Full-Endoscopic Lumbar Foraminotomy for Foraminal Stenosis in Spondylolisthesis: Two-Year Follow-Up Results
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
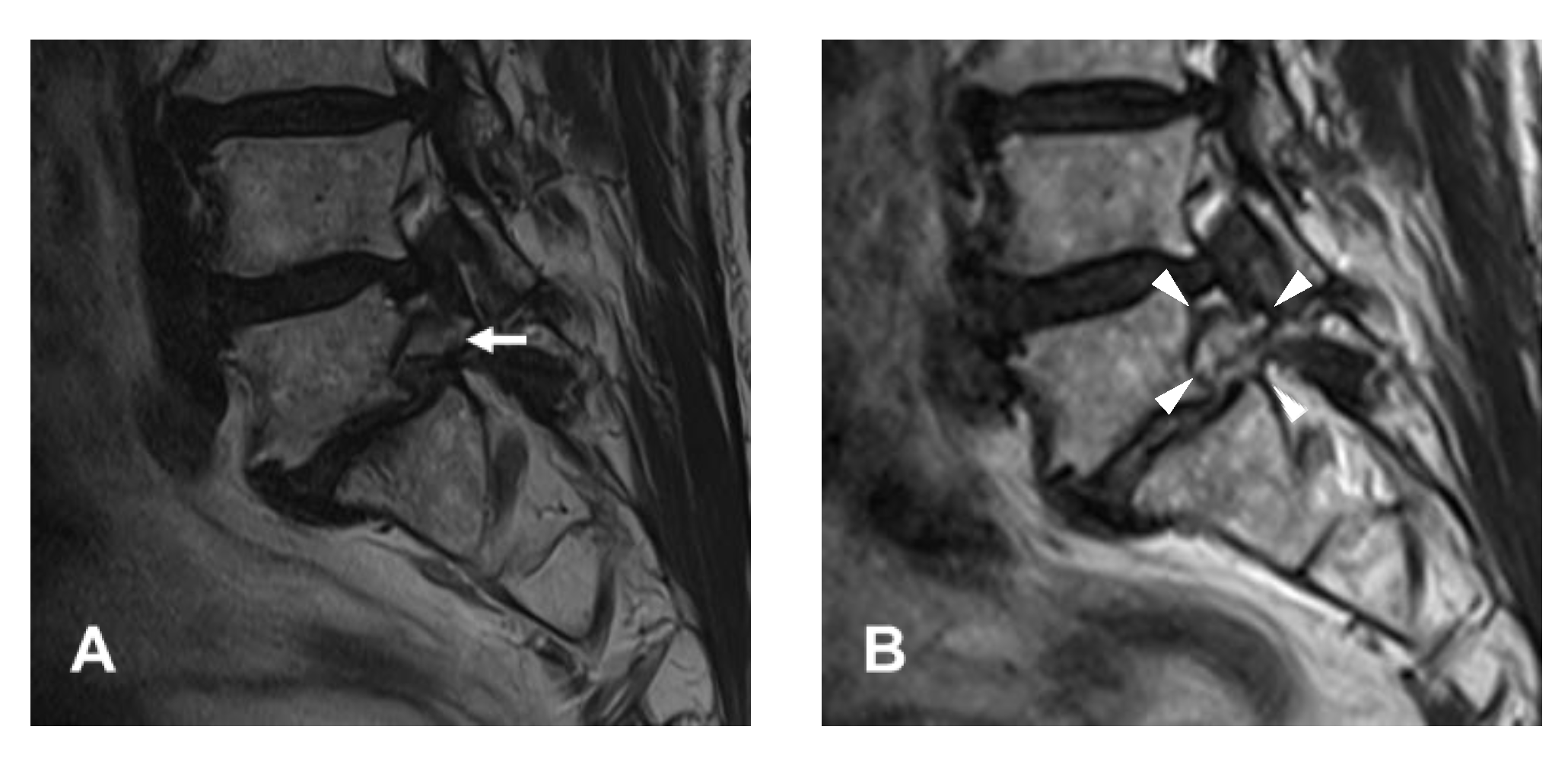
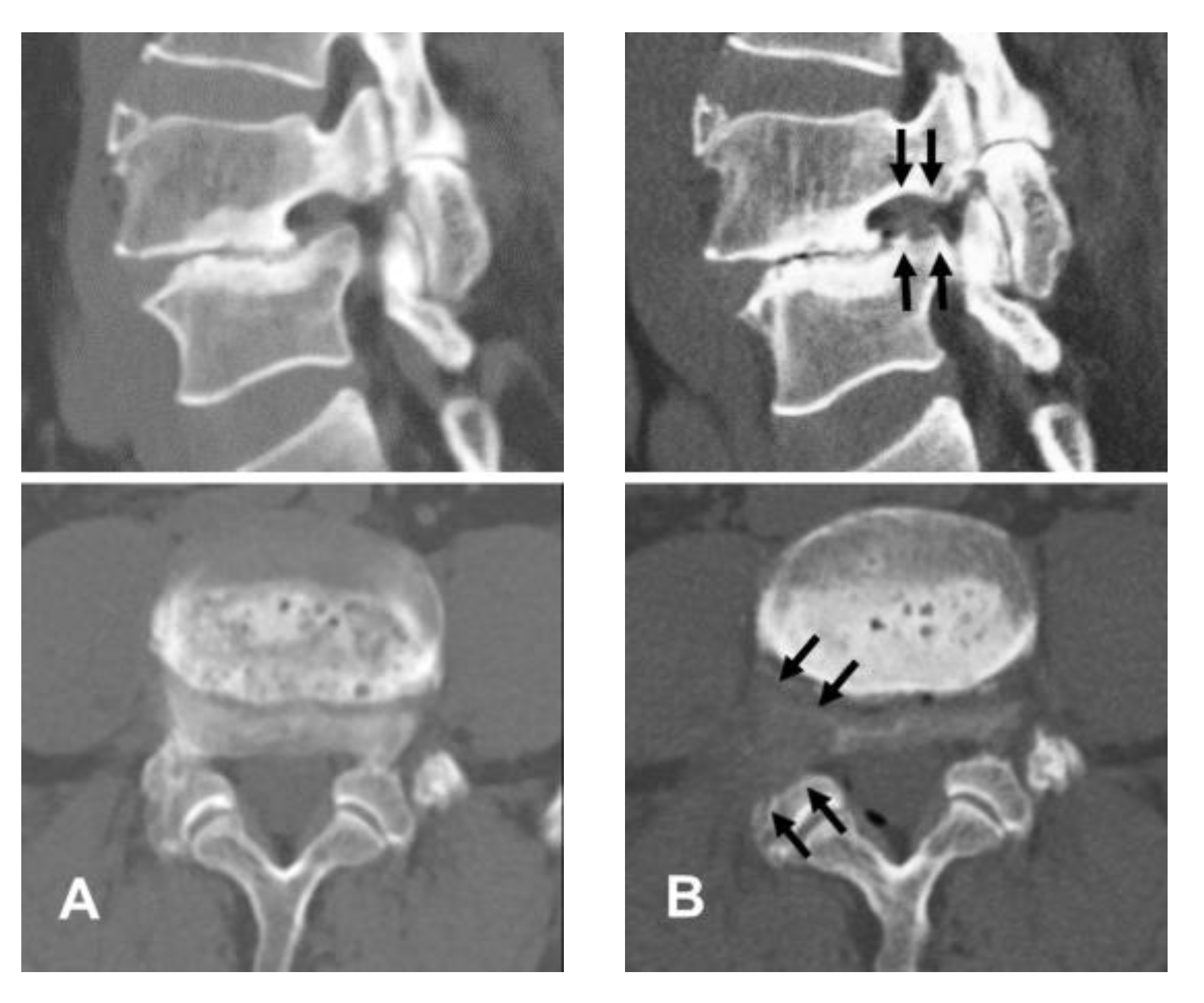
2.1. Patient Evaluation
2.2. Surgical Procedure
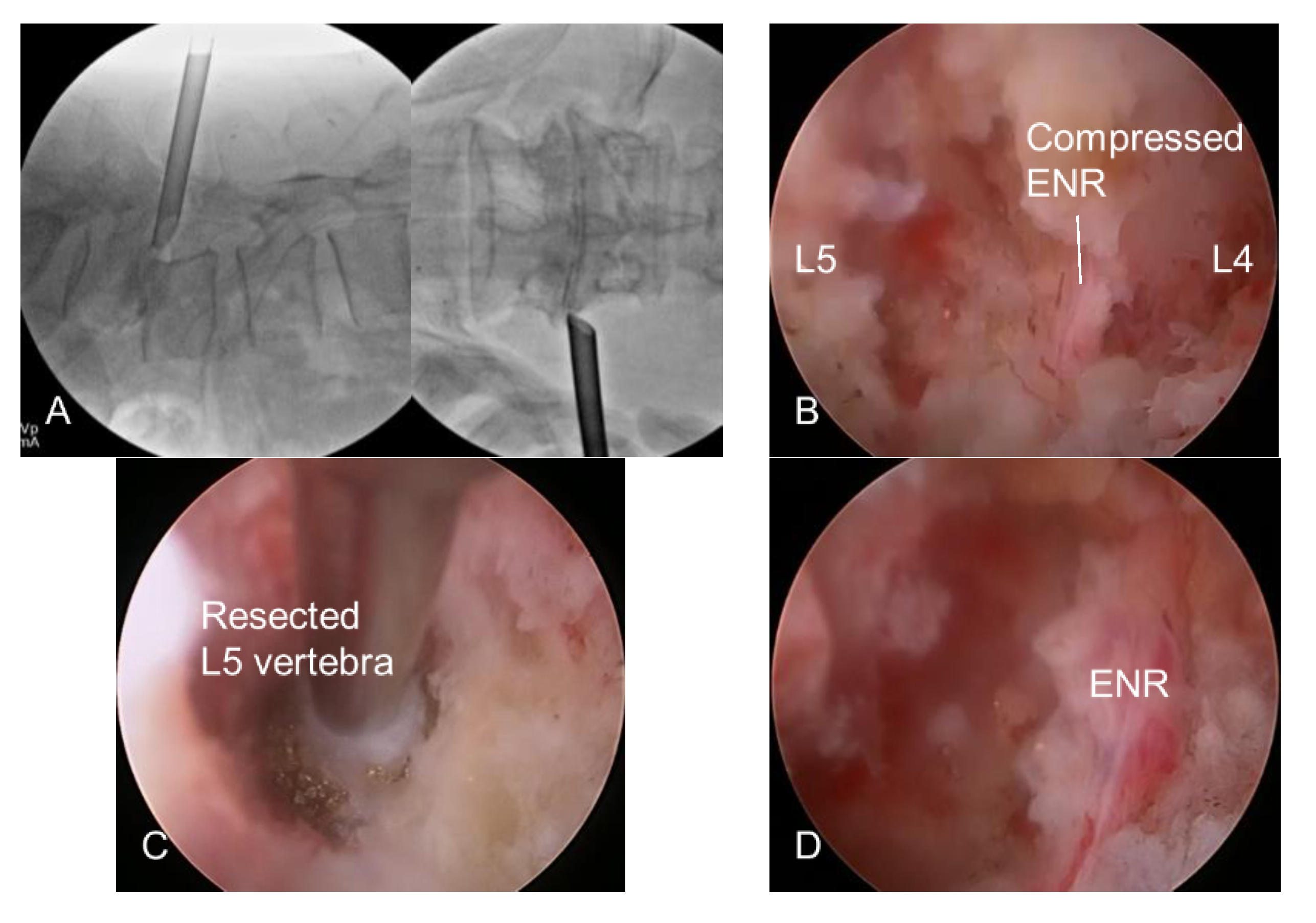
2.2.1. Transforaminal Approach
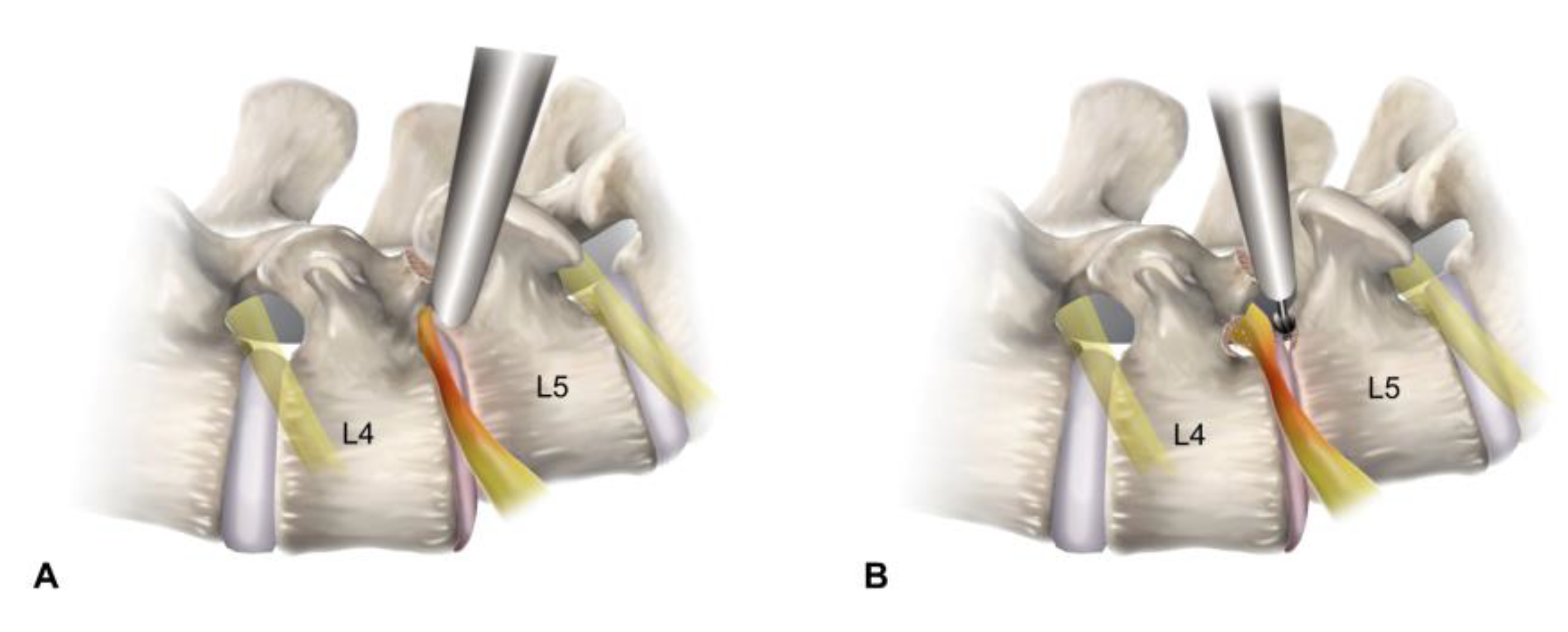
2.2.2. Endoscopic Bone Work
2.2.3. Endoscopic Soft Tissue Work
2.2.4. Finishing Point
2.3. Statistical Analysis
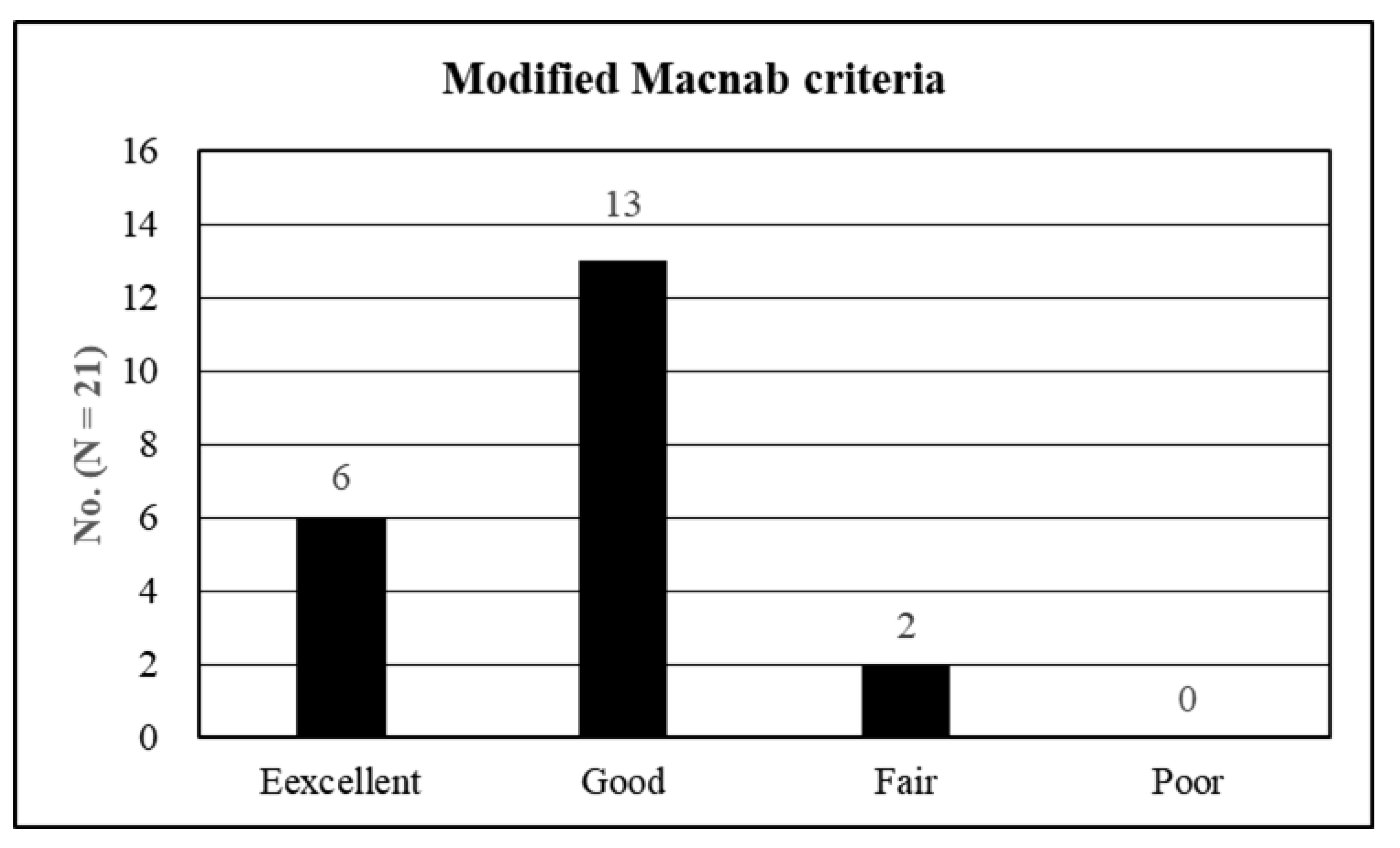
3. Results
4. Discussions
4.1. Diagnosis and Clinical Outcomes
4.2. Evolution of Full-Endoscopic Lumbar Foraminotomy
4.3. Current Full-Endoscopic Foraminotomy for Spondylolisthesis and Its Benefits
4.4. Technical Keys Specific to Foraminal Stenosis with Spondylolisthesis
4.5. Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Inose, H.; Kato, T.; Yuasa, M.; Yamada, T.; Maehara, H.; Hirai, T.; Yoshii, T.; Kawabata, S.; Okawa, A. Comparison of Decompression, Decompression Plus Fusion, and Decompression Plus Stabilization for Degenerative Spondylolisthesis: A Prospective, Randomized Study. Clin. Spine Surg. 2018, 31, E347–E352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austevoll, I.M.; Hermansen, E.; Fagerland, M.W.; Storheim, K.; Brox, J.I.; Solberg, T.; Rekeland, F.; Franssen, E.; Weber, C.; Brisby, H.; et al. Decompression with or without Fusion in Degenerative Lumbar Spondylolisthesis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 526–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, F.L.; Zhou, C.P.; Gao, Q.Y.; Du, M.R.; Gao, H.R.; Zhu, K.L.; Li, T.; Qian, J.X.; Yan, X.D. Decompression alone or decompression and fusion in degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. EClinicalMedicine 2022, 51, 101559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kambin, P.; Casey, K.; O’Brien, E.; Zhou, L. Transforaminal arthroscopic decompression of lateral recess stenosis. J. Neurosurg. 1996, 84, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, M.T.; Vajda, A.; Jakab, G.V.; Awan, S. Endoscopic laser foraminoplasty on the lumbar spine—Early experience. Minim. Invasive Neurosurg. 1998, 41, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, A.T.; Tsou, P.M. Posterolateral endoscopic excision for lumbar disc herniation: Surgical technique, outcome, and complications in 307 consecutive cases. Spine 2002, 27, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, Y.; Lee, S.H.; Park, W.M.; Lee, H.Y. Posterolateral percutaneous endoscopic lumbar foraminotomy for L5-S1 foraminal or lateral exit zone stenosis. Technical note. J. Neurosurg. 2003, 99, 320–323. [Google Scholar]
- Schubert, M.; Hoogland, T. Endoscopic transforaminal nucleotomy with foraminoplasty for lumbar disk herniation. Oper. Orthop. Traumatol. 2005, 17, 641–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.; Oh, H.K.; Kim, H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, H.N. Percutaneous endoscopic lumbar foraminotomy: An advanced surgical technique and clinical outcomes. Neurosurgery 2014, 75, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sairyo, K.; Chikawa, T.; Nagamachi, A. State-of-the-art transforaminal percutaneous endoscopic lumbar surgery under local anesthesia: Discectomy, foraminoplasty, and ventral facetectomy. J. Orthop. Sci. 2018, 23, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Wu, P.H.; Jang, I.T. Effect of Dorsal Root Ganglion Retraction in Endoscopic Lumbar Decompressive Surgery for Foraminal Pathology: A Retrospective Cohort Study of Interlaminar Contralateral Endoscopic Lumbar Foraminotomy and Discectomy versus Transforaminal Endoscopic Lumbar Foraminotomy and Discectomy. World Neurosurg. 2021, 148, e101–e114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Knight, M.; Goswami, A. Management of isthmic spondylolisthesis with posterolateral endoscopic foraminal decompression. Spine 2003, 28, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasper, G.P.; Francisco, G.M.; Telfeian, A.E. Transforaminal endoscopic discectomy with foraminoplasty for the treatment of spondylolisthesis. Pain Phys. 2014, 17, E703–E708. [Google Scholar]
- Yeung, A.; Kotheeranurak, V. Transforaminal Endoscopic Decompression of the Lumbar Spine for Stable Isthmic Spondylolisthesis as the Least Invasive Surgical Treatment Using the YESS Surgery Technique. Int. J. Spine Surg. 2018, 12, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, K.; Tezuka, F.; Manabe, H.; Morimoto, M.; Hayashi, F.; Takata, Y.; Sakai, T.; Yonezu, H.; Higashino, K.; Chikawa, T.; et al. Successful Endoscopic Surgery for L5 Radiculopathy Caused by Far-Lateral Disc Herniation at L5-S1 and L5 Isthmic Grade 2 Spondylolisthesis in a Professional Baseball Player. Int. J. Spine Surg. 2018, 12, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.F.; Jin, L.Y.; Lv, Z.D.; Su, X.J.; Wang, K.; Song, X.X.; Shen, H.X. Endoscopic Ventral Decompression for Spinal Stenosis with Degenerative Spondylolisthesis by Partially Removing Posterosuperior Margin Underneath the Slipping Vertebral Body: Technical Note and Outcome Evaluation. World Neurosurg. 2019, 126, e517–e525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Kadimcherla, P. Transforaminal Endoscopic Lumbar Decompression for Isthmic Spondylolisthesis: Technique Description and Clinical Outcome. Surg. Technol. Int. 2020, 36, 467–470. [Google Scholar]
- Telfeian, A.E.; Syed, S.; Oyelese, A.; Fridley, J.; Gokaslan, Z.L. Endoscopic Surgical Resection of the Retropulsed S1 Vertebral Endplate in L5-S1 Spondylolisthesis: Case Series. Pain Phys. 2020, 23, E629–E636. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Yuan, S.; Fan, N.; Du, P.; Li, J.; Yang, L.; Zhu, W.; Zang, L. Clinical Outcomes of Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy for the Treatment of Grade I and Grade II Degenerative Lumbar Spondylolisthesis: A Retrospective Study With a Minimum Five-Year Follow-up. Pain Phys. 2021, 24, E1291–E1298. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Lee, J.W.; Yeom, J.S.; Kim, K.J.; Kim, H.J.; Chung, S.K.; Kang, H.S. A practical MRI grading system for lumbar foraminal stenosis. AJR. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2010, 194, 1095–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, T.S.; Ahn, Y.; Lee, S.G.; Kim, W.K.; Son, S.; Kwon, J.H. Correlation between MRI Grading System and Surgical Findings for Lumbar Foraminal Stenosis. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2017, 60, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, Y. Percutaneous endoscopic decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2014, 11, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, Y.; Lee, S.G. Percutaneous endoscopic lumbar foraminotomy: How I do it. Acta. Neurochir. 2022, 164, 933–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.S.; Park, P.; Le, H.; Reisner, L.; Chou, D.; Mummaneni, P.V. Short-term and long-term outcomes of minimally invasive and open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusions: Is there a difference? Neurosurg. Focus 2013, 35, E6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, K.; Rao, P.J.; Kam, A.C.; Mobbs, R.J. Minimally invasive versus open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for treatment of degenerative lumbar disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Spine J. 2015, 24, 1017–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hey, H.W.; Hee, H.T. Open and minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: Comparison of intermediate results and complications. Asian Spine J. 2015, 9, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, M.J.; Mok, J.; Patel, P. Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Traditional Open Versus Minimally Invasive Techniques. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2018, 26, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, W.J.; Ashton-James, C.E.; Skorpil, N.E.; Heymans, M.W.; Forouzanfar, T. What constitutes a clinically important pain reduction in patients after third molar surgery? Pain Res. Manag. 2013, 18, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, L.C.; Tafazal, S.; Sell, P. The effect of duration of symptoms on standard outcome measures in the surgical treatment of spinal stenosis. Eur. Spine J. 2007, 16, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ostelo, R.W.; Deyo, R.A.; Stratford, P.; Waddell, G.; Croft, P.; Von Korff, M.; Bouter, L.M.; de Vet, H.C. Interpreting change scores for pain and functional status in low back pain: Towards international consensus regarding minimal important change. Spine 2008, 33, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunogi, J.; Hasue, M. Diagnosis and operative treatment of intraforaminal and extraforaminal nerve root compression. Spine 1991, 16, 1312–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donaldson, W.F., 3rd; Star, M.J.; Thorne, R.P. Surgical treatment for the far lateral herniated lumbar disc. Spine 1993, 18, 1263–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejeune, J.P.; Hladky, J.P.; Cotton, A.; Vinchon, M.; Christiaens, J.L. Foraminal lumbar disc herniation. Experience with 83 patients. Spine 1994, 19, 1905–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darden, B.V., 2nd; Wade, J.F.; Alexander, R.; Wood, K.E.; Rhyne, A.L., 3rd; Hicks, J.R. Far lateral disc herniations treated by microscopic fragment excision. Techniques and results. Spine 1995, 20, 1500–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, H.; Uchida, K.; Maezawa, Y.; Furusawa, N.; Okumura, Y.; Imura, S. Microsurgical nerve root canal widening without fusion for lumbosacral intervertebral foraminal stenosis: Technical notes and early results. Spinal Cord. 1996, 34, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, S.D.; Humphreys, S.C.; Eck, J.C.; Covington, L.A. The surgical treatment of far lateral L3-L4 and L4-L5 disc herniations. A modified technique and outcomes analysis of 25 patients. Spine 1999, 24, 1243–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.S.; Zidan, I.; Fujisawa, N.; Matsui, T. Microsurgical posterolateral transmuscular approach for lumbar foraminal stenosis. J. Spinal Disord. Tech. 2011, 24, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, M.T.; Goswami, A.; Patko, J.T.; Buxton, N. Endoscopic foraminoplasty: A prospective study on 250 consecutive patients with independent evaluation. J. Clin. Laser Med. Surg. 2001, 19, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, A.; Gore, S. Endoscopic foraminal decompression for failed back surgery syndrome under local anesthesia. Int. J. Spine Surg. 2014, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rhee, D.Y.; Ahn, Y. Full-Endoscopic Lumbar Foraminotomy for Foraminal Stenosis in Spondylolisthesis: Two-Year Follow-Up Results. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 3152. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123152
Rhee DY, Ahn Y. Full-Endoscopic Lumbar Foraminotomy for Foraminal Stenosis in Spondylolisthesis: Two-Year Follow-Up Results. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(12):3152. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123152
Chicago/Turabian StyleRhee, Do Yeon, and Yong Ahn. 2022. "Full-Endoscopic Lumbar Foraminotomy for Foraminal Stenosis in Spondylolisthesis: Two-Year Follow-Up Results" Diagnostics 12, no. 12: 3152. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123152
APA StyleRhee, D. Y., & Ahn, Y. (2022). Full-Endoscopic Lumbar Foraminotomy for Foraminal Stenosis in Spondylolisthesis: Two-Year Follow-Up Results. Diagnostics, 12(12), 3152. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123152






