Diagnostic Accuracy of Whole-Body Computed Tomography for Incidental Ovarian Tumors in Patients with Prior Breast Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. WBCT
2.3. Histopathologic Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
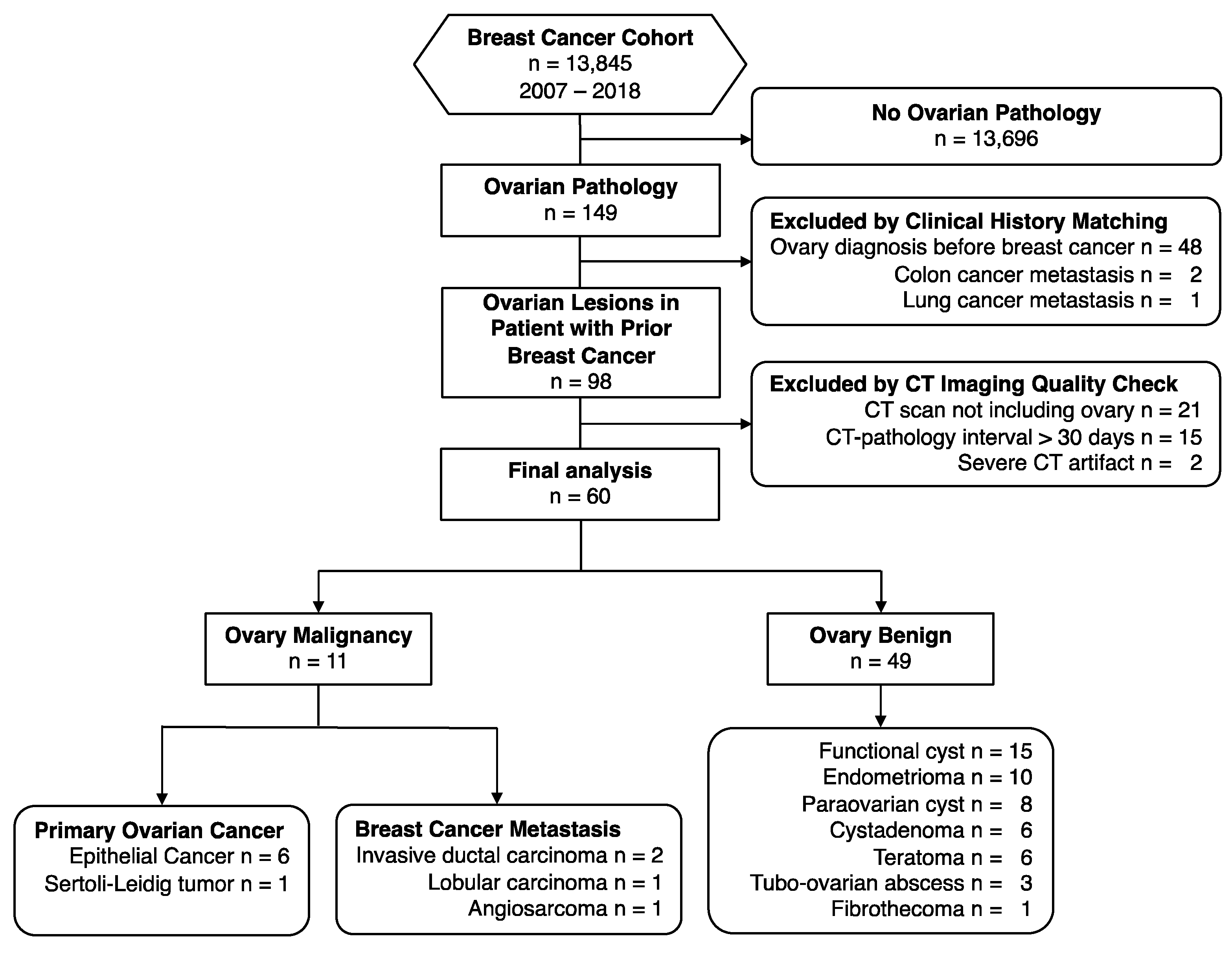
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Malignant Ovarian Lesions
3.3. Diagnostic Performance
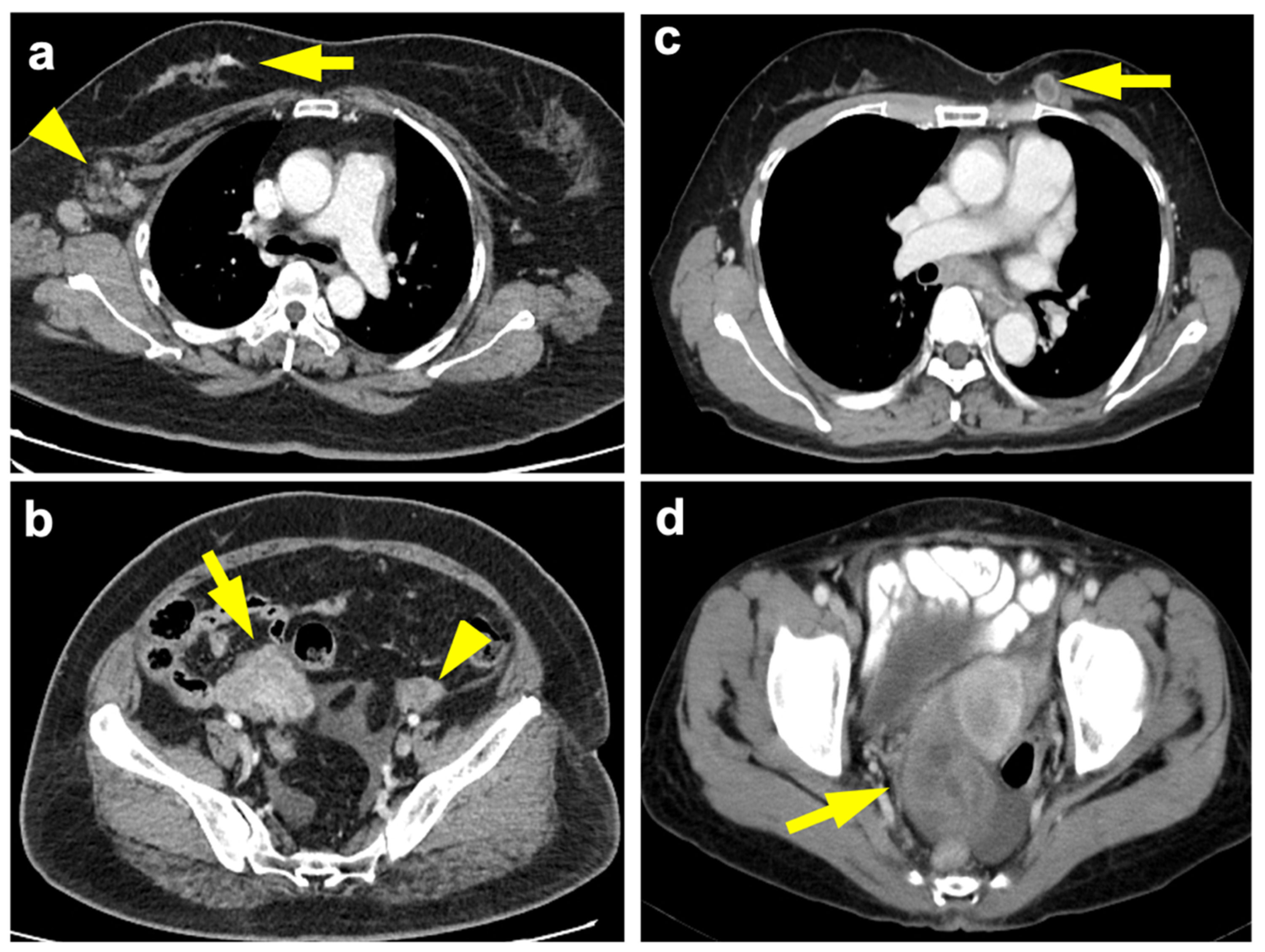
3.4. Breast-Ovarian Mutual Metastasis
4. Discussion
Limitation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, W.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, M.; Yao, Y.; Deng, Y. Ovarian metastasis from breast cancer: A comprehensive review. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2019, 21, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, I.T.; van Zwet, E.W.; Smit, V.T.; Liefers, G.J.; Kuppen, P.J.; Hilders, C.G.; Trimbos, J.B. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Ovarian Metastases in Breast Cancer Patients <41 Years of Age in the Netherlands: A Nationwide Retrospective Cohort Study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0168277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tserkezoglou, A.; Kontou, S.; Hadjieleftheriou, G.; Apostolikas, N.; Vassilomanolakis, M.; Sikiotis, K.; Salamalekis, E.; Tseke, P.; Magiakos, G. Primary and metastatic ovarian cancer in patients with prior breast carcinoma. Pre-operative markers and treatment results. Anticancer Res. 2006, 26, 2339–2344. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Simpkins, F.; Zahurak, M.; Armstrong, D.; Grumbine, F.; Bristow, R. Ovarian malignancy in breast cancer patients with an adnexal mass. Obstet. Gynecol. 2005, 105, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergfeldt, K.; Rydh, B.; Granath, F.; Gronberg, H.; Thalib, L.; Adami, H.O.; Hall, P. Risk of ovarian cancer in breast-cancer patients with a family history of breast or ovarian cancer: A population-based cohort study. Lancet 2002, 360, 891–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigorie, V.; Morice, P.; Duvillard, P.; Antoine, M.; Cortez, A.; Flejou, J.F.; Uzan, S.; Darai, E.; Barranger, E. Ovarian metastases from breast cancer: Report of 29 cases. Cancer 2010, 116, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Runowicz, C.D.; Leach, C.R.; Henry, N.L.; Henry, K.S.; Mackey, H.T.; Cowens-Alvarado, R.L.; Cannady, R.S.; Pratt-Chapman, M.L.; Edge, S.B.; Jacobs, L.A.; et al. American Cancer Society/American Society of Clinical Oncology Breast Cancer Survivorship Care Guideline. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 43–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gradishar, W.J.; Moran, M.S.; Abraham, J.; Aft, R.; Agnese, D.; Allison, K.H.; Blair, S.L.; Burstein, H.J.; Dang, C.; Elias, A.D.; et al. NCCN Guidelines Insights: Breast Cancer, Version 4. 2021: Featured Updates to the NCCN Guidelines. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2021, 19, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antila, R.; Jalkanen, J.; Heikinheimo, O. Comparison of secondary and primary ovarian malignancies reveals differences in their pre- and perioperative characteristics. Gynecol. Oncol. 2006, 101, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerriero, S.; Alcazar, J.L.; Pascual, M.A.; Ajossa, S.; Olartecoechea, B.; Hereter, L. Preoperative diagnosis of metastatic ovarian cancer is related to origin of primary tumor. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2012, 39, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testa, A.C.; Ferrandina, G.; Timmerman, D.; Savelli, L.; Ludovisi, M.; Van Holsbeke, C.; Malaggese, M.; Scambia, G.; Valentin, L. Imaging in gynecological disease (1): Ultrasound features of metastases in the ovaries differ depending on the origin of the primary tumor. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2007, 29, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruls, J.; Simons, M.; Overbeek, L.I.; Bulten, J.; Massuger, L.F.; Nagtegaal, I.D. A national population-based study provides insight in the origin of malignancies metastatic to the ovary. Virchows Arch. 2015, 467, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimino-Mathews, A. Novel uses of immunohistochemistry in breast pathology: Interpretation and pitfalls. Mod. Pathol. 2021, 34, 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, A.Y.; Watkins, J.C.; Young, R.H.; Lerwill, M.F. Lobular Carcinoma of the Breast Metastatic to the Ovary: A Clinicopathologic Study of 38 Cases. Am. J. Surg Pathol. 2022, 46, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaosmanoglu, A.D.; Onur, M.R.; Salman, M.C.; Usubutun, A.; Karcaaltincaba, M.; Ozmen, M.N.; Akata, D. Imaging in secondary tumors of the ovary. Abdom. Radiol. 2019, 44, 1493–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlicot, S.; Vincent-Salomon, A.; Medioni, J.; Genin, P.; Rosty, C.; Sigal-Zafrani, B.; Freneaux, P.; Jouve, M.; Thiery, J.P.; Sastre-Garau, X. Wide metastatic spreading in infiltrating lobular carcinoma of the breast. Eur. J. Cancer 2004, 40, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigelt, B.; Peterse, J.L.; van’t Veer, L.J. Breast cancer metastasis: Markers and models. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, C.; Becquet, M.; Lavoue, V.; Henno, S.; Leveque, J.; Ouldamer, L. Ovarian Metastases from Breast Cancer: A Series of 28 Cases. Anticancer Res. 2016, 36, 4195–4200. [Google Scholar]
- Skotnicki, P.; Sas-Korczynska, B.; Wohadlo, L.; Jakubowicz, J.; Blecharz, P.; Reinfuss, M.; Walasek, T. Distant metastases from invasive lobular breast carcinoma classic type—Treatment and prognosis. Eur. J. Gynaecol. Oncol. 2016, 37, 666–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerkauskaite, D.; Zilinskas, K.; Varnelis, P.; Oreibi, M.E.; Asejev, V.; Dulskas, A. Ovarian metastases from breast cancer: A report of 24 cases. J. Gynecol. Obstet. Hum. Reprod. 2021, 50, 102075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, E.K.; Roylance, R.; Rosenthal, A.N. Breast cancer metastasising to the pelvis and abdomen: What the gynaecologist needs to know. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2012, 119, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olawaiye, A.; Caesar, L.; Walsh, D.; Lyman, M.; Yeh, J.; Rodabaugh, K.; Marchetti, D.; Lele, S.; Odunsi, K. Analysis of the time interval between diagnoses in women with double primary breast and ovarian or primary peritoneal cancers. Gynecol. Oncol. 2004, 94, 796–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hann, L.E.; Lui, D.M.; Shi, W.; Bach, A.M.; Selland, D.L.; Castiel, M. Adnexal masses in women with breast cancer: US findings with clinical and histopathologic correlation. Radiology 2000, 216, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Waal, Y.R.; Thomas, C.M.; Oei, A.L.; Sweep, F.C.; Massuger, L.F. Secondary ovarian malignancies: Frequency, origin, and characteristics. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2009, 19, 1160–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, R.G.; Chung, M.; Granai, C.O.; Gajewski, W.; Steinhoff, M.M. Incidence of metastasis to the ovaries from nongenital tract primary tumors. Gynecol. Oncol. 2004, 93, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, I.T.; van der Steen, M.A.; Huisman, B.W.; Hilders, C.G.; Smit, V.T.; Vahrmeijer, A.L.; Sier, C.F.; Trimbos, J.B.; Kuppen, P.J. Morphological and phenotypical features of ovarian metastases in breast cancer patients. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kondi-Pafiti, A.; Kairi-Vasilatou, E.; Iavazzo, C.; Dastamani, C.; Bakalianou, K.; Liapis, A.; Hassiakos, D.; Fotiou, S. Metastatic neoplasms of the ovaries: A clinicopathological study of 97 cases. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2011, 284, 1283–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El hafez, A.; Monir, A. Diagnostic spectrum of ovarian masses in women with breast cancer; magnetic resonance imaging: Histopathology correlation. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2013, 17, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Barry, W.T.; Seah, D.S.; Tung, N.M.; Garber, J.E.; Lin, N.U. Patterns of recurrence and metastasis in BRCA1/BRCA2-associated breast cancers. Cancer 2020, 126, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, B.S.; Sharma, S.C.; Robin, T.P.; Sams, S.; Elias, A.D.; Kaklamani, V.; Kelly Marcom, P.; Schaefer, S.; Morris, G.J. Synchronous primary carcinoma of breast and ovary versus ovarian metastases. Semin. Oncol. 2015, 42, e13–e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| All | Ovary Malignancy | Ovary Benign | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 60) | (n = 11) | (n = 49) | ||
| Age, median (year) | 46 (24, 72) | 51 (32, 60) | 45 (24, 72) | 0.203 |
| Breast pathology | 0.390 | |||
| Invasive ductal carcinoma | 52 | 9 (81.8%) | 43 (87.8%) | |
| Lobular carcinoma | 3 | 1 (9.1%) | 2 (4.1%) | |
| Mucinous adenocarcinoma | 2 | 0 (0.0%) | 2 (4.1%) | |
| Malignant phyllodes tumor | 1 | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (2.0%) | |
| Papillary carcinoma | 1 | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (2.0%) | |
| Angiosarcoma | 1 | 1 (9.1%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| Morphology | 0.000 | |||
| Solid or solid-cystic | 11 | 11 (100.0%) | 1 (2.0%) | |
| Cystic | 49 | 0 (0.0%) | 48 (98.0%) | |
| Laterality | 0.154 | |||
| Bilateral | 8 | 3 (27.3%) | 5 (10.2%) | |
| Unilateral | 52 | 8 (72.7%) | 44 (89.8%) | |
| Interval, median (month) | 27 (0, 140) | 8 (0, 42) | 29 (1, 140) | 0.044 |
| T stage | 0.345 | |||
| 3–4 | 9 | 3 (27.3%) | 6 (12.2%) | |
| 1–2 | 51 | 8 (72.7%) | 43 (87.8%) | |
| N stage | 1.000 | |||
| 123 | 24 | 4 (36.4%) | 20 (40.8%) | |
| 0 | 36 | 7 (63.6%) | 29 (59.2%) | |
| M stage | 0.003 | |||
| 1 | 8 | 5 (45.5%) | 3 (6.1%) | |
| 0 | 52 | 6 (54.5%) | 46 (93.9%) |
| ID | Origin | Breast | Age | TNM | Interval (m) | Ovary | Modality | Feature * | Lat † | Only | CA125 | CA15-3 | CA19-9 | CEA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Breast | IDC | 48 | T4N1M1 | 6 | mIDC | CT | S | B | N | + | + | − | + |
| 2 | Breast | IDC | 55 | T2NM1 | 0 | mIDC | CT | S | U | Y | − | − | + | − |
| 3 | Breast | ILC | 54 | T3N2aM1 | 1 | mILC | CT | S | U | N | + | − | − | − |
| 4 | Breast | AS | 40 | T2N0M1 | 32 | mAS | US | S | B | N | − | − | N/A | − |
| 5 | Ovary | IDC | 58 | T1cN0M0 | 42 | SC | US | SC | B | Y | + | − | − | − |
| 6 | Ovary | IDC | 44 | T2N0M0 | 8 | SC | US | SC | U | Y | − | − | − | − |
| 7 | Ovary | IDC | 51 | T1cN3aM0 | 34 | CCC | US | SC | U | N | − | − | N/A | − |
| 8 | Ovary | IDC | 32 | T2N0M0 | 10 | CCC | CT | SC | U | Y | − | − | N/A | − |
| 9 | Ovary | IDC | 55 | T1cN2aM0 | 0 | SC | CT | SC | U | Y | + | + | − | N/A |
| 10 | Ovary | IDC | 60 | T1N0M0 | 1 | SC | CT | SC | U | Y | − | − | − | − |
| 11 | Ovary | IDC | 38 | T4N3M1 | 41 | SL | CT | S | U | N | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| FN | TP | TN | FP | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Malignant vs. Benign | |||||||||
| Solid/SC | 0 | 11 | 48 | 1 | 98.3 (91.1–100.0) | 100.0 (71.5–100.0) | 98.0 (89.1–99.9) | 91.7 (61.5–99.8) | 100.0 (92.6–100.0) |
| Bilateral | 8 | 3 | 44 | 5 | 78.3 (65.8–87.9) | 27.3 (6.0–61.0) | 89.8 (77.8–96.6) | 37.5 (8.5–75.5) | 84.6 (71.9–93.1) |
| Combined | 8 | 3 | 49 | 0 | 86.7 (75.4–94.1) | 27.3 (6.0–61.0) | 100.0 (92.7–100.0) | 100.0 (29.2–100.0) | 86.0 (74.2–93.7) |
| Metastasis vs. Primary | |||||||||
| Solid | 0 | 4 | 6 | 1 | 90.9 (58.7–99.8) | 100.0 (39.8–100.0) | 85.7 (42.1–99.6) | 80.0 (28.4–99.5) | 100.0 (54.1–100.0) |
| Bilateral | 2 | 2 | 6 | 1 | 72.7 (39.0–94.0) | 50.0 (6.8–93.2) | 85.7 (42.1–99.6) | 66.7 (9.4–99.2) | 75.0 (34.9–96.8) |
| Combined | 2 | 2 | 7 | 0 | 81.8 (48.2–97.7) | 50.0 (6.8–93.2) | 100.0 (59.0–100.0) | 100.0 (15.8–100.0) | 77.8 (40.0–97.2) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, P.-C.; Wu, R.-C.; Juan, Y.-H.; Ho, H.-Y.; Lin, Y.-C.; Huang, Y.-T.; Ng, S.-H.; Lai, C.-H.; Chao, A.; Lin, G. Diagnostic Accuracy of Whole-Body Computed Tomography for Incidental Ovarian Tumors in Patients with Prior Breast Cancer. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 347. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020347
Huang P-C, Wu R-C, Juan Y-H, Ho H-Y, Lin Y-C, Huang Y-T, Ng S-H, Lai C-H, Chao A, Lin G. Diagnostic Accuracy of Whole-Body Computed Tomography for Incidental Ovarian Tumors in Patients with Prior Breast Cancer. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(2):347. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020347
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Pei-Ching, Ren-Chin Wu, Yu-Hsiang Juan, Hui-Yu Ho, Yung-Chang Lin, Yi-Ting Huang, Shu-Hang Ng, Chyong-Huey Lai, Angel Chao, and Gigin Lin. 2022. "Diagnostic Accuracy of Whole-Body Computed Tomography for Incidental Ovarian Tumors in Patients with Prior Breast Cancer" Diagnostics 12, no. 2: 347. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020347
APA StyleHuang, P.-C., Wu, R.-C., Juan, Y.-H., Ho, H.-Y., Lin, Y.-C., Huang, Y.-T., Ng, S.-H., Lai, C.-H., Chao, A., & Lin, G. (2022). Diagnostic Accuracy of Whole-Body Computed Tomography for Incidental Ovarian Tumors in Patients with Prior Breast Cancer. Diagnostics, 12(2), 347. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020347









