Prospective Comparison of Nine Different Handheld Ultrasound (HHUS) Devices by Ultrasound Experts with Regard to B-Scan Quality, Device Handling and Software in Abdominal Sonography
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. HHUS Devices
2.3. Examiners
2.4. Testing of Devices
2.5. Evaluation Form
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Examiners
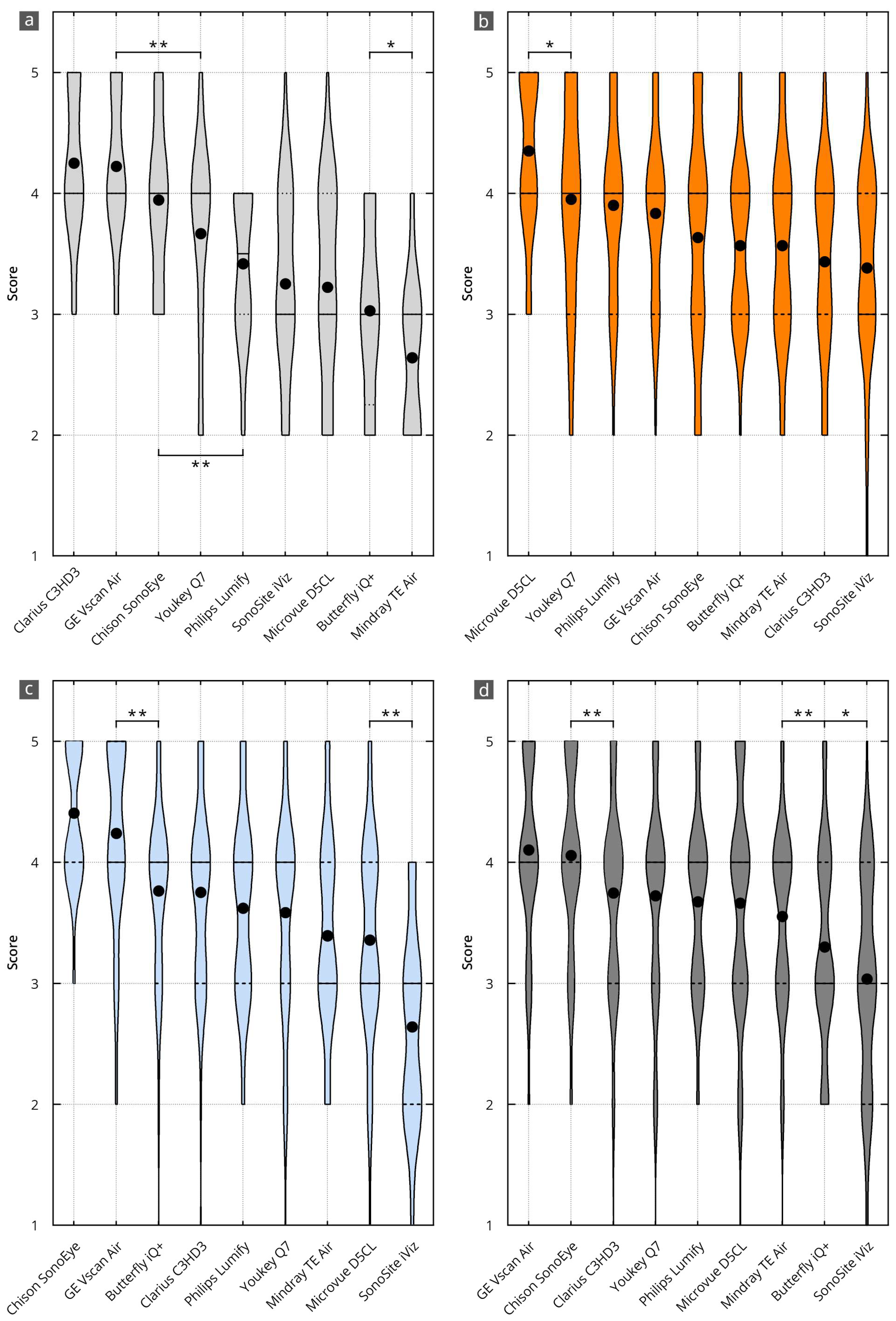
3.2. Results of the Ratings
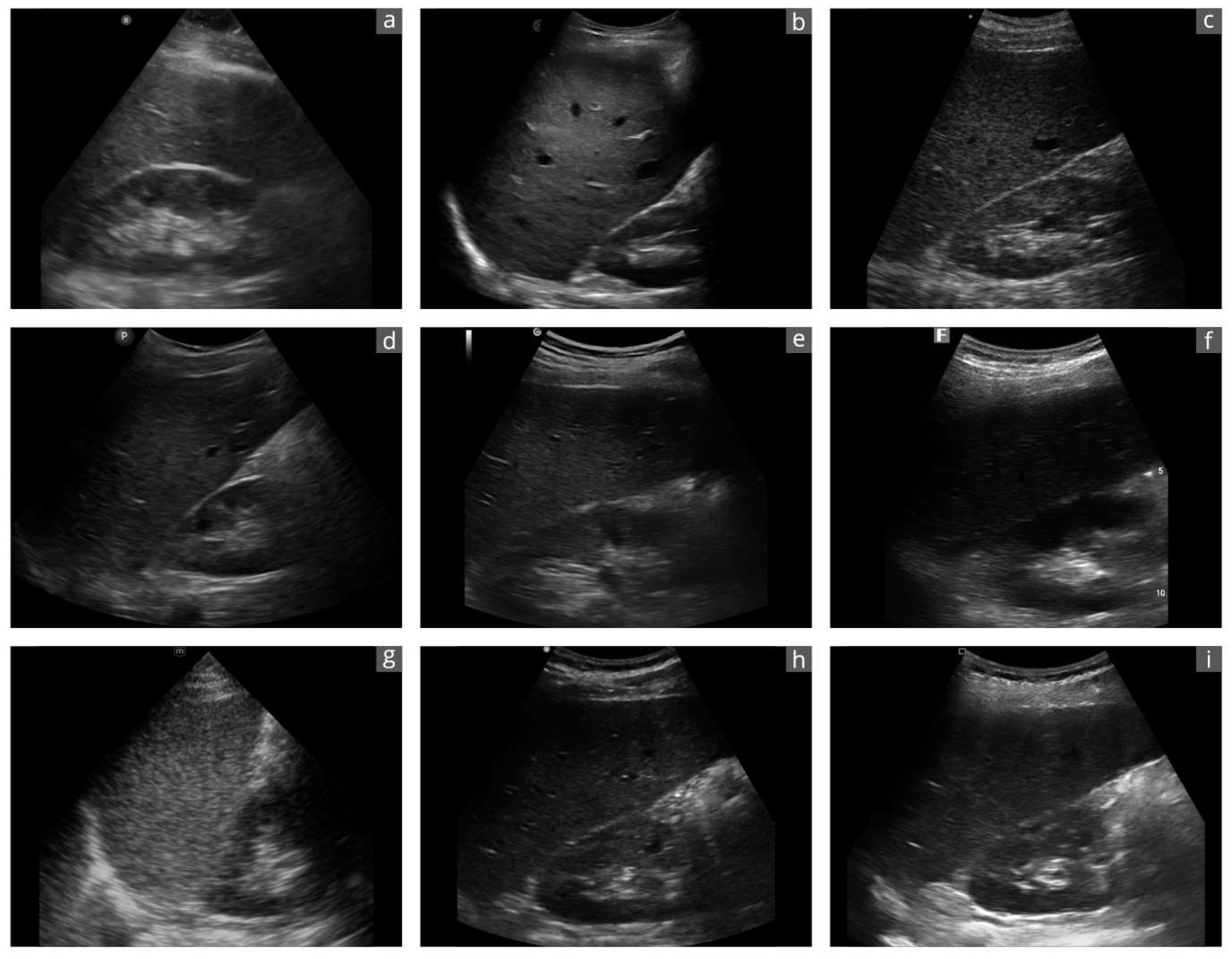
3.3. B-Mode Image Quality
3.4. Handling
3.5. Software
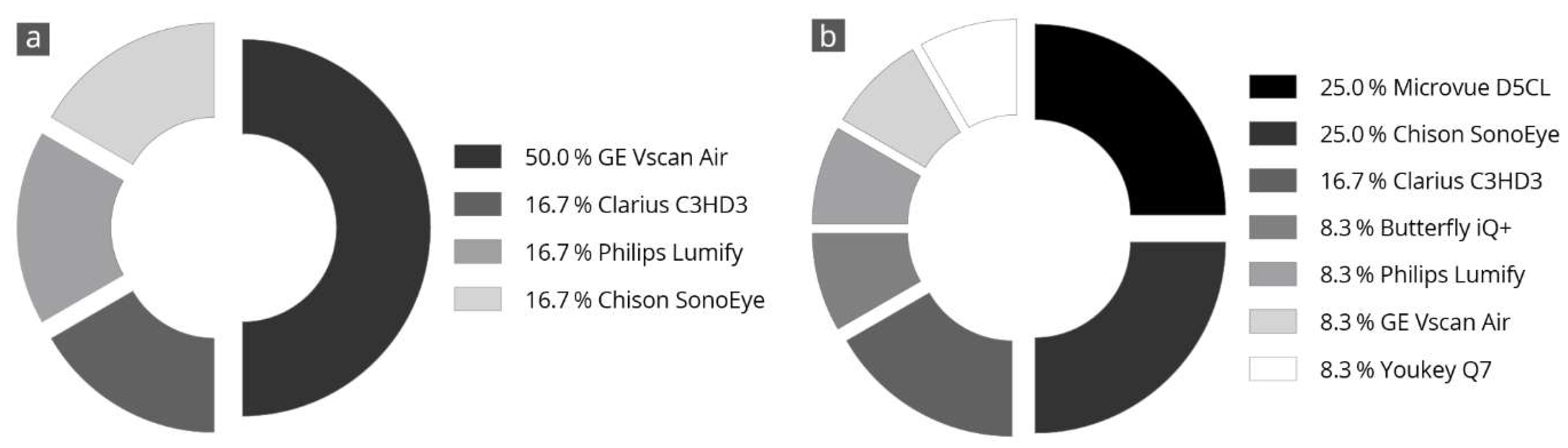
3.6. Overall Value
3.7. Final Subjective Overall Assessment
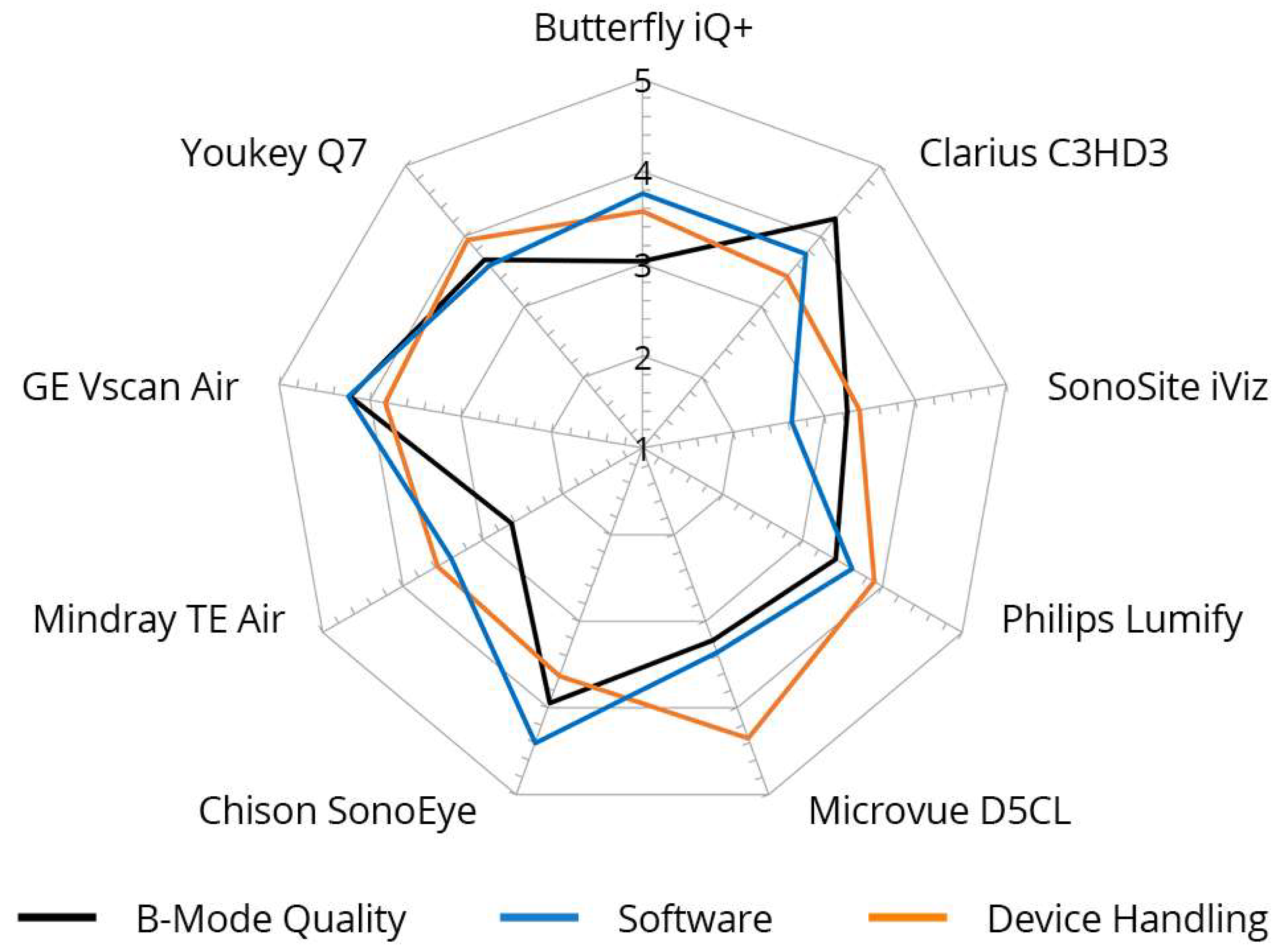
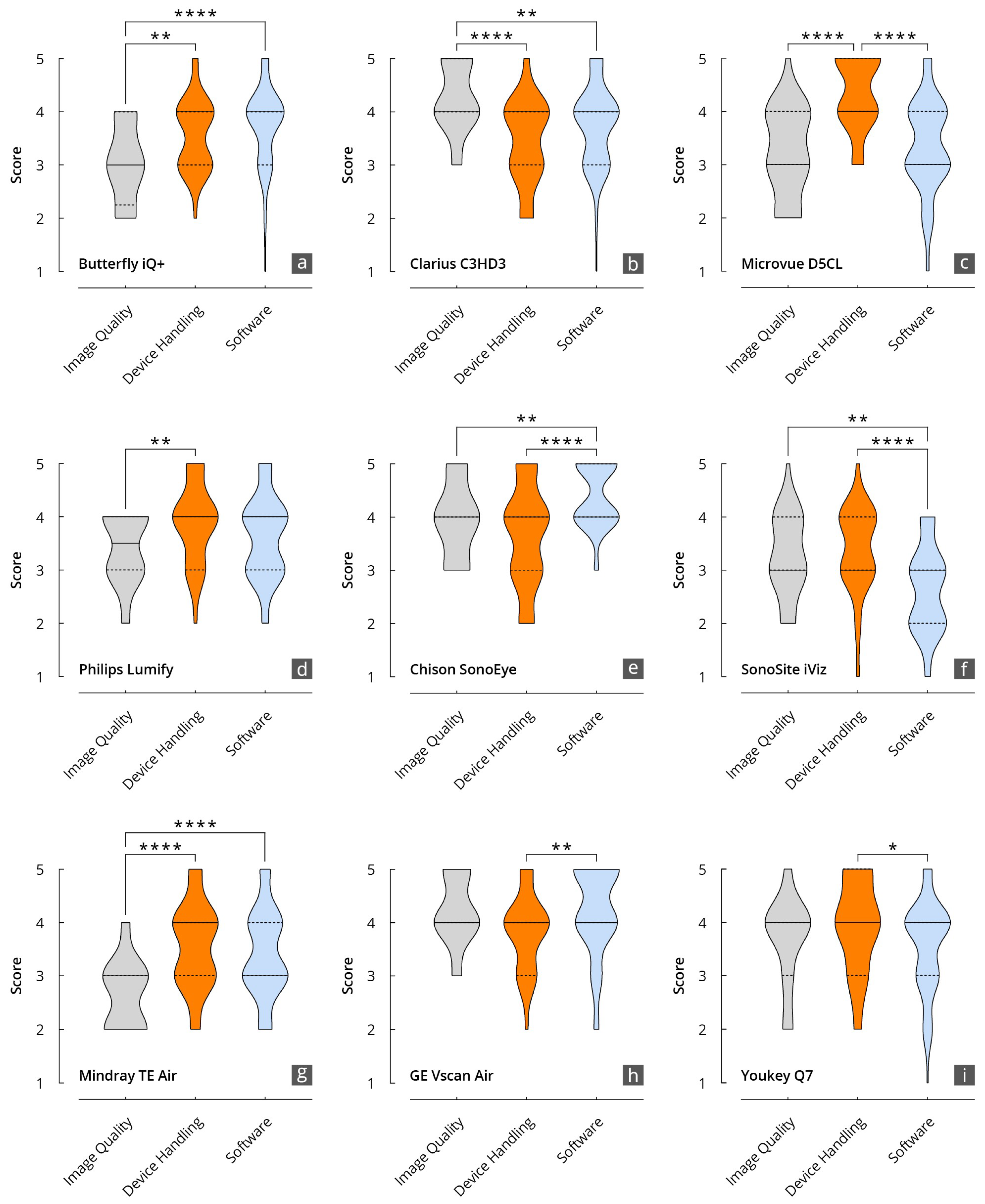
3.8. Inter-Category Comparison per Device
4. Discussion
4.1. B-Image Quality
4.2. Handling and Software
4.3. Overall Satisfaction
4.4. Clinical Importance and Perspective
4.5. Use in Ultrasound Training
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baribeau, Y.; Sharkey, A.; Chaudhary, O.; Krumm, S.; Fatima, H.; Mahmood, F.; Matyal, R. Handheld Point-of-Care Ultrasound Probes: The New Generation of POCUS. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2020, 34, 3139–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewar, Z.E.; Wu, J.; Hughes, H.; Adnani, A.; Christiansen, G.; Ovedovitz, L.; Rittenberger, J.C. A comparison of handheld ultrasound versus traditional ultrasound for acquisition of RUSH views in healthy volunteers. J. Am. Coll. Emerg. Physicians Open 2020, 1, 1320–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, F.J.; Siqueira, V.N.; Moises, V.A.; Gois, A.F.; Paola, A.A.; Carvalho, A.C.; Campos, O. Focused cardiac ultrasound using a pocket-size device in the emergency room. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2014, 103, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.J.; Guo, L.H.; Bo, X.W.; Sun, L.P.; Zhang, Y.F.; Chai, H.H.; Ye, R.Z.; Peng, C.Z.; Qin, C.; Xu, H.X. Tele-Mentored Handheld Ultrasound System for General Practitioners: A Prospective, Descriptive Study in Remote and Rural Communities. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, H.; Frauendorf, V.; Wischke, S.; Schimmath-Deutrich, C.; Kersten, M.; Nuernberg, M.; Nuernberg, D.; Jenssen, C. Ambulatory Use of Handheld Point-of-Care Ultrasound (HH-POCUS) in Rural Brandenburg—A Pilot Study. Ultraschall Med. 2022, 43, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreiros, A.P.; Cui, X.W.; Ignee, A.; De Molo, C.; Pirri, C.; Dietrich, C.F. EchoScopy in scanning abdominal diseases: Initial clinical experience. Z. Gastroenterol. 2014, 52, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreiros, A.P.; Dong, Y.; Ignee, A.; Wastl, D.; Dietrich, C.F. EchoScopy in scanning abdominal diseases; a prospective single center study. Med. Ultrason. 2019, 21, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frohlich, E.; Beller, K.; Muller, R.; Herrmann, M.; Debove, I.; Klinger, C.; Pauluschke-Frohlich, J.; Hoffmann, T.; Kreppenhofer, S.; Dietrich, C.F. Point of Care Ultrasound in Geriatric Patients: Prospective Evaluation of a Portable Handheld Ultrasound Device. Ultraschall Med. 2020, 41, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, D.; De Vita, E.; Mezzasalma, F.; Lanzarone, N.; Cameli, P.; Bianchi, F.; Perillo, F.; Bargagli, E.; Mazzei, M.A.; Volterrani, L.; et al. Portable Pocket-Sized Ultrasound Scanner for the Evaluation of Lung Involvement in Coronavirus Disease 2019 Patients. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2021, 47, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieleskiewicz, L.; Lopez, A.; Hraiech, S.; Baumstarck, K.; Pastene, B.; Di Bisceglie, M.; Coiffard, B.; Duclos, G.; Boussuges, A.; Bobbia, X.; et al. Bedside POCUS during ward emergencies is associated with improved diagnosis and outcome: An observational, prospective, controlled study. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, C.F.; Goudie, A.; Chiorean, L.; Cui, X.W.; Gilja, O.H.; Dong, Y.; Abramowicz, J.S.; Vinayak, S.; Westerway, S.C.; Nolsoe, C.P.; et al. Point of Care Ultrasound: A WFUMB Position Paper. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2017, 43, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.K.; Hai, J.; Chan, K.Y.E.; Un, K.C.; Zhou, M.; Huang, D.; Cheng, Y.Y.; Li, W.H.; Yin, L.X.; Yue, W.S.; et al. Point-of-care ultrasound augments physical examination learning by undergraduate medical students. Postgrad. Med. J. 2021, 97, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardim, N.; Dalen, H.; Voigt, J.U.; Ionescu, A.; Price, S.; Neskovic, A.N.; Edvardsen, T.; Galderisi, M.; Sicari, R.; Donal, E.; et al. The use of handheld ultrasound devices: A position statement of the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging (2018 update). Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 20, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portability, Insurance, and Accountability Act. Appropriate Use Criteria for Handheld/Pocket Ultrasound Devices. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2018, 72, e31–e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, M.B.; Cantisani, V.; Sidhu, P.S.; Badea, R.; Batko, T.; Carlsen, J.; Claudon, M.; Ewertsen, C.; Garre, C.; Genov, J.; et al. The Use of Handheld Ultrasound Devices—An EFSUMB Position Paper. Ultraschall Med. 2019, 40, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Society of Radiology (ESR). ESR statement on portable ultrasound devices. Insights Imaging 2019, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkel, D.; Albarri, E.; Yousefzada, M.; Boehm, M.; Gottwald, M.; Schneider, C. Differences in the B-mode imaging quality of ultrasound devices in the mid-price segment. Med. Ultrason. 2023, 25, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.N.; Rowland, J.; Haber, B.D.; Thom, S.; Jackson, B.; Volk, B.; Ehrman, R.R. The Use of Handheld Ultrasound Devices in Emergency Medicine. Curr. Emerg. Hosp. Med. Rep. 2021, 9, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenssen, C.; Ewertsen, C.; Piscaglia, F.; Dietrich, C.F.; Gilja, O.H.; Sidhu, P.S.; Saftoiu, A.; Popescu, A.; Sporea, I.; Cantisani, V.; et al. 50th years anniversary of EFSUMB: Initial roots, maturation, and new shoots. Ultraschall Med. 2022, 43, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza, G.M. Ultrasound Imaging: Something Old or Something New? Investig. Radiol. 2020, 55, 573–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S. Ultrasound Equipment—World Market Report-2021 Edition, 4th ed.; Signify Research: Cranfield, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich, C.F.; Bulla, P.; Dudwiesus, H.; Lo, H.; Hocke, M.; Hoffmann, B.; Horn, R.; Lehmann, B.; Morf, S.; Nuernberg, D.; et al. Perspectives and Challenges of hand-held Ultrasound. Z. Gastroenterol. 2023, 61, 836–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkel, D.; Stahlheber, H.; Chupina, V.; Schneider, C. Comparison of the quality of B-scan ultrasound in modern high-end devices. Z. Gastroenterol. 2018, 56, 1491–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burleson, S.L.; Swanson, J.F.; Shufflebarger, E.F.; Wallace, D.W.; Heimann, M.A.; Crosby, J.C.; Pigott, D.C.; Gullett, J.P.; Thompson, M.A.; Greene, C.J. Evaluation of a novel handheld point-of-care ultrasound device in an African emergency department. Ultrasound J. 2020, 12, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bönhof, J.A.; Seitz, K. Geräteauswahl, Geräteeinstellung und Dokumentation. In Sonografie Kompetent: Von der Indikation zur Interpretation; Seitz, K., Ed.; Georg Thieme Verlag KG Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany, 2016; pp. 27–46. [Google Scholar]
- Merkel, D.; Züllich, T.F.; Schneider, C.; Yousefzada, M.; Beer, D.; Ludwig, M.; Weimer, A.; Künzel, J.; Kloeckner, R.; Weimer, J.M. Prospective Comparison of Handheld Ultrasound Devices from Different Manufacturers with Respect to B-Scan Quality and Clinical Significance for Various Abdominal Sonography Questions. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weimer, J.M.; Beer, D.; Schneider, C.; Yousefzada, M.; Gottwald, M.; Züllich, T.F.; Weimer, A.; Jonck, C.; Buggenhagen, H.; Kloeckner, R.; et al. Inter-System Variability of Eight Different Handheld Ultrasound (HHUS) Devices—A Prospective Comparison of B-Scan Quality and Clinical Significance in Intensive Care. Diagnostics 2023, 14, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, M.T.; Voigt, L.; Nathanson, R.; Maw, A.M.; Johnson, G.; Dancel, R.; Mathews, B.; Moreira, A.; Sauthoff, H.; Gelabert, C.; et al. Comparison of four handheld point-of-care ultrasound devices by expert users. Ultrasound J. 2022, 14, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toscano, M.; Szlachetka, K.; Whaley, N.; Thornburg, L.L. Evaluating sensitivity and specificity of handheld point-of-care ultrasound testing for gynecologic pathology: A pilot study for use in low resource settings. BMC Med. Imaging 2020, 20, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rykkje, A.; Carlsen, J.F.; Nielsen, M.B. Hand-Held Ultrasound Devices Compared with High-End Ultrasound Systems: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, M.C. The Relationship Between the Number of Raters and the Validity of Performance Ratings. Ind. Organ. Psychol. 2016, 9, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Judmaier, G.; Seitz, K. How reliable is sonography of the upper abdomen with portable sonographic units? What does the future hold? Ultraschall Med. 2004, 25, 408–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, K.; Vasilakis, D.; Ziegler, M. Efficiency of a Portable B-Scan Ultrasound Device in Comparison to a High-End Machine in Abdominal Ultrasound. Results of a Pilot Study. Ultraschall Med. 2003, 24, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, C.M.; Seitz, K.; Leicht-Biener, U.; Mauch, M. Detection of therapeutically relevant diagnoses made by sonography of the upper abdomen: Portable versus high-end sonographic units—A prospective study. Ultraschall Med. 2004, 25, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stock, K.F.; Klein, B.; Steubl, D.; Lersch, C.; Heemann, U.; Wagenpfeil, S.; Eyer, F.; Clevert, D.A. Comparison of a pocket-size ultrasound device with a premium ultrasound machine: Diagnostic value and time required in bedside ultrasound examination. Abdom. Imaging 2015, 40, 2861–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavi, A.; Tzemah, S.; Hussein, A.; Bishara, I.; Shcherbakov, N.; Zelichenko, G.; Mashiah, A.; Gross, M.; Cherbinski, L.; Neemann, Z. A urologic stethoscope? Urologist performed sonography using a pocket-size ultrasound device in the point-of-care setting. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2017, 49, 1513–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D.; Marciano, F.; Cabassa, P. A multi-criteria methodology for evaluating alternative ultrasound devices. Ergonomics 2019, 62, 1301–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Medico, M.; Altieri, A.; Carnevale-Maffe, G.; Formagnana, P.; Casella, F.; Barchiesi, M.; Bergonzi, M.; Vattiato, C.; Casazza, G.; Cogliati, C. Pocket-size ultrasound device in cholelithiasis: Diagnostic accuracy and efficacy of short-term training. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2018, 13, 1121–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickes, S.; Treiber, G.; Monkemuller, K.; Peitz, U.; Csepregi, A.; Kahl, S.; Vopel, A.; Wolle, K.; Ebert, M.P.; Klauck, S.; et al. Impact of the operator’s experience on value of high-resolution transabdominal ultrasound in the diagnosis of choledocholithiasis: A prospective comparison using endoscopic retrograde cholangiography as the gold standard. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 41, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenker, C.; Gorg, C.; Jenssen, C.; Klein, S.; Neubauer, A.; Dietrich, C.F. The role of abdominal ultrasound in hematological diseases. Z. Gastroenterol. 2018, 56, 1063–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlas, T.; Blank, V.; Trenker, C.; Ignee, A.; Dietrich, C.F. Ultrasound systems for abdominal diagnostics—Current methods, clinical applications and new technologies. Z. Gastroenterol. 2023, 61, 1235–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Z.; Zhou, W.; Tradup, D.J.; Stekel, S.F.; Callstrom, M.R.; Hangiandreou, N.J. Systematic optimization of ultrasound grayscale imaging presets and its application in abdominal scanning. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2020, 21, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zander, D.; Hüske, S.; Hoffmann, B.; Cui, X.W.; Dong, Y.; Lim, A.; Jenssen, C.; Löwe, A.; Koch, J.B.H.; Dietrich, C.F. Ultrasound Image Optimization (“Knobology”): B-Mode. Ultrasound Int. Open 2020, 6, E14–E24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, I.; Schwarzenbach, H.R.; Tuma, J. Knobology (Important Device Settings). Praxis 2012, 101, 1207–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alasaarela, E.; Koivukangas, J. Evaluation of Image Quality of Ultrasound Scanners in Medical Diagnostics. J. Ultrasound Med. 1990, 9, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannila, V.; Sipila, O. Phantom-based quality assurance measurements in B-mode ultrasound. Acta Radiol. Short. Rep. 2013, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haller, K.; Kollmann, C. Qualitätssicherung. In Sono-Guide für MTRA/RT; Thieme Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany, 2010; pp. 45–47. [Google Scholar]
- Herzog, M.; Arsova, M.; Matthes, K.; Husman, J.; Toppe, D.; Kober, J.; Trittler, T.; Swist, D.; Dorausch, E.M.G.; Urbig, A.; et al. Technical assessment of resolution of handheld ultrasound devices and clinical implications. Ultraschall Med. 2024, 45, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Society of Radiology (ESR). Position statement and best practice recommendations on the imaging use of ultrasound from the European Society of Radiology ultrasound subcommittee. Insights Imaging 2020, 11, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.T.; Kum, H.C.; Park, S.; Ohsfeldt, R.L.; Shen, Y.; Parikh, N.D.; Singal, A.G. Hepatocellular Carcinoma Screening Is Associated with Increased Survival of Patients with Cirrhosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 976–987.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köpping-Segerling, C.C.; Pohl, M.; Canbay, A.; Best, J. Hepatozelluläres Karzinom—Screening und Surveillance. Die Gastroenterol. 2022, 17, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weimer, A.M.; Weimer, J.M.; Berthold, S.; Stein, S.; Müller, L.; Buggenhagen, H.; Balser, G.; Stankov, K.; Sgroi, M.; Schmidmaier, G.; et al. Shoulder and Knee Arthroscopy Access Point: Prospective Comparison of Sonographic and Palpatory Detection—Which Method is Better for Novices? Ultrasound Int. Open 2024, 10, a22710098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weimer, A.M.; Weimer, J.M.; Jonck, C.; Müller, L.; Stäuber, M.; Chrissostomou, C.D.; Buggenhagen, H.; Klöckner, R.; Pirlich, N.; Künzel, J.; et al. Ultrasound supported identification of the ligamentum conicum in teaching head and neck sonography. Laryngorhinootologie 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.L.; Wang, J.; Battisti, A.J.; Chen, A.; Fincke, J.; Wang, A.; Wagner, M.; Raju, B.; Baloescu, C. Interobserver Agreement and Correlation of an Automated Algorithm for B-Line Identification and Quantification with Expert Sonologist Review in a Handheld Ultrasound Device. J. Ultrasound Med. 2022, 41, 2487–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remus, C.; Zeiger, I.; Merkel, D.; Jenssen, C.; Nurnberg, D. HHUS (Handheld Ultrasound) and AI (Artificial Intelligence)—Data Collection Projekt to Improve VScan Air CL in Abdoinal Examination. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2022, 48, S76–S77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grobelski, J.; Recker, F.; Wilsmann-Theis, D.; Hartung, W.; Karakostas, P.; Brossart, P.; Schäfer, V.S. Establishment and validation of a didactic musculoskeletal ultrasound course for dermatologists using an innovative handheld ultrasound system—The MUDE study (Musculoskeletal Ultrasound in Dermatology). J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2021, 19, 1753–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weimer, J.M.; Rink, M.; Vieth, T.; Lauff, J.; Weimer, A.; Müller, L.; Stäuber, M.; Reder, S.R.; Buggenhagen, H.; Bellhäuser, H.; et al. Development and evaluation of a point-of-care ocular ultrasound curriculum for medical students—A proof-of-concept study. BMC Med. Educ. 2023, 23, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neubauer, R.; Bauer, C.J.; Dietrich, C.F.; Strizek, B.; Schäfer, V.S.; Recker, F. Evidence-based Ultrasound Education?—A Systematic Literature Review of Undergraduate Ultrasound Training Studies. Ultrasound Int. Open 2024, 10, a22750702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, C.F.; Sirli, R.L.; Barth, G.; Blaivas, M.; Daum, N.; Dong, Y.; Essig, M.; Gschmack, A.M.; Goudie, A.; Hofmann, T.; et al. Student ultrasound education—Current views and controversies. Ultraschall Med. 2024, 45, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weimer, J.; Rolef, P.; Müller, L.; Bellhäuser, H.; Göbel, S.; Buggenhagen, H.; Weimer, A.; Waezsada, E.; Kirchhoff, F.; Weinmann-Menke, J. FoCUS cardiac ultrasound training for undergraduates based on current national guidelines: A prospective, controlled, single-center study on transferability. BMC Med. Educ. 2023, 23, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weimer, J.; Dionysopoulou, A.; Strelow, K.-U.; Buggenhagen, H.; Weinmann-Menke, J.; Dirks, K.; Weimer, A.; Künzel, J.; Börner, N.; Ludwig, M.; et al. Undergraduate ultrasound training: Prospective comparison of two different peer assisted course models on national standards. BMC Med. Educ. 2023, 23, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosch, H.; Radzina, M.; Dietrich, C.F.; Nielsen, M.B.; Baumann, S.; Ewertsen, C.; Jenssen, C.; Kabaalioğlu, A.; Kosiak, W.; Kratzer, W.; et al. Ultrasound Curricula of Student Education in Europe: Summary of the Experience. Ultrasound Int. Open 2020, 6, E25–E33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recker, F.; Schäfer, V.S.; Holzgreve, W.; Brossart, P.; Petzinna, S. Development and implementation of a comprehensive ultrasound curriculum for medical students: The Bonn internship point-of-care-ultrasound curriculum (BI-POCUS). Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1072326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrokwa, S.K.; Ruby, L.C.; Heuvelings, C.C.; Bélard, S. Task shifting for point of care ultrasound in primary healthcare in low- and middle-income countries-a systematic review. eClinicalMedicine 2022, 45, 101333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weimer, J.M.; Kuhn, E.; Ludwig, M.; Malle, G.L.; Kapipi, G.; Schäfer, V.S.; Sadiq, A.; Henke, O. Effectiveness of an ultrasound basic cancer training program through on-site training and virtual case discussions in rural Tanzania: A proof-of-concept study. Ecancermedicalscience 2024, 18, 1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
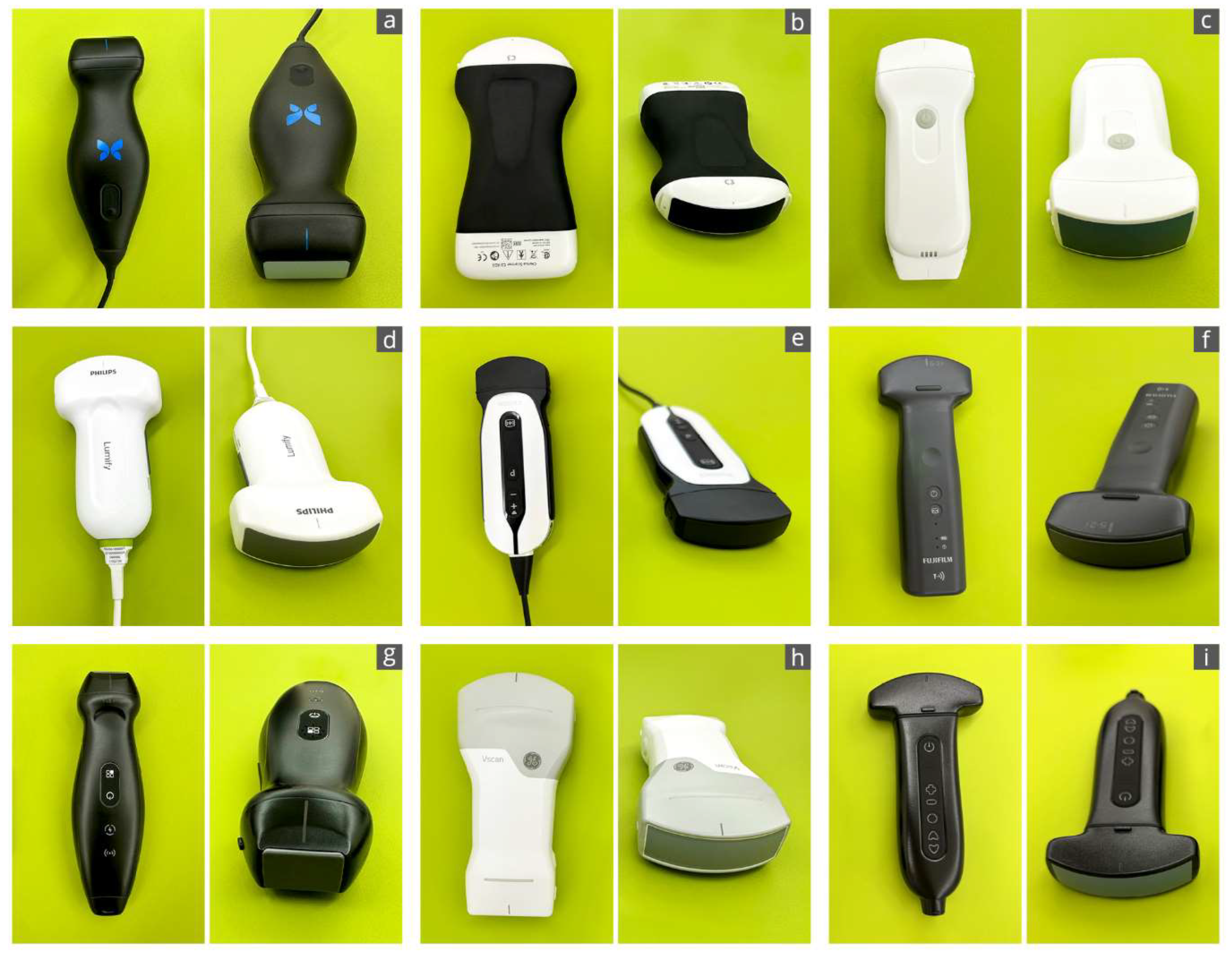

| Device Name | Manufacturer | City/Country | Image Transmission | Transducer | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Alpinion minisono * | Alpinion Medical Systems | Seoul, Republic of Korea | Wired | Linear or convex |
| 2 | Butterfly iQ+ | Butterfly Network, Inc. | Burlington, MA, USA | Wired | “All-in-one 1.75 D-Array” |
| 3 | Clarius C3HD3 | Clarius Mobile Health Corp. | Burnaby, BC, Canada | Cordless | Linear or convex |
| 4 | D5CL Microvue | Guangzhou SonoHealth Medical Technologies Co., Ltd. | Guangzhou, China | Cordless | Linear and convex in one |
| 5 | iSiniQ 30A * | Prunus Medical Shenzhen | Shenzhen, China | Cordless | Two attachable probes |
| 6 | Kosmos * | EchoNous EchoNous Inc. | Redmond, WA, USA | Wired | All-in-one transducer |
| 7 | mSonics MU 1 * | Lang Sheng Sozhou | Guangdong, China | Wired | Convex |
| 8 | Philips Lumify | Koninklijke Philips N.V. | Amsterdam, The Netherlands | Wired | Linear, convex, or broadband convex |
| 9 | SonoEye | CHISON Medical Technologies Co., Ltd. | Wuxi, China | Wired | Linear, convex, sector, or broadband convex |
| 10 | SonoSite iViz | FUJIFILM Corporation | Tokyo, Japan | Cordless | Linear or convex |
| 11 | Sonostar Uprobe-C4PL * | Universal Diagnostic Solutions | Vista, CA, USA | Cordless | Linear and convex in one |
| 12 | TE Air | Shenzhen Mindray Bio-Medical Electronics Co., Ltd. | Shenzhen, China | Cordless | Sector |
| 13 | Vscan Air | General Electric | Boston, MA, USA | Cordless | Convex/linear or sector/linear in one |
| 14 | Youkey Q7 | Wuhan Youkey Bio-Medical Electronics Co., Ltd. | Wuhan, China | Cordless | Four different replaceable transducers |
| Item | Butterfly iQ+ | Clarius C3HD3 | Sono-Site iViz | Philips Lumify | D5CL Microvue | SonoEye Chison | TE Air Mind-ray | Vscan Air GE | Youkey Q7 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All items | 3.6 ± 0.8 | 3.7 ± 0.8 | 3.0 ± 0.9 | 3.7 ± 0.8 | 3.7 ± 0.9 | 4.1 ± 0.8 | 3.3 ± 0.9 | 4.1 ± 0.8 | 3.7 ± 0.9 | <0.0001 | |
| B-mode image quality | Overall | 3.0 ± 0.7 | 4.3 ± 0.7 | 3.3 ± 0.8 | 3.4 ± 0.7 | 3.2 ± 0.8 | 3.9 ± 0.7 | 2.6 ± 0.6 | 4.2 ± 0.6 | 3.7 ± 0.8 | <0.0001 |
| Resolution | 3.0 ± 0.9 | 4.3 ± 0.7 | 3.1 ± 0.8 | 3.5 ± 0.7 | 3.2 ± 0.9 | 3.9 ± 0.8 | 2.5 ± 0.5 | 4.3 ± 0.5 | 3.7 ± 0.9 | <0.0001 | |
| Contrast | 3.0 ± 0.7 | 4.2 ± 0.7 | 3.3 ± 0.6 | 3.3 ± 0.6 | 3.3 ± 0.9 | 4.0 ± 0.7 | 2.7 ± 0.7 | 4.0 ± 0.7 | 3.5 ± 0.9 | <0.0001 | |
| Overall impression | 3.1 ± 0.7 | 4.3 ± 0.6 | 3.4 ± 0.9 | 3.5 ± 0.7 | 3.3 ± 0.8 | 3.9 ± 0.7 | 2.8 ± 0.8 | 4.3 ± 0.7 | 3.8 ± 0.7 | <0.0001 | |
| Handling | Overall | 3.6 ± 0.7 | 3.4 ± 0.8 | 3.4 ± 0.8 | 3.9 ± 0.8 | 4.4 ± 0.7 | 3.6 ± 0.9 | 3.6 ± 0.8 | 3.8 ± 0.7 | 4.0 ± 0.9 | <0.0001 |
| Haptics | 3.5 ± 0.5 | 3.3 ± 0.7 | 3.4 ± 0.7 | 4.2 ± 0.7 | 4.6 ± 0.5 | 3.2 ± 0.7 | 3.6 ± 0.8 | 4.0 ± 0.6 | 3.9 ± 0.8 | <0.0001 | |
| Weight | 3.2 ± 0.8 | 2.9 ± 0.9 | 3.8 ± 0.7 | 4.3 ± 0.6 | 4.6 ± 0.5 | 4.2 ± 0.8 | 3.8 ± 0.9 | 3.8 ± 0.8 | 4.2 ± 0.7 | <0.0001 | |
| Shape | 3.7 ± 0.7 | 3.3 ± 0.7 | 3.1 ± 0.9 | 3.9 ± 0.7 | 4.6 ± 0.5 | 3.1 ± 0.8 | 3.5 ± 0.9 | 3.8 ± 0.8 | 3.9 ± 1.0 | 0.0005 | |
| Connectivity | 4.0 ± 0.6 | 3.9 ± 0.7 | 3.5 ± 0.5 | 3.3 ± 0.9 | 4.0 ± 0.7 | 4.0 ± 1.0 | 3.6 ± 0.7 | 3.7 ± 1.0 | 3.9 ± 0.8 | 0.23 | |
| Overall impression | 3.5 ± 0.5 | 3.7 ± 0.8 | 3.1 ± 1.0 | 3.8 ± 0.6 | 4.0 ± 0.9 | 3.8 ± 1.0 | 3.4 ± 0.9 | 4.0 ± 0.4 | 3.8 ± 1.1 | 0.21 | |
| Software | Overall | 3.8 ± 0.7 | 3.7 ± 0.8 | 2.6 ± 0.8 | 3.6 ± 0.8 | 3.4 ± 0.9 | 4.4 ± 0.6 | 3.4 ± 0.8 | 4.2 ± 0.8 | 3.6 ± 0.9 | <0.0001 |
| Presets | 3.8 ± 0.7 | 3.9 ± 0.5 | 2.3 ± 0.8 | 3.6 ± 0.8 | 3.4 ± 0.7 | 4.5 ± 0.5 | 3.4 ± 0.9 | 4.0 ± 0.9 | 3.8 ± 0.7 | <0.0001 | |
| Depth | 3.9 ± 0.8 | 3.9 ± 0.7 | 2.7 ± 0.8 | 3.7 ± 0.7 | 2.7 ± 1.0 | 4.5 ± 0.5 | 3.5 ± 1.0 | 4.3 ± 1.1 | 3.6 ± 0.9 | <0.0001 | |
| Gain | 4.1 ± 0.5 | 3.9 ± 0.7 | 2.8 ± 0.7 | 3.7 ± 0.9 | 3.4 ± 0.8 | 4.3 ± 0.7 | 3.7 ± 1.0 | 4.4 ± 0.9 | 3.4 ± 1.1 | 0.0002 | |
| Duplex/PRF | 3.6 ± 1.1 | 3.3 ± 0.7 | - | 3.3 ± 0.6 | 3.4 ± 1.0 | 4.3 ± 0.7 | 3.2 ± 0.8 | 4.3 ± 0.6 | 3.5 ± 0.8 | 0.0008 | |
| Saving | 3.8 ± 0.6 | 3.7 ± 1.2 | 3.1 ± 0.9 | 3.8 ± 0.6 | 3.8 ± 0.7 | 4.4 ± 0.8 | 3.4 ± 0.9 | 4.0 ± 0.7 | 3.6 ± 0.9 | 0.04 | |
| Intuitiveness | 3.5 ± 0.7 | 3.8 ± 0.9 | 2.7 ± 0.7 | 3.7 ± 1.0 | 3.3 ± 0.9 | 4.3 ± 0.5 | 3.4 ± 0.7 | 4.5 ± 0.7 | 3.6 ± 0.8 | <0.0001 | |
| Overall impression | 3.6 ± 0.7 | 3.8 ± 0.8 | 2.2 ± 0.9 | 3.6 ± 0.9 | 3.4 ± 0.7 | 4.4 ± 0.5 | 3.2 ± 0.6 | 4.2 ± 0.9 | 3.6 ± 0.9 | <0.0001 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Merkel, D.; Lueders, C.; Schneider, C.; Yousefzada, M.; Ruppert, J.; Weimer, A.; Herzog, M.; Lorenz, L.A.; Vieth, T.; Buggenhagen, H.; et al. Prospective Comparison of Nine Different Handheld Ultrasound (HHUS) Devices by Ultrasound Experts with Regard to B-Scan Quality, Device Handling and Software in Abdominal Sonography. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1913. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14171913
Merkel D, Lueders C, Schneider C, Yousefzada M, Ruppert J, Weimer A, Herzog M, Lorenz LA, Vieth T, Buggenhagen H, et al. Prospective Comparison of Nine Different Handheld Ultrasound (HHUS) Devices by Ultrasound Experts with Regard to B-Scan Quality, Device Handling and Software in Abdominal Sonography. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(17):1913. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14171913
Chicago/Turabian StyleMerkel, Daniel, Christian Lueders, Christoph Schneider, Masuod Yousefzada, Johannes Ruppert, Andreas Weimer, Moritz Herzog, Liv Annebritt Lorenz, Thomas Vieth, Holger Buggenhagen, and et al. 2024. "Prospective Comparison of Nine Different Handheld Ultrasound (HHUS) Devices by Ultrasound Experts with Regard to B-Scan Quality, Device Handling and Software in Abdominal Sonography" Diagnostics 14, no. 17: 1913. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14171913
APA StyleMerkel, D., Lueders, C., Schneider, C., Yousefzada, M., Ruppert, J., Weimer, A., Herzog, M., Lorenz, L. A., Vieth, T., Buggenhagen, H., Weinmann-Menke, J., & Weimer, J. M. (2024). Prospective Comparison of Nine Different Handheld Ultrasound (HHUS) Devices by Ultrasound Experts with Regard to B-Scan Quality, Device Handling and Software in Abdominal Sonography. Diagnostics, 14(17), 1913. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14171913







