Parallel VMamba and Attention-Based Pneumonia Severity Prediction from CXRs: A Robust Model with Segmented Lung Replacement Augmentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Development of an innovative deep learning framework that integrates a parallel model with a VMamba encoder, leveraging both channel and spatial attention mechanisms to enhance severity score prediction accuracy from CXRs.
- Introduction of a specialized augmentation strategy, focusing on segmented lung regions. This method incorporates self-replacement and cross-replacement techniques to increase dataset diversity.
- Comprehensive evaluations across multiple datasets, accompanied by ablation studies that assess the model’s generalizability and robustness under different conditions.
2. Related Work
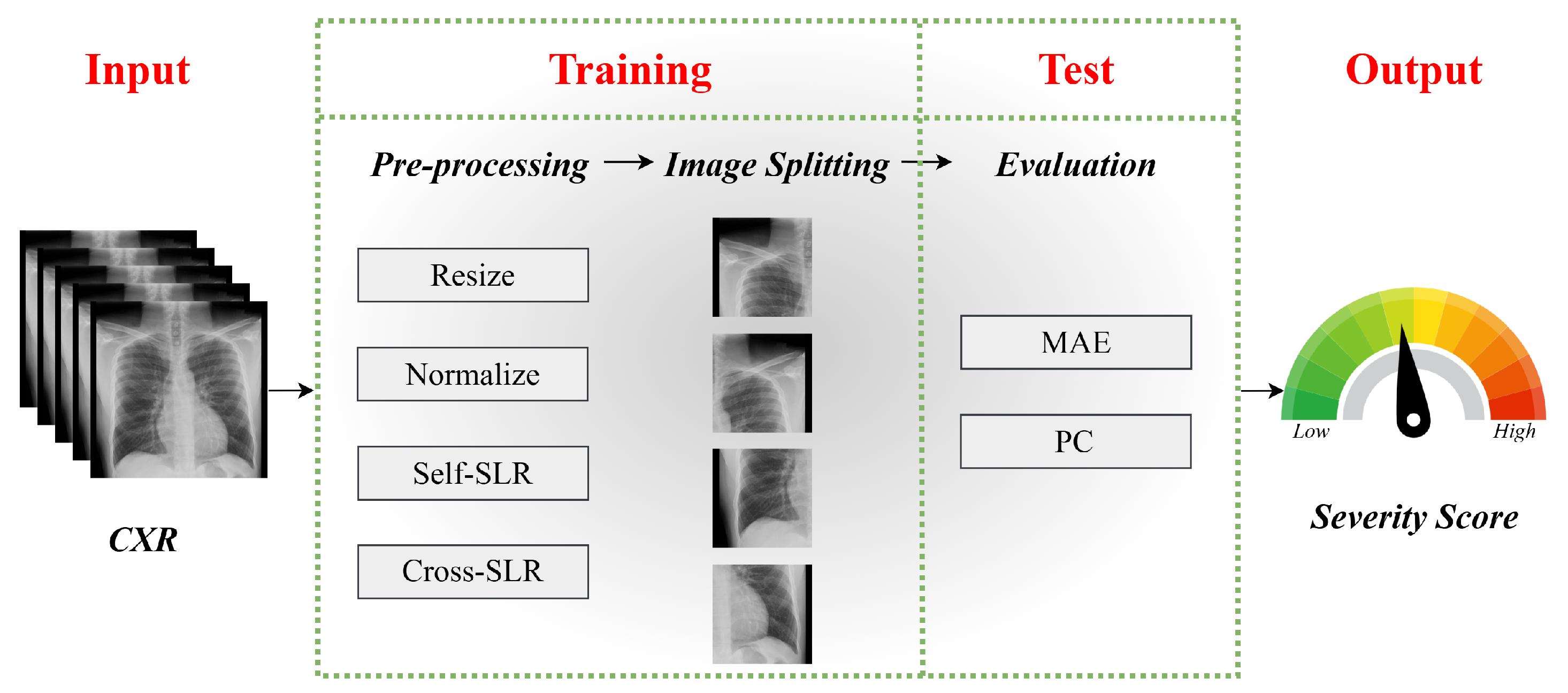
3. Proposed Methodology
3.1. Proposed Model
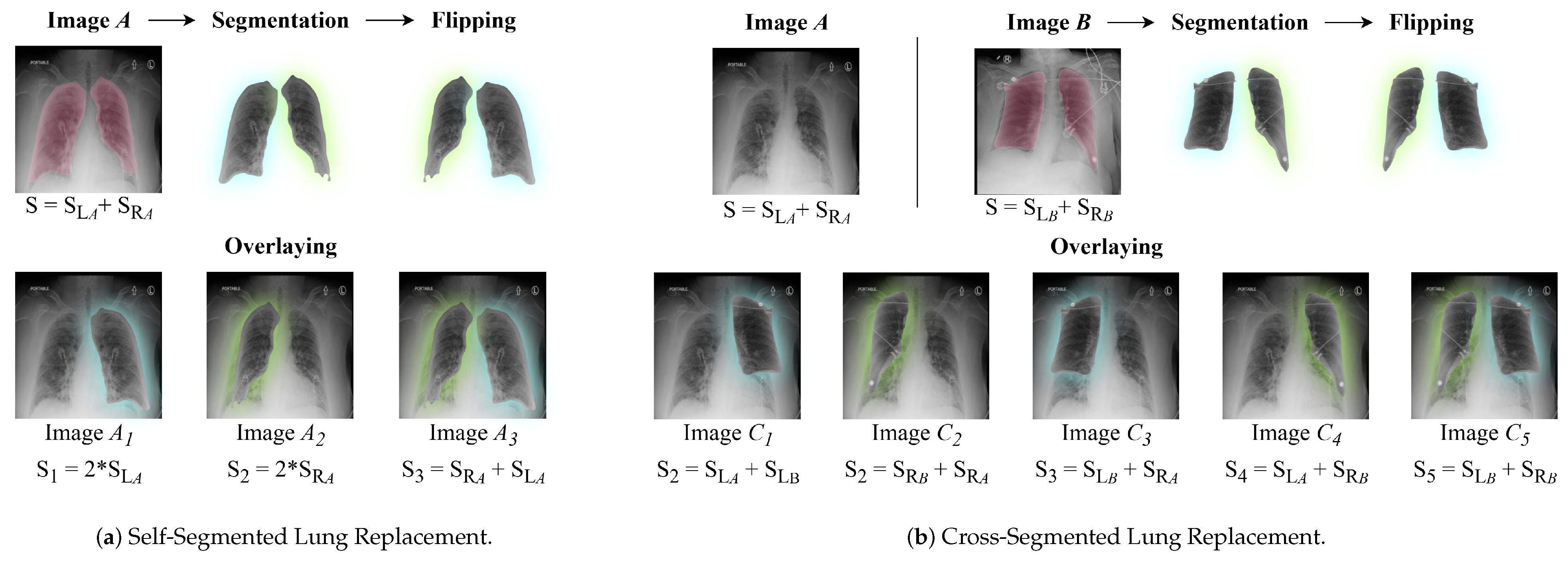
3.2. Data Augmentation: Segmented Lung Replacement
3.2.1. Self-Segmented Lung Replacement
3.2.2. Cross-Segmented Lung Replacement
4. Performance Evaluation
4.1. Datasets
4.1.1. RALO Dataset
4.1.2. COVID-19 Dataset
4.2. Experimental Results and Comparison
4.3. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lim, W.S. Pneumonia—Overview. In Encyclopedia of Respiratory Medicine; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; p. 185. [Google Scholar]
- Rubin, G.D.; Ryerson, C.J.; Haramati, L.B.; Sverzellati, N.; Kanne, J.P.; Raoof, S.; Schluger, N.W.; Volpi, A.; Yim, J.J.; Martin, I.B.; et al. The role of chest imaging in patient management during the COVID-19 pandemic: A multinational consensus statement from the Fleischner Society. Radiology 2020, 296, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litjens, G.; Kooi, T.; Bejnordi, B.E.; Setio, A.A.A.; Ciompi, F.; Ghafoorian, M.; van der Laak, J.A.; van Ginneken, B.; Sánchez, C.I. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 42, 60–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundervold, A.S.; Lundervold, A. An overview of deep learning in medical imaging focusing on MRI. Z. Med. Phys. 2019, 29, 102–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, D.; Wu, G.; Suk, H.I. Deep learning in medical image analysis. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 19, 221–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteva, A.; Robicquet, A.; Ramsundar, B.; Kuleshov, V.; DePristo, M.; Chou, K.; Cui, C.; Corrado, G.; Thrun, S.; Dean, J. A guide to deep learning in healthcare. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenspan, H.; van Ginneken, B.; Summers, R.M. Guest editorial deep learning in medical imaging: Overview and future promise of an exciting new technique. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 1153–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Peng, Y.; Lu, L.; Lu, Z.; Bagheri, M.; Summers, R.M. ChestX-ray8: Hospital-scale chest X-ray database and benchmarks on weakly-supervised classification and localization of common thorax diseases. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2097–2106. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, R.; Nayeem, M.K.; Santhiya, P.; Das, A. Early Diagnosis of Medical Images in Healthcare Management by Artificial Intelligence. In Decision Making Under Uncertainty Via Optimization, Modelling, and Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2025; pp. 427–440. [Google Scholar]
- Rudan, I.; O’Brien, K.L.; Nair, H.; Liu, L.; Theodoratou, E.; Qazi, S.; Luksic, I.; Mathers, C.; Black, R.E.; Campbell, H. Epidemiology and etiology of childhood pneumonia. Bull. World Health Organ. 2013, 91, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawzy, A.; Wang, D.; Esker, A.; Trost, J.G.; Chu, D.; Liu, D.; Singh, A.; Fang, R.; Wang, X.; Baker, E.; et al. AI-powered clinical decision support for COVID-19—insights from rapid development and deployment. NPJ Digit. Med. 2020, 3, 136. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, A.; Dao, T. Mamba: Linear-time sequence modeling with selective state spaces. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.00752. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Ruan, J. Mamba-Vision: A State Space Model for Efficient Video Understanding. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.06789. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhang, S. Mamba-Transformer: A Hybrid Architecture for Efficient Sequence Modeling. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.04567. [Google Scholar]
- Bougourzi, F.; Dornaika, F.; Taleb-Ahmed, A. Deep learning based face beauty prediction via dynamic robust losses and ensemble regression. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 242, 108246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammoudi, K.; Benhabiles, H.; Melkemi, M.; Dornaika, F.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Collard, D.; Scherpereel, A. Deep learning on chest X-ray images to detect and evaluate pneumonia cases at the era of COVID-19. J. Med. Syst. 2021, 45, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Li, M.D.; Capparelli, E.; Patel, S. Quantifying pneumonia severity using deep learning regression models. Med. Image Anal. 2020, 60, 101630. [Google Scholar]
- Ajagbe, S.A.; Adigun, M.O. Deep learning techniques for detection and prediction of pandemic diseases: A systematic literature review. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 5893–5927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Diggans, J.; Pankratz, D.; Huang, J.; Pagan, M.; Sindy, N.; Tom, E.; Anderson, J.; Choi, Y.; Lynch, D.A.; et al. Classification of usual interstitial pneumonia in patients with interstitial lung disease: Assessment of a machine learning approach using high-dimensional transcriptional data. Lancet Respir. Med. 2015, 3, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Opbroek, A.; Ikram, M.A.; Vernooij, M.W.; De Bruijne, M. Automatic brain tissue segmentation by multi-feature SVM classification. NeuroImage 2017, 125, 224–233. [Google Scholar]
- Ting, D.S.W.; Cheung, C.Y.; Lim, G.; Tan, G.S.; Quang, N.D.; Gan, A.; Agrawal, R.; Alam, S.M.; Yeo, I.Y.; Lee, S.E.e.a. Deep learning fundus image analysis for diabetic retinopathy and macular edema grading. Ophthalmology 2019, 126, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar]
- Hemdan, E.E.D.; Shouman, M.A.; Karar, M.E. COVIDX-Net: A framework of deep learning classifiers to diagnose COVID-19 in X-ray images. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.11055. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, X.; Yin, Y. Quantification and severity grading of COVID-19 in CT images using deep learning. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 134, 104323. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, M.P.; Mo, J.; Thomas, R.; Harrell, P.; Lall, C. AI-driven severity assessment of COVID-19 pneumonia using CT scans. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2020, 2, e200054. [Google Scholar]
- Irmak, E. COVID-19 disease severity assessment using CNN model. IET Image Process. 2021, 15, 1814–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombi, D.; Bodini, F.C.; Petrini, M.; Maffi, G.; Morelli, N.; Milanese, G.; Silva, M.; Sverzellati, N.; Michieletti, E. Well-aerated lung on admitting chest CT to predict adverse outcome in COVID-19 pneumonia. Radiology 2020, 296, E86–E96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.; Lin, Z.; Wang, L.; Chung, A.; Shen, B.; Abbasi, A.; Hoshmand-Kochi, M.; Duong, T. Towards computer-aided severity assessment via deep neural networks for geographic and opacity extent scoring of SARS-CoV-2 chest X-rays. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Xu, X.; Cheng, X.; Yu, H.; Zhao, H. Automated severity assessment of COVID-19 using convolutional neural networks with chest X-rays. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 114, 107746. [Google Scholar]
- Wehbe, R.M.; Sheng, J.; Dutta, S.; Chai, S.; Dravid, A.; Barutcu, S.; Wu, Y.; Cantrell, D.R.; Xiao, N.; Allen, B.D.; et al. DeepCOVID-XR: An artificial intelligence algorithm to detect COVID-19 on chest radiographs trained and tested on a large US clinical data set. Radiology 2021, 299, E167–E176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angara, S.; Thirunagaru, S. Study of Vision Transformers for COVID-19 Detection from Chest X-rays. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.09402. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan, K.S.; Krishnan, K.S. Vision transformer based COVID-19 detection using chest X-rays. In Proceedings of the 2021 6th International Conference on Signal Processing, Computing and Control (ISPCC), Solan, India, 7–9 October 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 644–648. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, B.; Zhou, X.; Li, W. Vision Transformer-based Model for Severity Quantification of Lung Pneumonia Using Chest X-ray Images. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.11935. [Google Scholar]
- Taslimi, S.; Taslimi, S.; Fathi, N.; Salehi, M.; Rohban, M.H. Swinchex: Multi-label classification on chest x-ray images with transformers. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.04246. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wen, Y. A transformer-based framework for automatic COVID19 diagnosis in chest CTs. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 513–518. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, X. CheX-DS: Improving Chest X-ray Image Classification with Ensemble Learning Based on DenseNet and Swin Transformer. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), Lisboa, Portugal, 3–6 December 2024; pp. 5295–5301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wienholt, P.; Hermans, A.; Khader, F.; Puladi, B.; Leibe, B.; Kuhl, C.; Nebelung, S.; Truhn, D. An Ordinal Regression Framework for a Deep Learning Based Severity Assessment for Chest Radiographs. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.05685. [Google Scholar]
- Aboutalebi, H.; Pavlova, M.; Shafiee, M.J.; Sabri, A.; Alaref, A.; Wong, A. COVID-Net CXR-S: Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Severity Assessment of COVID-19 Cases from Chest X-ray Images. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.00256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Ruan, J. FT-Mamba: A Novel Deep Learning Model for Efficient Tabular Regression. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), Lisboa, Portugal, 3–6 December 2024; pp. 3096–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, B. Mamba-Diffusion: Latent Diffusion Models with State Space Backbones for Efficient Data Generation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.08901. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Pan, Y.; Hong, Y. Mamba-GAN: Generative Adversarial Networks with State Space Models for High-Resolution Image Synthesis. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.07890. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Z.; Zhang, L. P-Mamba: Marrying Perona Malik Diffusion with Mamba for Efficient Pediatric Echocardiographic Left Ventricular Segmentation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.01111. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Li, X.; Xu, X. Mamba for Medical Imaging: Efficient Long-Range Dependency Modeling in 3D Volumes. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.05678. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, H.; Li, H. nnMamba: 3D Biomedical Image Segmentation, Classification and Landmark Detection with State Space Model. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.00505. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Pan, Y.; Hu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Hong, Y.; Yang, Y. Enhancing Chest X-ray Diagnostics with Neighbor-assisted Multimodal Integration. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), Lisboa, Portugal, 3–6 December 2024; pp. 3872–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaraman, S.; Liang, Z.; Xue, Z.; Antani, S. Addressing Class Imbalance with Latent Diffusion-based Data Augmentation for Improving Disease Classification in Pediatric Chest X-rays. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), Lisboa, Portugal, 3–6 December 2024; pp. 5059–5066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lin, Y.; Ding, X.; Li, X. Tri-Plane Mamba: Efficiently Adapting Segment Anything Model for 3D Medical Images. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.04377. [Google Scholar]
- Bansal, S.; Sreeharish, A.; Prasath, M.; Manikandan, S.; Madisetty, S.; Rehman, M.Z.U.; Raghaw, C.S.; Duggal, G.; Kumar, N. A Comprehensive Survey of Mamba Architectures for Medical Image Analysis: Classification, Segmentation, Restoration and Beyond. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.02362. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, W.; Ma, L. LightM-UNet: Mamba Assists in Lightweight UNet for Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.02828. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Li, L. Mamba-UNet: UNet-Like Pure Visual Mamba for Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.00505. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, J.; Ma, S. VM-UNet: Vision Mamba UNet for Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.00303. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Ma, C. Weak-Mamba-UNet: Visual Mamba Makes CNN and ViT Work Better for Scribble-based Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.01313. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, H.; Xie, L.; Wang, Y.; Ye, Q.; Jiao, J.; Liu, Y. Vmamba: Visual state space model. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2025, 37, 103031–103063. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Rahman Siddiquee, M.M.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. Unet++: A nested u-net architecture for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support: 4th International Workshop, DLMIA 2018, and 8th International Workshop, ML-CDS 2018, held in conjunction with MICCAI 2018, Granada, Spain, 20 September 2018; Proceedings 4. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J.P.; Dao, L.; Roth, K.; Morrison, P.; Bengio, Y.; Abbasi, A.F.; Shen, B.; Mahsa, H.K.; Ghassemi, M.; Li, H.; et al. Predicting covid-19 pneumonia severity on chest x-ray with deep learning. Cureus 2020, 12, e9448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danilov, V.; Proutski, A.; Kirpich, A.; Litmanovich, D.; Gankin, Y. Dataset for COVID-19 Segmentation and Severity Scoring. 2022. Available online: https://data.mendeley.com/datasets/36fjrg9s69/1 (accessed on 5 December 2024).
- Cohen, J.P.; Shen, B.; Abbasi, A.; Hoshmand-Kochi, M.; Glass, S.; Li, H.; Lungren, M.P.; Chaudhari, A.; Duong, T.Q. Radiographic Assessment of Lung Opacity Score Dataset. 2021. Available online: https://data.niaid.nih.gov/resources?id=zenodo_4633999 (accessed on 10 October 2024).
- Slika, B.; Dornaika, F.; Merdji, H.; Hammoudi, K. Lung pneumonia severity scoring in chest X-ray images using transformers. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2024, 62, 2389–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lin, Z.Q.; Wong, A. COVID-Net: A tailored deep convolutional neural network design for detection of covid-19 cases from chest x-ray images. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1251–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.; Sandler, M.; Chu, G.; Chen, L.C.; Chen, B.; Tan, M.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Pang, R.; Vasudevan, V.; et al. Searching for MobileNetV3. arXiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Slika, B.; Dornaika, F.; Hammoudi, K. Multi-Score Prediction for Lung Infection Severity in Chest X-Ray Images. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. Intell. 2024, 9, 2052–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Data | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dataset | Size | Training | Validation | Test |
| RALO [56] | 224 × 224 × 3 | 5634 | - | 495 |
| COVID-19 [57] | 224 × 224 × 3 | 1090 | 135 | 139 |
| Score | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dataset | Type | Min | Max | Increment | Mean | Std | Variance |
| RALO [56] | GE | 0 | 8.0 | 0.5 | 5.1075 | 2.0915 | 4.3745 |
| LO | 0 | 8.0 | 0.5 | 3.7355 | 1.5137 | 2.2913 | |
| COVID-19 [57] | COVID-19 score | 0 | 6.0 | 1 | 1.6015 | 2.1908 | 4.7998 |
| GE | LO | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | MAE ↓ | PC ↑ | MAE ↓ | PC ↑ | Nb of Pram. |
| COVID-NET [29] | 4.458 | 0.549 | 2.242 | 0.535 | 12 M |
| COVID-NET-S [60] | 4.698 | 0.591 | 2.254 | 0.529 | 12 M |
| ResNet50 [61] | 1.094 | 0.688 | 1.061 | 0.431 | 23 M |
| Swin Transformer [62] | 0.916 | 0.817 | 0.803 | 0.697 | 29 M |
| XceptionNet [63] | 0.854 | 0.821 | 0.768 | 0.701 | 23 M |
| Feature Extraction [56] | 0.967 | 0.753 | 0.865 | 0.711 | 20 M |
| MobileNetV3 [64] | 0.847 | 0.827 | 0.732 | 0.738 | 4.2 M |
| InceptionNet [65] | 0.702 | 0.886 | 0.609 | 0.829 | 24 M |
| ViTReg-IP [59] | 0.565 | 0.925 | 0.510 | 0.857 | 5.5 M |
| MViTReg-IP [66] | 0.531 | 0.938 | 0.462 | 0.881 | 11.2 M |
| Ours | 0.356 | 0.970 | 0.338 | 0.941 | 86 M |
| Dataset | Score | Train Size | Test Size | MAE ↓ | PC ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RALO [58] | Geographic Extent | 5634 | 495 | 0.356 | 0.970 |
| RALO [58] | Lung Opacity | 5634 | 495 | 0.338 | 0.941 |
| COVID-19 [57] | COVID Score | 1090 | 139 | 0.322 | 0.921 |
| GE | LO | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Augmentation | MAE ↓ | PC ↑ | MAE ↓ | PC ↑ |
| No Augmentation | 0.374 | 0.958 | 0.354 | 0.927 |
| Traditional Augmentation | 0.372 | 0.959 | 0.353 | 0.927 |
| Self-SLR | 0.366 | 0.963 | 0.348 | 0.934 |
| Cross-SLR | 0.360 | 0.966 | 0.342 | 0.938 |
| Attention | GE | LO | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Channel Attention | Spacial Attention | MAE ↓ | PC ↑ | MAE ↓ | PC ↑ |
| × | × | 0.432 | 0.939 | 0.402 | 0.922 |
| × | ✔ | 0.367 | 0.962 | 0.349 | 0.930 |
| ✔ | × | 0.362 | 0.966 | 0.341 | 0.937 |
| ✔ | ✔ | 0.356 | 0.970 | 0.338 | 0.941 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Slika, B.; Dornaika, F.; Hammoudi, K. Parallel VMamba and Attention-Based Pneumonia Severity Prediction from CXRs: A Robust Model with Segmented Lung Replacement Augmentation. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1301. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15111301
Slika B, Dornaika F, Hammoudi K. Parallel VMamba and Attention-Based Pneumonia Severity Prediction from CXRs: A Robust Model with Segmented Lung Replacement Augmentation. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(11):1301. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15111301
Chicago/Turabian StyleSlika, Bouthaina, Fadi Dornaika, and Karim Hammoudi. 2025. "Parallel VMamba and Attention-Based Pneumonia Severity Prediction from CXRs: A Robust Model with Segmented Lung Replacement Augmentation" Diagnostics 15, no. 11: 1301. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15111301
APA StyleSlika, B., Dornaika, F., & Hammoudi, K. (2025). Parallel VMamba and Attention-Based Pneumonia Severity Prediction from CXRs: A Robust Model with Segmented Lung Replacement Augmentation. Diagnostics, 15(11), 1301. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15111301






