Cumulative Effect of Metabolic Factors on Hepatic Steatosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
Objectives
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Clinical and Laboratory Assessments
Liver Fat Quantification
2.3. Observed Metabolic Risk Factors
- Obesity/overweight according to body mass index: normal weight (BMI: 18.5 kg/m2 to 24.9 kg/m2), overweight (BMI: 25.0 kg/m2 to 29.9 kg/m2), and obese (BMI: 30 kg/m2 or more).
- Hypercholesterolemia: total cholesterol > 5.2 mmol/L, or >200 mg/dL.
- Hypertriglyceridemia: triglycerides > 1.7 mmol/L, or >150 mg/dL.
- Impaired glucose metabolism: impaired fasting glucose ≥ 100 mg/dL or diagnosis of type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- Hypertension: blood pressure over 120/80 mmHg, or under treatment.
2.4. Cumulative Metabolic Risk Score
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
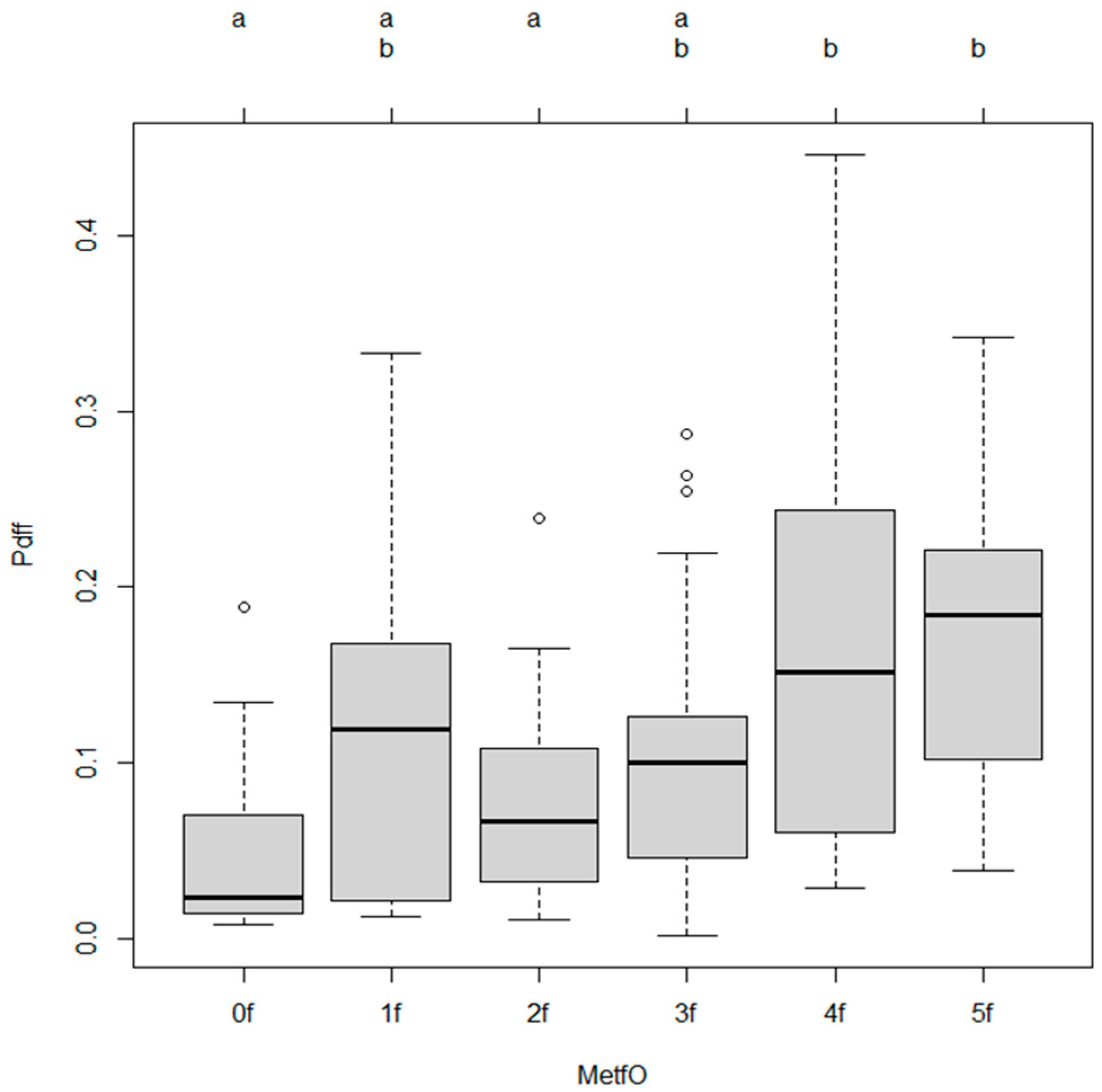
3.1. Association Between Metabolic Risk Factors and Hepatic Steatosis
3.2. Post Hoc Comparisons
3.3. Adjusted Odds Ratios for Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AHA | American Heart Association |
| AASLD | American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases |
| CLD | chronic liver disease |
| CVD | cardiovascular disease |
| CKD | chronic kidney disease |
| EASL | European Association for the Study of the Liver |
| ESC | European Society of Cardiology |
| FFA | free fatty acid |
| LDL | low-density lipoproteins |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharides |
| IL | interleukin |
| MR-PDFF | magnetic resonance imaging proton density fat fraction |
| MASLD | metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease |
| RAAS | renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| SNS | sympathetic nervous system |
| T2D | type 2 diabetes |
| TLR4 | toll-like receptor 4 |
| TNF | α tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| VLDL | very-low-density lipoproteins |
References
- Younossi, Z.M.; Kalligeros, M.; Henry, L. Epidemiology of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2025, 31 (Suppl), S32–S50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Stepanova, M.; Myers, R.P.; Younossi, I.; Henry, L. The potential role of fatigue in identifying patients with NASH and advanced fibrosis who experience disease progression. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 21, 970–977.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, A.A.; De Avila, L.; Kannan, S.; Paik, J.M.; Golabi, P.; Gerber, L.H.; Younossi, Z.M. Interrelationship between physical activity and depression in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Hepatol. 2022, 14, 612–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease—Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslam, M.; Newsome, P.N.; Sarin, S.K.; Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Dufour, J.-F.; Schattenberg, J.M.; et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petäjä, E.M.; Yki-Järvinen, H. Definitions of normal liver fat and the association of insulin sensitivity with acquired and genetic NAFLD. Nutrients 2021, 13, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caussy, C.; Reeder, S.B.; Sirlin, C.B.; Loomba, R. Noninvasive, quantitative assessment of liver fat by MRI-PDFF as an endpoint in NASH trials. Hepatology 2018, 68, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golabi, P.; Paik, J.M.; Kumar, A.; Al Shabeeb, R.; Eberly, K.E.; Cusi, K.; GunduRao, N.; Younossi, Z.M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and associated mortality in individuals with type 2 diabetes, pre-diabetes, metabolically unhealthy, and metabolically healthy individuals in the United States. Metabolism 2023, 146, 155642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Golabi, P.; Price, J.K.; Owrangi, S.; Gundu-Rao, N.; Satchi, R.; Paik, J.M. The global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis among patients with type 2 diabetes. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 22, 1999–2010.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchay, M.S.; Misra, A. From nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) to metabolic associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD): A journey over 40 years. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2020, 14, 695–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Zheng, R.-D.; Sun, X.-Q.; Ding, W.-J.; Wang, X.-Y.; Fan, J.-G. Gut microbiota dysbiosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2017, 16, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Obesity and Overweight. WHO Web Site. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 3 June 2024).
- Quek, J.; Chan, K.E.; Wong, Z.Y.; Tan, C.; Tan, B.; Lim, W.H.; Tan, D.J.H.; Tang, A.S.P.; Tay, P.; Xiao, J.; et al. Global prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in the overweight and obese population: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badmus, O.O.; Hinds, T.D., Jr.; Stec, D.E. Mechanisms Linking Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD) to Cardiovascular Disease. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2023, 25, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Rifai, M.; Silverman, M.G.; Nasir, K.; Budoff, M.J.; Blankstein, R.; Szklo, M.; Katz, R.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Blaha, M.J. The association of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, obesity, and metabolic syndrome, with systemic inflammation and subclinical atherosclerosis: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). Atherosclerosis 2015, 239, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Sechi, L.A.; Navarese, E.P.; Casu, G.; Vidili, G. Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and cardiovascular risk: A comprehensive review. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.; Desai, A.; Hamilton, G.; Wolfson, T.; Gamst, A.; Lam, J.; Clark, L.; Hooker, J.; Chavez, T.; Ang, B.D.; et al. Accuracy of MR imaging–estimated proton density fat fraction for classification of steatosis grade in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Radiology 2015, 274, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar-Gomez, E.; Chalasani, N. Non-invasive assessment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Clinical prediction rules and blood-based biomarkers. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Wang, L.; Evans, P.C.; Xu, S. NAFLD and NASH: Etiology, targets and emerging therapies. Drug Discov. Today 2024, 29, 103910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL); European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD); European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO). EASL-EASD-EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). J. Hepatol. 2024, 81, 492–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, H.; Craig, D.; Barker, R.; Spiers, G.; Stow, D.; Anstee, Q.M.; Hanratty, B. Metabolic risk factors and incident advanced liver disease in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A systematic review and meta-analysis of population-based observational studies. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.I. Fatty liver disease and cardiovascular risk: Impact of metabolic dysfunctions. Gut Liver 2022, 16, 497–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinella, M.E.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Siddiqui, M.S.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Caldwell, S.; Barb, D.; Kleiner, D.E.; Loomba, R. AASLD Practice Guidance on the clinical assessment and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1797–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, S.U.; Kim, H.C. Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and incident cardiovascular disease risk: A nationwide cohort study. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 19, 2138–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Petracca, G.; Beatrice, G.; Csermely, A.; Lonardo, A.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Tilg, H.; Byrne, C.D.; Targher, G. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and risk of incident chronic kidney disease: An updated meta-analysis. Gut 2022, 71, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cusi, K.; Isaacs, S.; Barb, D.; Basu, R.; Caprio, S.; Garvey, W.T.; Kashyap, S.; Mechanick, J.I.; Mouzaki, M.; Nadolsky, K.; et al. American Association of Clinical Endocrinology Clinical Practice Guideline for the diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in primary care and endocrinology clinical settings: Co-sponsored by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD). Endocr. Pract. 2022, 28, 528–562. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

| Parameter | Mean | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|
| BMI (kg/m2) | 29.1 | 4.7 |
| AST (U/L) | 37.1 | 25.3 |
| GPT (U/L) | 47.7 | 38.2 |
| GGT (U/L) | 129 | 273.2 |
| ALP (U/L) | 93.8 | 47.5 |
| Total bilirubin (umoL/L) | 14.3 | 7.4 |
| INR | 1.1 | 0.6 |
| Albumin (g/L) | 43.9 | 5 |
| Triglyceride (mmoL/L) | 2.3 | 3 |
| LDL-cholesterol (mmoL/L) | 3.7 | 1.3 |
| HDL-cholesterol (mmoL/L) | 1.3 | 0.3 |
| Thrombocyte (109/L) | 247 | 67 |
| Glucose (mmoL/L) | 5.9 | 1.6 |
| Variable | β (Estimate) | Standard Error | t-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cumulative Metabolic Risk (Metf) | 0.021 | 0.0053 | 4.005 | 0.0001 |
| Intercept | 0.0605 | 0.0158 | 3.838 | 0.0002 |
| MetfO Category vs. Reference (0f) | β (Estimate) | Standard Error | t-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MetfO1 | 0.0597 | 0.0315 | 1.896 | 0.0604 |
| MetfO2f | 0.0226 | 0.0305 | 0.742 | 0.4593 |
| MetfO3f | 0.0457 | 0.0302 | 1.514 | 0.1328 |
| MetfO4f | 0.1073 | 0.0307 | 3.500 | 0.0007 |
| MetfO5f | 0.1220 | 0.0356 | 3.427 | 0.0008 |
| Comparison | Mean Difference | 95% CI (Lower–Upper) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| MetfO4 vs. 0f | 0.1073 | 0.0185–0.1961 | 0.0084 |
| MetfO5 vs. 0f | 0.1220 | 0.0189–0.2250 | 0.0106 |
| MetfO4 vs. 2f | 0.0847 | 0.0169–0.1525 | 0.0057 |
| MetfO5 vs. 2f | 0.0993 | 0.0137–0.1850 | 0.0132 |
| Variable | Beta Estimate | 95% CI (Lower) | 95% CI (Upper) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metf (continuous) | 0.021 | 0.0107 | 0.0313 | 0.0001 *** |
| MetfO1f | 0.0597 | −0.0315 | 0.1509 | 0.0604 |
| MetfO2f | 0.0226 | −0.0657 | 0.1109 | 0.4593 |
| MetfO3f | 0.0457 | −0.0417 | 0.1331 | 0.1328 |
| MetfO4f | 0.1073 | 0.0185 | 0.1961 | 0.0007 *** |
| MetfO5f | 0.1220 | 0.0189 | 0.2250 | 0.0008 *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Egresi, A.; Kozma, B.; Karácsony, M.; Rónaszéki, A.; Werling, K.; Csongrády, B.; Novák, P.K.; Folhoffer, A.; Szijártó, A.; Hagymási, K. Cumulative Effect of Metabolic Factors on Hepatic Steatosis. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2406. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15182406
Egresi A, Kozma B, Karácsony M, Rónaszéki A, Werling K, Csongrády B, Novák PK, Folhoffer A, Szijártó A, Hagymási K. Cumulative Effect of Metabolic Factors on Hepatic Steatosis. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(18):2406. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15182406
Chicago/Turabian StyleEgresi, Anna, Brigitta Kozma, Márton Karácsony, Aladár Rónaszéki, Klára Werling, Barbara Csongrády, Pál Kaposi Novák, Anikó Folhoffer, Attila Szijártó, and Krisztina Hagymási. 2025. "Cumulative Effect of Metabolic Factors on Hepatic Steatosis" Diagnostics 15, no. 18: 2406. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15182406
APA StyleEgresi, A., Kozma, B., Karácsony, M., Rónaszéki, A., Werling, K., Csongrády, B., Novák, P. K., Folhoffer, A., Szijártó, A., & Hagymási, K. (2025). Cumulative Effect of Metabolic Factors on Hepatic Steatosis. Diagnostics, 15(18), 2406. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15182406





