Assessment of Aggregated and Exosome-Associated α-Synuclein in Brain Tissue and Cerebrospinal Fluid Using Specific Immunoassays
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Human Brain Post-Mortem Samples
2.3. Mice
2.4. CSF Collection
2.5. Isolation of Exosomes from CSF
2.6. Generation of α-Synuclein Fibrils and Oligomers
2.7. ELISA for the Measurement of Aggregated α-Synuclein
2.8. ELISA for the Measurement of Total α-Synuclein
2.9. Protein Extraction and Immunoblotting
2.10. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Development of a Novel ELISA for the Quantification of α-Synuclein Fibrillar and Oligomeric Forms
3.2. Validation of Fibrillar α-Synuclein ELISA
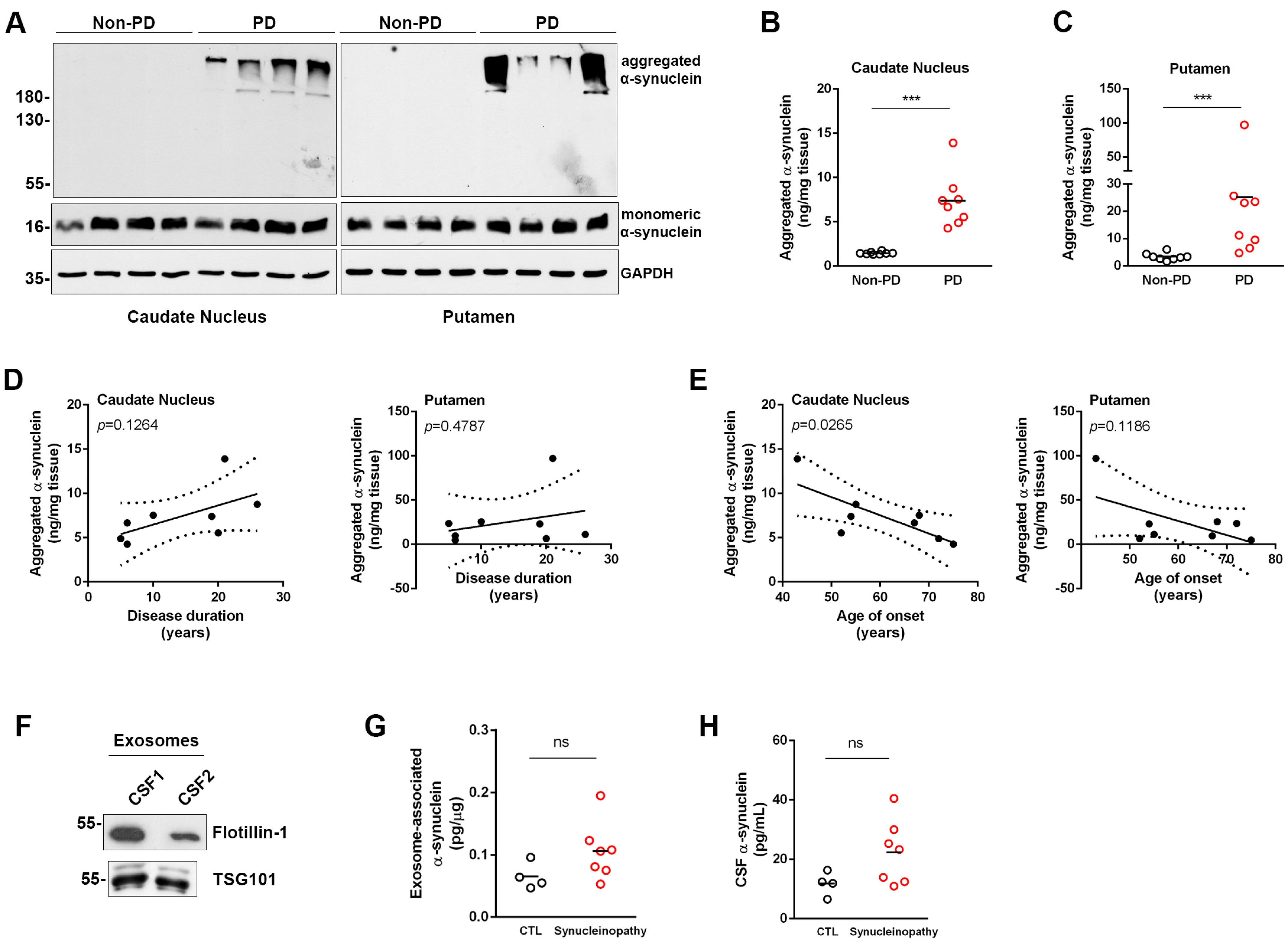
3.3. Assessment of Aggregated α-Synuclein in Human Post-Mortem Brain Tissue
3.4. Assessment of Aggregated and Total α-Synuclein in CSF and CSF-Derived Exosomes
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goedert, M.; Jakes, R.; Spillantini, M.G. The Synucleinopathies: Twenty Years On. J. Parkinsons. Dis. 2017, 7, S53–S71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Du, X.; Xie, X.; Liu, R. The Role of α -Synuclein Oligomers in Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braak, H.; Del Tredici, K.; Rüb, U.; De Vos, R.A.I.; Jansen Steur, E.N.H.; Braak, E. Staging of Brain Pathology Related to Sporadic Parkinson’s Disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2003, 24, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parnetti, L.; Gaetani, L.; Eusebi, P.; Paciotti, S.; Hansson, O.; El-Agnaf, O.; Mollenhauer, B.; Blennow, K.; Calabresi, P. CSF and Blood Biomarkers for Parkinson’s Disease. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Alvarado, M.; Dacosta-Aguayo, R.; Navalpotro-Gómez, I.; Gago, B.; Gorostidi, A.; Jiménez-Urbieta, H.; Quiroga-Varela, A.; Ruiz-Martínez, J.; Bergareche, A.; Rodríguez-Oroz, M.C. Ratios of Proteins in Cerebrospinal Fluid in Parkinson’s Disease Cognitive Decline: Prospective Study. Mov. Disord. 2018, 33, 1809–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, X.; Yeo, J.M.; Green, A.; Pal, S. The Diagnostic Utility of Cerebrospinal Fluid Alpha-Synuclein Analysis in Dementia with Lewy Bodies—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Park. Relat. Disord. 2013, 19, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinides, V.C.; Majbour, N.K.; Paraskevas, G.P.; Abdi, I.; Safieh-Garabedian, B.; Stefanis, L.; El-Agnaf, O.M.; Kapaki, E. Cerebrospinal Fluid α-Synuclein Species in Cognitive and Movements Disorders. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuda, T.; Qureshi, M.M.; Ardah, M.T.; Varghese, S.; Shehab, S.A.S.; Kasai, T.; Ishigami, N.; Tamaoka, A.; Nakagawa, M.; El-Agnaf, O.M.A. Detection of Elevated Levels of α-Synuclein Oligomers in CSF from Patients with Parkinson Disease. Neurology 2010, 75, 1766–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majbour, N.K.; Vaikath, N.N.; Van Dijk, K.D.; Ardah, M.T.; Varghese, S.; Vesterager, L.B.; Montezinho, L.P.; Poole, S.; Safieh-Garabedian, B.; Tokuda, T.; et al. Oligomeric and Phosphorylated Alpha-Synuclein as Potential CSF Biomarkers for Parkinson’s Disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2016, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hansson, O.; Hall, S.; Öhrfelt, A.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Minthon, L.; Nägga, K.; Londos, E.; Varghese, S.; Majbour, N.K.; et al. Levels of Cerebrospinal Fluid α-Synuclein Oligomers Are Increased in Parkinson’s Disease with Dementia and Dementia with Lewy Bodies Compared to Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2014, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parnetti, L.; Chiasserini, D.; Persichetti, E.; Eusebi, P.; Varghese, S.; Qureshi, M.M.; Dardis, A.; Deganuto, M.; De Carlo, C.; Castrioto, A.; et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid Lysosomal Enzymes and Alpha-Synuclein in Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2014, 29, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schweighauser, M.; Shi, Y.; Tarutani, A.; Kametani, F.; Murzin, A.G.; Ghetti, B.; Matsubara, T.; Tomita, T.; Ando, T.; Hasegawa, K.; et al. Structures of α-Synuclein Filaments from Multiple System Atrophy. Nature 2020, 585, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oueslati, A. Implication of Alpha-Synuclein Phosphorylation at S129 in Synucleinopathies: What Have We Learned in the Last Decade? J. Parkinson’s Dis. 2016, 6, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harischandra, D.S.; Rokad, D.; Neal, M.L.; Ghaisas, S.; Manne, S.; Sarkar, S.; Panicker, N.; Zenitsky, G.; Jin, H.; Lewis, M.; et al. Manganese Promotes the Aggregation and Prion-like Cell-to-Cell Exosomal Transmission of α-Synuclein. Sci. Signal. 2019, 12, eaau4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, Y.; Han, S.; Dong, Q.; Cui, M.; Tieu, K. Microglial Exosomes Facilitate A-Synuclein Transmission in Parkinson’s Disease. Brain 2020, 143, 1476–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuendl, A.; Kunadt, M.; Kruse, N.; Bartels, C.; Moebius, W.; Danzer, K.M.; Mollenhauer, B.; Schneider, A. Induction of α-Synuclein Aggregate Formation by CSF Exosomes from Patients with Parkinson’s Disease and Dementia with Lewy Bodies. Brain 2016, 139, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ngolab, J.; Trinh, I.; Rockenstein, E.; Mante, M.; Florio, J.; Trejo, M.; Masliah, D.; Adame, A.; Masliah, E.; Rissman, R.A. Brain-Derived Exosomes from Dementia with Lewy Bodies Propagate α-Synuclein Pathology. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2017, 5, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vella, L.J.; Hill, A.F.; Cheng, L. Focus on Extracellular Vesicles: Exosomes and Their Role in Protein Trafficking and Biomarker Potential in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, M.; Liu, C.; Cook, T.J.; Bullock, K.M.; Zhao, Y.; Ginghina, C.; Li, Y.; Aro, P.; Dator, R.; He, C.; et al. Plasma Exosomal α-Synuclein Is Likely CNS-Derived and Increased in Parkinson’s Disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2014, 128, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rani, K.; Mukherjee, R.; Singh, E.; Kumar, S.; Sharma, V.; Vishwakarma, P.; Bharti, P.S.; Nikolajeff, F.; Dinda, A.K.; Goyal, V.; et al. Neuronal Exosomes in Saliva of Parkinson’s Disease Patients: A Pilot Study. Park. Relat. Disord. 2019, 67, 21–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, H.B.; Ati, S.S. Evaluation of α -Synuclein in CNS-Originating Extracellular Vesicles for Evaluation of α -Synuclein in CNS-Originating Extracellular Vesicles for Parkinsonian Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Park. Relat. Disord. 2023. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeith, I.G.; Boeve, B.F.; Dickson, D.W.; Halliday, G.; Aarsland, D.; Attems, J.; Ballard, C.G.; Bayston, A.; Beach, T.G.; Chen-plotkin, A.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of Dementia with Lewy Bodies: Fourth Consensus Report of the DLB Consortium. Neurology 2017, 89, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Postuma, R.B.; Berg, D.; Stern, M.; Poewe, W.; Olanow, C.W.; Oertel, W.; Obeso, J.; Marek, K.; Litvan, I.; Lang, A.E.; et al. MDS Clinical Diagnostic Criteria for Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilman, S.; Wenning, G.K.; Low, P.A.; Brooks, D.J.; Mathias, C.J.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Wood, N.W.; Colosimo, C.; Dürr, A.; Fowler, C.J.; et al. Second Consensus Statement on the Diagnosis of Multiple System Atrophy. Neurology 2008, 71, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höglinger, G.U.; Respondek, G.; Stamelou, M.; Kurz, C.; Josephs, K.A.; Lang, A.E.; Mollenhauer, B.; Müller, U.; Nilsson, C.; Whitwell, J.L.; et al. Clinical Diagnosis of Progressive Supranuclear Palsy: The Movement Disorder Society Criteria. Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giasson, B.I.; Duda, J.E.; Quinn, S.M.; Zhang, B.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M.-Y. Neuronal-Synucleinopathy with Severe Movement Disorder in Mice Expressing A53T Human-Synuclein. Neuron 2002, 34, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emmanouilidou, E.; Minakaki, G.; Keramioti, M.V.; Xylaki, M.; Balafas, E.; Chrysanthou-Piterou, M.; Kloukina, I.; Vekrellis, K. GABA Transmission via ATP-Dependent K+ Channels Regulates α-Synuclein Secretion in Mouse Striatum. Brain 2016, 139, 871–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kapaki, E.; Paraskevas, G.P.; Emmanouilidou, E.; Vekrellis, K. The Diagnostic Value of CSF α-Synuclein in the Differential Diagnosis of Dementia with Lewy Bodies vs. Normal Subjects and Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 81654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papadopoulos, V.E.; Nikolopoulou, G.; Antoniadou, I.; Karachaliou, A.; Arianoglou, G.; Emmanouilidou, E.; Sardi, S.P.; Stefanis, L.; Vekrellis, K. Modulation of β-Glucocerebrosidase Increases α-Synuclein Secretion and Exosome Release in Mouse Models of Parkinson’s Disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018, 27, 1696–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaikath, N.N.; Majbour, N.K.; Paleologou, K.E.; Ardah, M.T.; van Dam, E.; van de Berg, W.D.J.; Forrest, S.L.; Parkkinen, L.; Gai, W.P.; Hattori, N.; et al. Generation and Characterization of Novel Conformation-Specific Monoclonal Antibodies for α-Synuclein Pathology. Neurobiol. Dis. 2015, 79, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karampetsou, M.; Ardah, M.T.; Semitekolou, M.; Polissidis, A.; Samiotaki, M.; Kalomoiri, M.; Majbour, N.; Xanthou, G.; El-Agnaf, O.M.A.; Vekrellis, K. Phosphorylated Exogenous Alpha-Synuclein Fibrils Exacerbate Pathology and Induce Neuronal Dysfunction in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vaikath, N.; Sudhakaran, I.; Abdi, I.; Gupta, V.; Majbour, N.; Ghanem, S.; Abdesselem, H.; Vekrellis, K.; El-Agnaf, O. Structural and Biophysical Characterization of Stable Alpha-Synuclein Oligomers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emmanouilidou, E.; Papagiannakis, N.; Kouloulia, S.; Galaziou, A.; Antonellou, R.; Papadimitriou, D.; Athanasiadou, A.; Bozi, M.; Koros, C.; Maniati, M.; et al. Peripheral Alpha-Synuclein Levels in Patients with Genetic and Non-Genetic Forms of Parkinson’s Disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2020, 73, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bougea, A.; Stefanis, L.; Emmanouilidou, E.; Vekrelis, K.; Kapaki, E. High Discriminatory Ability of Peripheral and CFSF Biomarkers in Lewy Body Diseases. J. Neural Transm. 2020, 127, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umemoto, A.; Yagi, H.; So, M.; Goto, Y. High-Throughput Analysis of Ultrasonication-Forced Amyloid Fibrillation Reveals the Mechanism Underlying the Large Fluctuation in the Lag Time. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 27290–27299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berkhoudt Lassen, L.; Gregersen, E.; Kathrine Isager, A.; Betzer, C.; Hahn Kofoed, R.; Henning Jensen, P. ELISA Method to Detect α-Synuclein Oligomers in Cell and Animal Models. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanouilidou, E.; Melachroinou, K.; Roumeliotis, T.; Garbis, S.D.; Ntzouni, M.; Margaritis, L.H.; Stefanis, L.; Vekrellis, K. Cell-Produced α-Synuclein Is Secreted in a Calcium-Dependent Manner by Exosomes and Impacts Neuronal Survival. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 6838–6851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herman, S.; Djaldetti, R.; Mollenhauer, B.; Offen, D. CSF-Derived Extracellular Vesicles from Patients with Parkinson’s Disease Induce Symptoms and Pathology. Brain 2023, 146, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wills, J.; Jones, J.; Haggerty, T.; Duka, V.; Joyce, J.N.; Sidhu, A. Elevated Tauopathy and Alpha-Synuclein Pathology in Postmortem Parkinson’s Disease Brains with and without Dementia. Exp. Neurol. 2010, 225, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Majbour, N.; Aasly, J.; Abdi, I.; Ghanem, S.; Erskine, D.; Van De Berg, W.; El-Agnaf, O. Disease-Associated α-Synuclein Aggregates as Biomarkers of Parkinson Disease Clinical Stage. Neurology 2022, 99, E2417–E2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairfoul, G.; McGuire, L.I.; Pal, S.; Ironside, J.W.; Neumann, J.; Christie, S.; Joachim, C.; Esiri, M.; Evetts, S.G.; Rolinski, M.; et al. Alpha-Synuclein RT-QuIC in the CSF of Patients with Alpha-Synucleinopathies. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2016, 3, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahnawaz, M.; Tokuda, T.; Waraga, M.; Mendez, N.; Ishii, R.; Trenkwalder, C.; Mollenhauer, B.; Soto, C. Development of a Biochemical Diagnosis of Parkinson Disease by Detection of α-Synuclein Misfolded Aggregates in Cerebrospinal Fluid. JAMA Neurol. 2017, 74, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groveman, B.R.; Orrù, C.D.; Hughson, A.G.; Raymond, L.D.; Zanusso, G.; Ghetti, B.; Campbell, K.J.; Safar, J.; Galasko, D.; Caughey, B. Rapid and Ultra-Sensitive Quantitation of Disease-Associated α-Synuclein Seeds in Brain and Cerebrospinal Fluid by ASyn RT-QuIC. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2018, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Synucleinopathy | Neurological Controls | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender (m/f) | 6/8 | 6/2 | 0.145 * |
| Age (years) | 64.5 (57–68) | 68.5 (61–69) | 0.368 ‡ |
| Disease duration (months) | 36 (30–60) | 30 (24–36) | 0.220 ‡ |
| MMSE | 28 (24–29) | 25 (23–29) | 0.607 ‡ |
| FAB | 14 (12–15) | 11.5 (8–12) | 0.066 ‡ |
| UPDRS III | 21 (0–51) | 16.5 (10–26) | 1.000 ‡ |
| Non PD | PD | |
|---|---|---|
| Age of death ± STDEV | 83 ± 9 | 75 ± 5 |
| Sex (male) % | 50 | 87.5 |
| Disease duration (years) ± STDEV | - | 14 ± 8 (range 5–26) |
| Age of onset (years) ± STDEV | - | 61 ± 11 (range 43–75) |
| Non Neurological CTLs | AD | Synucleinopathy | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aggregated α-synuclein (ng/mL) | 0.268 ± 0.013 (N = 2/7) | 0.414 ± 0.114 (N = 4/7) | 0.644 ± 0.183 (N = 2/10) |
| α-synuclein associated with CSF exosomes (pg/μg) | 0.065 ± 0.011 (N = 4/5) | - | 0.106 ± 0.017 (N = 7/14) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anagnostou, D.; Sfakianaki, G.; Melachroinou, K.; Soutos, M.; Constantinides, V.; Vaikath, N.; Tsantzali, I.; Paraskevas, G.P.; Agnaf, O.E.; Vekrellis, K.; et al. Assessment of Aggregated and Exosome-Associated α-Synuclein in Brain Tissue and Cerebrospinal Fluid Using Specific Immunoassays. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2192. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132192
Anagnostou D, Sfakianaki G, Melachroinou K, Soutos M, Constantinides V, Vaikath N, Tsantzali I, Paraskevas GP, Agnaf OE, Vekrellis K, et al. Assessment of Aggregated and Exosome-Associated α-Synuclein in Brain Tissue and Cerebrospinal Fluid Using Specific Immunoassays. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(13):2192. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132192
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnagnostou, Dimitrios, Garifalia Sfakianaki, Katerina Melachroinou, Miltiadis Soutos, Vassilios Constantinides, Nishant Vaikath, Ioanna Tsantzali, George P. Paraskevas, Omar El Agnaf, Kostas Vekrellis, and et al. 2023. "Assessment of Aggregated and Exosome-Associated α-Synuclein in Brain Tissue and Cerebrospinal Fluid Using Specific Immunoassays" Diagnostics 13, no. 13: 2192. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132192
APA StyleAnagnostou, D., Sfakianaki, G., Melachroinou, K., Soutos, M., Constantinides, V., Vaikath, N., Tsantzali, I., Paraskevas, G. P., Agnaf, O. E., Vekrellis, K., & Emmanouilidou, E. (2023). Assessment of Aggregated and Exosome-Associated α-Synuclein in Brain Tissue and Cerebrospinal Fluid Using Specific Immunoassays. Diagnostics, 13(13), 2192. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132192







