Diagnostic Reference Level of Radiation Dose and Image Quality among Paediatric CT Examinations in A Tertiary Hospital in Malaysia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. CT Acquisition Data Collection
2.2. Radiation Dose Calculation Software
2.3. Image Noise Evaluation
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zacharias, C.; Alessio, A.M.; Otto, R.K.; Iyer, R.S.; Philips, G.S.; Swanson, J.O.; Thapa, M.M. Pediatric CT: Strategies to lower radiation dose. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2013, 200, 950–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, J.K.; Reiman, R.E.; Nguyen, G.B.; Januzis, N.; Chin, B.; Lowry, C.; Yoshizumi, T.T. Lifetime Attributable Risk of Cancer FROM Radiation Exposure During Parathyroid Imaging: Comparison of 4D CT and Parathyroid Scintigraphy. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 204, W579–W585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogbole, G. Radiation dose in paediatric computed tomography: Risks and benefits. Ann. Ib. Postgrad. Med. 2010, 8, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrimpton, P.C.; Hillier, M.C.; Lewis, M.A.; Dunn, M. National survey of doses from CT in the UK: 2003. Br. J. Radiol. 2006, 79, 968–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Commission on Radiological Protection. ICRP publication 103. Ann. ICRP 2007, 37, 1–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaama, D.H.; Vassileva, J.; Mahdaly, G.; Shawki, M.; Salama, A.; Gilley, D.; Rehani, M.M. Establishing national diagnostic reference levels (DRLs) for computed tomography in Egypt. Phys. Med. 2017, 39, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, M.; Hashim, S.; Bradley, D.; Bakar, K.; Haron, M.; Kayun, Z. Radiation doses from computed tomography practice in Johor Bahru, Malaysia. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2016, 121, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Society of Radiology. European Guidelines on DRLs for Paediatric Imaging; PiDRL; European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2015; pp. 1–105. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, N.A.; Karim, M.K.A.; Hassan, H.A.; Kamarudin, M.A.; Wong, J.H.D.; Ibahim, M.J. Estimation of effective dose and organ cancer risk from paediatric computed tomography thorax—Abdomen—Pelvis examinations. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2019, 165, 108438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Journy, N.M.Y.; Dreuil, S.; Boddaert, N.; Chateil, J.-F.; Defez, D.; Ducou-Le-Pointe, H.; Garcier, J.-M.; Guersen, J.; Geryes, B.H.; Jahnen, A.; et al. Individual radiation exposure from computed tomography: A survey of paediatric practice in French university hospitals, 2010–2013. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 28, 630–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korir, G.K.; Wambani, J.S.; Korir, I.K.; Tries, M.A.; Boen, P.K. National diagnostic reference level initiative for computed tomography examinations in Kenya. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2015, 168, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehani, M.M. Limitations of diagnostic reference level (DRL) and introduction of acceptable quality dose (AQD). Br. J. Radiol. 2014, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edmonds, K. Diagnostic reference levels as a quality assurance tool. J. Med. Radiat. Sci. 2009, 56, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougeni, E.; Faulkner, K.; Panayiotakis, G. A review of patient dose and optimisation methods in adult and paediatric CT scanning. Eur. J. Radiol. 2012, 81, e665–e683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Quinn, B.; Pandit-taskar, N.; Behr, G.; Mahmood, U.; Long, D.; Xu, X.G.; Germain, J.S.; Dauer, L.T. Patient-specific organ and effective dose estimates in pediatric oncology computed tomography. Phys. Med. 2018, 45, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.-Y.; Do, K.-H.; Yang, D.H.; Cho, Y.A.; Yoon, H.-K.; Lee, J.S.; Koo, H.J.; Hyun, K. A Survey of Pediatric CT Protocols and Radiation Doses in South Korean Hospitals to Optimize the Radiation Dose for Pediatric CT Scanning. Medicine 2015, 94, e2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdun, F.R.; Gutiérrez, D.; Vader, J.P.; Aroua, A.; Alamo-Maestre, L.T.; Bochud, F.; Gudinchet, F. CT radiation dose in children: A survey to establish age-based diagnostic reference levels in Switzerland. Eur. Radiol. 2008, 18, 1980–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanski, M.; Nagel, H.D.; Stamm, G.; Paediatric, C.T. Exposure Practice in the Federal Republic of Germany: Results of a Nation-Wide Survey in 2005/06; MHH: Hannover, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Rawashdeh, M.; Abdelrahman, M.; Zaitoun, M.; Saade, C.; Alewaidat, H.A.; McEntee, M.F. Diagnostic reference levels for paediatric CT in Jordan. J. Radiol. Prot. 2019, 39, 1060–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbolatiana, R.; Luc, A.; Jeanne, R.M.; Andraimbololona, R.; Edmond, R.; Radaorolala, Z.J.L.; Harimalala, T.R. Establishing Diagnostic Reference Level for Computed Tomography Examination in Madagascar. Radiat. Sci. Technol. 2015, 1, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Anna, H.; Wallace, A.; Marks, P.; Edmonds, K.; Tingey, D.; Johnston, P. Australian diagnostic reference levels for multi detector computed tomography. Australas. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2013, 36, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.C.; Chang, K.H.; Hwang, J.H.; Nam, Y.C.; Han, D.K.; Yoon, J. Radiation dose for pediatric and young adult CT: A survey to establish age-based reference levels of 2015–2016 in Korea. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2017, 175, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassileva, J.; Rehani, M. Diagnostic reference levels. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 204, W1–W3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoramian, D.; Sistani, S.; Hejazi, P. Establishment of diagnostic reference levels arising from common CT examinations in Semnan County, Iran. Pol. J. Med Phys. Eng. 2019, 25, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolicchi, F.; Faggioni, L.; Bastiani, L.; Molinaro, S.; Puglioli, M.; Caramella, D.; Bartolozzi, C. Optimizing the Balance Between Radiation Dose and Image Quality in Pediatric Head CT: Findings Before and After Intensive Radiologic Staff Training. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2014, 202, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Quinn, B.M.; Mahmood, U.; Long, D.; Erdi, Y.; Germain, J.S.; Pandit-Taskar, N.; Xu, X.G.; Bolch, W.E.; Dauer, L.T. A comparison of pediatric and adult CT organ dose estimation methods. BMC Med. Imaging 2017, 17, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarb, F.; Rainford, L.; Mcentee, M.F. Radiography Developing optimized CT scan protocols: Phantom measurements of image quality. Radiography 2011, 17, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadakis, A.E.; Damilakis, J. Automatic Tube Current Modulation and Tube Voltage Selection in Pediatric Computed Tomography: A Phantom Study on Radiation Dose and Image Quality. Investig. Radiol. 2019, 54, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuasa, Y.; Shiinoki, T.; Onizuka, R.; Fujimoto, K. Estimation of effective imaging dose and excess absolute risk of secondary cancer incidence for four-dimensional cone-beam computed tomography acquisition. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2019, 20, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aborisade, C.; Famurewa, O.C.; Ibitoye, F.I.; Balogun, F.A. Organ Dose Distribution and Estimated Cancer Risk to Paediatric Patients Undergoing Computed Tomography in a Nigerian Tertiary Hospital. J. Adv. Med. Med. Res. 2019, 29, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, D.J.; Elliston, C.D.; Hall, E.J.; Berdon, W.E. Estimates of the cancer risks from pediatric CT radiation are not merely theoritical: Comment on point/counterpoint: In X-ray computed tomography, technique factors should be selected appropriate to patient size. Against the proposition. Med. Phys. 2001, 28, 2387–23899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Kalra, M.K. Scan parameters and CT radiation dose. In Radiation Dose from Multidetector CT; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 119–129. [Google Scholar]
- Buty, M.; Xu, Z.; Wu, A.; Gao, M.; Nelson, C.; Papadakis, G.Z.; Teomete, U.; Celik, H.; Turkbey, B.; Choyke, P.; et al. Quantitative Image Quality Comparison of Reduced- and Standard-Dose Dual-Energy Multiphase Chest, Abdomen, and Pelvis CT. Tomography 2017, 3, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlin, S.C.; Weinert, D.M.; Vasavada, P.S.; Martinez-Rios, C.; Parikh, R.A.; Wien, M.A.; Jordan, D.W.; Novak, R.D. Successful Dose Reduction Using Reduced Tube Voltage With Hybrid Iterative Reconstruction in Pediatric Abdominal CT. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 205, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waite, S.; Grigorian, A.; Alexander, R.G.; Macknik, S.L.; Carrasco, M.; Heeger, D.J.; Martinez-Conde, S. Analysis of perceptual expertise in radiology—Current knowledge and a new perspective. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Pien, H.; Do, S.; Singh, S.; Kalra, M.K. Conventional and Newer Reconstruction Techniques in CT. In Radiation Dose from Multidetector CT; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 143–156. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.E.; Choi, Y.H.; Cheon, J.-E.; Kim, W.S.; Kim, I.-O.; Cho, H.S.; Ryu, Y.J.; Kim, Y.J. Image quality and radiation dose of brain computed tomography in children: Effects of decreasing tube voltage from 120 kVp to 80 kVp. Pediatr. Radiol. 2017, 201, 710–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, H.; Padole, A.; Homayounieh, F.; Kruger, U.; Khera, R.D.; Nitiwarangkul, C.; Kalra, M.K.; Wang, G. Competitive performance of a modularized deep neural network compared to commercial algorithms for low-dose CT image reconstruction. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2019, 1, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
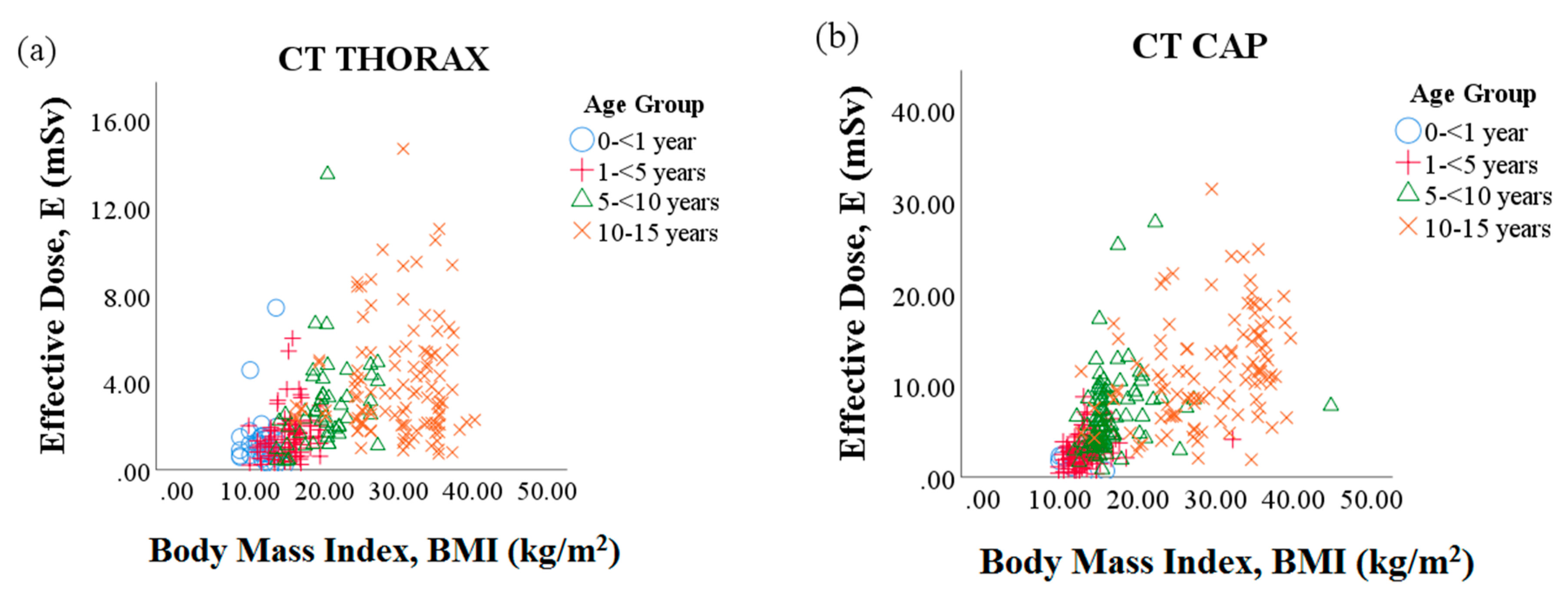
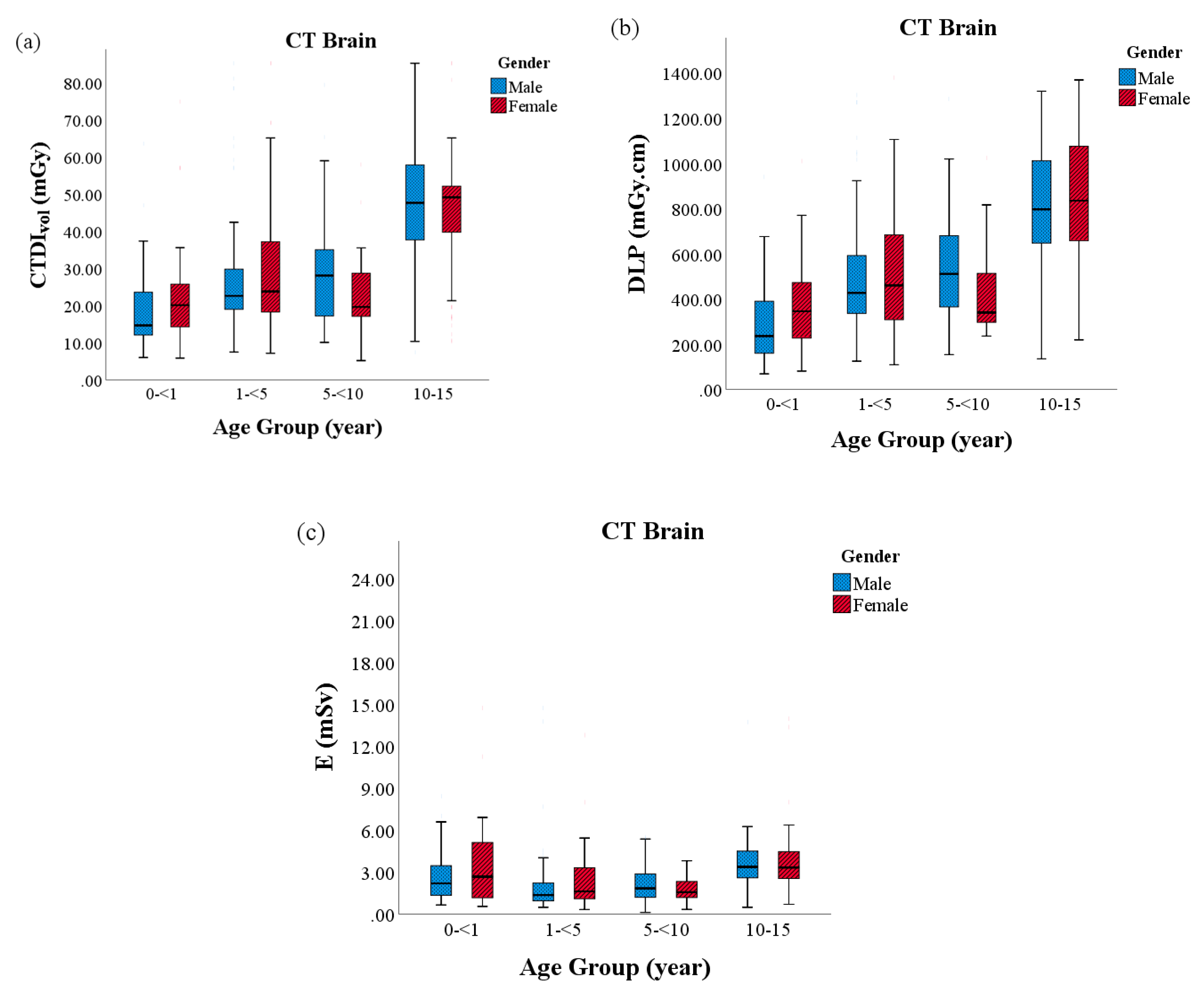

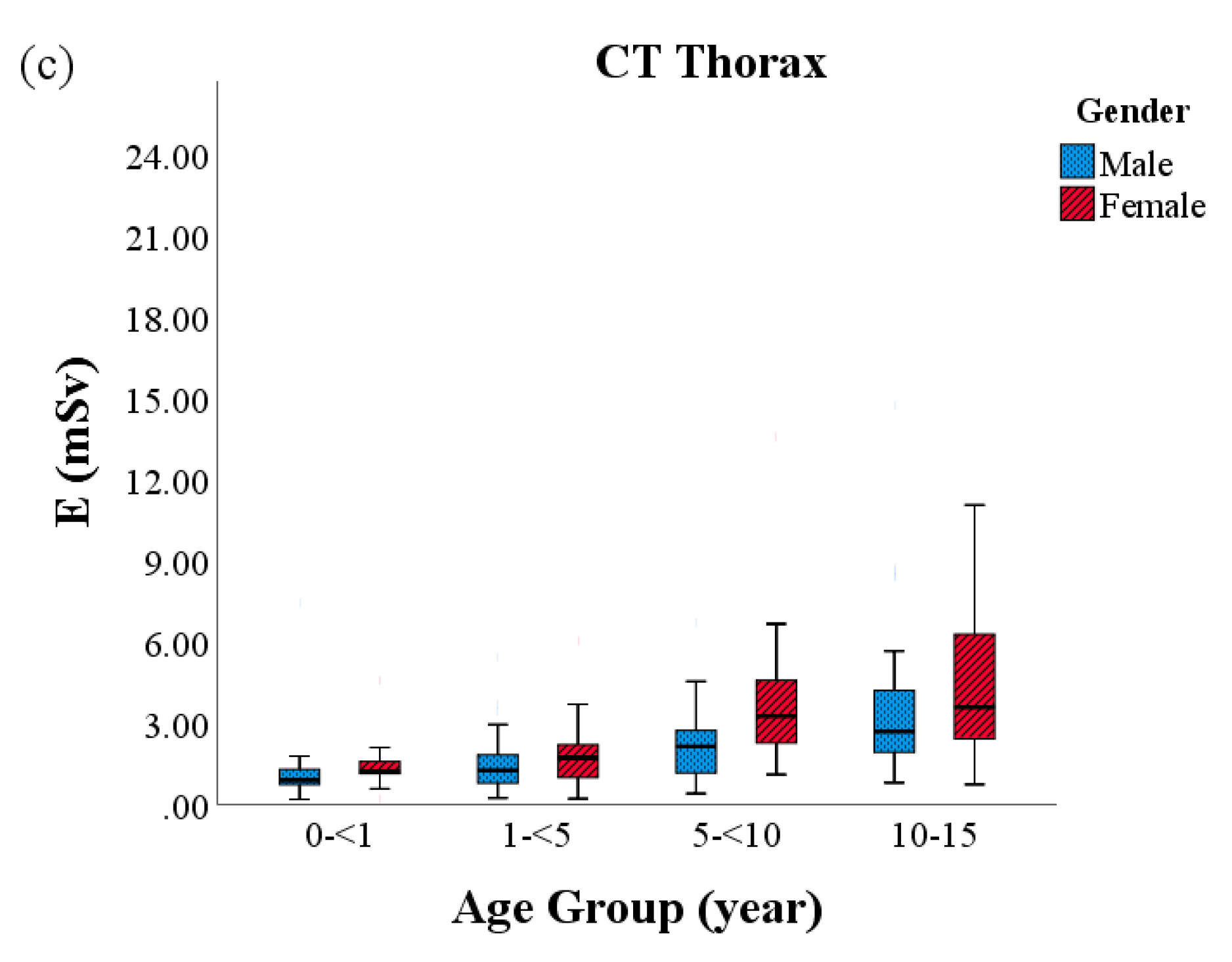
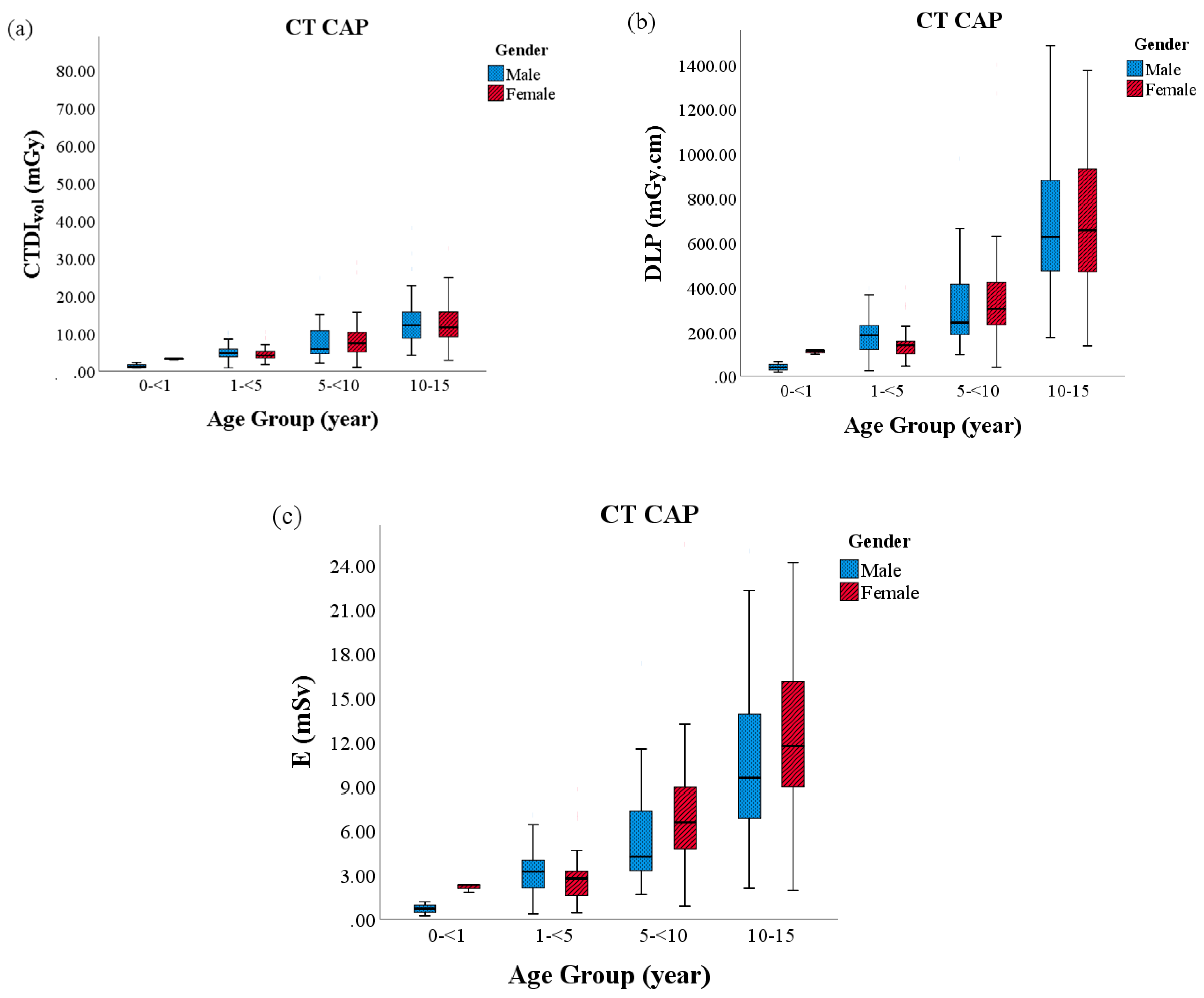
| CT Protocol | Parameters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age Group (Years) | Sex | N | Weight (kg) * | Height (cm) * | BMI (kg m−2) * | |
| CT Brain | Group 1 (0–<1) | M | 62 | 4.70 ± 1.4 | 42.95 ± 8.9 | 10.99 ± 1.5 |
| F | 32 | 4.76 ± 1.4 | 41.91 ± 11.4 | 13.23 ± 1.4 | ||
| Group 2 (1–<5) | M | 78 | 11.27 ± 3.4 | 75.93 ± 13.6 | 14.62 ± 3.2 | |
| F | 67 | 12.62 ± 2.5 | 94.63 ± 14.2 | 13.23 ± 1.4 | ||
| Group 3 (5–<10) | M | 57 | 24.82 ± 6.1 | 124.38 ± 10.5 | 19.42 ± 4.6 | |
| F | 39 | 17.67 ± 1.3 | 116.40 ± 7.5 | 15.20 ± 1.0 | ||
| Group 4 (10–15) | M | 164 | 49.14 ± 8.9 | 147.54 ± 8.6 | 33.24 ± 5.5 | |
| F | 100 | 54.31 ± 6.0 | 158.40 ± 11.7 | 34.26 ± 2.7 | ||
| CT Thorax | Group 1 (0–<1) | M | 25 | 5.09 ± 1.1 | 43.76 ± 9.8 | 11.72 ± 1.6 |
| F | 13 | 4.62 ± 1.4 | 41.62 ± 13.0 | 11.26 ± 1.6 | ||
| Group 2 (1–<5) | M | 63 | 12.39 ± 2.6 | 93.04 ± 8.3 | 14.75 ± 2.9 | |
| F | 22 | 13.38 ± 2.2 | 86.09 ± 2.1 | 15.53 ± 2.0 | ||
| Group 3 (5–<10) | M | 29 | 23.00 ± 5.7 | 120.77 ± 10.6 | 21.47 ± 2.8 | |
| F | 22 | 27.65 ± 4.2 | 128.57 ± 6.7 | 18.98 ± 4.1 | ||
| Group 4 (10–15) | M | 56 | 48.82 ± 8.6 | 161.65 ± 11.0 | 30.10 ± 4.4 | |
| F | 57 | 41.62 ± 11.5 | 155.37 ± 11.2 | 29.96 ± 6.7 | ||
| CT CAP | Group 1 (0–<1) | M | 3 | 4.35 ± 0.7 | 43.20 ± 3.4 | 13.39 ± 2.3 |
| F | 4 | 5.73 ± 0.5 | 41.18 ± 3.4 | 10.54 ± 1.0 | ||
| Group 2 (1–<5) | M | 55 | 12.52 ± 6.1 | 87.54 ± 15.2 | 13.91 ± 3.2 | |
| F | 40 | 11.06 ± 2.1 | 88.27 ± 12.8 | 12.50 ± 1.1 | ||
| Group 3 (5–<10) | M | 39 | 20.49 ± 8.1 | 110.91 ± 7.0 | 17.63 ± 13.2 | |
| F | 55 | 19.93 ± 17.1 | 116.57 ±10.8 | 17.27 ± 5.0 | ||
| Group 4 (10–15) | M | 59 | 47.31 ± 12.4 | 151.27 ± 16.4 | 28.03 ± 6.7 | |
| F | 51 | 42.98 ± 13.2 | 154.75 ± 11.9 | 30.24 ± 6.7 | ||
| Parameters | CT Protocol | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT Brain | CT Thorax | CT CAP | ||||||||||
| Age Group (years) | Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 | Group 4 | Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 | Group 4 | Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 | Group 4 |
| (0–<1) | (1–<5) | (5–<10) | (10–15) | (0–<1) | (1–<5) | (5–<10) | (10–15) | (0–<1) | (1–<5) | (5–<10) | (10–15) | |
| Tube Voltage (kVp) | 100 | 100 | 100,120 | 120 | 80,100 | 100 | 100,120 | 120 | 80 | 100 | 100,120 | 120 |
| Effective Tube current (mAs) * | 209.10 ± 27.0 (80–380) | 248.23 ± 35.9 (90–423) | 185.50 ± 20.5 (20–400) | 233.33 ± 24.8 (80–430) | 74.37 ± 44.8 (27–225) | 76.80 ± 34.2 (10–261) | 110.81 ± 54.5 (35–225) | 145.28 ± 52 (20–360 | 37.10 ± 5.2 (26–40) | 76.80 ± 34.2 (28–177) | 110.81 ± 54.5 (35–272) | 145.28 ± 52.0 (53–287) |
| Scan Range * | 11.91 ± 4.2 | 14.42 ± 1.6 | 14.53 ± 4.8 | 15.03 ± 4.7 | 12.22 ± 2.7 | 16.98 ± 15.2 | 18.81 ± 5.4 | 25.01 ± 5.2 | 28.92 ± 4.6 | 31.49 ± 1.6 | 40.77 ± 4.6 | 52.25 ± 10.5 |
| Pitch | 0.4–0.64 | 0.4–0.64 | 0.4–0.64 | 0.4–0.64 | 1–1.4 | 1–1.4 | 1–1.4 | 1–1.4 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.2–1.4 | 1.2–1.4 |
| Slice thickness (mm) | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0.8–5 | 3–5 | 3–5 | 3–5 | 3 | 3 | 3–5 | 3 |
| Collimation | 40 × 0.6 | 40 × 0.6 | 40 × 0.6 | 40 × 0.6 | 64 × 0.6 | 64 × 0.6 | 64 × 0.6 | 64 × 0.6 | 64 × 0.6 | 64 × 0.6 | 64 × 0.6 | 64 × 0.6 |
| Table feed | 11–16 | 11–16 | 11–16 | 11–16 | 26.9 | 26.9 | 26.9 | 26.9 | 26.9 | 26.9 | 26.9 | 26.9 |
| CT Procedure | Age Group (years) | CTDIvol (mGy) | DLP (mGy.cm) | E (mSv) | Noise Value (HU) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Median | Range (Min-Max) | Mean | Median | Range (Min–Max) | Mean | Median | Range (Min–Max) | Mean | Median | Range (Min–Max) | ||
| Brain | Group 1 (0–<1) | 27.2 | 22.64 | 3.6–123.1 | 308.9 | 250.1 | 69–1010 | 3.0 | 2.4 | 0.6–14.7 | 4.0 | 3.6 | 2.8–6.4 |
| Group 2 (1–<5) | 38.6 | 29.39 | 4.4–123.4 | 510.7 | 449.0 | 109–1379 | 2.2 | 1.5 | 0.3–14.7 | 3.2 | 3.1 | 1.5–6.2 | |
| Group 3 (5–<10) | 40.6 | 31.63 | 2.8–122.2 | 493.0 | 458.5 | 154–1285 | 2.1 | 1.7 | 0.1–5.5 | 3.8 | 3.3 | 2.6–5.5 | |
| Group 4 (10–15) | 69.1 | 68.61 | 10.0–124.4 | 811.4 | 814.1 | 135–1779 | 3.6 | 3.3 | 0.5–14.0 | 3.5 | 3.6 | 1.9–5.1 | |
| p-value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.184 | |||||||||
| Thorax | Group 1 (0–<1) | 4.3 | 3.7 | 0.8–23.9 | 59.0 | 46.9 | 10.5–393.6 | 1.3 | 1.0 | 0.2–7.4 | 21.9 | 23.1 | 8.7–29.0 |
| Group 2 (1–<5) | 4.6 | 4.2 | 0.6–16.7 | 79.5 | 66.7 | 9.3–358.1 | 1.6 | 1.4 | 0.2–6.0 | 21.0 | 22.5 | 12.8–29.1 | |
| Group 3 (5–<10) | 6.6 | 6.2 | 1.5–19.0 | 135.3 | 126.3 | 21.6–516.5 | 2.9 | 2.5 | 0.4–13.5 | 21.6 | 21.8 | 10.2–22.5 | |
| Group 4 (10–15) | 8.0 | 6.2 | 1.4–25.2 | 207.7 | 155.5 | 34.0–732.0 | 4.0 | 3.1 | 0.7–14.7 | 13.3 | 12.7 | 6.8–26.9 | |
| p-value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.042 | |||||||||
| CAP | Group 1 (0–<1) | 2.5 | 3.0 | 0.8–3.4 | 81.1 | 98.1 | 17.2–115.6 | 1.6 | 1.8 | 0.2–2.3 | 11.2 | 11.3 | 6.8–16.3 |
| Group 2 (1–<5) | 4.9 | 4.6 | 0.8–10.4 | 164.1 | 150.2 | 24.6–400.1 | 3.0 | 2.9 | 0.4–8.8 | 10.5 | 10.2 | 4.1–21.8 | |
| Group 3 (5–<10) | 8.2 | 7.1 | 1.0–28.8 | 347.0 | 292.6 | 39.7–1398.6 | 6.8 | 5.8 | 0.9–27.8 | 11.9 | 9.3 | 6.2–20.9 | |
| Group 4 (10–15) | 13.1 | 11.7 | 2.9–38.0 | 705.3 | 644.9 | 136.5–2223.2 | 11.7 | 11.1 | 1.9–31.5 | 9.9 | 9.8 | 7.0–13.4 | |
| p-value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.898 | |||||||||
| CT Procedure | Age Group (years) | CTDIvol(mGy) | DLP (mGy.cm) | E (mSv) | Noise Value (HU) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dose Reference Level | Dose Reference Range | Dose Reference Level | Dose Reference Range | Dose Reference Level | Dose Reference Range | Noise Reference Level | Noise Reference Range | ||
| Brain | Group 1 (0–<1) | 22.64 | 12.5–24.1 | 250.1 | 172.3–426.5 | 2.4 | 1.3–3.8 | 3.6 | 3.3–4.5 |
| Group 2 (1–<5) | 29.39 | 18.4–34.0 | 449.0 | 316.0–622.0 | 1.5 | 1.0–2.4 | 3.1 | 2.5–3.2 | |
| Group 3 (5–<10) | 31.63 | 17.2–32.1 | 458.5 | 324.0–645.5 | 1.7 | 1.2–2.6 | 3.3 | 3.0–4.7 | |
| Group 4 (10–15) | 68.61 | 39.7–57.8 | 814.1 | 657.5–1040.5 | 3.3 | 2.6–4.5 | 3.6 | 2.7–4.3 | |
| Thorax | Group 1 (0–<1) | 3.7 | 2.9–4.4 | 46.9 | 37.7–67.8 | 1.0 | 0.7–1.5 | 23.1 | 19.3–26.1 |
| Group 2 (1–<5) | 4.2 | 2.9–5.4 | 66.7 | 42.9–97.1 | 1.4 | 0.8–2.0 | 22.5 | 14.6–26.0 | |
| Group 3 (5–<10) | 6.2 | 4.3–7.8 | 126.3 | 85.6–163.2 | 2.5 | 1.7–3.4 | 21.8 | 14.2–26.1 | |
| Group 4 (10–15) | 6.2 | 4.7–10.5 | 155.5 | 119.3–283.5 | 3.1 | 2.2–5.3 | 12.7 | 8.84–15.8 | |
| CAP | Group 1 (0–<1) | 3.0 | 1.7–3.4 | 98.1 | 52.7–115.6 | 1.8 | 1.0–2.4 | 11.3 | 8.3–14.0 |
| Group 2 (1–<5) | 4.6 | 3.7–5.7 | 150.2 | 115.6–204.0 | 2.9 | 2.0–3.8 | 10.2 | 8.5–11.2 | |
| Group 3 (5–<10) | 7.1 | 4.9–10.6 | 292.6 | 208.7–419.4 | 5.8 | 4.0–8.6 | 9.3 | 7.8–15.5 | |
| Group 4 (10–15) | 11.7 | 8.9–15.8 | 644.9 | 472.0–911.1 | 11.1 | 7.6–15.1 | 9.8 | 9.4–10.3 | |
| CT Procedure | Age Group (Years) | This Study | Gao et al. (2018) | Rawashdeh et al. (2019) | Verdun et al. (2008) | Galanski et al. (2005) | EC (2015) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTDIvol | DLP | CTDIvol | DLP | CTDIvol | DLP | CTDIvol | DLP | CTDIvol | DLP | CTDIvol | DLP | ||
| Brain | Group 1 (0–<1) | 24 | 427 | 26 | 340 | 49 | 744 | 20 | 270 | 34 | 393 | 25 | 370 |
| Group 2 (1–<5) | 34 | 622 | 35 | 558 | 55 | 982 | 30 | 420 | 49 | 611 | 38 | 505 | |
| Group 3 (5–<10) | 32 | 646 | 38 | 607 | 65 | 1130 | 40 | 560 | 58 | 711 | 53 | 700 | |
| Group 4 (10–15) | 58 | 1041 | 48 | 815 | 61 | 1207 | 60 | 1000 | 65 | 920 | 60 | 900 | |
| Thorax | Group 1 (0–<1) | 4 | 68 | 1 | 28 | 5.6 | 124 | 5 | 110 | 7 | 93 | 3 | 80 |
| Group 2 (1–<5) | 5 | 97 | 4 | 101 | 7.4 | 222 | 8 | 200 | 8 | 137 | 6 | 115 | |
| Group 3 (5–<10) | 8 | 163 | 5 | 153 | 12.9 | 416 | 10 | 220 | 12 | 257 | 6 | 180 | |
| Group 4 (10–15) | 11 | 283 | 7 | 230 | 12.9 | 496 | 12 | 460 | 16 | 488 | 7 | 200 | |
| CAP | Group 1 (0–<1) | 3 | 116 | - | - | 16.1 | 509 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Group 2 (1–<5) | 6 | 204 | - | - | 16.1 | 787 | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Group 3 (5–<10) | 11 | 419 | - | - | 12.9 | 702 | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Group 4 (10–15) | 16 | 911 | 9 | 637 | 16.1 | 755 | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muhammad, N.A.; Abdul Karim, M.K.; Abu Hassan, H.; Ahmad Kamarudin, M.; Ding Wong, J.H.; Ng, K.H. Diagnostic Reference Level of Radiation Dose and Image Quality among Paediatric CT Examinations in A Tertiary Hospital in Malaysia. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10080591
Muhammad NA, Abdul Karim MK, Abu Hassan H, Ahmad Kamarudin M, Ding Wong JH, Ng KH. Diagnostic Reference Level of Radiation Dose and Image Quality among Paediatric CT Examinations in A Tertiary Hospital in Malaysia. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(8):591. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10080591
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuhammad, Nor Azura, Muhammad Khalis Abdul Karim, Hasyma Abu Hassan, Mazliana Ahmad Kamarudin, Jeannie Hsiu Ding Wong, and Kwan Hoong Ng. 2020. "Diagnostic Reference Level of Radiation Dose and Image Quality among Paediatric CT Examinations in A Tertiary Hospital in Malaysia" Diagnostics 10, no. 8: 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10080591
APA StyleMuhammad, N. A., Abdul Karim, M. K., Abu Hassan, H., Ahmad Kamarudin, M., Ding Wong, J. H., & Ng, K. H. (2020). Diagnostic Reference Level of Radiation Dose and Image Quality among Paediatric CT Examinations in A Tertiary Hospital in Malaysia. Diagnostics, 10(8), 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10080591






