Expression Analysis of Muscle-Specific miRNAs in Plasma-Derived Extracellular Vesicles from Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Cohort Characteristics
2.2. Isolation and Characterization of Extracellular Vesicles
2.3. Evaluation of EV-Derived miRNA Expression
2.4. miRNA Target Prediction and Pathway Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics and Enumeration of EV According to GOLD Groups
3.2. Muscle-Specific miRNAs Expression in Plasma-Derived EV
3.3. Classification Value of Triple Signature of EV-Derived myo-miRNAs
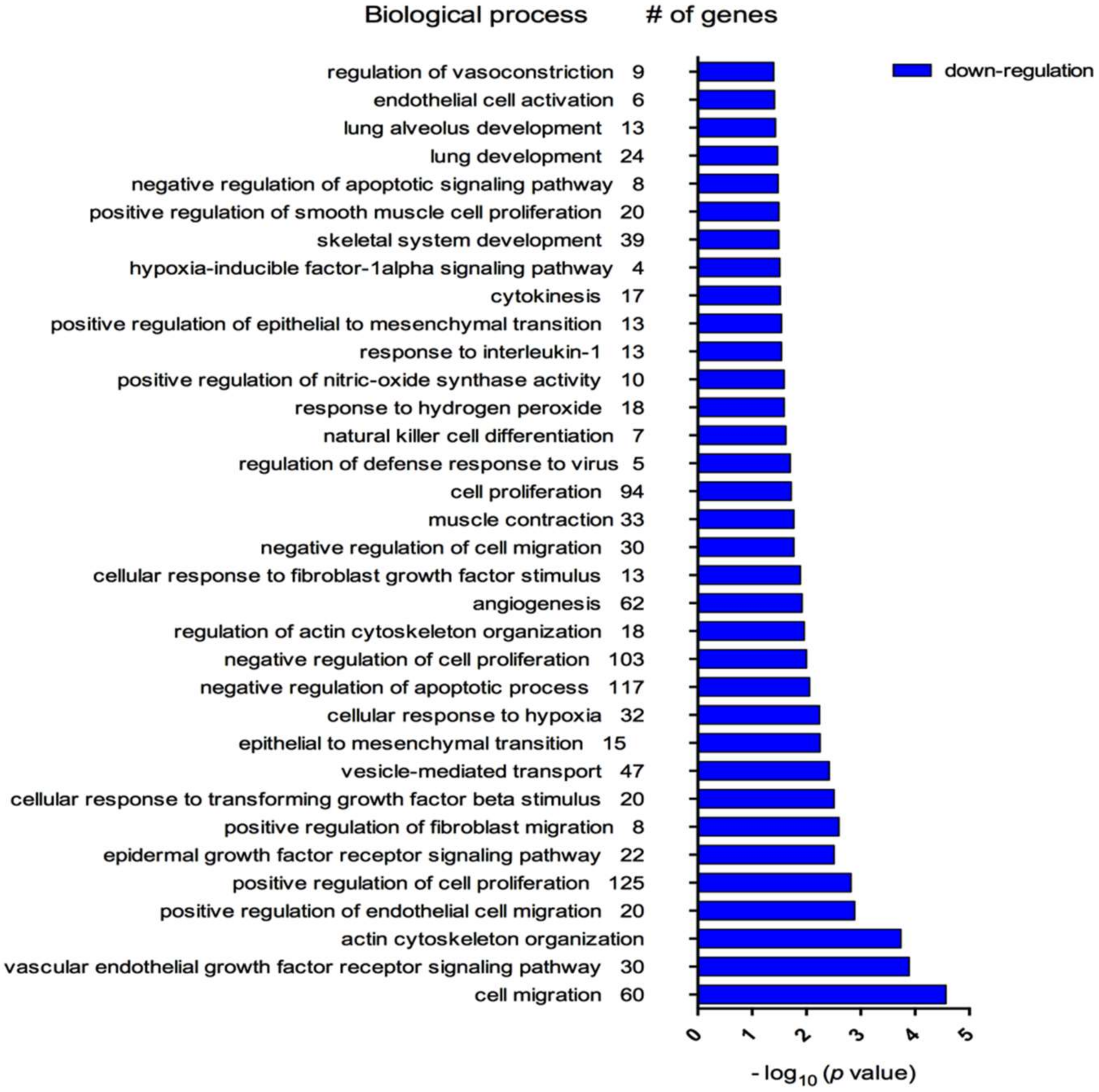
3.4. Biological Processes Associated with myo-miRNAs Modulation
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agusti, A.; Sobradillo, P.; Celli, B. Addressing the complexity of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: From phenotypes and biomarkers to scale-free networks, systems biology, and P4 medicine. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestbo, J.; Hurd, S.S.; Agustí, A.G.; Jones, P.W.; Vogelmeier, C.; Anzueto, A.; Barnes, P.J.; Fabbri, L.M.; Martinez, F.J.; Nishimura, M.; et al. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: GOLD executive summary. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 347–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, P.; Marott, J.L.; Vestbo, J.; Olsen, K.R.; Ingebrigtsen, T.S.; Dahl, M.; Nordestgaard, B.G. Prediction of the clinical course of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, using the new GOLD classification: A study of the general population. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celli, B.R.; Decramer, M.; Wedzicha, J.A.; Wilson, K.C.; Agustí, A.A.; Criner, G.J.; MacNee, W.; Make, B.J.; Rennard, S.I.; Stockley, R.A.; et al. An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: Research questions in COPD. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2015, 24, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sin, D.D.; Vestbo, J. Biomarkers in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2009, 6, 543–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannino, D.M. Biomarkers in COPD: The search continues! Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 45, 872–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agustí, A.; Celli, B.; Faner, R. What does endotyping mean for treatment in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease? Lancet 2017, 390, 980–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gon, Y.; Shimizu, T.; Mizumura, K.; Maruoka, S.; Hikichi, M. Molecular techniques for respiratory diseases: MicroRNA and extracellular vesicles. Respirology 2020, 25, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieri, D.; Neri, T.; Petrini, S.; Vagaggini, B.; Paggiaro, P.; Celi, A. Cell-derived microparticles and the lung. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2016, 25, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.J.; Baek, M.; Gusev, Y.; Brackett, D.J.; Nuovo, G.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Systematic evaluation of microRNA processing patterns in tissues, cell lines, and tumors. RNA 2007, 14, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, G.P.; Wang, D.-Z. Regulation of Skeletal Muscle by microRNAs. In Comprehensive Physiology; Terjung, R., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-0-470-65071-4. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzenbach, H.; Nishida, N.; Calin, G.A.; Pantel, K. Clinical relevance of circulating cell-free microRNAs in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 11, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, C.C.; Cheng, H.H.; Tewari, M. MicroRNA profiling: Approaches and considerations. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crist, C.G.; Buckingham, M. microRNAs gain magnitude in muscle. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 3627–3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siracusa, J.; Koulmann, N.; Banzet, S. Circulating myomiRs: A new class of biomarkers to monitor skeletal muscle in physiology and medicine. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2018, 9, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreiro, E. The role of MicroRNAs in COPD muscle dysfunction and mass loss: Implications on the clinic. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2016, 10, 1011–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigeyasu, K.; Toden, S.; Zumwalt, T.J.; Okugawa, Y.; Goel, A. Emerging Role of MicroRNAs as Liquid Biopsy Biomarkers in Gastrointestinal Cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 2391–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltais, F.; Decramer, M.; Casaburi, R.; Barreiro, E.; Burelle, Y.; Debigaré, R.; Dekhuijzen, P.N.R.; Franssen, F.; Gayan-Ramirez, G.; Gea, J.; et al. An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: Update on limb muscle dysfunction in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 189, e15–e62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neri, T.; Tavanti, L.; De Magistris, S.; Lombardi, S.; Romei, C.; Falaschi, F.; Paggiaro, P.; Celi, A. Endothelial Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Potential Biomarkers in Chronic Interstitial Lung Diseases. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2019, 49, 608–610. [Google Scholar]
- Petrini, S.; Neri, T.; Lombardi, S.; Cordazzo, C.; Balìa, C.; Scalise, V.; Paggiaro, P.; Pedrinelli, R.; Celi, A. Leptin induces the generation of procoagulant, tissue factor bearing microparticles by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1860, 1354–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpi, S.; Scoditti, E.; Massaro, M.; Polini, B.; Manera, C.; Digiacomo, M.; Esposito Salsano, J.; Poli, G.; Tuccinardi, T.; Doccini, S.; et al. The Extra-Virgin Olive Oil Polyphenols Oleocanthal and Oleacein Counteract Inflammation-Related Gene and miRNA Expression in Adipocytes by Attenuating NF-κB Activation. Nutrients 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelmeier, C.; Vestbo, J. COPD assessment: I, II, III, IV and/or A, B, C, D. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 43, 949–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polini, B.; Carpi, S.; Romanini, A.; Breschi, M.C.; Nieri, P.; Podestà, A. Circulating cell-free microRNAs in cutaneous melanoma staging and recurrence or survival prognosis. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2019, 32, 486–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horak, M.; Novak, J.; Bienertova-Vasku, J. Muscle-specific microRNAs in skeletal muscle development. Dev. Biol. 2016, 410, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; An, N.; Li, J.; Xia, J.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, P.; Liu, X.; Huang, H.; Gao, J.; Zhang, X. miRNA-206 regulates human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cell apoptosis via targeting in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 6223–6236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig-Vilanova, E.; Aguiló, R.; Rodríguez-Fuster, A.; Martínez-Llorens, J.; Gea, J.; Barreiro, E. Epigenetic mechanisms in respiratory muscle dysfunction of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreiro, E.; Sancho-Muñoz, A.; Puig-Vilanova, E.; Salazar-Degracia, A.; Pascual-Guardia, S.; Casadevall, C.; Gea, J. Differences in micro-RNA expression profile between vastus lateralis samples and myotubes in COPD cachexia. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 126, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, A.; Natanek, S.A.; Lewis, A.; Man, W.D.-C.; Hopkinson, N.S.; Polkey, M.I.; Kemp, P.R. Increased skeletal muscle-specific microRNA in the blood of patients with COPD. Thorax 2013, 68, 1140–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A.; Riddoch-Contreras, J.; Natanek, S.A.; Donaldson, A.; Man, W.D.-C.; Moxham, J.; Hopkinson, N.S.; Polkey, M.I.; Kemp, P.R. Downregulation of the serum response factor/miR-1 axis in the quadriceps of patients with COPD. Thorax 2012, 67, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuasa, K.; Hagiwara, Y.; Ando, M.; Nakamura, A.; Takeda, S.; Hijikata, T. MicroRNA-206 is highly expressed in newly formed muscle fibers: Implications regarding potential for muscle regeneration and maturation in muscular dystrophy. Cell Struct. Funct. 2008, 33, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacchiarelli, D.; Legnini, I.; Martone, J.; Cazzella, V.; D’Amico, A.; Bertini, E.; Bozzoni, I. miRNAs as serum biomarkers for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. EMBO Mol. Med. 2011, 3, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-F.; Tao, Y.; Li, J.; Deng, Z.; Yan, Z.; Xiao, X.; Wang, D.-Z. microRNA-1 and microRNA-206 regulate skeletal muscle satellite cell proliferation and differentiation by repressing Pax7. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 190, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Williams, A.H.; Maxeiner, J.M.; Bezprozvannaya, S.; Shelton, J.M.; Richardson, J.A.; Bassel-Duby, R.; Olson, E.N. microRNA-206 promotes skeletal muscle regeneration and delays progression of Duchenne muscular dystrophy in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 2054–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkerton, M.; Chinchilli, V.; Banta, E.; Craig, T.; August, A.; Bascom, R.; Cantorna, M.; Harvill, E.; Ishmael, F.T. Differential expression of microRNAs in exhaled breath condensates of patients with asthma, patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and healthy adults. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 217–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agusti, A.; Edwards, L.D.; Celli, B.; Macnee, W.; Calverley, P.M.A.; Müllerova, H.; Lomas, D.A.; Wouters, E.; Bakke, P.; Rennard, S.; et al. Characteristics, stability and outcomes of the 2011 GOLD COPD groups in the ECLIPSE cohort. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 42, 636–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agustí, A.; Edwards, L.D.; Rennard, S.I.; MacNee, W.; Tal-Singer, R.; Miller, B.E.; Vestbo, J.; Lomas, D.A.; Calverley, P.M.A.; Wouters, E.; et al. Persistent systemic inflammation is associated with poor clinical outcomes in COPD: A novel phenotype. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
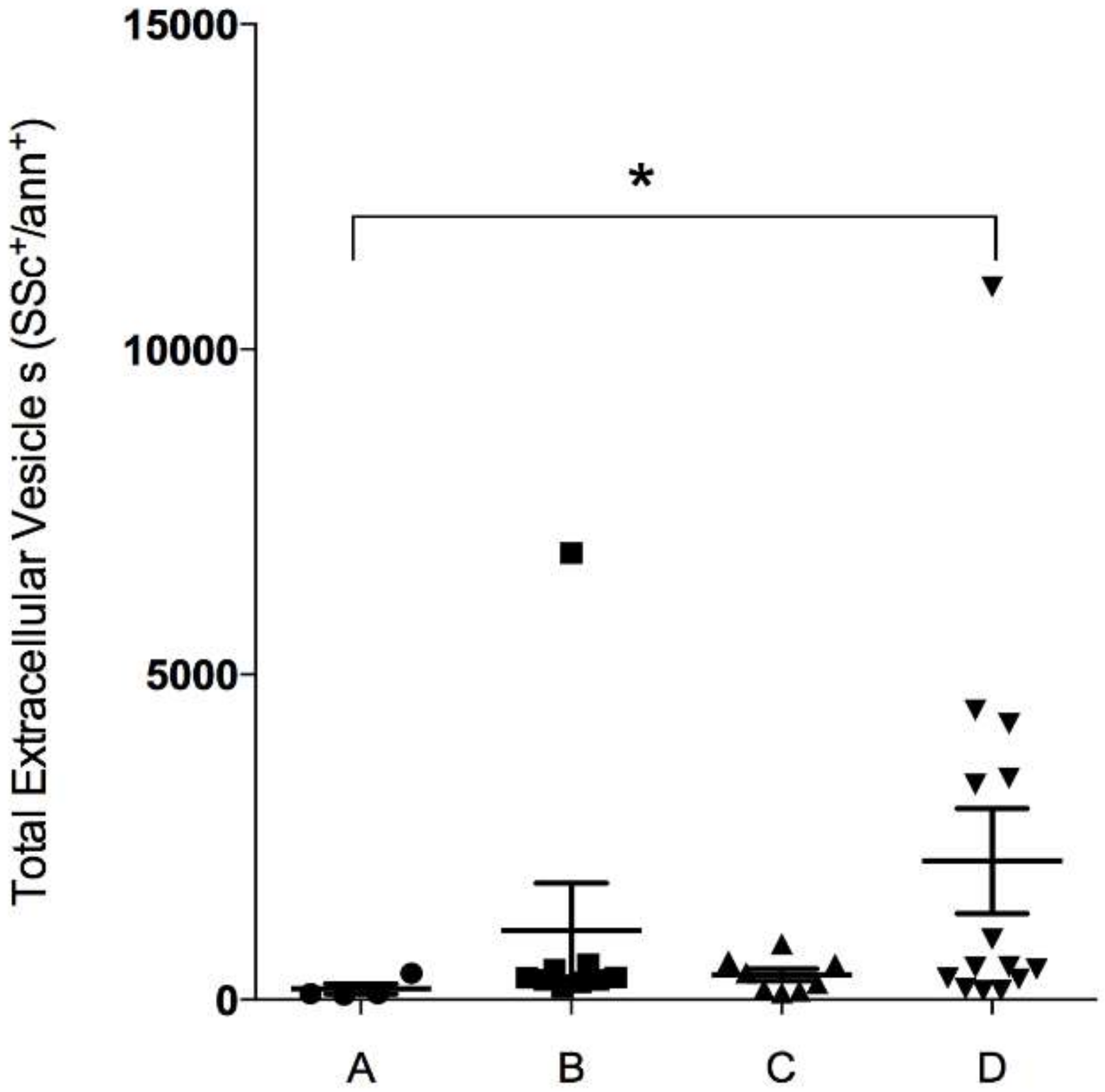
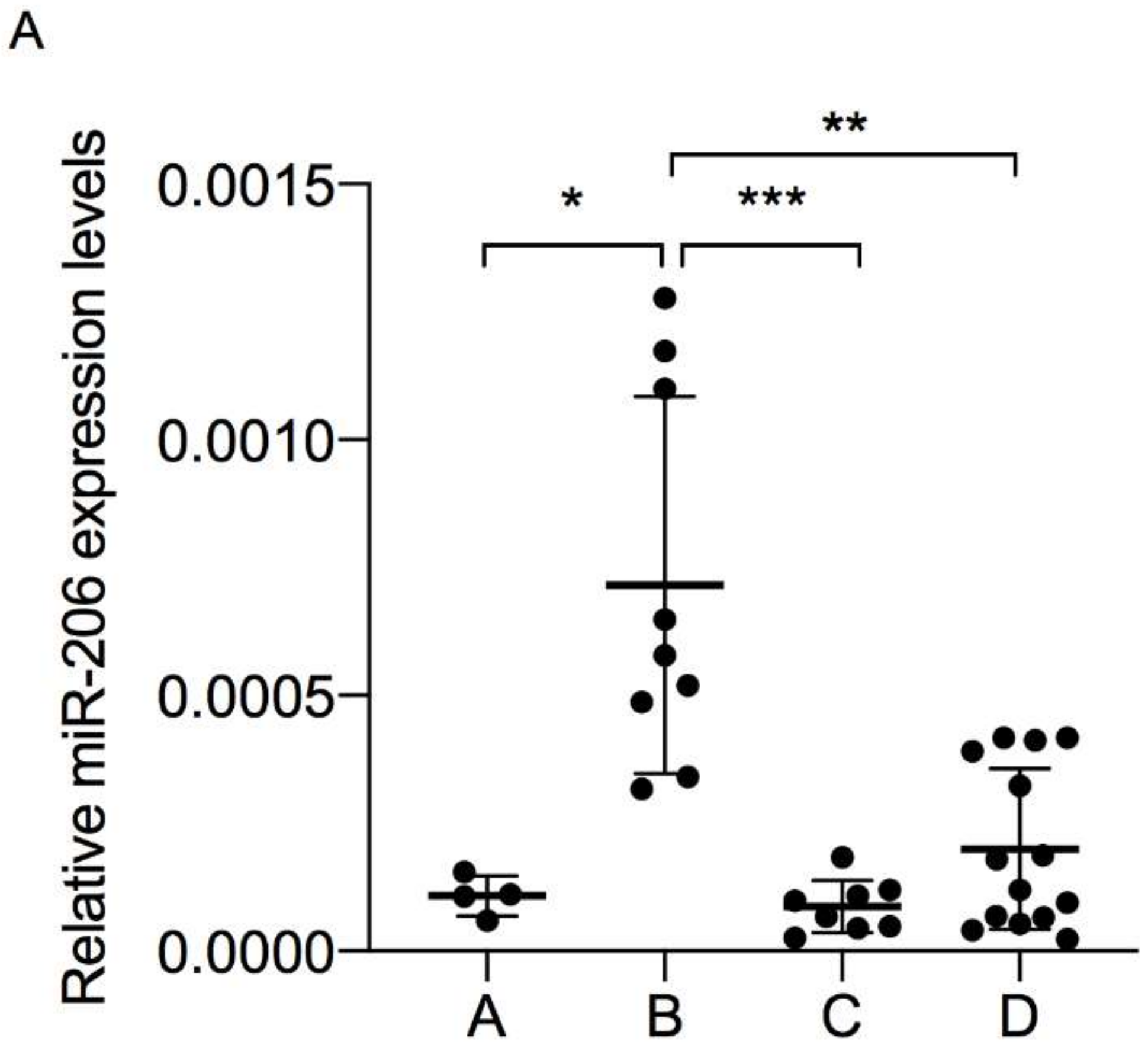
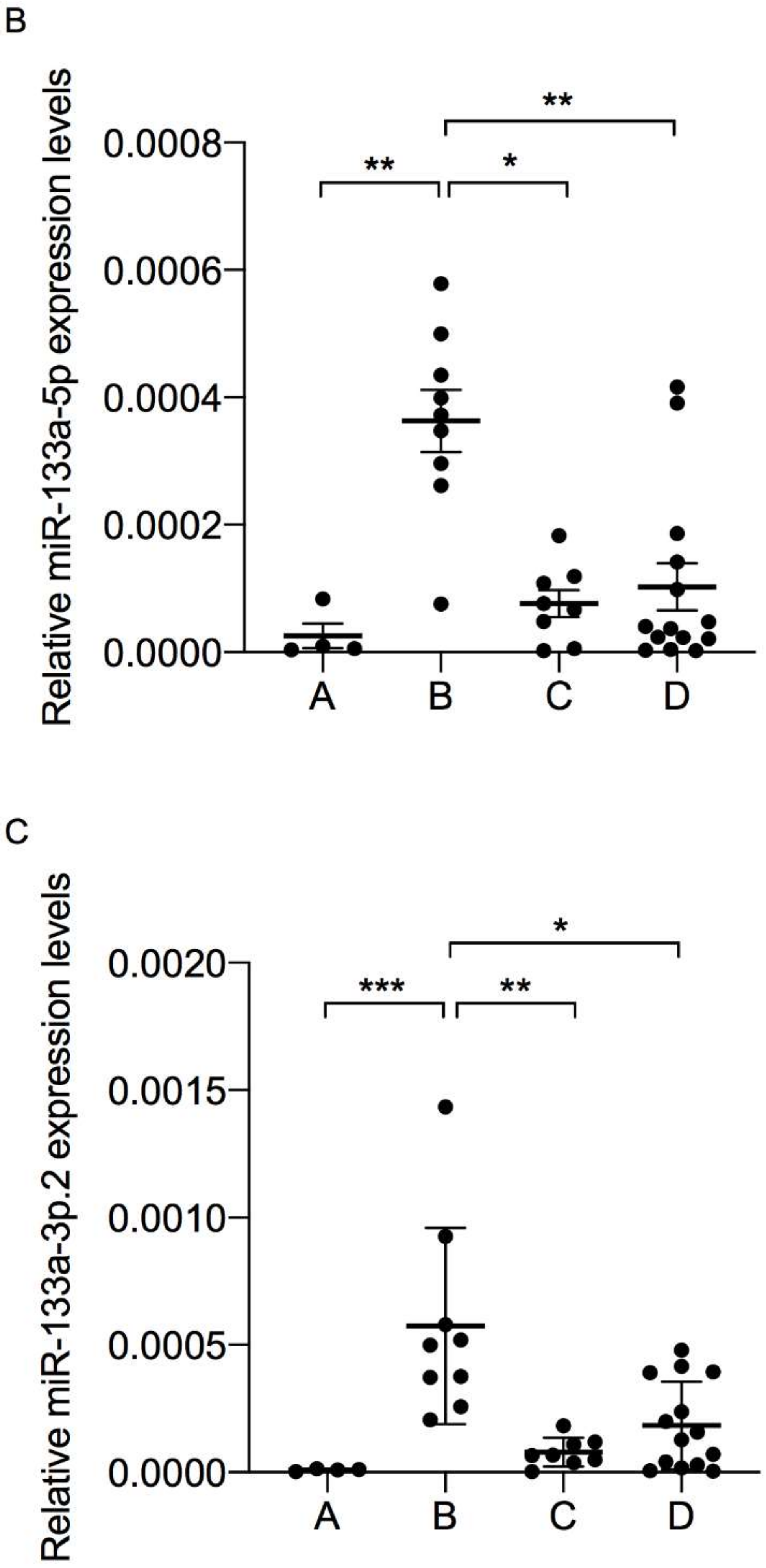
| Group A (n = 4) | Group B (n = 9) | Group C (n = 8) | Group D (n = 14) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male/Female | 4/0 | 6/3 | 8/0 | 8/6 | n.s. |
| Age (yrs) | 74.5 (10.0) | 70.0 (12.0) | 68 (12.0) | 71.5 (3.0) | n.s. |
| Smoking status (current/former) | 1/3 | 5/4 | 0/8 | 3/11 | n.s. |
| Pack-years | 39.0 (60.0) | 52.0 (18.5) | 50.0 (60.5) | 48.5 (33.0) | n.s. |
| Dyspnea, mMRC | 1.0 (1.0) | 1.0 (1.0) | 1.0 (1.0) | 2.0 (1.0) | 0.002 * |
| CAT | 7.5 (2.5) | 11.0 (6.0) | 8.0 (9.3) | 14.0 (9.5) | 0.003 * |
| BMI, Kg/m2 | 26.7 (10.3) | 31.7 (11.4) | 29.2 (7.5) | 27.4 (7.3) | n.s. |
| FEV1, L % pred. | 1.52 (0.59) 62.5 (30.0) | 1.65 (0.53) 62.0 (9.5) | 1.37 (0.46) 47.0 (17.3) | 0.99 (0.45) 50.0 (16.5) | 0.001 ° 0.004 ° |
| FEV1/FVC % | 52.0 (17.5) | 53.0 (15.5) | 42.5 (18.0) | 45.1 (16.0) | n.s. |
| DLCO, mL/min * mmHg % pred. | 16.9 (9.7) 84.0 (59.5) | 14.0 (8.7) 55.0 (29.5) | 24.5 (7.3) 96.5 (33.3) | 14.6 (8.6) 59.5 (17.0) | n.s. n.s. |
| Therapy | n.a. | ||||
| LAMA | 1 | ||||
| LABA-LAMA | 2 | 4 | 3 | 6 | |
| LABA-ICS | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| TRIPLE TH. | 2 | 4 | 2 | 7 | |
| LABA | 1 |
| EV-Derived Myo-miRna | AUC | 95% CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| GOLD Group B vs C | |||
| miR-206 | 78.89% | 63.4–93.7% | <0.0813 |
| miR-133a-5p | 75.33% | 55.2–88.4% | 0.0063 |
| miR-133a-3p.2 | 73.96% | 54.1–89.5% | 0.3533 |
| Triple signature | 89.74% | 70.8–92% | <0.0008 |
| GOLD Group B vs A | |||
| miR-206 | 78.74% | 51.5–90.6% | 0.0044 |
| miR-133a-5p | 83.82% | 52–92.5% | 0.0001 |
| miR-133a-3p.2 | 87.5% | 62.5–87.5% | 0.1709 |
| Triple signature | 83.9% | 58.5–91.6% | <0.0001 |
| GOLD Group B vs D | |||
| miR-206 | 67.09% | 49.5–80.2% | 0.0134 |
| miR-133a-5p | 73.41% | 55.7–86.9% | 0.0005 |
| miR-133a-3p.2 | 61.46% | 45.2–77% | 0.6595 |
| Triple signature | 69.4% | 53.8–83.4% | <0.0042 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carpi, S.; Polini, B.; Nieri, D.; Dubbini, N.; Celi, A.; Nieri, P.; Neri, T. Expression Analysis of Muscle-Specific miRNAs in Plasma-Derived Extracellular Vesicles from Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10070502
Carpi S, Polini B, Nieri D, Dubbini N, Celi A, Nieri P, Neri T. Expression Analysis of Muscle-Specific miRNAs in Plasma-Derived Extracellular Vesicles from Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(7):502. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10070502
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarpi, Sara, Beatrice Polini, Dario Nieri, Nevio Dubbini, Alessandro Celi, Paola Nieri, and Tommaso Neri. 2020. "Expression Analysis of Muscle-Specific miRNAs in Plasma-Derived Extracellular Vesicles from Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease" Diagnostics 10, no. 7: 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10070502
APA StyleCarpi, S., Polini, B., Nieri, D., Dubbini, N., Celi, A., Nieri, P., & Neri, T. (2020). Expression Analysis of Muscle-Specific miRNAs in Plasma-Derived Extracellular Vesicles from Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Diagnostics, 10(7), 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10070502







