The Role of Hyponatremia in Identifying Complicated Cases of Acute Appendicitis in the Pediatric Population
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
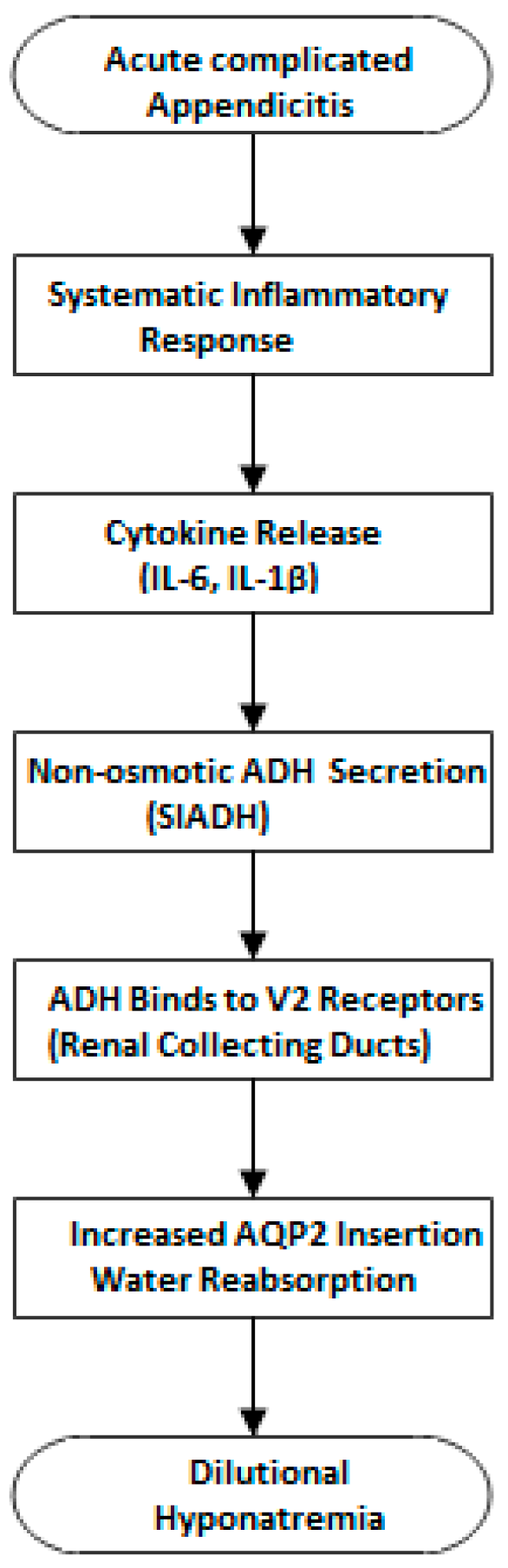
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buckius, M.T.; McGrath, B.; Monk, J.; Grim, R.; Bell, T.; Ahuja, V. Changing epidemiology of acute appendicitis in the United States: Study period 1993–2008. J. Surg. Res. 2012, 175, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumah, S.; Wester, T. Non-operative management of acute appendicitis in children. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2022, 39, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfollahzadeh, S.; Lopez, R.A.; Deppen, J.G. Appendicitis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK493193 (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- Risteski, T.; Sokolova, R.; Memeti, S.; Simeonov, R. Laparoscopic versus open appendectomy in pediatric patients: Operative and postoperative experience. J. Clin. Trials Exp. Investig. 2022, 1, 49–55. Available online: https://jctei.com/index.php/jctei/article/view/21 (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- Mariage, M.; Sabbagh, C.; Grelpois, G.; Prevot, F.; Darmon, I.; Regimbeau, J.-M. Surgeon’s Definition of Complicated Appendicitis: A Prospective Video Survey Study. Euroasian J. Hepato-Gastroenterol. 2019, 9, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kong, V.; Aldous, C.; Handley, J.; Clarke, D. The cost effectiveness of early management of acute appendicitis underlies the importance of curative surgical services to a primary healthcare programme. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2013, 95, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Hattabi, K.; Bouali, M.; El Berni, Y.; Bensardi, F.; El Bakouri, A.; Moufakkir, A.; Riad, N.; Fadil, A. Value of Alvarado scoring system in diagnosis of acute appendicitis. Ann. Med. Surg. 2022, 77, 103642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parveen, K.Z.; Avabratha, K.S.; Shetty, K. Pediatric appendicitis score in the diagnosis of childhood appendicitis: A validation study. Int. J. Contemp. Pediatr. 2017, 4, 2196–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.; Kolodziej, B.; Andersson, R.E. Validation of the Appendicitis Inflammatory Response (AIR) Score. World J. Surg. 2021, 45, 2081–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haak, F.; Kollmar, O.; Ioannidis, A.; Slotta, J.E.; Ghadimi, M.B.; Glass, T.; von Strauss Und Torney, M. Predicting complicated appendicitis based on clinical findings: The role of Alvarado and Appendicitis Inflammatory Response scores. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 2022, 407, 2051–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, S.N. Effectiveness of the PAS Scale for Diagnosing the Severity of Acute Appendicitis in Children: A Cohort Study. medRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trout, A.T.; Sanchez, R.; Ladino-Torres, M.F.; Pai, D.R.; Strouse, P.J. A critical evaluation of US for the diagnosis of pediatric acute appendicitis in a real-life setting: How can we improve the diagnostic value of sonography? Pediatr. Radiol. 2012, 42, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, E. Radiation From CT Scans in Young People Tied to Higher Cancer Risk. JAMA 2023, 330, 2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spasovski, G.; Vanholder, R.; Allolio, B.; Annane, D.; Ball, S.; Bichet, D.; Decaux, G.; Fenske, W.; Hoorn, E.J.; Ichai, C.; et al. Clinical practice guideline on diagnosis and treatment of hyponatraemia. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014, 29 (Suppl. 2), i1–i39, Erratum in Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014, 40, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swart, R.M.; Hoorn, E.J.; Betjes, M.G.; Zietse, R. Hyponatremia and Inflammation: The Emerging Role of Interleukin-6 in Osmoregulation. Nephron Physiol. 2010, 118, p45–p51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.Y.; Nassiri, N.; de Virgilio, C.; Ferebee, M.P.; Kaji, A.H.; Hamilton, C.E.; Saltzman, D.J. Association Between Hyponatremia and Complicated Appendicitis. JAMA Surg. 2015, 150, 911–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuschieri, S. The Strobe guidelines. Saudi J. Anaesth. 2019, 13 (Suppl. 1), S31–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lounis, Y.; Hugo, J.; Demarche, M.; Seghaye, M.-C. Influence of age on clinical presentation, diagnosis delay and outcome in pre-school children with acute appendicitis. BMC Pediatr. 2020, 20, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, K.J.; Nguyen, H.T.; Wulkan, M.L.; Raval, M.V. Association of Health Care Utilization with Rates of Perforated Appendicitis in Children 18 Years or Younger. JAMA Surg. 2018, 153, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macco, S.; Vrouenraets, B.C.; de Castro, S.M. Evaluation of scoring systems in predicting acute appendicitis in children. Surgery 2016, 160, 1599–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulik, D.M.; Uleryk, E.M.; Maguire, J.L. Does this child have appendicitis? A systematic review of clinical prediction rules for children with acute abdominal pain. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2013, 66, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaramhy, H.H. Acute appendicitis in young children less than 5 years: Review article. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2017, 43, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crocker, C.; Akl, M.; Abdolell, M.; Kamali, M.; Costa, A.F. Ultrasound and CT in the Diagnosis of Appendicitis: Accuracy with Consideration of Indeterminate Examinations According to STARD Guidelines. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 215, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, D.K. Acute appendicitis | Radiology Reference Article. Radiopaedia.org. 2025. Available online: https://radiopaedia.org/articles/acute-appendicitis (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Leite, N.P.; Pereira, J.M.; Cunha, R.; Pinto, P.; Sirlin, C. CT Evaluation of Appendicitis and Its Complications: Imaging Techniques and Key Diagnostic Findings. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2005, 185, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharias, C.; Alessio, A.M.; Otto, R.K.; Iyer, R.S.; Philips, G.S.; Swanson, J.O.; Thapa, M.M. Pediatric CT: Strategies to Lower Radiation Dose. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2013, 200, 950–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisnowski, J.L.; Sperling, V.R.; Panigrahy, A. Challenges in Pediatric Magnetic Resonance Imaging. In MR Spectroscopy of Pediatric Brain Disorders; Blüml, S., Panigrahy, A., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Królicka, A.L.; Kruczkowska, A.; Krajewska, M.; Kusztal, M.A. Hyponatremia in Infectious Diseases—A Literature Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Pratima, K.; Bhattacharya, R.; Ambedkar, S.N.; Saini, R.P. Hyponatremia in sepsis and its association with SOFA score: An observational cross-sectional study. J. Med. Sci. Res. 2023, 11, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, M.; Hernandez, M.; Cheungpasitporn, W.; Kashani, K.B.; Riaz, I.; Rangaswami, J.; Herzog, E.; Guglin, M.; Krittanawong, C. Hyponatremia in Heart Failure: Pathogenesis and Management. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2019, 15, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, S.; Thuluvath, P.J. Hyponatremia in cirrhosis: Pathophysiology and management. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 3197–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, C.B.; Gan, M.Y.; Tay, R.Y.K.; Loh, W.J.; Loh, N.-H.W. Association of Preoperative Hyponatremia with Surgical Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of 32 Observational Studies. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 108, 1254–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S.; Frøkiær, J.; Marples, D.; Kwon, T.-H.; Agre, P.; Knepper, M.A. Aquaporins in the Kidney: From Molecules to Medicine. Physiol. Rev. 2002, 82, 205–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landgraf, R.; Neumann, I.; Holsboer, F.; Pittman, Q.J. Interleukin-1β Stimulates both Central and Peripheral Release of Vasopressin and Oxytocin in the Rat. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1995, 7, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.; Khan, M.A.; Khan, J.; Ali, S.; Khattak, I.; Masood, A. Frequency and outcome of complicated appendicitis in toddlers and preschoolers. J. Pediatr. Adolesc. Surg. 2020, 1, 41–43. Available online: https://jpedas.org/ojs/index.php/jpedas/article/view/5 (accessed on 13 May 2025). [CrossRef]


| Characteristic | Total (N = 491) | AUA (N = 366) | ACA (N = 125) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (N, %) | 0.160 | |||
| Male | 296 (60.3) | 214 (58.5) | 82 (65.6) | |
| Female | 195 (39.7) | 152 (41.5) | 43 (34.4) | |
| Age (years) | 10.78 (3.05) | 11.02 (2.86) | 10 (3.46) | 0.010 |
| Min–Max | 1.5–16 | 4–16 | 1.5–15 |
| Characteristic | Total (N = 491) | AUA (N = 366) | ACA (N = 125) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRP (mg/dL) | 1.5 (0.5–4) | 1 (0.4–2.61) | 4.7 (2–9.17) | <0.001 |
| Urea (mmol/L) | 23 (19–27.25) | 24 (20–28) | 22 (19–27) | 0.055 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.6 (0.5–0.7) | 0.6 (0.5–0.7) | 0.58 (0.43–0.7) | 0.005 |
| K (mmol/L) | 4.3 (4–4.5) | 4.3 (4–4.6) | 4.2 (3.93–4.5) | 0.149 |
| Na (mmol/L) | 137 (136–139) | 138 (137–139) | 136 (133–137) | <0.001 |
| Hyponatremia (<135) | <0.001 | |||
| Yes | 56 (11.4%) | 8 (2.2%) | 48 (38.4%) | |
| No | 435 (88.6%) | 358 (97.8%) | 77 (61.6%) | |
| Hb (g/dL) | 13.1 (12.4–13.8) | 13.1 (12.5–13.9) | 12.8 (12–13.75) | 0.022 |
| Ht | 38.4 (36.6–40.6) | 38.5 (36.9–40.6) | 38 (35.9–40.05) | 0.022 |
| PLT (×109 PLTs per microliter of blood) | 291 (243–355) | 286 (242–347) | 317 (258–389) | 0.001 |
| MPV (fl) | 10 (9.4–10.6) | 10 (9.5–10.6) | 9.9 (9.2–10.5) | 0.057 |
| WBC (×103 WBCs per microliter of blood) | 14.5 (10.8–17.82) | 14 (10.22–17) | 17.2 (13.4–19.8) | <0.001 |
| NEUT | 78.5 (69.6–84.5) | 77 (67.5–82.7) | 82.7 (76.7–87.7) | <0.001 |
| LYM | 14.1 (8.8–21.3) | 15.6 (10.38–23.03) | 9.5 (6.2–14.8) | <0.001 |
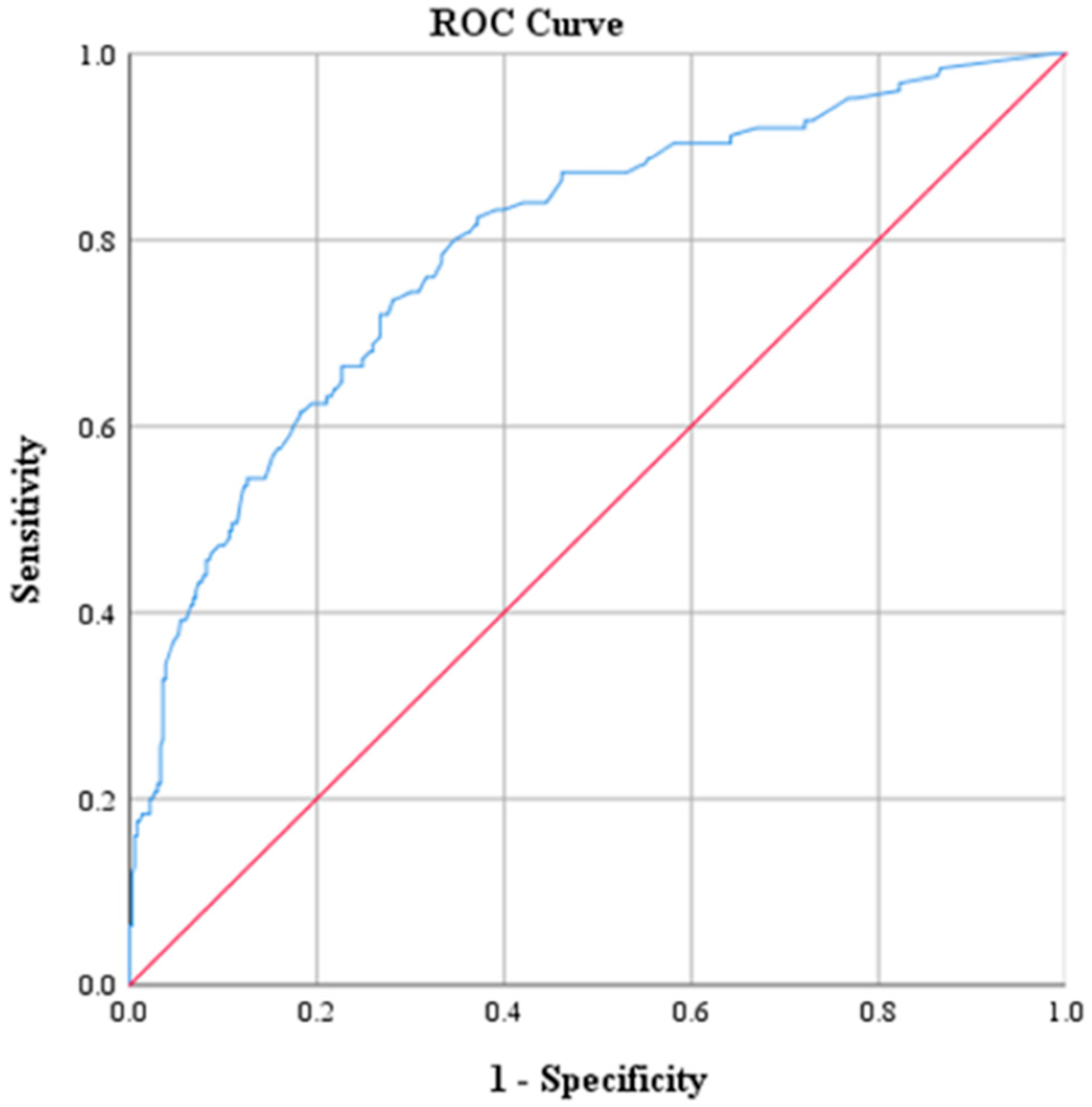
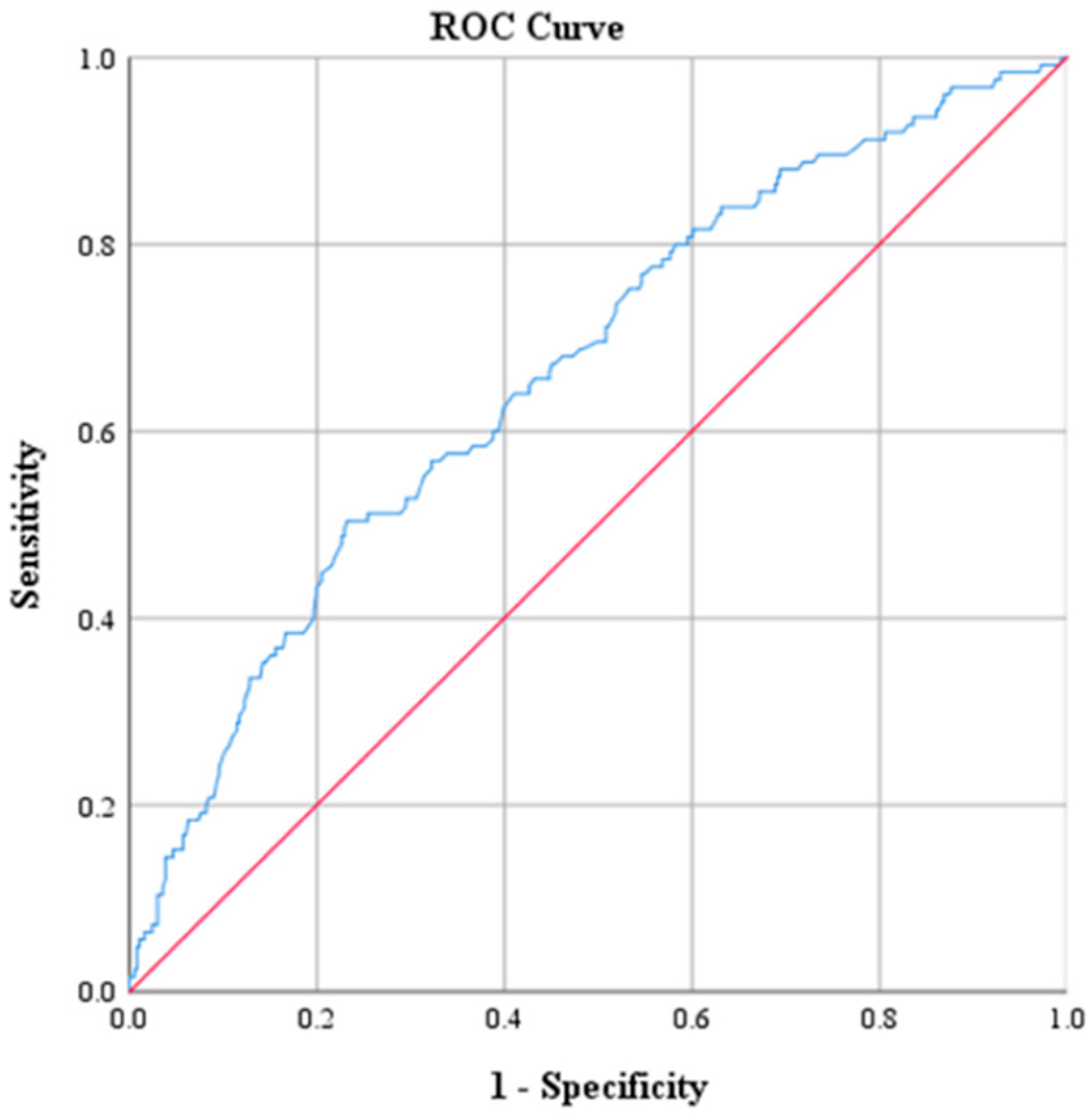
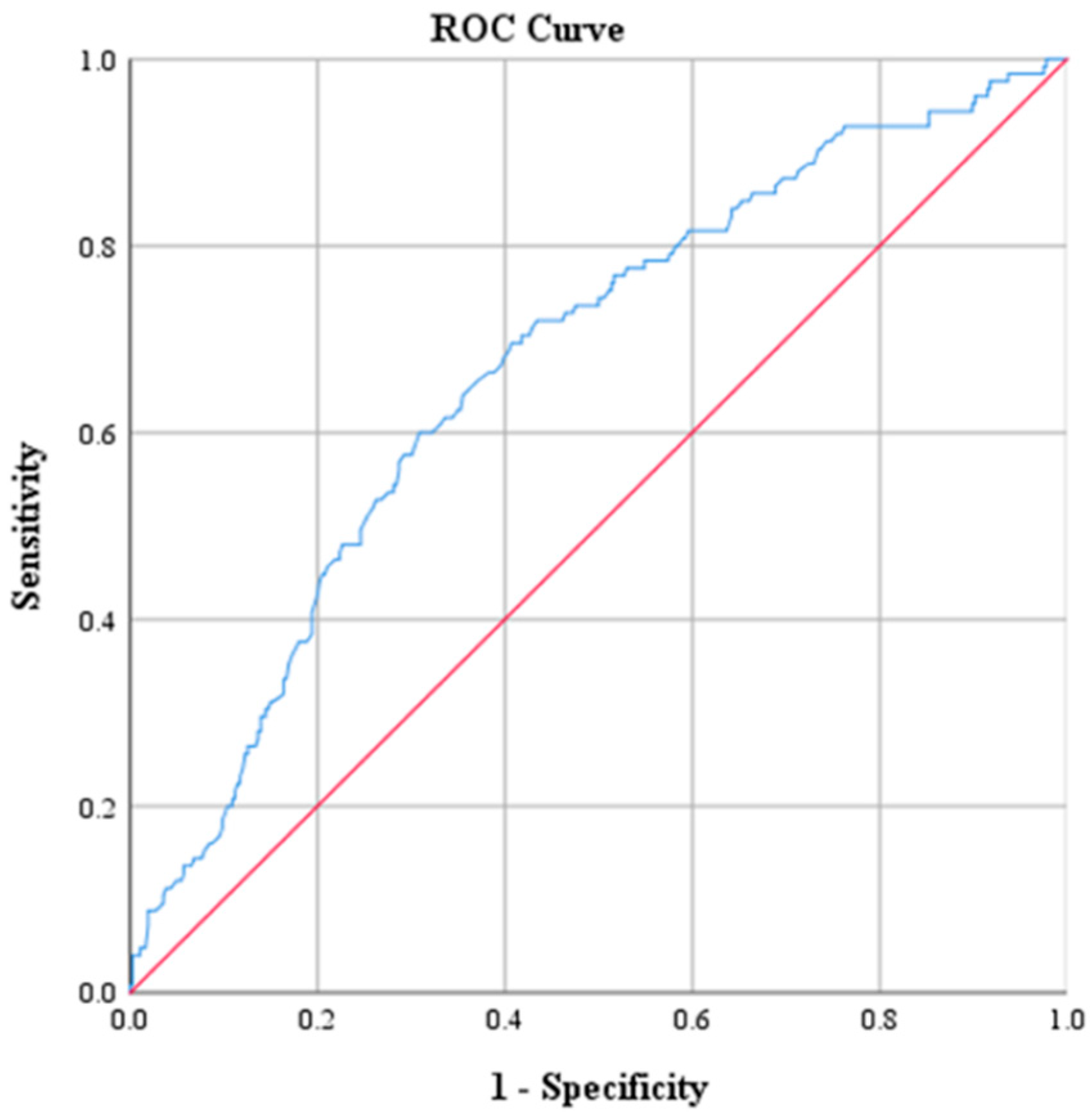
| AUC Value | p | 95% CI | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CRP | 0.793 | <0.001 | 0.746, 0.840 |
| Urea | 0.442 | 0.055 | 0.383, 0.502 |
| Creatinine | 0.417 | 0.006 | 0.357, 0.476 |
| K | 0.457 | 0.150 | 0.397, 0.516 |
| Na | 0.784 | <0.001 | 0.733, 0.834 |
| Hb | 0.432 | 0.023 | 0.370, 0.493 |
| Ht | 0.431 | 0.022 | 0.370, 0.493 |
| PLT | 0.595 | 0.001 | 0.536, 0.655 |
| MPV | 0.443 | 0.057 | 0.382, 0.504 |
| WBC | 0.664 | <0.001 | 0.609, 0.719 |
| NEUT | 0.671 | <0.001 | 0.617, 0.726 |
| LYM | 0.297 | <0.001 | 0.244, 0.349 |
| Variable | Cutoff Points | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRP (mg/dL) | 2.17 | 73.6 | 71.9 | 47.2 | 88.9 | 0.793 |
| PLT | 330.5 | 47.2 | 71.0 | 35.8 | 79.8 | 0.595 |
| WBC | 17.15 | 50.4 | 76.8 | 42.6 | 81.9 | 0.664 |
| NEUT | 81.05 | 60.0 | 69.1 | 39.9 | 83.5 | 0.671 |
| Na (mmol/L) | 135 | 48.0 | 92.1 | 85.7 | 82.3 | 0.784 |
| Univariate Logistic Regression | Multivariate Logistic Regression | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | |
| CRP ≥ 2.175 | 7.12 (4.5–11.26) | <0.001 | 5.71 (3.35–9.73) | <0.001 |
| Hyponatremia (<135), Yes | 27.9 (12.69–61.34) | <0.001 | 18.30 (7.67–43.63) | <0.001 |
| PLT ≥ 330.5 | 2.19 (1.44–3.33) | <0.001 | 1.43 (0.83–2.46) | 0.195 |
| WBC ≥ 17.15 | 3.36 (2.19–5.15) | <0.001 | 1.76 (0.96–3.23) | 0.066 |
| NEUT ≥ 81.05 | 3.36 (2.2–5.12) | <0.001 | 3.08 (1.72–5.53) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kottakis, G.; Bekiaridou, K.; Roupakias, S.; Pavlides, O.; Gogoulis, I.; Kosteletos, S.; Dionysis, T.N.; Marantos, A.; Kambouri, K. The Role of Hyponatremia in Identifying Complicated Cases of Acute Appendicitis in the Pediatric Population. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1384. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15111384
Kottakis G, Bekiaridou K, Roupakias S, Pavlides O, Gogoulis I, Kosteletos S, Dionysis TN, Marantos A, Kambouri K. The Role of Hyponatremia in Identifying Complicated Cases of Acute Appendicitis in the Pediatric Population. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(11):1384. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15111384
Chicago/Turabian StyleKottakis, George, Konstantina Bekiaridou, Stylianos Roupakias, Orestis Pavlides, Ioannis Gogoulis, Spyridon Kosteletos, Theodoros Nektarios Dionysis, Aggelos Marantos, and Katerina Kambouri. 2025. "The Role of Hyponatremia in Identifying Complicated Cases of Acute Appendicitis in the Pediatric Population" Diagnostics 15, no. 11: 1384. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15111384
APA StyleKottakis, G., Bekiaridou, K., Roupakias, S., Pavlides, O., Gogoulis, I., Kosteletos, S., Dionysis, T. N., Marantos, A., & Kambouri, K. (2025). The Role of Hyponatremia in Identifying Complicated Cases of Acute Appendicitis in the Pediatric Population. Diagnostics, 15(11), 1384. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15111384







