | 13 | 17.38 | 16.81 | 17.19 | 20.00 | 19.46 | ||||||
| Clinic Parameters | ESR1 | HCFC1 | KCNA1 | CACNG3 | EPC1 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Median | p | Median | p | Median | p | Median | p | Median | p | ||
| Gender | Female | 22 | 24.27 | 0.567 | 23.71 | 0.404 | 23.46 | 0.341 | 20.54 | 0.021 | 24.08 | 0.509 |
| Male | 24 | 26.63 | 27.15 | 27.38 | 30.08 | 26.81 | ||||||
| Smoking | No | 20 | 24.66 | 0.718 | 26.00 | 0.830 | 24.59 | 0.696 | 22.32 | 0.171 | 22.14 | 0.148 |
| Yes | 26 | 26.16 | 25.11 | 26.21 | 28.00 | 28.14 | ||||||
| Alcohol | No | 36 | 24.44 | 0.331 | 25.10 | 0.717 | 23.85 | 0.131 | 24.92 | 0.598 | 24.44 | 0.331 |
| Yes | 10 | 29.27 | 26.91 | 31.36 | 27.55 | 29.27 | ||||||
| Family history of malignancy | No | 21 | 25.04 | 0.838 | 27.96 | 0.271 | 24.52 | 0.661 | 27.30 | 0.419 | 26.74 | 0.579 |
| Yes | 25 | 25.89 | 23.41 | 26.33 | 23.96 | 24.44 | ||||||
| Diabetes mellitus | No | 26 | 26.04 | 0.769 | 26.18 | 0.710 | 24.14 | 0.468 | 25.39 | 0.953 | 25.93 | 0.815 |
| Yes | 20 | 24.82 | 24.64 | 27.23 | 25.64 | 24.95 | ||||||
| Comorbidity | No | 12 | 26.08 | 0.438 | 18.71 | 0.150 | 17.92 | 0.094 | 22.00 | 0.652 | 20.50 | 0.368 |
| Yes | 34 | 22.59 | 25.19 | 25.47 | 24.03 | 24.56 | ||||||
| Anatomical involvement | Head | 28 | 23.55 | 0.472 | 23.05 | 0.257 | 23.18 | 0.277 | 21.14 | 0.106 | 22.57 | 0.402 |
| Corpus | 10 | 19.95 | 19.60 | 19.50 | 22.90 | 21.50 | ||||||
| Tail | 8 | 27.75 | 29.94 | 29.63 | 32.50 | 29.25 | ||||||
| Degree of differentiation | Medium | 36 | 22.49 | 0.331 | 22.50 | 0.338 | 23.97 | 0.651 | 22.89 | 0.558 | 22.53 | 0.351 |
| Low | 10 | 27.15 | 27.10 | 21.80 | 25.70 | 27.00 | ||||||
| Surgical margin | No | 24 | 20.19 | 0.080 | 25.75 | 0.235 | 25.04 | 0.416 | 25.42 | 0.312 | 26.33 | 0.135 |
| Yes | 22 | 27.11 | 21.05 | 21.82 | 21.41 | 20.41 | ||||||
| LVI | No | 8 | 16.50 | 0.020 | 17.09 | 0.030 | 21.64 | 0.320 | 20.55 | 0.202 | 13.64 | 0.002 |
| Yes | 38 | 28.04 | 27.87 | 26.59 | 26.90 | 28.85 | ||||||
| PNI | No | 13 | 21.38 | 0.503 | 22.38 | 0.735 | 25.73 | 0.485 | 26.15 | 0.408 | 21.54 | 0.549 |
| Yes | 33 | 24.33 | 23.94 | 22.62 | 22.45 | 24.27 | ||||||
| T-stage | II | 17 | 18.29 | 0.120 | 27.82 | 0.212 | 24.12 | 0.153 | 25.65 | 0.494 | 25.71 | 0.695 |
| III | 21 | 27.29 | 21.81 | 26.10 | 23.55 | 22.24 | ||||||
| IV | 8 | 24.63 | 18.75 | 15.38 | 18.81 | 22.13 | ||||||
| Lymph node | Negative | 11 | 18.55 | 0.160 | 22.18 | 0.709 | 21.50 | 0.571 | 20.73 | 0.432 | 21.55 | 0.580 |
| Positive | 35 | 25.06 | 23.91 | 24.13 | 24.37 | 24.11 | ||||||
| M stage | No | 25 | 24.44 | 0.604 | 19.38 | 0.023 | 23.18 | 0.860 | 20.38 | 0.085 | 21.64 | 0.305 |
| Yes | 21 | 22.38 | 28.40 | 23.88 | 27.21 | 25.71 | ||||||
| WHO grade | Ib | 5 | 13.60 | 0.107 | 29.60 | 0.052 | 22.90 | 0.644 | 24.20 | 0.446 | 29.20 | 0.569 |
| IIa | 4 | 24.00 | 19.00 | 24.75 | 16.50 | 19.50 | ||||||
| IIb | 11 | 31.73 | 15.59 | 26.45 | 20.77 | 19.64 | ||||||
| III | 5 | 19.60 | 17.80 | 15.00 | 18.80 | 20.20 | ||||||
| IV | 21 | 22.38 | 28.40 | 23.88 | 27.21 | 25.71 | ||||||
| Locally advanced status | No | 9 | 18.22 | 0.198 | 24.89 | 0.738 | 23.72 | 0.958 | 20.78 | 0.508 | 24.89 | 0.741 |
| Yes | 37 | 24.78 | 23.16 | 23.45 | 24.16 | 23.16 | ||||||
| Treatment | Yok | 1 | 7.00 | 0.478 | 29.00 | 0.343 | 26.00 | 0.984 | 34.00 | 0.138 | 3.00 | 0.086 |
| CT | 27 | 23.07 | 25.78 | 23.26 | 26.02 | 26.15 | ||||||
| CRT | 18 | 25.06 | 19.78 | 23.72 | 19.14 | 20.67 | ||||||
| Recurrence | No | 39 | 25.64 | 0.867 | 25.49 | 0.989 | 25.84 | 0.685 | 25.40 | 0.900 | 25.33 | 0.834 |
| Yes | 7 | 24.64 | 25.57 | 23.43 | 26.14 | 26.57 | ||||||
| Distant metastasis | No | 33 | 25.96 | 0.721 | 24.75 | 0.560 | 24.14 | 0.290 | 23.58 | 0.136 | 24.83 | 0.604 |
| Yes | 13 | 24.32 | 27.43 | 29.00 | 30.43 | 27.21 | ||||||
| miRNA | Target Protein | β (Unstd.) | p-Value | R2 | Significant |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-222-3p | ESR1 | 0.438 | 0.588 | 0.007 | No |
| miR-3154 | HCFC1 | 0.663 | 0.397 | 0.016 | No |
| miR-3945 | KCNA1 | 0.259 | 0.038 | 0.094 | Yes |
| miR-4534 | CACNG3 | 0.025 | 0.968 | 0.000 | No |
| miR-4742 | EPC1 | 2.581 | 0.055 | 0.081 | Borderline |
| Marker | Expression Level | Estimate (Months) | Std. Error | 95% CI | Log Rank (Mantel–Cox) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||
| miR-222-3p | Low | 14.267 | 2.018 | 10.311 | 18.222 | 0.139 |
| High | 12.333 | 3.500 | 5.473 | 19.193 | ||
| Overall | 12.633 | 1.076 | 10.525 | 14.742 | ||
| miR-3154 | Low | 14.267 | 5.145 | 4.183 | 24.351 | 0.211 |
| High | 12.467 | 0.123 | 12.225 | 12.709 | ||
| Overall | 12.633 | 1.076 | 10.525 | 14.742 | ||
| miR-3945 | Low | 15.600 | 3.913 | 7.930 | 23.270 | 0.001 * |
| High | 5.333 | 1.321 | 2.744 | 7.923 | ||
| Overall | 12.633 | 1.076 | 10.525 | 14.742 | ||
| miR-4534 | Low | 14.267 | 2.149 | 10.054 | 18.480 | 0.208 |
| High | 12.333 | 3.274 | 5.916 | 18.750 | ||
| Overall | 12.633 | 1.076 | 10.525 | 14.742 | ||
| miR-4742 | Low | 14.267 | 2.100 | 10.151 | 18.383 | 0.130 |
| High | 12.467 | 2.214 | 8.128 | 16.805 | ||
| Overall | 12.633 | 1.076 | 10.525 | 14.742 | ||
| ESR1 | Low | 13.500 | 1.326 | 10.901 | 16.099 | 0.660 |
| High | 12.467 | 3.240 | 6.116 | 18.818 | ||
| Overall | 12.633 | 1.076 | 10.525 | 14.742 | ||
| HCFC1 | Low | 17.767 | 3.755 | 10.408 | 25.126 | 0.943 |
| High | 12.333 | 3.712 | 5.057 | 19.609 | ||
| Overall | 12.633 | 1.076 | 10.525 | 14.742 | ||
| KCNA1 | Low | 14.267 | 3.133 | 8.125 | 20.408 | 0.823 |
| High | 12.467 | 4.015 | 4.598 | 20.335 | ||
| Overall | 12.633 | 1.076 | 10.525 | 14.742 | ||
| CACNG3 | Low | 12.333 | 3.274 | 5.916 | 18.750 | 0.240 |
| High | 13.500 | 1.235 | 11.080 | 15.920 | ||
| Overall | 12.633 | 1.076 | 10.525 | 14.742 | ||
| EPC1 | Low | 12.467 | 2.829 | 6.922 | 18.012 | 0.432 |
| High | 12.633 | 3.289 | 6.187 | 19.079 | ||
| Overall | 12.633 | 1.076 | 10.525 | 14.742 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Şen, S.; Özgel, M.Ç.; Tunçer, Ş.B.; Bozbey, H.U.; Karabulut, S.; Taştekin, D. A Pilot Study of Exploring miRNA–Protein Interaction Networks in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Patients: Implications for Diagnosis and Prognosis. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2479. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192479
Şen S, Özgel MÇ, Tunçer ŞB, Bozbey HU, Karabulut S, Taştekin D. A Pilot Study of Exploring miRNA–Protein Interaction Networks in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Patients: Implications for Diagnosis and Prognosis. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(19):2479. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192479
Chicago/Turabian StyleŞen, Sena, Merve Çiğdem Özgel, Şeref Buğra Tunçer, Hamza Uğur Bozbey, Senem Karabulut, and Didem Taştekin. 2025. "A Pilot Study of Exploring miRNA–Protein Interaction Networks in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Patients: Implications for Diagnosis and Prognosis" Diagnostics 15, no. 19: 2479. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192479
APA StyleŞen, S., Özgel, M. Ç., Tunçer, Ş. B., Bozbey, H. U., Karabulut, S., & Taştekin, D. (2025). A Pilot Study of Exploring miRNA–Protein Interaction Networks in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Patients: Implications for Diagnosis and Prognosis. Diagnostics, 15(19), 2479. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192479






