Performance Evaluation of Four Deep Learning-Based CAD Systems and Manual Reading for Pulmonary Nodules Detection, Volume Measurement, and Lung-RADS Classification Under Varying Radiation Doses and Reconstruction Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
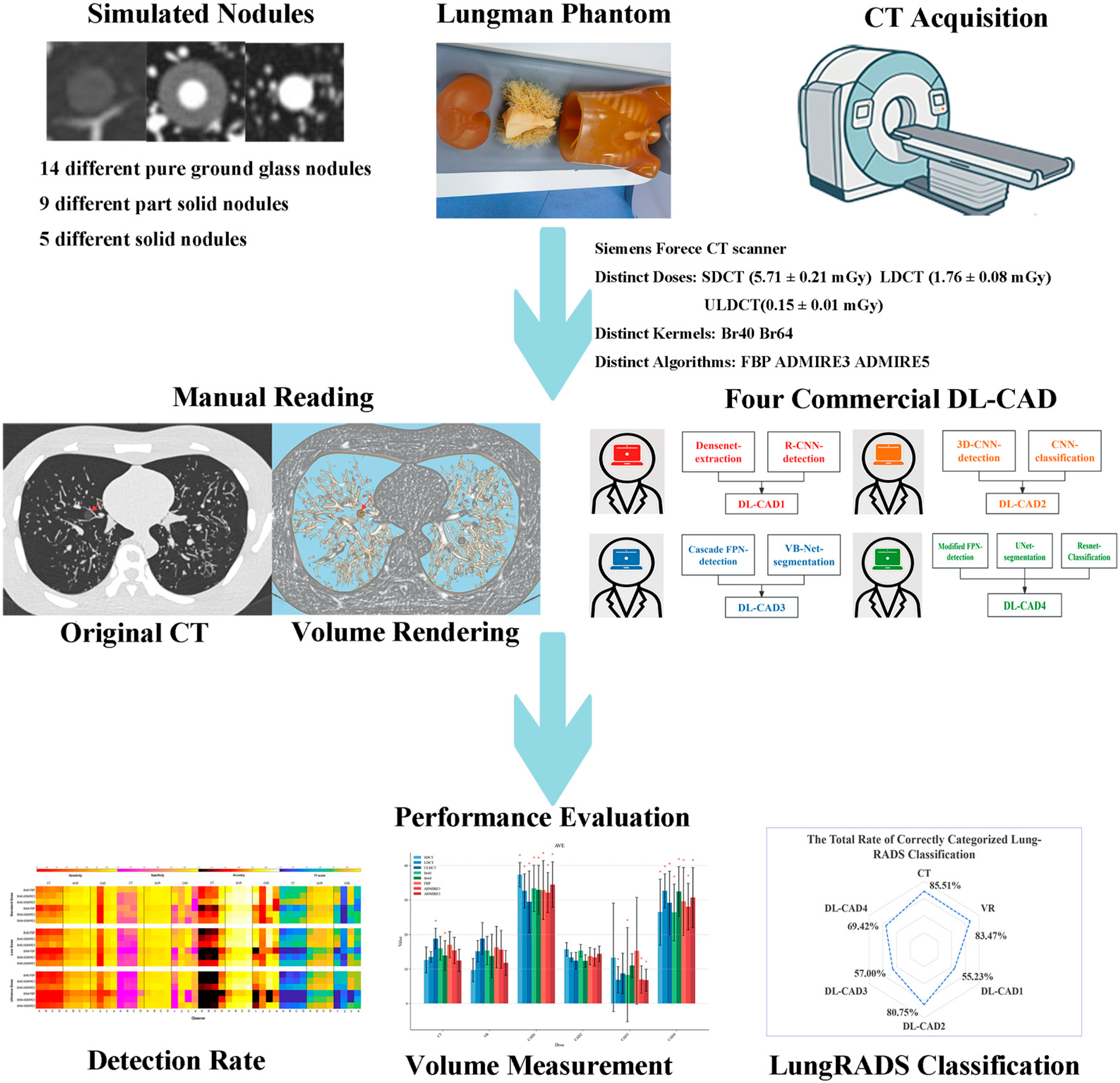
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chest Phantoms
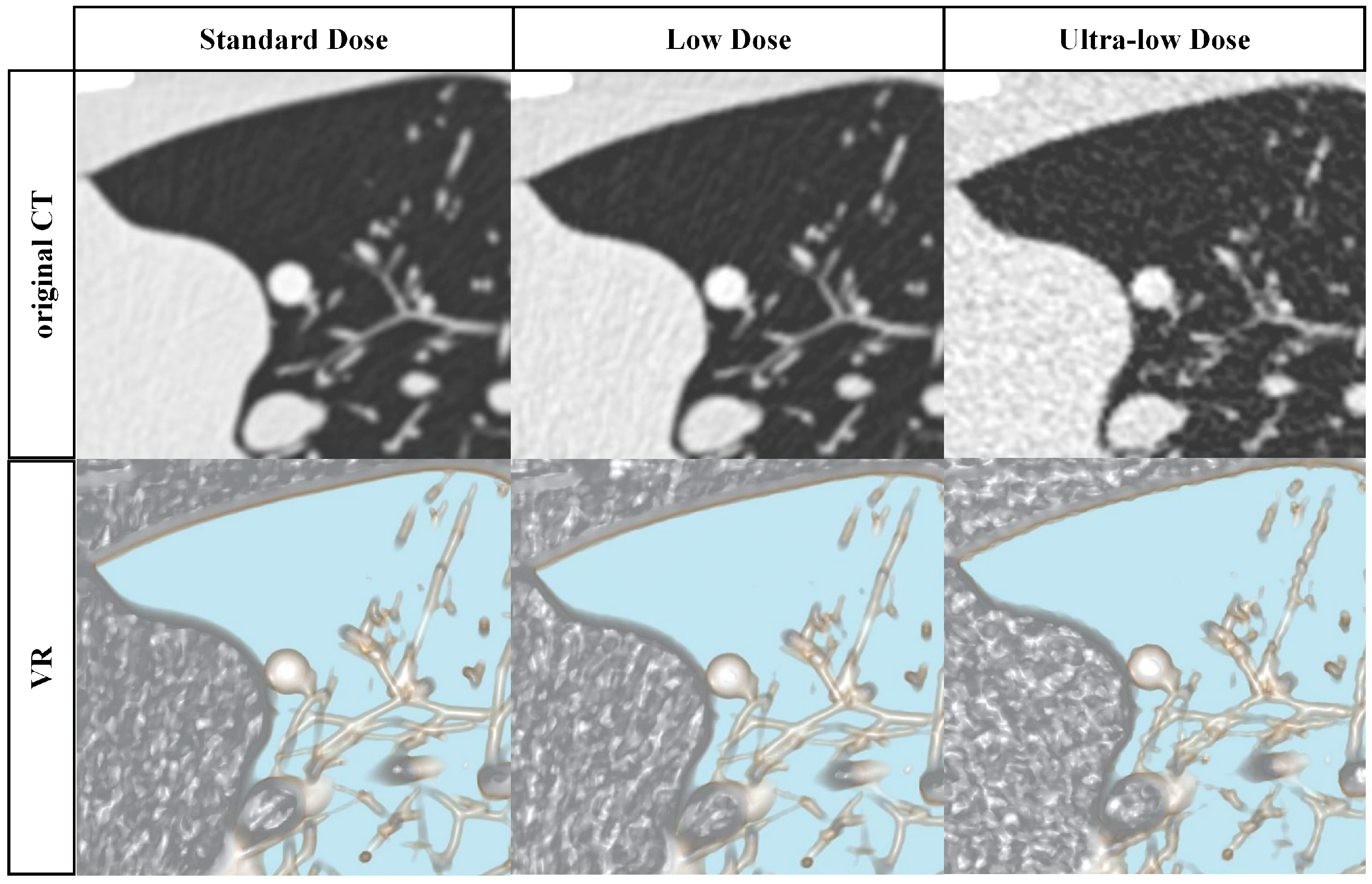
2.2. Image Acquisition and Reconstruction
2.3. Deep Learning CAD Systems
2.4. Image Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
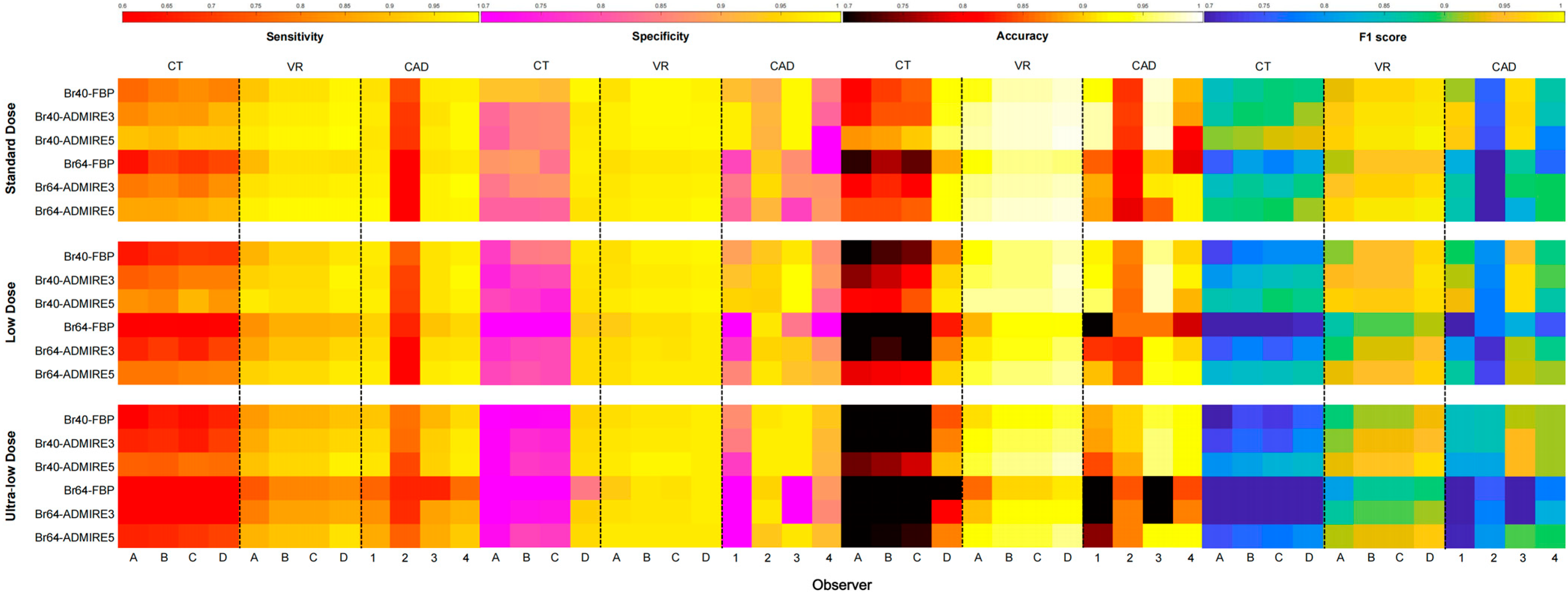
3.1. Overall Nodule Detection Performance
3.2. Subgroup Analysis of Nodule Detection
3.3. Volume Measurement
3.4. Lung-RADS Classification
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leiter, A.; Veluswamy, R.R.; Wisnivesky, J.P. The Global Burden of Lung Cancer: Current Status and Future Trends. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 20, 624–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henschke, C.I.; Yip, R.; Shaham, D.; Markowitz, S.; Cervera Deval, J.; Zulueta, J.J.; Seijo, L.M.; Aylesworth, C.; Klingler, K.; Andaz, S.; et al. A 20-Year Follow-up of the International Early Lung Cancer Action Program (I-ELCAP). Radiology 2023, 309, e231988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Koning, H.J.; van der Aalst, C.M.; de Jong, P.A.; Scholten, E.T.; Nackaerts, K.; Heuvelmans, M.A.; Lammers, J.-W.J.; Weenink, C.; Yousaf-Khan, U.; Horeweg, N.; et al. Reduced Lung-Cancer Mortality with Volume CT Screening in a Randomized Trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, D.E.; Kazerooni, E.A.; Baum, S.L.; Eapen, G.A.; Ettinger, D.S.; Hou, L.; Jackman, D.M.; Klippenstein, D.; Kumar, R.; Lackner, R.P.; et al. Lung Cancer Screening, Version 3.2018, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2018, 16, 412–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, R.J.; Schwartz, K.M.; Eckel, L.J.; Diehn, F.E.; Hunt, C.H.; Bartholmai, B.J.; Erickson, B.J.; Kallmes, D.F. The Effects of Changes in Utilization and Technological Advancements of Cross-Sectional Imaging on Radiologist Workload. Acad. Radiol. 2015, 22, 1191–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith-Bindman, R.; Miglioretti, D.L.; Johnson, E.; Lee, C.; Feigelson, H.S.; Flynn, M.; Greenlee, R.T.; Kruger, R.L.; Hornbrook, M.C.; Roblin, D.; et al. Use of Diagnostic Imaging Studies and Associated Radiation Exposure for Patients Enrolled in Large Integrated Health Care Systems 1996–2010. JAMA 2012, 307, 2400–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith-Bindman, R.; Miglioretti, D.L.; Larson, E.B. Rising Use of Diagnostic Medical Imaging in a Large Integrated Health System. Health Aff. 2008, 27, 1491–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosny, A.; Parmar, C.; Quackenbush, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Artificial Intelligence in Radiology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen, K.G.; Schalekamp, S.; Rutten, M.J.C.M.; van Ginneken, B.; de Rooij, M. Artificial Intelligence in Radiology: 100 Commercially Available Products and Their Scientific Evidence. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 3797–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cressman, S.; Peacock, S.J.; Tammemägi, M.C.; Evans, W.K.; Leighl, N.B.; Goffin, J.R.; Tremblay, A.; Liu, G.; Manos, D.; MacEachern, P.; et al. The Cost-Effectiveness of High-Risk Lung Cancer Screening and Drivers of Program Efficiency. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 1210–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Chi, J.; Liu, J.; Yang, L.; Zhang, B.; Yu, D.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, X. A Survey of Computer-Aided Diagnosis of Lung Nodules from CT Scans Using Deep Learning. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 137, 104806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreuder, A.; Scholten, E.T.; van Ginneken, B.; Jacobs, C. Artificial Intelligence for Detection and Characterization of Pulmonary Nodules in Lung Cancer CT Screening: Ready for Practice? Transl. Lung Cancer R 2021, 10, 2378–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedes Pinto, E.; Penha, D.; Ravara, S.; Monaghan, C.; Hochhegger, B.; Marchiori, E.; Taborda-Barata, L.; Irion, K. Factors Influencing the Outcome of Volumetry Tools for Pulmonary Nodule Analysis: A Systematic Review and Attempted Meta-Analysis. Insights Imaging 2023, 14, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, W.; Park, H.; Jung, K.-H.; Do, K.-H.; Seo, J.B. Computer-Aided Detection of Subsolid Nodules at Chest CT: Improved Performance with Deep Learning-Based CT Section Thickness Reduction. Radiology 2021, 299, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwyzer, M.; Messerli, M.; Eberhard, M.; Skawran, S.; Martini, K.; Frauenfelder, T. Impact of Dose Reduction and Iterative Reconstruction Algorithm on the Detectability of Pulmonary Nodules by Artificial Intelligence. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2022, 103, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, A.A.; Christe, A.; von Stackelberg, O.; Pohl, M.; Kauczor, H.-U.; Heußel, C.P.; Wielpütz, M.O.; Ebner, L. “Will I Change Nodule Management Recommendations If I Change My CAD System?”—Impact of Volumetric Deviation between Different CAD Systems on Lesion Management. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 33, 5568–5577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, B.A.; Brennan, P.C.; Mello-Thoms, C. A Review of Lung Cancer Screening and the Role of Computer-Aided Detection. Clin. Radiol. 2017, 72, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Zhang, T.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Qi, L.; Tan, F.; Daemen, J.H.T.; de Loos, E.R.; Qiu, B.; Gao, S. The Effectiveness of Three-Dimensional Reconstruction in the Localization of Multiple Nodules in Lung Specimens: A Prospective Cohort Study. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 1474–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-J.; Chu, Z.-G.; Li, D.; Jing, W.-W.; Shi, Q.-L.; Lv, F.-J. Accuracy of Solid Portion Size Measured on Multiplanar Volume Rendering Images for Assessing Invasiveness in Lung Adenocarcinoma Manifesting as Subsolid Nodules. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2024, 14, 1971–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peloschek, P.; Sailer, J.; Weber, M.; Herold, C.J.; Prokop, M.; Schaefer-Prokop, C. Pulmonary Nodules: Sensitivity of Maximum Intensity Projection versus That of Volume Rendering of 3D Multidetector CT Data. Radiology 2007, 243, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hop, J.F.; Walstra, A.N.H.; Pelgrim, G.-J.; Xie, X.; Panneman, N.A.; Schurink, N.W.; Faby, S.; van Straten, M.; de Bock, G.H.; Vliegenthart, R.; et al. Detectability and Volumetric Accuracy of Pulmonary Nodules in Low-Dose Photon-Counting Detector Computed Tomography: An Anthropomorphic Phantom Study. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, B.; Wang, G.; Wu, M.; Li, W.; Zheng, Y.; Chu, Z.; Lv, F. Influence of CT Effective Dose and Convolution Kernel on the Detection of Pulmonary Nodules in Different Artificial Intelligence Software Systems: A Phantom Study. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 126, 108928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Li, Q.; Ma, J.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, M.; Deng, Y.; Tu, W.; Wang, Y.; Fan, L.; Xia, C.; et al. Evaluating a Fully Automated Pulmonary Nodule Detection Approach and Its Impact on Radiologist Performance. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2019, 1, e180084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perl, R.M.; Grimmer, R.; Hepp, T.; Horger, M.S. Can a Novel Deep Neural Network Improve the Computer-Aided Detection of Solid Pulmonary Nodules and the Rate of False-Positive Findings in Comparison to an Established Machine Learning Computer-Aided Detection? Investig. Radiol. 2021, 56, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Sun, H.; Chen, Q.; Huang, Y.; Li, Q.; Tian, J.; Zheng, C.; Mao, X.; Jiang, X.; Cheng, Y.; et al. High-Resolution Computed Tomography with 1024-Matrix for Artificial Intelligence-Based Computer-Aided Diagnosis in the Evaluation of Pulmonary Nodules. J. Thorac. Dis. 2025, 17, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Gu, D.; Chen, Y.; Shao, Y.; Cao, X.; Liu, G.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Shen, D. An Artificial-Intelligence Lung Imaging Analysis System (ALIAS) for Population-Based Nodule Computing in CT Scans. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2021, 89, 101899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebner, L.; Roos, J.E.; Christensen, J.D.; Dobrocky, T.; Leidolt, L.; Brela, B.; Obmann, V.C.; Joy, S.; Huber, A.; Christe, A. Maximum-Intensity-Projection and Computer-Aided-Detection Algorithms as Stand-Alone Reader Devices in Lung Cancer Screening Using Different Dose Levels and Reconstruction Kernels. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2016, 207, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, E.K.; Ney, D.R.; Heath, D.G.; Corl, F.M.; Horton, K.M.; Johnson, P.T. Volume Rendering versus Maximum Intensity Projection in CT Angiography: What Works Best, When, and Why. RadioGraphics 2006, 26, 905–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.T.; Fishman, E.K. Enhancing Image Quality in the Era of Radiation Dose Reduction: Postprocessing Techniques for Body CT. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2018, 15, 486–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozuka, T.; Matsukubo, Y.; Kadoba, T.; Oda, T.; Suzuki, A.; Hyodo, T.; Im, S.; Kaida, H.; Yagyu, Y.; Tsurusaki, M.; et al. Efficiency of a Computer-Aided Diagnosis (CAD) System with Deep Learning in Detection of Pulmonary Nodules on 1-Mm-Thick Images of Computed Tomography. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2020, 38, 1052–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazis, S.P.; Dieckens, D.B.M.; Linsen, P.V.M.; Martins Jarnalo, C.O. Effect of CT Reconstruction Settings on the Performance of a Deep Learning Based Lung Nodule CAD System. Eur. J. Radiol. 2021, 136, 109526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gierada, D.S.; Rydzak, C.E.; Zei, M.; Rhea, L. Improved Interobserver Agreement on Lung-RADS Classification of Solid Nodules Using Semiautomated CT Volumetry. Radiology 2020, 297, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devaraj, A.; van Ginneken, B.; Nair, A.; Baldwin, D. Use of Volumetry for Lung Nodule Management: Theory and Practice. Radiology 2017, 284, 630–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Park, H.; Lee, S.M.; Ahn, Y.; Kim, W.; Jung, K.; Seo, J.B. Application of Computer-Aided Diagnosis for Lung-RADS Categorization in CT Screening for Lung Cancer: Effect on Inter-Reader Agreement. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 1054–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, A.A.; Wiescholek, N.; Müller, M.; Klaus, J.; Strodka, F.; Macek, A.; Primetis, E.; Drakopulos, D.; Huber, A.T.; Obmann, V.C.; et al. Impact of Artificial Intelligence Assistance on Pulmonary Nodule Detection and Localization in Chest CT: A Comparative Study among Radiologists of Varying Experience Levels. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 22447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, J.; Wen, D.; Xu, Z.; Meng, X.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Zheng, M. Improved Interobserver Agreement on Nodule Type and Lung-RADS Classification of Subsolid Nodules Using Computer-Aided Solid Component Measurement. Eur. J. Radiol. 2022, 152, 110339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaube, S.; Suresh, H.; Raue, M.; Merritt, A.; Berkowitz, S.J.; Lermer, E.; Coughlin, J.F.; Guttag, J.V.; Colak, E.; Ghassemi, M. Do as AI Say: Susceptibility in Deployment of Clinical Decision-Aids. Npj Digit. Med. 2021, 4, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Hong, H.; Nam, G.; Hwang, E.J.; Park, C.M. Effect of Human-AI Interaction on Detection of Malignant Lung Nodules on Chest Radiographs. Radiology 2023, 307, e222976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankier, A.A.; MacMahon, H.; Goo, J.M.; Rubin, G.D.; Schaefer-Prokop, C.M.; Naidich, D.P. Recommendations for Measuring Pulmonary Nodules at CT: A Statement from the Fleischner Society. Radiology 2017, 285, 584–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzone, P.J.; Lam, L. Evaluating the Patient with a Pulmonary Nodule: A Review. JAMA 2022, 327, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, J.; Prosper, A.E.; Wu, C.C.; Chung, J.; Lee, E.; Elicker, B.; Hunsaker, A.R.; Petranovic, M.; Sandler, K.L.; Stiles, B.; et al. ACR Lung-RADS V2022: Assessment Categories and Management Recommendations. Chest 2024, 165, 738–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, S.J.; Stone, E.; Baldwin, D.R.; Vliegenthart, R.; Lee, P.; Fintelmann, F.J. Lung Cancer Screening. Lancet 2023, 401, 390–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Standard Dose (n = 360) | Low Dose (n = 360) | Ultra-Low Dose (n = 360) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| #Datasets | 360 | 360 | 360 |
| Scanner | SOMATOMA Force | ||
| kVp | 120 kVp | 100 kVp | Sn100 kVp |
| mAs | 100 mAs | 50 mAs | 45 mAs |
| CTDIvol (mGy) | 5.71 ± 0.21 | 1.76 ± 0.08 | 0.15 ± 0.01 |
| mSv | 2.82 ± 0.11 | 0.87 ± 0.04 | 0.07 ± 0.01 |
| Reconstruction kernel | Br40, Br64 | ||
| Reconstruction algorithm | Filtered back projection, iterative reconstruction (ADMIRE−3, ADMIRE−5) | ||
| Slice thickness | 1 mm | ||
| CAD1 | CAD2 | CAD3 | CAD4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product | InferRead CT Lung | Lung CAD | uAI-ChestCare | LungDoc |
| Vendor | InferVision Medical Health | Siemens Healthcare | United Imaging Healthcare | Shukun Technology |
| Country | China | German | China | China |
| Version | Ifocr6.1.5.4 | VD20A | R001.0.1.42690 | V8.7.616.1 |
| Model | DenseNet + modified Faster R-CNN | 3D CNN + cascaded CNN | cascade FPN + VB-Net | modified FPN + UNet + ResNet |
| License | NMPA (II), MDR CE, FDA, PMDA | FDA, MDR CE, PMDA | MDR CE, NMPA (III) | MDR CE, NMPA (III) |
| Metric | Model | Dose | Kernel | Algorithm | Total | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SDCT | LDCT | ULDCT | Br40 | Br64 | FBP | ADMIRE−3 | ADMIRE−5 | |||
| Sensitivity | CAD1 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.88 | 0.95 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.94 | 0.95 | 0.93 |
| CAD2 | 0.63 * | 0.67 * | 0.73 | 0.73 * | 0.63 * | 0.69 * | 0.67 * | 0.67 * | 0.68 * | |
| CAD3 | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.85 | 0.94 | 0.90 | 0.89 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 0.92 | |
| CAD4 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.91 | 0.97 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.95 | |
| CT | 0.82 * | 0.73 * | 0.62 * | 0.77 * | 0.68 * | 0.63 * | 0.73 * | 0.81 | 0.72 * | |
| VR | 0.96 | 0.92 | 0.88 | 0.94 | 0.90 | 0.89 | 0.92 | 0.95 | 0.92 | |
| Specificity | CAD1 | 0.89 | 0.80 * | 0.66 * | 0.90 | 0.66 * | 0.72 * | 0.79 * | 0.84 * | 0.78 * |
| CAD2 | 0.92 | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.94 | |
| CAD3 | 0.92 | 0.94 | 0.84 * | 0.99 | 0.82 * | 0.86 * | 0.90 | 0.94 | 0.90 | |
| CAD4 | 0.80 * | 0.84 * | 0.91 | 0.86 | 0.84 * | 0.82 * | 0.87 * | 0.86 | 0.85 * | |
| CT | 0.89 | 0.82 * | 0.73 * | 0.84 * | 0.79 * | 0.78 * | 0.83 * | 0.83 * | 0.81 * | |
| VR | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.98 | |
| Accuracy | CAD1 | 0.92 | 0.86 | 0.74 * | 0.92 | 0.75 * | 0.79 | 0.84 * | 0.88 | 0.84 * |
| CAD2 | 0.82 * | 0.85 * | 0.88 | 0.86 * | 0.83 * | 0.85 | 0.85 * | 0.84 * | 0.85 * | |
| CAD3 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 0.84 | 0.97 | 0.85 | 0.87 | 0.91 | 0.94 | 0.91 | |
| CAD4 | 0.87 * | 0.89 | 0.91 | 0.90 | 0.87 | 0.86 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.89 | |
| CT | 0.85 * | 0.77 * | 0.68 * | 0.81 * | 0.73 * | 0.70 * | 0.77 * | 0.83 * | 0.77 * | |
| VR | 0.97 | 0.95 | 0.93 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.95 | 0.97 | 0.95 | |
| Model | Dose | Size | Density | Lung-RADS | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤5 mm | 5–10 mm | 10–15 mm | 15–20 mm | SN | GGN | PSN | 2 | 3 | 4A | 4B | ||
| CAD1 | 0.82 * | 0.92 | 0.96 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 0.82 | 0.99 | 0.88 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.99 | |
| Standard | 0.87 | 0.97 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 0.93 | 1.00 | 0.95 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 1.00 | |
| Low | 0.83 # | 0.96 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 0.87 | 1.00 | 0.92 # | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 | |
| Ultra-low | 0.76 # | 0.82 | 0.90 | 0.97 | 0.95 | 0.65 # | 0.97 | 0.77 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 0.97 | |
| CAD2 | 0.50 * | 0.70 * | 0.77 * | 0.70 * | 0.81 * | 0.50 * | 0.71 * | 0.53 * | 0.75 * | 0.88 * | 0.78 * | |
| Standard | 0.48 # | 0.68 # | 0.71 # | 0.60 # | 0.79 # | 0.46 # | 0.60 # | 0.50 # | 0.65 # | 0.84 # | 0.71 # | |
| Low | 0.47 # | 0.71 # | 0.76 # | 0.71 # | 0.80 # | 0.51 # | 0.69 | 0.53 # | 0.72 # | 0.89 # | 0.77 # | |
| Ultra-low | 0.55 | 0.69 # | 0.85 # | 0.81 # | 0.85 | 0.52 # | 0.82 # | 0.56 # | 0.87 # | 0.92 | 0.85 # | |
| CAD3 | 0.84 * | 0.92 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 0.96 | 0.86 | 0.99 | 0.85 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1.00 | |
| Standard | 0.89 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.95 | 0.96 | 1.00 | 0.93 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |
| Low | 0.86 | 0.95 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.96 | 0.92 | 1.00 | 0.89 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |
| Ultra-low | 0.77 # | 0.85 | 0.92 | 0.98 | 0.95 | 0.71 | 0.98 | 0.73 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 1.00 | |
| CAD4 | 0.90 * | 0.93 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.88 | 0.99 | 0.85 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | |
| Standard | 0.93 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 0.93 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |
| Low | 0.91 # | 0.96 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.91 | 1.00 | 0.89 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |
| Ultra-low | 0.86 # | 0.86 | 0.94 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.78 | 0.98 | 0.73 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 0.97 | |
| CT | 0.26 * | 0.73 * | 0.85 * | 0.93 | 0.68 * | 0.72 * | 0.91 | 0.54 * | 0.91 | 0.90 | 0.83 * | |
| Standard | 0.34 # | 0.87 | 0.93 | 0.99 | 0.76 # | 0.82 # | 0.98 | 0.66 # | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.94 | |
| Low | 0.26 # | 0.71 # | 0.86 # | 0.97 | 0.67 # | 0.73 # | 0.97 | 0.53 # | 0.98 | 0.90 # | 0.80 # | |
| Ultra-low | 0.17 # | 0.62 # | 0.76 # | 0.83 # | 0.61 # | 0.62 # | 0.79 # | 0.42 # | 0.77 # | 0.83 # | 0.74 # | |
| VR | 0.71 | 0.94 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 0.93 | 0.86 | 1.00 | 0.84 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.99 | |
| Standard | 0.84 | 0.97 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 1.00 | 0.93 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 | |
| Low | 0.70 | 0.94 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 0.93 | 0.86 | 1.00 | 0.84 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.99 | |
| Ultra-low | 0.59 | 0.90 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 0.89 | 0.78 | 0.99 | 0.76 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.98 | |
| Model | Dose (%) | Kernel (%) | Algorithm (%) | Total (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SDCT | LDCT | ULDCT | Br40 | Br64 | FBP | ADMIRE−3 | ADMIRE−5 | ||
| CAD1 | 37.32 ± 3.53 | 32.63 ± 4.95 | 29.45 ± 8.94 | 33.37 ± 6.74 | 32.91 ± 7.15 | 32.83 ± 8.56 | 32.12 ± 5.83 | 34.46 ± 6.62 | 33.14 ± 6.74 |
| CAD2 | 15.74 ± 1.95 | 13.39 ± 1.33 | 12.43 ± 2.43 | 15.35 ± 1.81 | 12.36 ± 1.79 | 13.74 ± 2.52 | 13.39 ± 2.51 | 14.42 ± 2.26 | 13.85 ± 2.33 |
| CAD3 | 13.34 ± 15.73 | 6.90 ± 3.82 | 8.73 ± 5.89 | 8.30 ± 13.63 | 11.02 ± 3.45 | 15.27 ± 15.50 | 6.95 ± 3.97 | 6.76 ± 3.19 | 9.66 ± 9.75 |
| CAD4 | 26.47 ± 9.56 | 32.63 ± 4.95 | 29.18 ± 9.16 | 26.41 ± 8.18 | 32.45 ± 7.19 | 29.59 ± 9.81 | 28.04 ± 6.80 | 30.66 ± 8.71 | 29.43 ± 8.09 |
| CT | 12.63 ± 3.78 | 13.50 ± 1.58 | 18.82 ± 2.90 | 16.02 ± 3.41 | 13.95 ± 4.31 | 17.05 ± 3.77 | 15.40 ± 3.83 | 12.49 ± 3.22 | 14.98 ± 3.91 |
| VR | 9.68 ± 3.38 | 15.18 ± 3.13 | 18.85 ± 4.58 | 15.37 ± 4.11 | 13.77 ± 6.33 | 16.29 ± 6.02 | 15.64 ± 5.47 | 11.79 ± 3.59 | 14.57 ± 5.24 |
| Model | Dose | 2 (%) | 3 (%) | 4A (%) | 4B (%) | Total (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAD1 | 50.53 * | 74.91 | 47.38 * | 73.40 | 55.23 * | |
| Standard | 49.82 # | 77.33 # | 47.09 # | 78.79 | 55.36 # | |
| Low | 52.41 # | 62.00 # | 42.00 # | 62.12 # | 51.53 # | |
| Ultra-low | 49.36 # | 85.39 | 53.05 # | 79.29 | 58.78 # | |
| CAD2 | 73.14 | 84.52 | 94.12 | 46.71 * | 80.75 | |
| Standard | 73.91 # | 94.38 | 93.04 | 35.62 # | 80.75 | |
| Low | 74.58 | 91.56 | 94.20 # | 59.95 # | 83.71 | |
| Ultra-low | 70.92 | 67.62 # | 95.12 # | 44.57 # | 77.17 | |
| CAD3 | 65.76 * | 41.56 * | 57.53 * | 33.84 * | 57.00 * | |
| Standard | 70.42 # | 40.67 # | 63.27 # | 33.33 # | 60.97 # | |
| Low | 68.91 # | 41.33 # | 54.23 # | 40.91 # | 58.44 # | |
| Ultra-low | 57.96 # | 42.67 # | 55.10 # | 27.27 # | 51.60 # | |
| CAD4 | 85.48 | 45.12 * | 65.71 * | 42.12 * | 69.42 * | |
| Standard | 81.36 | 54.67 # | 65.99 # | 50.00 # | 70.29 # | |
| Low | 81.40 | 47.15 # | 65.65 # | 46.97 # | 69.15 # | |
| Ultra-low | 93.68 # | 33.54 # | 65.51 # | 29.39 # | 68.81 | |
| CT | 86.02 | 83.26 | 85.41 | 88.33 | 85.51 | |
| Standard | 95.45 | 87.50 | 88.64 | 87.50 # | 90.83 | |
| Low | 85.45 | 83.33 | 85.11 | 90.00 | 85.29 | |
| Ultra-low | 77.14 | 78.95 | 82.50 | 87.50 # | 80.39 | |
| VR | 84.53 | 86.44 | 81.25 | 77.88 | 83.47 | |
| Standard | 92.21 | 92.00 | 83.33 | 72.73 | 88.20 | |
| Low | 84.81 | 84.00 | 79.17 | 90.91 | 83.44 | |
| Ultra-low | 76.56 | 83.33 | 81.25 | 70.00 | 78.77 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, S.; Gao, L.; Tan, M.; Zhang, K.; Lv, F. Performance Evaluation of Four Deep Learning-Based CAD Systems and Manual Reading for Pulmonary Nodules Detection, Volume Measurement, and Lung-RADS Classification Under Varying Radiation Doses and Reconstruction Methods. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1623. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131623
Chen S, Gao L, Tan M, Zhang K, Lv F. Performance Evaluation of Four Deep Learning-Based CAD Systems and Manual Reading for Pulmonary Nodules Detection, Volume Measurement, and Lung-RADS Classification Under Varying Radiation Doses and Reconstruction Methods. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(13):1623. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131623
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Sifan, Lingqi Gao, Maolu Tan, Ke Zhang, and Fajin Lv. 2025. "Performance Evaluation of Four Deep Learning-Based CAD Systems and Manual Reading for Pulmonary Nodules Detection, Volume Measurement, and Lung-RADS Classification Under Varying Radiation Doses and Reconstruction Methods" Diagnostics 15, no. 13: 1623. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131623
APA StyleChen, S., Gao, L., Tan, M., Zhang, K., & Lv, F. (2025). Performance Evaluation of Four Deep Learning-Based CAD Systems and Manual Reading for Pulmonary Nodules Detection, Volume Measurement, and Lung-RADS Classification Under Varying Radiation Doses and Reconstruction Methods. Diagnostics, 15(13), 1623. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131623






