Additional Value of PET and CT Image-Based Features in the Detection of Occult Lymph Node Metastases in Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review of the Literature
Abstract
:1. Introduction
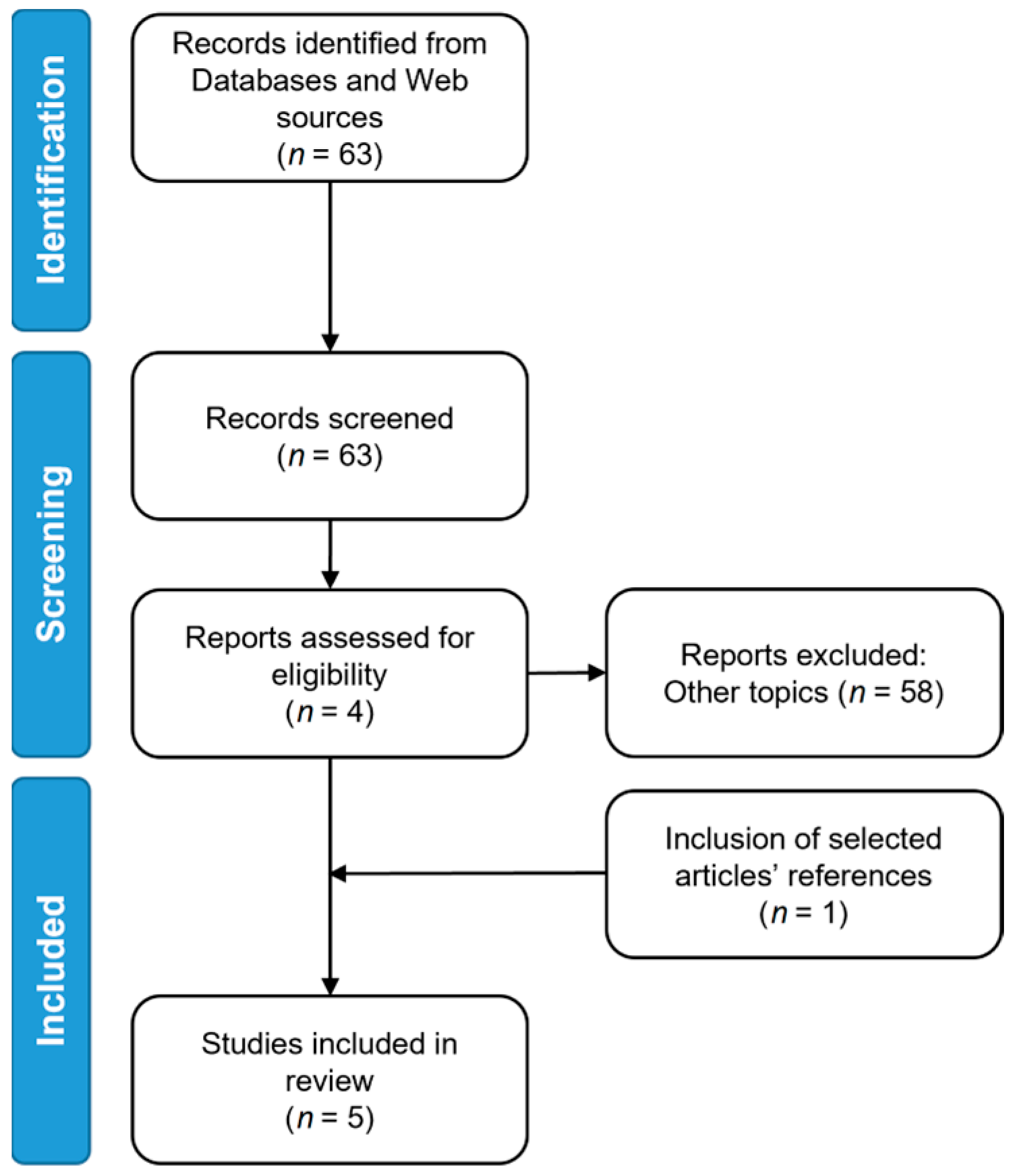
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Study Populations
3.2. The Workflow of Radiomic Analysis
3.2.1. Imaging Acquisition Protocol
3.2.2. ROI Segmentation
3.2.3. Feature Extraction
3.2.4. Feature Selection and Machine Learning Models
3.2.5. Deep-Learning Models
3.3. Model Results and Additional Value of Radiomics over Clinical Information
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations
4.1.1. Clinical Aspects
4.1.2. Technical Aspects
4.1.3. Sample Imbalance
4.1.4. External Validation and Sample Size
4.2. Future Perspectives
4.3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, J.R.; Yang, P.; Cassivi, S.D.; Schild, S.E.; Adjei, A.A. Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Treatment, and Survivorship. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Li, T.; Hong, J.; Zhang, M.; Ouyang, M.; Zheng, X.; Tang, K. 18F-FDG PET-based radiomics model for predicting occult lymph node metastasis in clinical N0 solid lung adenocarcinoma. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2021, 11, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grills, I.S.; Mangona, V.S.; Welsh, R.; Chmielewski, G.; McInerney, E.; Martin, S.; Wloch, J.; Ye, H.; Kestin, L.L. Outcomes after stereotactic lung radiotherapy or wedge resection for stage I non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yerokun, B.A.; Yang, C.F.J.; Gulack, B.C.; Li, X.; Mulvihill, M.S.; Gu, L.; Wang, X.; Harpole, D.H.; D’Amico, T.A.; Berry, M.F.; et al. A national analysis of wedge resection versus stereotactic body radiation therapy for stage IA non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2017, 154, 675–686.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Feng, H.; Zhao, H.; Hu, J.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, L.; Li, Y.; Lu, X.; et al. Sublobar resection is associated with better perioperative outcomes in elderly patients with clinical stage I non-small cell lung cancer: A multicenter retrospective cohort study. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, 1838–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, R.; Luan, T.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Sun, X.; Xing, L. A Radiomics Nomogram for Preoperative Prediction of Clinical Occult Lymph Node Metastasis in cT1-2N0M0 Solid Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Manag. Res. 2021, 13, 8157–8167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postmus, P.E.; Kerr, K.M.; Oudkerk, M.; Senan, S.; Waller, D.A.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Escriu, C.; Peters, S. Early and locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC): ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, iv1–iv21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, A.G.; Chansky, K.; Crowley, J.; Beyruti, R.; Kubota, K.; Turrisi, A.; Eberhardt, W.E.E.; Van Meerbeeck, J.; Rami-Porta, R. The International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer Lung Cancer Staging Project: Proposals for the Revision of the Clinical and Pathologic Staging of Small Cell Lung Cancer in the Forthcoming Eighth Edition of the TNM Classification for Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haas, A.R. Infectious complications from full extension endobronchial ultrasound transbronchial needle aspiration. Eur. Respir. J. 2009, 33, 935–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, N.; Shin, S.H.; Yoo, H.; Jhun, B.W.; Lee, K.; Um, S.-W.; Kim, H.; Jeong, B.-H. Infectious complications of EBUS-TBNA: A nested case-control study using 10-year registry data. Lung Cancer 2021, 161, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrager, J.B. Mediastinoscopy: Still the Gold Standard. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2010, 89, S2084–S2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um, S.-W.; Kim, H.K.; Jung, S.-H.; Han, J.; Lee, K.J.; Park, H.Y.; Choi, Y.S.; Shim, Y.M.; Ahn, M.-J.; Park, K.; et al. Endobronchial Ultrasound versus Mediastinoscopy for Mediastinal Nodal Staging of Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panunzio, A.; Sartori, P. Lung Cancer and Radiological Imaging. Curr. Radiopharm. 2020, 13, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstraw, P.; Chansky, K.; Crowley, J.; Rami-Porta, R.; Asamura, H.; Eberhardt, W.E.E.; Nicholson, A.G.; Groome, P.; Mitchell, A.; Bolejack, V.; et al. The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: Proposals for Revision of the TNM Stage Groupings in the Forthcoming (Eighth) Edition of the TNM Classification for Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ettinger, D.S.; Wood, D.E.; Aisner, D.L.; Akerley, W.; Bauman, J.R.; Bharat, A.; Bruno, D.S.; Chang, J.Y.; Chirieac, L.R.; D’Amico, T.A.; et al. Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer, Version 3.2022, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2022, 20, 497–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, S.S.; Lee, K.S.; Kim, B.-T.; Chung, M.J.; Lee, E.J.; Han, J.; Choi, J.Y.; Kwon, O.J.; Shim, Y.M.; Kim, S. Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: Prospective Comparison of Integrated FDG PET/CT and CT Alone for Preoperative Staging. Radiology 2005, 236, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobic-Saranovic, D.; Petrusic, I.; Artiko, V.; Pavlovic, S.; Subotic, D.; Saranovic, D.; Nagorni-Obradovic, L.; Petrovic, N.; Todorovic-Tirnanic, M.; Odalovic, S.; et al. Comparison of 18F-FDG PET/CT and MDCT for staging/restaging of non-small cell lung cancer. Neoplasma 2015, 62, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, L.; He, Z.Y.; Zhong, X.N.; Cui, M.L. (18)FDG-PET/CT for detection of mediastinal nodal metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 21, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ren, S.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, Q.; Chen, G.; Chen, H.; Xiang, J.; et al. Risk factors for predicting the occult nodal metastasis in T1–2N0M0 NSCLC patients staged by PET/CT: Potential value in the clinic. Lung Cancer 2013, 81, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, H.; Shaolei, L.; Nan, L.; Yumei, L.; Shanyuan, Z.; Fangliang, L.; Yue, Y. Occult mediastinal lymph node metastasis in FDG-PET/CT node-negative lung adenocarcinoma patients: Risk factors and histopathological study. Thorac. Cancer 2019, 10, 1453–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, H.K.; Jeon, K.; Koh, W.-J.; Suh, G.Y.; Kim, H.; Kwon, O.J.; Chung, M.P.; Lee, K.S.; Shim, Y.M.; Han, J.; et al. Occult nodal metastasis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer at clinical stage IA by PET/CT. Respirology 2010, 15, 1179–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Yoon, J.-K.; Park, K.J.; Lee, S.J. Prediction of occult lymph node metastasis using volume-based PET parameters in small-sized peripheral non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Imaging 2015, 15, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sobin, L.H.; Gospodarowicz, M.K.; Wittekind, C. (Eds.) TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours, 7th ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Caro, A.; Boada, M.; Cabanas, M.; Sanchez, M.; Arguis, P.; Lomena, F.; Ramirez, J.; Molins, L. False-negative rate after positron emission tomography/computer tomography scan for mediastinal staging in cI stage non-small-cell lung cancer. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2012, 42, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guinde, J.; Bourdages-Pageau, E.; Ugalde, P.A.; Fortin, M. Central location and risk of imaging occult mediastinal lymph node involvement in cN0T2-4 non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Dis. 2020, 12, 7156–7163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanzaki, R.; Higashiyama, M.; Fujiwara, A.; Tokunaga, T.; Maeda, J.; Okami, J.; Kozuka, T.; Hosoki, T.; Hasegawa, Y.; Takami, M.; et al. Occult mediastinal lymph node metastasis in NSCLC patients diagnosed as clinical N0-1 by preoperative integrated FDG-PET/CT and CT: Risk factors, pattern, and histopathological study. Lung Cancer 2011, 71, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, K.; Abe, K.; Yano, F.; Watanabe, S.; Iwasaki, Y.; Kosuda, S. Should mediastinoscopy actually be incorporated into the FDG PET strategy for patients with non-small cell lung carcinoma? Ann. Nucl. Med. 2005, 19, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Song, B.-I.; Hong, C.M.; Jeong, S.Y.; Lee, S.-W.; Lee, J.; Ahn, B.-C. Metabolic parameters using 18F-FDG PET/CT correlate with occult lymph node metastasis in squamous cell lung carcinoma. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2014, 41, 2051–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, M.; Tang, K.; Xu, M.; Lin, J.; Li, T.; Zheng, X. Prediction of Occult Lymph Node Metastasis Using Tumor-to-Blood Standardized Uptake Ratio and Metabolic Parameters in Clinical N0 Lung Adenocarcinoma. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2018, 43, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trister, A.D.; Pryma, D.A.; Xanthopoulos, E.; Kucharczuk, J.; Sterman, D.; Rengan, R. Prognostic value of primary tumor FDG uptake for occult mediastinal lymph node involvement in clinically N2/N3 node-negative non-small cell lung cancer. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 37, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaseda, K.; Watanabe, K.; Asakura, K.; Kazama, A.; Ozawa, Y. Identification of false-negative and false-positive diagnoses of lymph node metastases in non-small cell lung cancer patients staged by integrated 18F- fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography/computed tomography: A retrospective cohort study. Thorac. Cancer 2016, 7, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casiraghi, M.; Travaini, L.L.; Maisonneuve, P.; Tessitore, A.; Brambilla, D.; Agoglia, B.G.; Guarize, J.; Spaggiari, L. Lymph node involvement in T1 non-small-cell lung cancer: Could glucose uptake and maximal diameter be predictive criteria? Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2011, 39, e38–e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerfolio, R.J.; Bryant, A.S.; Ohja, B.; Bartolucci, A.A. The maximum standardized uptake values on positron emission tomography of a non-small cell lung cancer predict stage, recurrence, and survival. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2005, 130, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saito, Y.; Imai, K.; Ishiyama, K.; Saito, H.; Motoyama, S.; Sato, Y.; Konno, H.; Fujishima, S.; Hashimoto, M.; Minamiya, Y. New PET/CT criterion for nodal staging in non-small cell lung cancer: Measurement of the ratio of section area of standard uptake values ≥2.5/lymph node section area. Gen. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2017, 65, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Choe, J.G.; Pahk, K.; Choi, S.; Kwon, H.R.; Eo, J.S.; Seo, H.J.; Kim, C.; Kim, S. Ratio of Mediastinal Lymph Node SUV to Primary Tumor SUV in 18F-FDG PET/CT for Nodal Staging in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2017, 51, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, P.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Deist, T.M.; Peerlings, J.; de Jong, E.E.C.; van Timmeren, J.; Sanduleanu, S.; Larue, R.T.H.M.; Even, A.J.G.; Jochems, A.; et al. Radiomics: The bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lambin, P.; Rios-Velazquez, E.; Leijenaar, R.; Carvalho, S.; van Stiphout, R.G.P.M.; Granton, P.; Zegers, C.M.L.; Gillies, R.; Boellard, R.; Dekker, A.; et al. Radiomics: Extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Timmeren, J.E.; Cester, D.; Tanadini-Lang, S.; Alkadhi, H.; Baessler, B. Radiomics in medical imaging—“how-to” guide and critical reflection. Insights Imaging 2020, 11, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwanenburg, A. Radiomics in nuclear medicine: Robustness, reproducibility, standardization, and how to avoid data analysis traps and replication crisis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 2638–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-H.; Chang, C.-K.; Tu, C.-Y.; Liao, W.-C.; Wu, B.-R.; Chou, K.-T.; Chiou, Y.-R.; Yang, S.-N.; Zhang, G.; Huang, T.-C. Radiomic features analysis in computed tomography images of lung nodule classification. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chetan, M.R.; Gleeson, F.V. Radiomics in predicting treatment response in non-small-cell lung cancer: Current status, challenges and future perspectives. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Churchill, I.F.; Sullivan, K.A.; Simone, A.C.; Patel, Y.S.; Leontiadis, G.I.; Farrokhyar, F.; Gatti, A.A.; Hanna, W.C. Thoracic imaging radiomics for staging lung cancer: A systematic review and radiomic quality assessment. Clin. Transl. Imaging 2022, 10, 191–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-Junior, J.R.; Koenigkam-Santos, M.; Magalhães Tenório, A.P.; Faleiros, M.C.; Garcia Cipriano, F.E.; Fabro, A.T.; Näppi, J.; Yoshida, H.; de Azevedo-Marques, P.M. CT-based radiomics for prediction of histologic subtype and metastatic disease in primary malignant lung neoplasms. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2020, 15, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, Y.-S.; Yang, J. Deep learning-based auto-segmentation of lung tumor PET/CT scans: A systematic review. Clin. Transl. Imaging 2022, 10, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Deng, J.; She, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, B.; Ren, Y.; Wu, J.; Xie, D.; Sun, X.; Chen, C. Radiomics Signature Predicts the Recurrence-Free Survival in Stage I Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2020, 109, 1741–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; She, Y.; Deng, J.; Wang, T.; Ren, Y.; Su, H.; Wu, J.; Sun, X.; Jiang, G.; Fei, K.; et al. CT-based radiomics signature for the stratification of N2 disease risk in clinical stage I lung adenocarcinoma. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 876–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Yuan, M.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y.-D.; Li, H.; Yu, T.-F. Radiomics Approach to Prediction of Occult Mediastinal Lymph Node Metastasis of Lung Adenocarcinoma. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2018, 211, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Zhang, X.; Du, M.; Wang, P.; Xin, J. 18F-FDG PET/CT radiomics nomogram for predicting occult lymph node metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, M.; Zheng, R.; Wang, Y.; Zuo, Z.; Gu, L.; Tian, Y.; Wei, Y.; Huang, X.; Tang, K.; Wang, L. Deep Learning Analysis Using 18F-FDG PET/CT to Predict Occult Lymph Node Metastasis in Patients With Clinical N0 Lung Adenocarcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yushkevich, P.A.; Gao, Y.; Gerig, G. ITK-SNAP: An interactive tool for semi-automatic segmentation of multi-modality biomedical images. In Proceedings of the 2016 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 3342–3345. [Google Scholar]
- Dehmeshki, J.; Amin, H.; Valdivieso, M.; Ye, X. Segmentation of Pulmonary Nodules in Thoracic CT Scans: A Region Growing Approach. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2008, 27, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- John, J.; Mini, M.G. Multilevel Thresholding Based Segmentation and Feature Extraction for Pulmonary Nodule Detection. Procedia Technol. 2016, 24, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. IEEE Access 2015, 9, 16591–16603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haralick, R.M.; Shanmugam, K.; Dinstein, I. Textural Features for Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1973, SMC-3, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galloway, M.M. Texture analysis using gray level run lengths. Comput. Graph. Image Process. 2008, 4, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibault, G.; Angulo, J.; Meyer, F. Advanced statistical matrices for texture characterization: Application to DNA chromatin and microtubule network classification. In Proceedings of the Proceedings—International Conference on Image Processing, ICIP, Brussels, Belgium, 11–14 September 2011; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Amadasun, M.; King, R. Texural Features Corresponding to Texural Properties. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1989, 19, 1264–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Wee, W.G. Neighboring gray level dependence matrix for texture classification. Comput. Vis. Graph. Image Process. 1983, 23, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwanenburg, A.; Vallières, M.; Abdalah, M.A.; Aerts, H.J.W.L.; Andrearczyk, V.; Apte, A.; Ashrafinia, S.; Bakas, S.; Beukinga, R.J.; Boellaard, R.; et al. The Image Biomarker Standardization Initiative: Standardized Quantitative Radiomics for High-Throughput Image-based Phenotyping. Radiology 2020, 295, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Depeursinge, A.; Andrearczyk, V.; Whybra, P.; Van Griethuysen, J.; Müller, H.; Schaer, R.; Vallì Eres, M.; Zwanenburg, A. Standardised Convolutional Filtering for Radiomics Image Biomarker Standardisation Initiative (IBSI): Reference Manual. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2006.05470.pdf (accessed on 14 November 2022).
- Szczypiński, P.M.; Strzelecki, M.; Materka, A.; Klepaczko, A. MaZda-A software package for image texture analysis. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2009, 94, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Griethuysen, J.J.M.; Fedorov, A.; Parmar, C.; Hosny, A.; Aucoin, N.; Narayan, V.; Beets-Tan, R.G.H.; Fillion-Robin, J.-C.; Pieper, S.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Computational Radiomics System to Decode the Radiographic Phenotype. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e104–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the Inception Architecture for Computer Vision. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.-J.; Li, K.; Li, F.-F. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Traverso, A.; Wee, L.; Dekker, A.; Gillies, R. Repeatability and Reproducibility of Radiomic Features: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 102, 1143–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Delving Deep into Rectifiers: Surpassing Human-Level Performance on ImageNet Classification. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 1026–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Shi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, D.; Guizani, M. Deep Feature Learning for Medical Image Analysis with Convolutional Autoencoder Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Big Data 2021, 7, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q.V. EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 10691–10700. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely Connected Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2261–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An Image is Worth 16 × 16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Seto, K.; Kuroda, H.; Yoshida, T.; Sakata, S.; Mizuno, T.; Sakakura, N.; Hida, T.; Yatabe, Y.; Sakao, Y. Higher frequency of occult lymph node metastasis in clinical N0 pulmonary adenocarcinoma with ALK rearrangement. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 2117–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gillies, R.J.; Kinahan, P.E.; Hricak, H. Radiomics: Images Are More than Pictures, They Are Data. Radiology 2016, 278, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bortolotto, C.; Lancia, A.; Stelitano, C.; Montesano, M.; Merizzoli, E.; Agustoni, F.; Stella, G.; Preda, L.; Filippi, A.R. Radiomics features as predictive and prognostic biomarkers in NSCLC. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2021, 21, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braghetto, A.; Marturano, F.; Paiusco, M.; Baiesi, M.; Bettinelli, A. Radiomics and deep learning methods for the prediction of 2-year overall survival in LUNG1 dataset. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manafi-Farid, R.; Askari, E.; Shiri, I.; Pirich, C.; Asadi, M.; Khateri, M.; Zaidi, H.; Beheshti, M. [18F]FDG-PET/CT Radiomics and Artificial Intelligence in Lung Cancer: Technical Aspects and Potential Clinical Applications. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2022, 52, 759–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limkin, E.J.; Sun, R.; Dercle, L.; Zacharaki, E.I.; Robert, C.; Reuzé, S.; Schernberg, A.; Paragios, N.; Deutsch, E.; Ferté, C. Promises and challenges for the implementation of computational medical imaging (radiomics) in oncology. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 1191–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhao, H.; Guo, Y.; Meng, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Huai, X.; Wong, Q.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, H. A PET/CT nomogram incorporating SUVmax and CT radiomics for preoperative nodal staging in non-small cell lung cancer. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 6030–6038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq-Ul-Hassan, M.; Latifi, K.; Zhang, G.; Ullah, G.; Gillies, R.; Moros, E. Voxel size and gray level normalization of CT radiomic features in lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, L.; Huang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Liang, C.; Liang, C.; Liu, Z. Effects of contrast-enhancement, reconstruction slice thickness and convolution kernel on the diagnostic performance of radiomics signature in solitary pulmonary nodule. Nat. Publ. Gr. 2016, 6, 34921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orlhac, F.; Boughdad, S.; Philippe, C.; Stalla-Bourdillon, H.; Nioche, C.; Champion, L.; Soussan, M.; Frouin, F.; Frouin, V.; Buvat, I. A Postreconstruction Harmonization Method for Multicenter Radiomic Studies in PET. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chawla, N.V.; Bowyer, K.W.; Hall, L.O.; Kegelmeyer, W.P. SMOTE: Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2002, 16, 321–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Bai, Y.; Garcia, E.A.; Li, S. ADASYN: Adaptive synthetic sampling approach for imbalanced learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC), Auckland, New Zealand, 27–30 October 2019; pp. 1322–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zwanenburg, A.; Leger, S.; Agolli, L.; Pilz, K.; Troost, E.G.C.; Richter, C.; Löck, S. Assessing robustness of radiomic features by image perturbation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sorin, V.; Barash, Y.; Konen, E.; Klang, E. Creating Artificial Images for Radiology Applications Using Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)—A Systematic Review. Acad. Radiol. 2020, 27, 1175–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, M.D.; Dumontier, M.; Aalbersberg, I.J.; Appleton, G.; Axton, M.; Baak, A.; Blomberg, N.; Boiten, J.W.; da Silva Santos, L.B.; Bourne, P.E.; et al. The FAIR Guiding Principles for scientific data management and stewardship. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 160018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Authors [Ref.] | Year | Number of Patients | Mean Age ± SD (Testing Set) | Gender (M:F) | Smoker/ Non-Smoker | Design | Imaging Modality | Reference Standard | Histology | Tumour Location | Clinical T Stage | Mean T Diameter * ± SD (mm) | OLMs (%)/Non-OLMs (%) | Pathological N Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhong et al. [48] | 2018 | 492 | 61.4 ± 9.7 | 173:319 | 363/129 | R | Unenhanced CT | Histology | ADC | Upper = 270 Middle and lower = 222 | cT1-3 | 32.7 ± 15.2 | 78 (16)/414(84) | N/A |
| Zhang et al. [7] | 2021 | 160 (84) | N/A | 106:138 | 71/173 | R | Contrast-enhanced CT | Histology | ADC | Upper = 137 Middle and lower = 107 | cT1-2 | 30.4 ± 9.3 | 55(23)/189(77) | N/A |
| Wang et al. [3] | 2021 | 236 (134) | 62.95 ± 9.4 | 205:165 | N/A | R | [18F]FDG PET/CT | Histology | ADC | LLL = 57 LUL = 95 RLL = 85 RML = 27 RUL = 106 | N/A | 28.23 ± 10.26 | 98(26)/272(74) | pN0 = 272 pN1 = 46 pN2 = 52 |
| Qiao et al. [49] | 2022 | 159 (69) | N/A | 113:115 | 97/131 | R | [18F]FDG PET/CT | Histology | ADC SCC | LLL = 43 LUL = 55 RLL = 51 RML = 11 RUL = 68 | N/A | 32.0 [2.3–4.4] † | 85(37)/143(63) | N/A |
| Ouyang et al. [50] | 2022 | 376 (58) | N/A | 193:241 | 104/330 | R | [18F]FDG PET/CT | Histology | ADC | LLL = 66 LUL = 113 RLL = 91 RML = 34 RUL = 130 | N/A | 23.31 ± 10.36 | 91(21)/343(79) | pN0 = 343 |
| Authors | Segmentation | Feature Extraction | Methods | Results | SENS * (%) | SPEC * (%) | PPV * (%) | NPV * (%) | ACC * (%) | RQS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhong et al., 2018 [48] | Manual segmentation of primary tumour using CT | 300 radiomic features (first-order and texture features) Wavelet-based filtering | Feature reduction based on inter-reader reproducibility (assessed through the ICC) SVM classifier to derive a radiomic score Multivariate logistic regression to predict mediastinal LN metastasis from clinical features versus the radiomic score | Radiomic signature showed better predictive results compared to the clinical histopathological model (cross-validated SVM AUC = 0.97) | 94.8 § | 92 § | N/A | N/A | N/A | 36% |
| Zhang et al., 2021 [7] | Manual segmentation of primary tumour using CT and multiple reader segmentations for 30 patients | 851 radiomic features (shape, first-order, and texture features) Wavelet-based filtering | Feature reduction based on inter-reader reproducibility (assessed through the ICC) LASSO for radiomic feature selection and to derive a radiomic score Logistic regression with backward stepwise selection to integrate clinical features and radiomic score | Creation of a nomogram incorporating clinical and radiomic features (C-index = 0.81 in the validation cohort) | 76.5 ‡ | 64.3 ‡ | 36.6 ‡ | 91.0 ‡ | N/A | 42% |
| Wang et al., 2021 [3] | Manual segmentation of the primary tumour in PET images and double reader segmentations for 60 patients | 107 radiomic features (shape, first-order, and texture features) | Feature reduction based on inter- and intra-reader reproducibility (assessed through the ICC) LASSO for radiomic feature selection and to derive a radiomic score Logistic regression with backward stepwise selection to integrate clinical features and radiomic score | Creation of a nomogram incorporating clinical and radiomic features (C-index = 0.77 in the validation cohort) | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 39% |
| Qiao et al., 2022 [49] | Tumour segmentation in both CT and PET images using both manual and semi-automatic methods | 1316 radiomic features (shape, first-order, and texture features) Local binary pattern, Laplacian of Gaussian, and wavelet-based filtering | Feature selection using LASSO and extremely randomised trees Multivariate logistic regression to derive a radiomic score Logistic regression with backward stepwise selection to integrate clinical features and radiomic score | Creation of a PET/CT-based nomogram including clinical and radiomic features (AUC = 0.88 on the test set) | 72.9 ◊ | 87 ◊ | 76.8 ◊ | 84.5 ◊ | 81.8 ◊ | 39% |
| Ouyang et al., 2022 [50] | Segmentations were not performed; axial, coronal, and transversal 2D slices were used | Deep-features of the CNN | Development of a CNN model (Inception v3) to predict OLM from PET, CT, and PET and CT images | The model based on both PET and CT imaging achieved the best performances (AUC = 0.87 in the prospective test set) | 87.5 ◊ | 80 ◊ | N/A | N/A | 81 ◊ | 13% † |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guglielmo, P.; Marturano, F.; Bettinelli, A.; Sepulcri, M.; Pasello, G.; Gregianin, M.; Paiusco, M.; Evangelista, L. Additional Value of PET and CT Image-Based Features in the Detection of Occult Lymph Node Metastases in Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2153. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132153
Guglielmo P, Marturano F, Bettinelli A, Sepulcri M, Pasello G, Gregianin M, Paiusco M, Evangelista L. Additional Value of PET and CT Image-Based Features in the Detection of Occult Lymph Node Metastases in Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(13):2153. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132153
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuglielmo, Priscilla, Francesca Marturano, Andrea Bettinelli, Matteo Sepulcri, Giulia Pasello, Michele Gregianin, Marta Paiusco, and Laura Evangelista. 2023. "Additional Value of PET and CT Image-Based Features in the Detection of Occult Lymph Node Metastases in Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review of the Literature" Diagnostics 13, no. 13: 2153. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132153
APA StyleGuglielmo, P., Marturano, F., Bettinelli, A., Sepulcri, M., Pasello, G., Gregianin, M., Paiusco, M., & Evangelista, L. (2023). Additional Value of PET and CT Image-Based Features in the Detection of Occult Lymph Node Metastases in Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Diagnostics, 13(13), 2153. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132153






