Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Breast Imaging: A Scientometric Umbrella Review
Abstract
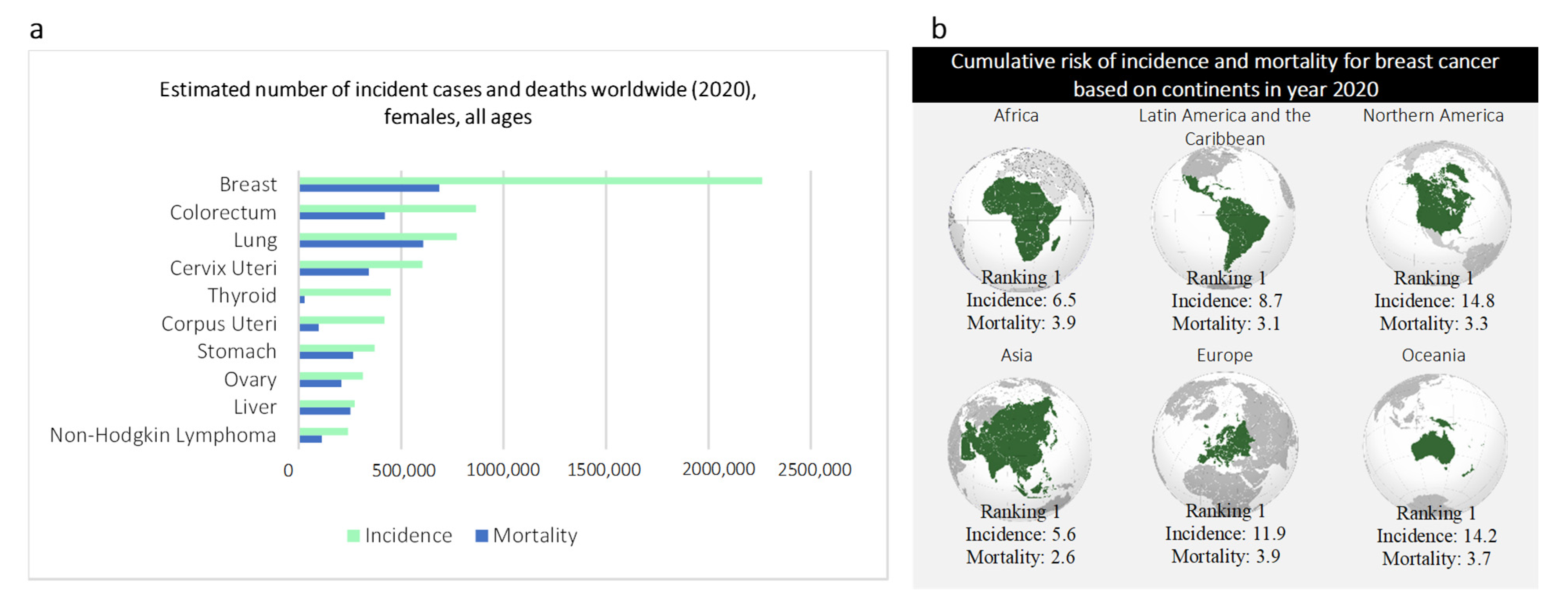
:1. Introduction
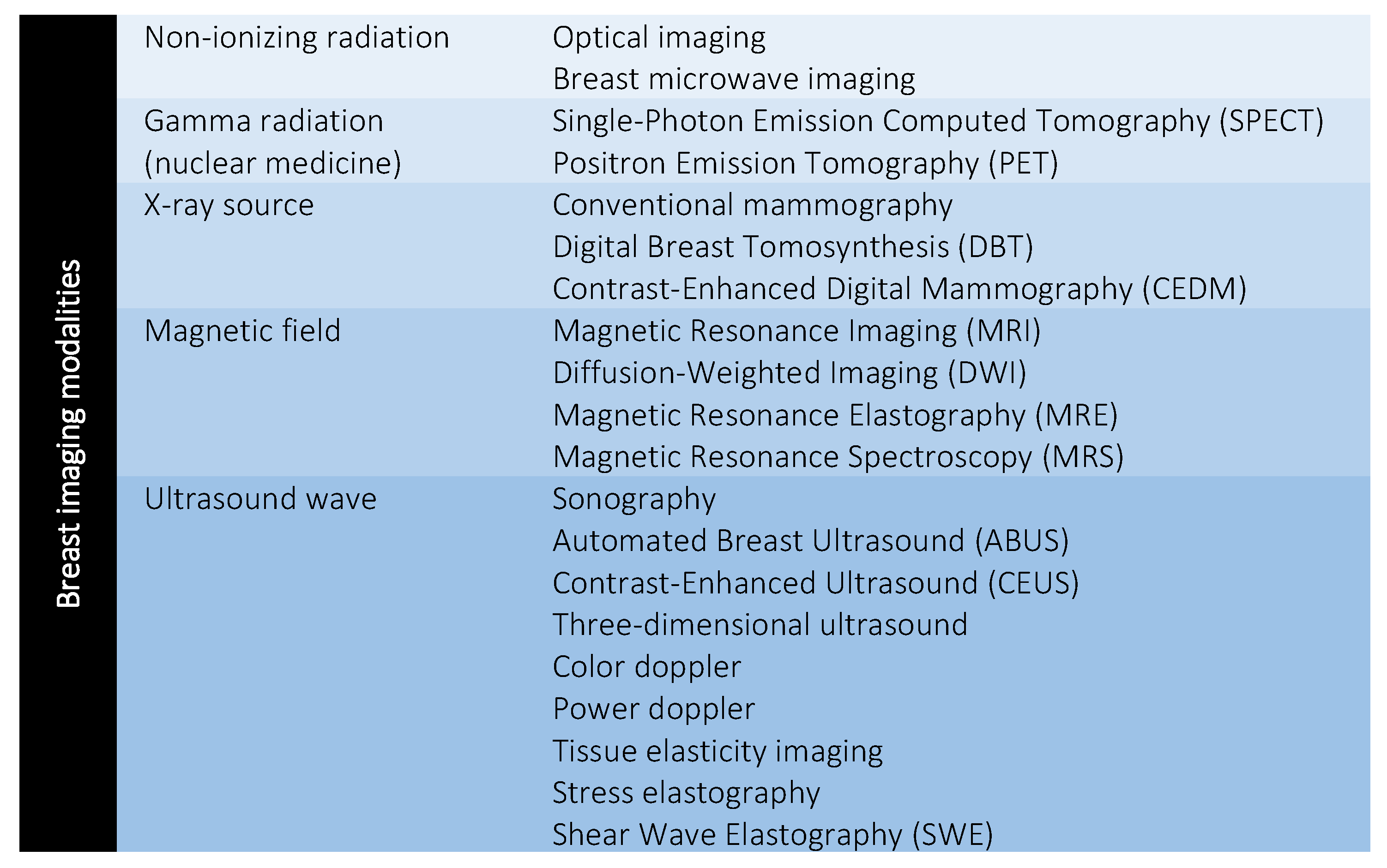
1.1. Breast Imaging Modalities
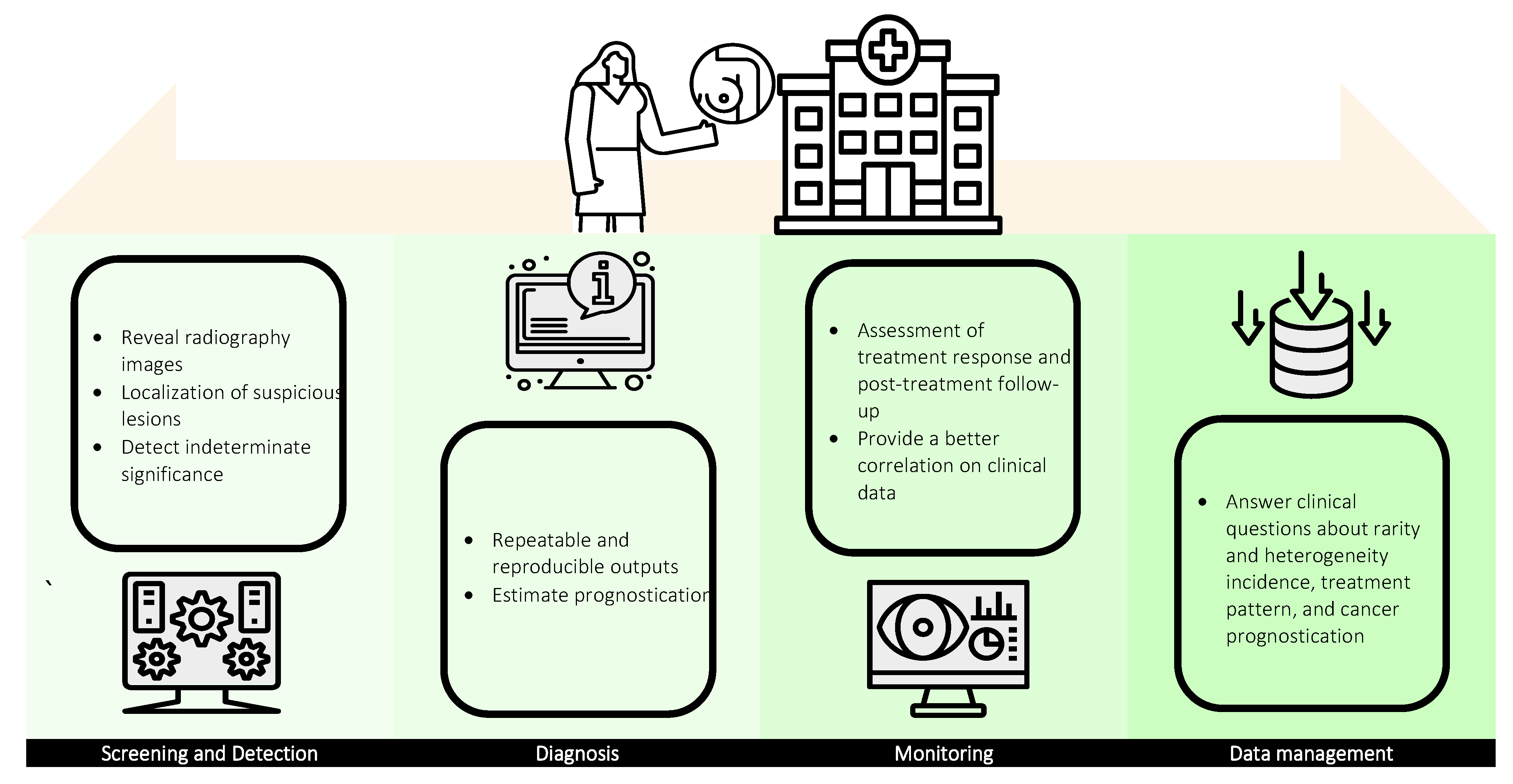
1.2. AI in Breast Imaging
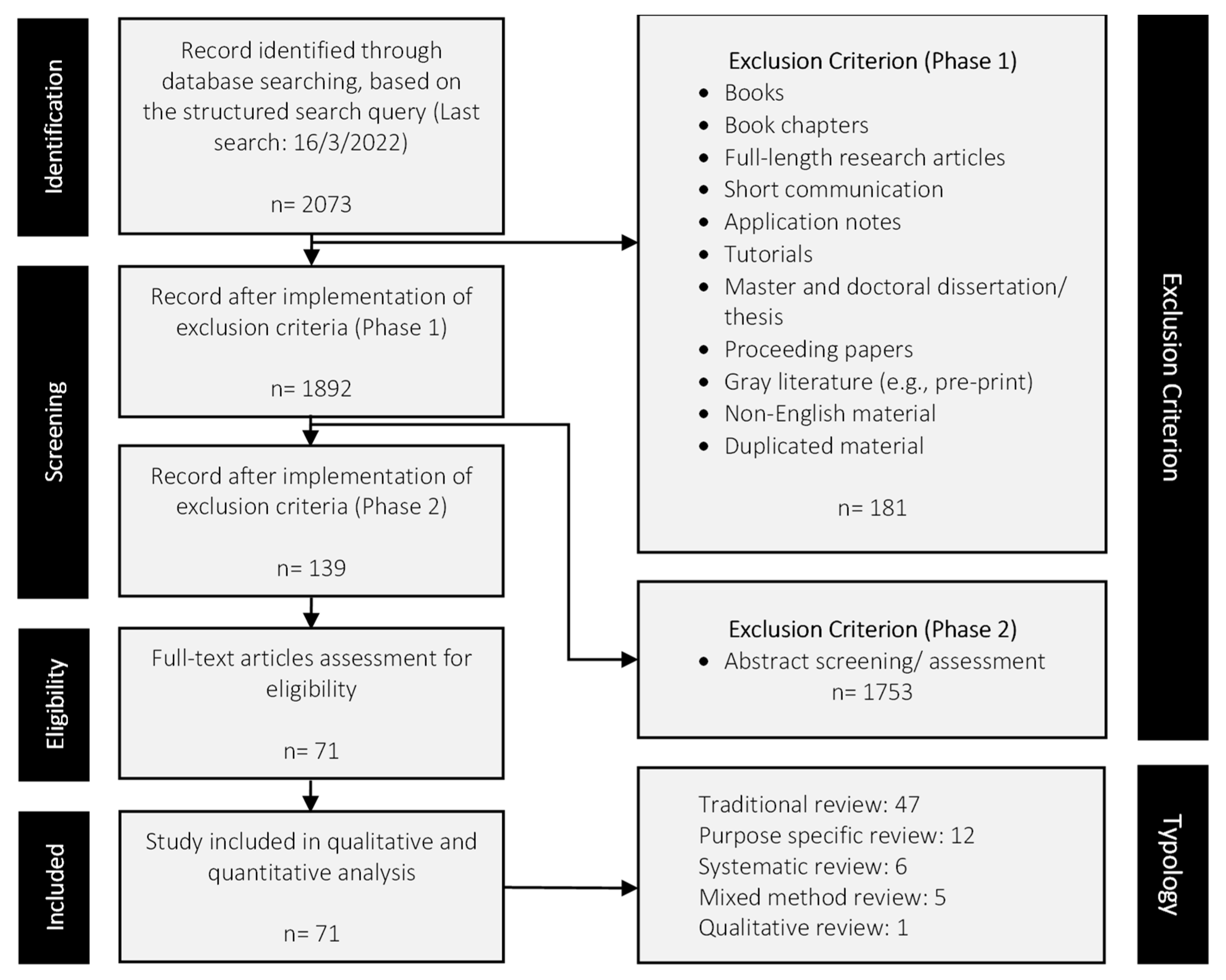
2. Systematic Literature Search Methodology
2.1. Research Question
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Study Selection
2.4. Assessment of Reporting and Study Quality
2.5. Data Extraction
2.6. Data Reporting
2.7. Threats to Study Validity
3. Results
3.1. Typology of the Included Review Works
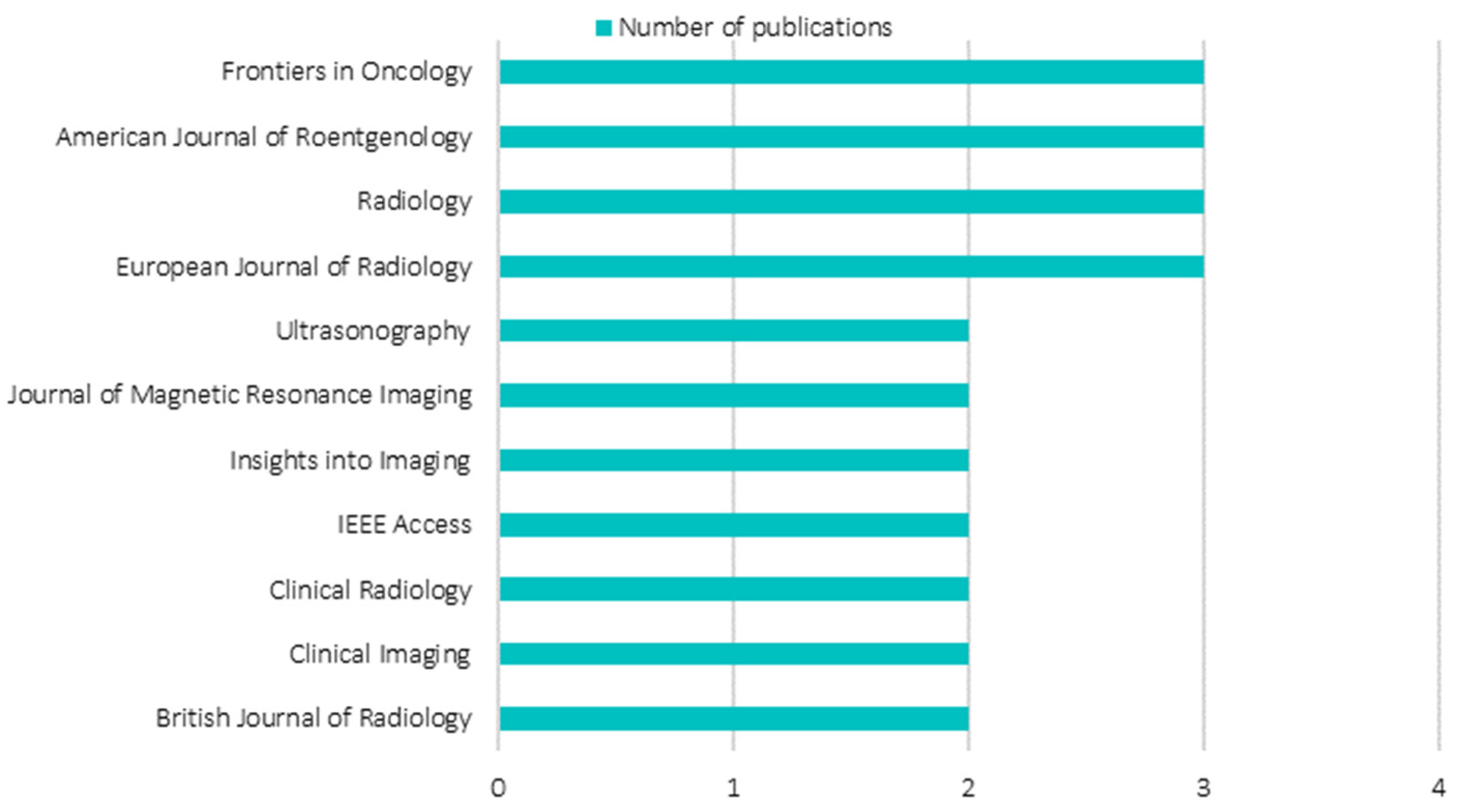
3.2. Distribution of the Most Contributing Journals
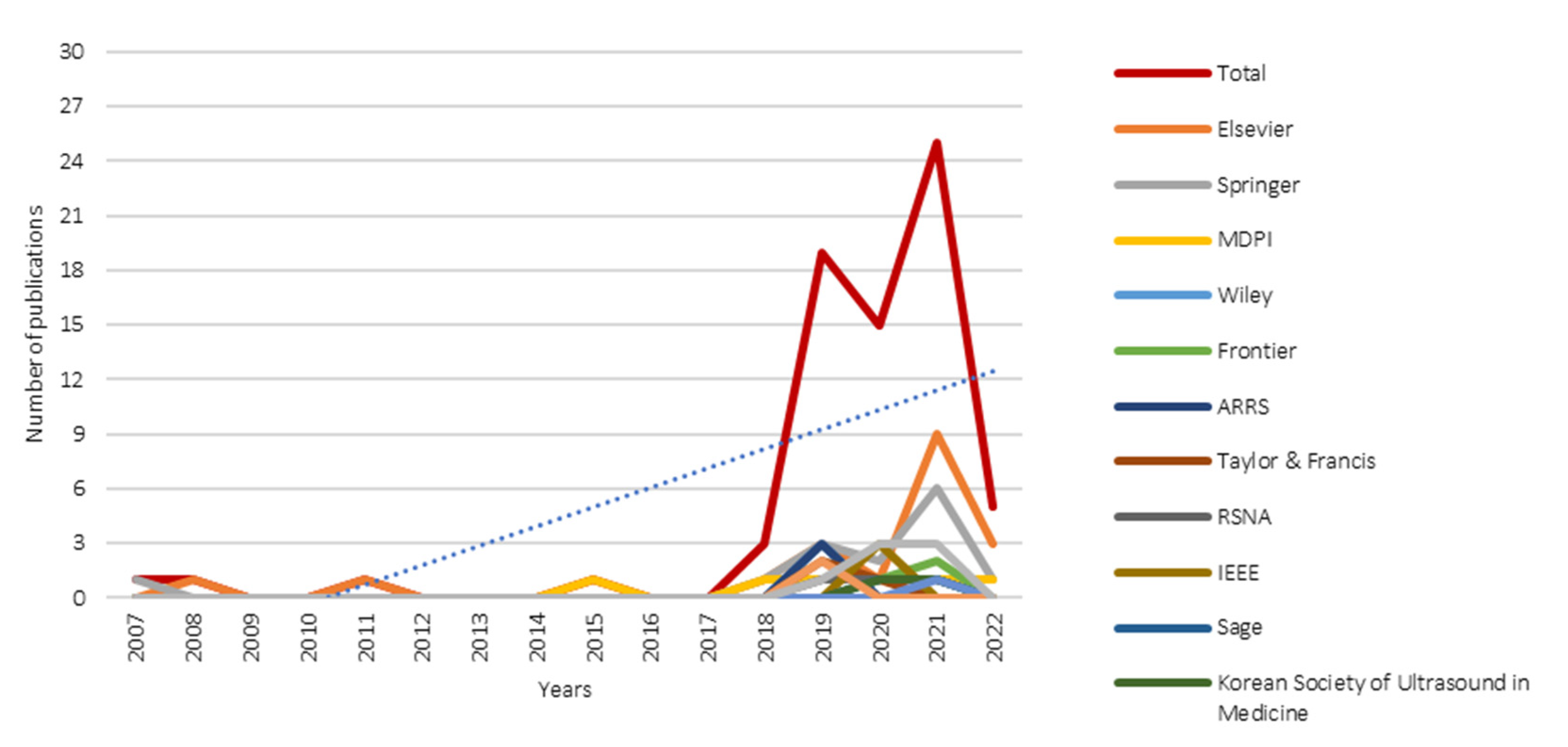
3.3. Distribution of the Most Contributing Publishers
3.4. Temporal Scientometric Analysis
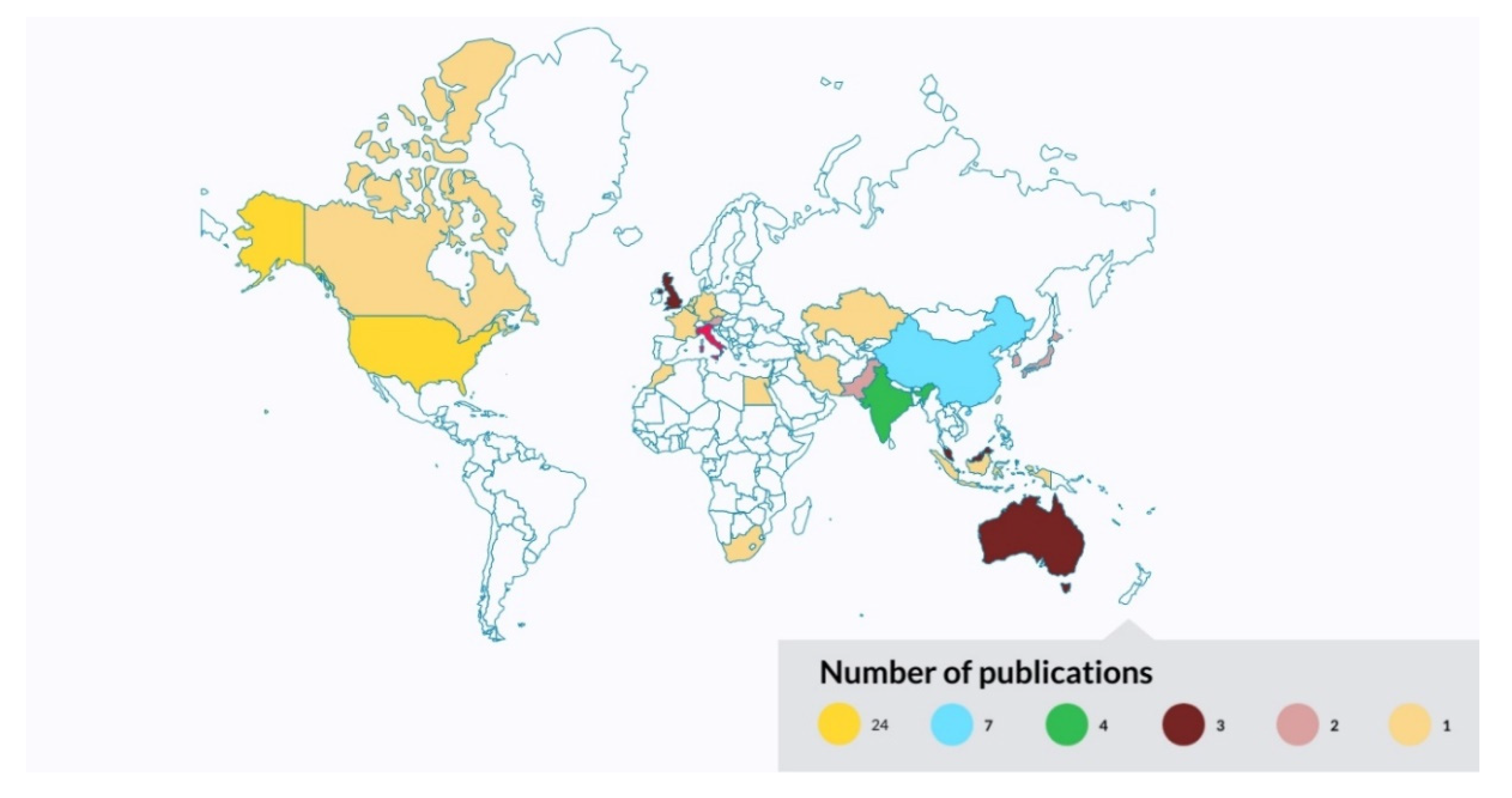
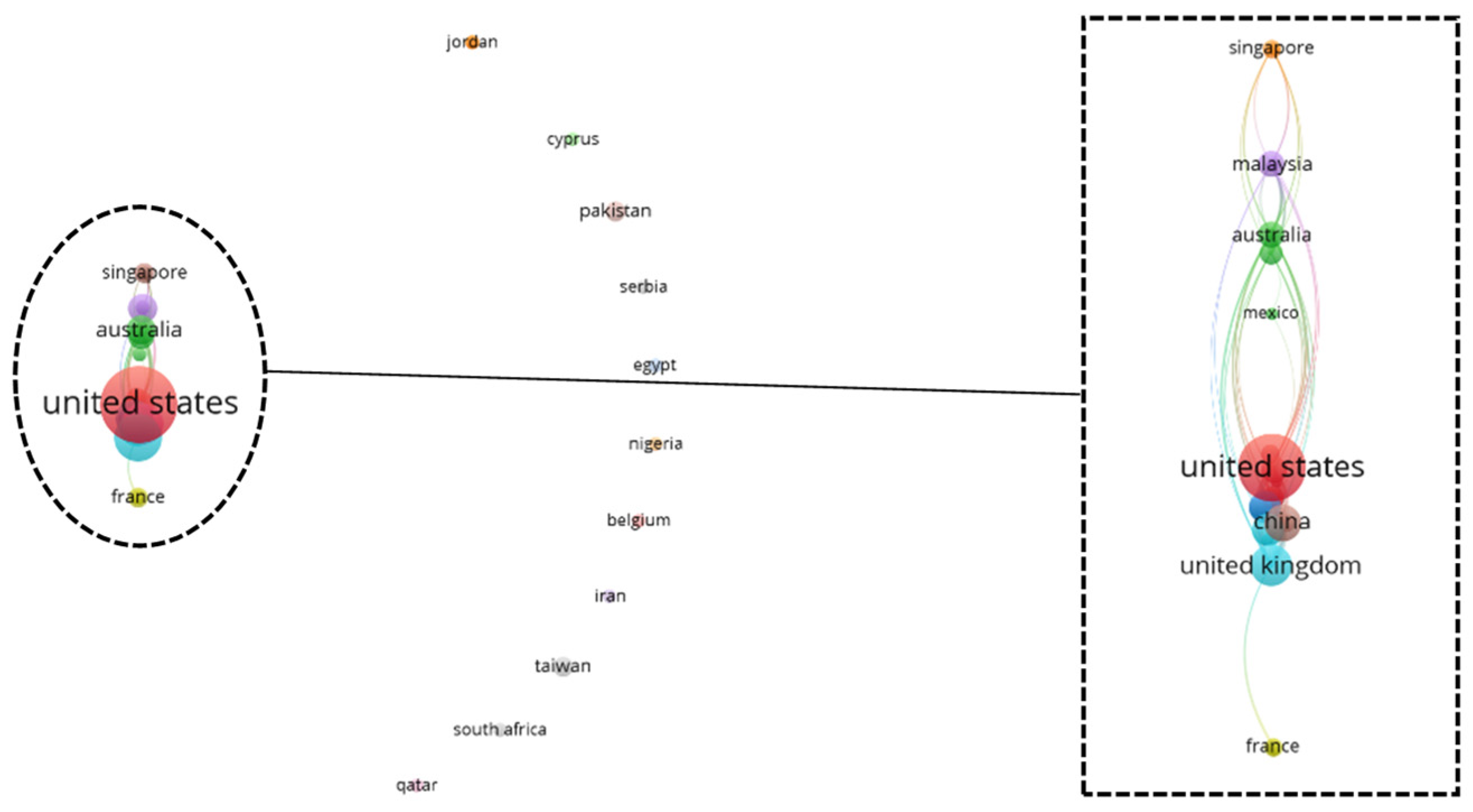
3.5. Geographical Scientometric Analysis
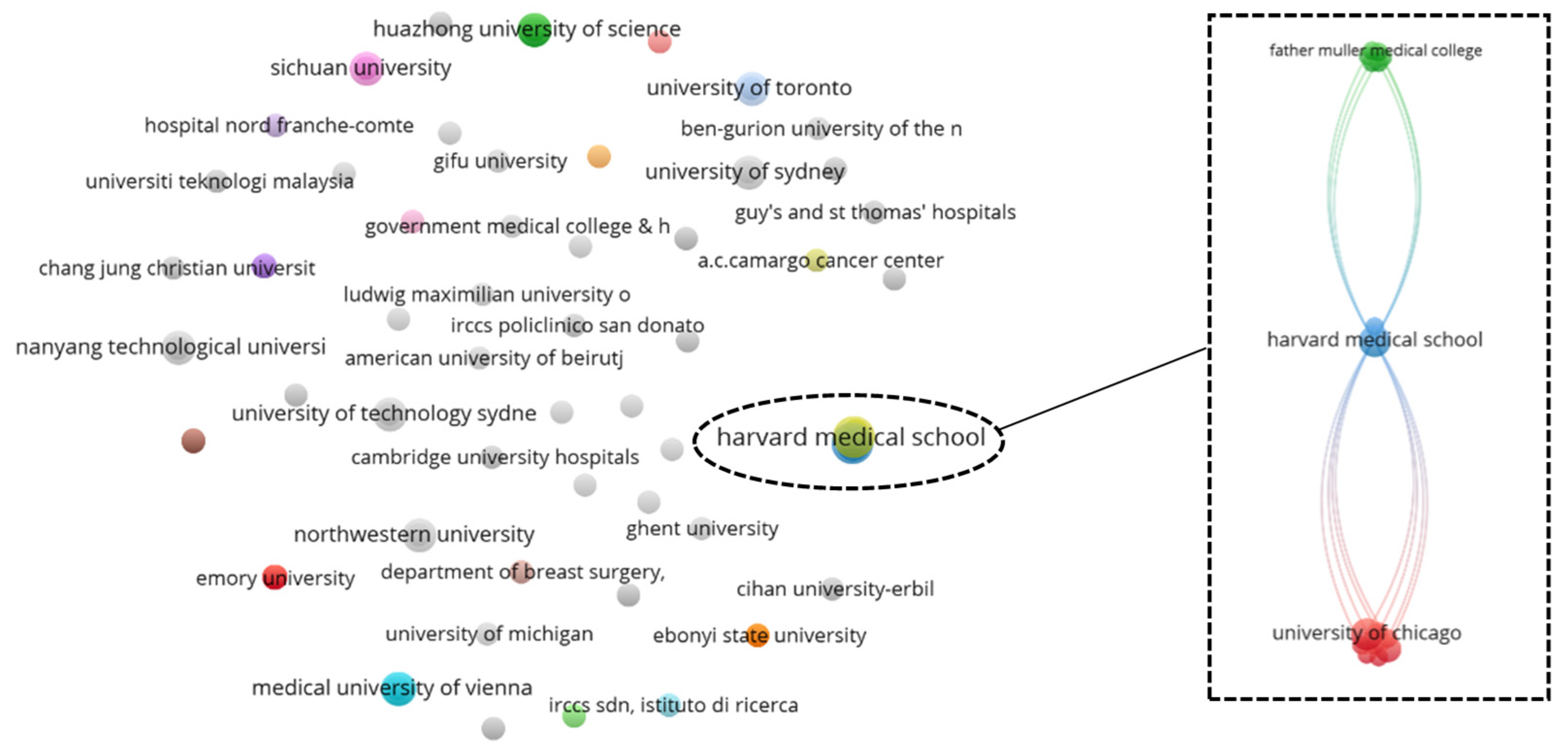
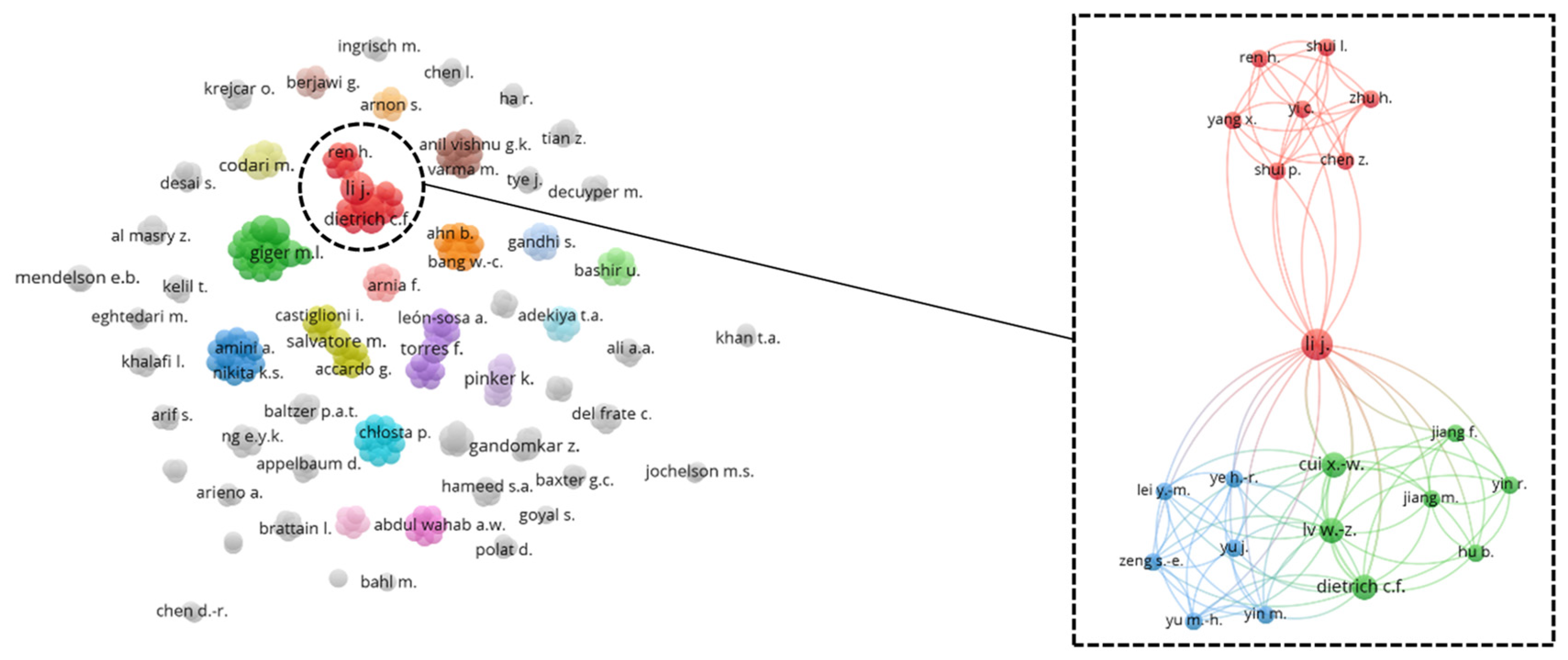
3.6. Bibliographic Coupling Network Analysis: Country
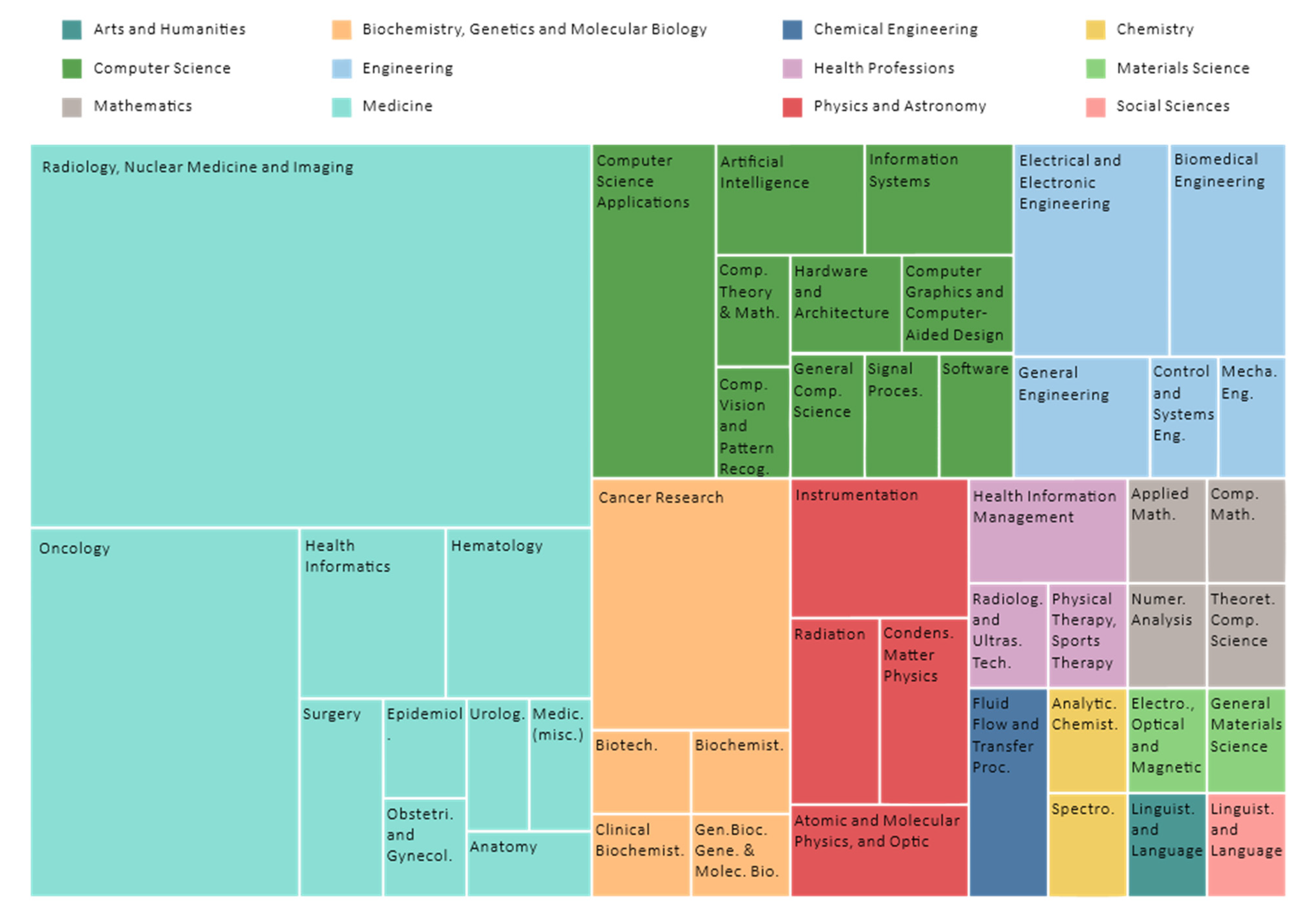
3.7. Subject Area Profiling
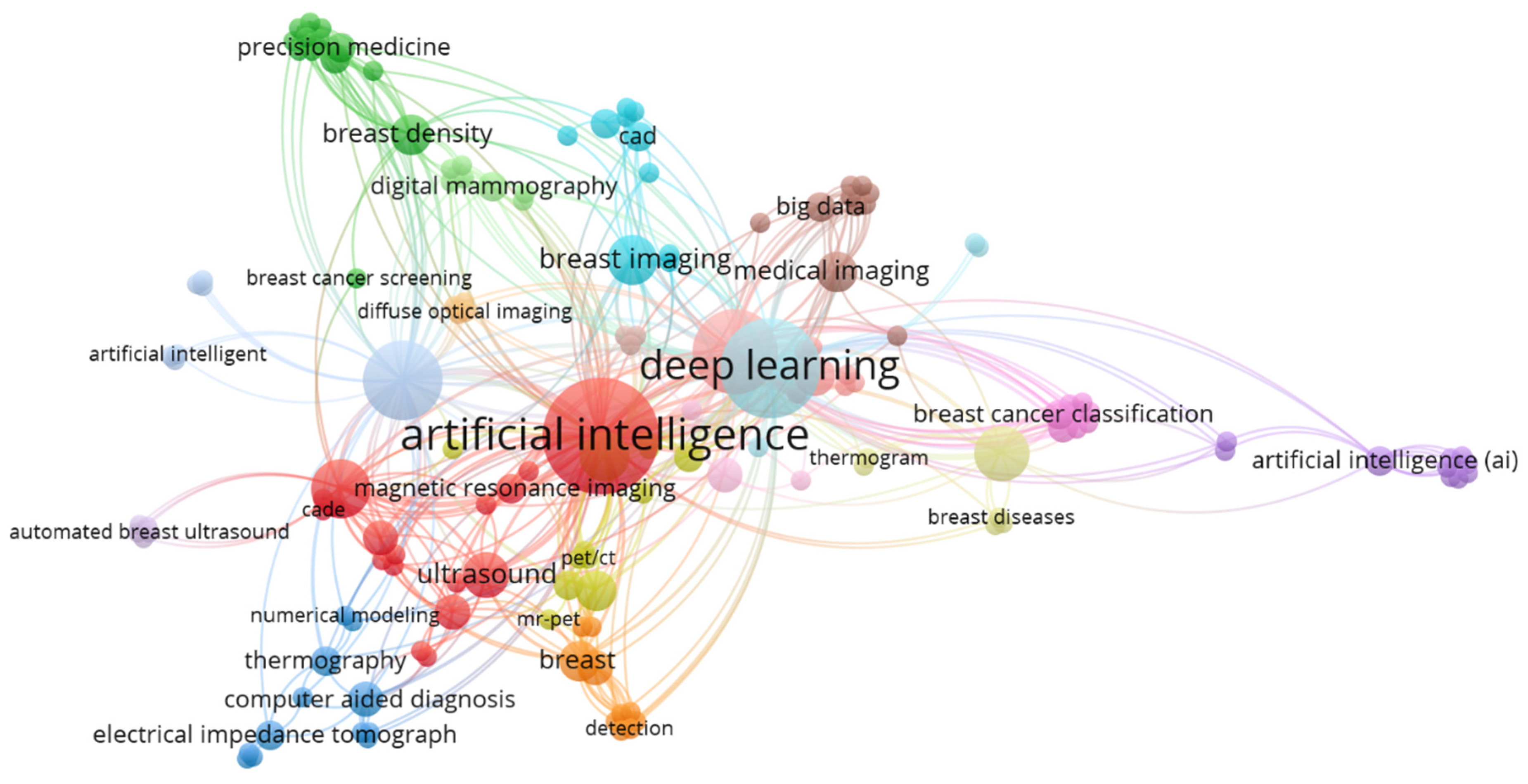
3.8. Keywords Co-Occurrence Network
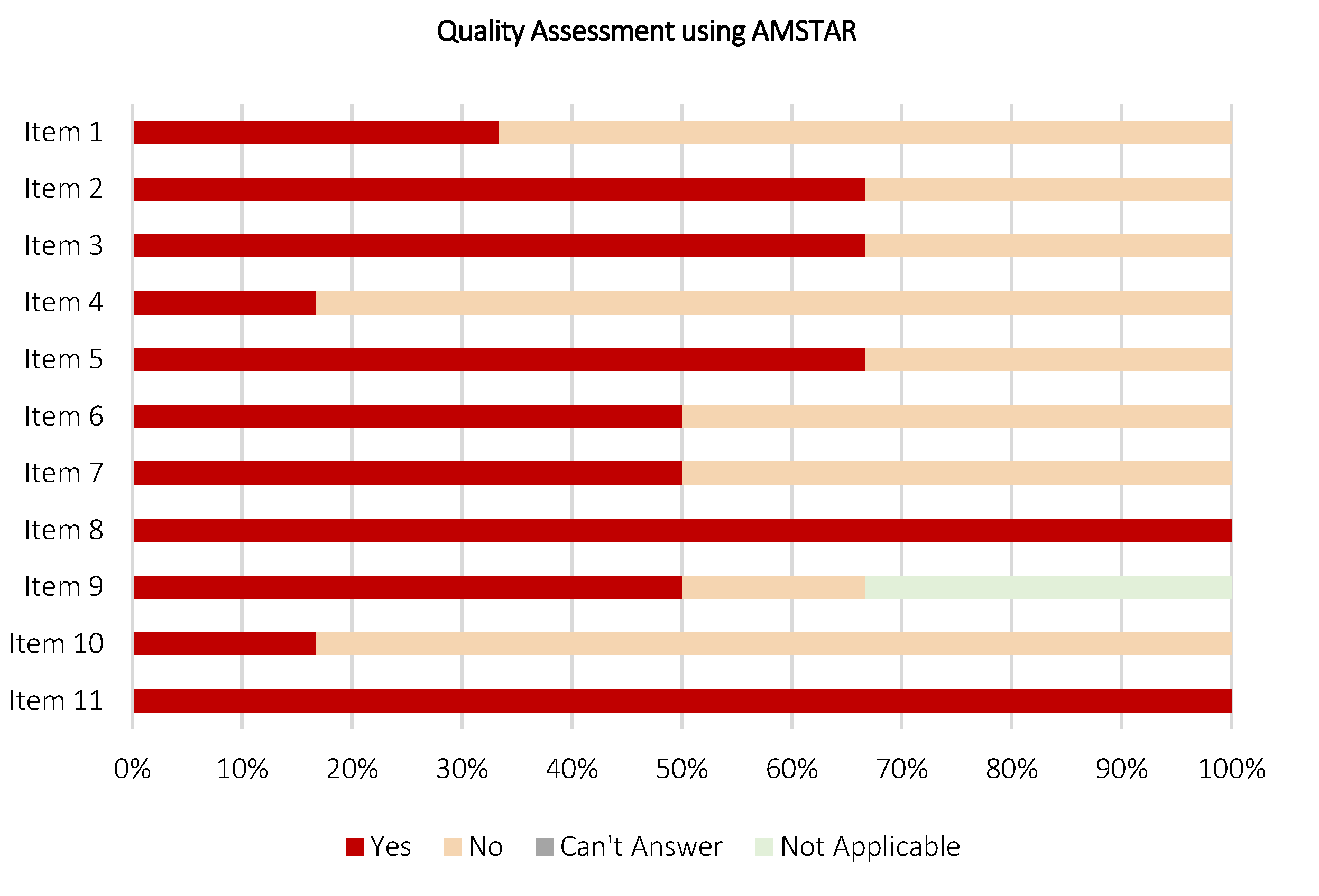
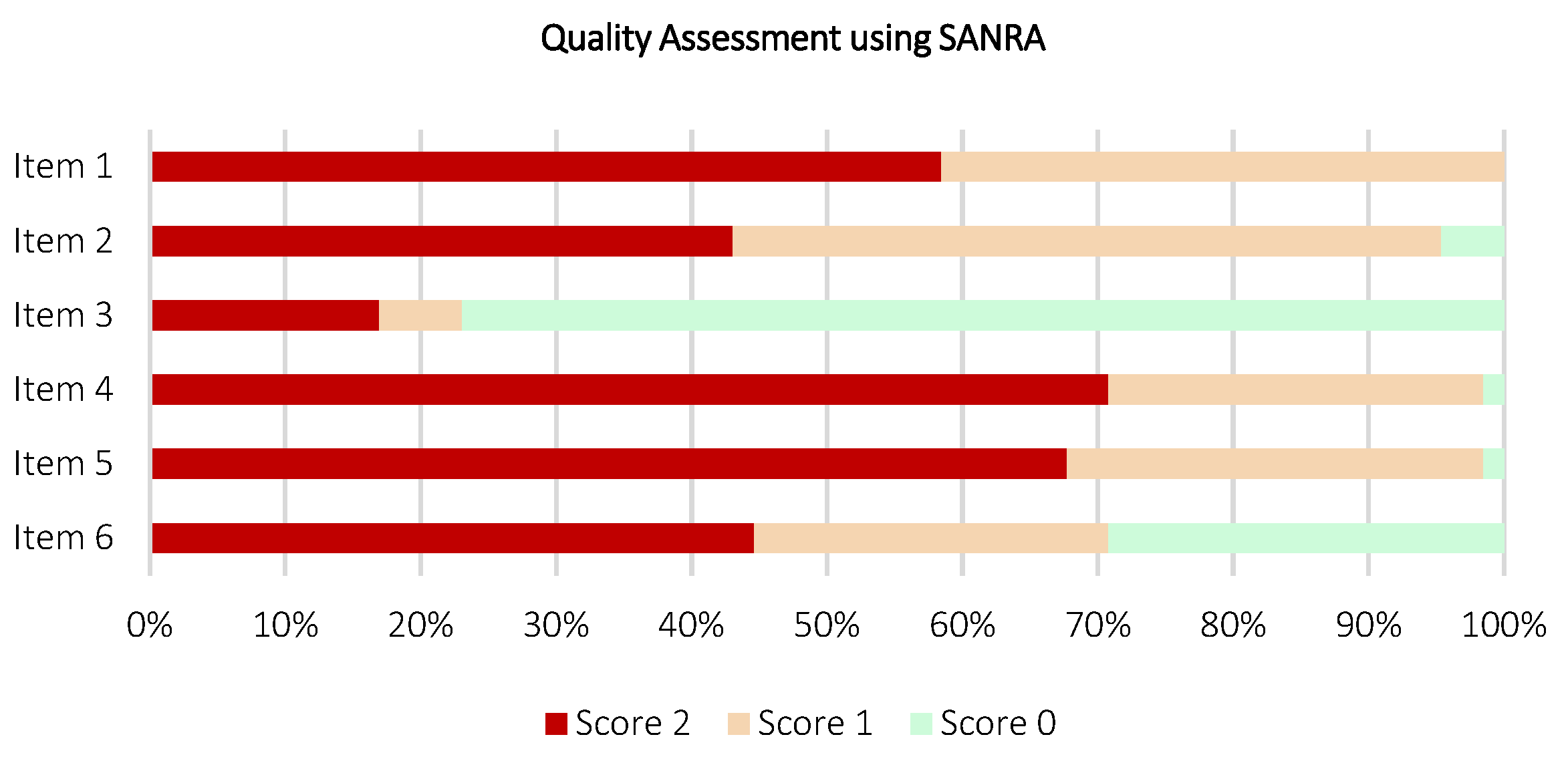
3.9. Quality Assessment of the Included Review Works
4. Self-Assessment, Limitations, Challenges, and Future Direction
4.1. Self-Assessment
4.2. Limitation
4.3. Challenges and Future Direction
5. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| No. | References | Imaging Modalities | AI Techniques | Cited By * | Highlights |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Review | |||||
| 1 | [84] | Thermography | CNN | 21 |
|
| 2 | [85] | Thermography | ANN: RBFN, KNN, PNN, SVM, ResNet50, SeResNet50, V Net, Bayes Net, CNN, C-DCNN, VGG-16, Hybrid (ResNet-50 and V-Net), ResNet101, DenseNet, and InceptionV3 | 11 |
|
| 3 | [86] | X-ray, CT, ultrasound, MRI, nuclear, and microscopy | Deep learning | 38 |
|
| 4 | [87] | Mammogram, ultrasound, and MRI | Machine learning and deep learning | 1 |
|
| 5 | [88] | Mammogram, ultrasound, MRI, FDG PET/CT | Augmented intelligence and machine learning | 16 |
|
| 6 | [89] | Mammogram, ultrasound, MRI, | Machine learning, CADe, ANN, CNN, and NLP | 36 |
|
| 7 | [90] | Mammogram and ultrasound | Machine learning | 1 |
|
| 8 | [91] | Thermography and electrical impedance tomography | Machine learning and CADe | 15 |
|
| 9 | [92] | Transillumination imaging, diffuse optical imaging, and near-infrared spectroscopy | Machine learning | 13 |
|
| 10 | [93] | Mammogram, Tomosynthesis, ultrasound, DBCT, MRI, DWI, CT, NIR fluorescence, and SPECT | SVM, ANN, and robotics | 6 |
|
| 11 | [94] | PET and MRI | Fuzzy logic and neural network | 26 |
|
| 12 | [9] | Mammogram, tomosynthesis, DCE-MRI, and ultrasound | CADe and CADx systems | 449 |
|
| 13 | [95] | MRI | Analytical radiomic-based (human-engineered) and deep learning-based CADe | 44 |
|
| 14 | [96] | MRI | Machine learning and deep learning | 4 |
|
| 15 | [97] | MRI | 3D printing, augmented reality. Radiomics, and machine learning | 12 |
|
| 16 | [98] | Mammogram, ultrasound, and MRI | ANN, CNN, CADe, and GANs | 0 |
|
| 17 | [99] | Mammogram | Machine learning (supervised, unsupervised, reinforcement, and deep learning) | 6 |
|
| 18 | [100] | Mammogram and DBT | Deep learning | 89 |
|
| 19 | [101] | Ultrasonography | CNN | 9 |
|
| 20 | [102] | Mammogram, ultrasound, and MRI | Deep learning and CADe | 32 |
|
| 21 | [103] | Mammogram | Machine learning and radiomics | 19 |
|
| 22 | [104] | Mammogram, sonography, MRI, and image-guided biopsy | Deep learning and radiomics | 2 |
|
| 23 | [105] | Mammogram, ultrasound, PET, and MRI | ANN, SVM, and radiomics | 1 |
|
| 24 | [106] | Ultrasound | Deep learning | 5 |
|
| 25 | [107] | Mammogram and ultrasound | Eye tracking tool and CADe | 10 |
|
| 26 | [108] | Mammogram | CADe, CADx, machine learning, deep learning, and CNN | 48 |
|
| 27 | [109] | Mammogram and tomosynthesis | Deep learning | 0 |
|
| 28 | [110] | Nuclear medicine | Deep learning and radiomics | 1 |
|
| 29 | [111] | MRI, CT, PET, SPECT, ultrasound, tomosynthesis, and radiology | Neural network, deep learning, and machine learning | 227 |
|
| 30 | [112] | Mammogram, ultrasound, MRI, and tomosynthesis | ANN, CADe, CADx, CNN, deep learning, and machine learning | 8 |
|
| 31 | [113] | Mammogram, ultrasound, and MRI | Deep learning | 5 |
|
| 32 | [114] | Mammogram, ultrasound, MRI | SNN, SDAE, DBN, and CNN | 2 |
|
| 33 | [115] | Mammogram, ultrasound, MRI, and tomosynthesis | Deep learning and AI-CADe | 79 |
|
| 34 | [116] | Tomosynthesis, CT, and FDG PET/CT | ANN, DNN, SVM | 84 |
|
| 35 | [117] | Ultrasound | Machine learning and deep learning | 8 |
|
| 36 | [118] | Mammogram, tomosynthesis, ultrasonography, and MRI | CADe, radiomics, IoT, and machine learning tools | 17 |
|
| 37 | [119] | Mammogram and CT | Deep learning, CADe | 6 |
|
| 38 | [120] | Mammogram, ultrasound, PET, CT, and MRI | CADe, ANN | 127 |
|
| 39 | [121] | Ultrasound | CADx | 20 |
|
| 40 | [122] | Mammogram, ultrasound, MRI, and thermography | Machine learning, deep learning, and CADx | 42 |
|
| 41 | [123] | Mammogram | Radiomics | 0 |
|
| 42 | [124] | MRI and DCE-MRI | Radiogenomics | 0 |
|
| 43 | [125] | Tomosynthesis, MRI, ultrasound, MBI | Machine learning and CADx | 3 |
|
| 44 | [126] | Thermography | SVM, ANN, and CADx | 42 |
|
| 45 | [127] | Mammogram | AI-CADe | 62 |
|
| 46 | [128] | Mammogram and MRI | CNN | 1 |
|
| 47 | [70] | General breast imaging | Machine learning, ANN, deep learning | 11 |
|
| Purpose Specific Review | |||||
| 48 | [129] | Mammogram, ultrasound, SWE, SWV, and sonoelastography | CADx, SVM, CNN, LASSO, and ridge regression | 4 |
|
| 49 | [130] | Mammogram, ultrasound, and MRI | Deep learning and radiogenomics | 13 |
|
| 50 | [131] | Mammogram, ultrasound, and tomosynthesis | Machine learning and deep learning | 54 |
|
| 51 | [132] | EIT | PSO, ANN, GA, and other machine learning algorithms | 44 |
|
| 52 | [133] | DOT | Deep learning | 3 |
|
| 53 | [134] | Ultrasound | Deep learning | 2 |
|
| 54 | [135] | PET/CT and PET/MRI | Radiomics | 16 |
|
| 55 | [136] | Mammogram | CADe and CADx | 28 |
|
| 56 | [137] | Mammogram, ultrasound, DBT, and MRI | Deep learning, CADe, and CADx | 3 |
|
| 57 | [138] | Ultrasound | CADe and CNN | 0 |
|
| 58 | [139] | Thermography | SVM, ANN, BN, CADe, CNN, and GA | 0 |
|
| 59 | [140] | Thermography | ANN | 13 |
|
| Systematic Review | |||||
| 60 | [141] | Mammogram, ultrasound, MRI, DBPET, DWI, PWI, CT, PET/CT, and PET/MRI | Radiomics, machine learning, and deep learning | 5 |
|
| 61 | [142] | Thermography | SVM, ANN, DNN, and RNN | 81 |
|
| 62 | [143] | Mammogram, CT, and MRI | Machine learning, deep learning, and ANN, | 1 |
|
| 63 | [144] | Mammogram, ultrasound, CT, and MRI | Deep CNN | 2 |
|
| 64 | [65] | Mammogram, DCE-MRI | Machine learning and deep learning | 3 |
|
| 65 | [64] | Mammogram, ultrasound | CNN, ANN, DNN, MLP, SVM, DT, GA, KNN, NB, LR, LA, and GMM | 12 |
|
| Mixed Method Review | |||||
| 66 | [145] | Ultrasound and tomosynthesis | DNN, RCNN, faster RCNN, deep CNN, and ReLU | 4 |
|
| 67 | [146] | Mammogram, tomosynthesis, ultrasound, tomography, and MRI | Multilayered DNN | 12 |
|
| 68 | [147] | Mammogram and MRI | Radiomics | 22 |
|
| 69 | [148] | MRI | Machine learning and transfer learning | 0 |
|
| 70 | [149] | Mammogram, ultrasound, and MRI | ANN, SNN, CNN, and CADe | 41 |
|
| Qualitative Review | |||||
| 71 | [150] | Mammogram, CT, and MRI | Machine learning | 51 |
|
| No. | References | Items | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | ||
| Systematic Review | ||||||||||||
| 1 | [141] | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | ∅ | − | + |
| 2 | [142] | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | ∅ | − | + |
| 3 | [143] | − | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | − | + |
| 4 | [144] | − | + | + | − | + | + | − | + | − | − | + |
| 5 | [65] | + | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | − | + |
| 6 | [64] | + | + | + | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | + |
| Analysis | ||||||||||||
| + | 2 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 6 | 3 | 1 | 6 | |
| − | 4 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 5 | 0 | |
| ⊗ | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| ∅ | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total | 6 | |||||||||||
| No. | References | Items | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||
| Traditional Review | |||||||
| 1 | [84] | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 2 | [85] | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 3 | [86] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 4 | [87] | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 5 | [88] | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| 6 | [89] | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 7 | [90] | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 8 | [91] | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 9 | [92] | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 10 | [93] | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 11 | [94] | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 12 | [9] | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 13 | [95] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 14 | [96] | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 15 | [97] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| 16 | [98] | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 17 | [99] | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 18 | [100] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 19 | [101] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 20 | [102] | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 21 | [103] | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 22 | [104] | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 23 | [105] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 24 | [106] | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 25 | [70] | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 26 | [107] | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 27 | [108] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 28 | [109] | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 29 | [110] | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 30 | [111] | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| 31 | [112] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 32 | [113] | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| 33 | [114] | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 34 | [115] | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| 35 | [116] | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 36 | [117] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| 37 | [118] | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 38 | [119] | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| 39 | [120] | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 40 | [121] | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 41 | [122] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 42 | [123] | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 43 | [124] | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 44 | [125] | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 45 | [126] | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 46 | [127] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 47 | [128] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Purpose Specific Review | |||||||
| 48 | [129] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 49 | [130] | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 50 | [131] | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 51 | [132] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 52 | [133] | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 53 | [134] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 54 | [135] | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 55 | [136] | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 56 | [137] | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 57 | [138] | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 58 | [139] | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| 59 | [140] | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Mixed Method Review | |||||||
| 60 | [145] | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 61 | [146] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 62 | [147] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 63 | [148] | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 64 | [149] | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Qualitative Review | |||||||
| 65 | [150] | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| Analysis | |||||||
| Score 0 | 0 | 3 | 50 | 1 | 1 | 19 | |
| Score 1 | 27 | 34 | 4 | 18 | 20 | 17 | |
| Score 2 | 38 | 28 | 11 | 46 | 44 | 29 | |
| Total | 65 | ||||||
References
- Faguet, G.B. A brief history of cancer: Age-old milestones underlying our current knowledge database. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 2022–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US National Library of Medicine. An ancient Medical Treasure at your fingertips. NLM Tech Bull 2010. Available online: https://www.nlm.nih.gov/pubs/techbull/ma10/ma10_hmd_reprint_papyrus.html (accessed on 30 October 2022).
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, J.; Zhou, C.; Guo, X.; Sun, J.; Xue, F.; Zhang, J.; Lu, Z.; Fu, Z.; Xu, A. Female Breast Cancer Mortality Clusters in Shandong Province, China: A Spatial Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akin, O.; Brennan, S.; Dershaw, D.D.; Ginsberg, M.S.; Gollub, M.J.; Schöder, H.; Panicek, D.; Hricak, H. Advances in oncologic imaging. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2012, 62, 364–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, W.P. Breast cancer screening: Successes and challenges. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2012, 62, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, S.W.; Tabár, L.; Yen, A.M.; Dean, P.B.; Smith, R.A.; Jonsson, H.; Törnberg, S.; Chen, S.L.-S.; Chiu, S.Y.; Fann, J.C.; et al. Mammography screening reduces rates of advanced and fatal breast cancers: Results in 549,091 women. Cancer 2020, 126, 2971–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napel, S.; Mu, W.; Jardim-Perassi, B.V.; Aerts, H.J.W.L.; Gillies, R.J. Quantitative imaging of cancer in the postgenomic era: Radio(geno)mics, deep learning, and habitats. Cancer 2018, 124, 4633–4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, W.L.; Hosny, A.; Schabath, M.B.; Giger, M.L.; Birkbak, N.; Mehrtash, A.; Allison, T.; Arnaout, O.; Abbosh, C.; Dunn, I.F.; et al. Artificial intelligence in cancer imaging: Clinical challenges and applications. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 127–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.; Deng, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhou, J.; Jia, X.; Xiao, T.; Zhou, S.; Li, J.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Lymph node metastasis prediction of papillary thyroid carcinoma based on transfer learning radiomics. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Herrington, D.M. Machine intelligence enabled radiomics. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2021, 3, 838–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Whitehead, T.D.; Quirk, J.D.; Salter, A.; Ademuyiwa, F.O.; Li, S.; An, H.; Shoghi, K.I. Optimal co-clinical radiomics: Sensitivity of radiomic features to tumour volume, image noise and resolution in co-clinical T1-weighted and T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Ebiomedicine 2020, 59, 102963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, L.P.; Nordstrom, R.J.; Zhang, H.; Tandon, P.; Zhang, Y.; Redmond, G.; Farahani, K.; Kelloff, G.; Henderson, L.; Shankar, L.; et al. The Quantitative Imaging Network: NCI’s Historical Perspective and Planned Goals. Transl. Oncol. 2014, 7, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nordstrom, R.J. The Quantitative Imaging Network in Precision Medicine. Tomography 2016, 2, 239–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Timmeren, J.E.; Cester, D.; Tanadini-Lang, S.; Alkadhi, H.; Baessler, B. Radiomics in medical imaging-”how-to” guide and critical reflection. Insights Imaging 2020, 11, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, W.; Seetha, S.T.; Refaee, T.A.G.; Lieverse, R.I.Y.; Granzier, R.W.Y.; Ibrahim, A.; Keek, S.A.; Sanduleanu, S.; Primakov, S.P.; Beuque, M.P.L.; et al. Radiomics: From qualitative to quantitative imaging. Br. J. Radiol. 2020, 93, 20190948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, R.J.; Kinahan, P.E.; Hricak, H. Radiomics: Images Are More than Pictures, They Are Data. Radiology 2016, 278, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aerts, H.J.W.L. The Potential of Radiomic-Based Phenotyping in Precision Medicine. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 1636–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Whitehead, T.D.; Li, S.; Ademuyiwa, F.O.; Wahl, R.L.; Dehdashti, F.; Shoghi, K.I. Co-clinical FDG-PET radiomic signature in predicting response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 49, 550–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnih, V.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Silver, D.; Rusu, A.A.; Veness, J.; Bellemare, M.G.; Graves, A.; Riedmiller, M.; Fidjeland, A.K.; Ostrovski, G.; et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature 2015, 518, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moravčík, M.; Schmid, M.; Burch, N.; Lisý, V.; Morrill, D.; Bard, N.; Davis, T.; Waugh, K.; Johanson, M.; Bowling, M. DeepStack: Expert-level artificial intelligence in heads-up no-limit poker. Science 2017, 356, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, W.; Droppo, J.; Huang, X.; Seide, F.; Seltzer, M.L.; Stolcke, A.; Yu, D.; Zweig, G. Toward Human Parity in Conversational Speech Recognition. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2017, 25, 2410–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendleton, S.D.; Andersen, H.; Du, X.; Shen, X.; Meghjani, M.; Eng, Y.H.; Rus, D.; Ang, M. Perception, Planning, Control, and Coordination for Autonomous Vehicles. Machines 2017, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosny, A.; Parmar, C.; Quackenbush, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Artificial intelligence in radiology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, A.; Clowes, M.; Preston, L.; Booth, A. Meeting the review family: Exploring review types and associated information retrieval requirements. Health Inf. Libr. J. 2019, 36, 202–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slim, K.; Marquillier, T. Umbrella reviews: A new tool to synthesize scientific evidence in surgery. J. Visc. Surg. 2022, 159, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Song, M. Visualizing a field of research: A methodology of systematic scientometric reviews. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalaf, J.M. Mammography: A history of success and scientific enthusiasm. Radiol. Bras. 2014, 47, VII–VIII. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trivedi, U.; Omofoye, T.S.; Marquez, C.; Sullivan, C.R.; Benson, D.M.; Whitman, G.J. Mobile Mammography Services and Underserved Women. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, V.M.; Levin, D.C.; Parker, L.; Cavanaugh, B.; Frangos, A.J.; Sunshine, J.H. How Widely Is Computer-Aided Detection Used in Screening and Diagnostic Mammography? J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2010, 7, 802–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britt, K.L.; Cuzick, J.; Phillips, K.-A. Key steps for effective breast cancer prevention. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 417–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loibl, S.; Poortmans, P.; Morrow, M.; Denkert, C.; Curigliano, G. Breast cancer. Lancet 2021, 397, 1750–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iranmakani, S.; Mortezazadeh, T.; Sajadian, F.; Ghaziani, M.F.; Ghafari, A.; Khezerloo, D.; Musa, A.E. A review of various modalities in breast imaging: Technical aspects and clinical outcomes. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2020, 51, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friedewald, S.M. Breast Cancer Screening: The Debate that Never Ends. Optim. Breast Cancer Manag. 2018, 173, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheel, J.R.; Lee, J.M.; Sprague, B.L.; Lee, C.I.; Lehman, C.D. Screening ultrasound as an adjunct to mammography in women with mammographically dense breasts. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 212, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ohuchi, N.; Suzuki, A.; Sobue, T.; Kawai, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Zheng, Y.-F.; Shiono, Y.N.; Saito, H.; Kuriyama, S.; Tohno, E.; et al. Sensitivity and specificity of mammography and adjunctive ultrasonography to screen for breast cancer in the Japan Strategic Anti-cancer Randomized Trial (J-START): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada-Shoji, N.; Suzuki, A.; Ishida, T.; Zheng, Y.-F.; Narikawa-Shiono, Y.; Sato-Tadano, A.; Ohta, R.; Ohuchi, N. Evaluation of Adjunctive Ultrasonography for Breast Cancer Detection Among Women Aged 40–49 Years With Varying Breast Density Undergoing Screening Mammography. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2121505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, V.; Enslin, S.; Gross, S.A. History of artificial intelligence in medicine. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2020, 92, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamamoto, R.; Suvarna, K.; Yamada, M.; Kobayashi, K.; Shinkai, N.; Miyake, M.; Takahashi, M.; Jinnai, S.; Shimoyama, R.; Sakai, A.; et al. Application of Artificial Intelligence Technology in Oncology: Towards the Establishment of Precision Medicine. Cancers 2020, 12, 3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luchini, C.; Pea, A.; Scarpa, A. Artificial intelligence in oncology: Current applications and future perspectives. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 126, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teare, P.; Fishman, M.; Benzaquen, O.; Toledano, E.; Elnekave, E. Malignancy Detection on Mammography Using Dual Deep Convolutional Neural Networks and Genetically Discovered False Color Input Enhancement. J. Digit. Imaging 2017, 30, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenbagavalli, P.; Thangarajan, R. Aiding the Digital Mammogram for Detecting the Breast Cancer Using Shearlet Transform and Neural Network. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2018, 19, 2665–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A.; Marcon, M.; Ghafoor, S.; Wurnig, M.C.; Frauenfelder, T.; Boss, A. Deep Learning in Mammography. Investig. Radiol. 2017, 52, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oren, O.; Gersh, B.J.; Bhatt, D.L. Artificial intelligence in medical imaging: Switching from radiographic pathological data to clinically meaningful endpoints. Lancet Digit. Health 2020, 2, e486–e488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heuvel, T.V.D.; van der Eerden, A.; Manniesing, R.; Ghafoorian, M.; Tan, T.; Andriessen, T.; Vyvere, T.V.; Hauwe, L.V.D.; Romeny, B.T.H.; Goraj, B.; et al. Automated detection of cerebral microbleeds in patients with traumatic brain injury. NeuroImage Clin. 2016, 12, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Greene, F.L.; Sobin, L.H. The Staging of Cancer: A Retrospective and Prospective Appraisal. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2008, 58, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Santos, M.; Gomes, C.; Marcos, R.; Santos, A.; De Matos, A.; Lopes, C.; Dias-Pereira, P. Value of the Nottingham Histological Grading Parameters and Nottingham Prognostic Index in Canine Mammary Carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 4127–4219. [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe, C.C. Measures of Response: RECIST, WHO, and New Alternatives. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 3245–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, L.M.; Rowe, R.G.; Acharya, P.T.; Swenson, D.W.; Meyer, S.C.; Clinton, C.M.; Guo, D.; Sridharan, M.; London, W.B.; Grier, H.E.; et al. Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) following neoadjuvant chemotherapy in osteosarcoma. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2018, 65, e26896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laney, D. 3D data management: Controlling data volume, velocity, and variety. META Group Res. Note 2001, 6, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Dash, S.; Shakyawar, S.K.; Sharma, M.; Kaushik, S. Big data in healthcare: Management, analysis and future prospects. J. Big Data 2019, 6, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Int. J. Surg. 2021, 88, 105906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shea, B.J.; Grimshaw, J.M.; A Wells, G.; Boers, M.; Andersson, N.; Hamel, C.; Porter, A.C.; Tugwell, P.; Moher, D.; Bouter, L.M. Development of AMSTAR: A measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2007, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baethge, C.; Goldbeck-Wood, S.; Mertens, S. SANRA—A scale for the quality assessment of narrative review articles. Res. Integr. Peer Rev. 2019, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perianes-Rodriguez, A.; Waltman, L.; van Eck, N.J. Constructing bibliometric networks: A comparison between full and fractional counting. J. Inf. 2016, 10, 1178–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larivière, V.; Haustein, S.; Mongeon, P. The Oligopoly of Academic Publishers in the Digital Era. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Association, I.P. The Global Publishing Industry in 2018. Available online: https://www.wipo.int/edocs/pubdocs/en/wipo_pub_1064_2019.pdf (accessed on 17 June 2022).
- Tan, X.J.; Cheor, W.L.; Yeo, K.S.; Leow, W.Z. Expert systems in oil palm precision agriculture: A decade systematic review. J. King Saud Univ. -Comput. Inf. Sci. 2022, 34, 1569–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momeni, F.; Mayr, P.; Fraser, N.; Peters, I. What happens when a journal converts to open access? A bibliometric analysis. Scientometrics 2021, 126, 9811–9827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaston, T.E.; Ounsworth, F.; Senders, T.; Ritchie, S.; Jones, E. Factors affecting journal submission numbers: Impact factor and peer review reputation. Learn. Publ. 2020, 33, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanyam, K. Bibliometric studies of research collaboration: A review. J. Inf. Sci. 1983, 6, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egghe, L.; Rousseau, R. Co-citation, bibliographic coupling and a characterization of lattice citation networks. Scientometrics 2002, 55, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerouaoui, H.; Idri, A. Reviewing Machine Learning and Image Processing Based Decision-Making Systems for Breast Cancer Imaging. J. Med. Syst. 2021, 45, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, Y.; Gupta, S.; Singla, R.; Hu, Y.-C. A Systematic Review of Artificial Intelligence Techniques in Cancer Prediction and Diagnosis. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2022, 29, 2043–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieper, D.; Lorenz, R.C.; Rombey, T.; Jacobs, A.; Rissling, O.; Freitag, S.; Matthias, K. Authors should clearly report how they derived the overall rating when applying AMSTAR 2—A cross-sectional study. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2021, 129, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, C.; Wang, R.; Liu, Z.; Wang, M.; Tan, H.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Sun, H.; Yang, R.; et al. Annotation-efficient deep learning for automatic medical image segmentation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aganj, I.; Harisinghani, M.G.; Weissleder, R.; Fischl, B. Unsupervised Medical Image Segmentation Based on the Local Center of Mass. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purushotham, S.; Meng, C.; Che, Z.; Liu, Y. Benchmarking deep learning models on large healthcare datasets. J. Biomed. Inform. 2018, 83, 112–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickman, S.E.; Baxter, G.C.; Gilbert, F.J. Adoption of artificial intelligence in breast imaging: Evaluation, ethical constraints and limitations. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 125, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ginneken, B.; Schaefer-Prokop, C.M.; Prokop, M. Computer-aided Diagnosis: How to Move from the Laboratory to the Clinic. Radiology 2011, 261, 719–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilad-Bachrach, R.; Dowlin, N.; Laine, K.; Lauter, K.; Naehrig, M.; Wernsing, J. CryptoNets: Applying Neural Networks to Encrypted Data with High Throughput and Accuracy. Microsoft Res. Technol. Rep. 2016, 48, 1–12. Available online: http://proceedings.mlr.press/v48/gilad-bachrach16.pdf%0Ahttp://research.microsoft.com/apps/pubs/?id=260989 (accessed on 30 October 2022).
- George, A.; Walsh, T. Artificial intelligence is breaking patent law. Nature 2022, 605, 616–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serafimova, S. Whose morality? Which rationality? Challenging artificial intelligence as a remedy for the lack of moral enhancement. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2020, 7, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köbis, N.; Bonnefon, J.-F.; Rahwan, I. Bad machines corrupt good morals. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2021, 5, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, R. Artificial intelligence predicts patients’ race from their medical images. MIT News, 17 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Tsamados, A.; Aggarwal, N.; Cowls, J.; Morley, J.; Roberts, H.; Taddeo, M.; Floridi, L. The ethics of algorithms: Key problems and solutions. AI Soc. 2022, 37, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, S.R.H.; Speth, R.; Eastham, S.; Dedoussi, I.C.; Ashok, A.; Malina, R.; Keith, D.W. Impact of the Volkswagen emissions control defeat device on US public health. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 114005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challenges in digital medicine applications in under-resourced settings. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3020. [CrossRef]
- Vourgidis, I.; Mafuma, S.J.; Wilson, P.; Carter, J.; Cosma, G. Medical Expert Systems—A Study of Trust and Acceptance by Healthcare Stakeholders; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Phillips, R.V.; Malenica, I.; Bishara, A.; Hubbard, A.E.; Celi, L.A.; Pirracchio, R. Clinical artificial intelligence quality improvement: Towards continual monitoring and updating of AI algorithms in healthcare. Npj Digit. Med. 2022, 5, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, N. On the Road to Convergence Research. BioScience 2019, 69, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, A.M.; Ahmed, M.E.; Pavlidis, I. Grand challenges and emergent modes of convergence science. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2021, 8, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roslidar, R.; Rahman, A.; Muharar, R.; Syahputra, M.R.; Arnia, F.; Syukri, M.; Pradhan, B.; Munadi, K. A Review on Recent Progress in Thermal Imaging and Deep Learning Approaches for Breast Cancer Detection. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 116176–116194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Husaini, M.A.S.; Habaebi, M.H.; Hameed, S.A.; Islam, R.; Gunawan, T.S. A Systematic Review of Breast Cancer Detection Using Thermography and Neural Networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 208922–208937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panayides, A.S.; Amini, A.; Filipovic, N.D.; Sharma, A.; Tsaftaris, S.A.; Young, A.A.; Foran, D.J.; Do, N.V.; Golemati, S.; Kurc, T.; et al. AI in Medical Imaging Informatics: Current Challenges and Future Directions. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2020, 24, 1837–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.-M.; Yin, M.; Yu, M.-H.; Yu, J.; Zeng, S.-E.; Lv, W.-Z.; Li, J.; Ye, H.-R.; Cui, X.-W.; Dietrich, C.F. Artificial Intelligence in Medical Imaging of the Breast. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 600557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arieno, A.; Chan, A.; Destounis, S.V. A Review of the Role of Augmented Intelligence in Breast Imaging: From Automated Breast Density Assessment to Risk Stratification. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2019, 212, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellen, B.M. Artificial Intelligence in Breast Imaging: Potentials and Limitations. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2019, 212, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Chou, S.-H.S.; Brattain, L.; Lehman, C.D.; Samir, A.E. Data Engineering for Machine Learning in Women’s Imaging and Beyond. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2019, 213, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuluaga-Gomez, J.; Zerhouni, N.; Al Masry, Z.; Devalland, C.; Varnier, C. A survey of breast cancer screening techniques: Thermography and electrical impedance tomography. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 2019, 43, 305–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pal, U.M.; Saxena, M.; Vishnu, G.K.A.; Parsana, D.; Sarvani, B.S.R.; Varma, M.; Jayachandra, M.; Kurpad, V.; Baruah, D.; Gogoi, G.; et al. Optical spectroscopy-based imaging techniques for the diagnosis of breast cancer: A novel approach. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2020, 55, 778–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruleba, K.; Obaido, G.; Ogbuokiri, B.; Fadaka, A.; Klein, A.; Adekiya, T.; Aruleba, R. Applications of Computational Methods in Biomedical Breast Cancer Imaging Diagnostics: A Review. J. Imaging 2020, 6, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, U.; Mallia, A.; Stirling, J.; Joemon, J.; MacKewn, J.; Charles-Edwards, G.; Goh, V.; Cook, G.J. PET/MRI in Oncological Imaging: State of the Art. Diagnostics 2015, 5, 333–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sheth, D.; Giger, M.L. Artificial intelligence in the interpretation of breast cancer on MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 51, 1310–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer-Bäse, A.; Morra, L.; Meyer-Bäse, U.; Pinker, K. Current Status and Future Perspectives of Artificial Intelligence in Magnetic Resonance Breast Imaging. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2020, 2020, 6805710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenwood, H.I.; Wilmes, L.J.; Kelil, T.; Joe, B.N. Role of Breast MRI in the Evaluation and Detection of DCIS: Opportunities and Challenges. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 52, 697–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, S. An Overview of Current Trends, Techniques, Prospects, and Pitfalls of Artificial Intelligence in Breast Imaging. Rep. Med. Imaging 2021, 14, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahl, M. Artificial Intelligence: A Primer for Breast Imaging Radiologists. J. Breast Imaging 2020, 2, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geras, K.J.; Mann, R.M.; Moy, L. Artificial Intelligence for Mammography and Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: Current Concepts and Future Perspectives. Radiology 2019, 293, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, C.; Kim, W.H. Artificial intelligence in breast ultrasonography. Ultrasonography 2021, 40, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.-P.; Samala, R.K.; Hadjiiski, L.M. CAD and AI for breast cancer—Recent development and challenges. Br. J. Radiol. 2020, 93, 20190580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jochelson, M.S.; Lobbes, M.B.I. Contrast-enhanced Mammography: State of the Art. Radiology 2021, 299, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Figueiredo, G.N.; Ingrisch, M.; Fallenberg, E.M. Digital Analysis in Breast Imaging. Breast Care 2019, 14, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietzel, M.; Clauser, P.; Kapetas, P.; Schulz-Wendtland, R.; Baltzer, P.A.T. Images Are Data: A Breast Imaging Perspective on a Contemporary Paradigm. Rofo 2021, 193, 898–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, J.; Kang, H.K.; Kwon, J.-H.; Kim, K.-S.; Park, M.H.; Seong, Y.K.; Kim, D.W.; Ahn, B.; Ha, K.; Lee, J.; et al. Technology trends and applications of deep learning in ultrasonography: Image quality enhancement, diagnostic support, and improving workflow efficiency. Ultrasonography 2021, 40, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandomkar, Z.; Mello-Thoms, C. Visual search in breast imaging. Br. J. Radiol. 2019, 92, 20190057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, H. AI-based computer-aided diagnosis (AI-CAD): The latest review to read first. Radiol. Phys. Technol. 2020, 13, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastounioti, A.; Desai, S.; Ahluwalia, V.S.; Conant, E.F.; Kontos, D. Artificial intelligence in mammographic phenotyping of breast cancer risk: A narrative review. Breast Cancer Res. 2022, 24, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decuyper, M.; Maebe, J.; Van Holen, R.; Vandenberghe, S. Artificial intelligence with deep learning in nuclear medicine and radiology. EJNMMI Phys. 2021, 8, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesapane, F.; Codari, M.; Sardanelli, F. Artificial intelligence in medical imaging: Threat or opportunity? Radiologists again at the forefront of innovation in medicine. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2018, 2, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ou, W.C.; Polat, D.; Dogan, B.E. Deep learning in breast radiology: Current progress and future directions. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 4872–4885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitencourt, A.; Naranjo, I.D.; Gullo, R.L.; Saccarelli, C.R.; Pinker, K. AI-enhanced breast imaging: Where are we and where are we heading? Eur. J. Radiol. 2021, 142, 109882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.M.; Khan, R.A.; Arif, S.; Sajid, U. Artificial intelligence for breast cancer analysis: Trends & directions. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 142, 105221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, E.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Hickman, S.; Gilbert, F. Artificial intelligence in breast imaging. Clin. Radiol. 2019, 74, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Yang, J.; Fong, S.; Zhao, Q. Artificial intelligence in cancer diagnosis and prognosis: Opportunities and challenges. Cancer Lett. 2019, 471, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.-T.; Chen, L.; Yue, W.-W.; Xu, H.-X. Artificial intelligence in ultrasound. Eur. J. Radiol. 2021, 139, 109717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barba, D.; León-Sosa, A.; Lugo, P.; Suquillo, D.; Torres, F.; Surre, F.; Trojman, L.; Caicedo, A. Breast cancer, screening and diagnostic tools: All you need to know. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2021, 157, 103174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, H.; Rubin, D. Challenges and opportunities for artificial intelligence in oncological imaging. Clin. Radiol. 2021, 76, 728–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraishi, J.; Li, Q.; Appelbaum, D.; Doi, K. Computer-Aided Diagnosis and Artificial Intelligence in Clinical Imaging. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2011, 41, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.-R.; Hsiao, Y.-H. Computer-aided Diagnosis in Breast Ultrasound. J. Med. Ultrasound 2008, 16, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Houssein, E.H.; Emam, M.M.; Ali, A.A.; Suganthan, P.N. Deep and machine learning techniques for medical imaging-based breast cancer: A comprehensive review. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 167, 114161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siviengphanom, S.; Gandomkar, Z.; Lewis, S.J.; Brennan, P.C. Mammography-based Radiomics in Breast Cancer: A Scoping Review of Current Knowledge and Future Needs. Acad. Radiol. 2021, 29, 1228–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.-X.; Hadjiloucas, S.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, Z. MRI radiogenomics for intelligent diagnosis of breast tumors and accurate prediction of neoadjuvant chemotherapy responses-a review. Comput. Methods Prog. Biomed. 2022, 214, 106510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghieh, D.; Saade, C.; Najem, E.; El Zeghondi, R.; Rawashdeh, M.; Berjawi, G. Staying abreast of imaging—urrent status of breast cancer detection in high density breast. Radiography 2021, 27, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Hernandez, J.-L.; Recinella, A.N.; Kandlikar, S.G.; Dabydeen, D.; Medeiros, L.; Phatak, P. Technology, application and potential of dynamic breast thermography for the detection of breast cancer. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 131, 558–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazal, M.I.; Patel, M.E.; Tye, J.; Gupta, Y. The past, present and future role of artificial intelligence in imaging. Eur. J. Radiol. 2018, 105, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutasa, S.; Sun, S.; Ha, R. Understanding artificial intelligence based radiology studies: CNN architecture. Clin. Imaging 2021, 80, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, R.; Jiang, M.; Lv, W.-Z.; Jiang, F.; Li, J.; Hu, B.; Cui, X.-W.; Dietrich, C.F. Study Processes and Applications of Ultrasomics in Precision Medicine. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shui, L.; Ren, H.; Yang, X.; Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Yi, C.; Zhu, H.; Shui, P. The Era of Radiogenomics in Precision Medicine: An Emerging Approach to Support Diagnosis, Treatment Decisions, and Prognostication in Oncology. Front. Oncol. 2021, 10, 570465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houssami, N.; Kirkpatrick-Jones, G.; Noguchi, N.; Lee, C.I. Artificial Intelligence (AI) for the early detection of breast cancer: A scoping review to assess AI’s potential in breast screening practice. Expert Rev. Med. Dev. 2019, 16, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.A.; Ling, S.H. Review on Electrical Impedance Tomography: Artificial Intelligence Methods and its Applications. Algorithms 2019, 12, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balasubramaniam, G.M.; Wiesel, B.; Biton, N.; Kumar, R.; Kupferman, J.; Arnon, S. Tutorial on the Use of Deep Learning in Diffuse Optical Tomography. Electronics 2022, 11, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olveres, J.; González, G.; Torres, F.; Moreno-Tagle, J.C.; Carbajal-Degante, E.; Valencia-Rodríguez, A.; Méndez-Sánchez, N.; Escalante-Ramírez, B. What is new in computer vision and artificial intelligence in medical image analysis applications. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2021, 11, 3830–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castiglioni, I.; Gallivanone, F.; Soda, P.; Avanzo, M.; Stancanello, J.; Aiello, M.; Interlenghi, M.; Salvatore, M. AI-based applications in hybrid imaging: How to build smart and truly multi-parametric decision models for radiomics. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 46, 2673–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazzocchi, M.; Mazzarella, F.; Del Frate, C.; Girometti, F.; Zuiani, C. CAD systems for mammography: A real opportunity? A review of the literature. Radiol. Med. 2007, 112, 329–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retson, T.A.; Eghtedari, M. Computer-Aided Detection/Diagnosis in Breast Imaging: A Focus on the Evolving FDA Regulations for Using Software as a Medical Device. Curr. Radiol. Rep. 2020, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spear, G.G.; Mendelson, E.B. Automated breast ultrasound: Supplemental screening for average-risk women with dense breasts. Clin. Imaging 2020, 76, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashekova, A.; Zhao, Y.; Ng, E.Y.; Zarikas, V.; Fok, S.C.; Mukhmetov, O. Early detection of the breast cancer using infrared technology—A comprehensive review. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2022, 27, 101142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, A.; Hassanipour, F. Infrared imaging for breast cancer detection: An objective review of foundational studies and its proper role in breast cancer screening. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2019, 97, 244–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, V.; Accardo, G.; Perillo, T.; Basso, L.; Garbino, N.; Nicolai, E.; Maurea, S.; Salvatore, M. Assessment and Prediction of Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer: A Comparison of Imaging Modalities and Future Perspectives. Cancers 2021, 13, 3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mambou, S.J.; Maresova, P.; Krejcar, O.; Selamat, A.; Kuca, K. Breast Cancer Detection Using Infrared Thermal Imaging and a Deep Learning Model. Sensors 2018, 18, 2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hameed, B.Z.; Prerepa, G.; Patil, V.; Shekhar, P.; Raza, S.Z.; Karimi, H.; Paul, R.; Naik, N.; Modi, S.; Vigneswaran, G.; et al. Engineering and clinical use of artificial intelligence (AI) with machine learning and data science advancements: Radiology leading the way for future. Ther. Adv. Urol. 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piruzan, E.; Vosoughi, N.; Mahdavi, S.R.; Khalafi, L.; Mahani, H. Target motion management in breast cancer radiation therapy. Radiol. Oncol. 2021, 55, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, W.T.; Sadeghi-Naini, A.; Lu, F.-I.; Gandhi, S.; Meti, N.; Brackstone, M.; Rakovitch, E.; Curpen, B. Computational Radiology in Breast Cancer Screening and Diagnosis Using Artificial Intelligence. Can. Assoc. Radiol. J. 2020, 72, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, R.M.; Hooley, R.; Barr, R.G.; Moy, L. Novel Approaches to Screening for Breast Cancer. Radiology 2020, 297, 266–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillies, R.J.; Schabath, M.B. Radiomics Improves Cancer Screening and Early Detection. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2020, 29, 2556–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Qin, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhu, D.; Gao, F.; Zhou, X. A meta-analysis of the diagnostic performance of machine learning-based MRI in the prediction of axillary lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients. Insights Imaging 2021, 12, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtaza, G.; Shuib, L.; Wahab, A.W.A.; Mujtaba, G.; Nweke, H.F.; Al-Garadi, M.A.; Zulfiqar, F.; Raza, G.; Azmi, N.A. Deep learning-based breast cancer classification through medical imaging modalities: State of the art and research challenges. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2020, 53, 1655–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Society of Radiology (ESR). Impact of artificial intelligence on radiology: A EuroAIM survey among members of the European Society of Radiology. Insights Imaging 2019, 10, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Operator | Dimensions | Keywords, Synonyms, and Alternative Terms |
|---|---|---|
| AND | AI | artificial intelligence OR AI OR machine learning OR deep learning OR expert system |
| Breast imaging | breast imaging OR breast imaging modality |
| Item | Description | Rating | Justification |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Was an ‘a priori’ design provided? | + | Yes, the research questions and inclusion criteria are provided in Section 2.1 and Section 2.3, respectively |
| 2 | Was there duplicate study selection and data extraction? | + | Yes, excluded as detailed in Figure 4 |
| 3 | Was a comprehensive literature search performed? | + | Yes, as detailed in Section 2.2 |
| 4 | Was the status of publication (i.e., grey literature) used as an inclusion criterion? | − | No, inclusion criterion is provided in Section 2.3 |
| 5 | Was a list of studies (included and excluded) provided? | + | Yes, provided in Appendix A |
| 6 | Were the characteristics of the included studies provided? | + | Yes, provided in Appendix A |
| 7 | Was the scientific quality of the included studies assessed and documented? | + | Yes, as detailed in Section 3.9 |
| 8 | Was the scientific quality of the included studies used appropriately in formulating conclusions? | + | Yes, the scientific quality of the included review works from different perspectives were considered (Section 3). Recommendations and future direction are provided in Section 4.3 |
| 9 | Were the methods used to combine the findings of studies appropriate? | + | Yes, as detailed in Section 2.6 |
| 10 | Was the likelihood of publication bias assessed? | + | Yes, as detailed in Section 2.7 and Section 4.2 |
| 11 | Was the conflict of interest stated? | + | Yes, as detailed in the Conflicts of Interest Section |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, X.J.; Cheor, W.L.; Lim, L.L.; Ab Rahman, K.S.; Bakrin, I.H. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Breast Imaging: A Scientometric Umbrella Review. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 3111. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123111
Tan XJ, Cheor WL, Lim LL, Ab Rahman KS, Bakrin IH. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Breast Imaging: A Scientometric Umbrella Review. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(12):3111. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123111
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Xiao Jian, Wai Loon Cheor, Li Li Lim, Khairul Shakir Ab Rahman, and Ikmal Hisyam Bakrin. 2022. "Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Breast Imaging: A Scientometric Umbrella Review" Diagnostics 12, no. 12: 3111. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123111
APA StyleTan, X. J., Cheor, W. L., Lim, L. L., Ab Rahman, K. S., & Bakrin, I. H. (2022). Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Breast Imaging: A Scientometric Umbrella Review. Diagnostics, 12(12), 3111. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123111







