Association of [18F]-FDG PET/CT-Derived Radiomic Features with Clinical Outcomes and Genomic Profiles in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Population Study
2.2. Image Acquisition and Analysis
2.3. Radiomic Workflow
2.4. Statistical Analysis and Model Building
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Radiomic Analysis
3.3. Machine Learning Models’ Performances
4. Discussion
5. Study Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scarfò, L.; Ferreri, A.J.; Ghia, P. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2016, 104, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cronin, K.A.; Ries, L.A.; Edwards, B.K. The surveillance, epidemiology, and end results (SEER) program of the National Cancer Institute. Cancer 2014, 120, 3755–3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallek, M.; Shanafelt, T.D.; Eichhorst, B. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Lancet 2018, 391, 1524–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, P.J.; Parikh, S.A. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia treatment algorithm 2022. Blood Cancer J. 2022, 12, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichhorst, B.; Robak, T.; Montserrat, E.; Ghia, P.; Niemann, C.U.; Kater, A.P.; Gregor, M.; Cymbalista, F.; Buske, C.; Hillmen, P.; et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, F.; Dalla-Favera, R. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: From genetics to treatment. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 684–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crassini, K.; Stevenson, W.S.; Mulligan, S.P.; Best, O.G. Molecular pathogenesis of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 186, 668–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianfelici, V.; Levato, L.; Molica, S. The Evolution of Targeted Therapies in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2020, 15, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollstedt, J.; Mansouri, L.; Rosenquist, R. Precision diagnostics in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Past, present and future. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1146486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallek, M.; Al-Sawaf, O. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia:2022 update on diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96, 1679–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Pagel, J.M. Current and future treatment strategies in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seiffert, M.; Dietrich, S.; Jethwa, A.; Glimm, H.; Lichter, P.; Zenz, T. Exploiting biological diversity and genomic aberrations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2012, 53, 1023–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeu, F.; Diaz-Navarro, A.; Delgado, J.; Puente, X.S.; Campo, E. Genomic and Epigenomic Alterations in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2020, 15, 149–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontecha, M.B.; Anadón, M.D.R.; Mercado Guzmán, V.; Stanganelli, C.; Galvano, C.; Tosin, F.; Bordone, J.; Bezares, R.; Rodríguez, C.; Heller, V.; et al. Genetic variability profiling of the p53 signaling pathway in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Individual and combined analysis of TP53, MDM2 and NQO1 gene variants. Ann. Hematol. 2024, 103, 5703–5712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Falco, F.; Sabatini, R.; Del Papa, B.; Falzetti, F.; Di Ianni, M.; Sportoletti, P.; Baldoni, S.; Screpanti, I.; Marconi, P.; Rosati, E. Notch signaling sustains the expression of Mcl-1 and the activity of eIF4E to promote cell survival in CLL. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 16559–16572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grants, J.M.; May, C.; Bridgers, J.; Huang, S.; Gillis, S.; Meissner, B.; Boyle, M.; Ben-Neriah, S.; Hung, S.; Duns, G.; et al. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia IGHV Somatic Hypermutation Detection by Targeted Capture Next-Generation Sequencing. Clin. Chem. 2024, 70, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenz, T.; Vollmer, D.; Trbusek, M.; Smardova, J.; Benner, A.; Soussi, T.; Helfrich, H.; Heuberger, M.; Hoth, P.; Fuge, M.; et al. TP53 mutation profile in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Evidence for a disease specific profile from a comprehensive analysis of 268 mutations. Leukemia 2010, 24, 2072–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeu, F.; Delgado, J.; Royo, C.; Baumann, T.; Stankovic, T.; Pinyol, M.; Jares, P.; Navarro, A.; Martín-García, D.; Beà, S.; et al. Clinical impact of clonal and subclonal TP53, SF3B1, BIRC3, NOTCH1, and ATM mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2016, 127, 2122–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puente, X.S.; Pinyol, M.; Quesada, V.; Conde, L.; Ordóñez, G.R.; Villamor, N.; Escaramis, G.; Jares, P.; Beà, S.; González-Díaz, M.; et al. Whole-genome sequencing identifies recurrent mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nature 2011, 475, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puente, X.S.; Bea, S.; Valdes-Mas, R.; Villamor, N.; Guiterrez-Abril, J.; Martin-Subero, J.I.; Munar, M.; Rubio-Perez, C.; Jares, P.; Aymerich, M.; et al. Non-coding recurrent muta-tions in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nature 2015, 526, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauro, F.R.; Chauvie, S.; Paoloni, F.; Biggi, A.; Cimino, G.; Rago, A.; Gentile, M.; Morabito, F.; Coscia, M.; Bellò, M.; et al. Diagnostic and prognosticrole of PET/CT in patients with chroniclymphocyticleukemia and progressive disease. Leukemia 2015, 29, 1360–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molica, S. FDG/PET in CLL today. Blood 2014, 123, 2749–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheson, B.D.; Fisher, R.I.; Barrington, S.F.; Cavalli, F.; Schwartz, L.H.; Zucca, E.; Lister, T.A.; Alliance, Australasian Leukaemia and Lymphoma Group; Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; European Mantle Cell Lymphoma Consortium; et al. Recommendations for initial evaluation, staging, and response assessment of Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma: The Lugano classification. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3059–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrington, S.F.; Mikhaeel, N.G.; Kostakoglu, L.; Meignan, M.; Hutchings, M.; Müeller, S.P.; Schwartz, L.H.; Zucca, E.; Fisher, R.I.; Trotman, J.; et al. Role of imaging in the staging and response assessment of lymphoma: Consensus of the International Conference on Malignant Lymphomas Imaging Working Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3048–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, M.J.; Bowen, D.A.; Wiseman, G.A.; Rabe, K.G.; Slager, S.L.; Schwager, S.M.; Call, T.G.; Viswanatha, D.S.; Zent, C.S. Use of positron emission tomography-computed tomography in the management of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2014, 55, 2079–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rossi, D.; Gaidano, G. Richter syndrome. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2013, 792, 173–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albano, D.; Rizzo, A.; Racca, M.; Muoio, B.; Bertagna, F.; Treglia, G. The Diagnostic Performance of 2-[18F]FDG PET/CT in Identifying Richter Transformation in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: An Updated Systematic Review and Bivariate Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2024, 16, 1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Albano, D.; Camoni, L.; Rodella, C.; Giubbini, R.; Bertagna, F. 2-[18F]-FDG PET/CT Role in Detecting Richter Transformation of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia and Predicting Overall Survival. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2021, 21, e277–e283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falchi, L.; Keating, M.J.; Marom, E.M.; Truong, M.T.; Schlette, E.J.; Sargent, R.L.; Trinh, L.; Wang, X.; Smith, S.C.; Jain, N.; et al. Correlation between FDG/PET, histology, characteristics, and survival in 332 patients with chronic lymphoid leukemia. Blood 2014, 123, 2783–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chauvie, S.; Ceriani, L.; Zucca, E. Radiomics in Malignant Lymphomas. In Lymphoma; Gallamini, A., Juweid, M., Eds.; Exon Publications: Brisbane, Australia, 2021; Chapter 5. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alderuccio, J.P.; Reis, I.M.; Hamadani, M.; Nachiappan, M.; Leslom, S.; Kahl, B.S.; Ai, W.Z.; Radford, J.; Solh, M.; Ardeshna, K.M.; et al. PET/CT Biomarkers Enable Risk Stratification of Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Enrolled in the LOTIS-2 Clinical Trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 30, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ceriani, L.; Gritti, G.; Cascione, L.; Pirosa, M.C.; Polino, A.; Ruberto, T.; Stathis, A.; Bruno, A.; Moccia, A.A.; Giovanella, L.; et al. SAKK38/07 study: Integration of baseline metabolic heterogeneity and metabolic tumor volume in DLBCL prognostic model. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 1082–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Genta, S.; Ghilardi, G.; Cascione, L.; Juskevicius, D.; Tzankov, A.; Schär, S.; Milan, L.; Pirosa, M.C.; Esposito, F.; Ruberto, T.; et al. Integration of Baseline Metabolic Parameters and Mutational Profiles Predicts Long-Term Response to First-Line Therapy in DLBCL Patients: A Post Hoc Analysis of the SAKK38/07 Study. Cancers 2022, 14, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mikhaeel, N.G.; Smith, D.; Dunn, J.T.; Phillips, M.; Møller, H.; Fields, P.A.; Wrench, D.; Barrington, S.F. Combination of baseline metabolic tumour volume and early response on PET/CT improves progression-free survival prediction in DLBCL. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2016, 43, 1209–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ceriani, L.; Milan, L.; Cascione, L.; Gritti, G.; Dalmasso, F.; Esposito, F.; Pirosa, M.C.; Schär, S.; Bruno, A.; Dirnhofer, S.; et al. Generation and validation of a PET radiomics model that predicts survival in diffuse large B cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP14: A SAKK 38/07 trial post-hoc analysis. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 40, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eertink, J.J.; Pfaehler, E.A.G.; Wiegers, S.E.; van de Brug, T.; Lugtenburg, P.J.; Hoekstra, O.S.; Zijlstra, J.M.; de Vet, H.C.W.; Boellaard, R. Quantitative Radiomics Features in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Does Segmentation Method Matter? J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Alderuccio, J.P.; Kuker, R.A.; Yang, F.; Moskowitz, C.H. Quantitative PET-based biomarkers in lymphoma: Getting ready for primetime. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 20, 640–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippi, L.; Bianconi, F.; Schillaci, O.; Spanu, A.; Palumbo, B. The Role and Potential of 18F-FDG PET/CT in Malignant Melanoma: Prognostication, Monitoring Response to Targeted and Immunotherapy, and Radiomics. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hasanabadi, S.; Aghamiri, S.M.R.; Abin, A.A.; Abdollahi, H.; Arabi, H.; Zaidi, H. Enhancing Lymphoma Diagnosis, Treatment, and Follow-Up Using 18F-FDG PET/CT Imaging: Contribution of Artificial Intelligence and Radiomics Analysis. Cancers 2024, 16, 3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zanoni, L.; Bezzi, D.; Nanni, C.; Paccagnella, A.; Farina, A.; Broccoli, A.; Casadei, B.; Zinzani, P.L.; Fanti, S. PET/CT in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma: An Update. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2023, 53, 320–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jesus, F.M.; Yin, Y.; Mantzorou-Kyriaki, E.; Kahle, X.U.; de Haas, R.J.; Yakar, D.; Glaudemans, A.W.J.M.; Noordzij, W.; Kwee, T.C.; Nijland, M. Machine learning in the differentiation of follicular lymphoma from diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with radiomic [18F]FDG PET/CT features. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 49, 1535–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kummar, S.; Lu, R. Using Radiomics in Cancer Management. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2024, 8, e2400155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, F.; Mezzanotte, V.; Tesei, C.; Luciano, A.; Gigliotti, P.E.; Nunzi, A.; Secchi, R.; Angeloni, C.; Pitaro, M.; Meconi, F.; et al. CT Images in Follicular Lymphoma: Changes after Treatment Are Predictive of Cardiac Toxicity in Patients Treated with Anthracycline-Based or R-B Regimens. Cancers 2024, 16, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lee, J.G.; Jun, S.; Cho, Y.W.; Lee, H.; Kim, G.B.; Seo, J.B.; Kim, N. Deep Learning in Medical Imaging: General Overview. Korean J. Radiol. 2017, 18, 570–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ranschaert, E.R.; Morozov, S.; Algra, P.R. (Eds.) Artificial Intelligence in Medical Imaging: Opportunities, Applications and Risks; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Manco, L.; Maffei, N.; Strolin, S.; Vichi, S.; Bottazzi, L.; Strigari, L. Basic of machine learning and deep learning in imaging for medical physicists. Phys. Med. 2021, 83, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Sang, S.; Deng, S. Radiomic Features of 18F-FDG PET in Hodgkin Lymphoma Are Predictive of Outcomes. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2021, 2021, 6347404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mayerhoefer, M.E.; Riedl, C.C.; Kumar, A.; Gibbs, P.; Weber, M.; Tal, I.; Schilksy, J.; Schöder, H. Radiomic features of glucose metabolism enable prediction of outcome in mantle cell lymphoma. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 2760–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Jia, T.; Zhang, B.; Dai, N.; Sang, S.; Deng, S. Prognostic Value of Radiomic Features of 18F-FDG PET/CT in Patients With B-Cell Lymphoma Treated with CD19/CD22 Dual-Targeted Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 834288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- van Timmeren, J.E.; Cester, D.; Tanadini-Lang, S.; Alkadhi, H.; Baessler, B. Radiomics in medical imaging-“how-to” guide and critical reflection. Insights Imaging 2020, 11, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mayerhoefer, M.E.; Materka, A.; Langs, G.; Häggström, I.; Szczypiński, P.; Gibbs, P.; Cook, G. Introduction to Radiomics. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 61, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Boellaard, R.; Delgado-Bolton, R.; Oyen, W.J.; Giammarile, F.; Tatsch, K.; Eschner, W.; Verzijlbergen, F.J.; Barrington, S.F.; Pike, L.C.; Weber, W.A.; et al. FDG PET/CT: EANM procedure guidelines for tumour imaging: Version 2.0. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2015, 42, 328–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fedorov, A.; Beichel, R.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Finet, J.; Fillion-Robin, J.C.; Pujol, S.; Bauer, C.; Jennings, D.; Fennessy, F.; Sonka, M.; et al. 3D Slicer as an image computing platform for the Quantitative Imaging Network. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 30, 1323–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rai, K.R.; Jain, P. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)-Then and now. Am. J. Hematol. 2016, 91, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
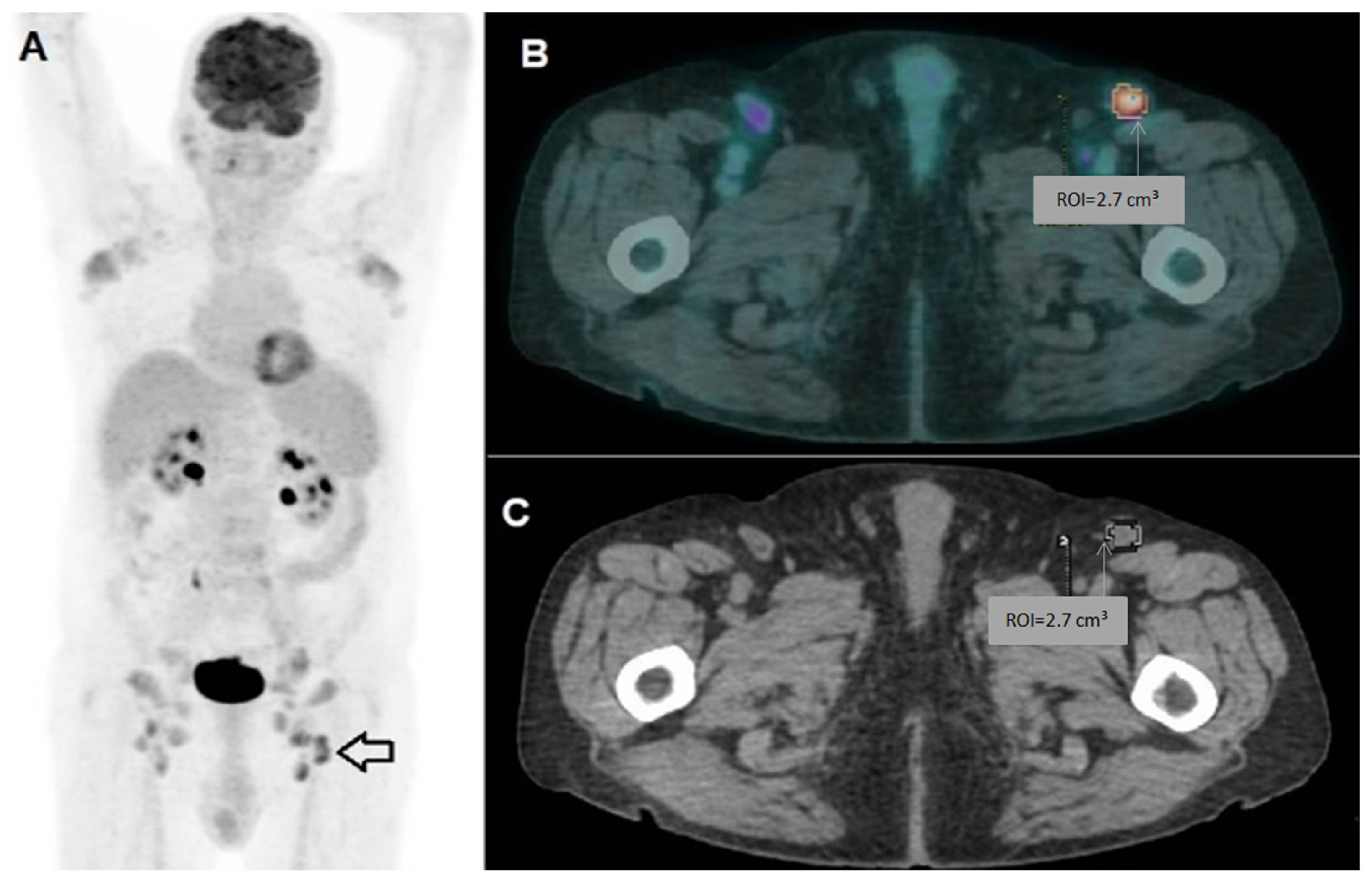
| Patient Characteristics | PR_0 | PR_1 | TP53_0 | TP53_1 | NOTCH1_0 | NOTCH1_1 | IGVH_0 | IGVH_1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients | 40 | 10 | 38 | 12 | 38 | 12 | 35 | 15 |
| Age [year] | ||||||||
| Mean ± St.dev. | 63.13 ± 12.94 | 57.53 ± 8.76 | 61.36 ± 12.01 | 63.99 ± 13.85 | 63.66 ± 10.55 | 56.52 ± 16.45 | 60.8 ± 13.57 | 64.82 ± 8.44 |
| SUV max | 3.87 ± 2.6 | 5.83 ± 3.79 | 4.58 ± 3.14 | 3.29 ± 1.91 | 4.42 ± 3.29 | 3.78 ± 1.18 | 4.77 ± 3.19 | 3.07 ± 1.78 |
| SUV peak | 1.66 ± 1.09 | 2.44 ± 1.59 | 1.93 ± 1.31 | 1.45 ± 0.87 | 1.88 ± 1.38 | 1.62 ± 0.44 | 2.04 ± 1.31 | 1.3 ± 0.84 |
| SUV mean | 2.34 ± 1.52 | 3.51 ± 2.28 | 2.73 ± 1.84 | 2.11 ± 1.27 | 2.66 ± 1.95 | 2.34 ± 0.62 | 2.87 ± 1.85 | 1.89 ± 1.22 |
| MTV | 33.8 ± 96.42 | 29.35 ± 59.46 | 35.42 ± 97.99 | 24.64 ± 56.41 | 35.36 ± 101.38 | 24.84 ± 27.75 | 42.43 ± 105.19 | 9.96 ± 11 |
| TLG | 79.89 ± 235.23 | 53.6 ± 69.34 | 87.64 ± 238.38 | 31.69 ± 67.2 | 78.71 ± 238.19 | 60.73 ± 85.32 | 99.14 ± 248.37 | 15.29 ± 18 |
| Spleen SUV max | 2.93 ± 0.81 | 2.93 ± 0.95 | 3.01 ± 0.7 | 2.68 ± 1.15 | 2.84 ± 0.85 | 3.24 ± 0.69 | 3.01 ± 0.76 | 2.73 ± 0.97 |
| Spleen max diam. [cm] | 14.85 ± 3.46 | 13.43 ± 1.27 | 14.85 ± 3.4 | 13.63 ± 2.2 | 14.87 ± 3.36 | 13.56 ± 2.35 | 13.79 ± 2.08 | 16.4 ± 4.53 |
| Lymph nodes/bulky max diam. [mm] | 41.48 ± 28.68 | 36.57 ± 13.53 | 43 ± 28.61 | 32.25 ± 14.37 | 37.35 ± 20.58 | 50.63 ± 39.55 | 45.13 ± 28.91 | 29.3 ± 13.43 |
| β2-microglobulin levels | 3.03 ± 1.85 | 3.32 ± 1.04 | 3.03 ± 1.7 | 3.29 ± 1.85 | 3.18 ± 1.59 | 2.8 ± 2.14 | 3.34 ± 1.8 | 2.49 ± 1.36 |
| LDH [U/L] | 231.25 ± 95.17 | 333 ± 195.61 | 254.18 ± 138.8 | 245.75 ± 76.1 | 250.46 ± 125.37 | 257.84 ± 135.93 | 277.2 ± 140.88 | 192.2 ± 41.01 |
| Parameter | PR | TP53 | NOTCH1 | IGVH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age [year] | 0.33 | 0.58 | 0.25 | 0.58 |
| SUV max | 0.33 | 0.24 | 0.64 | 0.24 |
| SUV peak | 0.42 | 0.24 | 0.50 | 0.24 |
| SUV mean | 0.34 | 0.28 | 0.57 | 0.28 |
| MTV | 0.78 | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.12 |
| TLG | 0.46 | 0.10 | 0.20 | 0.10 |
| Spleen SUV max | 0.97 | 0.36 | 0.26 | 0.36 |
| Spleen max diam. [cm] | 0.58 | 0.45 | 0.28 | 0.45 |
| Lymph nodes/bulky max diam. [mm] | 0.86 | 0.60 | 0.40 | 0.60 |
| β2-microglobulin levels | 0.39 | 0.68 | 0.43 | 0.68 |
| LDH | 0.12 | 0.79 | 0.34 | 0.79 |
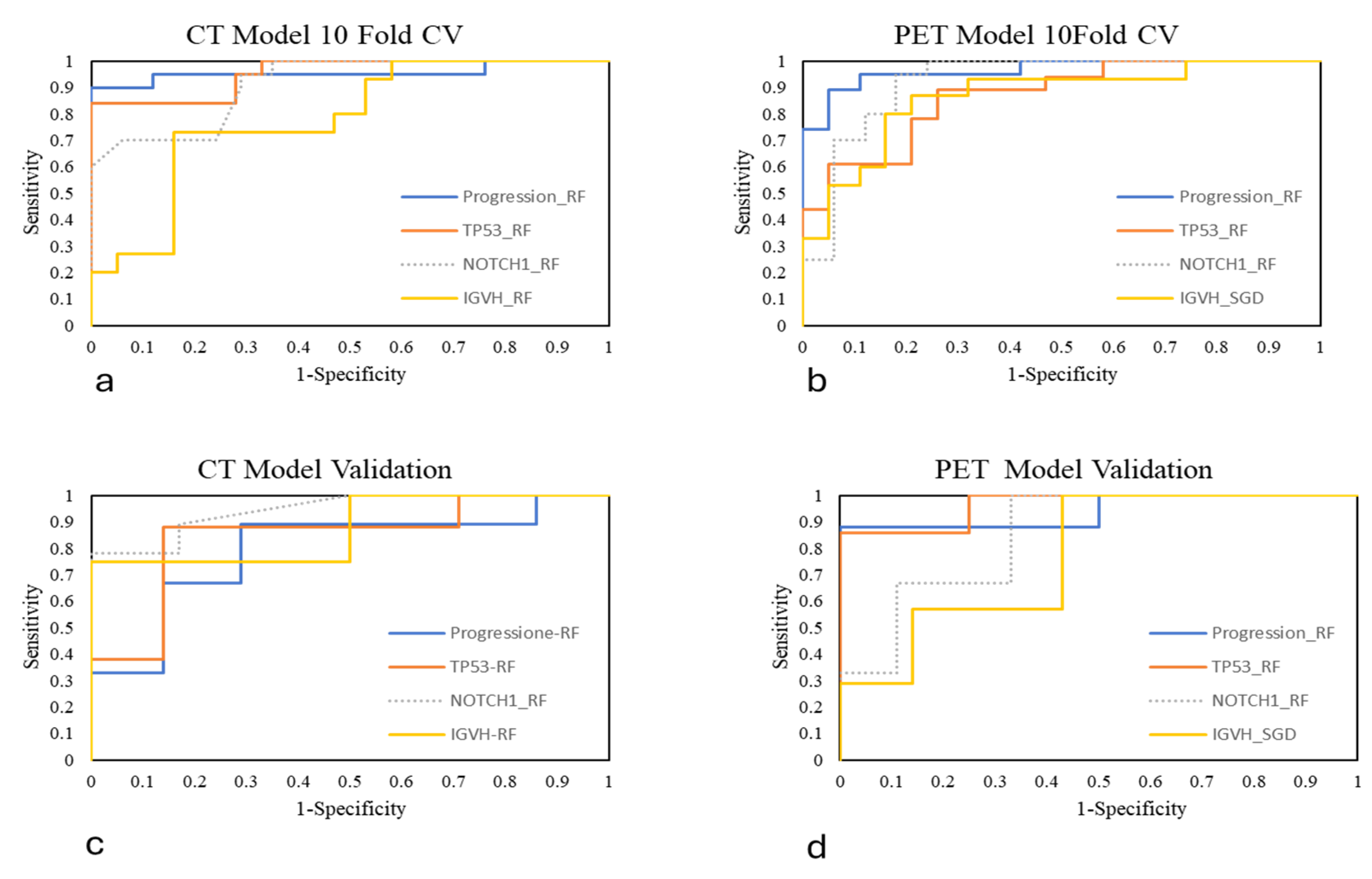
| CT_10-Fold CV | AUC | CA | Precision | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Progression_RF | 0.96 | 0.92 | 0.92 | 0.92 | 0.93 |
| TP53_RF | 0.95 | 0.81 | 0.81 | 0.81 | 0.81 |
| NOTCH1_RF | 0.91 | 0.81 | 0.84 | 0.81 | 0.83 |
| IGVH_RF | 0.78 | 0.68 | 0.69 | 0.68 | 0.69 |
| PET_10-Fold CV | |||||
| Progression_RF | 0.96 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.90 |
| TP53_RF | 0.87 | 0.81 | 0.82 | 0.81 | 0.82 |
| NOTCH1_RF | 0.92 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.86 |
| IGVH_SGD | 0.84 | 0.77 | 0.79 | 0.77 | 0.79 |
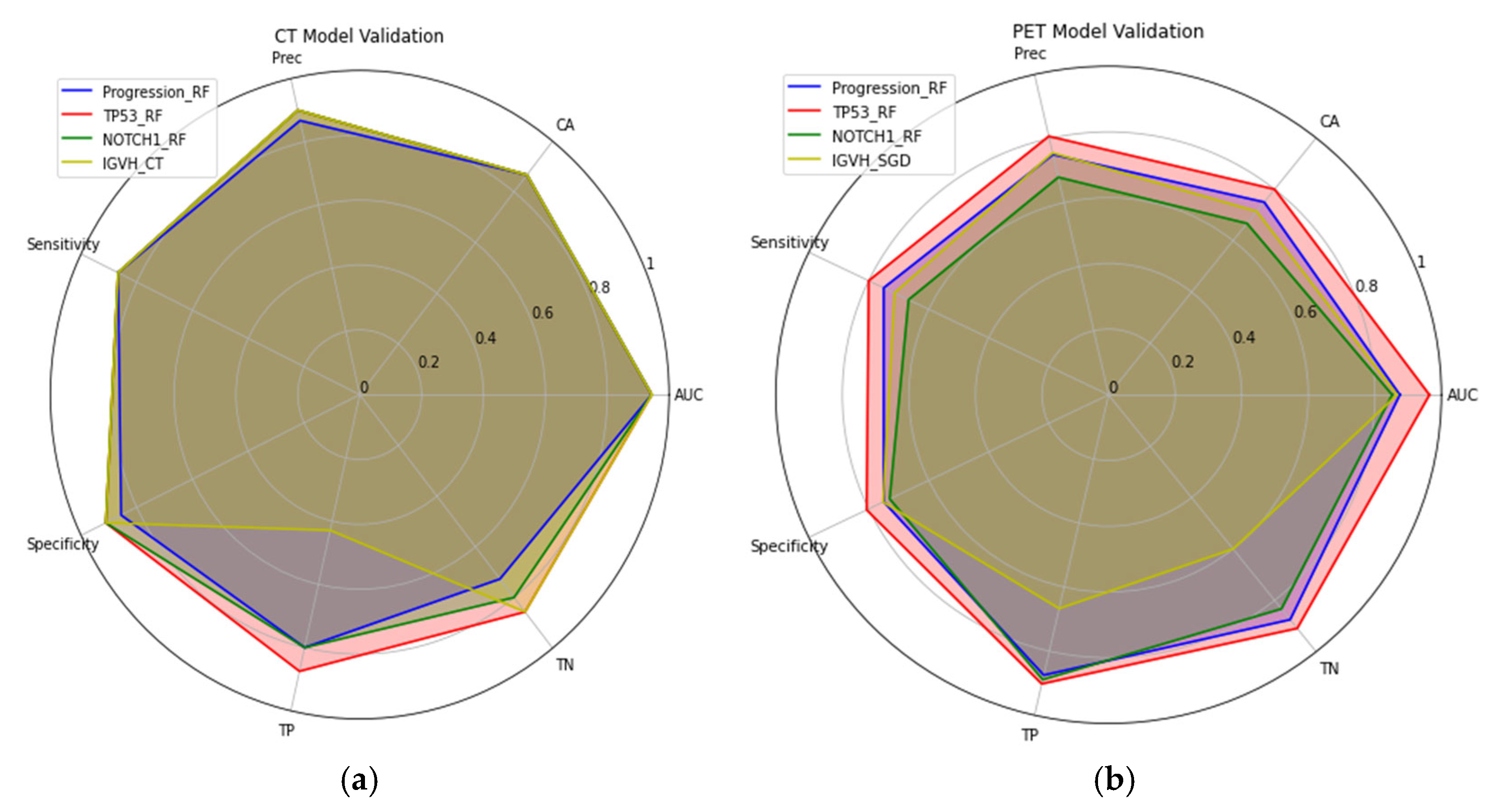
| CT Model | AUC | CA | Precision | Sensitivity | Specificity | TP | TN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Progression_RF | 0.94 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.86 | 0.80 | 0.73 |
| TP53_RF | 0.94 | 0.87 | 0.90 | 0.87 | 0.91 | 0.87 | 0.86 |
| NOTCH1_RF | 0.94 | 0.87 | 0.90 | 0.87 | 0.91 | 0.80 | 0.8 |
| IGVH_RF | 0.94 | 0.87 | 0.90 | 0.87 | 0.91 | 0.43 | 0.86 |
| PET Model | |||||||
| Progression_RF | 0.88 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.87 | 87.50 |
| TP53_RF | 0.96 | 0.80 | 0.81 | 0.80 | 0.81 | 0.90 | 0.91 |
| NOTCH1_RF | 0.85 | 0.67 | 0.68 | 0.67 | 0.73 | 0.89 | 0.83 |
| IGVH_SGD | 0.87 | 0.71 | 0.76 | 0.71 | 0.75 | 0.67 | 0.60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Esposito, F.; Manco, L.; Manenti, G.; Pupo, L.; Nunzi, A.; Laureana, R.; Guarnera, L.; Marinoni, M.; Buzzatti, E.; Gigliotti, P.E.; et al. Association of [18F]-FDG PET/CT-Derived Radiomic Features with Clinical Outcomes and Genomic Profiles in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1281. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15101281
Esposito F, Manco L, Manenti G, Pupo L, Nunzi A, Laureana R, Guarnera L, Marinoni M, Buzzatti E, Gigliotti PE, et al. Association of [18F]-FDG PET/CT-Derived Radiomic Features with Clinical Outcomes and Genomic Profiles in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(10):1281. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15101281
Chicago/Turabian StyleEsposito, Fabiana, Luigi Manco, Guglielmo Manenti, Livio Pupo, Andrea Nunzi, Roberta Laureana, Luca Guarnera, Massimiliano Marinoni, Elisa Buzzatti, Paola Elda Gigliotti, and et al. 2025. "Association of [18F]-FDG PET/CT-Derived Radiomic Features with Clinical Outcomes and Genomic Profiles in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia" Diagnostics 15, no. 10: 1281. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15101281
APA StyleEsposito, F., Manco, L., Manenti, G., Pupo, L., Nunzi, A., Laureana, R., Guarnera, L., Marinoni, M., Buzzatti, E., Gigliotti, P. E., Micillo, A., Scribano, G., Venditti, A., Postorino, M., & Del Principe, M. I. (2025). Association of [18F]-FDG PET/CT-Derived Radiomic Features with Clinical Outcomes and Genomic Profiles in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Diagnostics, 15(10), 1281. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15101281










