Metformin and Risk of New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation in Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
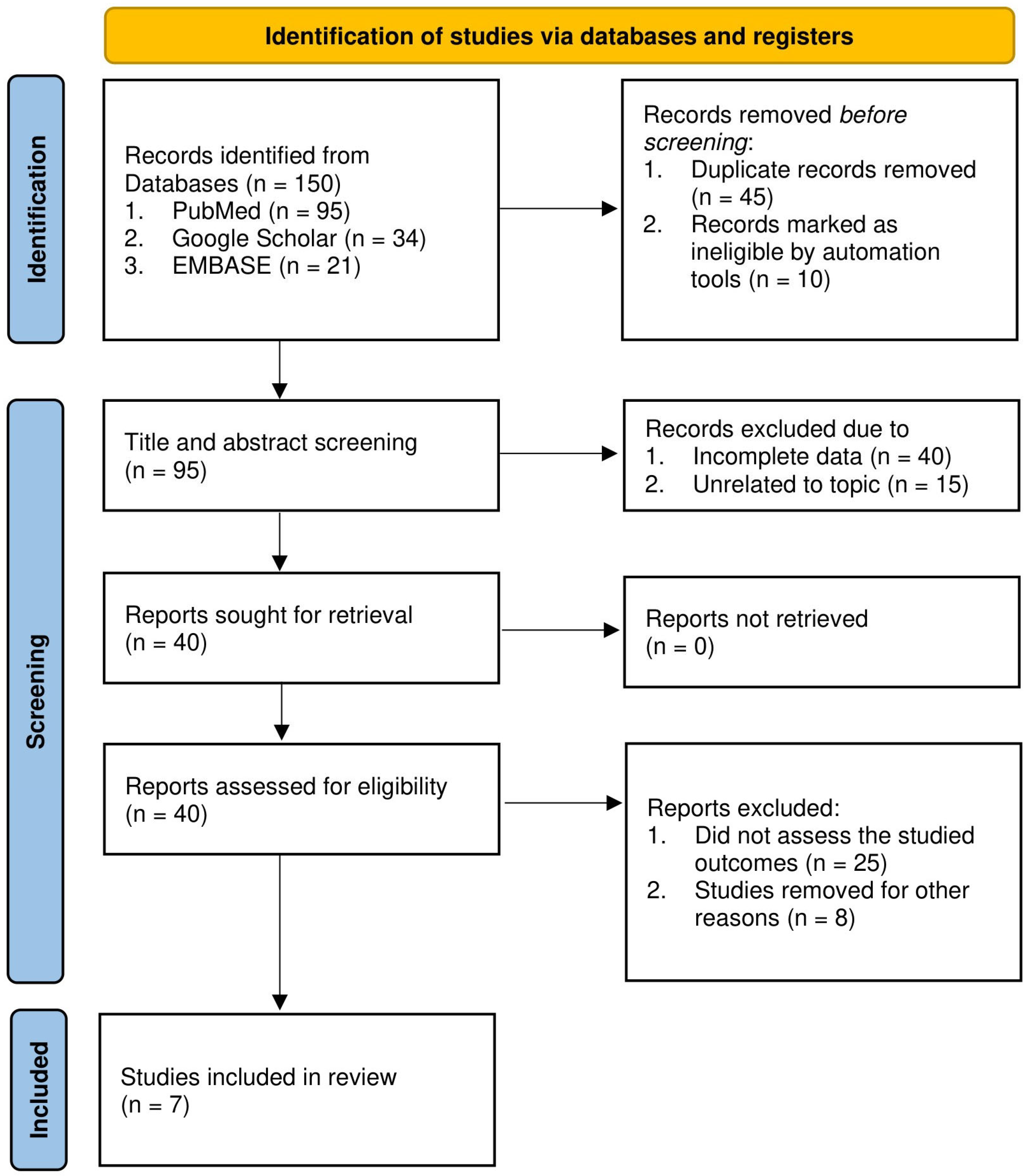
2. Methods
2.1. Data Sources and Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Ethical Considerations
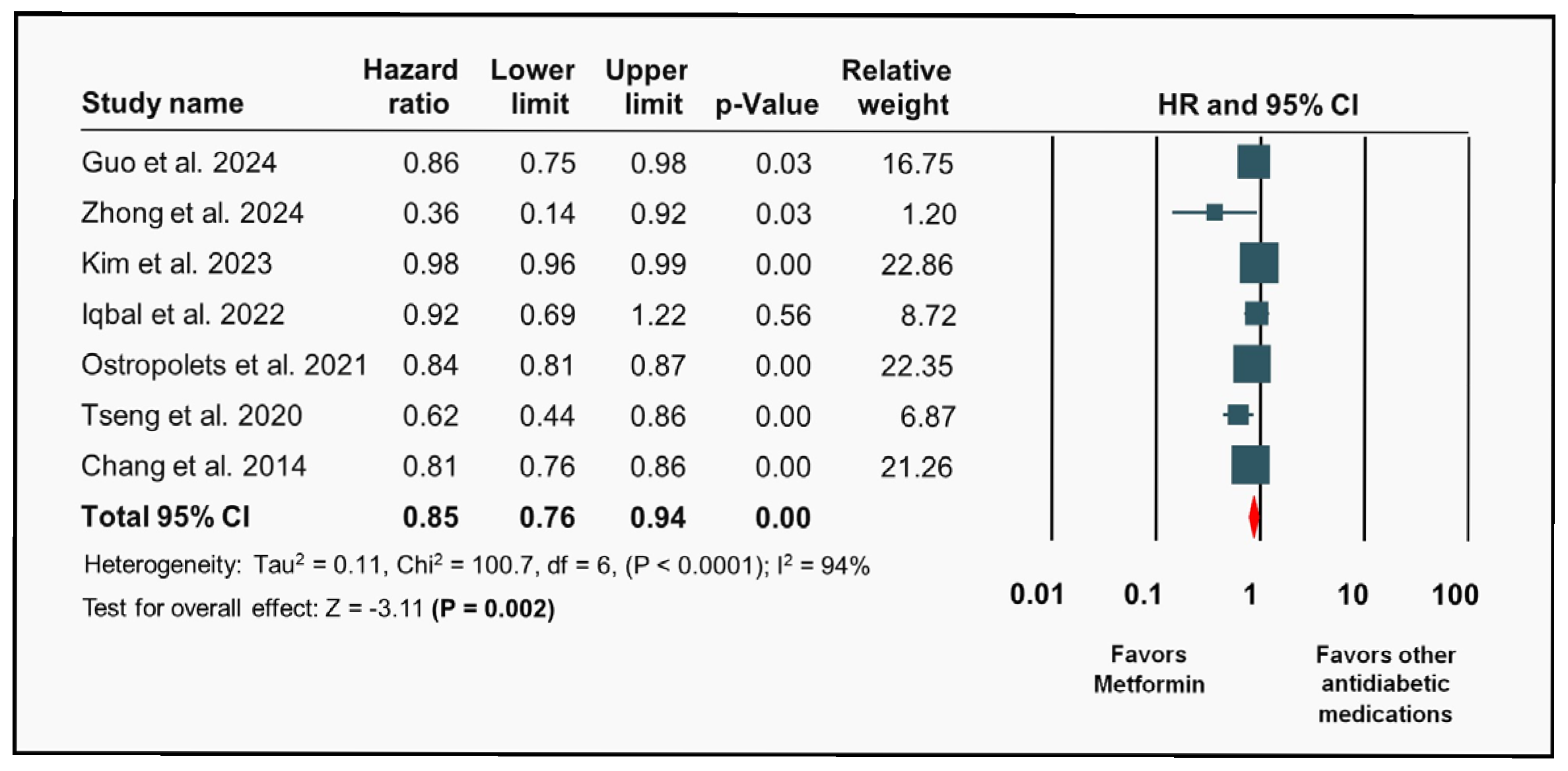
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Metformin and Risk of Atrial Fibrillation
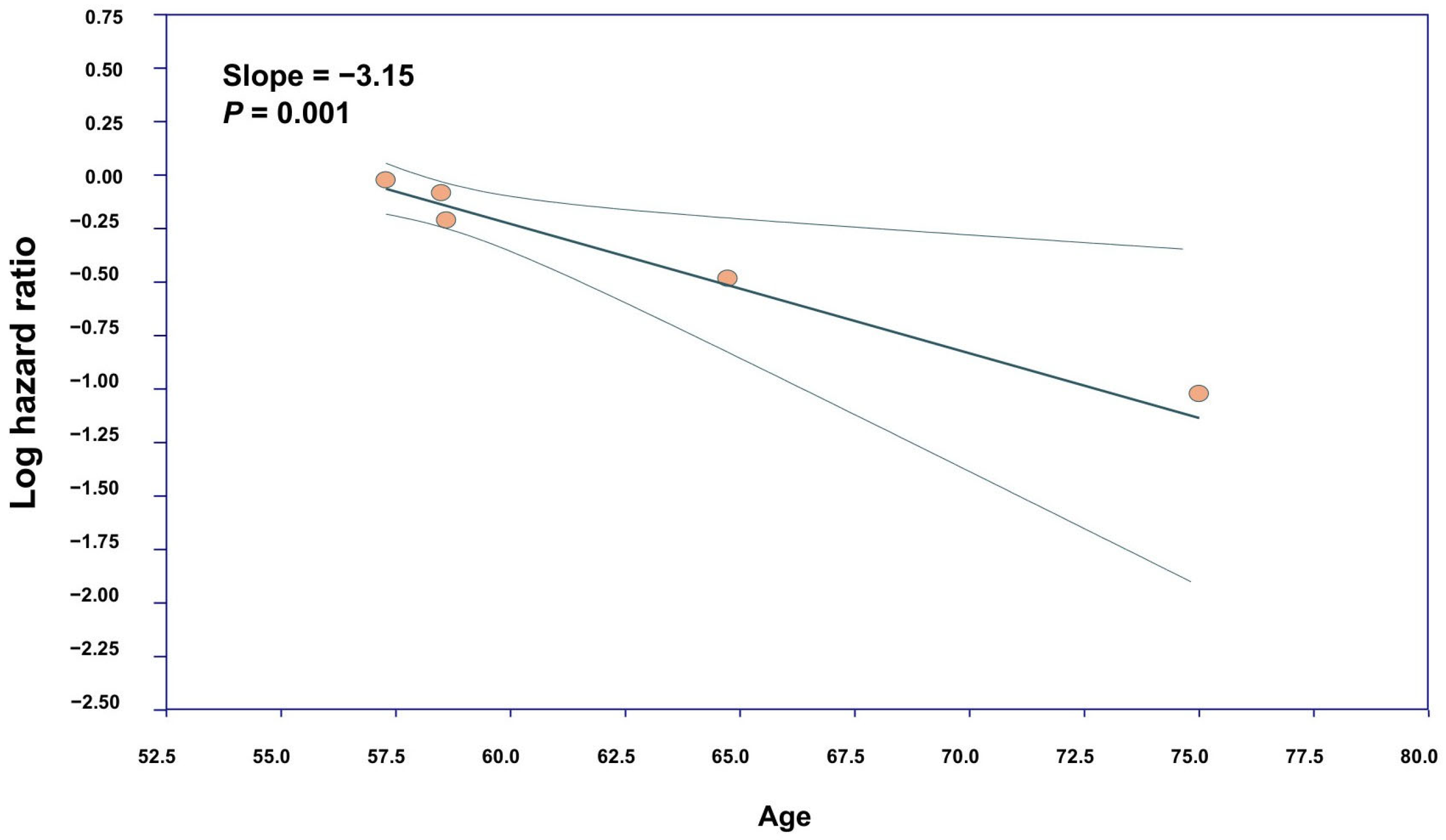
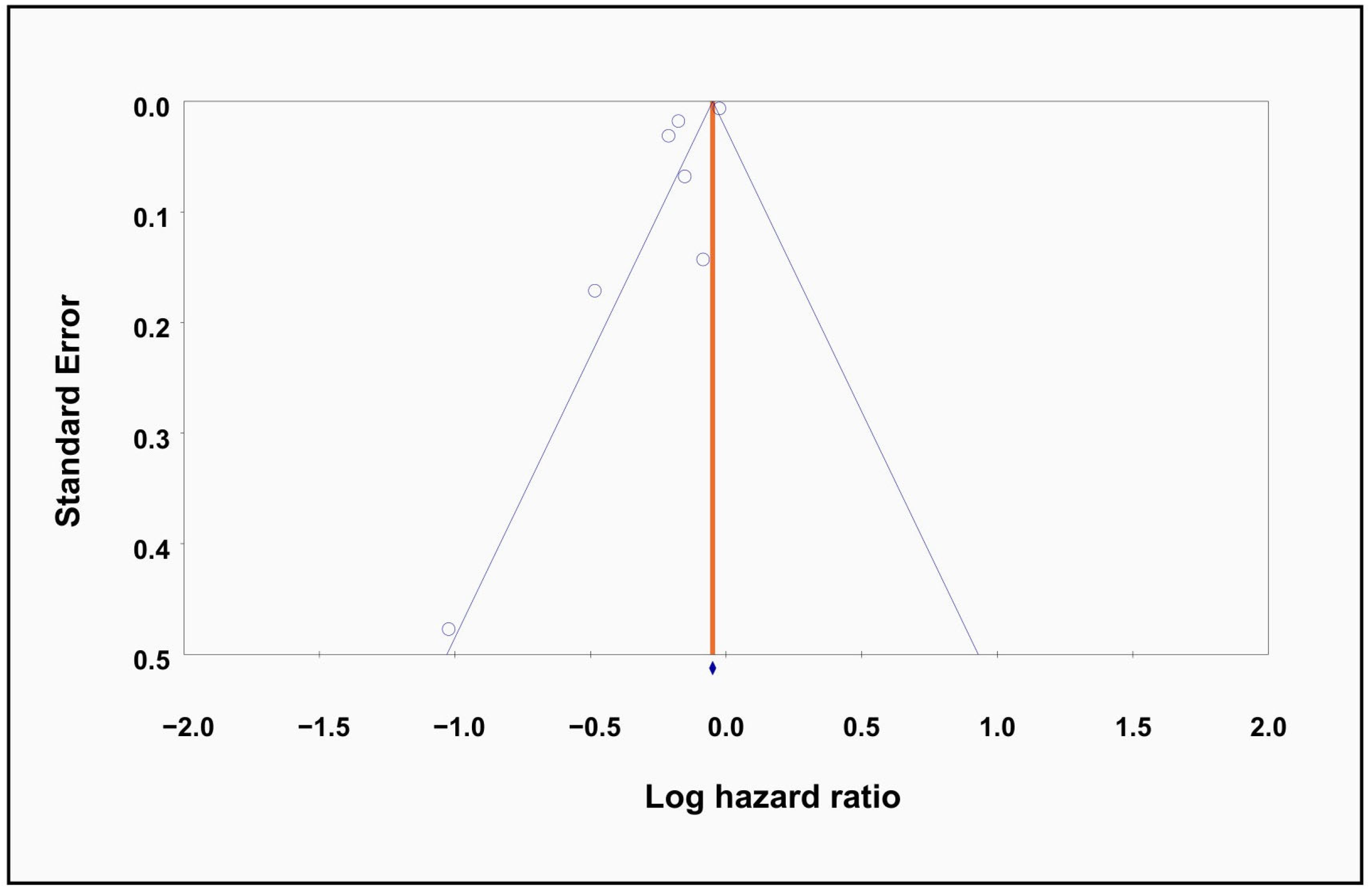
3.3. Meta-Regression and Publication Bias
3.4. Risk of Bias Assessment
4. Discussion
4.1. Interpretation of Individual Studies
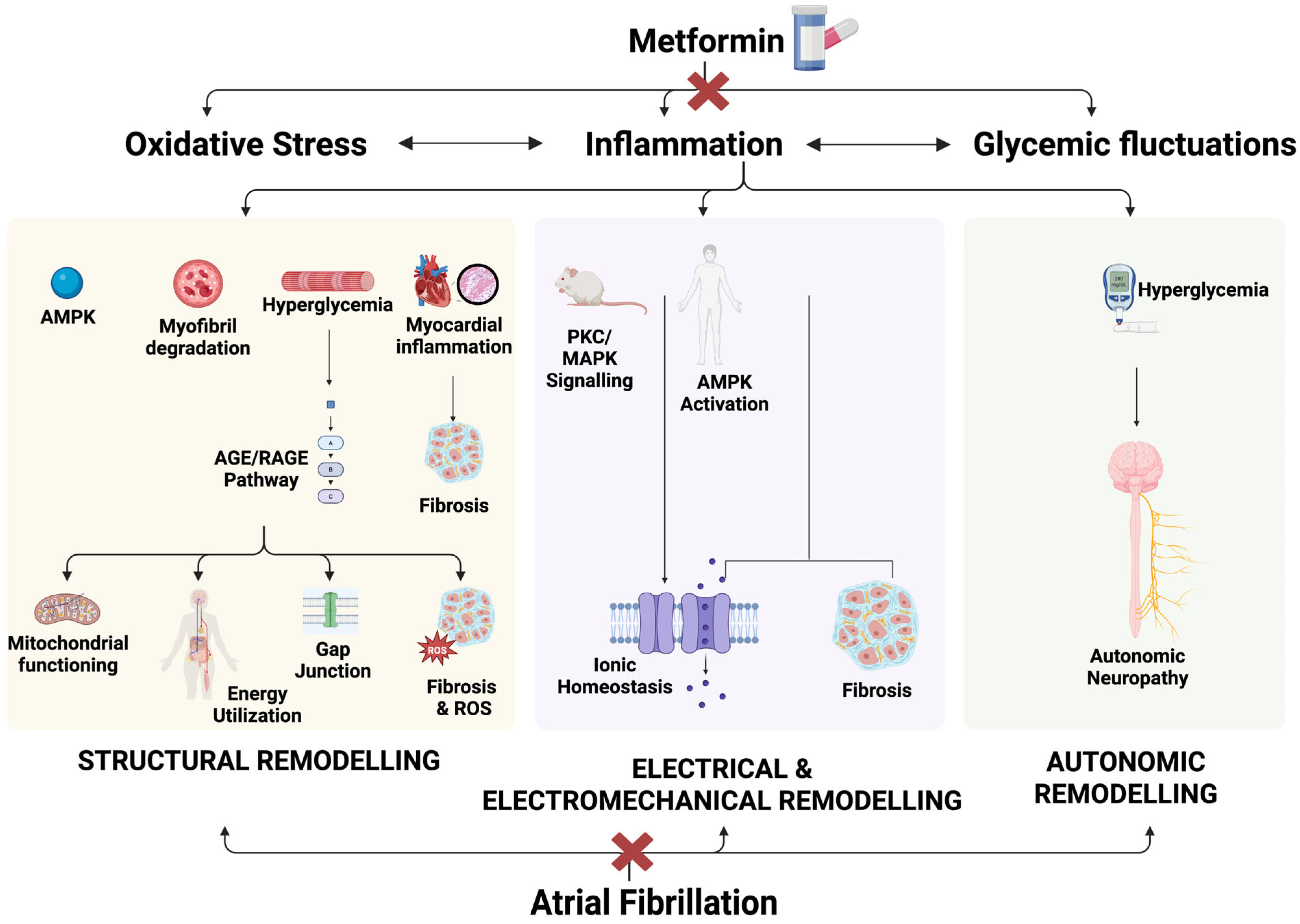
4.2. Pathophysiology of Development of Atrial Fibrillation in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
4.3. Association of Metformin Against New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
4.4. Sensitivity and Meta-Regression Analyses
4.5. Strengths and Limitations
4.6. Clinical Implications
4.7. Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AF | Atrial Fibrillation |
| T2DM | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus |
| CMA | Comprehensive Meta-Analysis |
| HR | Hazard Ratio |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| OSF | Open Science Framework |
| MeSH | Medical Subject Headings |
| CS | Cross-Sectional (study design) |
| CC | Case–Control (study design) |
| CKD | Chronic Kidney Disease |
| HTN | Hypertension |
| HF | Heart Failure |
| RC | Retrospective Cohort (study design) |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| USA | United States of America |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| TGF-β | Transforming Growth Factor-beta |
| AGEs | Advanced Glycation End products |
| SCN5A | Sodium Channel (gene/protein) |
| AMPK | AMP-activated Protein Kinase |
| PPARα | Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Alpha |
| CPT-1 | Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase 1 |
| VLCAD | Very-long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase |
| PKC | Protein Kinase C |
| ERK | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| SK | Small-conductance Calcium-activated Potassium (channel) |
| MAPK | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase |
References
- Joglar, J.A.; Chung, M.K.; Armbruster, A.L.; Benjamin, E.J.; Chyou, J.Y.; Cronin, E.M.; Deswal, A.; Eckhardt, L.L.; Goldberger, Z.D.; Gopinathannair, R.; et al. 2023 ACC/AHA/ACCP/HRS Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Atrial Fibrillation: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2024, 149, e1–e156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colilla, S.; Crow, A.; Petkun, W.; Singer, D.E.; Simon, T.A.; Liu, X. Estimates of Current and Future Incidence and Prevalence of Atrial Fibrillation in the U.S. Adult Population. Am. J. Cardiol. 2013, 112, 1142–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Diabetes Statistics Report. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/php/data-research/index.html (accessed on 15 May 2024).
- Ostropolets, A.; Elias, P.A.; Reyes, M.V.; Wan, E.Y.; Pajvani, U.B.; Hripcsak, G.; Morrow, J.P. Metformin Is Associated with a Lower Risk of Atrial Fibrillation and Ventricular Arrhythmias Compared with Sulfonylureas: An Observational Study. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2021, 14, e009115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopoulou, M.; Theofilis, P.; Kordalis, A.; Papageorgiou, A.; Sagris, M.; Oikonomou, E.; Tousoulis, D. Diabetes Mellitus and Atrial Fibrillation-from Pathophysiology to Treatment. World J. Diabetes 2023, 14, 512–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.-H.; Wu, L.-S.; Chiou, M.-J.; Liu, J.-R.; Yu, K.-H.; Kuo, C.-F.; Wen, M.-S.; Chen, W.-J.; Yeh, Y.-H.; See, L.-C. Association of Metformin with Lower Atrial Fibrillation Risk among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Population-Based Dynamic Cohort and in Vitro Studies. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2014, 13, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Green, J.B.; Halperin, J.L.; Piccini, J.P. Atrial Fibrillation and Diabetes Mellitus. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, Y.-H.; Kuo, C.-T.; Chan, T.-H.; Chang, G.-J.; Qi, X.-Y.; Tsai, F.; Nattel, S.; Chen, W.-J. Transforming growth factor-β and oxidative stress mediate tachycardia-induced cellular remodelling in cultured atrial-derived myocytes. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 91, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calixto, M.C.; Lintomen, L.; André, D.M.; Leiria, L.O.; Ferreira, D.; Lellis-Santos, C.; Anhê, G.F.; Bordin, S.; Landgraf, R.G.; Antunes, E.; et al. Metformin Attenuates the Exacerbation of the Allergic Eosinophilic Inflammation in High-Fat-Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-F.; Young, K.-C.; Bai, C.-H.; Yu, B.-C.; Ma, C.-T.; Chien, Y.-C.; Su, H.-C.; Wang, H.-Y.; Liao, C.-S.; Lai, H.-W.; et al. Blockade of reactive oxygen species and Akt activation is critical for anti-inflammation and growth inhibition of metformin in phosphatase and tensin homolog-deficient RAW264.7 cells. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2013, 35, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, Z.K.; Refaat, R.; Selima, E.; Sarha, A.E.; Ismail, M.A. The combined effect of metformin and l-cysteine on inflammation, oxidative stress and insulin resistance in streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetes in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 714, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.S.; Bang, B.-R.; Kwon, H.-S.; Moon, K.-A.; Kim, T.-B.; Lee, K.-Y.; Moon, H.-B.; Cho, Y.S. Metformin reduces airway inflammation and remodeling via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 84, 1660–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klempfner, R.; Leor, J.; Tenenbaum, A.; Fisman, E.Z.; Goldenberg, I. Effects of a vildagliptin/metformin combination on markers of atherosclerosis, thrombosis, and inflammation in diabetic patients with coronary artery disease. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2012, 11, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Effect of intensive blood-glucose control with metformin on complications in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 34). Lancet 1998, 352, 854–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lai, S.; Lv, A.; Su, Q.; Dong, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Tang, W.; Zhao, J.; Cui, L.; et al. Effects of Metformin Versus Glipizide on Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and Coronary Artery Disease. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 1304–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruthur, N.M.; Tseng, E.; Hutfless, S.; Wilson, L.M.; Suarez-Cuervo, C.; Berger, Z.; Chu, Y.; Iyoha, E.; Segal, J.B.; Bolen, S. Diabetes Medications as Monotherapy or Metformin-Based Combination Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2016, 164, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrie, J.R.; Chaturvedi, N.; Ford, I.; Brouwers, M.C.G.J.; Greenlaw, N.; Tillin, T.; Hramiak, I.; Hughes, A.D.; Jenkins, A.J.; Klein, B.E.K.; et al. Cardiovascular and metabolic effects of metformin in patients with type 1 diabetes (REMOVAL): A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017, 5, 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, S.; Ferrell, W.; Greer, I.A.; Petrie, J.R.; Cobbe, S.M.; Sattar, N. Effects of Metformin on Microvascular Function and Exercise Tolerance in Women With Angina and Normal Coronary Arteries. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 48, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuinness, L.A.; Higgins, J.P.T. Risk-of-bias VISualization (robvis): An R package and Shiny web app for visualizing risk-of-bias assessments. Res. Synth. Methods 2021, 12, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borenstein, M.; Hedges, L.; Higgins, J.; Rothstein, H. Comprehensive Meta-Analysis (Version 3); Biostat, Inc.: Englewood, NJ, USA. Available online: https://www.meta-analysis.com/ (accessed on 18 May 2025).
- Guo, T.S.; Zhao, C.Y.; Chen, T.; Tang, M.Y.; Ning, Y.Y.; Wang, D.L.; Yuan, Z.Y.; Li, G. The effect of metformin use on the risk of atrial fibrillation in patients with type 2 diabetes: Data from the UK biobank. Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45 (Suppl. 1), ehae666.3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, B.; Min, C.; Cho, W.; Yon, D.K.; Kim, J.Y.; Han, K.-D.; Rhee, E.-J.; Lee, W.-Y.; et al. Association between antidiabetic drugs and the incidence of atrial fibrillation in patients with type 2 diabetes: A nationwide cohort study in South Korea. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 198, 110626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; Tekin, Z.; Kattan, M.W.; Ji, X.; Milinovich, A.; Pantalone, K.M.; Zimmerman, R.S.; Chung, M.K.; Kashyap, S.R. Association between first-line monotherapy with metformin and the risk of atrial fibrillation (AMRAF) in patients with type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2022, 36, 108315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, C.H. Metformin Use Is Associated with a Lower Incidence of Hospitalization for Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Med. 2021, 7, 592901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Bai, J.; Qu, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Hao, H.; Qiao, S.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Si, J.; et al. Metformin reduces new-onset atrial fibrillation risk rather than atrial fibrillation burden in type 2 diabetes patients: A case-control study. Heliyon 2024, 10, e30992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.J.; Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Gong, G.; Liu, X.; Guan, H. Global burden of type 2 diabetes mellitus from 1990 to 2021, with projections of prevalence to 2044: A systematic analysis across SDI levels for the global burden of disease study 2021. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1501690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlrogge, A.H.; Brederecke, J.; Schnabel, R.B. Global Burden of Atrial Fibrillation and Flutter by National Income: Results From the Global Burden of Disease 2019 Database. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2023, 12, e030438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liou, Y.S.; Yang, F.Y.; Chen, H.Y.; Jong, G.P. Antihyperglycemic drugs use and new-onset atrial fibrillation: A population-based nested case control study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, I.; Frangogiannis, N.G. Diabetes-associated cardiac fibrosis: Cellular effectors, molecular mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2016, 90, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Fu, H.; Li, J.; Yang, W.; Cheng, L.; Liu, T.; Li, G. Hyperglycemia aggravates atrial interstitial fibrosis, ionic remodeling and vulnerability to atrial fibrillation in diabetic rabbits. Anatol. J. Cardiol. 2012, 12, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Yamashita, T.; Sekiguchi, A.; Tsuneda, T.; Sagara, K.; Takamura, M.; Kaneko, S.; Aizawa, T.; Fu, L. AGEs-RAGE system mediates atrial structural remodeling in the diabetic rat. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2008, 19, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Whaley-Connell, A.; Sowers, J.R. Diabetic cardiomyopathy: A hyperglycaemia- and insulin-resistance-induced heart disease. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Fanous, K.I.; Marei, I.; Ding, H.; Ladjimi, M.; MacDonald, R.; Hollenberg, M.D.; Anderson, T.J.; Hill, M.; Triggle, C.R. Repurposing Metformin for the Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation: Current Insights. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2024, 20, 255–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, T.-F.; Suenari, K.; Chang, S.-L.; Lin, Y.-J.; Lo, L.-W.; Hu, Y.-F.; Tuan, T.-C.; Tai, C.-T.; Tsao, H.-M.; Li, C.-H.; et al. Atrial substrate properties and outcome of catheter ablation in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation associated with diabetes mellitus or impaired fasting glucose. Am. J. Cardiol. 2010, 106, 1615–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, H.; Liu, C.; Li, J.; Zhou, C.; Cheng, L.; Liu, T.; Li, G. Impaired atrial electromechanical function and atrial fibrillation promotion in alloxan-induced diabetic rabbits. Cardiol. J. 2013, 20, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayhan, S.; Ozturk, S.; Alcelik, A.; Ozlu, M.F.; Erdem, A.; Memioglu, T.; Ozdemir, M.; Yazici, M. Atrial conduction time and atrial mechanical function in patients with impaired fasting glucose. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2012, 35, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuehl, M.; Stevens, M.J. Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathies as complications of diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2012, 8, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otake, H.; Suzuki, H.; Honda, T.; Maruyama, Y. Influences of autonomic nervous system on atrial arrhythmogenic substrates and the incidence of atrial fibrillation in diabetic heart. Int. Heart J. 2009, 50, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulian, A.; Cancello, R.; Girola, A.; Gilardini, L.; Alberti, L.; Croci, M.; Micheletto, G.; Danelli, P.; Invitti, C. In vitro and in vivo Effects of Metformin on Human Adipose Tissue Adiponectin. Obes. Facts 2011, 4, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turi, V.-R.; Luca, C.T.; Gaita, D.; Iurciuc, S.; Petre, I.; Iurciuc, M.; Horvath, T.; Cozma, D. Diagnosing Arterial Stiffness in Pregnancy and Its Implications in the Cardio-Renal-Metabolic Chain. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.V.; Scherer, P.E. Adiponectin, the past two decades. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 8, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marfella, R.; Amarelli, C.; Cacciatore, F.; Balestrieri, M.L.; Mansueto, G.; D’oNofrio, N.; Esposito, S.; Mattucci, I.; Salerno, G.; De Feo, M.; et al. Lipid Accumulation in Hearts Transplanted From Nondiabetic Donors to Diabetic Recipients. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 1249–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Ye, S.; Scalzo, R.L.; Reusch, J.E.B.; Greyson, C.R.; Schwartz, G.G. Metformin prevents ischaemic ventricular fibrillation in metabolically normal pigs. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1550–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, F.; Liu, Y.; Tu, T.; Li, B.; Xiao, Y.; Ma, Y.; Qin, F.; Xie, J.; Zhou, S.; Liu, Q. Metformin regulates lipid metabolism in a canine model of atrial fibrillation through AMPK/PPAR-α/VLCAD pathway. Lipids Health Dis. 2019, 18, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.H.; Hua, N.; Fu, X.; Pan, Y.L.; Li, B.; Li, X.D. Metformin regulates atrial SK2 and SK3 expression through inhibiting the PKC/ERK signaling pathway in type 2 diabetic rats. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2018, 18, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlá, A.K.; Lobato, N.S.; Fortes, Z.B.; Oigman, W.; Neves, M.F. Cardiac fibrosis and vascular remodeling are attenuated by metformin in obese rats. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 165, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Seufert, J.; Lübben, G.; Dietrich, K.; Bates, P.C. A comparison of the effects of thiazolidinediones and metformin on metabolic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin. Ther. 2004, 26, 805–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 9. Pharmacologic Approaches to Glycemic Treatment: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2025. Diabetes Care 2025, 48 (Suppl. 1), S181–S206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurren, K.M.; Dunham, M.W. Are thiazolidinediones a preferred drug treatment for type 2 diabetes? Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2021, 22, 131–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesto, R.W.; Bell, D.; Bonow, R.O.; Fonseca, V.; Grundy, S.M.; Horton, E.S.; Le Winter, M.; Porte, D.; Semenkovich, C.F.; Smith, S.; et al. Thiazolidinedione use, fluid retention, and congestive heart failure: A consensus statement from the American Heart Association and American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, S.V.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Echouffo-Tcheugui, J.B.; Tang, F.; Lam, C.S.; Sperling, L.S.; Kosiborod, M. Understanding Contemporary Use of Thiazolidinediones. Circ. Heart Fail. 2019, 12, e005855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, J.C.; Mao, C.; Zhou, Y.; Gore-Panter, S.R.; Rennison, J.H.; Lovano, B.S.; Castel, L.; Shin, J.; Gillinov, A.M.; Smith, J.D.; et al. Transcriptomics-based network medicine approach identifies metformin as a repurposable drug for atrial fibrillation. Cell Rep. Med. 2022, 3, 100749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Author | Study Design | Country | Type | Size | Age, in Years (Mean ± SD) | Female n (%) | Duration, in Years | Co-Morbidities | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alcohol n (%) | Smoking n (%) | HTN n (%) | HF n (%) | Stroke n (%) | CKD n (%) | ||||||||
| Gou et al., 2024 [22] | CS | UK | M | 10,011 | - | - | Until 2023 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Zhong et al., 2024 [26] | CC | China | S | 227 | 74.87 ± 9.2 | 93 (40.97%) | 4 | 24 (10.5) | 42 (18.5) | 169 (74) | 33 (14.5) | 35 (15.4) | 53 (23.3) |
| Kim et al., 2023 [23] | RC | South Korea | M | 2,515,468 | 57.28 ± 11.72 | 1,000,904 (39.79%) | 9 | 252,222 (10) | 658,980 (26.2) | 1,414,087 (56.2) | 34,009 (1.35) | 111,906 (4.45) | 283,816 (11.3) |
| Iqbal et al., 2022 [24] | RC | USA | S | 5664 | 61.39 ± 3.39 | 3311 (58.45%) | 10 | 662 (11.7) | 649 (11.5) | 3530 (62.3%) | 107 (1.89) | 197 (3.5) | 19 (0.34) |
| Ostropolets et al., 2021 [4] | RC | USA | M | 645,785 | NR | 325,504 (48.9%) | 2.7 | NR | NR | 133,221 (70) | 8875 (4.67) | NR | 18,542 (9.75) |
| Tseng 2020 [25] | RC | Taiwan | M | 195,064 | 64.73 ± 12.21 | 91,702 (47.0%) | 5 | 12,849 (6.6) | 6946 (3.5) | 163,385 (83.8) | NR | 104,965 (53.8) | NR |
| Chang et al., 2014 [6] | RC | Taiwan | M | 645,710 | 58.6 ± 17.1 | 93,014 (50.4%) | 5.4 | NR | NR | 82,081 (58) | 12,563 (8.9) | 14,557 (10.3) | 25,237 (17.9) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vempati, R.; Damarlapally, N.; Roy, P.; Mylavarapu, M.; Vasudevan, S.S.; Reguram, R.; Vora, T.; Jain, H.; Ahmed, R.; Krishnamoorthy, G. Metformin and Risk of New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation in Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2288. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15182288
Vempati R, Damarlapally N, Roy P, Mylavarapu M, Vasudevan SS, Reguram R, Vora T, Jain H, Ahmed R, Krishnamoorthy G. Metformin and Risk of New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation in Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(18):2288. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15182288
Chicago/Turabian StyleVempati, Roopeessh, Nanush Damarlapally, Poulami Roy, Maneeth Mylavarapu, Srivatsa Surya Vasudevan, Reshma Reguram, Tanisha Vora, Hritvik Jain, Raheel Ahmed, and Geetha Krishnamoorthy. 2025. "Metformin and Risk of New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation in Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Diagnostics 15, no. 18: 2288. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15182288
APA StyleVempati, R., Damarlapally, N., Roy, P., Mylavarapu, M., Vasudevan, S. S., Reguram, R., Vora, T., Jain, H., Ahmed, R., & Krishnamoorthy, G. (2025). Metformin and Risk of New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation in Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics, 15(18), 2288. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15182288






