Current Status of Artificial Intelligence-Based Computer-Assisted Diagnosis Systems for Gastric Cancer in Endoscopy
Abstract
:1. Background
2. Method
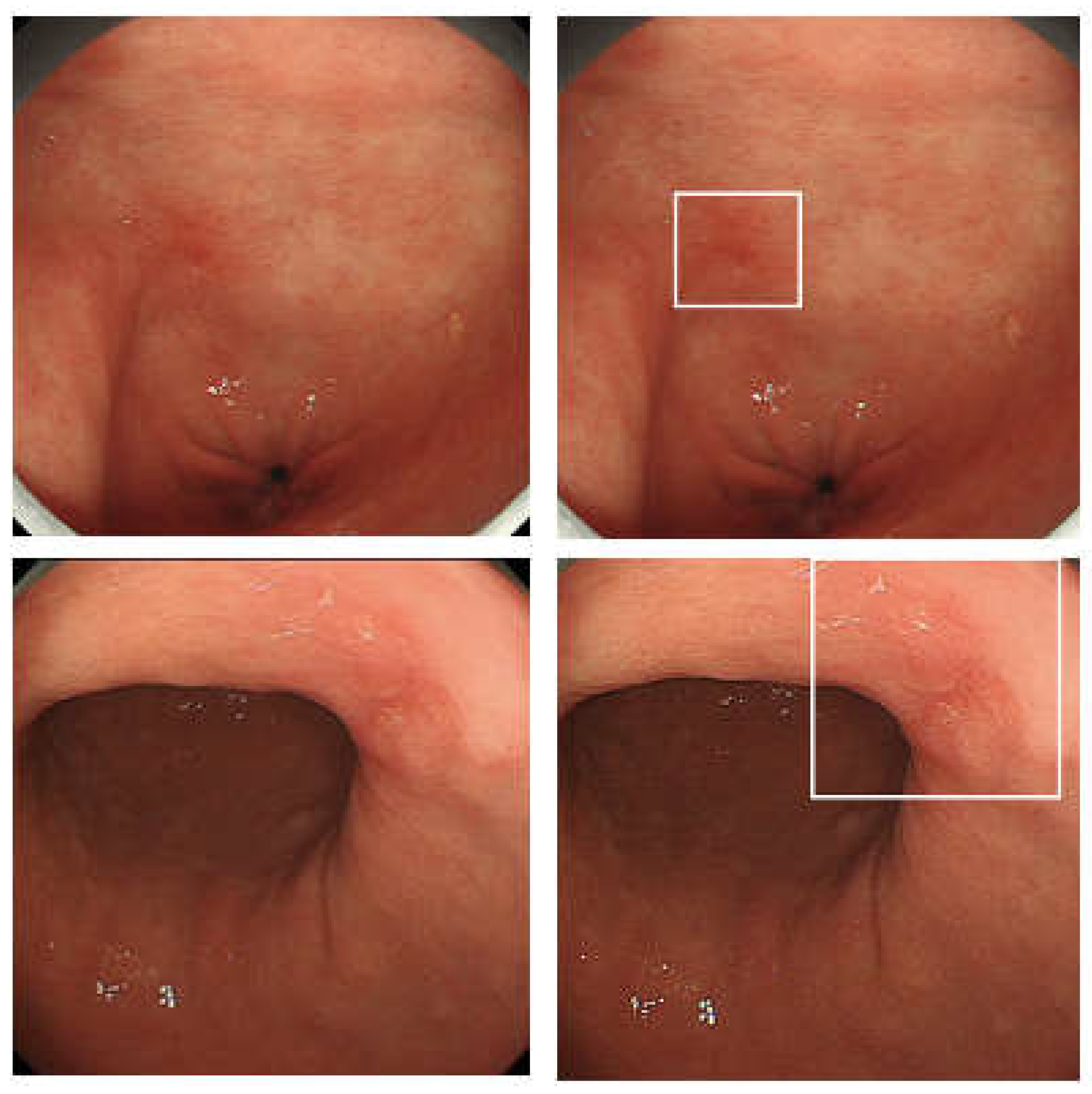
2.1. Endoscopic CAD for Gastric Cancers
2.2. Endoscopic CADe for Gastric Cancers
2.3. Endoscopic CADx for Gastric Cancers
2.4. Endoscopic CADx for Diagnosing Various Features of Gastric Cancers
2.5. Endoscopic CADx for Helicobacter Pylori Infection
2.6. Endoscopic CAD for Quality Assurance
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
| Study Design | Reference, Year | Modality | Training Dataset | Validation/Test Dataset | AUC | Accuracy (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Retrospective | Hirasawa, 2018 [9] | WLI, CE, NBI | 51,558 images (13,584 GC images) | 296 GC images | n/a | n/a | 92.2 | n/a |
| Yoon, 2019 [36] | WLI | 11,539 images (1705 GC images) | 11,539 images (1705 GC images) | 0.981 | n/a | 91 | 97.6 | |
| Ishioka, 2019 [10] | WLI, CE, NBI | 51,558 images (13,584 GC images) | 68 videos with GC | n/a | n/a | 94.1 | n/a | |
| Ikenoyama, 2021 [11] | WLI, CE, NBI | 51,558 images (13,584 GC images) | 2940 GC images of 140 patients | 0.757 | n/a | 58.4 | 87.3 | |
| Nam, 2022 [41] | WLI | 1009 images (110 GU, 620 EGC, 279 AGC) | 112 images (internal test), 245 images (external test) | 0.78 (internal test), 0.73 (external test) | n/a | n/a | n/a | |
| Niikura, 2022 [14] | WLI | 51,558 images (13,584 GC images) | 500 patients (51 AGC, 49 EGC patients) | n/a | n/a | 100 | n/a | |
| Prospective | Luo, 2019 [13] | WLI | 141,570 images (26,172 GC/EC images) | 66,750 images (4317 GC/EC images) | 0.974 | 92.7 | 94.6 | 92.6 |
| ENDOANGEL | ||||||||
| Prospective | Wu, 2022 [16] | WLI | 24,704 images (15,341 GC); ENDOANGEL-CNN1a (detection module) | 100 lesions from 96 patients | n/a | 91 | 87.81 | 93.22 |
| Wu, 2022 [17] | WLI | 21,000 images (15,341 GC); ENDOANGEL-LD CNN1 | internal test1: 1198 images (1000 GC), internal test2: 5488 images (338 neoplastic), external test: 15,886 images (774 neoplastic) | 98.3 (internal test1), 96.9 (internal test2), 95.6 (external test), 100 (videos) | 98.4 (internal test1), 90.6 (internal test2) and 90.8 (external test) | |||
| RCT | Wu, 2021 [15] | WLI | 18,579 images (12,447 GC) | 1012 patients (93 patients with GC) | Findings: The gastric neoplasm miss rate was significantly lower in the AI-first group than in the routine- first group (6.1% vs 27.3%, p = 0.015). | |||
| Study Design | Reference, Year | Modality | Training Dataset | Validation/Test Dataset | AUC | Accuracy (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CADx-neoplastic/non-neoplastic | Retrospective | Li, 2020 [22] | M-NBI | 2088 images (1702 EGC) | 341 images (170 EGC) | n/a | 90.91 | 91.18 | 90.64 |
| Horiuchi, 2020 [24] | M-NBI | 2570 images (1492 EGC) | 258 images (151 EGC) | 0.85 | 85.3 | 95.4 | 71 | ||
| Horiuchi, 2020 [25] | M-NBI | 2570 images (1492 EGC) | 174 videos (87 with EGC) | 0.8684 | 85.1 | 87.4 | 82.8 | ||
| Namikawa, 2020 [12] | WLI, NBI | 18,410 images (2649 GC, 4826 GU) | 739 EGC and 720 GU images | n/a | 99.0 (GC), 93.3 (GU) | 99.0 (GC), 93.3 (GU) | 93.3 (GC), 99.0 (GU) | ||
| Ueyama, 2021 [23] | M-NBI | 5574 images (3797 EGC) | 2300 images (1430 EGC) | n/a | 98.7 | 98 | 100 | ||
| Hu, 2021 [26] | M-NBI | Images from 170 patients with EGC | 73 patients (Internal test), 52 patients (External test) | 0.808 (Internal test), 0.813 (External test) | 77.0 (Internal test), 76.3 (External test) | 79.2 (Internal test), 78.2 (External test) | 74.5 (Internal test), 74.1 (External test) | ||
| Nam, 2022 [41] | WLI | 1009 images (110 GU, 620 EGC, 279 AGC) | 112 images (internal test), 245 images (external test) | Internal test 0.89 External test 0.82 | Internal test GU 95, EGC 89, AGC 93 External test: GU 86, EGC 79 AGC 79 | Internal test GU 63 EGC 94 AGC 90 External test GU 68 EGC 77 AGC 56 | Internal test GU 98 EGC 82 AGC 94 External test GU 50 EGC 89 AGC 47 | ||
| Yuan, 2022 [28] | WLI | 29,809 images | 1579 images | n/a | 85.7 | n/a | n/a | ||
| Ishioka, 2022 [27] | WLI | 40,162 images (18,027 EGC) | 315 mages (150 EGC) | n/a | 70.8 | 84.7 | 58.2 | ||
| ENDOANGEL | |||||||||
| Prospective | Wu, 2022 [16] | M-NBI | 8301 WLI images (4442 neoplastic images); ENDOANGEL-CNN1b (WLI), 4667 M-NBI images (1950 EGC images); ENDOANGEL-CNN2 (M-NBI) | 100 lesions from 96 patients | n/a | 89 | 100 | 82.54 | |
| Wu, 2022 [17] | 9824 images (5359 neoplastic images); ENDOANGEL-LD CNN2 | Internal test1: 1198 images (1000 abnormal), Internal test2: 5488 images (338 neoplastic) External test: 15,886 images (774 neoplastic) 100 videos (38 neoplastic) | 0.960 (internal test1), | Internal test1: 86.0 Internal test2: 88.8 External test: 88.6 Videos: 72.0 | Internal test1: 94.0 Internal test2: 92.9 External test: 91.7 Videos: 100 | Internal test1: 84.0 Internal test2: 88.8 External test: 88.2 Videos: 53.2 | |||
| CADx-Invasion depth, pathological status | Retrospective | Kubota, 2012 [60] | WLI | 902 GC images | 902 GC images | n/a | 64.7 | n/a | n/a |
| Yoon, 2019 [37] | WLI | 1750 GC images | 1705 GC images | 0.851 | n/a | 79.2 | 77.8 | ||
| Zhu, 2019 [39] | WLI | 790 GC images | 203 GC images | 0.94 | 89.16 | 76.47 | 95.56 | ||
| Nagao, 2020 [38] | WLI, CE, NBI | 13,628 GC images | 2929 GC images | 0.959 (WLI), 0.9048 (NBI), 0.9491 (CE) | 94.49 (WLI), 94.30 (NBI), 95.50 (CE) | 84.42 (WLI), 75.00 (NBI), 87.50 (CE) | 99.37 (WLI), 100 (NBI), 100 (CE) | ||
| Cho, 2020 [37] | WLI | 2899 images | 206 images | 0.887 | 77.3 | 80.4 | 80.7 | ||
| Tang, 2021 [40] | WLI | 3407 images from 666 GC patients | 228 images | 0.942 | 88.2 | 90.5 | 85.3 | ||
| Ling 2021 [44] | M-NBI | 2217 GC images | 1870 GC images | n/a | 86.2 | Differentiated: 88.6, Undifferentiated: 78.6 | Differentiated: 78.6, Undifferentiated: 88.6 | ||
| Nam, 2022 [41] | WLI | 1009 images (110 GU, 620 EGC, 279 AGC) | 112 images (internal test), 245 images (external test) | Internal test: 0.78, External test: 0.73 | Internal test: 77, External test: 72 | Internal test: 86, External test: 73 | Internal test: 66 External test: 94 | ||
| Prospective | Wu, 2022 [16] | WLI, M-NBI | 3407 WLI images; ENDOANGEL-CNN3 (invasion depth), 2217 M-NBI images (1131 differentiated a 1086 undifferentiated); ENDOANGEL-CNN4 (differentiation status) | 28 lesions from 28 patients | n/a | 78.6 (submucosal invasion), 71.4(undifferentiated EGC) | 70.0 (submucosal invasion), 50.0 (undifferentiated EGC) | 83.3 (submucosal invasion), 80.0 (undifferentiated EGC) | |
| Study Design | Reference, Year | Modality | Training Dataset | Validation/Test Dataset | AUC | Accuracy (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Retrospective | Shichijo, 2017 [47] | WLI, CE, NBI | 32,208 images from 1750 patients (753 HP-positive) | 11,481 images from 397 patients (72 HP-positive) | 0.93 | 87.70% | 88.9 | 87.4 |
| Shichijo, 2019 [48] | WLI | 98,564 images from 5236 patients (742 HP positive, 3649 HP negative, and 845 HP eradicated) | 23,699 images from 847 patients (70 positive, 493 negative, and 284 eradicated) | n/a | 80 (HP negative), 84 (HP eradicated), 48 (HP positive) | n/a | n/a | |
| Zheng, 2019 [61] | WLI | 11,729 images from 1959 patients (847 HP positive) | 3755 images form 452 patients (310 HP positive) | 0.97 | 93.8 | 91.6 | 98.6 | |
| Guimarães, 2020 [62] | WLI | 200 images (100 HP positive) | 70 images (30 HP positive) | 0.981 | 92.9 | 100 | 87.5 | |
| Zhang, 2020 [63] | WLI | A total of 5470 images (3042 with atrophic gastritis), 70% for training and 30% for testing | 0.99 | 94.2 | 94.5 | 94 | ||
| Prospective | Itoh, 2018 [64] | WLI | 149 images (70 HP positive) | 30 images (15 HP positive) | 0.956 | n/a | 86.7 | 86.7 |
| Nakashima, 2018 [49] | WLI, BLI, LCI | 2592 images from 162 patients (75 HP positive) | 60 patients (30 HP-positive) | 0.66 (WLI), 0.96 (BLI), 0.95 (LCI) | n/a | 66.7 (WLI), 96.7 (BLI), 96.7 (LCI) | 60.0 (WLI), 86.7 (BLI), 83.3 (LCI) | |
| Nakashima, 2020 [50] | WLI, LCI | 12,887 images from 395 patients (138 HP positive, 141 HP negative, 116 HP eradicated) | 120 videos (40 HP positive, 40 HP negative, 40 HP eradicated) | 0.82 (LCI, HP positive), 0.90 (LCI, HP negative), 0.77 (LCI, HP eradicated) | HP Positive 77.5 (WLI), 82.5 (LCI) HP negative 75.0 (WLI), 84.2 (LCI) HP eradicated 74.2 (WLI), 79.2 (LCI) | HP Positive 60.0 (WLI), 62.5 (LCI) HP negative 95.0 (WLI), 92.5 (LCI) HP eradicated 35.0 (WLI), 65.0 (LCI) | HP Positive 86.2 (WLI), 92.5 (LCI) HP negative 65.0 (WLI), 80.0 (LCI) HP eradicated 93.8 (WLI), 86.2 (LCI) | |
| Xu, 2021 [51] | M-NBI, M-BLI | 354 patients | 77 videos | 0.878 | 87.8 | 96.7 | 73 | |
| Reference, Year | Study Design | Application | Modality | Training Dataset | Validation/Test Dataset | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wu, 2019 [52] | Retrospective | Classification of observed location | WLI | 24,549 images | 170 images | Accuracy: 90 (into 10 parts), 65.9 (into 26 parts) |
| Wu, 2019 [53] | RCT | Monitoring blind spots | WLI | 34,513 images | 107 videos | Accuracy: 90.0% Sensitivity: 87.5%, Specificity 95.0% |
| Li, 2022 [55] | Prospective | Monitoring EGD quality | WLI | 170,297 images and 149 videos | 17,787 patients | AI out put the EGD quality monitoring scores. The cancer detection rate (r = 0.775) and early cancer detection rate (r = 0.756) were positively correlated with total score. |
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Litjens, G.; Kooi, T.; Bejnordi, B.E.; Setio, A.A.A.; Ciompi, F.; Ghafoorian, M.; van der Laak, J.A.W.M.; van Ginneken, B.; Sánchez, C.I. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 42, 60–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, K.; Fung, K.-M.; Thai, T.C.; Moore, K.; Mannel, R.S.; Liu, H.; Zheng, B.; Qiu, Y. Recent advances and clinical applications of deep learning in medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 2022, 79, 102444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, P.; Houghton, J. Carcinogenesis of Helicobacter pylori. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 659–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katai, H.; Ishikawa, T.; Akazawa, K.; Isobe, Y.; Miyashiro, I.; Oda, I.; Tsujitani, S.; Ono, H.; Tanabe, S.; Fukagawa, T.; et al. Five-year survival analysis of surgically resected gastric cancer cases in Japan: A retrospective analysis of more than 100,000 patients from the nationwide registry of the Japanese Gastric Cancer Association (2001–2007). Gastric Cancer 2018, 21, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Januszewicz, W.; Witczak, K.; Wieszczy, P.; Socha, M.; Turkot, M.H.; Wojciechowska, U.; Didkowska, J.; Kaminski, M.F.; Regula, J. Prevalence and risk factors of upper gastrointestinal cancers missed during endoscopy: A nationwide registry-based study. Endoscopy 2022, 54, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosokawa, O.; Hattori, M.; Douden, K.; Hayashi, H.; Ohta, K.; Kaizaki, Y. Difference in accuracy between gastroscopy and colonoscopy for detection of cancer. Hepatogastroenterology 2007, 54, 442–444. [Google Scholar]
- Menon, S.; Trudgill, N. How commonly is upper gastrointestinal cancer missed at endoscopy? A meta-analysis. Endosc. Int. Open 2014, 2, E46–E50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirasawa, T.; Aoyama, K.; Tanimoto, T.; Ishihara, S.; Shichijo, S.; Ozawa, T.; Ohnishi, T.; Fujishiro, M.; Matsuo, K.; Fujisaki, J.; et al. Application of artificial intelligence using a convolutional neural network for detecting gastric cancer in endoscopic images. Gastric Cancer 2018, 21, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishioka, M.; Hirasawa, T.; Tada, T. Detecting gastric cancer from video images using convolutional neural networks. Dig. Endosc. 2019, 31, e34–e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ikenoyama, Y.; Hirasawa, T.; Ishioka, M.; Namikawa, K.; Yoshimizu, S.; Horiuchi, Y.; Ishiyama, A.; Yoshio, T.; Tsuchida, T.; Takeuchi, Y.; et al. Detecting early gastric cancer: Comparison between the diagnostic ability of convolutional neural networks and endoscopists. Dig. Endosc. 2021, 33, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namikawa, K.; Hirasawa, T.; Nakano, K.; Ikenoyama, Y.; Ishioka, M.; Shiroma, S.; Tokai, Y.; Yoshimizu, S.; Horiuchi, Y.; Ishiyama, A.; et al. Artificial intelligence-based diagnostic system classifying gastric cancers and ulcers: Comparison between the original and newly developed systems. Endoscopy 2020, 52, 1077–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Xu, G.; Li, C.; He, L.; Luo, L.; Wang, Z.; Jing, B.; Deng, Y.; Jin, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Real-time artificial intelligence for detection of upper gastrointestinal cancer by endoscopy: A multicentre, case-control, diagnostic study. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1645–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niikura, R.; Aoki, T.; Shichijo, S.; Yamada, A.; Kawahara, T.; Kato, Y.; Hirata, Y.; Hayakawa, Y.; Suzuki, N.; Ochi, M.; et al. Artificial intelligence versus expert endoscopists for diagnosis of gastric cancer in patients who have undergone upper gastrointestinal endoscopy. Endoscopy 2022, 54, 780–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Shang, R.; Sharma, P.; Zhou, W.; Liu, J.; Yao, L.; Dong, Z.; Yuan, J.; Zeng, Z.; Yu, Y.; et al. Effect of a deep learning-based system on the miss rate of gastric neoplasms during upper gastrointestinal endoscopy: A single-centre, tandem, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 6, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wang, J.; He, X.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, L.; Shang, R.; Dong, Z.; et al. Deep learning system compared with expert endoscopists in predicting early gastric cancer and its invasion depth and differentiation status (with videos). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2022, 95, 92–104.e103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Xu, M.; Jiang, X.; He, X.; Zhang, H.; Ai, Y.; Tong, Q.; Lv, P.; Lu, B.; Guo, M.; et al. Real-time artificial intelligence for detecting focal lesions and diagnosing neoplasms of the stomach by white-light endoscopy (with videos). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2022, 95, 269–280.e266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.; Anagnostopoulos, G.K.; Ragunath, K. Magnifying endoscopy for diagnosing and delineating early gastric cancer. Endoscopy 2009, 41, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyaoka, M.; Yao, K.; Tanabe, H.; Kanemitsu, T.; Otsu, K.; Imamura, K.; Ono, Y.; Ishikawa, S.; Yasaka, T.; Ueki, T.; et al. Diagnosis of early gastric cancer using image enhanced endoscopy: A systematic approach. Transl. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyama, H.; Nakanishi, H.; Yao, K. Image-Enhanced Endoscopy and Its Corresponding Histopathology in the Stomach. Gut Liver 2021, 15, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dohi, O.; Yagi, N.; Majima, A.; Horii, Y.; Kitaichi, T.; Onozawa, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Tomie, A.; Kimura-Tsuchiya, R.; Tsuji, T.; et al. Diagnostic ability of magnifying endoscopy with blue laser imaging for early gastric cancer: A prospective study. Gastric Cancer 2017, 20, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, X.; Sang, J.; Ding, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, J.; Chen, M.; Jin, C.; et al. Convolutional neural network for the diagnosis of early gastric cancer based on magnifying narrow band imaging. Gastric Cancer 2020, 23, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ueyama, H.; Kato, Y.; Akazawa, Y.; Yatagai, N.; Komori, H.; Takeda, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Ueda, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Hojo, M.; et al. Application of artificial intelligence using a convolutional neural network for diagnosis of early gastric cancer based on magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 36, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horiuchi, Y.; Aoyama, K.; Tokai, Y.; Hirasawa, T.; Yoshimizu, S.; Ishiyama, A.; Yoshio, T.; Tsuchida, T.; Fujisaki, J.; Tada, T. Convolutional Neural Network for Differentiating Gastric Cancer from Gastritis Using Magnified Endoscopy with Narrow Band Imaging. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 1355–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horiuchi, Y.; Hirasawa, T.; Ishizuka, N.; Tokai, Y.; Namikawa, K.; Yoshimizu, S.; Ishiyama, A.; Yoshio, T.; Tsuchida, T.; Fujisaki, J.; et al. Performance of a computer-aided diagnosis system in diagnosing early gastric cancer using magnifying endoscopy videos with narrow-band imaging (with videos). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2020, 92, 856–865.e851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Gong, L.; Dong, D.; Zhu, L.; Wang, M.; He, J.; Shu, L.; Cai, Y.; Cai, S.; Su, W.; et al. Identifying early gastric cancer under magnifying narrow-band images with deep learning: A multicenter study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2021, 93, 1333–1341.e1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishioka, M.; Osawa, H.; Hirasawa, T.; Kawachi, H.; Nakano, K.; Fukushima, N.; Sakaguchi, M.; Tada, T.; Kato, Y.; Shibata, J.; et al. Performance of an artificial intelligence-based diagnostic support tool for early gastric cancers: Retrospective study. Dig. Endosc. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.L.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, W.; Luo, Q.; Zeng, X.H.; Yi, Z.; Hu, B. Artificial intelligence for diagnosing gastric lesions under white-light endoscopy. Surg. Endosc. 2022, 36, 9444–9453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, S.G.; Windsor, J.A. Redefining early gastric cancer. Surg. Endosc. 2016, 30, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, X.B. Endoscopic prediction of tumor margin and invasive depth in early gastric cancer. J. Dig. Dis. 2015, 16, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, T.; Okuyama, Y.; Kobori, O.; Shimizu, T.; Morioka, Y. Early gastric cancer. Endoscopic diagnosis of depth of invasion. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1990, 35, 1340–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Kim, S.G.; Im, J.P.; Kim, J.S.; Jung, H.C.; Song, I.S. Comparison of endoscopic ultrasonography and conventional endoscopy for prediction of depth of tumor invasion in early gastric cancer. Endoscopy 2010, 42, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, S.; Oda, I.; Shimazu, T.; Kinjo, T.; Tada, K.; Sakamoto, T.; Kusano, C.; Gotoda, T. Depth-predicting score for differentiated early gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer 2011, 14, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsujii, Y.; Kato, M.; Inoue, T.; Yoshii, S.; Nagai, K.; Fujinaga, T.; Maekawa, A.; Hayashi, Y.; Akasaka, T.; Shinzaki, S.; et al. Integrated diagnostic strategy for the invasion depth of early gastric cancer by conventional endoscopy and EUS. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2015, 82, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagahama, T.; Yao, K.; Imamura, K.; Kojima, T.; Ohtsu, K.; Chuman, K.; Tanabe, H.; Yamaoka, R.; Iwashita, A. Diagnostic performance of conventional endoscopy in the identification of submucosal invasion by early gastric cancer: The “non-extension sign” as a simple diagnostic marker. Gastric Cancer 2017, 20, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, H.J.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.H.; Keum, J.S.; Oh, S.I.; Jo, J.; Chun, J.; Youn, Y.H.; Park, H.; Kwon, I.G.; et al. A Lesion-Based Convolutional Neural Network Improves Endoscopic Detection and Depth Prediction of Early Gastric Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, B.J.; Bang, C.S.; Lee, J.J.; Seo, C.W.; Kim, J.H. Prediction of Submucosal Invasion for Gastric Neoplasms in Endoscopic Images Using Deep-Learning. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagao, S.; Tsuji, Y.; Sakaguchi, Y.; Takahashi, Y.; Minatsuki, C.; Niimi, K.; Yamashita, H.; Yamamichi, N.; Seto, Y.; Tada, T.; et al. Highly accurate artificial intelligence systems to predict the invasion depth of gastric cancer: Efficacy of conventional white-light imaging, nonmagnifying narrow-band imaging, and indigo-carmine dye contrast imaging. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2020, 92, 866–873.e861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, Q.C.; Xu, M.D.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, J.; Zhong, Y.S.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Chen, W.F.; Yao, L.Q.; Zhou, P.H.; et al. Application of convolutional neural network in the diagnosis of the invasion depth of gastric cancer based on conventional endoscopy. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2019, 89, 806–815.e801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Zhou, J.; Wang, L.; Ni, M.; Chen, M.; Hassan, S.; Luo, R.; Chen, X.; He, X.; Zhang, L.; et al. A Novel Model Based on Deep Convolutional Neural Network Improves Diagnostic Accuracy of Intramucosal Gastric Cancer (With Video). Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 622827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, J.Y.; Chung, H.J.; Choi, K.S.; Lee, H.; Kim, T.J.; Soh, H.; Kang, E.A.; Cho, S.J.; Ye, J.C.; Im, J.P.; et al. Deep learning model for diagnosing gastric mucosal lesions using endoscopic images: Development, validation, and method comparison. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2022, 95, 258–268.e210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Japanese Gastric Cancer Association. Japanese gastric cancer treatment guidelines 2018 (5th edition). Gastric Cancer 2021, 24, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakayoshi, T.; Tajiri, H.; Matsuda, K.; Kaise, M.; Ikegami, M.; Sasaki, H. Magnifying endoscopy combined with narrow band imaging system for early gastric cancer: Correlation of vascular pattern with histopathology (including video). Endoscopy 2004, 36, 1080–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, T.; Wu, L.; Fu, Y.; Xu, Q.; An, P.; Zhang, J.; Hu, S.; Chen, Y.; He, X.; Wang, J.; et al. A deep learning-based system for identifying differentiation status and delineating the margins of early gastric cancer in magnifying narrow-band imaging endoscopy. Endoscopy 2021, 53, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugano, K.; Tack, J.; Kuipers, E.J.; Graham, D.Y.; El-Omar, E.M.; Miura, S.; Haruma, K.; Asaka, M.; Uemura, N.; Malfertheiner, P.; et al. Kyoto global consensus report on Helicobacter pylori gastritis. Gut 2015, 64, 1353–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shichijo, S.; Nomura, S.; Aoyama, K.; Nishikawa, Y.; Miura, M.; Shinagawa, T.; Takiyama, H.; Tanimoto, T.; Ishihara, S.; Matsuo, K.; et al. Application of Convolutional Neural Networks in the Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori Infection Based on Endoscopic Images. EBioMedicine 2017, 25, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, K.; Nagata, N.; Shimbo, T.; Nakashima, R.; Furuhata, E.; Sakurai, T.; Akazawa, N.; Yokoi, C.; Kobayakawa, M.; Akiyama, J.; et al. Accuracy of endoscopic diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection according to level of endoscopic experience and the effect of training. BMC Gastroenterol. 2013, 13, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shichijo, S.; Endo, Y.; Aoyama, K.; Takeuchi, Y.; Ozawa, T.; Takiyama, H.; Matsuo, K.; Fujishiro, M.; Ishihara, S.; Ishihara, R.; et al. Application of convolutional neural networks for evaluating Helicobacter pylori infection status on the basis of endoscopic images. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 54, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, H.; Kawahira, H.; Kawachi, H.; Sakaki, N. Artificial intelligence diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection using blue laser imaging-bright and linked color imaging: A single-center prospective study. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2018, 31, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, H.; Kawahira, H.; Kawachi, H.; Sakaki, N. Endoscopic three-categorical diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection using linked color imaging and deep learning: A single-center prospective study (with video). Gastric Cancer 2020, 23, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhou, W.; Wu, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Mu, G.; Huang, X.; Li, Y.; Yuan, J.; Zeng, Z.; et al. Artificial intelligence in the diagnosis of gastric precancerous conditions by image-enhanced endoscopy: A multicenter, diagnostic study (with video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2021, 94, 540–548.e544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Zhou, W.; Wan, X.; Zhang, J.; Shen, L.; Hu, S.; Ding, Q.; Mu, G.; Yin, A.; Huang, X.; et al. A deep neural network improves endoscopic detection of early gastric cancer without blind spots. Endoscopy 2019, 51, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, W.; An, P.; Shen, L.; Liu, J.; Jiang, X.; Huang, X.; Mu, G.; Wan, X.; et al. Randomised controlled trial of WISENSE, a real-time quality improving system for monitoring blind spots during esophagogastroduodenoscopy. Gut 2019, 68, 2161–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, L.; He, X.; Liu, M.; Xie, H.; An, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Ai, Y.; Tong, Q.; Guo, M.; et al. Evaluation of the effects of an artificial intelligence system on endoscopy quality and preliminary testing of its performance in detecting early gastric cancer: A randomized controlled trial. Endoscopy 2021, 53, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.D.; Li, H.Z.; Chen, S.S.; Jin, C.H.; Chen, M.; Cheng, M.; Ma, M.J.; Zhang, X.P.; Wang, X.; Zhou, J.B.; et al. Correlation of the detection rate of upper GI cancer with artificial intelligence score: Results from a multicenter trial (with video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2022, 95, 1138–1146.e1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramamurthy, K.; George, T.T.; Shah, Y.; Sasidhar, P. A Novel Multi-Feature Fusion Method for Classification of Gastrointestinal Diseases Using Endoscopy Images. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Kudo, S.E.; East, J.E.; Rastogi, A.; Bretthauer, M.; Misawa, M.; Sekiguchi, M.; Matsuda, T.; Saito, Y.; Ikematsu, H.; et al. Cost savings in colonoscopy with artificial intelligence-aided polyp diagnosis: An add-on analysis of a clinical trial (with video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2020, 92, 905–911.e901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Areia, M.; Mori, Y.; Correale, L.; Repici, A.; Bretthauer, M.; Sharma, P.; Taveira, F.; Spadaccini, M.; Antonelli, G.; Ebigbo, A.; et al. Cost-effectiveness of artificial intelligence for screening colonoscopy: A modelling study. Lancet Digit. Health 2022, 4, e436–e444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Mantero, A.; Delgado, C.; Dominguez, B.; Nuchovich, N.; Goldberg, D.S. Eastern European and Asian-born populations are prone to gastric cancer: An epidemiologic analysis of foreign-born populations and gastric cancer. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2021, 34, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, K.; Kuroda, J.; Yoshida, M.; Ohta, K.; Kitajima, M. Medical image analysis: Computer-aided diagnosis of gastric cancer invasion on endoscopic images. Surg. Endosc. 2012, 26, 1485–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Zhang, X.; Kim, J.J.; Zhu, X.; Ye, G.; Ye, B.; Wang, J.; Luo, S.; Li, J.; Yu, T.; et al. High Accuracy of Convolutional Neural Network for Evaluation of Helicobacter pylori Infection Based on Endoscopic Images: Preliminary Experience. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2019, 10, e00109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimaraes, P.; Keller, A.; Fehlmann, T.; Lammert, F.; Casper, M. Deep-learning based detection of gastric precancerous conditions. Gut 2020, 69, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Yuan, F.; Zhang, K.; Huo, L.; Dong, Z.; Lang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Gao, Z.; et al. Diagnosing chronic atrophic gastritis by gastroscopy using artificial intelligence. Dig. Liver Dis. 2020, 52, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Itoh, T.; Kawahira, H.; Nakashima, H.; Yata, N. Deep learning analyzes Helicobacter pylori infection by upper gastrointestinal endoscopy images. Endosc. Int. Open 2018, 6, E139–E144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ochiai, K.; Ozawa, T.; Shibata, J.; Ishihara, S.; Tada, T. Current Status of Artificial Intelligence-Based Computer-Assisted Diagnosis Systems for Gastric Cancer in Endoscopy. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 3153. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123153
Ochiai K, Ozawa T, Shibata J, Ishihara S, Tada T. Current Status of Artificial Intelligence-Based Computer-Assisted Diagnosis Systems for Gastric Cancer in Endoscopy. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(12):3153. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123153
Chicago/Turabian StyleOchiai, Kentaro, Tsuyoshi Ozawa, Junichi Shibata, Soichiro Ishihara, and Tomohiro Tada. 2022. "Current Status of Artificial Intelligence-Based Computer-Assisted Diagnosis Systems for Gastric Cancer in Endoscopy" Diagnostics 12, no. 12: 3153. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123153
APA StyleOchiai, K., Ozawa, T., Shibata, J., Ishihara, S., & Tada, T. (2022). Current Status of Artificial Intelligence-Based Computer-Assisted Diagnosis Systems for Gastric Cancer in Endoscopy. Diagnostics, 12(12), 3153. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123153





