Evaluating the Efficiency of the Cobas 6800 System for BK Virus Detection in Plasma and Urine Samples
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Cobas 6800 BKV Test
2.3. Cobas PCR Medium
2.4. Cobas 6800 BKV Test Imprecision
2.5. Real-Q BKV Quantitative Assay
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cobas 6800 BKV Test Imprecision
3.2. Agreement between Qualitative Data from Cobas 6800 BKV Test and Real-Q BKV Quantification Assay of Plasma and Urine Samples
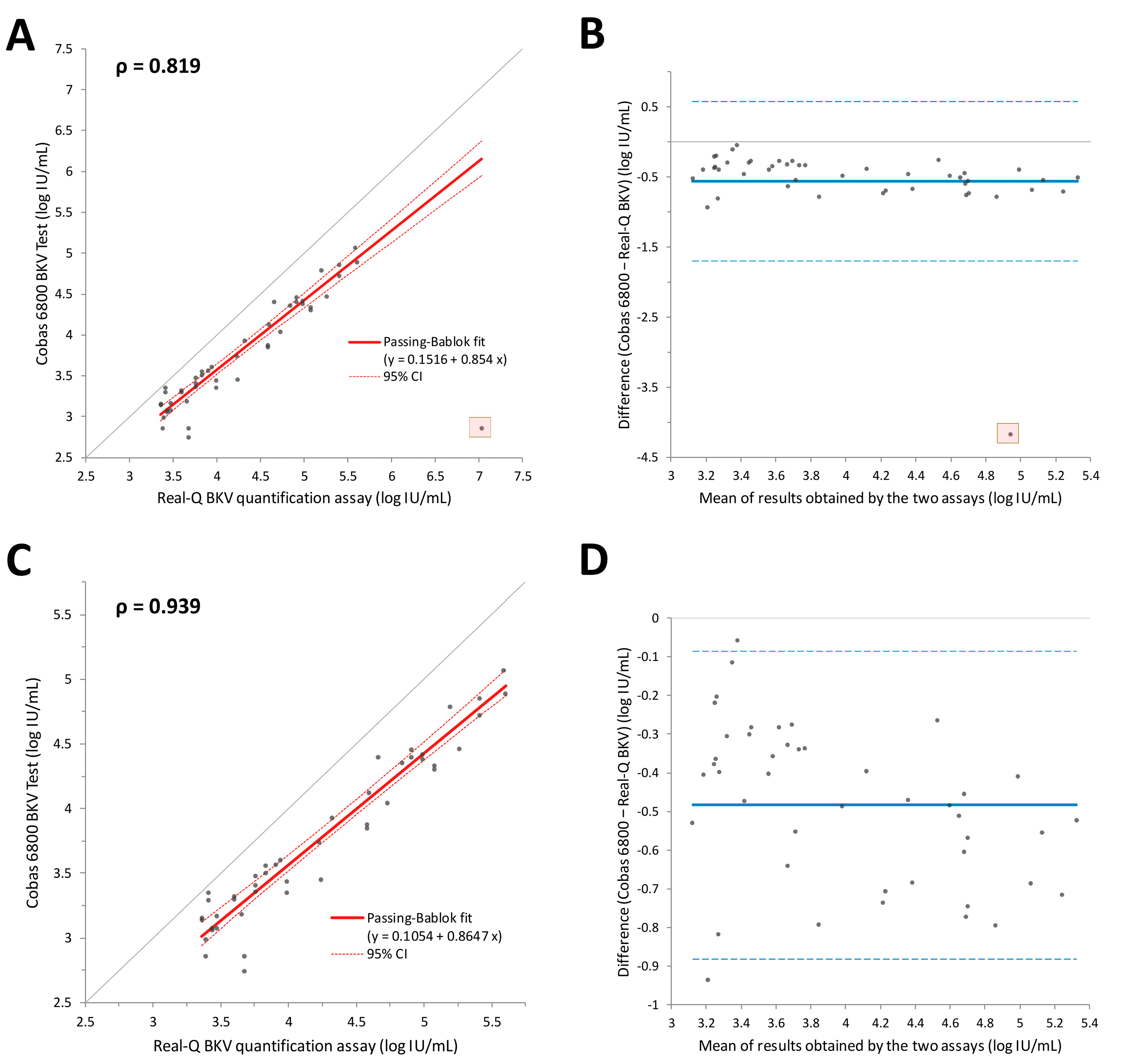
3.3. Comparison of Quantitative Data from the Two Assays on Plasma Samples
3.4. Comparison of Quantitative Data from the Two Assays on Urine Samples
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gardner, S.D.; Field, A.M.; Coleman, D.V.; Hulme, B. New human papovavirus (b.K.) isolated from urine after renal transplantation. Lancet 1971, 1, 1253–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.V. Human polyomavirus bkv and renal disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2000, 15, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowles, W.A. Discovery and epidemiology of the human polyomaviruses bk virus (bkv) and jc virus (jcv). Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2006, 577, 19–45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pahari, A.; Rees, L. Bk virus-associated renal problems—Clinical implications. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2003, 18, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kant, S.; Dasgupta, A.; Bagnasco, S.; Brennan, D.C. Bk virus nephropathy in kidney transplantation: A state-of-the-art review. Viruses 2022, 14, 1616. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Borriello, M.; Ingrosso, D.; Perna, A.F.; Lombardi, A.; Maggi, P.; Altucci, L.; Caraglia, M. Bk virus infection and bk-virus-associated nephropathy in renal transplant recipients. Genes 2022, 13, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gras, J.; Le Flécher, A.; Dupont, A.; Vérine, J.; Amara, A.; Delaugerre, C.; Molina, J.M.; Peraldi, M.N. Characteristics, risk factors and outcome of bkv nephropathy in kidney transplant recipients: A case–control study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 74. [Google Scholar]
- Lorant, C.; Westman, G.; Bergqvist, A.; von Zur-Mühlen, B.; Eriksson, B.-M. Risk factors for developing bk virus-associated nephropathy: A single-center retrospective cohort study of kidney transplant recipients. Ann. Transplant. 2022, 27, e934738-1–e934738-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, Z.; Yaghobi, R.; Afshari, A.; Roozbeh, J.; Mokhtari, M.J.; Hosseini, A.M. The effect of bkv reactivation on cytokines behavior in kidney transplanted patients. BMC Nephrol. 2022, 23, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Shanmugham, S.; Bhadauria, D.; Agrawal, V.; Jain, M.; Yaccha, M.; Kaul, A.; Vamsidhar, V.; Meyyappan, J.; Prasad, N. The diagnostic and therapeutic dilemma of the co-existence of bk virus nephropathy with acute rejection—An experience from a single centre and review of the literature. Transpl. Immunol. 2022, 72, 101581. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Hughes, C.; Ding, R.; Snopkowski, C.; Salinas, T.; Schwartz, J.; Dadhania, D.; Suthanthiran, M. Development of a bak gene based standard curve for absolute quantification of bk virus in real time quantitative pcr assay and noninvasive diagnosis of bk virus nephropathy in kidney allograft recipients. J. Immunol. Methods 2022, 509, 113341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kien, T.Q.; Kien, N.X.; Thang, L.V.; Nghia, P.B.; Van, D.T.; Duc, N.V.; Ha, D.M.; Dung, N.T.T.; Ha, N.T.T.; Loan, V.T. Stepwise reduction of mycophenolate mofetil with conversion to everolimus for the treatment of active bkv in kidney transplant recipients: A single-center experience in vietnam. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demey, B.; Bentz, M.; Descamps, V.; Morel, V.; Francois, C.; Castelain, S.; Helle, F.; Brochot, E. Bk polyomavirus bkv-mir-b1-5p: A stable micro-rna to monitor active viral replication after kidney transplantation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, W.Y.; Kang, S.S.; Jin, K.; Park, S.B.; Choe, M.; Han, S. Long-term prognosis of bk virus-associated nephropathy in kidney transplant recipients. Kidney Res. Clin. Pr. 2018, 37, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, C.; Bergallo, M.; Astegiano, S.; Terlizzi, M.E.; Sidoti, F.; Segoloni, G.P.; Cavallo, R. Monitoring of bk virus replication in the first year following renal transplantation. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2008, 23, 3333–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, M.; Villanego, F.; Orellana, C.; Vigara, L.; Montiel, N.; Aguilera, A.; Amaro, J.; Garcia, T.; Mazuecos, A. Impact of Bk Polyomavirus Plasma Viral Load in Kidney Transplant Outcomes; Transplant. Proc.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 2457–2461. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Wang, C.X.; Zhang, L.; Fei, J.G.; Deng, S.X.; Qiu, J.; Li, J.; Chen, G.D.; Fu, Q.; Chen, L.Z. Monitoring of polyomavirus bk replication and impact of preemptive immunosuppression reduction in renal-transplant recipients in china: A 5-year single-center analysis. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 81, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drachenberg, C.B.; Hirsch, H.H.; Ramos, E.; Papadimitriou, J.C. Polyomavirus disease in renal transplantation: Review of pathological findings and diagnostic methods. Hum. Pathol. 2005, 36, 1245–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.L.; Doucette, K.; LeBlanc, B.; Cockfield, S.M.; Preiksaitis, J.K. Monitoring of polyomavirus bk virus viruria and viremia in renal allograft recipients by use of a quantitative real-time pcr assay: One-year prospective study. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 3568–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, H.H.; Knowles, W.; Dickenmann, M.; Passweg, J.; Klimkait, T.; Mihatsch, M.J.; Steiger, J. Prospective study of polyomavirus type bk replication and nephropathy in renal-transplant recipients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechert, C.J.; Schnadig, V.J.; Payne, D.A.; Dong, J. Monitoring of bk viral load in renal allograft recipients by real-time pcr assays. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2010, 133, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, R.R.; Dagostin, S.; Shah, K.V. Detection of bk virus and jc virus in urine and brain tissue by the polymerase chain reaction. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1989, 27, 1174–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickeleit, V.; Klimkait, T.; Binet, I.F.; Dalquen, P.; Del Zenero, V.; Thiel, G.; Mihatsch, M.J.; Hirsch, H.H. Testing for polyomavirus type bk DNA in plasma to identify renal-allograft recipients with viral nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, W.; Telenti, A.; Proper, J.; Aksamit, A.; Smith, T. Survey of urine from transplant recipients for polyomaviruses jc and bk using the polymerase chain reaction. Mol. Cell. Probes 1991, 5, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limaye, A.P.; Jerome, K.R.; Kuhr, C.S.; Ferrenberg, J.; Huang, M.-L.; Davis, C.L.; Corey, L.; Marsh, C.L. Quantitation of bk virus load in serum for the diagnosis of bk virus–associated nephropathy in renal transplant recipients. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 183, 1669–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaub, S.; Hirsch, H.; Dickenmann, M.; Steiger, J.; Mihatsch, M.; Hopfer, H.; Mayr, M. Reducing immunosuppression preserves allograft function in presumptive and definitive polyomavirus-associated nephropathy. Am. J. Transplant. 2010, 10, 2615–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aretzweiler, G.; Leuchter, S.; Simon, C.O.; Marins, E.; Frontzek, A. Generating timely molecular diagnostic test results: Workflow comparison of the cobas® 6800/8800 to panther. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2019, 19, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. User Verification of Precision and Estimation of Bias; approved guideline; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostaing, L.; Wéclawiak, H.; Mengelle, C.; Kamar, N. Viral infections after kidney transplantation. Minerva Urol. Nephrol. 2011, 63, 59–71. [Google Scholar]
- Canchola, J.; Tang, S.; Hemyari, P.; Paxinos, E.; Marins, E. Correct use of percent coefficient of variation (% cv) formula for log-transformed data. MOJ Proteom. Bioinform. 2017, 6, 316–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennert, H.; Jenkins, S.G.; Azurin, C.; Sipley, J. Evaluation of a bk virus viral load assay using the qiagen artus bk virus rg pcr test. J. Clin. Virol. 2012, 54, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gard, L.; Niesters, H.G.; Riezebos-Brilman, A. A real time genotyping pcr assay for polyomavirus bk. J. Virol. Methods 2015, 221, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rennert, H.; Fernandes, H.; Gilani, Z.; Sipley, J. Development of a bk virus real-time quantitative assay using the biomérieux analyte-specific reagents in plasma specimens. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2015, 144, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNees, A.L.; White, Z.S.; Zanwar, P.; Vilchez, R.A.; Butel, J.S. Specific and quantitative detection of human polyomaviruses bkv, jcv, and sv40 by real time pcr. J. Clin. Virol. 2005, 34, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geneproof Bk Virus (bkv) Mc Pcr Kit. Available online: https://www.geneproof.com/geneproof-bk-virus-bkv-mc-pcr-kit/p6830 (accessed on 5 January 2023).
- Bk Virus R-Gene® Real-Time Pcr Kit for the Detection and Quantification of Bk Virus (bkv) DNA. Available online: https://www.biomerieux-diagnostics.com/bk-virus-r-gener#Everything%20you%20need%20in%20one%20kit (accessed on 5 January 2023).
- Realstar® Bkv Pcr Kit 1.0. Available online: https://www.altona-diagnostics.com/files/public/Content%20Homepage/-%2002%20RealStar/MAN%20-%20CE%20-%20EN/RealStar%20BKV%20PCR%20Kit%201.0_WEB_CE_EN-S04.pdf (accessed on 5 January 2023).
- Jin, L.; Gibson, P.E.; Knowles, W.A.; Clewley, J.P. Bk virus antigenic variants: Sequence analysis within the capsid vp1 epitope. J. Med. Virol. 1993, 39, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Bueno, M.; Kant, J.; Martinson, J.; Randhawa, P. Genotyping schemes for polyomavirus bk, using gene-specific phylogenetic trees and single nucleotide polymorphism analysis. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 2285–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Iwaki, K.K.; Qazi, S.H.; Garcia-Gomez, J.; Zeng, D.; Matsuda, Y.; Matsuda, K.; Martinez, M.E.; Toyoda, M.; Kore, A.; Stevens, W.T.; et al. Development of a real-time quantitative pcr assay for detection of a stable genomic region of bk virus. Virol. J. 2010, 7, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiley, D.M.; Sloots, T.P. Sequence variation in primer targets affects the accuracy of viral quantitative pcr. J. Clin. Virol. 2005, 34, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, A.; Pryce, T.M.; Chakera, A.; Boan, P. Bk virus subtype correlation with viral loads in western australia. Pathology 2022, 54, 968–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnayake, A.V.Y.; Fernando, N.; Gajanayake, T.; Handunnetti, S.M.; Jayamaha, S.C.J. Molecular characterization of bk virus detected in renal transplant patients in sri lanka: A preliminary study. Indian J. Med. Res. 2022, 156, 500–507. [Google Scholar]
- Kien, T.Q.; Toan, P.Q.; Nghia, P.B.; Van, D.T.; Duc, N.V.; Ha, D.M.; Dung, N.T.T.; Ha, N.T.T.; Quyen, L.T.B.; Vinh, H.T. Genomic mutations of bk polyomavirus in patients after kidney transplantation: A cross-sectional study in vietnam. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gras, J.; Nere, M.L.; Peraldi, M.N.; Bonnet-Madin, L.; Salmona, M.; Taupin, J.L.; Desgrandchamps, F.; Verine, J.; Brochot, E.; Amara, A. Bk virus genotypes and humoral response in kidney transplant recipients with bkv associated nephropathy. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2023, 25, e14012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrader, C.; Schielke, A.; Ellerbroek, L.; Johne, R. Pcr inhibitors-occurrence, properties and removal. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 113, 1014–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodowanec, A.C.; Simon, D.M. Bk virus screening and management practices among us renal transplant programs: A survey. Transpl. Int. 2015, 28, 1339–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabardi, S.; Pavlakis, M.; Tan, C.; Francis, J.; Cardarelli, F.; Asch, W.; Bodziak, K.; Chobanian, M.; Gilligan, H.; Gohh, R. New england bk consortium: Regional survey of bk screening and management protocols in comparison to published consensus guidelines. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2018, 20, e12985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boan, P.; Hewison, C.; Swaminathan, R.; Irish, A.; Warr, K.; Sinniah, R.; Pryce, T.M.; Flexman, J. Optimal use of plasma and urine bk viral loads for screening and predicting bk nephropathy. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskin, B.; Goebel, J. Cost-efficient screening for bk virus in pediatric kidney transplantation: A single-center experience and review of the literature. Pediatr. Transplant. 2010, 14, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Cobas 6800 BKV Test | Real-Q BKV Quantification Assay * | |
|---|---|---|
| Principle | Real-time quantitative PCR | Real-time quantitative PCR |
| Sample type | Plasma and urine | Serum, plasma, and urine |
| Sample volume | ||
| Plasma | 375 uL | 320 uL |
| Urine | 575 uL | 320 uL |
| Total duration | ~180 min | ~280 min (120 min for DNA extraction, 40 min for pipetting, and 120 min for amplification) |
| Hands-on time | - | ~40 min (thawing reagents and aliquoting and mixing) |
| Assay targets | VP2 and small t-antigen | VP1 |
| Subtypes detected | Ia, Ic, II, III, and IV | Not specified |
| Limit of detection | ||
| Plasma | 21.5 IU/mL | 71.4 IU/mL (183 copies/mL) |
| Urine | 12.2 IU/mL | Not specified |
| Linear range | ||
| Plasma | 21.5 IU/mL to 1 × 108 IU/mL | 195 IU/mL to 1.95 × 1012 IU/mL (500 copies/mL to 5 × 1012 copies/mL) |
| Urine | 200 IU/mL to 1 × 108 IU/mL | Not specified |
| Imprecision | ||
| Plasma | 6.92–25.74%CV | 11.58%CV |
| Urine | 4.61–11.55%CV | Not specified |
| Standard Materials’ | Mean (Log IU/mL) | SD (Log IU/mL) | Lognormal %CV * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Measurand Levels | |||
| Cobas 6800/8800 EBV/BKV control kit | |||
| High | 6.10 | 0.06 | 13.86 |
| Low | 2.86 | 0.10 | 23.82 |
| AcroMetrix BKV control materials | |||
| High | 4.95 | 0.14 | 33.83 |
| Low | 3.52 | 0.09 | 19.88 |
| Real-Q BKV Quantification Assay | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cobas 6800 BKV Test | Plasma Samples | Urine Samples in PCR Media | Fresh Raw Urine Samples | |||
| Negative | Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | Positive | |
| Negative | 33 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 4 | 0 |
| Positive | 9 | 46 | 0 | 22 | 0 | 22 |
| Concordance rate, % | 89.8 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |||
| κ | 0.793 | 1.000 | 1.000 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, J.; Kim, S.; Kwak, E.; Park, Y. Evaluating the Efficiency of the Cobas 6800 System for BK Virus Detection in Plasma and Urine Samples. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2860. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13172860
Song J, Kim S, Kwak E, Park Y. Evaluating the Efficiency of the Cobas 6800 System for BK Virus Detection in Plasma and Urine Samples. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(17):2860. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13172860
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Junhyup, Sinyoung Kim, Eunmin Kwak, and Younhee Park. 2023. "Evaluating the Efficiency of the Cobas 6800 System for BK Virus Detection in Plasma and Urine Samples" Diagnostics 13, no. 17: 2860. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13172860
APA StyleSong, J., Kim, S., Kwak, E., & Park, Y. (2023). Evaluating the Efficiency of the Cobas 6800 System for BK Virus Detection in Plasma and Urine Samples. Diagnostics, 13(17), 2860. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13172860






