Abstract
Ultrasound imaging is the first-line investigation for patients with abdominal symptoms, as it effectively depicts the gastrointestinal tract and enables the diagnosis of multiple pathological conditions. Among different recent ultrasound technological advancements, elastography enables the evaluation of various tissue characteristics, such as neoplastic transformation or fibroinflammatory status. In recent years, ultrasound elastography has been utilized extensively for the study of liver diseases and in numerous other clinical settings, including gastrointestinal diseases. Current guidelines suggest the use of transabdominal ultrasound elastography to characterize bowel wall lesions, to assess gastrointestinal contractility, to diagnose and grade chronic pancreatitis; however, no specific indications are provided. In the present paper, we summarize the evidence concerning the application of different ultrasound elastography modalities in gastrointestinal non-liver diseases.
1. Introduction
Ultrasound (US) imaging is the first-line investigation for patients with abdominal symptoms, as it effectively depicts the gastrointestinal tract and enables the diagnosis of multiple pathological conditions [1]. Recent technological advancements have resulted in the development of several kinds of US-based methodologies that enable the evaluation of various tissue characteristics. The term “multiparametric ultrasound” refers to the application of all these techniques to achieve the diagnosis [2,3]. Among these, elastography is one of the most promising.
Elasticity is a property of a tissue to resist deformation and revert to its original shape after being subjected to a stress. Neglecting the viscous component, elastic properties of a tissue can be described according to Hooke’s law (Equation (1)):
where σ is the stress applied, ε is the strain produced, and E is the elastic modulus or Young’s modulus. High Young’s modulus indicates that the applied stress results in less strain; consequently, the tissue has low elasticity (or high stiffness), and vice versa. When shear stress produces a shear strain tangential to the surface, elastic modulus is indicated as shear modulus (G) [4].
Shear modulus is related to speed propagation of shear waves in a medium and to Young’s modulus. Equation (2) described this relationship under the assumption that for incompressible medium, the Poisson’s ratio (v) is approximatively 0.5:
where G is the shear modulus, cs is the shear wave speed, and is the medium density. Speed of shear waves is higher in medium with higher stiffness [5]. Thus, elastography techniques can be divided into two categories: strain elastography (SE) and shear wave elastography (SWE). The SE is based on Young’s modulus estimation; strain is induced manually applying pressure or using acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI). Due to the inability to assess the stress distribution, the SE provides a qualitative (i.e., colour-based classification) or semi-quantitative (i.e., strain ratio, scores) assessment of the examined tissue. Strain ratio is the ratio between normal (high strain, low stiffness) and pathological (low strain, high stiffness) tissue. Thus, it is higher in high-stiffness tissue [6].
In the SWE, the study of shear waves properties is used to calculate shear modulus or shear wave velocity and estimate tissue stiffness. Shear waves can be generated by mechanical vibration in one-dimensional or two-dimensional transient elastography or by an ARFI in point- and two-dimensional shear wave elastography (p-SWE and 2D-SWE, respectively). The results of SWE can be displayed as either shear wave speed (m/s) or shear or Young’s modulus (kPa) due to the relation expressed in Equation (2) [5,7], but elasticity scale allows for more discrimination between stiffness values [8].
In pathological phenomena such as neoplastic transformation and fibroinflammatory status, the elastic properties of tissue change and elastography could theoretically be a reliable method for detecting and quantifying these changes [9,10].
After its development in the 1990s [11], early applications of US elastography included the study of neoplastic lesions and fibroinflammatory status in easily accessible tissues, such as the breast, prostate and liver tissues [12,13]. In more recent times, US elastography has been utilised extensively in numerous clinical settings, including gastroenterology, but not limited to the study of liver diseases.
Current guidelines suggest the use of transabdominal ultrasound elastography (US-E) to characterise bowel wall lesions, assess gastrointestinal contractility, diagnose and grade chronic pancreatitis (CP); however, no specific indications are provided [14,15].
In the present paper, we summarize the evidence concerning the application of different US-E modalities in gastrointestinal non-liver diseases.
2. Upper Gastrointestinal Tract
Few studies employed the US-E to evaluate the relationship between esophagogastric wall elasticity and motility, and only two case reports describe the US-E characteristics of gastric wall neoplasia.
Real-time SE using the cardiovascular pulsation as pressure was used to count the change in stiffness (CS) of esophagogastric junction (EGJ) for ≥15 s in patients undergoing esophagogastroduodenoscopy. The number of CS was significantly lower in patients with reflux esophagitis compared to patients with non-reflux esophagitis and in multivariate analysis; the absence or presence of reflux esophagitis was the only significant factor related to CS. Furthermore, CS showed an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.84 for the diagnosis of reflux esophagitis. These results suggest that US-E might be useful to assess the EGJ function [16]. In another study, the US-E was used to assess the oesophagus involvement in systemic sclerosis (SSc). Particularly, the 2D-SWE of the abdominal oesophagus and EGJ showed no difference between patients with SSc and controls, but interestingly, after drinking water, the decrease in the SWE values was greater for controls than for patients with SSc, suggesting a reduced elasticity in the SSc group [17]. Using a specific method called strain rate imaging [18], Ahmed et al., demonstrated that US-E can distinguish specific subtypes of functional dysplasia, supporting the clinical Rome III classification [19]. Regarding neoplastic disorders, two case reports described the US-E features of large gastric cancer and gastrointestinal stromal tumour, respectively. In both lesions, the stiffness was increased [20,21].
Further studies are needed to establish the role of US-E in assessing the organic lesions and motility disorders of the upper gastrointestinal tract.
3. Lower Gastrointestinal Tract
Despite the methodological limits imposed by the normal anatomy and physiology of the lower gastrointestinal tract [22], one of the most relevant application of US-E entails the non-invasive assessment of chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Studies concerning the use of the US-E in IBD are listed in Table 1, while an example image of US-E of the intestinal wall is depicted in Figure 1.

Table 1.
Transabdominal ultrasound elastography (US-E) in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
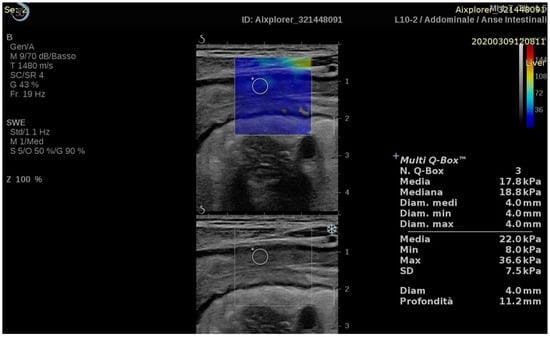
Figure 1.
Longitudinal 2D-shear wave elastography (upper part of the image) and corresponding B-mode (lower part of the image) of the terminal ileum measured with SSI.
US-E showed a practical usefulness also in the emergency setting of acute appendicitis, while no studies investigated the role of US-E in patients with other common acute intestinal disorders such as diverticulitis.
3.1. Inflammatory Bowel Disease
The IBD are characterized by chronic intestinal wall inflammation caused by immunoinflammatory altered mechanisms [39]. Despite the fact that Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC) share numerous pathogenetic mechanisms, their histopathological and clinical features are distinct. In CD, inflammation involves the entire intestinal wall and is more closely associated with fibrotic progression than in UC, where inflammation involves only the mucosal and submucosal layers of the intestinal wall. Moreover, CD can affect all digestive tracts, but it is most prevalent in the terminal ileum, whereas UC is restricted to the colon and ileocecal valve [40,41]. Considering these assumptions, it is understandable why the US-E has been investigated substantially more in the CD than the UC.
3.1.1. US-E, Disease Activity and Fibro-Inflammatory Characterization in Crohn’s Disease
Normal stiffness of terminal ileum in 139 healthy volunteers was described by Zhao et al., using 2D-SWE. The mean 2D-SWE value was 1.08 ± 0.25 m/s (or 3.84 ± 1.84 kPa). Different physiological factors such as gender, age, body mass index (BMI), profundity and bowel wall thickness did not appear to significantly influence these values [42]. Higher-than-normal p-SWE values were observed in two cohorts of apparently “normal” terminal ileum and sigma of CD patients; however, these values were lower than those in inflamed ileum and sigma (1.42 vs. 2.73 m/s in the ileum and 1.81 vs. 2.22 m/s in the sigma) [30]. This suggests that patients with CD have increased bowel wall stiffness outside of acute inflammatory episodes, and that this stiffness increases during disease flare-ups.
As only the inflammatory form is medically treatable, the most investigated applications of US-E in IBD concern its ability to differentiate between inflammatory and fibrotic bowel lesions.
In an ex vivo human study analysing 17 bowel segments resected for known or suspected IBD, Dillman et al., demonstrated that the p-SWE values were significantly higher in high-fibrosis segments compared to low-fibrosis ones, whereas there was no difference between high-inflammation and low-inflammation segments. Furthermore, the p-SWE results moderately correlated with the fibrosis score but not correlated with inflammation [43]. In another study, Baumgart et al., demonstrated that real-time SE values measured in vivo were significantly correlated with the fibrosis score and tensiometer-measured strain of surgically resected tissue [44]. Thus, elastography seem to be effectively related to bowel fibrosis.
Different studies assessed the association between fibrosis and qualitative, semi-quantitative and quantitative US-E. A semi-quantitative SE-based score was lower for inflammatory stenosis than for fibrotic stenosis, indicating that fibrotic stenosis is significantly stiffer [35]. The strain ratio increased with fibrosis progression and showed an excellent accuracy to diagnose severe fibrosis (AUC of 0.91). In addition, fibrosis was the only factor independently associated with strain ratio [36]. On the contrary, Serra et al., found no significant correlation between the strain ratio and histologically assessed fibrosis, inflammatory scores and clinically and biochemically assessed disease activity [34].
Recent studies have expanded the evidence regarding the role of SWE in IBD assessment. In a prospective study including 35 patients undergoing resection within one week after US-E, the 2D-SWE results were significantly higher in severe fibrosis compared to moderate and mild fibrosis (23 ± 6.3 vs. 17.4 ± 3.8 and 14.4 ± 2.1 kPa). A cut-off value of 22.6 kPa distinguished severe from mild/moderate fibrosis with high accuracy (AUC, sensitivity and specificity of 0.82, 70% and 91%, respectively). However, no differences were observed between consecutive inflammation grades [29]. Compared to SE, the p-SWE showed a better performance in predicting predominantly inflammatory or fibrotic strictures with an accuracy, specificity, sensitivity, positive and negative predictive values of 96%, 100%, 75%, 100% and 95.5% respectively, using a cut-off value of 2.73 m/s [27].
Since inflammatory and fibrotic tissue have distinct vascularization, a combination of US techniques could further differentiate the two categories. Inflammatory and fibrotic bowel stenosis showed differences in both the 2D-SWE and contrast-enhanced US (CEUS) parameters (peak enhancement, time to peak and AUC) [26]. In addition, the p-SWE showed a negative moderate correlation with peak enhancement [33]. Confirming this, a combined score based on real-time SE, B-mode and CEUS showed a higher accuracy to distinguish inflammatory and fibrotic tissue than each single technique [32].
3.1.2. US-E in Ulcerative Colitis
Only few studies, as far as we are aware, has examined patients with UC. Ishikawa et al., were the first to demonstrate alterations in SE related to colonoscopy findings and disease activity in UC [38]. Subsequently, Goertz et al., compared the p-SWE values measured in all colon segments of twenty patients with UC to those of thirteen healthy controls. The p-SWE values for the transverse and sigmoid colons were significantly higher in patients with UC compared to controls (1.94 vs. 1.55 m/s, p = 0.045 and 2.18 vs. 1.76 m/s, p = 0.032, respectively). Mayo subscore and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels were not significantly correlated with the p-SWE values within the colon segments, indicating that disease activity is not related to the SWE values [28]. Similarly, in a prospective study conducted by Yamada et al., 26 patients with UC who underwent colonoscopy were enrolled. The 2D-SWE of the sigmoid-colon performed 48 h before or after colonoscopy had significantly higher results in the mucosal healing group than in the active phase group (2.4 vs. 1.62 m/s, p = 0.007) and negatively correlated with clinical severity score [25]. In active UC, oedema, erosion, crypt abscess and necrosis may cause tissue softness.
3.1.3. US-E and IBD in Paediatric Population
In paediatric patients with CD, Fufezan et al., demonstrated that US-E findings were related to disease activity. A qualitative and semi-quantitative evaluation of 48 bowel segments based on the SE colour code and strain ratio was performed. Both methods showed a significant correlation with fat infiltration and disease activity markers [37]. Recently, using histology on ileal resected strictures as a reference method, Abu-Ata et al., showed a significant association between the values of the 2D-SWE of bowel wall and the entire elastogram of the right lower abdominal quadrant and mucosal inflammation and muscularis mucosa inner layer’s smooth muscle hypertrophy, while no correlation was demonstrated with fibrosis [23].
3.1.4. US-E and IBD Treatment
Several therapeutic alternatives are currently available for IBD. Among them, antitumour necrosis factor (TNF) or anti-interleukins is widely used in moderate-to-severe disease [45,46]. US-E could provide prognostic information regarding the response to treatment and its management.
In a prospective study conducted by Orlando et al., the strain ratio at baseline and 14 and 52 weeks after starting anti-TNF therapy was evaluated. The strain ratio at baseline was significantly higher in patients who underwent surgery during the follow-up compared to the non-surgical group (2.22 vs. 1.48, p = 0.009) and was significantly lower in patients who achieved mucosal healing (defined as bowel wall thickness ≤ 3.0 mm) after 14 week of anti-TNF therapy compared to patients who did not achieve this outcome (1.06 vs. 1.58, p = 0.03) [31]. In contrast, Chen et al., evaluating response to therapy at 14 weeks with clinical and endoscopic assessments, found that the 2D-SWE values decreased substantially after 14 weeks in patients who responded to therapy, suggesting the use of SWE for the early assessment of response to therapy [24]. Further research and validations using different biological therapies and larger sample sizes are required to validate the clinical utility of US-E, perhaps including the use of multiparametric US to optimise non-invasive strategies [47].
3.2. Appendicitis
Multiple studies demonstrated that US-E of appendix differs significantly between patients with acute appendicitis (AA) and healthy controls.
In a prospective study including 11 healthy volunteers and 41 patients with suspected AA, the 2D-SWE had higher results in definitive AA cases compared to patients with suspected but unconfirmed AA and controls (25 vs. 10.4 and 8.3 kPa, p < 0.001). A cut-off of 12.5 kPa resulted in AUC, sensitivity and specificity values for predicting AA of 97%, 93% and 100%, respectively [48]. In another study, the 2D-SWE values for the appendix and mesenteric fat were significantly higher in patients with AA than in healthy controls (33.35 ± 11.11 vs. 16.51 ± 3.71 kPa and 33.35 ± 11.9 vs. 16.29 ± 4.2 kPa, respectively, p < 0.001). However, appendix diameter measured at conventional US showed an AUC comparable to the 2D-SWE values for distinguishing patients with AA from controls (0.996 vs. 0.998) [49].
Indeed, standard B-mode exhibits a remarkable ability to detect acute inflammatory processes affecting the appendix. In this setting, the real advantage of US-E may lie in its capacity to enhance the diagnostic accuracy of the B-mode when it does not reveal the typical features of appendicitis (such as appendix diameter ≥ 6 mm, wall thickening, echogenicity of periappendiceal adipose tissue, periappendiceal fluid). In a prospective study by Kapoor et al., real-time SE correctly identified all 25 patients with AA, while the B-mode missed three cases [50]. In another study, p-SWE improved traditional US diagnostic efficacy for AA when appendix diameter was inferior to 6 mm [51]. Furthermore, all three negative appendicectomy cases reported in the study by Isik et al., were false positives in B-mode and true negatives in 2D-SWE, considering the optimal cut-off value of 14.5 kPa (AUC 0.93) [52].
Lastly, a relationship between US-E and the severity of AA was demonstrated. A mild/moderate grade of AA assigned by SE demonstrated a high negative predictive value for phlegmonous and perforated appendicitis (99.4 and 100%, respectively) [53].
3.3. Neoplastic Bowel Lesions
To the best of our knowledge, only one study analysed the difference in the SE values between colorectal adenocarcinoma and adenomas. In this study, Havre et al., prospectively enrolled patients with scheduled elective bowel resection. The strain ratio measurement and qualitative classification of lesions were performed. Adenocarcinomas were classified in increased tissue hardness categories and showed a strain ratio significantly higher than that in adenomas. However, no significant correlation was found between strain ratio and the grading of adenocarcinomas or in advanced T stages [54].
4. Pancreas
Clinical studies regarding the use of US-E in pancreatic diseases are listed in Table 2, while an example of a US-E exam of the pancreas is depicted in Figure 2.
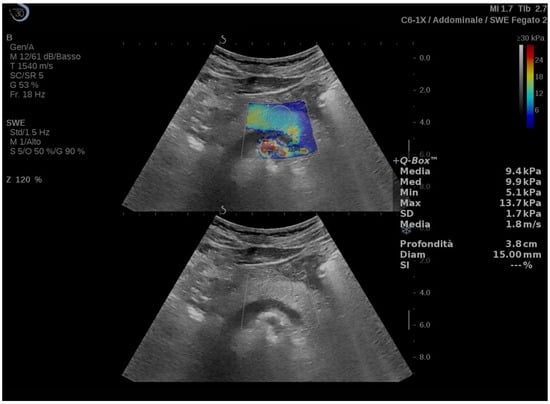
Figure 2.
Transverse 2D-shear wave elastography (upper part of the image) and corresponding B-mode (lower part of the image) of the pancreatic body measured with SSI.
Defining normal elastography values for the pancreatic parenchyma is challenging since, even when using the same method, there is a degree of variation among the healthy control populations presented across the studies. One of the largest healthy cohorts consisting in 210 subjects was presented by Xie et al. Normal pancreatic head and body’s p-SWE values were 1.18 ± 0.23 m/s and 1.20 ± 0.20 m/s, respectively, and were not related to age, gender, BMI, waist circumference and organ dimensions [55]. In contrast, Stumpf et al., reported a lower p-SWE value in men than in women, as well as an the increase with age and a correlation with BMI. Alcohol and tobacco use were not associated with the p-SWE value [56].

Table 2.
Transabdominal ultrasound elastography (US-E) in pancreatic diseases.
Table 2.
Transabdominal ultrasound elastography (US-E) in pancreatic diseases.
| First Author (Year) | Pancreatic Disease | Aim | Study Design (N) | US Device | Elastography Technique | Main Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sezgin (2022) [57] | PS | Compare PS to non-PS Correlation with metabolic parameters | Prospective (total 125: PS 68, non-PS 57) | Aplio 500, Toshiba | 2D-SWE | 2D-SWE was higher in PS than in controls (9.08 ± 2.29 vs. 7.13 ± 1.85, p = 0.000). In PS group, 2D-SWE values were significantly correlated with waist circumference (r = 0.335; p = 0.023) and insulin resistance (r = 0.338, p = 0.004). |
| Iino (2021) [58] | PC | Differential diagnosis of lesions | Prospective (total 85: PDAC 36, non-PDAC 16, controls 33) | Aplio 500, Canon | 2D-SWE | 2D-SWE values were higher in PDAC than in non-PDAC (9.8 vs. 7.5 kPa, p = 0.0045). |
| Sezgin (2021) [59] | AP | Compare AP to healthy controls Correlation with AP severity and evolution | Prospective (total 155: AP 81, controls 74) | Aplio 500, Toshiba | 2D-SWE | 2D-SWE values were higher in AP than in controls (10.97 ± 2.26 vs. 7.72 ± 2.50 kPa, p = 0.000) and were not different between mild and severe AP. 2D-SWE values decreased after clinical improvement but remained higher than those in controls after 1 month. |
| Suzuki (2021) [60] | AIP | Compare AIP to healthy controls Relation with response to therapy | Prospective (total 57: controls 34, AIP 23) | Aplio i900, Canon | 2D-SWE | 2D-SWE values were higher in AIP than in controls (30.9 vs. 6.6 kPa, p < 0.001). Decrease in 2D-SWE values was greater than change in the size of the pancreas (p = 0.026). |
| Sanjeevi (2020) [61] | RAP | Compare RAP to healthy controls | Prospective (total 66: controls 35, RAP 31) | Acuson 2000, Siemens | p-SWE | p-SWE values were higher in RAP than in controls (1.27 ± 0.50 vs. 1.00 ± 0.17 m/s, p = 0.001) and correlated with the number of pain episodes. |
| Durmaz (2018) [62] | AP | Compare AP to CP and healthy controls Diagnose AP | Prospective (total 120: controls 70, AP 50) | Aplio 500, Toshiba | 2D-SWE | 2D-SWE values were higher in AP than in controls (3.48 ± 0.52 vs. 2.60 ± 1.63 m/s or 45.71 ± 10.72 vs. 23.77 ± 6.72 kPa, p < 0.001). The sensitivity and specificity were both 98%, using elastic modulus, and 96% and 98.3%, respectively, using SW velocity. |
| Kaya (2018) [63] | AP | Compare AP to healthy controls Diagnose AP Correlation with clinical-laboratory outcome | Prospective (total 187: controls 79, AP 108) | Acuson 2000, Siemens | p-SWE | p-SWE values were higher in AP than in controls (2.43 ± 0.08 vs. 1.27 ± 0.025 m/s, p < 0.001). The sensitivity was 100%, and the specificity to diagnose AP was 98%. No correlation with hospitalization, amylase and blood leukocyte. |
| Kuwahara (2018) [64] | CP | Correlation with endoscopic ultrasound findings | Retrospective (85) | iU22, Philips | p-SWE | Hyperechoic foci with shadowing and lobularity with honeycombing were independently related to p-SWE (B = 2.92 (95% CI 2.12–5.71, p < 0.001) and B = 3.91 (95% CI 1.22–4.62, p = 0.001), respectively). |
| He (2017) [65] | PS | Compare DM to healthy controls Compare complicated DM to uncomplicated DM | Prospective (total 230: controls 115, complicated DM 68, uncomplicated DM 47) | Acuson S2000, Siemens | p-SWE | p-SWE values were higher in DM than in controls (p < 0.001). p-SWE values for pancreatic body were higher in complicated DM than in uncomplicated DM (p < 0.01). |
| Pozzi (2017) [66] | CP | Compare CP to healthy controls Correlation with CP severity | Prospective (total 94: control 42, CP 52) | iU22, Philips | p-SWE | p-SWE values were higher in CP than in controls (4.3 ± 2.4 vs. 2.8 ± 1.1 kPa, p = 0.001). Disease duration, analgesics administration and low body weight were independently associated with p-SWE values. |
| Kuwahara (2016) [67] | - | Correlation with histological pancreatic fibrosis | Retrospective (53) | iU22, Philips | p-SWE | p-SWE values correlated with histological pancreatic fibrosis stage. The AUC for ≥mild, ≥moderate and severe fibrosis was 0.85, 0.84 and 0.87. |
| Llamoza-Torres (2016) [68] | CP | Diagnose CP | Retrospective (total 33: normal 16, CP 17) | Acuson S2000, Siemens | p-SWE | p-SWE values for pancreatic body were higher in CP compared to normal group (1.57 vs. 1.27 m/s, p = 0.037); AUC 0.71 (95% CI 0.532–0.895) to diagnose CP |
| Xie (2015) [55] | AP | Compare AP to healthy controls | Prospective (total 254: controls 210, AP 44) | Acuson S2000, Siemens | p-SWE | p-SWE showed no differences between AP and healthy controls (1.21 ± 0.20 vs. 1.18 ± 0.20 m/s (pancreatic head) and 1.25 ± 0.19 m/s (pancreatic body)). |
| Goya (2014) [69] | AP | Compare B-mode, CT and elastography to diagnose AP | Prospective (88) | Acuson S2000, Siemens | p-SWE | p-SWE showed higher accuracy than B-mode and CT to diagnose AP with 100% sensitivity and 98% specificity |
| Park (2013) [70] | PC | Differential diagnosis benign and malignant lesions | Retrospective (total 27: benign 8, malignant 19) | Acuson S2000, Siemens | p-SWE | Relative p-SWE values were higher for malignancies than for benign lesions (1.5 ± 0.8 vs. 0.4 ± 0.3 m/s, p = 0.011) |
| Mateen (2012) [71] | AP | Compare AP to CP and healthy controls Diagnose AP | Prospective (total 166: controls 52, CP 46, AP 68) | Acuson S2000, Siemens | p-SWE | p-SWE values were higher in AP compared to CP and healthy controls (3.28 ± 0.85 vs. 1.28 ± 0.29 vs. 1.25 ± 0.23 m/s, p < 0.001). Sensitivity, specificity, PPV and NPV of p-SWE to differentiate AP vs. CP and healthy controls were 97.1%, 92.9%, 90.4% and 97.8%, respectively. |
| Yashima (2012) [72] | CP | Compare CP to healthy controls Diagnose CP | Prospective (total 98: controls 52, CP 46) | Acuson S2000, Siemens | p-SWE | p-SWE values for pancreatic head, body and tail were higher in CP than in controls (1.23 ± 0.34, 1.30 ± 0.34 and 1.24 ± 0.50 vs. 1.65 ± 0.71, 2.09 ± 1.03 and 1.68 ± 0.84 m/s, respectively, p < 0.001). Considering pancreatic body, AUC was 0.78 with sensitivity, specificity, PPV and NPV of 75%, 72%, 69% and 78%, respectively. |
Abbreviations: N, number of patients; AIP, autoimmune pancreatitis; AP, acute pancreatitis; AUC, area under the curve; CP, chronic pancreatitis; CT, computed tomography; DM, diabetes mellitus; NPV, negative predictive value; PC, pancreatic cancer; PDAC, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; PPV, positive predictive value; PS, pancreatic steatosis; p-SWE, point shear eave elastography; RAP, recurrent acute pancreatitis; SW, shear wave; SWE, shear wave elastography.
4.1. Acute Pancreatitis
Different studies investigated the ability of US-E to distinguish acute pancreatitis (AP) from normal pancreas or other pancreatic diseases. Mateen et al., found that the p-SWE values were higher in AP patients (n = 68) compared to healthy subjects (n = 52) and CP patients (n = 46) (3.28 ± 0.85 vs. 1.28 ± 0.29 and 1.25 ± 0.24 m/s, p < 0.001). Using a cut-off value of 2.2 m/s, the negative predictive value of p-SWE to distinguish AP from healthy controls and CP patients was 97.8%. Interestingly, five patients with AP had the p-SWE values higher than the upper detection limit, but different grey scale and colour scale scores, suggesting that the combination of two elastography techniques could improve the distinction between the inflamed tissue and tissue necrosis [71]. In contrast, Xie et al., found no significant difference between patients with AP (n = 44) and healthy controls in the p-SWE results [55]. Given that PA is usually diagnosed based on clinical and laboratory findings in typical cases, US-E could improve the diagnostic accuracy in unclear cases, even when imaging is inconclusive. Using a cut-off value of 1.63 m/s, the p-SWE showed better performance than computerized tomography (CT) in diagnosing AP (diagnosed based on clinical and laboratory findings), with a sensitivity and specificity of 100% and 98%, respectively [69]. Similarly, Durmaz et al., showed that in clinically and laboratory-diagnosed AP patients with normal US and normal contrast-enhanced CT, the 2D-SWE values were significantly higher than those in asymptomatic volunteers (41.67 ± 9.65 vs. 23.77 ± 6.72 kPa, p < 0.001) [62].
Given that universal normal or pathological elastography values have not been clearly determined, it would be highly interesting to investigate the relationship between the change in elastography values between the initial time and subsequent follow-up and prognostic outcomes. In a prospective study classifying AP according to Atlanta criteria, the 2D-SWE values in patients with mild AP trended to be higher than those in patients with severe AP (9.05 ± 1.44 vs. 8.61 ± 1.72 kPa); however, the difference was not significant. After clinical improvement, the 2D-SWE values decreased considerably compared to the initial value (10.97 vs. 8.8 kPa, p = 0.000) but remained elevated after 1 month. Furthermore, 2D-SWE was not correlated with hospitalization and biochemical parameters [59]. Confirming this, Kaya et al., showed no correlation between the p-SWE values and the length of hospitalization, amylase and white blood cell count. Furthermore, the p-SWE value was not different between patients who developed complication and those who did not (2.70 ± 0.247 vs. 2.36 ± 0.63, p = 0.151) [63]. Further studies to evaluate the variation of the SWE values during the AP evolution are clearly warranted.
Another important issue is to clarify if US-E can early detect the evolution of AP in CP patients. In patients with idiopathic recurrent AP and without endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) criteria of CP, the mean p-SWE value was significantly higher compared to that of healthy controls (1.27 ± 0.50 vs. 1.00 ± 0.17 m/s, p = 0.001) and showed a positive correlation with the number of pain episodes, suggesting that fibrosis increases after each episode [61].
The US-E could be useful also to monitor response to therapy. In patients with type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis (n = 23), the 2D-SWE values were significantly higher than those in healthy controls (n = 34) (30.9 vs. 6.6 kPa, p = 0.001) and decreased over two weeks of steroids therapy more than the change in the pancreatic parenchyma size, proving to be a sensitive tool in monitoring response to therapy. Interestingly, the SW dispersion slope, which reflects the viscosity of a tissue and is related to necroinflammation more than fibrosis, was significantly different between patients with autoimmune pancreatitis and controls (15.3, IQR 4.2 vs. 13, IQR 3.4, p = 0.011) [60].
4.2. Chronic Pancreatitis
CP is characterised by the progressive replacement of pancreatic parenchyma with fibrotic tissue and the potential of progression to exocrine and endocrine insufficiency [73]. As far as we are aware, only one study has histologically demonstrated the relation between fibrosis and the US-E findings. In fifty-three patients undergoing surgical pancreatic procedures for different indications (mainly malignancies and cystic lesion), preoperative p-SWE and histological analysis of the same region were performed. The p-SWE results demonstrated a significant positive correlation with the fibrosis stage and an AUC of 0.85, 0.84, and 0.87 for differentiating between mild or higher, moderate or higher and severe fibrosis, respectively [67].
Regarding the diagnostic value of US-E in CP, in a prospective study including patients with suspected CP (diagnosed with EUS), the p-SWE of the pancreatic body had significantly higher results in patients with the confirmed diagnosis of CP compared to patients without CP (1.57 vs. 1.27 m/s, p = 0.037), with an AUC of 0.71 for diagnosed CP. Furthermore, the p-SWE value correlated with the number of the EUS criteria for CP [68]. Similarly, Kuwahara et al., showed a correlation between the p-SWE values, Rosemont classification, Japan Pancreas Society clinical diagnostic criteria 2009 and the numbers of the EUS criteria for CP, obtaining an AUC of 0.77 for definitive or suggestive CP diagnosis. At multivariate regression, hyperechoic foci with shadowing and lobularity with honeycombing were independently related to the p-SWE values [64]. Compared to Llamoza-Torres et al.’s study, Yashima et al., described significantly higher values of p-SWE in each part of the pancreas (head, body and tail) compared to those in healthy volunteers (1.65 ± 0.71, 2.09 ± 1.03, 1.68 ± 0.84 m/s vs. 1.23 ± 0.34, 1.30 ± 0.34 and 1.24 ± 0.50 m/s, respectively, p < 0.001) [72]. Notably, 74% of CP cases in this study were categorised as Cambridge grade V, and 76% of patients had alcoholic CP, indicating that the SWE values may increase as CP progresses and may be influenced by the CP aetiology. Supporting this, the p-SWE values were significantly higher in the CP patients with the disease duration > 10 years, who required chronic analgesics, and who had a lower body weight, and all of the results were independently associated with the p-SWE values [66]. Further studies are required to confirm the association between the progression of CP and changes in the US-E findings and to investigate the role of elastography in predicting exocrine pancreatic insufficiency.
4.3. Metabolic Associated Pancreatic Disease
Pancreatic steatosis (PS) is an emerging pathological entity that can contribute to the development and progression of pancreatic inflammatory and neoplastic disease, as well as endocrine systemic alteration and metabolic disorders [74]. Therefore, PS, non-alcoholic fatty pancreas disease (NAFPD) and non-alcoholic fatty steatopancreatitis are the terms used to defined specific conditions [75].
As triglyceride accumulation modifies the viscoelastic properties of tissue, US-E may reflect these alterations; however, a comparison with histological data is not easily achievable. Recently, Sezgin et al., showed that the 2D-SWE values were significantly higher in PS patients compared to non-PS group (9.08 ± 2.29 vs. 7.13 ± 1.85 kPa, p = 0.000). In addition, the 2D-SWE values correlated with BMI, waist circumference and serum triglycerides, progressively increased in B-mode classes of PS, and were significantly higher in patients with metabolic syndrome [57]. These results suggest that the stiffness of the pancreas increases with the PS grade and reflects the impairment of the pancreatic function and the progression of metabolic disorder. Supporting this, the p-SWE values for the pancreas body were significantly higher in patient with diabetes mellitus and microangiopathy compared to those in patients with uncomplicated diabetes (p < 0.01) [65].
4.4. Pancreatic Cancer
Although the US-E has been shown to improve the diagnostic accuracy of the B-mode in determining the precise type of pancreatic lesions [76], contradictory evidence exists regarding the validity of the absolute SWE value in discriminating pancreatic lesions. Some authors showed a significantly higher SWE value in tumour site compared to normal pancreas [77]. Other studies indicates that absolute SWE values of pancreatic cancer and normal parenchyma [78] or benign lesions and malignant ones are not significantly different [70]. On the other hand, relative SWE values provide greater potential for mass differentiation. Park et al., reported that the difference in the mean p-SWE values between lesion and adjacent parenchyma (relative p-SWE value) was significantly lower for benign lesions (mass forming pancreatitis and autoimmune pancreatitis) than for malignant lesions (pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PDAC), neuroendocrine malignant tumour, metastasis) (0.4 ± 0.3 vs. 1.5 ± 0.8 m/s p = 0.011) [70]. Likewise, the 2D-SWE tumour/parenchyma ratio > 2.42 kPa in histologically defined pancreatic lesions demonstrated an AUC of 0.77 for distinguishing PDAC from non-PDAC [58].
The US-E may also have a prognostic role in pancreatic cancer. Preliminary results of the study conducted by Kawada et al., demonstrated that strain ratio modification was related to response to therapy [79]. Further research is needed to establish the real diagnostic and prognostic role of quantitative US-E in pancreatic cancer.
5. Gallbladder
5.1. Inflammatory Diseases
By using conventional US, acute cholecystitis is diagnosed with 81% sensitivity and 80% specificity [80]. When classical B-mode US features of acute cholecystitis (presence of gallstone, sonographic Murphy sign, gallbladder wall thickening) are not detected, the diagnosis could be challenging. Can US-E enhance the diagnostic efficacy of B-mode in the diagnosis of acute cholecystitis and how? US-E could provide additional information to conventional B-mode findings by analysing the change in elasticity of pericholecystic liver parenchyma caused by pathophysiological changes in acute cholecystitis. It was demonstrated that the 2D-SWE values for the gallbladder bed of the liver were significantly higher in patients with acute cholecystitis compared to patients with non-acute cholecystitis (8.2 vs. 5.8 kPa, p = 0.045). A cut-off value of 8 kPa showed an AUC of 0.69 with high specificity (90%) and low sensitivity (57.1%) and categorized the 2D-SWE value as the only factor significantly related to acute cholecystitis [81]. Similarly, Kim et al., demonstrated that the addition of p-SWE findings to conventional US significantly enhanced the AUC of two examiners in the diagnosis of acute cholecystitis from 0.79 and 0.78 to 0.96, respectively [82].
5.2. Benign and Malignant Lesions
US-E could be an additional tool to distinguish malignancies from benign condition of gallbladder wall. Using SE, gallbladder polyps were characterized by medium-high strain (soft or moderately soft) compared to only one single small nodule (measuring 19 mm) defined as gallbladder carcinoma which exhibited low strain (high stiffness) [83]. Considering differential diagnosis between benign wall thickening and gallbladder carcinoma, Kapoor et al., reported that the p-SWE values could distinguish between the two conditions with 92.8% accuracy [84]. Furthermore, the 2D-SWE showed an AUC of 0.92 to differentiate gallbladder carcinoma from chronic cholecystitis, resulting in a significantly lower value for chronic cholecystitis compared to gallbladder carcinoma and apparently non-involved wall in gallbladder carcinoma (12.3 vs. 35.0 and vs. 18.3 kPa, respectively, p = 0.01) [85].
6. Conclusions
In this review, we examined the numerous applications of elastography in a wide range of gastrointestinal disorders other than the well-established use in liver diseases. Elastography could be a useful adjunct to conventional US in an emergency setting. Elastography has the potential to be an efficient non-invasive diagnostic and characterization tool for acute and chronic conditions of the bowel, pancreas and gallbladder, and finally, it could be an easily accessible and low-cost tool for assessing or monitoring the response to specific treatments. On the other hand, the limitations of current research and the resulting inability to provide detailed indications from international guidelines prevent the application of elastography in routine clinical practise. Additional research is required to standardize the methodology of this technique and to understand the real importance of US-E in all the illustrated conditions.
Author Contributions
M.P. (Mattia Paratore), M.G. and M.A.Z. contributed to conceptualization, review of the literature and collection of data, writing the first draft, review and editing. M.E.A., L.E.D.V., G.C., L.R., M.P. (Maurizio Pompili) and A.G. contributed to conceptualization, supervision, review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Atkinson, N.S.S.; Bryant, R.V.; Dong, Y.; Maaser, C.; Kucharzik, T.; Maconi, G.; Asthana, A.K.; Blaivas, M.; Goudie, A.; Gilja, O.H.; et al. WFUMB Position Paper. Learning Gastrointestinal Ultrasound: Theory and Practice. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2016, 42, 2732–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grgurevic, I.; Salkic, N.; Bozin, T.; Mustapic, S.; Matic, V.; Dumic-Cule, I.; Tjesic Drinkovic, I.; Bokun, T. Magnitude Dependent Discordance in Liver Stiffness Measurements Using Elastography Point Quantification with Transient Elastography as the Reference Test. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 2448–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, P. Multiparametric Ultrasound (MPUS) Imaging: Terminology Describing the Many Aspects of Ultrasonography. Ultraschall Med. 2015, 36, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiina, T.; Nightingale, K.R.; Palmeri, M.L.; Hall, T.J.; Bamber, J.C.; Barr, R.G.; Castera, L.; Choi, B.I.; Chou, Y.-H.; Cosgrove, D.; et al. WFUMB Guidelines and Recommendations for Clinical Use of Ultrasound Elastography: Part 1: Basic Principles and Terminology. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2015, 41, 1126–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigrist, R.M.S.; Liau, J.; Kaffas, A.E.; Chammas, M.C.; Willmann, J.K. Ultrasound Elastography: Review of Techniques and Clinical Applications. Theranostics 2017, 7, 1303–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, C.F.; Barr, R.G.; Farrokh, A.; Dighe, M.; Hocke, M.; Jenssen, C.; Dong, Y.; Saftoiu, A.; Havre, R.F. Strain Elastography—How To Do It? Ultrasound Int. Open 2017, 3, E137–E149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gennisson, J.-L.; Deffieux, T.; Fink, M.; Tanter, M. Ultrasound Elastography: Principles and Techniques. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2013, 94, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trout, A.T.; Qiu, L.; Dillman, J.R. Practical Considerations for Pancreas Ultrasound Elastography: Reply to Rojas-Rojas et al. Pediatr. Radiol. 2021, 51, 1770–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, A.; Grajo, J.R.; Dhyani, M.; Anthony, B.W.; Samir, A.E. Principles of ultrasound elastography. Abdom. Radiol. 2018, 43, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.-W.; Li, K.-N.; Yi, A.-J.; Wang, B.; Wei, Q.; Wu, G.-G.; Dietrich, C.F. Ultrasound Elastography. Endosc. Ultrasound 2022, 11, 252–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ophir, J.; Céspedes, I.; Ponnekanti, H.; Yazdi, Y.; Li, X. Elastography: A Quantitative Method for Imaging the Elasticity of Biological Tissues. Ultrason. Imaging 1991, 13, 111–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochlin, D.L.; Ganatra, R.H.; Griffiths, D.F.R. Elastography in the Detection of Prostatic Cancer. Clin. Radiol. 2002, 57, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garra, B.S.; Cespedes, E.I.; Ophir, J.; Spratt, S.R.; Zuurbier, R.A.; Magnant, C.M.; Pennanen, M.F. Elastography of Breast Lesions: Initial Clinical Results. Radiology 1997, 202, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosgrove, D.; Piscaglia, F.; Bamber, J.; Bojunga, J.; Correas, J.-M.; Gilja, O.; Klauser, A.; Sporea, I.; Calliada, F.; Cantisani, V.; et al. EFSUMB Guidelines and Recommendations on the Clinical Use of Ultrasound Elastography. Part 2: Clinical Applications. Ultraschall Med. 2013, 34, 238–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Săftoiu, A.; Gilja, O.H.; Sidhu, P.S.; Dietrich, C.F.; Cantisani, V.; Amy, D.; Bachmann-Nielsen, M.; Bob, F.; Bojunga, J.; Brock, M.; et al. The EFSUMB Guidelines and Recommendations for the Clinical Practice of Elastography in Non-Hepatic Applications: Update 2018. Ultraschall Med. 2019, 40, 425–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhara, H.; Hirooka, Y.; Kawashima, H.; Ohno, E.; Ishikawa, T.; Nakamura, M.; Miyahara, R.; Ishigami, M.; Hashimoto, S.; Goto, H. Transabdominal Ultrasound Elastography of the Esophagogastric Junction Predicts Reflux Esophagitis. J. Med. Ultrason. 2019, 46, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, D.; Zeng, X.; Hou, Y.; Liu, H. Esophagus Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis: Ultrasound Parameters and Association with Clinical Manifestations. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2021, 23, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilja, O.H.; Heimdal, A.; Hausken, T.; Gregersen, H.; Matre, K.; Berstad, A.; Ødegaard, S. Strain during Gastric Contractions Can Be Measured Using Doppler Ultrasonography. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2002, 28, 1457–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.B.; Matre, K.; Hausken, T.; Gregersen, H.; Gilja, O.H. Rome III Subgroups of Functional Dyspepsia Exhibit Different Characteristics of Antral Contractions Measured by Strain Rate Imaging—A Pilot Study. Ultraschall Med. 2012, 33, E233–E240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantisani, V.; Rubini, A.; Miniagio, G. CEUS and Strain Elastography in Gastric Carcinoma. J. Ultrasound 2013, 16, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, W.-C.; Lee, P.-C.; Lin, M.-T.; Chang, C.-H.; Wang, H.-P. Adding Trans-Abdominal Elastography to the Diagnostic Tool for an Ileal Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor: A Case Report. BMC Med. Imaging 2019, 19, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannetti, A.; Biscontri, M.; Matergi, M. Feasibility of Real-Time Strain Elastography in Colonic Diseases. J. Ultrasound 2014, 17, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Ata, N.; Dillman, J.R.; Rubin, J.M.; Collins, M.H.; Johnson, L.A.; Imbus, R.S.; Bonkowski, E.L.; Denson, L.A.; Higgins, P.D.R. Ultrasound Shear Wave Elastography in Pediatric Stricturing Small Bowel Crohn Disease: Correlation with Histology and Second Harmonic Imaging Microscopy. Pediatr. Radiol. 2023, 53, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-J.; Chen, B.-L.; Liang, M.-J.; Chen, S.-L.; Li, X.-H.; Qiu, Y.; Pang, L.-L.; Xia, Q.-Q.; He, Y.; Zeng, Z.-R.; et al. Longitudinal Bowel Behavior Assessed by Bowel Ultrasound to Predict Early Response to Anti-TNF Therapy in Patients with Crohn’s Disease: A Pilot Study. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2022, 28, S67–S75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, K.; Ishikawa, T.; Kawashima, H.; Ohno, E.; Iida, T.; Ishikawa, E.; Mizutani, Y.; Sawada, T.; Maeda, K.; Yamamura, T.; et al. Evaluation of Ulcerative Colitis Activity Using Transabdominal Ultrasound Shear Wave Elastography. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2022, 12, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Huang, P.-L.; Kang, N.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, M.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Cao, X.-C.; Dai, X.-C. The Clinical Value of Multimodal Ultrasound for the Evaluation of Disease Activity and Complications in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2020, 9, 4146–4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.-S.; Fang, Y.; Wan, J.; Zhao, C.-K.; Xiang, L.-H.; Liu, H.; Pu, H.; Xu, G.; Zhang, K.; Xu, X.-R.; et al. Usefulness of Strain Elastography, ARFI Imaging, and Point Shear Wave Elastography for the Assessment of Crohn Disease Strictures. J. Ultrasound Med. 2019, 38, 2861–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goertz, R.S.; Lueke, C.; Schellhaas, B.; Pfeifer, L.; Wildner, D.; Neurath, M.F.; Strobel, D. Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse (ARFI) Shear Wave Elastography of the Bowel Wall in Healthy Volunteers and in Ulcerative Colitis. Acta Radiol. Open 2019, 8, 205846011984096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Mao, R.; Md, X.L.; Cao, Q.; Chen, Z.; Liu, B.; Chen, S.; Chen, B.; He, Y.; Zeng, Z.; et al. Real-Time Shear Wave Ultrasound Elastography Differentiates Fibrotic from Inflammatory Strictures in Patients with Crohn’s Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2018, 24, 2183–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goertz, R.S.; Lueke, C.; Wildner, D.; Vitali, F.; Neurath, M.F.; Strobel, D. Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse (ARFI) Elastography of the Bowel Wall as a Possible Marker of Inflammatory Activity in Patients with Crohn’s Disease. Clin. Radiol. 2018, 73, 678.e1–678.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando, S.; Fraquelli, M.; Coletta, M.; Branchi, F.; Magarotto, A.; Conti, C.B.; Mazza, S.; Conte, D.; Basilisco, G.; Caprioli, F. Ultrasound Elasticity Imaging Predicts Therapeutic Outcomes of Patients with Crohn’s Disease Treated with Anti-Tumour Necrosis Factor Antibodies. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2018, 12, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quaia, E.; Gennari, A.G.; Cova, M.A.; Van Beek, E.J.R. Differentiation of Inflammatory From Fibrotic Ileal Strictures among Patients with Crohn’s Disease Based on Visual Analysis: Feasibility Study Combining Conventional B-Mode Ultrasound, Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound and Strain Elastography. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2018, 44, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Gui, X.; Chen, W.; Fung, T.; Novak, K.; Wilson, S.R. Ultrasound Shear Wave Elastography and Contrast Enhancement: Effective Biomarkers in Crohn’s Disease Strictures. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2017, 23, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra, C.; Rizzello, F.; Pratico’, C.; Felicani, C.; Fiorini, E.; Brugnera, R.; Mazzotta, E.; Giunchi, F.; Fiorentino, M.; D’Errico, A.; et al. Real-Time Elastography for the Detection of Fibrotic and Inflammatory Tissue in Patients with Stricturing Crohn’s Disease. J. Ultrasound 2017, 20, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sconfienza, L.M.; Cavallaro, F.; Colombi, V.; Pastorelli, L.; Tontini, G.; Pescatori, L.; Esseridou, A.; Savarino, E.; Messina, C.; Casale, R.; et al. In-Vivo Axial-Strain Sonoelastography Helps Distinguish Acutely-Inflamed from Fibrotic Terminal Ileum Strictures in Patients with Crohn’s Disease: Preliminary Results. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2016, 42, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraquelli, M.; Branchi, F.; Cribiù, F.M.; Orlando, S.; Casazza, G.; Magarotto, A.; Massironi, S.; Botti, F.; Contessini-Avesani, E.; Conte, D.; et al. The Role of Ultrasound Elasticity Imaging in Predicting Ileal Fibrosis in Crohn’s Disease Patients. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 2605–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fufezan, O.; Asavoaie, C.; Tamas, A.; Farcau, D.; Serban, D. Bowel Elastography—A Pilot Study for Developing an Elastographic Scoring System to Evaluate Disease Activity in Pediatric Crohn’s Disease. Med. Ultrason. 2015, 17, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, D.; Ando, T.; Watanabe, O.; Ishiguro, K.; Maeda, O.; Miyake, N.; Nakamura, M.; Miyahara, R.; Ohmiya, N.; Hirooka, Y.; et al. Images of Colonic Real-Time Tissue Sonoelastography Correlate with Those of Colonoscopy and May Predict Response to Therapy in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2011, 11, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adolph, T.E.; Meyer, M.; Schwärzler, J.; Mayr, L.; Grabherr, F.; Tilg, H. The Metabolic Nature of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 753–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magro, F.; Langner, C.; Driessen, A.; Ensari, A.; Geboes, K.; Mantzaris, G.J.; Villanacci, V.; Becheanu, G.; Borralho Nunes, P.; Cathomas, G.; et al. European Consensus on the Histopathology of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2013, 7, 827–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magro, F.; Gionchetti, P.; Eliakim, R.; Ardizzone, S.; Armuzzi, A.; Barreiro-de Acosta, M.; Burisch, J.; Gecse, K.B.; Hart, A.L.; Hindryckx, P.; et al. Third European Evidence-Based Consensus on Diagnosis and Management of Ulcerative Colitis. Part 1: Definitions, Diagnosis, Extra-Intestinal Manifestations, Pregnancy, Cancer Surveillance, Surgery, and Ileo-Anal Pouch Disorders. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2017, 11, 649–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.-Y.; Gao, X.; Zhuang, H.; Wu, Y.-T.; Luo, Y.; Jing, J.-G.; Zhang, Y. Using Shear Wave Elasticity in Normal Terminal Ileum of a Healthy Southwest Chinese Population: A Pilot Study of Reference Elasticity Ranges. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2021, 11, 2677–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dillman, J.R.; Stidham, R.W.; Higgins, P.D.R.; Moons, D.S.; Johnson, L.A.; Keshavarzi, N.R.; Rubin, J.M. Ultrasound Shear Wave Elastography Helps Discriminate Low-Grade from High-Grade Bowel Wall Fibrosis in Ex Vivo Human Intestinal Specimens. J. Ultrasound Med. 2014, 33, 2115–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgart, D.C.; Müller, H.P.; Grittner, U.; Metzke, D.; Fischer, A.; Guckelberger, O.; Pascher, A.; Sack, I.; Vieth, M.; Rudolph, B. US-Based Real-Time Elastography for the Detection of Fibrotic Gut Tissue in Patients with Stricturing Crohn Disease. Radiology 2015, 275, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raine, T.; Bonovas, S.; Burisch, J.; Kucharzik, T.; Adamina, M.; Annese, V.; Bachmann, O.; Bettenworth, D.; Chaparro, M.; Czuber-Dochan, W.; et al. ECCO Guidelines on Therapeutics in Ulcerative Colitis: Medical Treatment. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2022, 16, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, J.; Bonovas, S.; Doherty, G.; Kucharzik, T.; Gisbert, J.P.; Raine, T.; Adamina, M.; Armuzzi, A.; Bachmann, O.; Bager, P.; et al. ECCO Guidelines on Therapeutics in Crohn’s Disease: Medical Treatment. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2020, 14, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puca, P.; Del Vecchio, L.E.; Ainora, M.E.; Gasbarrini, A.; Scaldaferri, F.; Zocco, M.A. Role of Multiparametric Intestinal Ultrasound in the Evaluation of Response to Biologic Therapy in Adults with Crohn’s Disease. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, S.-W.; Kim, I.Y.; Kim, Y.W. Quantitative Measurement of Elasticity of the Appendix Using Shear Wave Elastography in Patients with Suspected Acute Appendicitis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keven, A.; Tekin, A.F.; Arslan, F.Z.; Özer, H.; Durmaz, M.S. Two-Dimensional Shear Wave Elastography Can Improve the Diagnostic Accuracy of Ultrasonography in Acute Appendicitis. J. Ultrasound 2022, 26, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, A.; Kapoor, A.; Mahajan, G. Real-Time Elastography in Acute Appendicitis. J. Ultrasound Med. 2010, 29, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goya, C.; Hamidi, C.; Okur, M.H.; Icer, M.; Oguz, A.; Hattapoglu, S.; Cetincakmak, M.G.; Teke, M. The Utility of Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Imaging in Diagnosing Acute Appendicitis and Staging Its Severity. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2014, 20, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isik, İ.A.; Ozkan, M.B. Evaluation of the Clinical Effectiveness of Shear Wave Elastography in Pediatric Cases with Acute Appendicitis. Ultrasound Q. 2021, 37, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslan, H.; Akdemir, Z.; Yavuz, A.; Gökçal, F.; Parlakgümüş, C.; İslamoglu, N.; Akdeniz, H. Efficacy of Strain Elastography in Diagnosis and Staging of Acute Appendicitis in Pediatric Patients. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havre, R.; Leh, S.; Gilja, O.; Ødegaard, S.; Waage, J.; Baatrup, G.; Nesje, L. Strain Assessment in Surgically Resected Inflammatory and Neoplastic Bowel Lesions. Ultraschall Med. 2012, 35, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Zou, L.; Yao, M.; Xu, G.; Zhao, L.; Xu, H.; Wu, R. A Preliminary Investigation of Normal Pancreas and Acute Pancreatitis Elasticity Using Virtual Touch Tissue Quantification (VTQ) Imaging. Med. Sci. Monit. 2015, 21, 1693–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpf, S.; Jaeger, H.; Graeter, T.; Oeztuerk, S.; Schmidberger, J.; Haenle, M.M.; Kratzer, W. Elasto-Study Group Ulm Influence of Age, Sex, Body Mass Index, Alcohol, and Smoking on Shear Wave Velocity (p-SWE) of the Pancreas. Abdom. Radiol. 2016, 41, 1310–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sezgin, O.; Yaraş, S.; Özdoğan, O. Pancreatic Steatosis Is Associated with Both Metabolic Syndrome and Pancreatic Stiffness Detected by Ultrasound Elastography. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2022, 67, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iino, Y.; Maruyama, H.; Mikata, R.; Yasui, S.; Koroki, K.; Nagashima, H.; Awatsu, M.; Shingyoji, A.; Kusakabe, Y.; Kobayashi, K.; et al. Percutaneous Two-Dimensional Shear Wave Elastography for Diagnosis of Pancreatic Tumor. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezgin, O.; Yaraş, S.; Özdoğan, O. The Course and Prognostic Value of Increased Pancreas Stiffness Detected by Ultrasound Elastography during Acute Pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2021, 21, 1285–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Ishikawa, T.; Ohno, E.; Iida, T.; Uetsuki, K.; Yashika, J.; Yamada, K.; Yoshikawa, M.; Furukawa, K.; Nakamura, M.; et al. An Initial Trial of Quantitative Evaluation of Autoimmune Pancreatitis Using Shear Wave Elastography and Shear Wave Dispersion in Transabdominal Ultrasound. Pancreatology 2021, 21, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjeevi, R.; John, R.A.; Kurien, R.T.; Dutta, A.K.; Simon, E.G.; David, D.; Joseph, A.J.; Chowdhury, S.D. Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Imaging of Pancreas in Patients with Early Onset Idiopathic Recurrent Acute Pancreatitis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 32, 950–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durmaz, M.S.; Arslan, S.; Özbakır, B.; Güngör, G.; Tolu, İ.; Arslan, F.Z.; Sivri, M.; Koplay, M. Effectiveness of Shear Wave Elastography in the Diagnosis of Acute Pancreatitis on Admission. Med. Ultrason. 2018, 20, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, M.; Değirmenci, S.; Göya, C.; Tuncel, E.T.; Uçmak, F.; Kaplan, M.A. The Importance of Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse (ARFI) Elastography in the Diagnosis and Clinical Course of Acute Pancreatitis. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 29, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwahara, T.; Hirooka, Y.; Kawashima, H.; Ohno, E.; Ishikawa, T.; Yamamura, T.; Furukawa, K.; Funasaka, K.; Nakamura, M.; Miyahara, R.; et al. Usefulness of Shear Wave Elastography as a Quantitative Diagnosis of Chronic Pancreatitis: CP Diagnosis by SW-Elastography. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 33, 756–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, X.P.; Zheng, J.-J.; Jin, C.-X. Pancreatic Elastography From Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Imaging for Evaluation of Diabetic Microangiopathy. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2017, 209, 775–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzi, R.; Parzanese, I.; Baccarin, A.; Giunta, M.; Conti, C.B.; Cantù, P.; Casazza, G.; Tenca, A.; Rosa, R.; Gridavilla, D.; et al. Point Shear-Wave Elastography in Chronic Pancreatitis: A Promising Tool for Staging Disease Severity. Pancreatology 2017, 17, 905–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwahara, T.; Hirooka, Y.; Kawashima, H.; Ohno, E.; Sugimoto, H.; Hayashi, D.; Morishima, T.; Kawai, M.; Suhara, H.; Takeyama, T.; et al. Quantitative Evaluation of Pancreatic Tumor Fibrosis Using Shear Wave Elastography. Pancreatology 2016, 16, 1063–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llamoza-Torres, C.J.; Fuentes-Pardo, M.; Álvarez-Higueras, F.J.; Alberca-de-las-Parras, F.; Carballo-Álvarez, F. Usefulness of Percutaneous Elastography by Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse for the Non-Invasive Diagnosis of Chronic Pancreatitis. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2016, 108, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goya, C.; Hamidi, C.; Hattapoğlu, S.; Cetincakmak, M.; Teke, M.; Degirmenci, M.; Kaya, M.; Bilici, A. Use of Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Elastography to Diagnose Acute Pancreatitis at Hospital Admission Comparison with Sonography and Computed Tomography. J. Ultrasound Med. Off. J. Am. Inst. Ultrasound Med. 2014, 33, 1453–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.K.; Jo, J.; Kwon, H.; Cho, J.H.; Oh, J.Y.; Noh, M.H.; Nam, K.J. Usefulness of Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Elastography in the Differential Diagnosis of Benign and Malignant Solid Pancreatic Lesions. Ultrasonography 2013, 33, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateen, M.A.; Muheet, K.A.; Mohan, R.J.; Rao, P.N.; Majaz, H.M.K.; Rao, G.V.; Reddy, D.N. Evaluation of Ultrasound Based Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse (ARFI) and ESie Touch Sonoelastography for Diagnosis of Inflammatory Pancreatic Diseases. J. Pancreas 2012, 13, 36–44. [Google Scholar]
- Yashima, Y.; Sasahira, N.; Isayama, H.; Kogure, H.; Ikeda, H.; Hirano, K.; Mizuno, S.; Yagioka, H.; Kawakubo, K.; Sasaki, T.; et al. Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Elastography for Noninvasive Assessment of Chronic Pancreatitis. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 47, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleeff, J.; Whitcomb, D.C.; Shimosegawa, T.; Esposito, I.; Lerch, M.M.; Gress, T.; Mayerle, J.; Drewes, A.M.; Rebours, V.; Akisik, F.; et al. Chronic Pancreatitis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3, 17060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramkissoon, R.; Gardner, T.B. Pancreatic Steatosis: An Emerging Clinical Entity. Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol. ACG 2019, 114, 1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, M.M.; van Geenen, E.J.M. The Clinical Significance of Pancreatic Steatosis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 8, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, H.; Hirooka, Y.; Itoh, A.; Kawashima, H.; Hara, K.; Nonogaki, K.; Kasugai, T.; Ohno, E.; Ohmiya, N.; Niwa, Y.; et al. Feasibility of Tissue Elastography Using Transcutaneous Ultrasonography for the Diagnosis of Pancreatic Diseases. Pancreas 2009, 38, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaro, R.; Dina, L.; Pojoga, C.; Vesa, S.; Badea, R. Evaluation of the Pancreatic Tumors by Transabdominal Shear Wave Elastography: Preliminary Results of a Pilot Study. Med. Ultrason. 2018, 20, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Ishikawa, T.; Ohno, E.; Iida, T.; Furukawa, K.; Nakamura, M.; Honda, T.; Ishigami, M.; Kinoshita, F.; Kawashima, H.; et al. Variability Measurements Provide Additional Value to Shear Wave Elastography in the Diagnosis of Pancreatic Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawada, N.; Tanaka, S.; Uehara, H.; Katayama, K.; Hosoki, T.; Takami, M.; Tomita, Y. Alteration of Strain Ratio Evaluated by Transabdominal Ultrasound Elastography May Predict the Efficacy of Preoperative Chemoradiation Performed for Pancreatic Ductal Carcinoma: Preliminary Results. Hepatogastroenterology 2014, 61, 480–483. [Google Scholar]
- Kiewiet, J.J.S.; Leeuwenburgh, M.M.N.; Bipat, S.; Bossuyt, P.M.M.; Stoker, J.; Boermeester, M.A. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Diagnostic Performance of Imaging in Acute Cholecystitis. Radiology 2012, 264, 708–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, A.; Lee, E.S.; Park, H.J.; Park, S.B.; Kim, H.S.; Choi, B.I. Added Value of 2D Shear Wave Imaging of the Gallbladder Bed of the Liver for Acute Cholecystitis. Ultrasonography 2020, 39, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.E.; Choi, D.S.; Bae, K.; Cho, J.M.; Jeong, C.Y.; Kim, H.O. Added Value of Point Shear-Wave Elastography in the Diagnosis of Acute Cholecystitis. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 1517–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teber, M.A.; Tan, S.; Dönmez, U.; İpek, A.; Uçar, A.E.; Yıldırım, H.; Aslan, A.; Arslan, H. The Use of Real-Time Elastography in the Assessment of Gallbladder Polyps: Preliminary Observations. Med. Ultrason. 2014, 16, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, A.; Kapoor, A.; Mahajan, G. Differentiating Malignant from Benign Thickening of the Gallbladder Wall by the Use of Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Elastography. J. Ultrasound Med. 2011, 30, 1499–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soundararajan, R.; Dutta, U.; Bhatia, A.; Gupta, P.; Nahar, U.; Kaman, L.; Bhattacharya, A.; Kumar, A.; Sandhu, M.S. Two-dimensional Shear Wave Elastography: Utility in Differentiating Gallbladder Cancer from Chronic Cholecystitis. J. Ultrasound Med. 2023, 42, 1577–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).