GM-VGG-Net: A Gray Matter-Based Deep Learning Network for Autism Classification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset
2.2. Preprocessing of MRI-T1 Images
2.3. Conventional VGG-16 Architecture
2.4. Proposed Deep Learning GM-VGG-Net Architecture
2.4.1. Input Layer Unit
2.4.2. Hidden Layer Unit
2.4.3. Fully Connected Layer Unit
2.4.4. Output Layer Unit
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Data
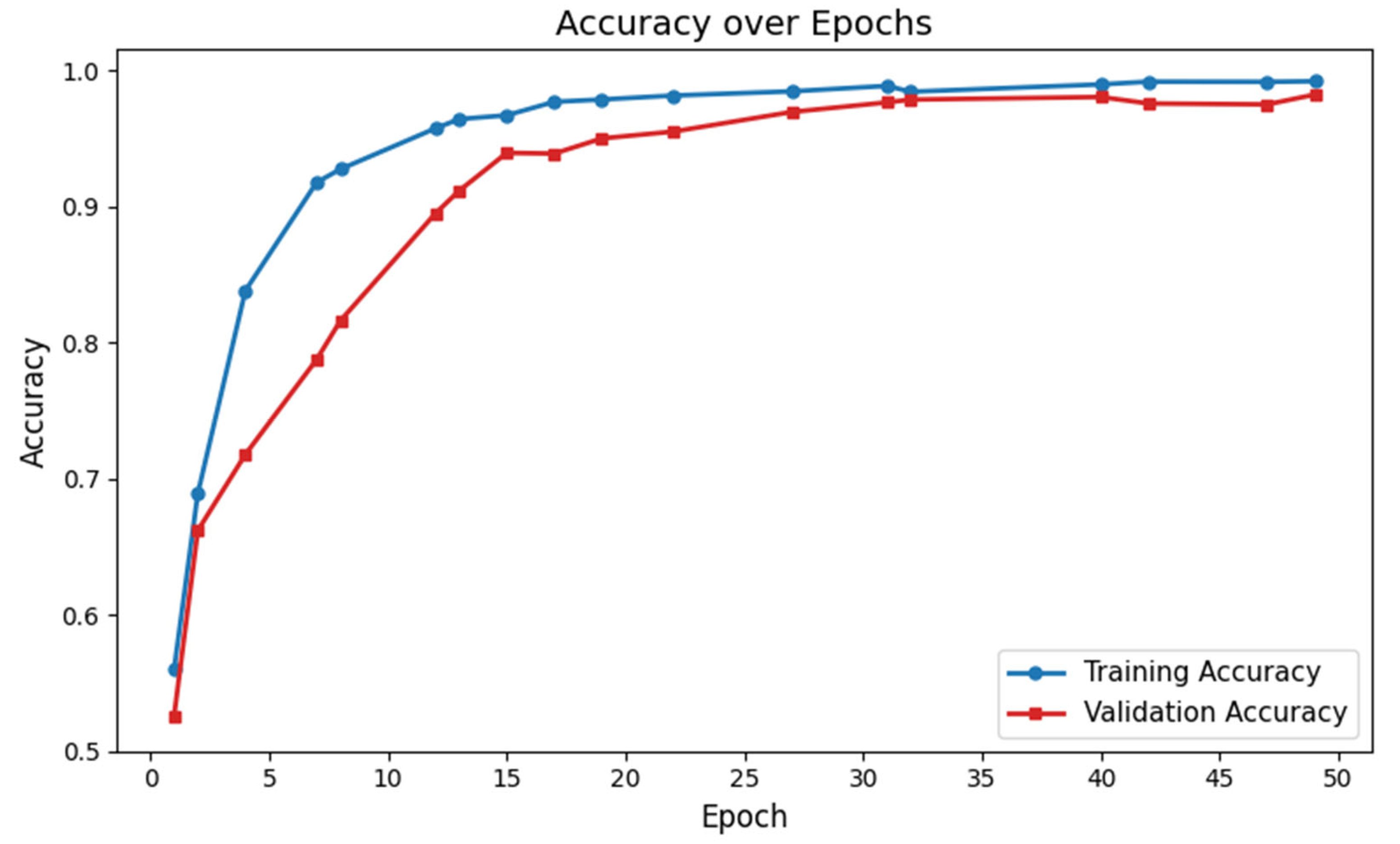
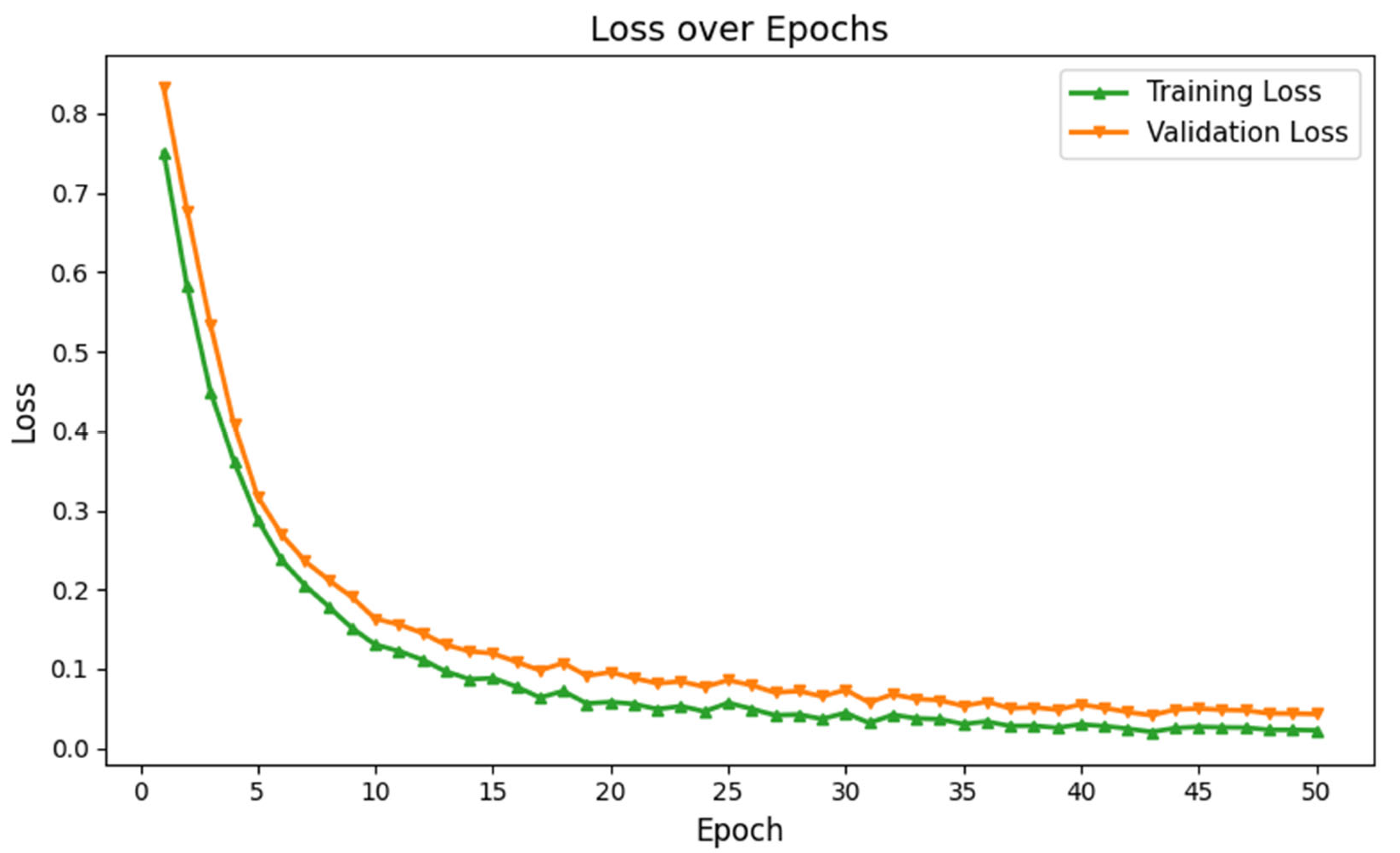
3.2. Performance Evaluation of GM-VGG Net Classifier
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hodges, H.; Fealko, C.; Soares, N. Autism spectrum disorder: Definition, epidemiology, causes, and clinical evaluation. Transl. Pediatr. 2020, 9 (Suppl. S1), S55–S65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lord, C.; Brugha, T.S.; Charman, T.; Cusack, J.; Dumas, G.; Frazier, T.; Jones, E.J.H.; Jones, R.M.; Pickles, A.; State, M.W.; et al. Autism spectrum disorder. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2020, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Zhang, H.; Qiu, T. Deep learning approach to predict autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Psychiatry 2024, 24, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, M.Z.; Shahriar, M.A.; Mahamood, M.N.; Alnajjar, F.; Pramanik, M.I.; Ahad, M.A.R. Deep learning with image-based autism spectrum disorder analysis: A systematic review. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 127, 107185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiee, F.; Rezvani Habibabadi, R.; Motaghi, M.; Yousem, D.M.; Yousem, I.J. Brain MRI in Autism Spectrum Disorder: Narrative Review and Recent Advances. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2022, 55, 1613–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Xu, D.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, H. Application of Multimodal MRI in the Early Diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Review. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yao, L.; Zhang, W.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, L.; Gao, X.; Shah, C.; Li, S.; Tao, B.; Gong, Q.; et al. Gray matter abnormalities in pediatric autism spectrum disorder: A meta-analysis with signed differential mapping. Eur. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2017, 26, 933–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, L.; Chantiluke, K.; Cubillo, A.I.; Smith, A.B.; Simmons, A.; Mehta, M.A.; Rubia, K. Disorder-specific grey matter deficits in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder relative to autism spectrum disorder. Psychol. Med. 2015, 45, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, N.; Travers, B.G.; Bigler, E.D.; Prigge, M.B.; Froehlich, A.L.; Nielsen, J.A.; Cariello, A.N.; Zielinski, B.A.; Anderson, J.S.; Fletcher, P.T.; et al. Longitudinal volumetric brain changes in autism spectrum disorder ages 6–35 years. Autism Res. 2015, 8, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Hua, T.; Tang, H.; Yang, R.; Huang, L.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Tang, G. Gender and age related brain structural and functional alterations in children with autism spectrum disorder. Cereb. Cortex 2024, 34, bhae283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbard, C.R.; Ren, J.; Seunarine, K.K.; Clayden, J.D.; Skuse, D.H.; Clark, C.A. White matter microstructure correlates with autism trait severity in a combined clinical–control sample of high-functioning adults. NeuroImage Clin. 2013, 3, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohta, H.; Aoki, Y.Y.; Itahashi, T.; Kanai, C.; Fujino, J.; Nakamura, M.; Kato, N.; Hashimoto, R.-I. White matter alterations in autism spectrum disorder and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in relation to sensory profile. Mol. Autism 2020, 11, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimond, D.; Schuetze, M.; Smith, R.E.; Dhollander, T.; Cho, I.; Vinette, S.; Ten Eycke, K.; Lebel, C.; McCrimmon, A.; Dewey, D.; et al. Reduced White Matter Fiber Density in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Cereb. Cortex 2019, 29, 1778–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Hu, X.; Jiao, J.; Yuan, D.; Li, S.; Luo, T.; Wang, M.; Situ, M.; Sun, X.; Huang, Y. Brain white matter microstructure abnormalities in children with optimal outcome from autism: A four-year follow-up study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElNakieb, Y.; Ali, M.T.; Elnakib, A.; Shalaby, A.; Soliman, A.; Mahmoud, A.; Ghazal, M.; Barnes, G.N.; El-Baz, A. The Role of Diffusion Tensor MR Imaging (DTI) of the Brain in Diagnosing Autism Spectrum Disorder: Promising Results. Sensors 2021, 21, 8171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Kumar, P.; Chen, H.; Shrivastava, A. Deep Multimodal Learning for the Diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Imaging 2020, 6, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinsfeld, A.S.; Franco, A.R.; Craddock, R.C.; Buchweitz, A.; Meneguzzi, F. Identification of autism spectrum disorder using deep learning and the ABIDE dataset. NeuroImage Clin. 2018, 17, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan Aghdam, M.; Sharifi, A.; Pedram, M.M. Combination of rs-fMRI and sMRI Data to Discriminate Autism Spectrum Disorders in Young Children Using Deep Belief Network. J. Digit. Imaging 2018, 31, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, J.A.; Zielinski, B.A.; Fletcher, P.T.; Alexander, A.L.; Lange, N.; Bigler, E.D.; Lainhart, J.E.; Anderson, J.S. Multisite functional connectivity MRI classification of autism: ABIDE results. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.S.; Nielsen, J.A.; Froehlich, A.L.; DuBray, M.B.; Druzgal, T.J.; Cariello, A.N.; Cooperrider, J.R.; Zielinski, B.A.; Ravichandran, C.; Fletcher, P.T.; et al. Functional connectivity magnetic resonance imaging classification of autism. Brain 2011, 134, 3742–3754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subah, F.Z.; Deb, K.; Dhar, P.K.; Koshiba, T. A Deep Learning Approach to Predict Autism Spectrum Disorder Using Multisite Resting-State fMRI. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Xu, J. Detection of ASD Children through Deep-Learning Application of fMRI. Children 2023, 10, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saponaro, S.; Lizzi, F.; Serra, G.; Mainas, F.; Oliva, P.; Giuliano, A.; Calderoni, S.; Retico, A. Deep learning based joint fusion approach to exploit anatomical and functional brain information in autism spectrum disorders. Brain Inform. 2024, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Q.; Wang, Y.; Ping, B.; Li, D.; Du, J.; Qin, Y.; Lu, H.; Wan, X.; Xiang, J. Deep convolutional neural network VGG-16 model for differential diagnosing of papillary thyroid carcinomas in cytological images: A pilot study. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 4876–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martino, A.; Yan, C.G.; Li, Q.; Denio, E.; Castellanos, F.X.; Alaerts, K.; Anderson, J.S.; Assaf, M.; Bookheimer, S.Y.; Dapretto, M.; et al. The autism brain imaging data exchange: Towards a large-scale evaluation of the intrinsic brain architecture in autism. Mol. Psychiatry 2014, 19, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburner, J.; Friston, K.J. Computing average shaped tissue probability templates. NeuroImage 2009, 45, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburner, J. A fast diffeomorphic image registration algorithm. NeuroImage 2007, 38, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburner, J. Computational anatomy with the SPM software. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2009, 27, 1163–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, E.; Deng, F.; Patel, S.K.; Sedrak, M.S.; Kim, H.; Razavi, M.; Sun, C.L.; Root, J.C.; Ahles, T.A.; Dale, W.; et al. Cortical thinning in chemotherapy-treated older long-term breast cancer survivors. Brain Imaging Behav. 2023, 17, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitwell, J.L. Voxel-based morphometry: An automated technique for assessing structural changes in the brain. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 9661–9664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashburner, J.; Friston, K.J. Voxel Based Morphometry. In Encyclopedia of Neuroscience; Squire, L.R., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp. 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischmeister, F.P.S.; Höllinger, I.; Klinger, N.; Geissler, A.; Wurnig, M.C.; Matt, E.; Rath, J.; Robinson, S.D.; Trattnig, S.; Beisteiner, R. The benefits of skull stripping in the normalization of clinical fMRI data. NeuroImage Clin. 2013, 3, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhtasim, D.A.; Pavel, M.I.; Tan, S.Y. A Patch-Based CNN Built on the VGG-16 Architecture for Real-Time Facial Liveness Detection. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, X.; Wu, S.; Miao, J.; Wang, G.; Sun, L. Lightweight-VGG: A Fast Deep Learning Architecture Based on Dimensionality Reduction and Nonlinear Enhancement for Hyperspectral Image Classification. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klangbunrueang, R.; Pookduang, P.; Chansanam, W.; Lunrasri, T. AI-Powered Lung Cancer Detection: Assessing VGG16 and CNN Architectures for CT Scan Image Classification. Informatics 2025, 12, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glover, G.H. Overview of functional magnetic resonance imaging. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2011, 22, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | CN | ASD |
|---|---|---|
| N | 140 | 132 |
| Age (mean ± SD) | 14.62 ± 4.34 | 14.89 ± 4.29 (p = 0.23) |
| Age (male) (mean ± SD) | 14.97 ± 4.14 | 15.75 ± 3.77 |
| N (male) | 68 | 67 |
| Age (female) (mean ± SD) | 13.57 ± 4.56 | 14.02 ± 4.60 |
| N (female) | 72 | 65 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Optimizer | Adam |
| Learning Rate | 0.001 |
| Epochs | 50 |
| Trainable Parameters | 5,174,721 |
| Non-Trainable Parameters | 1984 |
| Total Parameters | 5,176,705 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Daniel, E.; Gulati, A.; Saxena, S.; Urgun, D.A.; Bista, B. GM-VGG-Net: A Gray Matter-Based Deep Learning Network for Autism Classification. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1425. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15111425
Daniel E, Gulati A, Saxena S, Urgun DA, Bista B. GM-VGG-Net: A Gray Matter-Based Deep Learning Network for Autism Classification. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(11):1425. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15111425
Chicago/Turabian StyleDaniel, Ebenezer, Anjalie Gulati, Shraya Saxena, Deniz Akay Urgun, and Biraj Bista. 2025. "GM-VGG-Net: A Gray Matter-Based Deep Learning Network for Autism Classification" Diagnostics 15, no. 11: 1425. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15111425
APA StyleDaniel, E., Gulati, A., Saxena, S., Urgun, D. A., & Bista, B. (2025). GM-VGG-Net: A Gray Matter-Based Deep Learning Network for Autism Classification. Diagnostics, 15(11), 1425. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15111425






