Attenuation Correction of Long Axial Field-of-View Positron Emission Tomography Using Synthetic Computed Tomography Derived from the Emission Data: Application to Low-Count Studies and Multiple Tracers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Cohort
2.2. Data Acquisition
2.3. Pre-Processing
2.4. Synthetic CT Generation
2.5. PET Reconstruction
2.6. Data Analysis
2.6.1. Synthetic CT Analysis
2.6.2. Qualitative Analysis
2.6.3. Quantitative Analysis
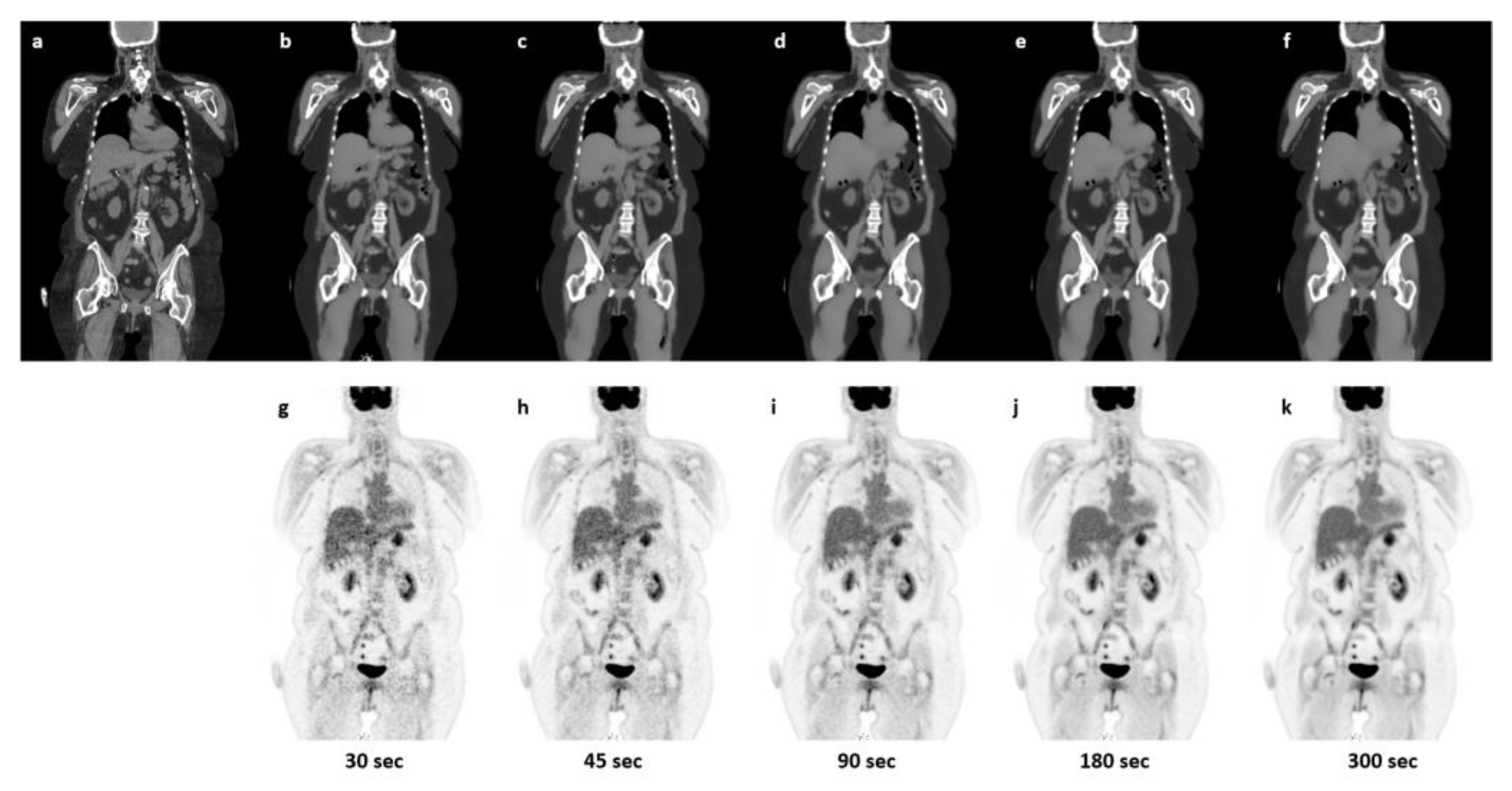
2.6.4. Robustness towards Reduced Count-Rate
3. Results
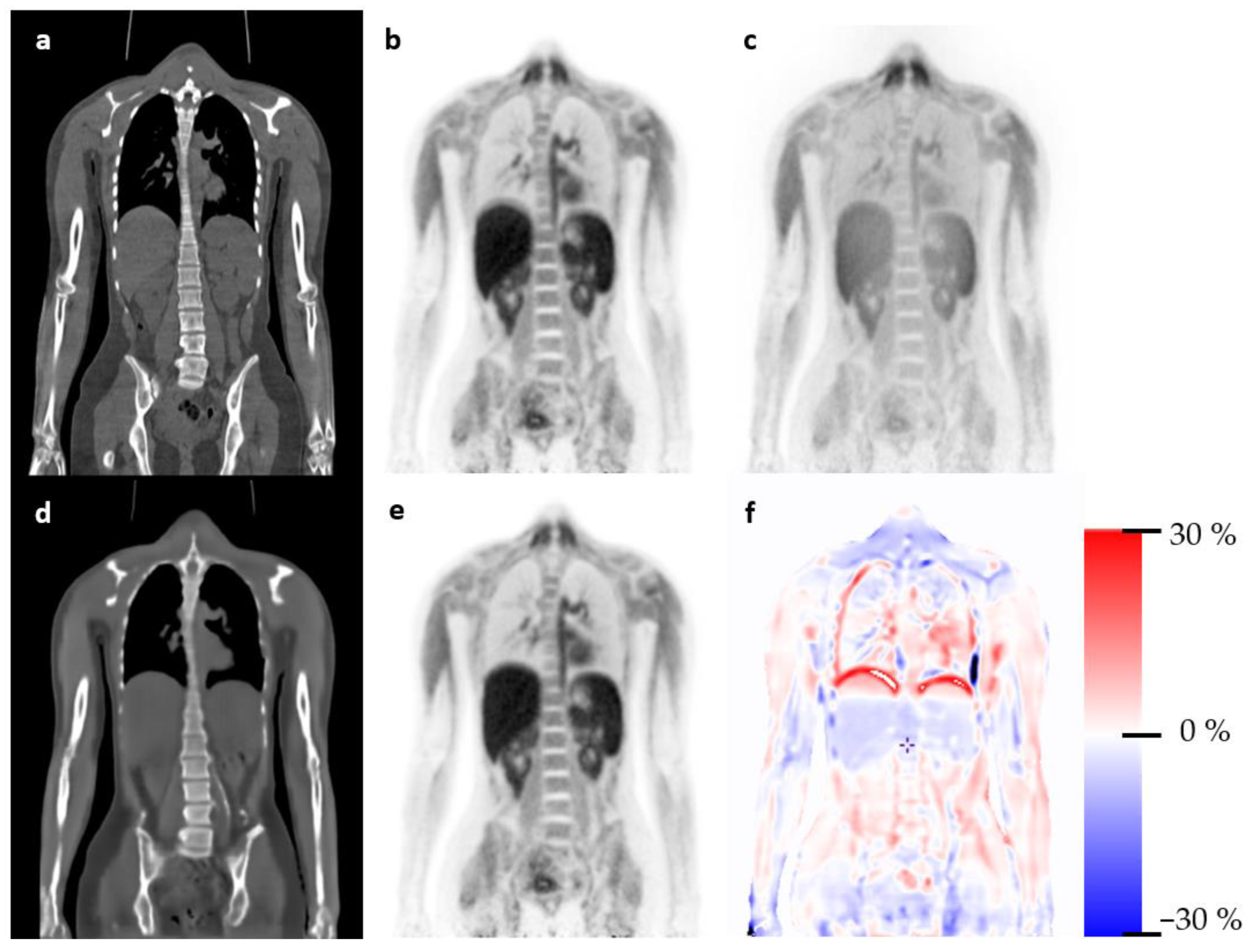
3.1. Qualitative Evaluation
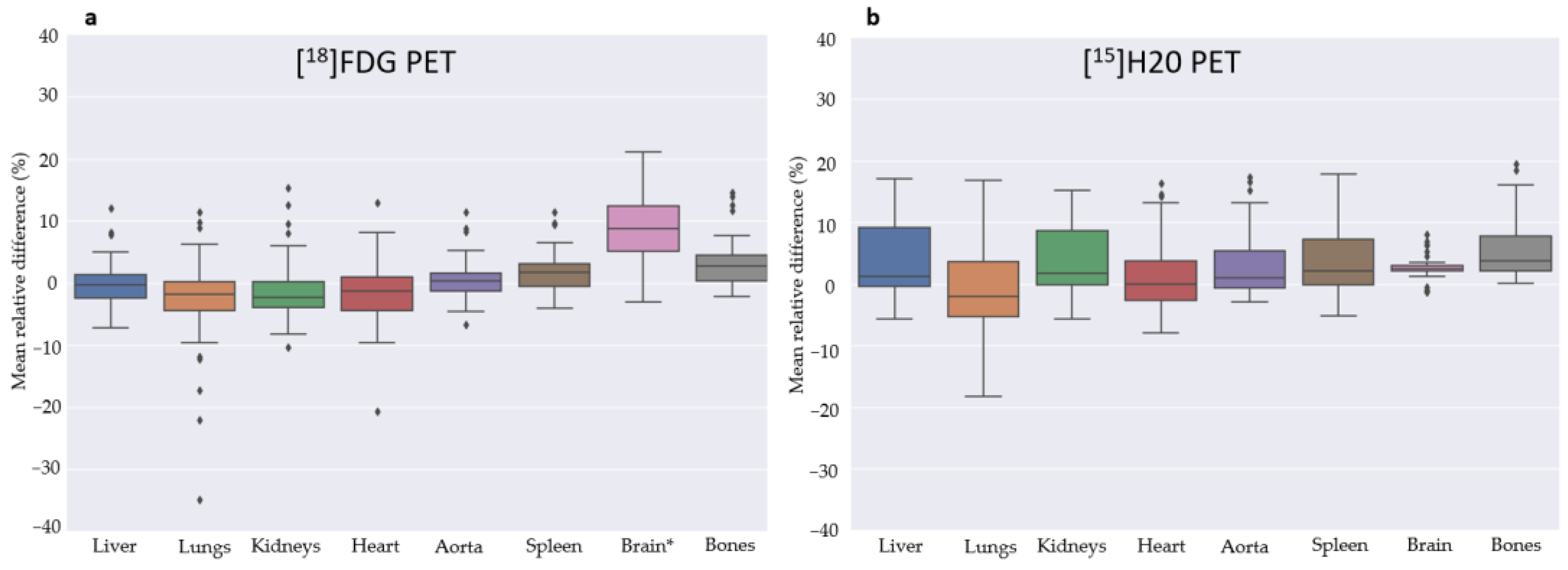
3.2. Quantitative Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Sluis, J.; de Jong, J.; Schaar, J.; Noordzij, W.; van Snick, P.; Dierckx, R.; Borra, R.; Willemsen, A.; Boellaard, R. Performance Characteristics of the Digital Biograph Vision PET/CT System. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surti, S.; Viswanath, V.; Daube-Witherspoon, M.E.; Conti, M.; Casey, M.E.; Karp, J.S. Benefit of Improved Performance with State-of-the Art Digital PET/CT for Lesion Detection in Oncology. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 61, 1684–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- d’Este, S.H.; Andersen, F.L.; Andersen, J.B.; Jokobsen, A.L.; Saxtoft, E.S.; Schulze, C.; Hansen, N.L.; Andersen, K.F.; Reichkendler, M.H.; Højgaard LFisher, B.M. Potential clinical impact from LAFOV PET/CT: A systematic evaluation of image quality and lesion detection. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prenosil, G.A.; Sari, H.; Fürstner, M.; Afshar-Oromieh, A.; Shi, K.; Rominger, A.; Hentschel, M. Performance Characteristics of the Biograph Vision Quadra PET/CT System with a Long Axial Field of View Using the NEMA NU 2-2018 Standard. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherry, S.R.; Jones, T.; Karp, J.S.; Qi, J.; Moses, W.W.; Badawi, R.D. Total-Body PET: Maximizing sensitivity to create new opportunities for clinical research and patient care. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberts, I.; Hünermund, J.N.; Prenosil, G.; Mingels, C.; Bohn, K.P.; Viscione, M.; Sari, H.; Vollnberg, B.; Shi, K.; Afshar-Oromieh, A.; et al. Clinical performance of long axial field of view PET/CT: A head-to-head intra-individual comparison of the Biograph Vision Quadra with the Biograph Vision PET/CT. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 2395–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyer, T.; Townsend, D.W.; Brun, T.; Kinahan, P.E.; Charron, M.; Roddy, R.; Jerin, J.; Young, J.; Byars, L.; Nutt, R. A combined PET/CT scanner for clinical oncology. J. Nucl. Med. 2000, 41, 1369–1379. [Google Scholar]
- Korsholm, K.; Aleksyniene, R.; Albrecht-Beste, E.; Vadstrup, E.S.; Andersen, F.L.; Fischer, B.M. Staging of breast cancer in pregnancy with ultralow dose [18F]-FDG-PET/CT. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2023, 50, 1534–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberts, I.; Schepers, R.; Zeimpekis, K.; Sari, H.; Rominger, A.; Afshar-Oromieh, A. Combined [68 Ga]Ga-PSMA-11 and low-dose 2-[18F]FDG PET/CT using a long-axial field of view scanner for patients referred for [177Lu]-PSMA-radioligand therapy. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2023, 50, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, E.; García-Velloso, M.J.; Aquerreta, J.D.; Rosales, J.J.; Bastidas, J.F.; Soriano, I.; Irazola, L.; Rodríguez-Otero, P.; Quincoces, G.; Martí-Climent, J.M. Ultra-low dose whole-body CT for attenuation correction in a dual tracer PET/CT protocol for multiple myeloma. Phys. Med. 2021, 84, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 2672–2680. [Google Scholar]
- Arabi, H.; Zeng, G.; Zheng, G.; Zaidi, H. Novel adversarial semantic structure deep learning for MRI-guided attenuation correction in brain PET/MRI. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 2746–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X. MR-based synthetic CT generation using a deep convolutional neural network method. Med. Phys. 2017, 44, 1408–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, K.; Yang, J.; Kim, K.; El Fakhri, G.; Seo, Y.; Li, Q. Attenuation correction for brain PET imaging using deep neural network based on Dixon and ZTE MR images. Phys. Med. Biol. 2018, 63, 125011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladefoged, C.N.; Hansen, A.E.; Henriksen, O.M.; Bruun, F.J.; Eikenes, L.; Øen, S.K.; Karlberg, A.; Højgaard, L.; Law, I.; Andersen, F.L. AI-driven attenuation correction for brain PET/MRI: Clinical evaluation of a dementia cohort and importance of the training group size. Neuroimage 2020, 222, 117221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leynes, A.P.; Yang, J.; Wiesinger, F.; Kaushik, S.S.; Shanbhag, D.D.; Seo, Y.; Hope, T.A.; Larson, P.E.Z. Zero-Echo-Time and Dixon Deep Pseudo-CT (ZeDD CT): Direct Generation of Pseudo-CT Images for Pelvic PET/MRI Attenuation Correction Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks with Multiparametric MRI. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradshaw, T.J.; Zhao, G.; Jang, H.; Liu, F.; McMillan, A.B. Feasibility of Deep Learning-Based PET/MR Attenuation Correction in the Pelvis Using Only Diagnostic MR Images. Tomography 2018, 4, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahangari, S.; Olin, A.B.; Federspiel, K.M.; Jakoby, B.; Andersen, T.L.; Hansen, A.E.; Fischer, B.M.; Littrup Andersen, F. A deep learning-based whole-body solution for PET/MRI attenuation correction. EJNMMI Phys. 2022, 9, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmen, H.V.; Massa, H.; Hurley, S.; Cho, S.; Bradshaw, T.; McMillan, A. A deep learning-based approach for direct whole-body PET attenuation correction. J. Nucl. Med. May 2019, 60 (Suppl. S1), 569. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, R.; Xue, S.; Hu, J.; Sari, H.; Mingels, C.; Zeimpekis, K.; Prenosil, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Viscione, M.; et al. Using domain knowledge for robust and generalizable deep learning-based CT-free PET attenuation and scatter correction. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Lei, Y.; Wang, T.; Higgins, K.; Liu, T.; Curran, W.J.; Mao, H.; Nye, J.A.; Yang, X. Deep learning-based attenuation correction in the absence of structural information for whole-body positron emission tomography imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65, 055011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Zhang, Y. Do gans actually learn the distribution? An empirical study. arXiv 2017, arXiv:abs/1706.08224. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Liu, C. Deep-learning-based methods of attenuation correction for SPECT and PET. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2022, 30, 1859–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armanious, K.; Hepp, T.; Küstner, T.; Dittmann, H.; Nikolaou, K.; La Fougère, C.; Yang, B.; Gatidis, S. Independent attenuation correction of whole body [18F]FDG-PET using a deep learning approach with Generative Adversarial Networks. EJNMMI Res. 2020, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, D.G.; Rechner, L.A.; Appelt, A.L.; Berthelsen, A.K.; Costa, J.C.; Friborg, J.; Persson, G.F.; Bangsgaard, J.P.; Specht, L.; Aznar, M.C. Metal artefact reduction for accurate tumour delineation in radiotherapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2018, 126, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-García, F.; Sparks, R.; Ourselin, S. TorchIO: A Python library for efficient loading, preprocessing, augmentation and patch-based sampling of medical images in deep learning. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 208, 106236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghesu, F.C.; Georgescu, B.; Zheng, Y.; Grbic, S.; Maier, A.; Hornegger, J.; Comaniciu, D. Multi-Scale Deep Reinforcement Learning for Real-Time 3D-Landmark Detection in CT Scans. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 41, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, D.W. A combined PET/CT scanner: The choices. J. Nucl. Med. 2001, 42, 533–534. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamoto, Y.; Chin, B.B.; Cohade, C.; Osman, M.; Tatsumi, M.; Wahl, R.L. PET/CT: Artifacts caused by bowel motion. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2004, 25, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Li, Y.; Zou, S.; Xue, H.; Sang, Z.; Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Liang, D.; Zheng, H. Obtaining PET/CT images from non-attenuation corrected PET images in a single PET system using Wasserstein generative adversarial networks. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65, 215010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.; Bohn, K.P.; Guo, R.; Sari, H.; Viscione, M.; Rominger, A.; Li, B.; Shi, K. Development of a deep learning method for CT-free correction for an ultra-long axial field of view PET scanner. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2021, 2021, 4120–4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, H.B.W.; Law, I.; Andersen, T.L.; Andersen, F.L.; Fischer, B.M.; Vestergaard, M.B.; Larsson, T.S.W.; Lindberg, U. Brain perfusion estimation by Tikhonov model-free deconvolution in a long axial field of view PET/CT scanner exploring five different PET tracers. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2023, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Cohort | Radiotracer | PET/CT Scanner | Inclusion Period |
|---|---|---|---|
| Train (n = 858) | [18F]FDG | Siemens Vision 600 | January 2021 to May 2022 |
| Test (n = 78) | [18F]FDG | Siemens Vision 600 | May 2022 to September 2022 |
| Test (n = 36) | [18F]FDG | LAFOV Siemens Vision Quadra | November 2021 to August 2022 |
| Train (n = 34) | [15O]H2O | LAFOV Siemens Vision Quadra | November 2021 to Marts 2023 |
| Test (n = 12) | [15O]H2O | LAFOV Siemens Vision Quadra | October 2022 to June 2023 |
| Patient No. | Artifact | Overall Image Quality Score: | Quality Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Metal implant in tooth (1) | 0 | No significant impact |
| 5 | 1 | Possible metal artifact. Two Lesions on left flank easier seen on sPET | |
| 7 | Tiny banana artifact on both recons (1) | 0 | |
| 10 | Banana artifact on PET (2) | 1 | sPET best |
| 16 | Arm movement, both recons score (1) | 0 | No clinical impact |
| 19 | Banana artifact on PET (2) | 1 | PET best |
| 20 | Tiny banana artifact on PET (1) | 0 | |
| 22 | Banana artifact on both recons (PET (2) sPET (1)) | 1 | PET best |
| 25 | Streaking across abdomen on sPET (2) | 1 | No significant impact. PET best (1) |
| 32 | Lacking detail and streak in PET (1) | 1 | No significant impact. Very obese patient. sPET best (1) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Montgomery, M.E.; Andersen, F.L.; d’Este, S.H.; Overbeck, N.; Cramon, P.K.; Law, I.; Fischer, B.M.; Ladefoged, C.N. Attenuation Correction of Long Axial Field-of-View Positron Emission Tomography Using Synthetic Computed Tomography Derived from the Emission Data: Application to Low-Count Studies and Multiple Tracers. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3661. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13243661
Montgomery ME, Andersen FL, d’Este SH, Overbeck N, Cramon PK, Law I, Fischer BM, Ladefoged CN. Attenuation Correction of Long Axial Field-of-View Positron Emission Tomography Using Synthetic Computed Tomography Derived from the Emission Data: Application to Low-Count Studies and Multiple Tracers. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(24):3661. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13243661
Chicago/Turabian StyleMontgomery, Maria Elkjær, Flemming Littrup Andersen, Sabrina Honoré d’Este, Nanna Overbeck, Per Karkov Cramon, Ian Law, Barbara Malene Fischer, and Claes Nøhr Ladefoged. 2023. "Attenuation Correction of Long Axial Field-of-View Positron Emission Tomography Using Synthetic Computed Tomography Derived from the Emission Data: Application to Low-Count Studies and Multiple Tracers" Diagnostics 13, no. 24: 3661. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13243661
APA StyleMontgomery, M. E., Andersen, F. L., d’Este, S. H., Overbeck, N., Cramon, P. K., Law, I., Fischer, B. M., & Ladefoged, C. N. (2023). Attenuation Correction of Long Axial Field-of-View Positron Emission Tomography Using Synthetic Computed Tomography Derived from the Emission Data: Application to Low-Count Studies and Multiple Tracers. Diagnostics, 13(24), 3661. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13243661










