Quantitative Characterization of Corneal Collagen Architecture Using Intensity Gradient Modeling and Gaussian PDF Fitting
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Corneal Structure
1.2. Imaging the Cornea
1.3. Quantitative Analysis of the Corneal Images and Limitations
1.4. Purpose and Scope of the Work
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. SHG Microscope and Image Acquisition
2.2. Corneal Samples
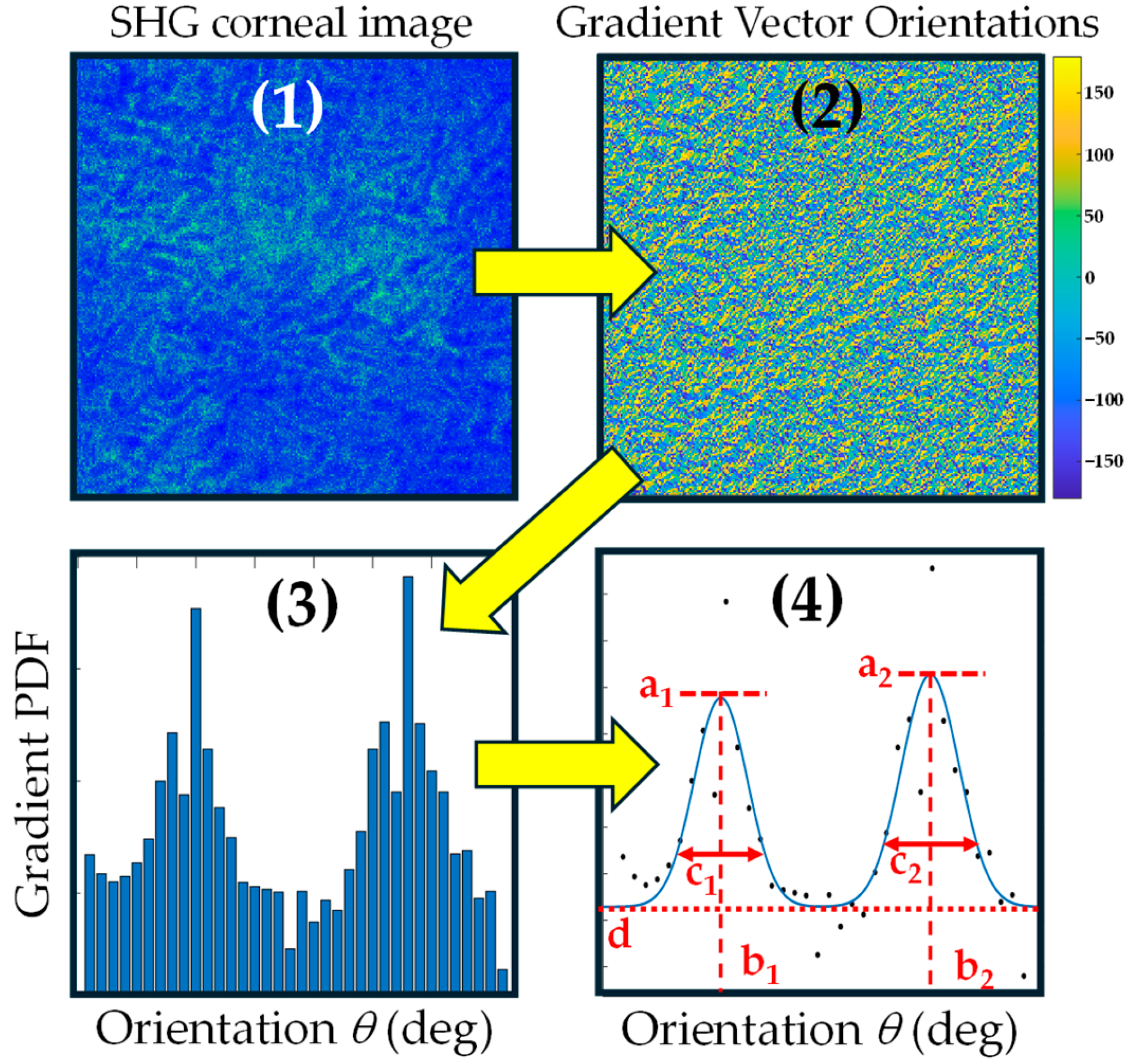
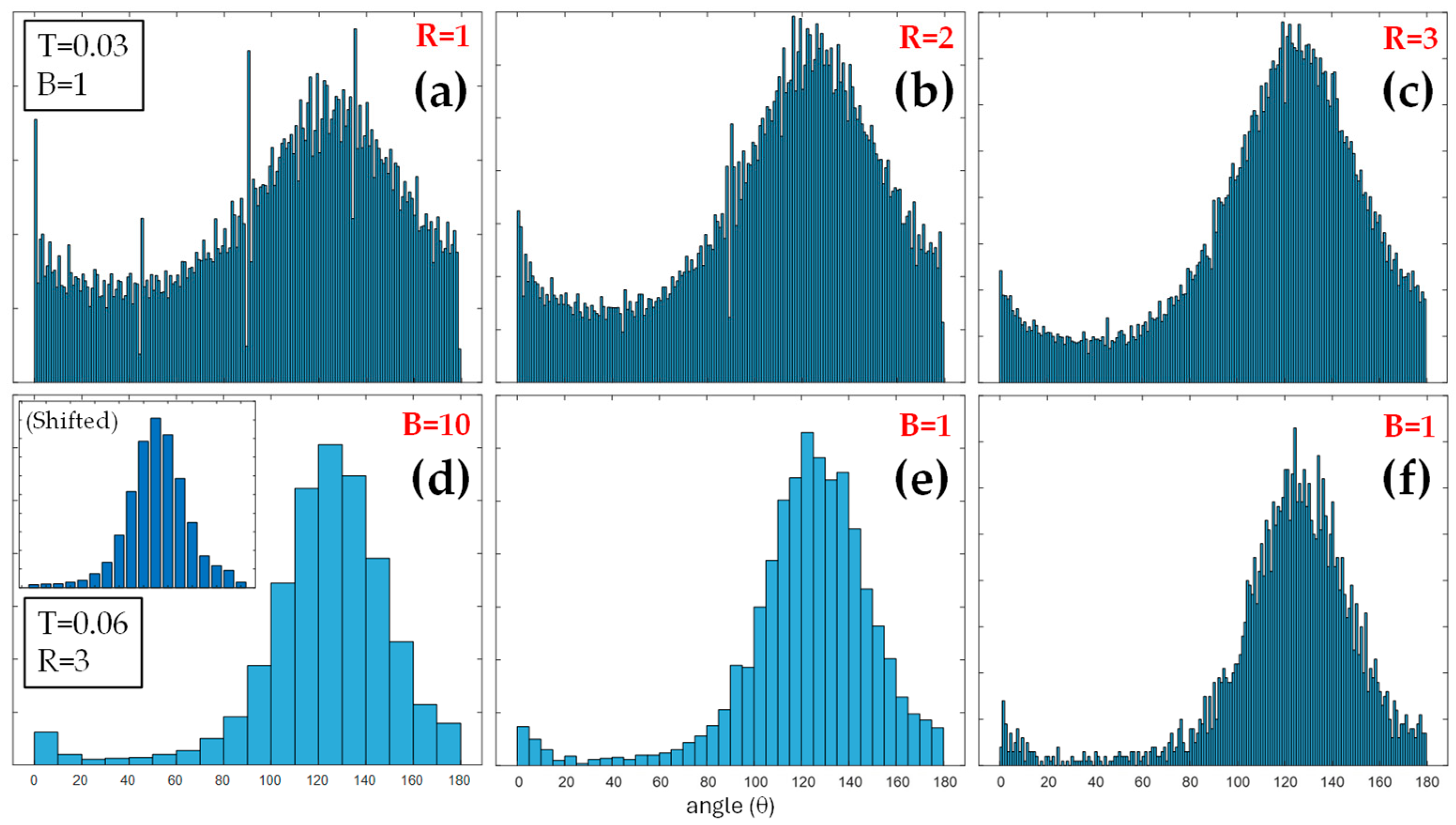
2.3. Algorithm and Method of Analysis
3. Results
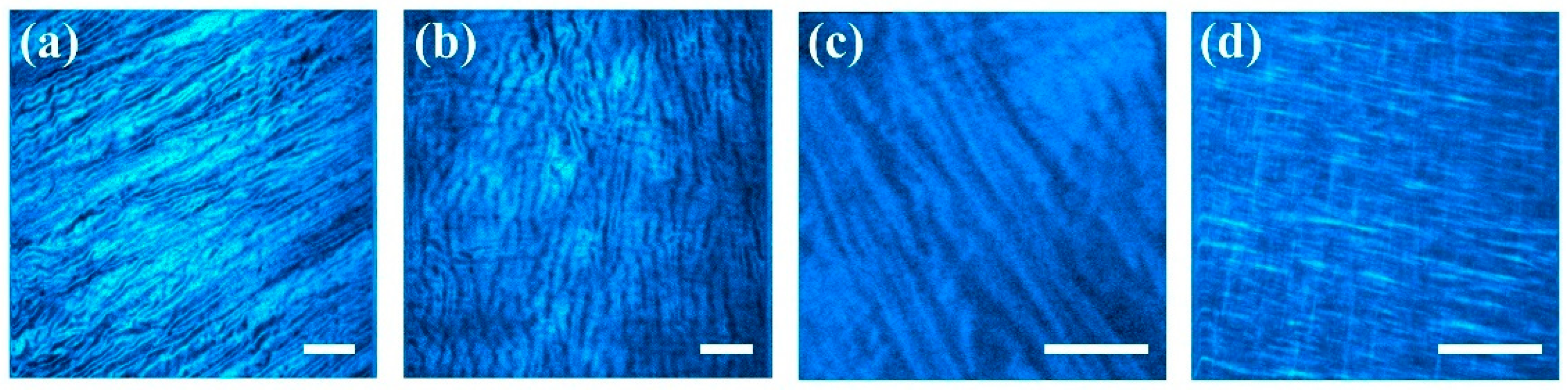
3.1. Corneal Images and Algorithm Parameters Optimization
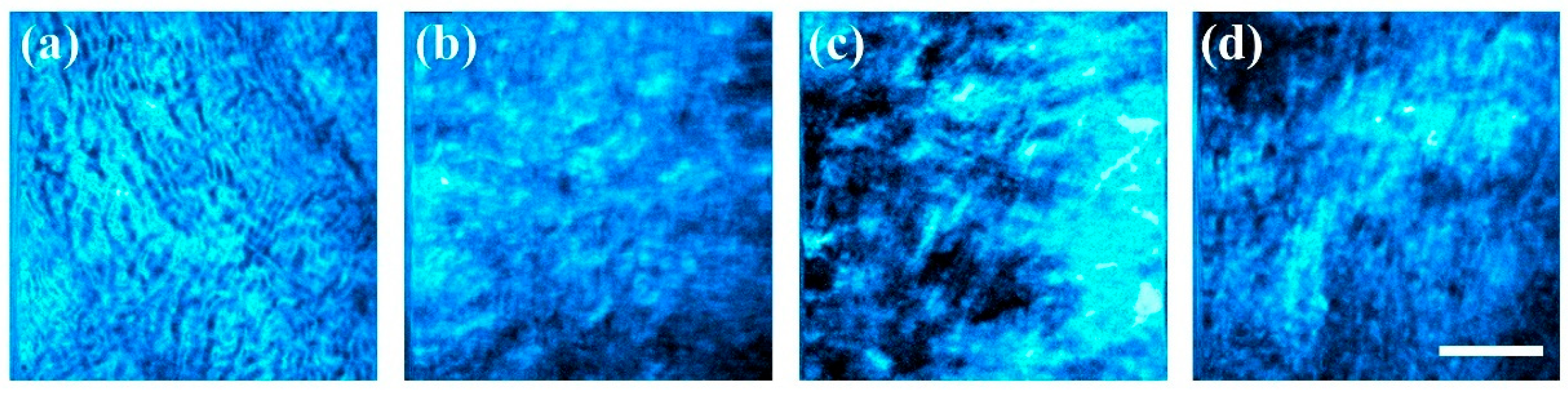
3.2. Comparison of Collagen Distribution Across Species
3.3. Cornea Healing in a Rabbit Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meek, K.M.; Knupp, C. Corneal structure and transparency. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2015, 49, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurice, D.M. The structure and transparency of the cornea. J. Physiol. 1957, 77, 371–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komai, Y.; Ushiki, T. The three-dimensional organization of collagen fibrils in the human cornea and sclera. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1991, 32, 2244–2258. [Google Scholar]
- Winkler, M.; Shoa, G.; Xie, Y.; Petsche, S.J.; Pinsky, P.M.; Juhasz, T.; Brown, D.J.; Jester, J.V. Three-Dimensional Distribution of Transverse Collagen Fibers in the Anterior Human Corneal Stroma. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 7293–7301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, L.J.; Pels, E.; Vrensen, G.F. The specific architecture of the anterior stroma accounts for maintenance of corneal curvature. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2001, 85, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishige, N.; Petroll, M.W.; Nishida, T.; Kenney, C.M.; Jester, J.V. Noninvasive corneal stromal collagen imaging using two-photon-generated second-harmonic signals. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2006, 32, 1784–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mega, Y.; Robitaille, M.; Zareian, R.; McLean, J.; Ruberti, J.; DiMarzio, C. Quantification of lamellar orientation in corneal collagen using second harmonic generation images. Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 3312–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinowitz, Y.S. Keratoconus. Surv. Ophthalmol. 1998, 42, 297–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, S.; Morgan, S.R.; Meek, K.M. Keratoconus: Cross-linking the window of the eye. Ther. Adv. Rare Dis. 2021, 2, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollensak, G.; Spoerl, E.; Seiler, T. Riboflavin/ultraviolet-a–induced collagen crosslinking for the treatment of keratoconus. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2003, 135, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporossi, A.; Mazzotta, C.; Baiocchi, S.; Caporossi, T. Long-term results of riboflavin ultraviolet a corneal collagen cross-linking for keratoconus in Italy: The Siena eye cross study. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2010, 149, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlhaas, M.; Spoerl, E.; Schilde, T.; Unger, G.; Wittig, C.; Pillunat, L.E. Biomechanical evidence of the distribution of cross-links in corneas treated with riboflavin and ultraviolet A light. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2006, 32, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, A.T.; Nassif, N.; Zoumi, A.; Tromberg, B.J. Selective corneal imaging using combined second-harmonic generation and two-photon excited fluorescence. Opt. Lett. 2002, 27, 2082–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, J.M.; Gualda, E.J.; Artal, P. Analysis of corneal stroma organization with wavefront optimized nonlinear microscopy. Cornea 2011, 30, 692–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latour, G.; Gusachenko, I.; Kowalczuk, L.; Lamarre, I.; Schanne-Klein, M.-C. In vivo structural imaging of the cornea by polarization-resolved second harmonic microscopy. Biomed. Opt. Express 2012, 3, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila, F.J.; Gambín, A.; Artal, P.; Bueno, J.M. In vivo two-photon microscopy of the human eye. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, A.; Guimarães, P.; Domingues, J.P.; Quadrado, M.J.; Morgado, A.M. Two-Photon Imaging for Non-Invasive Corneal Examination. Sensors 2022, 22, 9699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, A.; Breunig, H.G.; König, A.; Schindele, A.; Hager, T.; Seitz, B.; König, K. High-resolution, label-free two-photon imaging of diseased human corneas. J. Biomed. Opt. 2018, 23, 036002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, A.; Breunig, H.G.; König, A.; Schindele, A.; Hager, T.; Seitz, B.; Morgado, A.M.; König, K. Assessment of human corneas prior to transplantation using high-resolution two-photon imaging. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2018, 59, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila, F.J.; Artal, P.; Bueno, J.M. Quantitative discrimination of healthy and diseased corneas with second harmonic generation microscopy. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2019, 83, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, J.M.; Ávila, F.J.; Lorenzo-Martín, E.; Gallego-Muñoz, P.; Martínez-García, C.M. Assessment of the corneal collagen organization after chemical burn using second harmonic generation microscopy. Biomed. Opt. Express 2021, 12, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Nadiarynkh, O.; Plotnikov, S.; Campagnola, P.J. Second harmonic generation microscopy for quantitative analysis of collagen fibrillar structure. Nat Protoc. 2012, 7, 654–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.Y.; Lee, J.K.; Chuck, R.S. Second Harmonic Generation Imaging Analysis of Collagen Arrangement in Human Cornea. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 5622–5629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, J.M.; Ávila, F.J.; Artal, P. Second harmonic generation microscopy: A tool for quantitative analysis of tissues. In Microscopy and Analysis; Stanciu, S.G., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aptel, F.; Olivier, N.; Deniset-Besseau, A.; Legeais, J.-M.; Plamann, K.; Schanne-Klein, M.-C.; Beaurepaire, E. Multimodal nonlinear imaging of the human cornea. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 2459–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredfeldt, J.S.; Liu, Y.; Pehlke, C.A.; Conklin, M.W.; Szulczewski, J.M.; Inman, D.R.; Keely, P.J.; Nowak, R.D.; Mackie, T.R.; Eliceiri, K.W. Computational segmentation of collagen fibers from second-harmonic generation images of breast cancer. J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 19, 016007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.A.R.; Mehta, M.R.; Toussaint, K.C. Fourier transform-second-harmonic generation imaging of biological tissues. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 14534–14542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazaryan, A.; Tsai, H.F.; Hayrapetyan, G.; Chen, W.-L.; Chen, Y.-F.; Jeong, M.Y.; Kim, C.-S.; Chen, S.-J.; Dong, C.-Y. Analysis of collagen fiber domain organization by Fourier second harmonic generation microscopy. J. Biomed. Opt. 2013, 18, 31105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, J.M.; Palacios, R.; Chessey, M.K.; Ginis, H. Analysis of spatial lamellar distribution from adaptive-optics second harmonic generation corneal images. Biomed. Opt. Express 2013, 4, 1006–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.-Y.; Chang, Y.-L.; Lo, W.; Hsueh, C.-M.; Chen, W.-L.; Ghazaryan, A.A.; Hu, P.-S.; Young, T.-H.; Chen, S.-J.; Dong, C.-Y. Characterizing the morphologic changes in collagen crosslinked–treated corneas by Fourier transform–second harmonic generation imaging. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2013, 39, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, M.; Merino, D.; Loza-Alvarez, P.; Lombardo, G. Translational label-free nonlinear imaging biomarkers to classify the human corneal microstructure. Biomed. Opt. Express 2015, 6, 2803–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila, F.J.; Bueno, J.M. Analysis and quantification of collagen organization with the structure tensor in second harmonic microscopy images of ocular tissues. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 9848–9854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, J.M.; Ávila, F.J.; Martínez-García, M.C. Quantitative analysis of the corneal collagen distribution after in vivo crosslinking with second harmonic microscopy. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 3860498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, J.M.; Martínez-Ojeda, R.M.; Fernández, E.J.; Feldkaemper, M. Quantitative structural organization of the sclera in chicks after deprivation myopia measured with second harmonic generation microscopy. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1462024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, J.M.; Martínez-Ojeda, R.M.; Yago, I.; Ávila, F.J. Collagen organization, polarization sensitivity and image quality in human corneas using second harmonic generation microscopy. Photonics 2022, 9, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teulon, C.; Gusachenko, I.; Latour, G.; Schanne-Klein, M.C. Theoretical, numerical and experimental study of geometrical parameters that affect anisotropy measurements in polarization-resolved SHG microscopy. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 2666–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila, F.; del Barco, O.; Bueno, J.M. Polarization response of second-harmonic images for different collagen spatial distributions. J. Biomed. Opt. 2016, 21, 066015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanciu, S.G.; Ávila, F.J.; Hristu, R.; Bueno, J.M. A Study on image quality in polarization-resolved second harmonic generation microscopy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejim, Z.; Navarro, L.; Morin, C.; Badel, P. Quantitative analysis of second harmonic generated images of collagen fibers: A review. Res. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 39, 273–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altendorf, H.; Decencière, E.; Jeulin, D.; Peixoto, P.D.S.; Deniset-Besseau, A.; Angelini, E.; Mosser, G.; Schanne-Klein, M.-C. Imaging and 3D morphological analysis of collagen fibrils. J. Microsc. 2012, 247, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Fehrenbach, J.; Desmaison, A.; Lobjois, V.; Ducommun, B.; Weiss, P. Structure Tensor Based Analysis of Cells and Nuclei Organization in Tissues. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilbury, K.; Han, X.; Brooks, P.C.; Khalil, A. Multiscale anisotropy analysis of second-harmonic generation collagen imaging of mouse skin. J. Biomed. Opt. 2021, 26, 065002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.L.; Brewer, M.A.; Nadiarnykh, O.; Hocker, J.; Singh, V.; Mackie, T.R.; Campagnola, P.J. Texture analysis applied to second harmonic generation image data for ovarian cancer classification. J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 19, 096007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Li, H.; Wang, C.; Gou, S.; Fu, L. Characterization of collagen fibers by means of texture analysis of second harmonic generation images using orientation-dependent gray level co-occurrence matrix method. J. Biomed. Opt. 2012, 17, 026007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrill, E.E.; Tulepbergenov, A.N.; Stender, C.J.; Lamichhane, R.; Brown, R.J.; Lujan, T.J. A validated software application to measure fiber organization in soft tissue. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2016, 15, 1467–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurrala, R.; Byrne, C.E.; Brown, L.M.; Tiongco, R.F.P.; Matossian, M.D.; Savoie, J.J.; Collins-Burow, B.M.; Burow, M.E.; Martin, E.C.; Lau, F.H. Quantifying breast cancer-driven fiber alignment and collagen deposition in primary human breast tissue. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 618448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredfeldt, J.S.; Liu, Y.; Conklin, M.W.; Keely, P.J.; Mackie, T.R.; Eliceiri, K.W. Automated quantification of aligned collagen for human breast carcinoma prognosis. J. Pathol. Inform. 2014, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiddy, M.A. The radon transform and some of its applications. Opt. Acta Int. J. Opt. 1985, 32, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaub, N.J.; Kirkpatrick, S.J.; Gilbert, R.J. Automated methods to determine electrospun fiber alignment and diameter using the Radon transform. BioNanoScience 2013, 3, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, J.-B.; Pan, J.-S. Feature point matching based on distinct wavelength phase congruency and log-Gabor filters in infrared and visible images. Sensors 2019, 19, 4244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, P.; Morgado, M.; Batista, A. On the quantitative analysis of lamellar collagen arrangement with second-harmonic generation imaging. Biomed. Opt. Express 2024, 15, 2666–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorsetz, M.; Artal, P.; Bueno, J.M. Performance evaluation of a sensorless adaptive optics multiphoton microscope. J. Microsc. 2016, 261, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayala, A.; Orenes-Miñana, G.; Standret, I.; Bueno, J.M.; Fernandez, E.J. Automatic Characterization of Morphological Structures and Their Orientation in Biomedical Images. In Libro de Resúmenes, XIV Reunión Nacional de Óptica, Murcia, Spain, 3–5 July 2024; Bueno García, J.M., Ed.; Sociedad Española de Óptica: Madrid, Spain, 2024; pp. 280–281. ISBN 978-84-09-66738-3. [Google Scholar]
- Anton, S.R.; Martínez-Ojeda, R.M.; Hristu, R.; Stanciu, G.A.; Toma, A.; Banica, C.K.; Fernández, E.J.; Huttunen, M.J.; Bueno, J.M.; Stanciu, S.G. Automated Detection of Corneal Edema with Deep Learning-Assisted Second Harmonic Generation Microscopy. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2023, 29, 7201010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


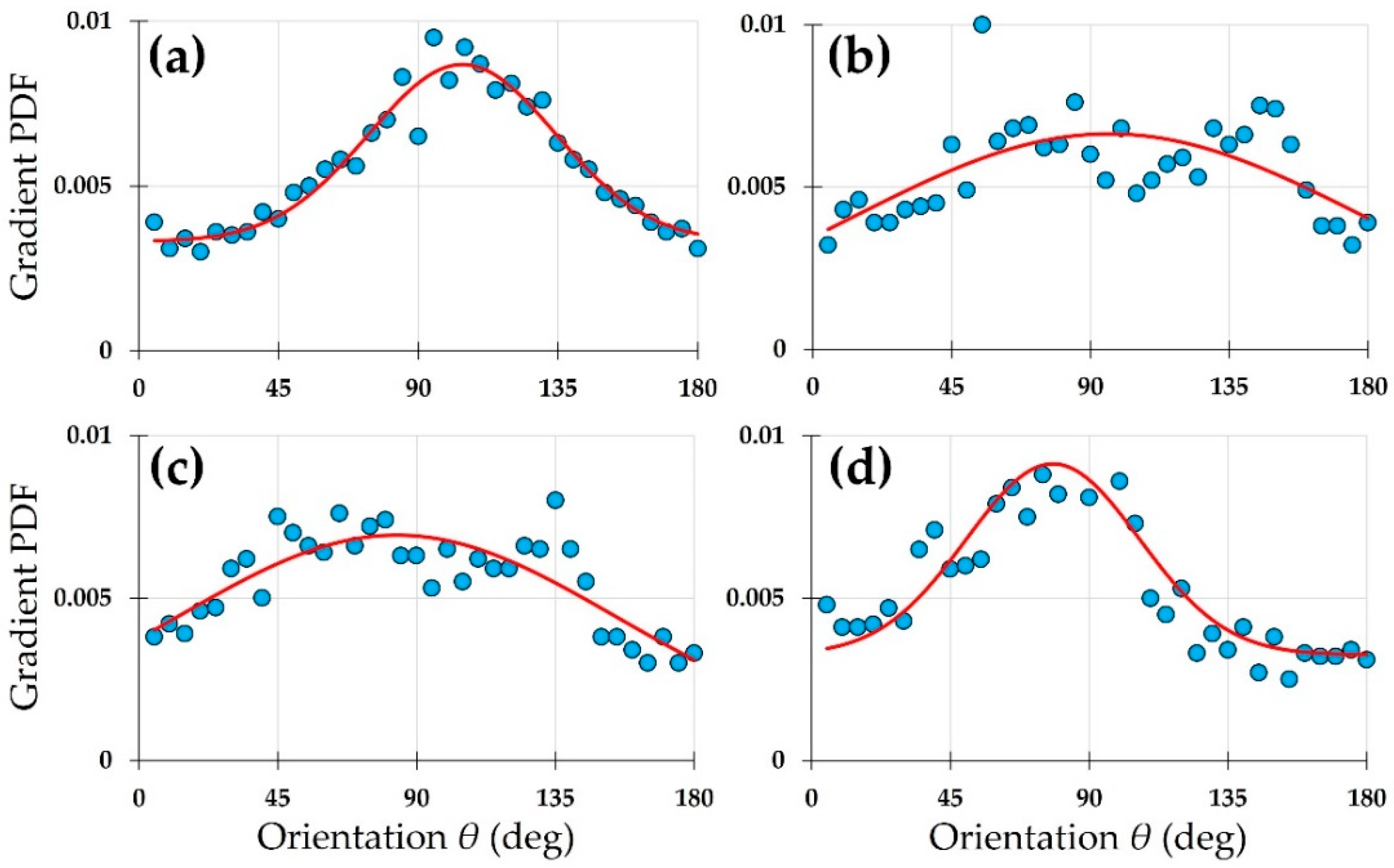
| SHG Image | a1 | b1 | c1 | a2 | b2 | c2 | d | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | 0.0108 | 98.2 | 25.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0018 | 0.99 |
| (b) | 0.0019 | 7.6 | 10.9 | 0.0045 | 110.9 | 25.5 | 0.0038 | 0.68 |
| (c) | 0.0029 | 85.4 | 37.3 | 0.0013 | 171.3 | 27.1 | 0.0037 | 0.78 |
| (d) | 0.0069 | 72.2 | 29.1 | 0.0008 | 170.0 | 5.2 | 0.0027 | 0.93 |
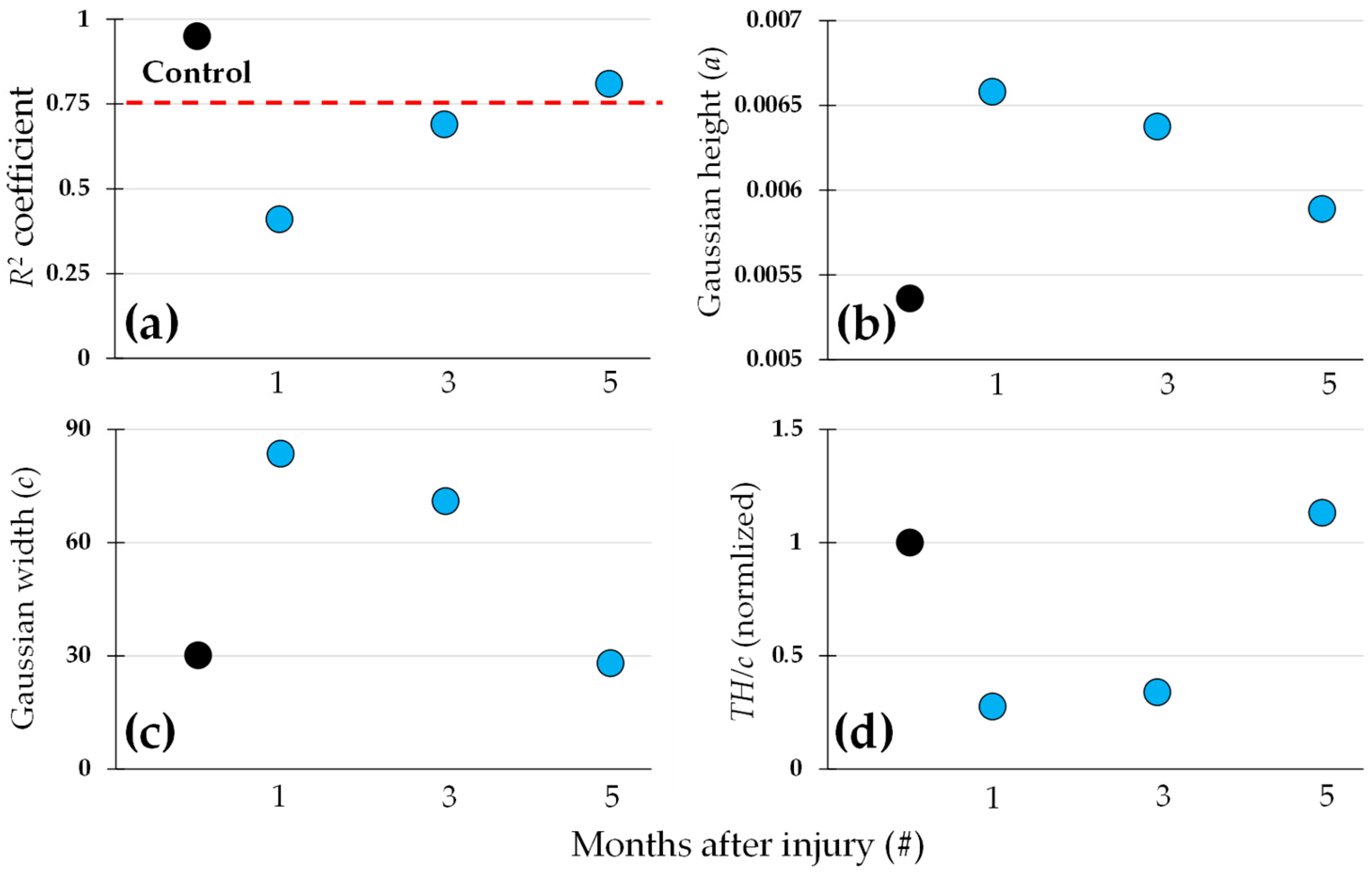
| a | b | c | d | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 0.0054 | 104.1 | 30.1 | 0.0033 | 0.95 |
| 1 month | 0.0066 | 96.1 | 83.6 | 0.0001 | 0.41 |
| 3 months | 0.0064 | 83.5 | 71.0 | 0.0006 | 0.69 |
| 5 months | 0.0059 | 78.2 | 28.0 | 0.0033 | 0.81 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernandez, E.J.; Bueno, J.M. Quantitative Characterization of Corneal Collagen Architecture Using Intensity Gradient Modeling and Gaussian PDF Fitting. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1738. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15141738
Fernandez EJ, Bueno JM. Quantitative Characterization of Corneal Collagen Architecture Using Intensity Gradient Modeling and Gaussian PDF Fitting. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(14):1738. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15141738
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernandez, Enrique J., and Juan M. Bueno. 2025. "Quantitative Characterization of Corneal Collagen Architecture Using Intensity Gradient Modeling and Gaussian PDF Fitting" Diagnostics 15, no. 14: 1738. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15141738
APA StyleFernandez, E. J., & Bueno, J. M. (2025). Quantitative Characterization of Corneal Collagen Architecture Using Intensity Gradient Modeling and Gaussian PDF Fitting. Diagnostics, 15(14), 1738. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15141738







